Light Modulation and Biophoton Emissions: A Proof-of-Principle Study of Direct and Proximal Cellular Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.1.1. B16-BL6
2.1.2. MCF-7 Cells
2.2. Equipment
2.2.1. Application of LED
2.2.2. Photomultiplier Tube (PMT)
2.3. Exposure Protocol
2.4. Viability Assessment
2.4.1. Obtaining Cell Pellet
2.4.2. Cell Counting with a Hemocytometer
2.4.3. Cell Counting with CountessTM
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
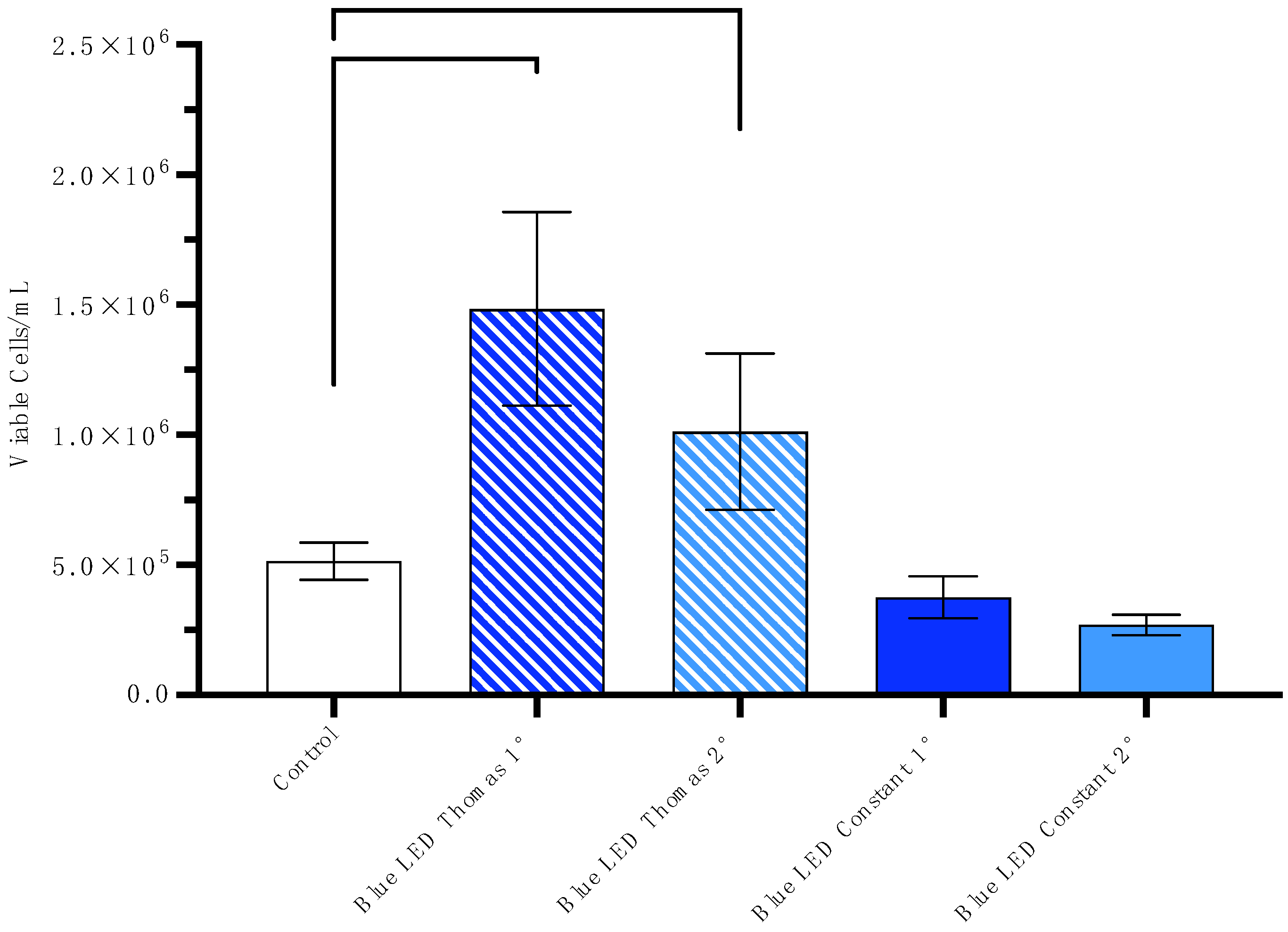
3.1. Increase in Viable Cells/mL After Exposure to the Blue Thomas-Patterned LED
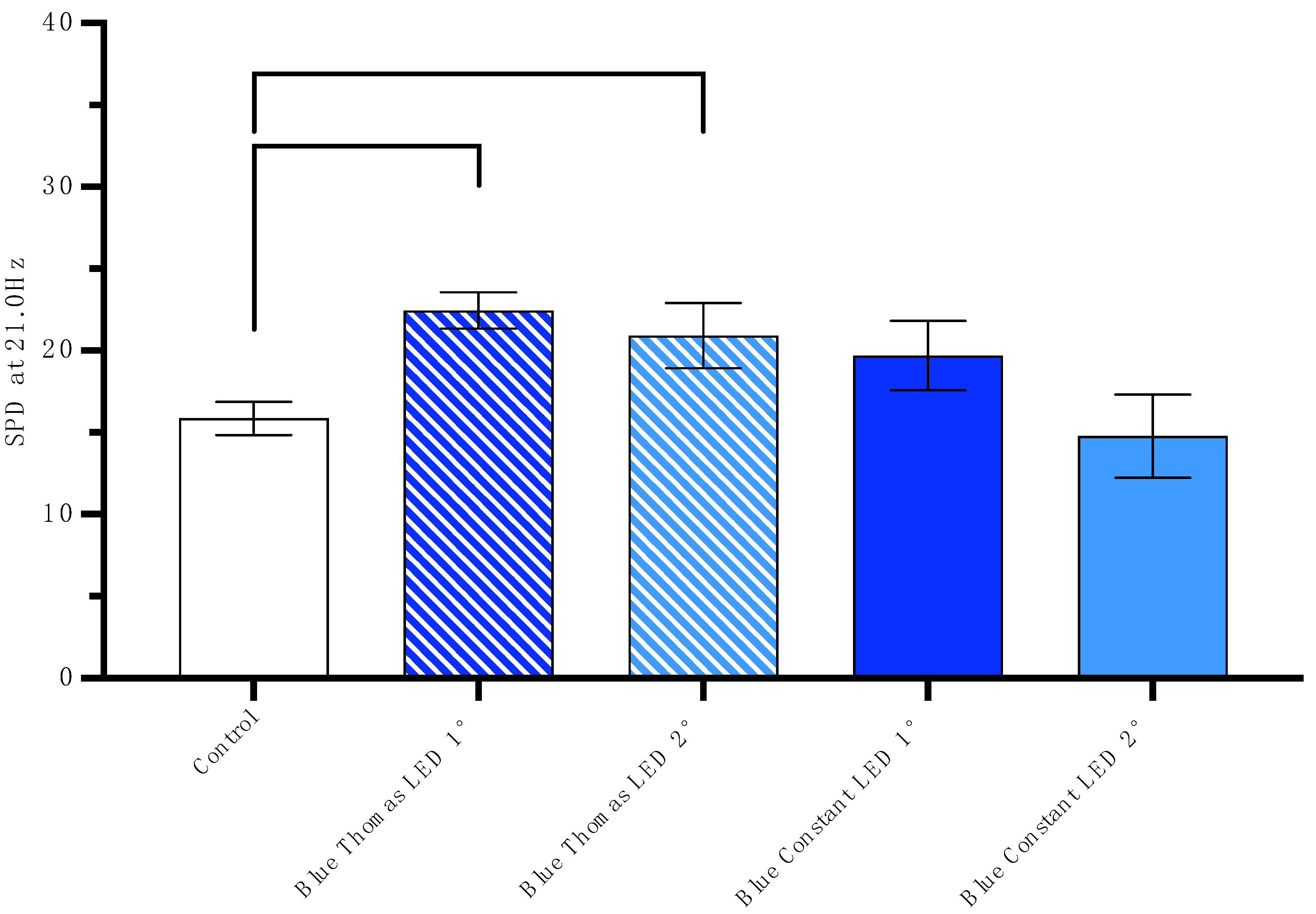
3.2. SPD of Photon Emission 24 h After Cells Are Exposed to the Blue Thomas-Patterned LED
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| % | Percent |
| A + A | Antibiotic and Antimycotic Cell Culture Solution |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| B16-BL6 | B16-BL6 Mouse Melanoma Cells |
| cm | Centimeter |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| DAC | Digital-to-Analogue Converter |
| EMF | Electromagnetic Field |
| Hz | Hertz |
| LED | Light-emitting Diode |
| LTP | Long-term Potentiation |
| MCF-7 | MCF-7 Human Cancerous Breast Cell |
| mL | Milliliter |
| mm | Millimeter |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Hydrogen |
| nm | Nanometer |
| PMT | Photomultiplier Tube |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| UPE | Ultraweak Photon Emission |
| μL | Microliter |
| μT | Micro Tesla |
References
- Tessaro, L.W.; Dotta, B.T.; Persinger, M.A. Bacterial biophotons as non-local information carriers: Species-specific spectral characteristics of a stress response. MicrobiologyOpen 2018, 8, e00761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fels, D. Correction: Cellular communication through light. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifra, M.; Fields, J.Z.; Farhadi, A. Electromagnetic cellular interactions. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2011, 105, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafur, J.; Van Wijk, E.P.A.; Van Wijk, R.; Mills, P.J. Biophoton detection and low-intensity light therapy: A potential clinical partnership. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2010, 28, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučera, O.; Cifra, M. Cell-to-cell signaling through light: Just a ghost of chance? Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Miyashiro, T. Quorum sensing in the squid-vibrio symbiosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 16386–16401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niggli, H.J. Biophoton re-emission studies in carcinogenic mouse melanoma cells. In Recent Advances in Biophoton Research and Its Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 1992; pp. 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Dai, J. Biophotons as neural communication signals demonstrated by in situ Biophoton autography. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2010, 9, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wijk, R.; Kobayashi, M.; Van Wijk, E.P.A. Anatomic characterization of human ultra-weak photon emission with a moveable photomultiplier and CCD imaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2006, 83, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotta, B.T.; Buckner, C.A.; Lafrenie, R.M.; Persinger, M.A. Photon emissions from human brain and cell culture exposed to distally rotating magnetic fields shared by separate light-stimulated brains and cells. Brain Res. 2011, 1388, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, F.-A.; Gu, Q.; Li, K.-H. Biophoton emission: Experimental background and theoretical approaches. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 1994, 8, 1269–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifra, M.; Pospíšil, P. Ultra-weak photon emission from biological samples: Definition, mechanisms, properties, detection and applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 139, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.J.; Popp, F.A. Biological Organization: A possible mechanism based on the coherence of “biophotons”. In Biophotons; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, N.J.; Persinger, M.A.; Karbowski, L.M.; Dotta, B.T. Ultraweak photon emissions as a non-invasive, early-malignancy detection tool: An in vitro and in vivo study. Cancers 2020, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leulmi, S.; Chauchet, X.; Morcrette, M.; Ortiz, G.; Joisten, H.; Sabon, P.; Livache, T.; Hou, Y.; Carrière, M.; Lequien, S.; et al. Triggering the apoptosis of targeted human renal cancer cells by the vibration of anisotropic magnetic particles attached to the cell membrane. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15904–15914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhu, G.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y. The strong inhibitory effect of combining anti-cancer drugs AT406 and rocaglamide with blue led irradiation on colorectal cancer cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 30, 101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, T.; Kishi, R.; Sato, K.; Sato, K. Blue light exposure enhances oxidative stress, causes DNA damage, and induces apoptosis signaling in B16F1 melanoma cells. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2022, 883–884, 503562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, P.-S.; Na, K.S.; Hwang, H.; Jeong, H.-S.; Lim, S.; Sohn, M.-H.; Jeong, H.-J. Effect of blue light emitting diodes on melanoma cells: Involvement of apoptotic signaling. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 142, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, M.; Kawashima, Y.; Katoh, O.; Watanabe, H. Blue light inhibits the growth of B16 Melanoma Cells. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2002, 93, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peidaee, P.; Almansour, N.; Shukla, R.; Pirogova, E. The cytotoxic effects of low intensity visible and infrared light on Human breast cancer (MCF7) cells. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 6, e201303015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Forman, H.J.; Torres, M.; Fukuto, J. Redox signaling. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 234–235, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binhi, V.N.; Chernavskii, D.S. Stochastic dynamics of magnetosomes in Cytoskeleton. Europhys. Lett. (EPL) 2005, 70, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncato, F.; Regev, O.; Yadav, S.K.; Alon, R. Microtubule destabilization is a critical checkpoint of chemotaxis and transendothelial migration in melanoma cells but not in T cells. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2021, 15, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borys, F.; Joachimiak, E.; Krawczyk, H.; Fabczak, H. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors affecting microtubule dynamics in normal and cancer cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmati-Carrion, M.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Hardeland, R.; Madrid, J.; Rol, M. A comparison of B16 melanoma cells and 3T3 fibroblasts concerning cell viability and Ros production in the presence of melatonin, tested over a wide range of concentrations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3901–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-L.; Voon, C.P.; Guan, X.; Yang, Y.; Gardeström, P.; Lim, B.L. In Planta study of photosynthesis and photorespiration using NADPH and NADH/NAD+ fluorescent protein sensors. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Levac, S.J.; Dotta, B.T. Light Modulation and Biophoton Emissions: A Proof-of-Principle Study of Direct and Proximal Cellular Effects. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9858. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189858
Levac SJ, Dotta BT. Light Modulation and Biophoton Emissions: A Proof-of-Principle Study of Direct and Proximal Cellular Effects. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9858. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189858
Chicago/Turabian StyleLevac, Samuel J., and Blake T. Dotta. 2025. "Light Modulation and Biophoton Emissions: A Proof-of-Principle Study of Direct and Proximal Cellular Effects" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9858. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189858
APA StyleLevac, S. J., & Dotta, B. T. (2025). Light Modulation and Biophoton Emissions: A Proof-of-Principle Study of Direct and Proximal Cellular Effects. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9858. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189858




