Enhancing the Performance of Polypropylene/High-Density Polyethylene Blends by the Use of a Compatibilizer and Montmorillonite Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Clay/Polyolefin Composites
2.2.2. Injection Molding
2.2.3. X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD)
2.2.4. Melt Flow Index (MFI)
2.2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.7. Tensile Tests
3. Results
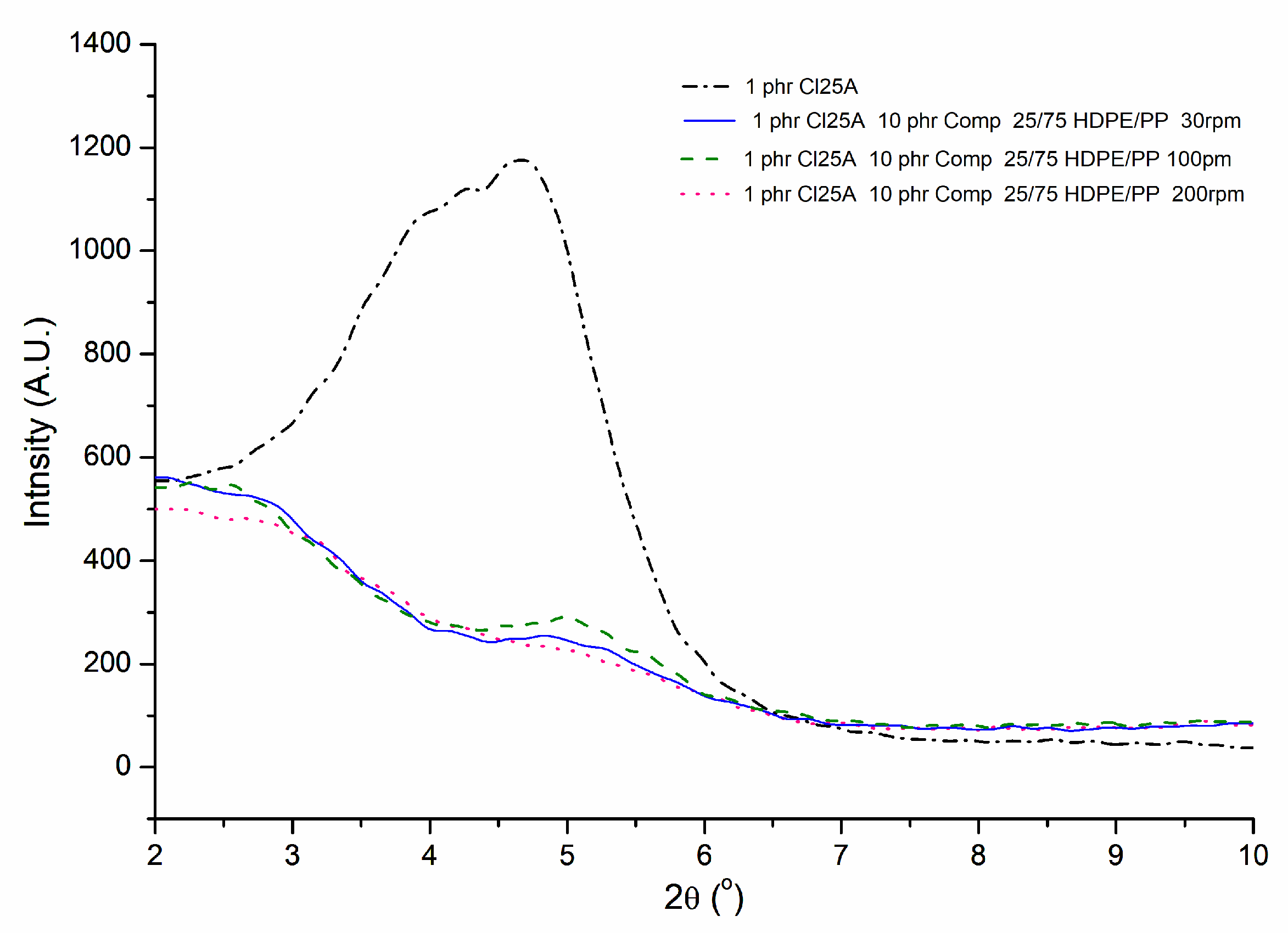
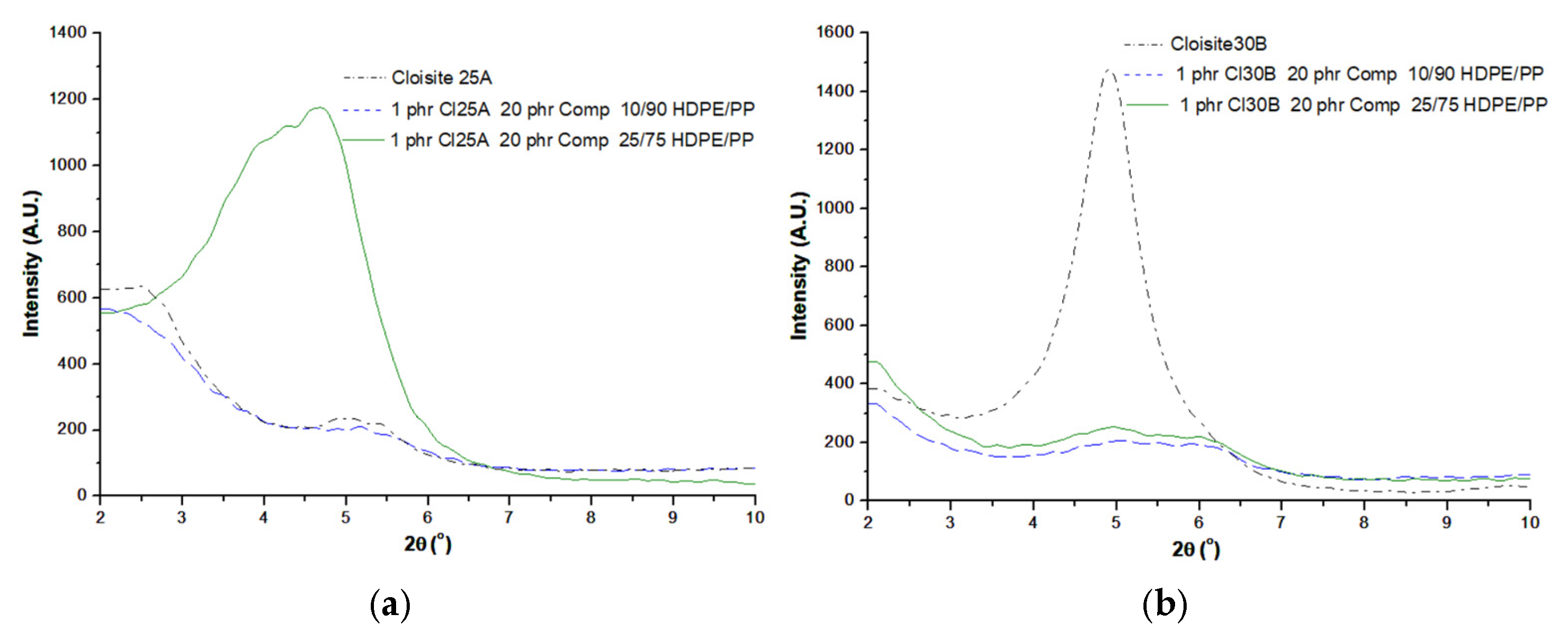
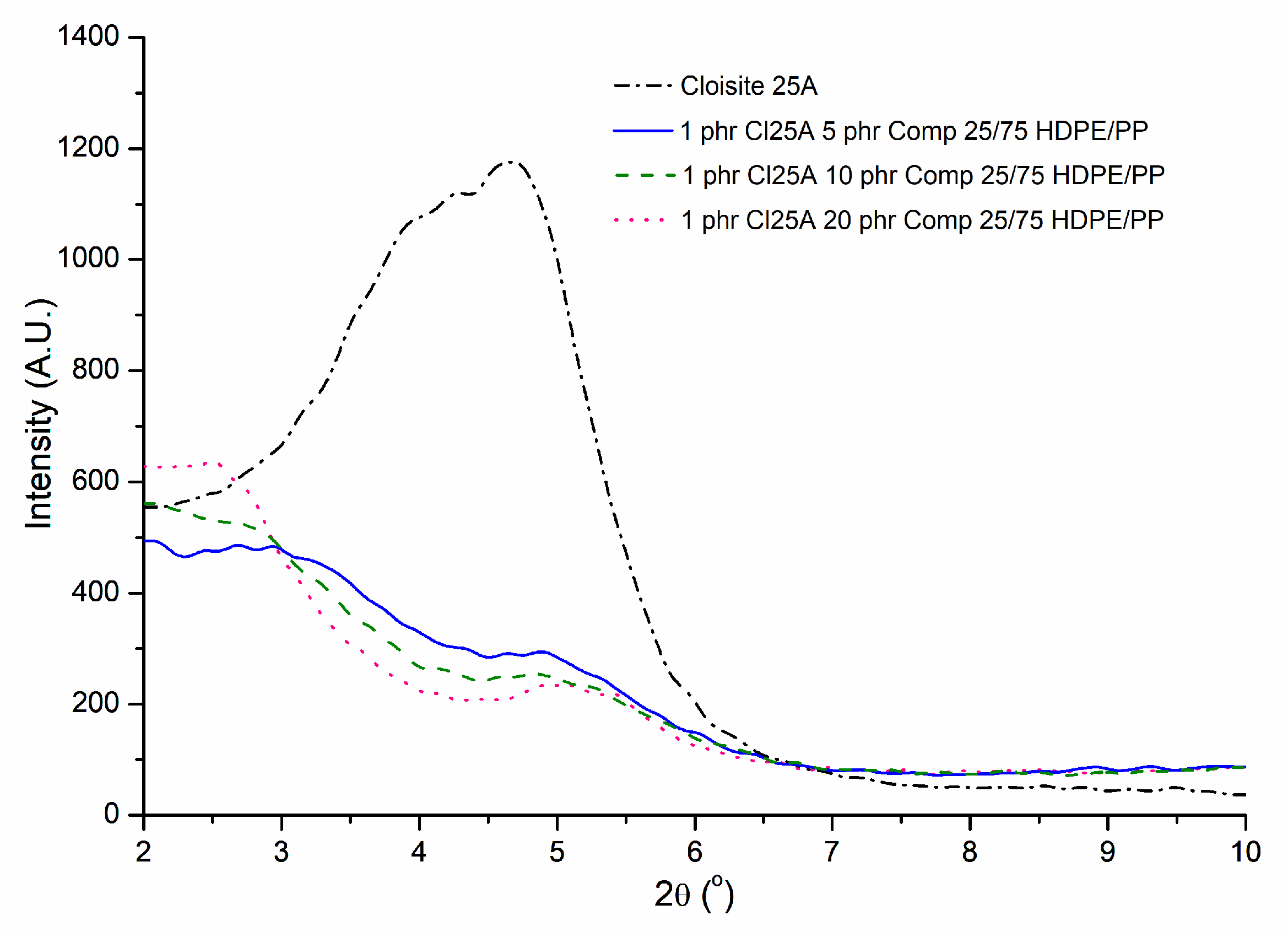
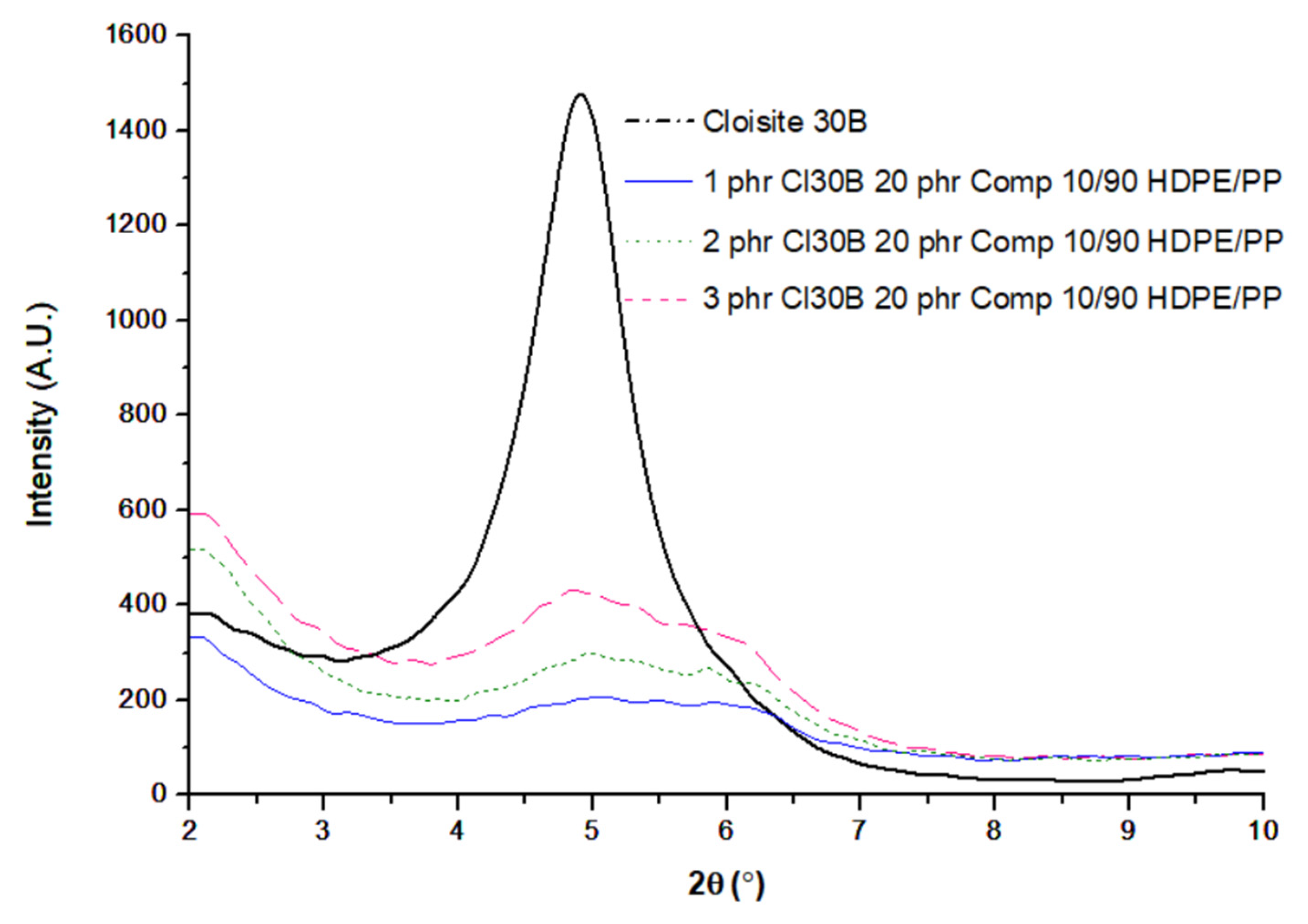
3.1. XRD
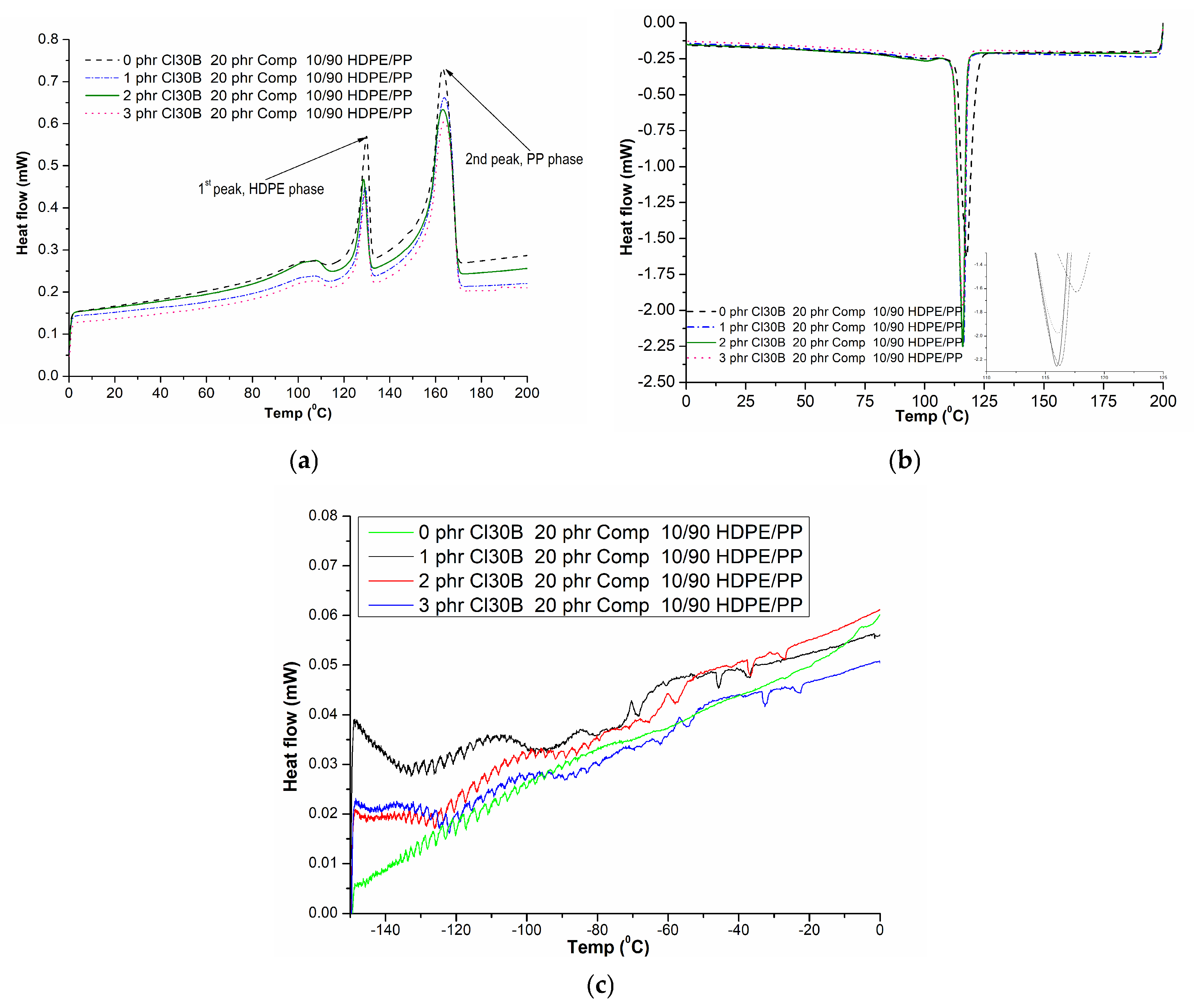
3.2. DSC
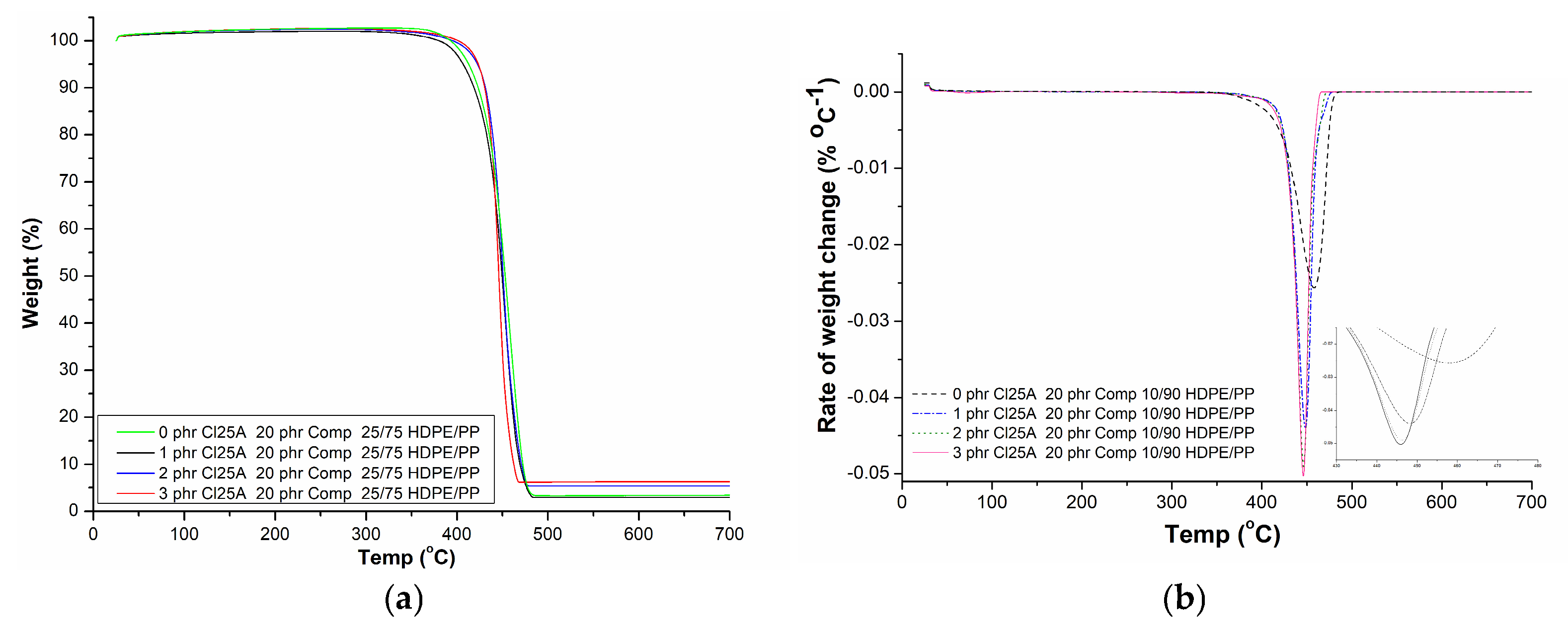
3.3. TGA
3.4. MFI
3.5. Tensile Tests
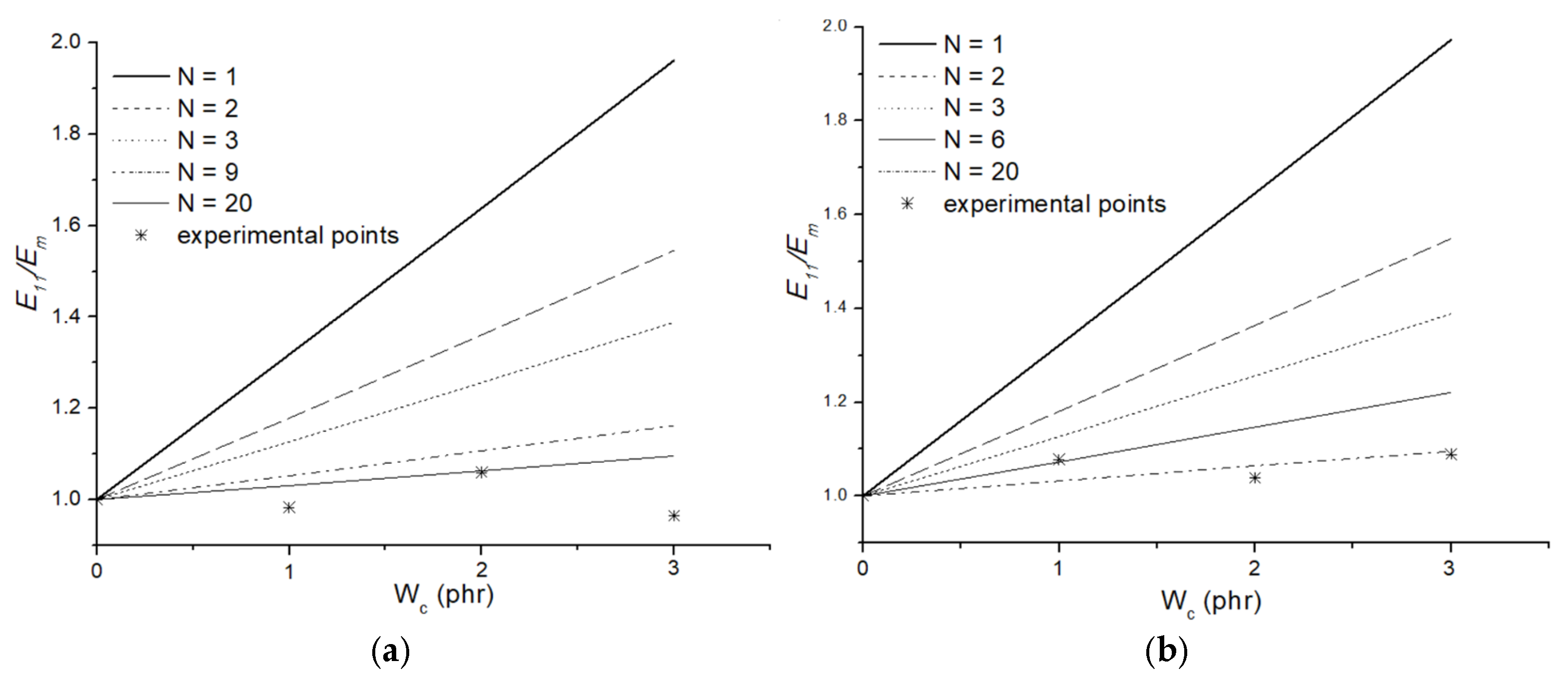
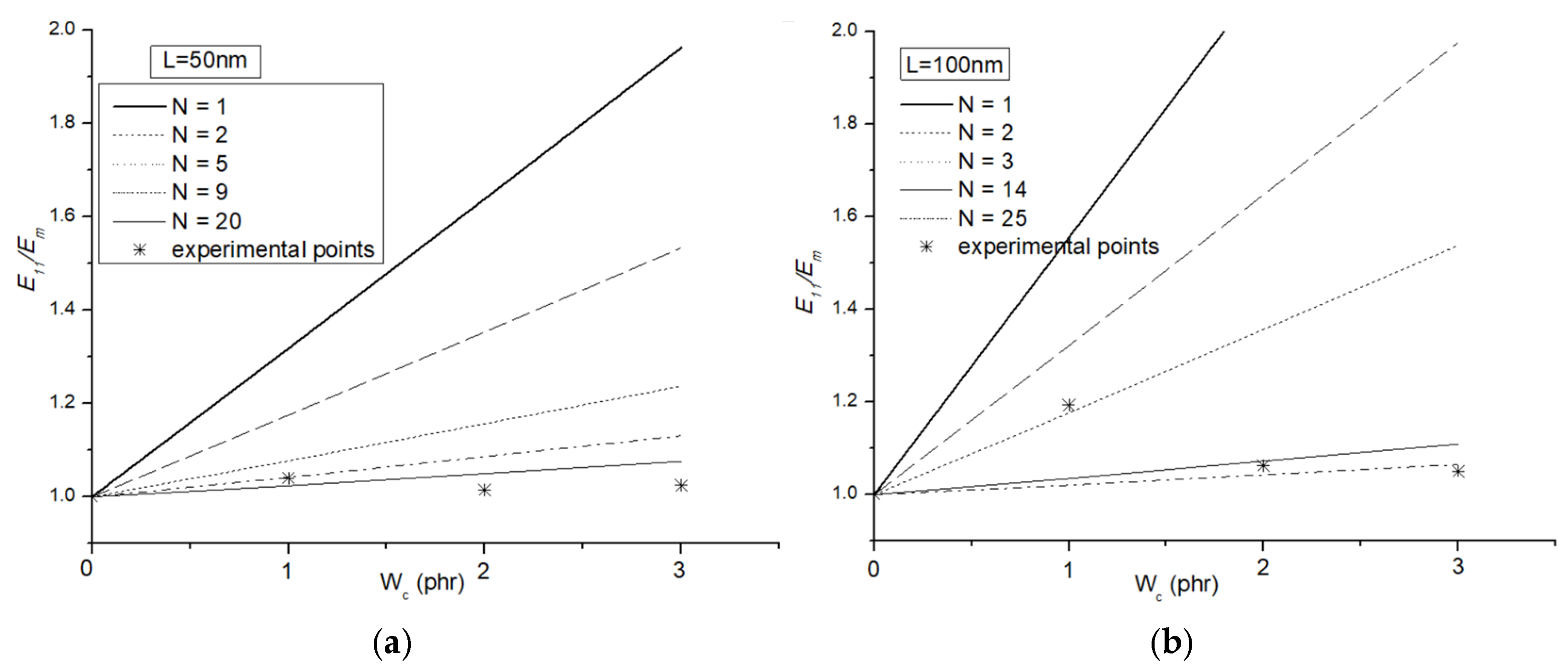
3.6. Micromechanical Modeling: Halpin–Tsai Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gardielli, F.; Coiai, S.; Passaglia, E.; Pucci, A.; Ruggeri, G. Review Nanocomposites based on polyolefins and functional thermoplastic materials. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 805–836. [Google Scholar]
- Gopakumar, T.G.; Lee, J.A.; Kontopoulou, M.; Parent, J.S. Influence of clay exfoliation on the physical properties of montmorillonite/polyethylene composites. Polymer 2002, 43, 5483–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Xu, W.; Guo, H.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, S.; Song, Q. Preparation and characterization of PE and PE-g-MAH/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 2539–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avella, M.; Cosco, S.; Volpe, G.D.; Errico, M.E. Crystallization behavior and properties of exfoliated isotactic polypropylene/organoclay nanocomposites. Advanc. Polym. Technol. 2005, 24, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton-That, M.-T.; Leelapornpisit, W.; Utracki, L.A.; Perrin-Sarazin, F.; Denault, J.; Cole, K.C.; Bureau, M.N. Effect of crystallization on intercalation of clay-polyolefin nanocomposites and their performance. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, D.D.; Wilkie, C.A. Polyethylene and polypropylene nanocomposites based on a three component oligomerically-mofified clay. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, J.; Li, H. Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene/polypropylene/organo-montmorillonite nanocomposites: Phase morphology, rheological, and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krump, H.; Luyt, A.S.; Hudec, I. Effect of different modified clays on the thermal and physical properties of polypropylene-montmorillonite nanocomposites. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 2877–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesti, M.; Lorenzetti, A.; Bon, D.; Besco, S. Thermal behaviour of compatibilised polypropylene nanocomposite: Effect of processing conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.S.; Liberman, S.A.; Oviedo, M.A.S.; Mauler, R.S. Polyolefin-based nanocomposite: The effect of organoclay modifier. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eteläaho, P.; Nevalainen, K.; Suihkonen, R.; Vuorinen, J.; Järvelä, P. Effects of Two different maelic anhydride-modified adhesion promoters (PP-g-MA) on the structure and Mechanical properties of nanofilled polyolefins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, F.-C.; Yen, H.-Z.; Lee, C.-E. Characterization of PP/HDPE blend-based nanocomposites using different maleated polyolefins as compatibilizers. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tladi Gideon Mofokeng, T.G.; Ray, S.S.; Ojijo, V. Structure–property relationship in PP/LDPE blend composites: The role of nanoclay localization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigail-Cedeño, A.; Diaz-Barrios, A.; Alban, B.; Caceres, J.; Pilataxi, J.; Molina, V.; Lazo, M. The effect of Olefin Block Copolymer and Organoclays in Recycled HPE/PP nanocomposites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2205, 020073. [Google Scholar]
- Jeevan, K.P.; Prasad, R.K. Influence of nanoclay reinforcement on thermal and mechanical properties of high-density polyethylene and polypropylene blends. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2025, 48, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufassa, S.; Doufnoune, R.; Hellati, A.; Haddaoui, N.; Cagiao, M.E. Effect of compatibilizing agents on the physical properties of iPP/HDPE organoclay blends. J. Polym. Eng. 2013, 33, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Zhou, Y.-G.; Wu, H.-H. Influence of mechanical properties of polypropylene/low-density polyethylene nanocomposites: Compatibility and crystallization. Nanomat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 7, 1847980417715929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Pan, L.; Du, H.-Z.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y.-S. Effect of Olefin-based Compatibilizers on the Formation of Cocontinuous Structure in Immiscible HDPE/iPP blends. Chin. J. Polym Sci. 2020, 38, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, A.; Naveh, N. Compatibilization of Post-Consumer Recycled Polypropylene/Polyethylene Binary Blends. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, M.; Qaiser, A.A. Effect of Various Compatibilizer Systems on the Upcycling of Comingled Plastic Waste Through in situ Reactive Compatibilization Technique. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2025, 142, e57357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, A.; Jaffer, S.; Sain, M. Review on modification strategies of polyethylene/polypropylene immiscible thermoplastic polymer blends for enhancing their mechanical behavior. J. Elastomers Plast. 2018, 51, 291–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Elder, T.; Peng, Y. Enhancing Polyoropylene/Polyethylene Blend Performance Through Compatibilization for A sustainable Future: A Mini Review Focusing on Establishing Bio-Derived Filler Based Hybrid Compatibilizer System. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, 46, 2400724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehiyan, R.; El-Samak, A.A.; Kamkar, M.; Erfanian, E.; Hodge, S.A.; Sundararaj, U.; McNally, T. Unveiling the Significance of Graphene Nanoplatelet (GNP) Localization in Tuning the Performance of PP/HDPE Blends. Materials 2024, 17, 5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantou, M.; Gavriel, M.; Tarantili, P.A. Effect of Compatibilizer and Organoclay Reinforcement on Morphology and Properties of Styrene Copolymer Blends. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darras, O.; Sequela, R. Surface free energy of the chain-folding crystal faces of ethylene-butene random copolymers. Polymer 1993, 34, 2946–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Z.D.; Janimak, J.J.; Zhang, A.Q.; Hsieh, E.T. Isotacticity effect on crystallization and melting in polypropylene fractions: 1. Crystalline structures and thermodynamic property changes. Polymer 1991, 32, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, N.; Boyce, M.C.; Parks, D.M.; Rutledge, G.C.; Abes, J.I.; Cohen, R.E. Multiscale micromechanical modeling of polymer/clay nanocomposites and the effective clay particle. Polymer 2004, 45, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manevitch, O.L.; Rutledge, G.C. Elastic Properties of a Single Lamella of Montmorillonite by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Brinson, L.C. Reinforcing efficiency of nanoparticles: A simple comparison for polymer nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cloisite 30B | Cloisite 25A | |
|---|---|---|
| Organic modifier |  Methyl, tallow, bis-2-hydroxylethyl, and quaternary ammonium | 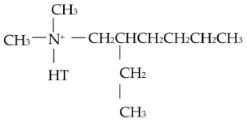 Dimethyl, hydrogenated tallow, and 2-ethylhexyl quaternary ammonium |
| Modifier concentration | 90 meq/100 g clay | 95 meq/100 g clay |
| Weight loss in ignition | 30% | 34% |
| Temperature (°C) | Screw Rotation Speed (rpm) | Feeder Screw Rotation Speed (rpm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Extruder Barrel Zones | |||||||
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | Die | ||
| 185 | 190 | 190 | 190 | 190 | 190 | 30–200 | 20–70 |
| Temperature (°C) | Injection Pressure (bar) | Packing Pressure (bar) | Cooling Time (s) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Injection Barrel Zones | ||||||||
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | (8 ccm) | (10 ccm) | ||
| 190 | 195 | 195 | 195 | 200 | 850 | 800 | 270 | 5 |
| Clay Type | Clay (phr) | Τm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Τc (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Peak | 2nd Peak | 1st Peak | 2nd Peak | ||||
| HDPE | - | - | 134.7 ± 0.15 | - | 209.06 ± 1.63 | - | 119.7 ± 1.25 |
| PP | - | - | - | 164.3 ± 0.11 | - | 90.29 ± 1.35 | 121.0 ± 1.22 |
| COMP | - | - | 111.0 ± 0.11 | - | 98.29 ± 1.45 | - | 99.1 ± 1.33 |
| 10/90 (w/w) HDPE/PP + 20 phr COMP | 0 | 129.6 ± 0.25 | 162.7 ± 0.14 | 17.09 ± 1.17 | 59.30 ± 1.25 | 118.3 ± 1.55 | |
| Cl 25A | 1 | 130.5 ± 0.16 | 163.8 ± 0.36 | 17.76 ± 2.64 | 61.12 ± 2.28 | 117.2 ± 0.18 | |
| Cl 25A | 2 | 129.4 ± 0.18 | 163.4 ± 0.26 | 13.16 ± 2.33 | 62.54 ± 2.28 | 116.5 ± 0.44 | |
| Cl 25A | 3 | 129.6 ± 0.36 | 163.6 ± 0.28 | 14.05 ± 1.03 | 57.21 ± 0.59 | 116.3 ± 0.30 | |
| Cl 30B | 1 | 128.8 ± 0.39 | 163.2 ± 0.60 | 11.62 ± 0.40 | 59.85 ± 4.91 | 116.6 ± 0.38 | |
| Cl 30B | 2 | 128.3 ± 0.45 | 163.1 ± 0.32 | 11.66 ± 0.50 | 56.44 ± 0.38 | 117.2 ± 0.72 | |
| Cl 30B | 3 | 129.5 ± 0.64 | 163.2 ± 0.55 | 11.45 ± 0.95 | 57.04 ± 0.09 | 117.1 ± 0.46 | |
| 25/75 (w/w) HDPE/PP + 20 phr COMP | 0 | 131.1 ± 0.45 | 162.8 ± 0.28 | 33.10 ± 3.15 | 49.57 ± 1.09 | 117.9 ± 0.12 | |
| Cl 25A | 1 | 131.9 ± 0.11 | 162.5 ± 0.38 | 42.74 ± 6.31 | 47.09 ± 3.95 | 118.0 ± 0.57 | |
| Cl 25A | 2 | 131.6 ± 0.32 | 163.1 ± 0.22 | 38.05 ± 4.52 | 42.72 ± 2.04 | 117.7 ± 0.27 | |
| Cl 25A | 3 | 132.1 ± 0.23 | 163.4 ± 0.64 | 34.54 ± 0.94 | 41.86 ± 1.53 | 117.5 ± 0.01 | |
| Cl 30B | 1 | 131.8 ± 0.20 | 163.1 ± 0.64 | 41.37 ± 5.26 | 40.51 ± 2.68 | 117.7 ± 0.30 | |
| Cl 30B | 2 | 131.5 ± 0.52 | 163.0 ± 0.42 | 35.21 ± 4.91 | 44.50 ± 1.28 | 118.0 ± 0.69 | |
| Cl 30B | 3 | 132.0 ± 0.08 | 163.1 ± 0.06 | 41.10 ± 3.90 | 44.67 ± 1.95 | 118.9 ± 0.40 | |
| Clay Type | Clay (phr) | Xc (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xc, HDPE | Xc, PP | |||
| HDPE | - | - | 71.6 ± 0.56 | - |
| PP | - | - | - | 43.6 ± 0.65 |
| COMP | - | - | 33.7 ± 0.50 | - |
| 10/90 (w/w) HDPE/PP + 20 phr COMP | 0 | 5.9 ± 0.40 | 28.6 ± 0.60 | |
| Cl 25A | 1 | 6.1 ± 0.90 | 29.5 ± 1.10 | |
| Cl 25A | 2 | 4.5 ± 0.80 | 30.2 ± 1.10 | |
| Cl 25A | 3 | 4.8 ± 0.35 | 27.6 ± 0.29 | |
| Cl 30B | 1 | 4.0 ± 0.14 | 28.9 ± 2.37 | |
| Cl 30B | 2 | 4.0 ± 0.17 | 27.3 ± 0.18 | |
| Cl 30B | 3 | 3.9 ± 0.33 | 27.6 ± 0.04 | |
| 25/75 (w/w) HDPE/PP + 20 phr COMP | 0 | 11.3 ± 1.08 | 23.9 ± 0.53 | |
| Cl 25A | 1 | 14.6 ± 2.16 | 22.7 ± 1.91 | |
| Cl 25A | 2 | 13.0 ± 1.55 | 20.6 ± 0.99 | |
| Cl 25A | 3 | 11.8 ± 0.32 | 20.2 ± 0.74 | |
| Cl 30B | 1 | 14.2 ± 1.80 | 19.6 ± 1.29 | |
| Cl 30B | 2 | 12.1 ± 1.68 | 21.5 ± 0.62 | |
| Cl 30B | 3 | 14.1 ± 1.34 | 21.6 ± 0.94 | |
| HDPE/PP | Clay Type | Content (phr) | Τonset (°C) | Τpeak (°C) | Residue (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100/0 (w/w) | - | - | 456.3 ± 0.82 | 476.4 ± 0.55 | 3.97 ± 0.46 |
| 0/100 (w/w) | - | - | 392.0 ± 0.45 | 433.9 ± 0.35 | 4.27 ± 0.76 |
| COMP | - | - | 446.4 ± 0.64 | 472.4 ± 0.73 | 4.27 ± 0.75 |
| 10/90 (w/w) + 20 phr COMP | - | - | 430.3 ± 2.95 | 457.9 ± 2.26 | 4.29 ± 0.74 |
| Cl 25A | 1 | 434.2 ± 2.48 | 448.0 ± 1.04 | 4.40 ± 0.18 | |
| Cl 25A | 2 | 433.8 ± 2.17 | 446.4 ± 0.19 | 5.03 ± 0.71 | |
| Cl 25A | 3 | 436.2 ± 1.81 | 446.1 ± 0.80 | 5.90 ± 0.90 | |
| Cl 30B | 1 | 439.0 ± 0.98 | 453.5 ± 1.21 | 4.05 ± 0.34 | |
| Cl 30B | 2 | 431.6 ± 1.27 | 449.9 ± 3.20 | 4.85 ± 1.08 | |
| Cl 30B | 3 | 428.0 ± 3.01 | 447.2 ± 2.32 | 4.54 ± 0.46 | |
| 25/75 (w/w) + 20 phr COMP | - | - | 435.7 ± 4.57 | 453.7 ± 2.76 | 4.63 ± 0.74 |
| Cl 25A | 1 | 434.7 ± 3.56 | 454.1 ± 0.82 | 4.29 ± 0.93 | |
| Cl 25A | 2 | 433.1 ± 3.90 | 448.2 ± 2.08 | 5.41 ± 0.30 | |
| Cl 25A | 3 | 434.8 ± 0.72 | 448.2 ± 1.48 | 6.31 ± 0.02 | |
| Cl 30B | 1 | 430.8 ± 5.83 | 452.9 ± 2.79 | 4.91 ± 0.93 | |
| Cl 30B | 2 | 430.8 ± 0.75 | 448.0 ± 2.47 | 4.57 ± 0.52 | |
| Cl 30B | 3 | 431.9 ± 1.10 | 447.6 ± 0.62 | 6.81 ± 1.45 |
| HDPE/PP | Clay Type | Clay/COMP (phr) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Modulus of Elasticity (MPa) | MFI (g/10 min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | - | - | 27.48 ± 0.35 | 764.64 ± 22.15 | 0.98 ± 0.09 |
| PP | - | - | 38.80 ± 0.24 | 1165.89 ± 33.14 | 2.69 ± 0.18 |
| COMP | - | - | 10.00 ± 0.46 | 207.90 ± 16.20 | 0.69 ± 0.07 |
| 10/90 (w/w) | - | 0/20 | 34.36 ± 0.40 | 1058.16 ± 45.72 | 2.804 ± 0.15 |
| Cl 25A | 1/20 | 34.06 ± 0.53 | 1039.75 ± 63.01 | 2.433 ± 0.09 | |
| Cl 25A | 2/20 | 35.33 ± 0.24 | 1120.67 ± 43.25 | 2.271 ± 0.18 | |
| Cl 25A | 3/20 | 33.99 ± 0.35 | 1020.22 ± 26.97 | 2.242 ± 0.11 | |
| Cl 30B | 1/20 | 35.03 ± 0.39 | 1100.38 ± 35.21 | 2.496 ± 0.11 | |
| Cl 30B | 2/20 | 34.51 ± 0.43 | 1073.87 ± 28.60 | 2.513 ± 0.25 | |
| Cl 30B | 3/20 | 34.34 ± 0.22 | 1084.02 ± 39.52 | 2.490 ± 0.30 | |
| 25/75 (w/w) | - | 0/20 | 34.21 ± 1.04 | 985.87 ± 36.67 | 2.058 ± 0.15 |
| Cl 25A | 1/20 | 34.14 ± 0.68 | 1062.33 ± 35.96 | 1.987 ± 0.18 | |
| Cl 25A | 2/20 | 34.88 ± 0.60 | 1023.51 ± 29.03 | 1.829 ± 0.17 | |
| Cl 25A | 3/20 | 34.78 ± 0.37 | 1073.44 ± 37.41 | 1.836 ± 0.19 | |
| Cl 30B | 1/20 | 36.96 ± 0.59 | 1176.90 ± 32.78 | 1.871 ± 0.11 | |
| Cl 30B | 2/20 | 34.59 ± 0.32 | 1047.71 ± 51.21 | 2.000 ± 0.16 | |
| Cl 30B | 3/20 | 33.94 ± 0.51 | 1035.58 ± 23.13 | 1.928 ± 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moraitis, G.; Tarantili, P.A. Enhancing the Performance of Polypropylene/High-Density Polyethylene Blends by the Use of a Compatibilizer and Montmorillonite Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11998. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211998
Moraitis G, Tarantili PA. Enhancing the Performance of Polypropylene/High-Density Polyethylene Blends by the Use of a Compatibilizer and Montmorillonite Nanoparticles. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):11998. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211998
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoraitis, Georgios, and Petroula A. Tarantili. 2025. "Enhancing the Performance of Polypropylene/High-Density Polyethylene Blends by the Use of a Compatibilizer and Montmorillonite Nanoparticles" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 11998. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211998
APA StyleMoraitis, G., & Tarantili, P. A. (2025). Enhancing the Performance of Polypropylene/High-Density Polyethylene Blends by the Use of a Compatibilizer and Montmorillonite Nanoparticles. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 11998. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211998







