1. Introduction
The memory requirements in computing environments have become higher due to the rise of AI, cloud, and Internet of Things technologies [
1,
2,
3,
4]. As a result, computing systems (i.e., smartphones, tablets, and edge devices) have gradually increased the memory capacity to meet the memory requirements of applications [
5]. For example, the latest commercial smartphones and edge devices have up to 16 GB and 4 GB, respectively [
6,
7]. This change means that the memory capacity on the devices is an important venue for efficiently enabling diverse services (e.g., Smart Home and Industrial IoT with on-device AI) [
1,
8,
9]. However, many devices still face an out-of-memory (OOM) issue because of further increases in the demand for memory by runnable applications as the available memory space grows [
2,
10]. Thus, the hardware extension to address the OOM issue will reveal a memory shortage over time [
8,
11].
Meanwhile, operating systems (e.g., Linux and Android) have traditionally tried to make memory space available by reclaiming free space in the software aspect, and they commonly employ two mechanisms. One is an out-of-memory killer (OOMK), which is triggered when available free space on memory drops below the predefined threshold (e.g., 122 MB) [
12,
13]. To reclaim space in memory, it kills one or more applications consuming large amounts of memory, regardless of human intent [
5,
10]. This means that all used pages are reclaimed at once when the corresponding application is killed. The OOMK mechanism is effective in reclaiming a large amount of free space, but it can cause unintended behaviors like so-symbol lookup and XML overhead [
10]. An alternative to the OOMK mechanism is the
swap mechanism [
3,
8,
14]. It has gained a great deal of traction as a solution to the OOM issue in operating systems [
5,
15]. When the available memory space is insufficient, the swap mechanism first finds pages that have low re-access probability and then swaps them out to the swap memory space inside the secondary storage devices (e.g., HDDs or SSDs) to make free space [
3,
8,
15]. Intuitively, the swap mechanism is considered more efficient than the OOMK because it selects the victim pages to be swapped out using the temporal locality of the pages, and it can avoid unnecessary resource reclamation [
16,
17].
With the advancement of IoT technologies and the increasing applications that consume much more memory, research efforts are being made to handle memory resources more efficiently [
5,
10,
11,
15,
18,
19,
20,
21]. A recent proposal attempted to orchestrate OOMK and swap to reduce the number of memory reclamations and the launch latency of applications [
10]. Some previous studies proposed new swap policies where user preference and re-access possibilities are more prioritized for victim page selection [
5,
11]. Prior work went into designing the new swap mechanism to prevent random writes caused by
swap-out operations [
15], and some researchers proposed ZNSwap, where swap operations are piggybacked on host-side garbage collection for ZNS SSDs [
18]. Unfortunately, although efforts have been made to enhance the swap mechanism, it still introduces significant and unpredictable overhead. Especially, the overhead can gradually increase as the pre-reserved swap memory space inside the storage device gets fragmented over time; we call this the
swap memory fragmentation (SMF) problem.
The root cause of the SMF issue is that the swap mechanism reuses swap pages that were invalidated by the
swap-in operations, resulting in additional overhead. In other words, after the swap memory is fragmented, the swap mechanism has to spend time finding the invalidated swap pages while delaying block allocation for
swap-out operations in the swap memory space. Furthermore, scattered writes from a series of
swap-out operations negatively affect I/O throughput because they lead to performing random writes; this leads to long seek time in HDDs and additional die or chip-level collisions in SSDs. In general, prior studies on swap optimization have focused on improving victim-page selection or reducing write amplification, while rarely addressing fragmentation that accumulates inside the swap memory space itself [
5,
10,
11,
18]. Although IOSR [
15] attempted to reduce swap-space fragmentation through allocation control, its approach was preventive rather than corrective. This overlooked fragmentation gradually degrades swap efficiency, motivating the need for a kernel-level mechanism that can directly compact fragmented swap regions.
In this paper, we first note why the SMF issue occurs over time in detail. Then, we propose an extension of the traditional swap mechanism, called VSwap, that optimizes the swap memory space for defragmentation purposes. The key idea of VSwap is to enable efficient data migration with minimal I/O cost. If swap memory reaches its capacity limit, VSwap triggers virtual vswap-in and vswap-out to gather valid swap pages across multiple swap clusters into a new swap cluster; a swap cluster consists of a fixed number of swap pages, and it is a unit of swap memory management. We also design an I/O monitor to avoid interference from VSwap with normal I/O operations issued by running applications. Unlike previous approaches that rely on specific storage or file system implementations (e.g., ZNSwap), VSwap is the first kernel-level swap defragmentation mechanism that operates generically across both HDDs and SSDs. It achieves this through a vswap-in and vswap-out operation collaborating with an I/O monitor, which performs defragmentation transparently during idle periods to minimize interference with normal I/O operations. We implemented a prototype of VSwap on the Linux kernel (v5.15), and used the original swap mechanism as the baseline for comparison. Compared to baseline, VSwap shows better performance by up to 48.18% in the synthetic workload, where the swap memory is highly fragmented. Finally, we summarize our contributions as follows:
Identification of SMF issue. Previous studies have focused on swap-out operations to accelerate the performance of the swap mechanism. However, we highlighted an in-depth analysis of the swap memory space and side effects. Our analysis revealed that the swap memory space suffers from excessive swap-in and swap-out operations, resulting in performance degradation during execution.
Design and development of VSwap. We designed VSwap that efficiently addresses the above SMF issue with negligible extra overhead. Also, we implemented VSwap as a novel extension to the original swap mechanism to be generic to support any computing devices (i.e., Smartphones, Tablets, and Edge IoT devices).
Comprehensive evaluation. We conducted comprehensive evaluations on synthetic and real-world workloads to compare VSwap with the traditional swap mechanism (i.e., baseline). Then, we performed a top-down analysis to clearly confirm the effectiveness of VSwap.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. After diving into the traditional swap mechanism and the motivation for our work in
Section 2,
Section 3 proposes
VSwap to mitigate the performance drop caused by the SMF issue. The evaluation results of
VSwap are shown in
Section 4, and related work is given in
Section 5. Finally,
Section 6 concludes this research.
3. Design and Implementation
In this section, we introduce VSwap, a novel extension mechanism, called VSwap, that is designed to optimize swap memory space in computing environments that require more memory capacity than physical memory. The design goals of VSwap are to (1) instantly identify fragmented swap clusters in the swap memory space and (2) migrate valid swap pages scattered across multiple clusters to a new cluster to secure available free clusters in advance. The challenges in achieving the goal are threefold. First, data migration in the swap memory space incurs extra I/O operations to the underlying storage device. Second, it must be able to run the migration without interfering with the execution of latency-sensitive applications. Third, the solution should operate transparently to the official memory subsystem in the kernel with simple code modifications.
3.1. Basic Operations with Two Auxiliary Tables
As
VSwap is an extension of the traditional swap mechanism, it follows the basic rules in the page allocation or reclamation procedure in the swap memory space. In our extension, we slightly modify
swap-in and
swap-out operations to update two auxiliary tables: reverse Swap-to-PTE (S2P) map tables and a fragment table.
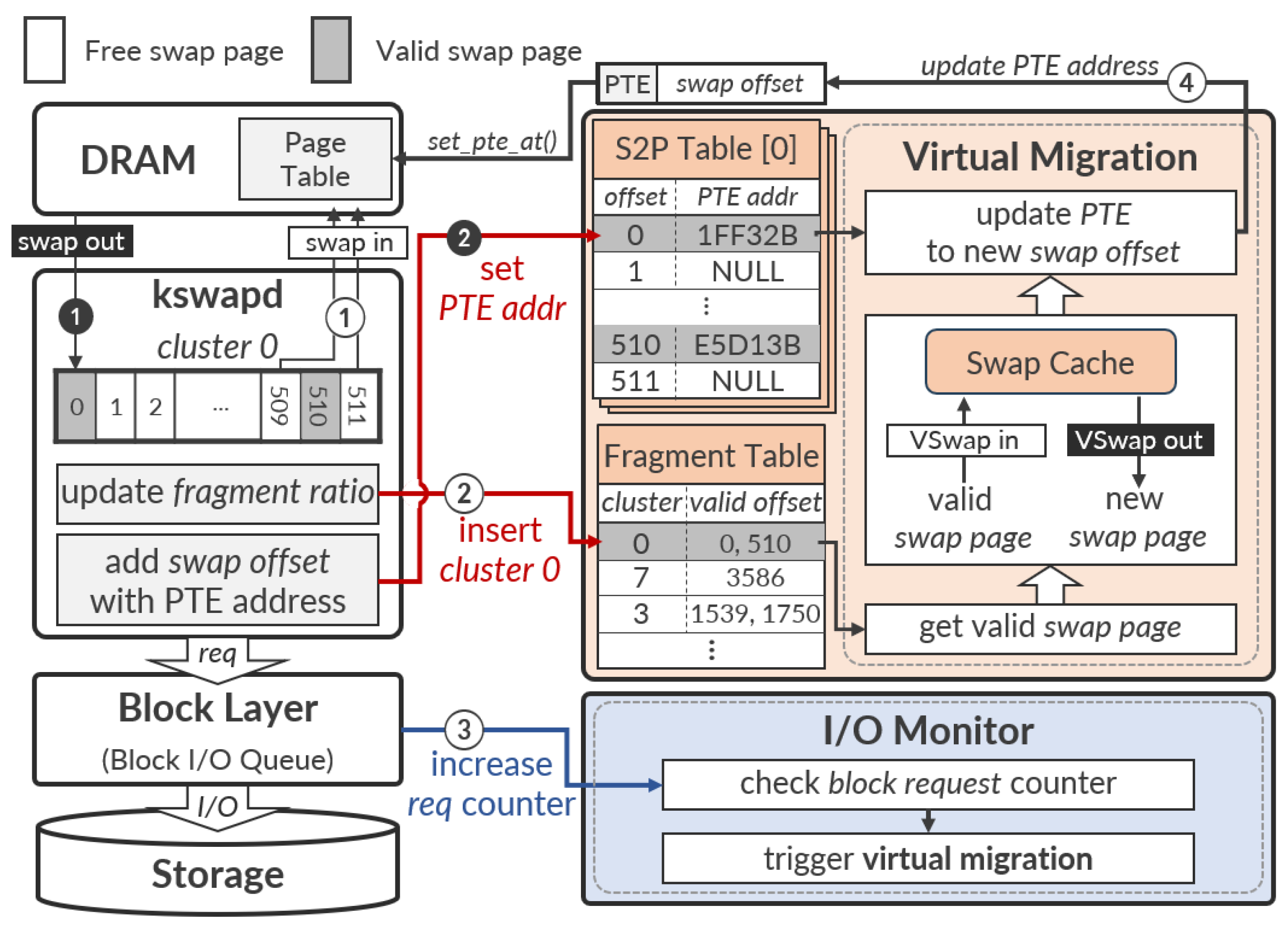
Figure 2 shows the overall architecture of
VSwap and its internal operations. In the figure, the black circled numbers (➊, ➋) indicate the
swap-out flow handled by
kswapd, while the white circled numbers (①–④) represent the subsequent
swap-in and
VSwap flow that performs background defragmentation during idle periods.
Reverse S2P map table: It maps the offset of a swapped page within the swap memory space (i.e., swap offset) to the address of the page table entry dedicated to the swapped page (i.e., PTE address). This table plays an important role in updating the swap offset that resides in the PTE after performing the
virtual migration; we will discuss this in the next section in detail. For implementation, we modified the
swap-out operation to inject a new procedure that inserts a pair of points (swap offset, PTE address) into the S2P table. For example, when a page 0 is swapped with
swap-out to the swap memory space inside the secondary storage media,
VSwap records a pair of points (0, 1FF32B) in the S2P map table (denote ➊–➋ in
Figure 2).
Fragment table: It is designed to find fragmented clusters in the swap memory space quickly. To do so,
VSwap monitors the
fragmented ratio of each cluster, which means how many swap pages within a cluster leave a “valid” state. Whenever a swap page is swapped from the swap memory space to the host DRAM,
VSwap weights the ratio of a targeted cluster to reflect invalidation of the corresponding swap page. A lower ratio indicates that there are fewer swap pages with a “valid” state in the cluster.
VSwap inserts the cluster into the fragment table if its ratio drops below the predefined threshold (e.g., 5% of the total number of swap pages in a cluster). For example, if the fragmented ratio of the cluster 0 drops below the threshold after completing
swap-in operations for swap page 509 and 511 in order,
VSwap inserts the cluster 0 into the fragment table (denote ①–② in
Figure 2). This is because the cluster only has two valid swap pages (offset 0 and offset 510). Note that if the fragmented ratio of a cluster becomes 0, which means all swap pages in the cluster are marked with “invalid”,
VSwap removes the cluster in the fragment table because the memory subsystem in the kernel reclaims the whole swap memory space dedicated to the cluster for reuse later.
3.2. Virtual Swap Operations
Now, we discuss the key idea, called virtual migration, and how it tackles the challenges mentioned above. The procedures of the virtual migration are illustrated in Algorithm 1.
Virtual migration: To efficiently migrate valid pages in the swap memory space, we designed
virtual migration, a simple and transparent swap migration mechanism. In
VSwap, the virtual migration leverages two key swap operations with the auxiliary tables above: a
vswap-in that reads a swap page across multiple clusters listed on the fragment table, and a
vswap-out that writes data in the page into a different cluster in the swap memory space. We implement both operations atomically to ensure data consistency (see Algorithm 1, line 7). The
swap-in operation for migrated swap pages must be transparent to upper layers. To achieve this,
VSwap scans the
reverse S2P table for the corresponding PTE address and updates the swap offset in that PTE entry (see Algorithm 1, line 8). This process, called
address remapping, enables the kernel to access the page from the new swap offset during a page fault without additional handling. In other words, if a page fault occurs due to the swapped page, the memory subsystem in the kernel normally reads the contents of the swapped page from the migrated new swap offset instead of the original swapped offset without impairing use.
| Algorithm 1 Pseudo code of the virtual migration |
- 1:
// this function is started or stopped by I/O monitor - 2:
Function: virtual_migration(fragment_table, S2P_table, reserved_cluster) - 3:
for each fragmented_cluster in fragment_table do - 4:
for each valid_page in fragmented_cluster do - 5:
new_page ← get_swap_page (reserved_cluster) - 6:
PTE_addr ← S2P_table[valid_page] - 7:
virtual_swap_in_out(valid_page, new_page) - 8:
update_PTE(PTE_addr, new_page) - 9:
swap_free(valid_page) - 10:
end for - 11:
status ← check_I/O_monitor() - 12:
if status is busy then - 13:
return - 14:
end if - 15:
end for
|
Efficient data placement for virtual migration: Unfortunately, an extra I/O overhead while running the virtual migration is inevitable in that the migration needs to read the swap pages from the original location and write them to the new location. We can help to make the right data placement that mitigates the overhead by using the following hardware and software features. (1) To do so, we utilize the hardware characteristic that sequential writes are much faster than random writes; it can help to reduce the latency of seek and rotation time in HDDs and the garbage collection overhead in SSDs. To take advantage of this, VSwap assigns swap pages to be used in the virtual migration in a log-structured fashion. The migrated swap pages have consecutive swap offsets in a cluster for sequential writes. (2) We also consider the “hotness” (i.e., swap-in likelihood) of swap pages. In other words, swap pages left in fragmented clusters for a long time have a low possibility of swap-in operation in a short time. Thus, it is valuable to gather them in the same cluster in the swap memory space because it reduces the possibility of being fragmented in the future. To enable the benefits from both features, VSwap tries to locate as many swap pages in the same cluster as possible.
I/O Monitoring for low interference: To address the second challenge, we newly designed
I/O monitor that continuously tracks I/O operations issued by applications and decides whether to start migrating in the background (denote ③–④ in
Figure 2). To do so, the monitor periodically collects the read and write operations issued to the underlying storage device from the applications in order. We also built it to wake up the I/O monitor at the end of a time quanta (e.g., 5 s) to run it with minimal interference. The monitor calculates a metric that indicates the total number of I/O requests accumulated within the specified time period. If the metric drops below the predefined threshold,
VSwap recognizes it as an idle state, and the I/O monitor triggers to run the virtual migration (denote ④ in
Figure 2). The monitor also controls whether to perform the migration operation continuously or not. If the metric rises above the threshold during migration operations, the I/O monitor updates the state from “idle” to “busy” to terminate the running migration (see Algorithm 1 line 12–line 14). This I/O monitor is a key component of
VSwap, designed to ensure transparency to high-priority applications by deferring migration activities to idle periods. As a result,
VSwap minimizes interference with foreground I/O workloads and maintains stable overall performance.
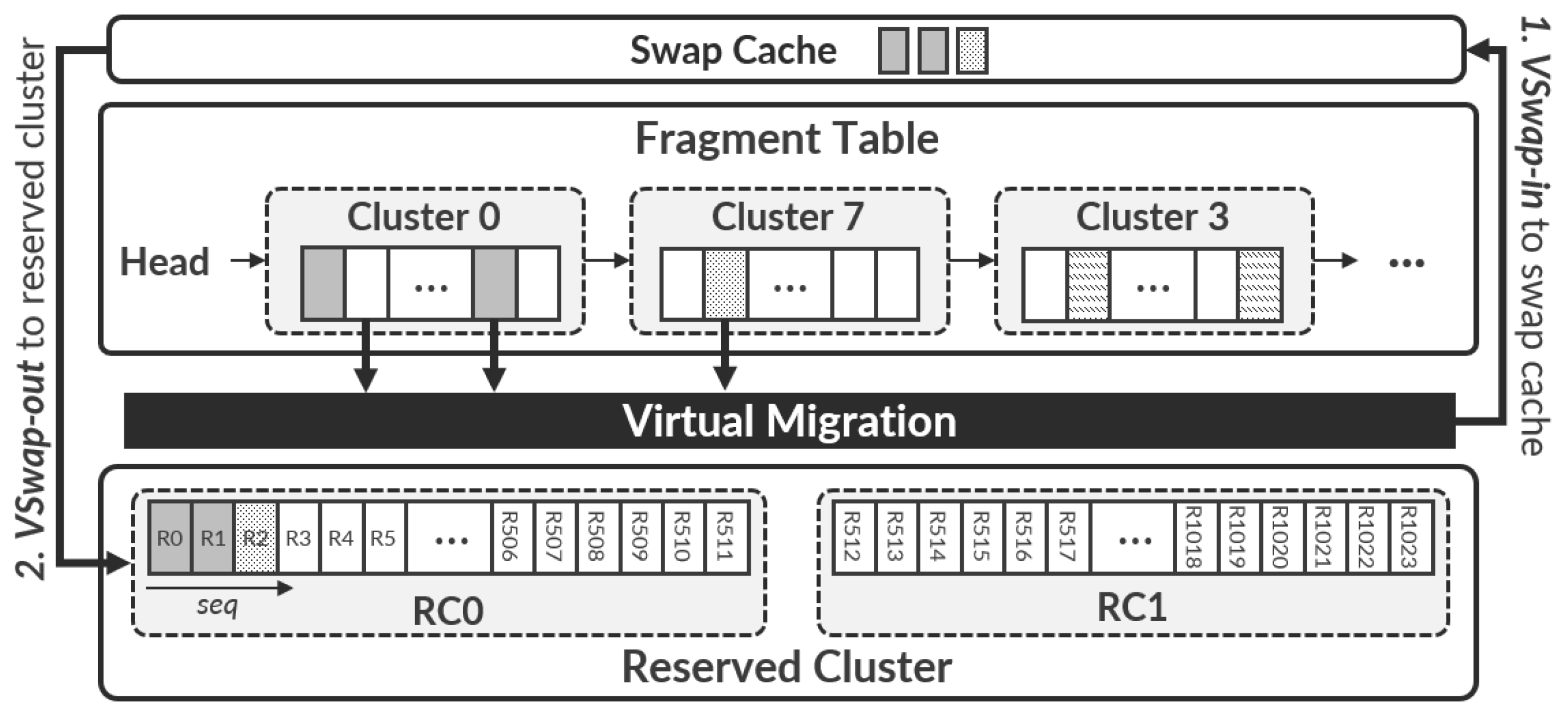
Reserved clusters: To efficiently support the virtual migration,
VSwap pre-reserves a pair of clusters, called the reserved cluster (RC) 0 and 1, in the swap memory space (see
Figure 3). As illustrated in
Figure 3, the virtual migration proceeds in two steps: (1)
vswap-in loads valid swap pages from fragmented clusters into the swap cache, and (2)
vswap-out writes them sequentially into the reserved clusters (RC0 or RC1). Once RC0 becomes full,
VSwap alternates to RC1 to continue migration without interruption.
VSwap first assigns one side of the pair (i.e., RC 0) when a swap page is required in the virtual migration and ensures that one side always has available swap memory spaces. When all swap pages within the assigned RC 0 are used,
VSwap quickly assigns the other side of the pair (i.e., RC 1), and it converts RC 0 to a normal cluster so that the contents of the swapped pages can be read later by a
swap-in operation.
VSwap newly allocates the other available cluster as the reserved cluster (i.e., RC 0) so that a pair of clusters is always maintained.
4. Evaluation
In this section, we present the performance effectiveness of VSwap in various real-world workloads and offer a summary of the benefits from utilizing virtual migration. We evaluated VSwap to answer the following questions:
Can VSwap accelerate swapping processing while the underlying swap memory space ages?
How many free clusters can VSwap maintain compared to traditional swap mechanisms?
What are the tradeoffs in VSwap design?
4.1. Experimental Setup
We conducted all experiments on a machine equipped with a 16-core Intel i9-12900KF CPU, 32 GB DRAM, and a 250 GB Samsung 870 EVO SSD. To enable the swap mechanism, we allocate a consecutive 2 GB space within the SSD as the swap memory space. There are 1024 clusters in the swap memory space, and each cluster is in turn composed of 512 swap pages whose size is 4KB. To measure the performance of the swap mechanism, we pre-consumed almost all pages in the physical memory pool on the host DRAM with dummy data, leaving just 500 MB of available free space. Thus, the swap mechanism will be triggered after consuming 500 MB of memory space.
We implemented a prototype of VSwap in the Linux kernel (version 5.15) on Ubuntu 20.04, using the default kernel configuration with minimal code modifications for integration. The fragmentation threshold was empirically set to 5%. Note that higher thresholds may cause excessive page migration, leading to unnecessary I/O overhead. And lower thresholds can reduce the positive effectiveness of defragmentation. We compared it with two approaches: the Ideal and Base approaches. We define the Ideal as when the available swap memory space is always sufficient to allocate new swap pages, so the swap mechanism is lightweight and efficient. To achieve the Ideal condition, we allocate 100 GB as the swap memory space, unlike Base and VSwap. On the other hand, Base refers to the traditional swap mechanism.
For a comprehensive evaluation, we used two synthetic workloads and four real-world workloads. For the synthetic workloads, we utilized a synthetic benchmark mentioned in
Section 2.2 and pmbench [
28], which simulates a practical and intensive memory access. We also compared
VSwap on memory-intensive real-world workloads: Memcached [
29] with YCSB-A [
30], Metis [
31,
32] with word counts and page view counts, and Mobilenet for AI workloads. In each test, we compare
VSwap with Ideal, whose performance is normalized to 1. We executed all experiments five times and took the average as the performance result, and set time intervals to make an idle state between experiments.
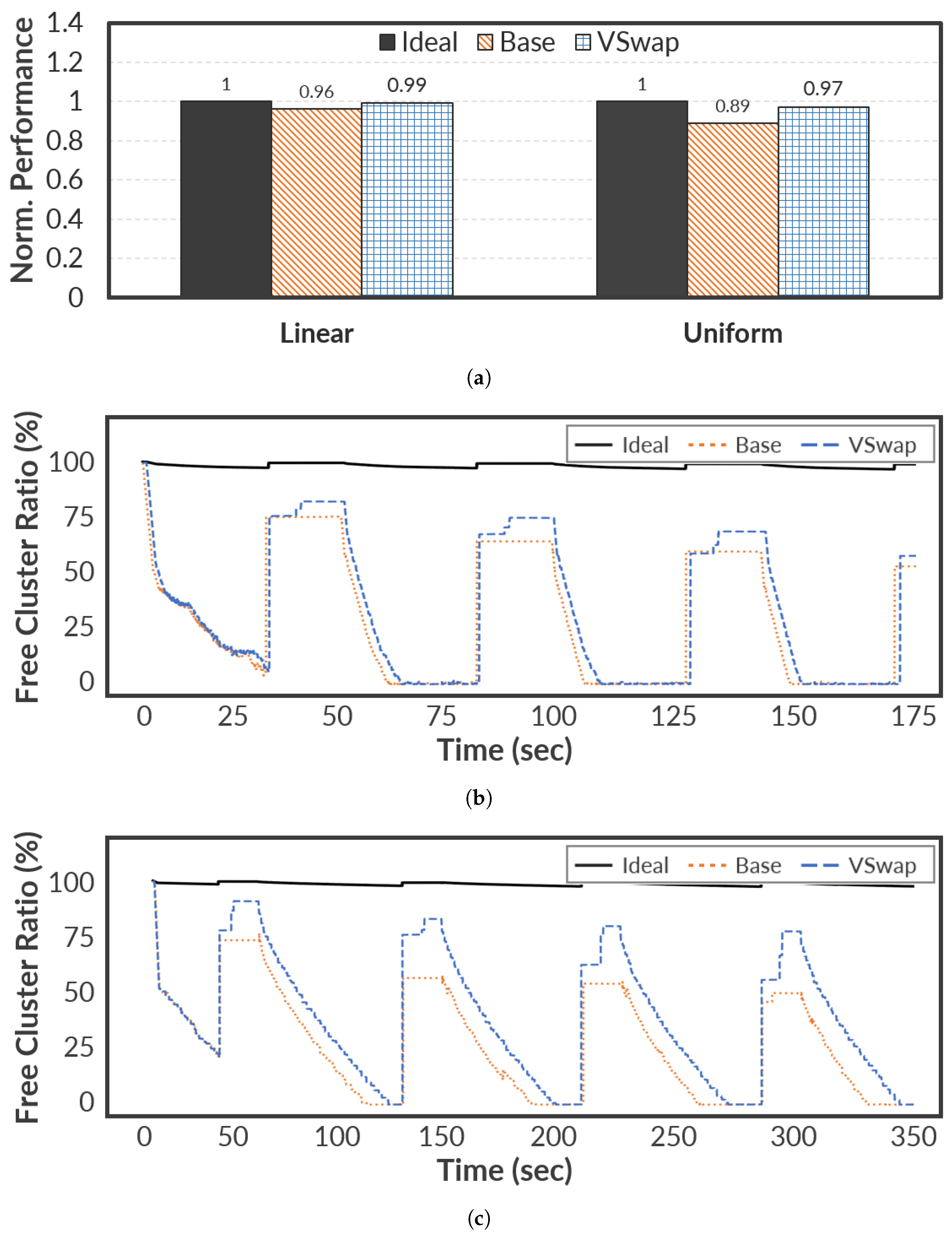
4.2. Synthetic Workloads
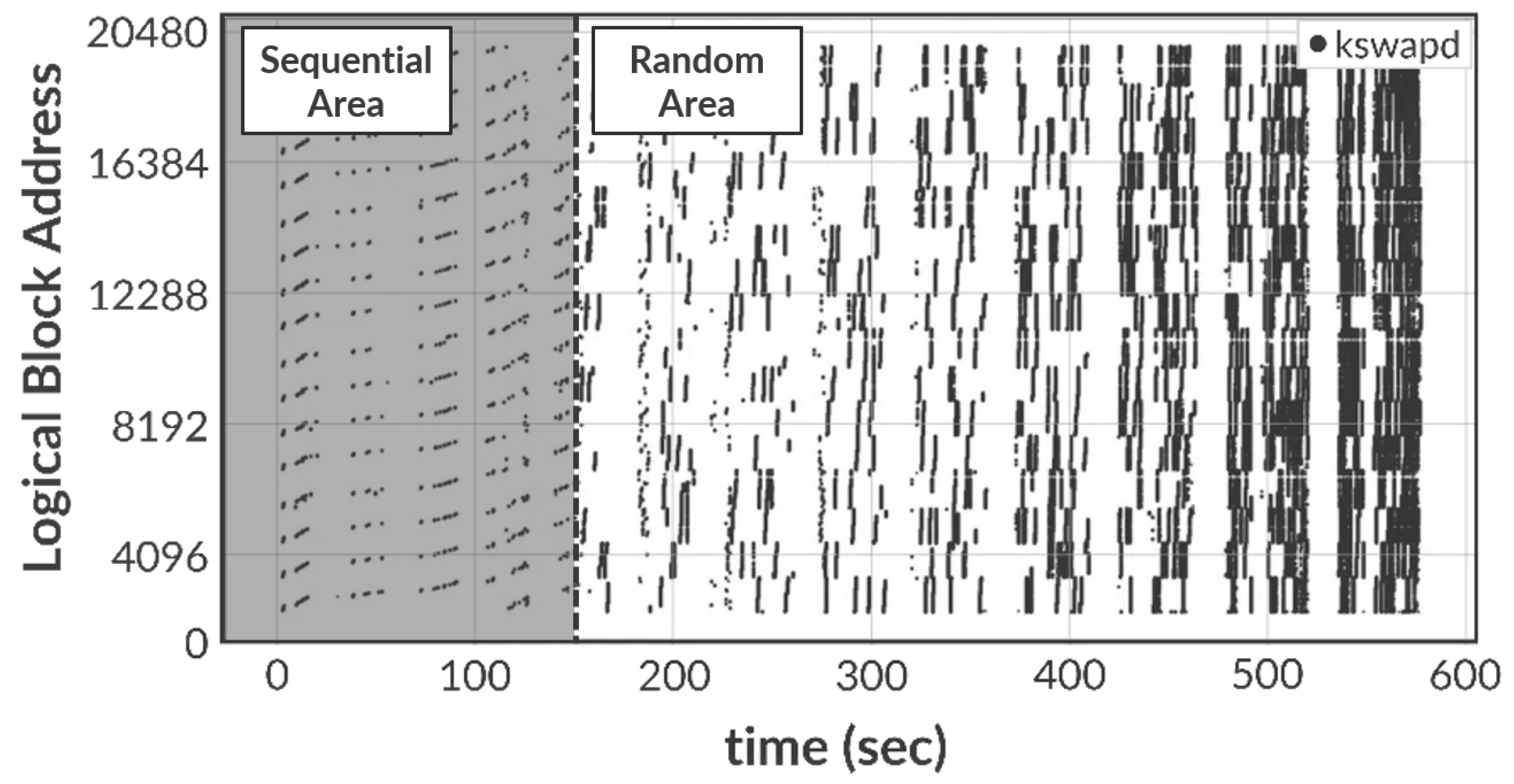
We first examine the performance while running the
swap-out operations based on the synthetic benchmark (see
Figure 1 in
Section 2.2). This is because the devised benchmark can show an intuitive performance and memory consumption.
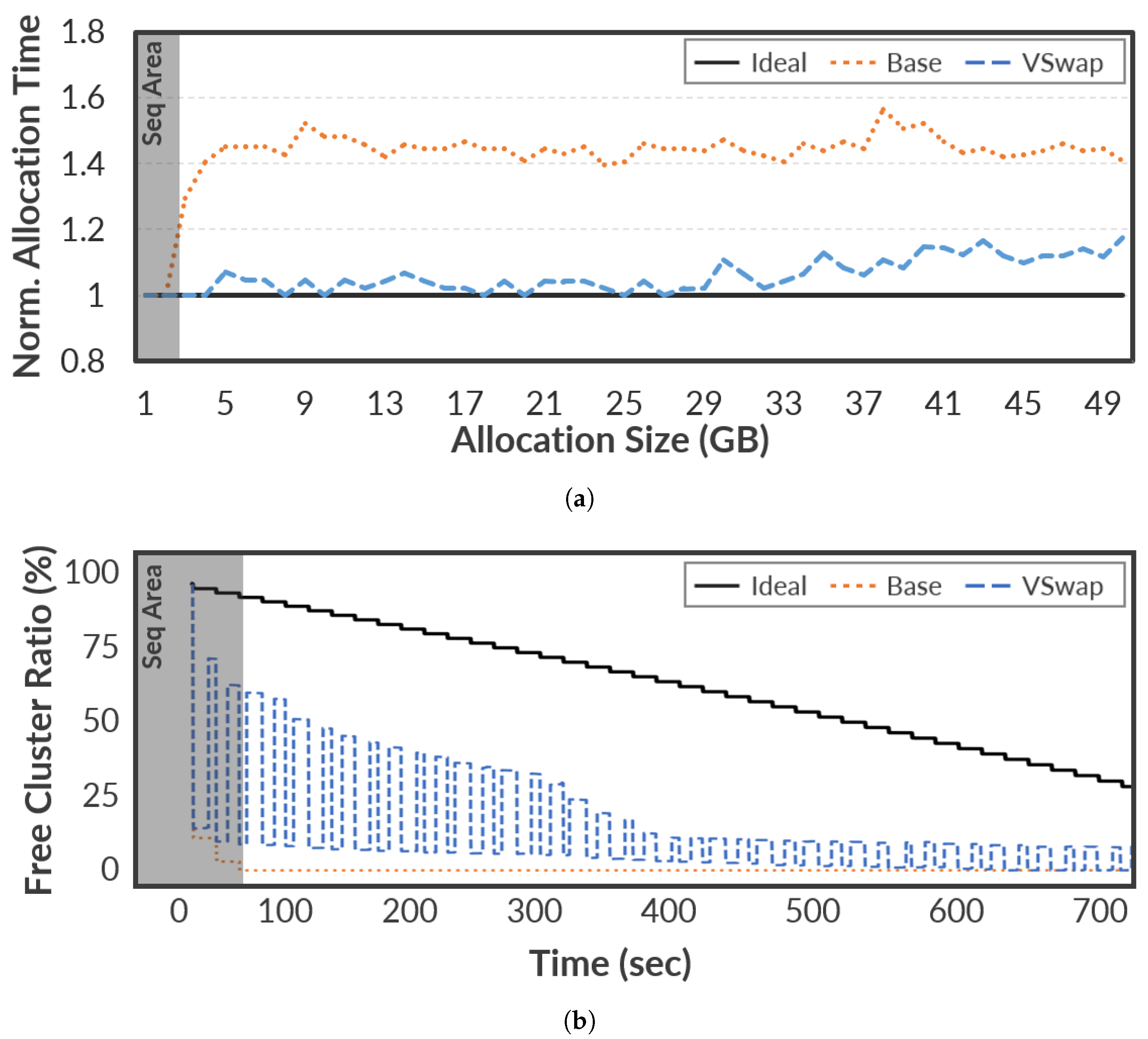
Figure 4 shows the normalized memory allocation time and the number of free clusters within the swap memory space. In
Figure 4a, the x-axis represents the accumulated allocation size as the logical time orders in the designed benchmark, where the allocation of 1GB is repeated 50 times. As shown in
Figure 4, Ideal shows the best performance and a good free cluster ratio, even though the benchmark requires intensive memory allocation. Of course, the number of free clusters decreases over time, but it never affects the latency of memory allocation because Ideal always allocates free clusters without the scanning operations for the
swap map mentioned in
Section 2.1.
In
Figure 4,
VSwap shows similar performance trends observed in Ideal, although it has only 2 GB swap memory space; the performance up to 29 iterations is very similar.
Figure 4b explains the intuitive reason behind the similarity between Ideal and
VSwap. As shown in
Figure 4b,
VSwap quickly recovers free clusters under the memory-intensive workload by using the
virtual migration operations. Thus, it can offer free clusters without the scanning operations. Unfortunately,
VSwap reveals a negative impact behind the 400 s in terms of free cluster ratio. The reason is that reclaiming free clusters is limited in that the accumulated valid pages increase over time. Despite such a limitation,
Figure 4b also confirms that the
virtual migration contributes significantly to performance improvements.
VSwap improves performance by up to 48.18% compared to the Base. The performance improvement can have additional implications in that the underlying storage device has a positive impact on I/O performance due to sequential writes. It is important to note that this performance gain is achieved despite the I/O monitoring and migration overheads introduced by
VSwap. This is because the advantage of maintaining sequential write patterns through virtual migration clearly outweighs the minor cost of these background operations.
To clearly confirm the effectiveness of
VSwap, we also performed an evaluation based on the pmbench benchmark that is widely used to profile paging performance while triggering fault-intensive memory operations.
Figure 5 shows the evaluation results on the pmbench benchmark. As shown in
Figure 5a,
VSwap shows a good performance and similar performance to the Ideal on both Linear and Uniform workload. Especially, it improves the performance by up to 4.47% on average compared with the Base on the Uniform workload. The reason for the small performance gap compared to that of
Figure 4 is that pmbench continuously requires memory space. The memory space used is reclaimed during the idle time before the next benchmark runs (see
Figure 5b,c). Such a pattern can provide opportunities where Base can simply obtain free clusters without the scanning operations because reclaiming is easily available. Note that
VSwap efficiently maintains more available clusters than Base. In
Figure 5c,
VSwap can efficiently secure the number of free clusters by up to 26.85% and it leads to a performance gain. These results demonstrate that
VSwap mitigates the SMF issue by continuously reclaiming fragmented clusters through virtual migration, as indicated by the increased free cluster ratio in
Figure 5b,c.
4.3. Real-World Workloads
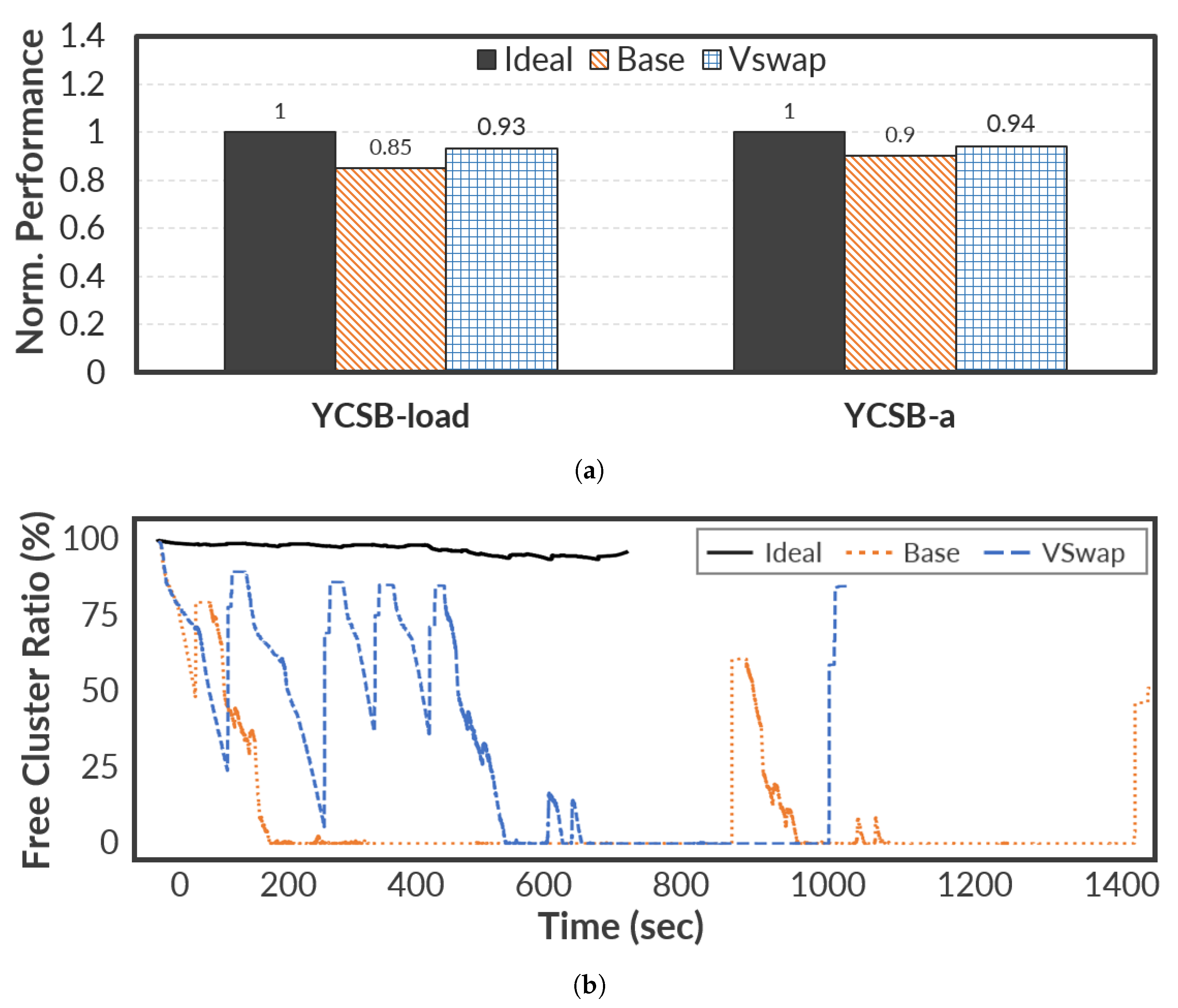
To produce more meaningful test results, we compared VSwap on the real-world benchmarks: Memcached with YCSB and Metis.
For evaluation, we first selected Memcached with the YCSB benchmark, which is one of the standard frameworks for evaluating performance while consuming memory space.
Figure 6 shows the results of the evaluation running the YCSB load and the YCSB-a workload, which simulates a read-heavy scenario with a Zipfian distribution. For better understanding,
Figure 6a shows the average performance of YCSB load and YCSB-a separately. As shown in
Figure 6a, the performance gain of the YCSB load is better than that of YCSB-a;
VSwap improves the overall performance up to 9.36% and 6.26% compared to Base for the YCSB load and YCSB-a, respectively. This is because YCSB load performs sequential writes to record initial data in the database (recordcount = 1,000,000) while YCSB-a is a mixed workload (read 50% and update 50%). Meanwhile,
Figure 6a shows the trends of the free cluster ratios when running consecutively the YCSB load and YCSB-A. Unlike synthetic workloads, the free cluster ratios in
Figure 6b fluctuate significantly in the YCSB workload; sometimes, the gap between
VSwap and Base is greater than 75%. The reason why the performance gain is not significant compared to the gap of the free cluster ratio is as follows. First,
VSwap cannot have the opportunity to run the
virtual migration because YCSB-a constantly issues I/O requests. Note that the
virtual migration only works in the idle state to avoid interference with application performance. Second, since read and update operations can be handled based on the DRAM page cache, the use of the swap mechanism may result in a small performance gain.
Furthermore, we performed more experiments using Metis, which is a multi-core MapReduce library; it requires the allocation, reallocation, and deallocation of numerous memory chunks to efficiently handle the internal three states (i.e., Map, Reduce, and Merge) [
31,
32]. To compare the Base with
VSwap, we ran two workloads inside Metis: (1) Word Count workloads with 18 threads and a 300 MB dataset; (2) Page View Count using 4 threads with a 500 MB dataset.
Figure 7 shows average performance and free cluster ratios in five consecutive experiments. As shown in
Figure 7a,
VSwap shows enhanced performance by 10.32% in Word Count and 8.21% in Page View Count on average in multiple runs. In addition,
Figure 7b,c clearly shows that
VSwap eagerly reclaims swap pages, which are no longer used and unneeded, in idle time. This eager reclaim has a positive impact on performance in terms of memory allocation because it reduces the scanning time for the
swap map. In other words,
VSwap quickly assigns an empty swap cluster by securing as many free clusters as possible in advance when the request for memory allocation occurs on the fly.
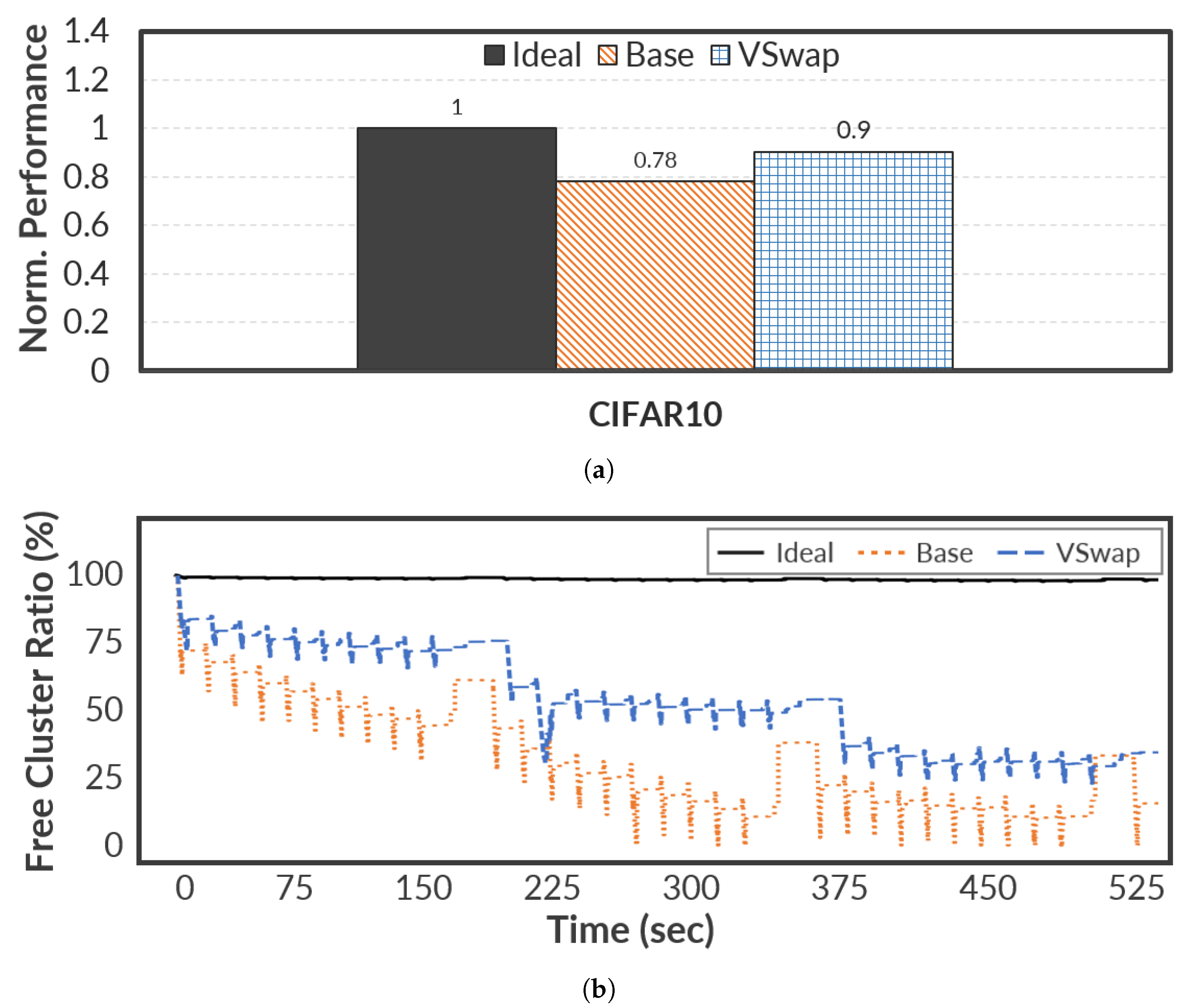
4.4. Real-World AI Workload
In general, AI workloads require and consume a vast volume of memory space to perform the training and inference process [
33]. To confirm the performance benefit of
VSwap, we additionally compared
VSwap on the MobileNet V2 model, which is one of the AI workloads on mobile devices. For evaluation, we employ the CIFAR-10 dataset, which is a widely used benchmark in machine learning and computer vision to evaluate image classification models. In the evaluation, the MobileNet V2 model only performs an inference process based on 1,280 images without any learning process to emulate the edge IoT or mobile environment [
6,
33].
To measure the performance of the inference process, we executed MobileNet five consecutive times with 15 s intervals.
Figure 8 shows the average performance normalized to the Ideal and the ratios of free cluster on the MobileNet. As shown in
Figure 8a,
VSwap achieves a similar effect to the Ideal case, and improves overall performance by up to 27.35% compared to Base on average. We can describe the performance benefit of
VSwap in
Figure 8b. Note that MobileNet periodically requires CPU resources to perform the inference process, resulting in an idle state. This implies that
VSwap efficiently reclaims free clusters by migrating the scattered valid swap pages across clusters into the reserved cluster of
VSwap (i.e., RC0 or RC1) during the inference time.
In general, VSwap shows high performance for real-world workloads, including server and edge IoT environments. We believe the performance gains of VSwap over diverse memory-intensive workloads are due to the virtual migration and storage-friendly write patterns.
4.5. Limitation and Tradeoffs
The overhead of VSwap can be categorized into two parts: memory space and performance overhead. First, VSwap requires extra memory space to maintain auxiliary tables (i.e., S2P and fragment table). Thus, we used 25 KB as the linked list pointer to implement the single fragment table; 16 bytes were allocated for list_head, and a total of 24 KB were used to assign 8 bytes pointers to each cluster. When the fragmented ratio of a cluster drops below the predefined threshold, the pointer of the fragment table is updated to point to the next fragmented cluster. We also used the total of 8 MB memory space to maintain S2P tables; 2 GB of swap memory space has a total of 524,288 pages, and each swap page additionally consumes 16 bytes to find the corresponding PTE address.
In terms of CPU overhead, VSwap introduces only a small processing load because the I/O monitoring and migration tasks are lightweight and event-driven. Note that the I/O monitor is periodically triggered (every five seconds) to collect block request counters. Most of the migration time spends I/O transfer during Virtual Swap-in/out, rather than CPU computation. Finally, the migration is triggered only during idle periods, ensuring negligible interference with user applications.
Meanwhile, VSwap never triggers the virtual migration in busy times when some I/O operations are ongoing to the underlying storage device. This is because it can hurt the performance and latency of ongoing applications. Fortunately, most computing systems have their own scheduling policies to efficiently share limited hardware resources, so that an idle state periodically occurs in real-world systems.
5. Related Work
This section discusses prior studies on swap mechanisms for various devices and fragmentation mitigation techniques.
Edge device. As applications demand more memory, an efficient swap mechanism has become essential in edge devices [
10,
11,
14]. SmartSwap [
11] predicts rarely used applications in mobile devices and performs process-level early swap-out of their pages. MemSaver [
14] records event-based hot page history in mobile devices and selectively swaps out other pages of background applications. SWAM [
10] selects the victim pages for swap-out based on their application access or reference history. Then, it decides between a storage-based slow path and a compressed-memory-based fast path according to the characteristics of the victim page.
Storage device. To address the performance and lifetime issues of storage devices, many studies have focused on an efficient swap mechanism [
2,
8,
15]. IOSR [
15] addresses swap memory space pollution by employing process-oriented allocation, which predicts the swap page counts of each process and allocates space accordingly rather than in cluster units. DISS [
8] improves swap efficiency on storage devices by invalidating unused swap pages in application-specific regions, which reduces storage space overhead and I/O interference. Wang et al. [
2] mitigates flash lifetime degradation caused by random writes in swap I/O by buffering and compressing swap pages in groups.
Fragment mitigation. Fragmentation is a traditional issue in systems that operate with large write units (e.g., blocks or segments), as partially valid data within these units prevents efficient space reclamation [
8,
18,
34,
35]. To mitigate fragmentation, many systems employ various data relocation techniques that compact valid data and free up contiguous space. For example, SSDs perform internal garbage collection to reclaim space by relocating valid pages within a block [
8,
18]. ZNSwap [
18] extends this concept to the kernel level, relocating valid swap data at the zone level to meet the sequential write constraints of Zoned Namespace (ZNS) SSDs. F2FS [
34] performs segment cleaning by moving valid data from low-utilization segments to newly allocated contiguous space to improve write efficiency. Similarly, RocksDB [
35], a database based on the Log-Structured Merge (LSM) tree, performs compaction to merge duplicate or obsolete data from upper levels into lower levels, thereby reducing fragmentation and improving storage efficiency.
In summary, prior research on swap mechanisms has mainly focused on optimizing page selection or allocation efficiency, while existing fragmentation within the swap memory space has remained largely unaddressed [
2,
3,
5]. Edge device level techniques (e.g., SmartSwap [
11], MemSaver [
14], DISS [
8], IOSR [
15]) improve swapping policies or space utilization, but they cannot compact fragmented swap regions once fragmentation occurs. Fragmentation mitigation methods at the storage or filesystem layer (e.g., F2FS [
34], RocksDB [
35], ZNSwap [
18]) perform compaction on data blocks rather than swap clusters, and thus cannot directly resolve swap-space fragmentation at the kernel level. In contrast,
VSwap bridges this gap by introducing a kernel-level compaction mechanism that proactively mitigates swap memory fragmentation through virtual migration and address remapping.
6. Conclusions
Today, applications that consume a larger volume of memory space are increasing in various environments, such as IoT and embedded environments. In this paper, this study introduces the swap mechanism that dynamically extends memory space using the storage device and explores the swap memory fragmentation (SMF) issue that leads to unacceptable performance collapse. Then, we proposed VSwap as an extension of the traditional swap mechanism to address some challenges with the SMF issue. To confirm the effectiveness of VSwap, we conducted comprehensive evaluations with synthetic and real-world workloads. Our evaluation results clearly show that VSwap can achieve good performance up to 48.18% and 27.35% compared to the traditional swap mechanism for synthetic and real-world workloads, respectively. By performing a performance analysis, we found that the virtual migration of VSwap accounts for a significant portion of performance improvement by harvesting as many free clusters as possible in advance. Finally, we believe that VSwap would guide a new direction of performance improvement for various systems (e.g., servers, tablets, and IoT devices) that suffer from memory pressure and hardware limitations. Although VSwap introduces a small amount of memory overhead due to the additional S2P and fragment tables, this overhead can grow proportionally with larger swap configurations. As future work, we plan to design a more memory-efficient S2P structure to improve scalability in resource-constrained environments.