Effect of Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rate in Mountainous Photovoltaic Power Stations on the Ecological Environment of Mountainous Landscapes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Soil Data Collection and Measurement
2.2.2. Vegetation Data Collection and Measurement
3. Results
3.1. Data Processing and Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Vegetation Community Conditions
3.1.1. Data Processing
3.1.2. Data Analysis
3.2. Impact Analysis of Photovoltaic Coverage Rate on the Mountain Landscape Ecological Environment
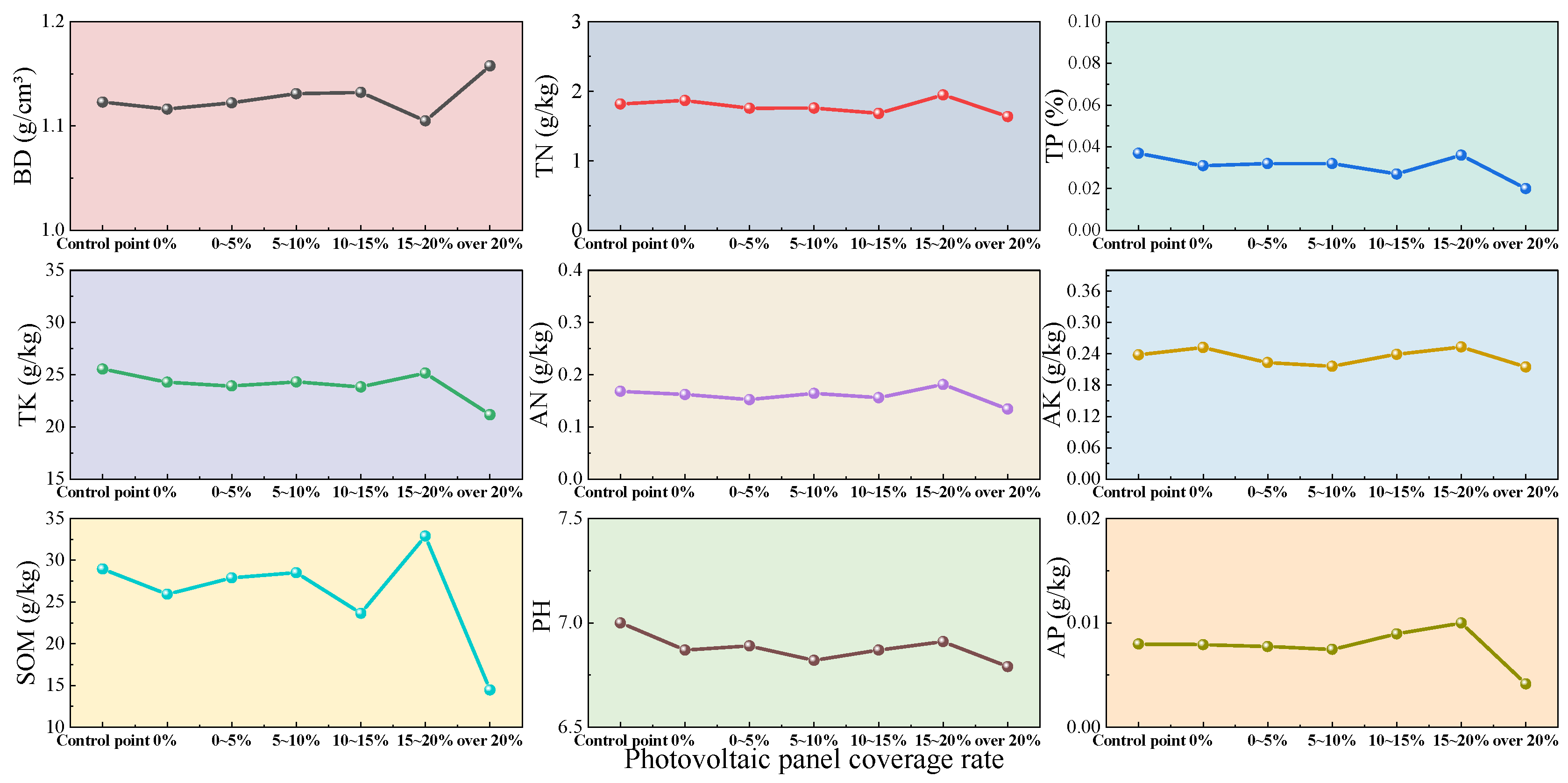
3.2.1. Effect of Photovoltaic Coverage Rate on Soil Physicochemical Properties
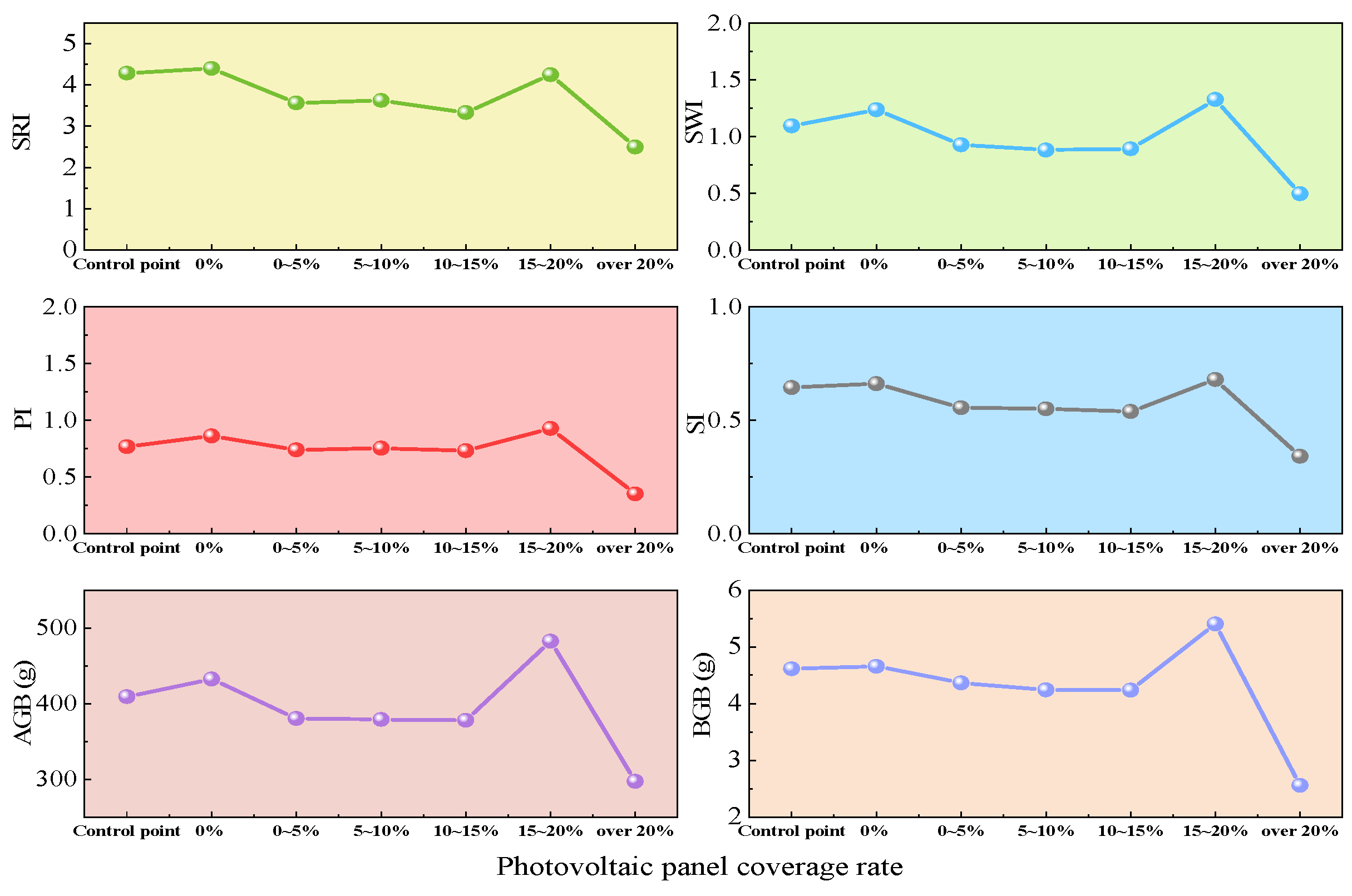
3.2.2. Effect of Photovoltaic Coverage Rate on Vegetation Community Conditions
3.3. Determination of Optimal Interval for Mountain Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Based on Euclidean Distance
3.3.1. Euclidean Distance Principle
3.3.2. Determination of Optimal Range of Photovoltaic Panel Coverage
4. Discussion
4.1. Reasons for Effect of Mountain Photovoltaic Panel Coverage on Soil Physicochemical Properties
4.2. Reasons for Effect of Mountain Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rate on Vegetation Community
4.3. Reasons for Ranking of Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rate in Mountainous Areas and Similarity of the Landscape Ecological Environment of Control Point
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BD | Bulk density |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| TK | Total potassium |
| AN | Alkali-hydrophobic nitrogen |
| AK | Available potassium |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| AP | Available phosphorus |
| SRI | Species Richness index |
| SWI | Shannon–Wiener index |
| SI | Simpson index |
| PI | Pielou index |
| AGB | Above-ground biomass |
| BGB | Underground biomass |
References
- Sui, X.; Wei, Y.; Luo, X.L.; Wu, S.N. Research on ecological photovoltaic models in vulnerable areas for “dual carbon” goals. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2022, 43, 56–63. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2021-0837 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Tang, Y.; Sun, H.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, D.; Sun, H. Research on Large-scale Photovoltaic Electrical Construction Technology in the Northern Xinjiang Region: A Case Study of a project in Nalik. Constr. Des. Eng. 2025, 4, 142–144. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13616/j.cnki.gcjsysj.2025.02.247 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Sati, V.P. Sustainable Mountain Development: Challenges and Opportunities. In Towards Sustainable Livelihoods and Ecosystems in Mountain Regions; ESE; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 8, pp. 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Li, C.; Cao, D.M.; Zhang, M.; Li, M. Difficulties and Measures in the construction and Management of mountain photovoltaic power stations. China Power Enterp. Manag. 2024, 27, 46–47. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPOgmnCwJYMocthcIMmbo-dy98GXFrZed-r-7siJ5LFeb8voJAGz9AhZ6fyjjVuxywMXiOSXy3RUYayR1ZTJbn9Vt9rLwT9YpOYC83F8yo93LatA9q38LE6OcduhjCJUsyKQwzfDyz_AisWb6lr_DMs1PgCJ3mtE-mgdOavxTJsZ0CUMnqKTeSITB5Ob2K1LG34=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Ding, C.X.; Li, X.F.; Su, D.R.; Liu, Y. Meta-analysis of the impact of photovoltaic power stations on regional microclimate-vegetation-soil characteristics. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2025, 4, 2641–2651. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3362.S.20250610.1815.014 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Qu, W.H. Effects of Different Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rates on Photothermal Environment Inside Photovoltaic Arrays and Peanut Growth. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Information Engineering University, Nanjing, China, 2024. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27248/d.cnki.gnjqc.2024.000563 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Wu, T.; Duan, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.N.; Wang, X.Z.; Guo, Z.G. Effects of Different photovoltaic array Construction on natural restoration of plant communities and physicochemical properties of soil in desert grassland. Pratacult. Sci. 2024, 1, 1–13. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/62.1069.S.20240710.2152.002 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Chen, W.W. Approaches to soil erosion control in Large mountain photovoltaic power stations. Yunnan Electr. Power 2025, 5, 5–9. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPNjUwmPT671UMpIQX5fhwWw1dCfOkPqiAE8cBpfQ7NoxEevKW_ONUzGwxPxkSivjNMUUf2FlESTbv-zHQDkz5XjnWEHjoTuLO2t1IH_aq6-udC3HSl0LflfEGqzX9wHi9rqHadydmfesYLJI1_fOR7qAwYTKPni1UfdPL7NrDPAePDR3mGToNSk&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Yang, Y.Y.; Su, S.L.; Cao, E.Z.; Li, H.Y.; Chi, H.M.; Lin, K.; Wu, X.D.; He, W.Q.; Yang, H.T. Effects of large-scale photovoltaic power stations in deserts on phenotypes and biomass allocation of sand-fixing plants. J. Desert Res. 2020, 45, 162–172. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPP-i8uthcWcApuPbQCrBmnjYKQQxEEvy3yps4Sp6slXBxAx52MXF69ryIrBZvegCkV0ERF1pcKfYsXio1jjWqNfrhXqJv-WFMv5-asoisLhs5PIIrfsViBukXp1XS-AxAypEuQbESZkaLwv-w79PwpEeuxcGJsslFiMLvNkyG7wV-wWdfhW9YAggAUDi0Dusdw=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Ren, N.P.; Li, Y.K.; Zhu, B.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Liang, W.C.; Liu, X.P. Effects of Photovoltaic Panels on Plant Community Characteristics and Species Diversity in Meadow Steppe Ecosystems. China J. Ecol. 2024, 43, 766–772. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13292/j.1000-4890.202403.045 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Lambert, Q.; Bischoff, A.; Enea, M.; Gros, R. Photovoltaic power stations: An opportunity to promote European semi-natural grasslands? Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 37845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.S.; Cagle, A.E.; Macknick, J.; Bloom, D.E.; Caplan, J.S.; Ravi, S. Effects of Revegetation on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in Solar Photovoltaic Infrastructure. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.Y.; Wu, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, F.M.; Wang, Y. Analysis of High Temperature Weather Characteristics in Chaoyang County: A Case Study of 14–15 June. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 37, 235. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPOgaFsBylb8RoFPYn7nXL2Ej6Y4K5zWbTsahAIbdUaiRVKJb1OROpkvgpqQva9hcap2Lp0SFIjaao05UK59AD0rdrtngsFrJhEpD435mZC8QsSvDtlxQsXkjjy1PfQsHjCJ28eCsagF6DzPYMV9vPayTe1tDONDxPRJbX6fggVSn2exnaUYFFjkXoyqCc1kVF8=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Gu, Z.T.; Li, R.C.; Xu, M.J. Evaluation of resilience of natural ecosystems in Chaoyang County, Liaoning Province. China Energy Environ. Prot. 2023, 45, 118–126. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19389/j.cnki.1003-0506.2023.11.018 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Tan, Z.X.; Chen, X.C.; Xiao, S.; Zhou, H.K.; Qu, J.P. Effects of the Talatan Photovoltaic Power Station in Qinghai Province on vegetation diversity. Qinghai Sci. Technol. 2023, 30, 10–18. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPNaJMpfYrKNWhHainL5cExekCLFgW6kU1CKU04BQrwDeSljdBSSvGq6dEFYTzHN6XfylSL1MZrWESleEBf46EmQWM0FxxjEHjIxdvGoolQEr5pMaBNKTrkq4K3mItjs-LXCreTTCZKZr6hp7UNE1dYI3SUQJVdr77Up-uPZDDS_fqaECPyRXQVCMEwsLDBxXmQ=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Wang, P.; Hua, H.L.; Ding, Z.Q.; Yu, X.Y.; Tan, X.A.; Li, Y.H. The Effects of Altitude and Land Use on Organic Matter and Integrated Fertility of Soils in the Northern Tropics Mountain. Trop. Geogr. 2023, 43, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Du, Y.G.; Xu, Q.M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Qu, J.P. The impact of grazing on the soil organic carbon content in alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Grassl. Turf 2023, 43, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.R.; Wang, X.J. The impact of Photovoltaic power station projects on soil and vegetation: A Case Study of the Desert and Gobi Area in the Hexi Corridor of Gansu Province. China Soil. Water Conserv. Sci. 2019, 17, 132–138. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16843/j.sswc.2019.02.016 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Yuan, J.M.; Gao, Y. Spatial differentiation characteristics of soil nutrients in the area of tracking photovoltaic arrays in sandy areas. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2025, 2, 1–10. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2024.0304 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Li, B.P.; Pan, Y.; Xu, G.; Yuan, C.; Wang, J.D. Research on the impact on the surrounding ecological environment during the construction of wind farms. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2024, 49, 190–194. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPPfonkuQ9gY_hyOHO4v8GjV8iHFdYWsRYwZoxrxvCjkHvhGyzJVGn9NGjSjh7JjcqpVPn5yf6Le8M4a4NxkC3di1cnKfSZmRJMDPf3NlTJ2tAil8se8vxWKUKxJHz_QEBk7g0eCQy5fE02ad-HI2fkvZUFvSohTMeBQV0OTfP2p59g3hiqn5HiNpZ046WkGUxc=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Hao, X.Z.; Yu, H.; Wu, X.Y.; Feng, T.J.; Wang, C.; Tian, L.H.; Tan, M.D.; Peng, H.W.; Wang, P. The Impact of Typical Photovoltaic Power Station Construction on Vegetation Attributes and Soil Properties in the Desert Areas of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 5510–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, H.Y.; Cui, Y.Y.; Ye, D.L.; Zhang, X.P.; La, B. Analysis of Vegetation Community Recovery Process after Photovoltaic Construction: A Case Study of the Gonghe Photovoltaic Park in Qinghai. Chin. Wild Plant Resour. 2024, 43, 124–130. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPPHbLUOPOkjnYZZrB4lMNnfFkIUUePbYWhjPYFrM428lAqVKLT0AGCeHI6wt7WMJIrD3J0fU1GESLFtDytQtQgd9qgRwxvTyDtpK7JFxGtMU3UuW4lBIMKuhnnL5_GEA8fg7AbwwzDbuL28WKh6TjA_niS_cn65tGUvVDrAtUzQD8C9UTi2J0whZGVPkyZ_blA=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Bao, P.A.; Ji, B.; Sun, G.; Zhang, N.; Wu, X.D.; He, J.L.; Wang, Z.J.; Tian, Y. Effects of photovoltaic power station construction on plant communities and soil characteristics. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2024, 33, 23–33. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/62.1105.S.20240923.1713.046 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Lu, Y.D.; Feng, J.; Shao, Z.; Fu, G.M.; Lu, Y.R.; Li, H.Y. Responses to mowing and long-term grazing of plant community species composition and diversity in Songnen meadow steppe. Pratacult. Sci. 2024, 41, 271–283. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPM7fKp8bnWOGQKdC85gjVaezLzolDLiJxJPfer74fIef3seTB9_3UsjsOFB2FFme8oTSi4sW-2z6ABqggIFNNlnf2u1Zvpt_7Chxj7OLnZH_RUtaYUL3DeKnVzejd61f6gxP4z2lKoOSUWvdDA_E91kVcHlTWtfIEEqpDHfsz7boBnlVNYfD1FwWZLe8MFtHPU=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Wang, Z.H.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Z.W.; Liu, H.M. Analysis of the correlation between the importance values of dominant populations and species diversity in desert steppe after spring rest. Chin. J. Grassl. 2025, 1, 45–53. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16742/j.zgcdxb.20230368 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Zhou, R.F.; Wu, Y.G.; Ye, Z.L.; Chen, X.R.; Xu, D.M.; Chen, D.L. Community characteristics and α diversity of low mountain evergreen broad-leaved forest in Baishanzu Reserve. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2014, 29, 62–66. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPNwCU3-uSeKnhHpw69e_S_igb29LJSsvBAANo1DifJz9960fPFi-d1TbFR_cjH_j52OVVgmgTxvVxwzEiWxrN5kRGJIMgFcj8L0A0shBZAN_dq31BkpxonQbCYTeUiTj6Ar7CEtlXHGtAm_5uam1ngz3DjHxjT5EQ4CaXUEAFUK0afurWgGIvGD&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Yue, S.J. Qinghai Desert Large-Scale pv Development Ecological Environment Effect Research. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2022. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27398/d.cnki.gxalu.2022.000129 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Liu, R.; Yang, X.J.; Gao, R.R.; Hou, X.; Hou, L.; Huang, Z.; Cornelissen, J. Allometry rather than abiotic drivers explains biomass allocation among leaves, stems and roots of Artemisia across a large environmental gradient in China. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 1026–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.D.; Ni, W.L. A dynamic population Size control method based on Euclidean distance. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2022, 44, 2195–2206. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPPq_DENfXwMbeZrXKwvx940e_4AaTQ4eugd3kNNK5YvZ054lm4CcUYAyJhKFcV5nkGidvOxlBSHpmKSm2dsshM9fkwTNs9fVOZUShuMHNKkC71Ga5CCVeEVLVL2n2JEUDRGiZbFWgx2SfGit1bG-f-RnEj6KrRYN5RqIEPZi3MtxQS-BHHMpnxGI9ZDZYA0C4A=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- She, H.Y.; Wu, X.S. Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm Incorporating Euclidean Distance and Multiple Search Strategies. Transducer Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 37, 132–135. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13873/J.1000-9787(2018)09-0132-04 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Liu, J.F.; Liao, K.; Yan, Z.Z.; Huang, S.D.; Wang, X.; Zheng, P.X. Fetal monitor data anomaly detection method based on Euclidean distance. China Med. Equip. 2024, 21, 163–166. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPNXhfTo0ulJAH99pMCAmBcwdt7j0lJ5qYlvWvg17MA3xotbujIYKEh8cZEKVwk3zr-EVLYFKU_6Equg2PqCc6TZn_bxg9kiIPZdyZC8tZX90qh0uFC3xWwkMIYDCBKPCfYky22zhdGh4CBCkfci66zdzS4ZvU1XEyYCGQfCCbLc45wpn1nus0wKgEj5j39h1iI=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Dong, H.R.; Fu, Y.J.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Y.Q.; Chen, J.; Xie, D.H. Adaptive oversampling based on Euclidean distance clustering. Print. Digit. Media Technol. Study 2023, 8, 26–41. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19370/j.cnki.cn10-1886/ts.2023.05.003 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Sun, W.Q.; Chu, B.; Ye, G.H.; Cai, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Hua, L.M. Study on the Effects of Photovoltaic Power Stations on Soil Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity in Alpine Meadows. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2025, 4, 1–15. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3362.S.20241023.1116.002 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Salamanca, F.; Georgescu, M.; Mahalov, A.; Moustaoui, M.; Martilli, A. Citywide impacts of cool roof and rooftop solar photovoltaic deployment on near-surface air temperature and cooling energy demand. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2016, 161, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, A.M.; Krayenhoff, E.S.; Georgescu, M.; Sailor, D.J. The observed effects of utility-scale photovoltaicson near-surface air temperature and energy balance. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 989–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.H.; Long, H.Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Qiu, W.W.; Lei, Q.L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Mu, Z. Analysis of spatial variation characteristics and influencing factors of surface soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in Hebei Province. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2016, 22, 937–948. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3996.s.20160505.1658.006 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Quan, S.M.; Wang, X.K.; Hu, F. Total nitrogen content changes and influencing factors in farmland soil in Jiangsu Province. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2018, 41, 1078–1084. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPOlNtGu0yy4MbspJ1VjoO1cnTqD0LBfvidYmM3VRjyLWQA5sAyK9Njb7cFapBn3Tbd2y4Il3pN7GEJA52VA5XKbF2KGxCLug_1qb_QOYMMzj9h-0jWw3nKmWITW_O9l_5g722KDQgJxjD6OH9ygmDt-w5EAhKZMLhuKsa-X-2ENLgCO035ShMltFiBnBC5hL8Y=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Yu, H.M.; Duan, Y.H.; Mulder, J.; Dörsch, P.; Zhu, W.X.; Ri, X.; Huang, K.; Zheng, Z.T.; Kai, R.H.; Wang, C.; et al. Universal tempera-true sensitivity of denitrification nitrogenlosses in forest soils. Nat. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.L.; Bi, R.T.; Wang, J.; Yuan, S.F. Soil fertility characteristics of sloping cultivated land in different microhabitats in Xinzhou, a typical mountainous area of North China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 27, 205–208. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2013.05.025 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, Z.C.; Gao, X.Q.; Luo, Y. Characteristics of summer sunny surface fluxes in large-scale photovoltaic power stations in Gobi. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2021, 42, 138–144. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2020-0844 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Jiao, J.Y.; Tzanopoulos, J.; Xofis, P.; Mitchley, J. Factors affecting distribution of vegetation types on abandoned cropland in the hilly -gullied Loess Plateau region of China. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Song, Z.W.; Bates, S.T.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Schilling, J.S.; Kennedy, P.G. FUNGuild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Research on the Seasonal Dynamic Changes of Soil Microorganisms in the Desert Steppe of Inner Mongolia. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Normal University, Hohhot, China, 2008. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPNNo1Zq0nI_ljgZSQXztfD3ZCHXg47gvVrsXrzECptFs0bI5PwFTbt1KSsZ_fvhN6ZN5YZetxzvC46BLF_1GqaCGqhz_jrEkQPECWn5cKh1SxngnV8Oucdxkhy7T30EGPJMk6IH9A9YARWxXO9QtlZLVc3w_P2XQrWmwqsagOFM3eWBc8g2IGwTol-FQRugiOE=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Li, Y. Effects of Photovoltaic Panel Arrays on Hydrolase Activity and Enzyme Stoichiometric Characteristics in Degraded Grassland of Songnen Plain. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2023. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27011/d.cnki.gdbsu.2023.001287 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Panagos, P.; De Rosa, D.; Liakos, L.; Labouyrie, M.; Borrelli, P.; Ballabio, C. Soil bulk density assessment in Europe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.G.; Zhang, Y.P.; Wang, R.Q. Diffusion of phosphate in soils I. the influence of soil moisture, texture and temperature as well as their interactions. Acta Pedol. Sin. 1996, 33, 148–156. Available online: https://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=2136876 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Yuanm, Z.Y.; Deng, B.L.; Guo, X.M.; Niu, D.K.; Hu, Y.W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, W.Y. Total nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium distribution patterns and responses to different degrees of degradation in mountain meadow soil of Wugong Mountain. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2015, 30, 14–20. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPNOhIxCUyOFYGHuiXXlQwLt0ao6ME0-0NZ-8RvHYdgwxjgfmlDP50auPH5SX3BztV2KBHHinzS_5VJiGu9TQSJuTubGlZ8JFY-uad2yQUwwHXlzT2v22c7A4Jg0JX0WLG_w2mkIRnqhUUSolJGYqrSsBEQ2GVUzV_jA6WM_LcV87J9OAflUiaeCEKzof5GMjzg=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Lei, Z.Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.N. Analysis of soil potassium distribution characteristics in different ecosystems of Horqin Sandy Land. J. Liaoning Tech. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2024, 43, 719–725. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPM-qOXKaHUbwx8lR_GKnpmBYbAzfavA0z1gRm4aN1EINC2-Un_OaYCQj9AC0Qz3NpMSqHvQO7gssxP1jNBpbRWG-LYV3NDw8cjos3_8EcBfEBfJavGfJDldeW6Veo14sICE_JAChLi38AiMwiap2fxNF53dJIxH4tUNLLkYnhAhaNM7n_ODUjTiN4n6YZcSGO4=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Thomas, T.W.; Grzegorz, S.; Shawan, D.; James, M.C.; Pauline, F.G. Soil moisture evaporative losses in response to wet-dry cycles in a semiarid climate. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.J.; Peng, P.Q.; Liu, Q.; Rong, X.M. Soil microbial biomass nitrogen and its role in the nitrogen cycle. Chin. J. Ecol. 2006, 4, 443–448. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hQuCc5bkPPMRnWoVZD6HjjYHsDwbLmNQZaVsA7h_0VR3pTYPUKCWt01c2SzxQx0Snt0xUD4E5gD5B6_KmycQI96YvHihlknLHo7yK1JPRxdfBuCYFeeOYL6kezCg6FO-ok6O7roz5p36Gdt3soQnAdkPQyq16pVvaLZK5-pVNsn0ghRqhuslDEoTPGkbwAiJ&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Zhu, Y.G.; Zhao, J.H.; Xiao, Y.Y.; Liu, H.; Dai, Z.M. Research progress on efficient nitrogen use under corn-soybean intercropping conditions. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull. 2020, 26, 95–97. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2020.22.037 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Tang, J.; Wang, C.Q.; Li, B.; Zeng, J.; Li, Q.Q.; XU, Q.; Li, Y.D.; Li, S. Upper hilly soil organic matter and alkali solution nitrogen siltstones space mutation characteristics research. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 19, 124–130. Available online: https://www.nkdb.net/CN/10.13304/j.nykjdb.2016.644 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Wang, T.; Wang, D.X.; Guo, T.D.; Zhang, G.G.; Zhao, S.X.; Niu, H.C.; Lu, S.Y.; Lin, H. The effects of photovoltaic power station construction on soil and vegetation. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 23, 90–94. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2016.03.016 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Li, T.; Yu, L.; Wan, G.H.; Li, J.W.; Lu, G.J.; Dong, Y.H. Spatio-temporal Variation of Farmland Soil pH and Associated Affecting Factors in the Past 30 Years of Shandong Province, China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2021, 58, 180–190. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/32.1119.p.20200518.1057.006 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Jin, H.J.; Wang, J.H.; Li, Y.; Ma, Q.L.; Zhang, D.K.; Liu, Y.J.; Chen, F.; Xu, L.H. Characteristics of changes in soil chemical properties during desertification reversal in the southern margin of the Tengger Desert. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 5, 119–124. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2008.05.003 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Guo, Q. Effects of Photovoltaic Panel Arrays on Plant Communities and Soil Characteristics in Songnen Degraded Grassland. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2022. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27011/d.cnki.gdbsu.2022.000219 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Tian, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, B.L.; Wu, J.H. Effects of Photovoltaic Power Station Construction on Terrestrial Environment: Retrospect and Prospect. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 239–247. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13227/j.hjkx.202301152 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Shang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Chang, L. Spatial heterogeneity of vegetation communities and soil properties in a desert solar photovoltaic power station of the Hexi Corridor, northwestern China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscatelli, M.C.; Marabottini, R.; Massaccesi, L.; Marinari, S. Soil properties changes after seven years of ground mounted photovoltaic panels in Central Italy coastal area. Geoderma Reg. 2022, 29, e00500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.J.; Xu, S.; Zhou, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Qin, J.; Wang, H.K.; Li, X. Meeting China’s electricity demand with renewable energy over Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Q.; Hernandez, R.R.; Blackburn, G.A.; Davies, G.; Hunt, M.; Whyatt, J.D.; Armstrong, A. Groundmounted photovoltaic solar parks promote land surface cool is-lands in arid ecosystems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Transit. 2021, 1, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Zhang, W.F.; Dong, Z.J.; Zhan, X.L. Carbon neutral background under the influence of the photovoltaic array micro climate in desert region. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2023, 59, 228–236+245. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13432/j.cnki.jgsau.2024.05.025 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Zhang, S.L.; Wu, T.J.; Liu, Z.G.; Yang, Z.W.; Huang, B.; Zhan, X.Q.; Wu, L.R. Alpine high-altitude grassland ecological benefit evaluation of the construction of the photovoltaic power station. Grassl. Turf 2025, 1, 1–14. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/62.1156.S.20250314.1827.002 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Pratt, R.N.; Kopp, G.A. Velocity measurements around low-profile, tilted, solar arrays mounted on largeflat-roofs, For wall normal wind directions. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 2, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.W.; Gao, X.Q.; Lu, F.; Hui, X.Y.; Ma, L.Y.; Hou, X.H.; Li, H.L. Study on the influence of Photovoltaic Power stations on solar radiation field in Golmud Desert area. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2015, 36, 2160–2166. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=A2TeIUkP3I1-xtqolaagp94pOZz6a0hTmcrnWH7w5eK_8lhL_pK19DCBMcGsxtuhHNQYhBvqwbNx9RYlJnD5ZLFtxUWzz56MR5M4ckN1ZM352D5LV3QLM4iwhjou-vVm7W5Y3Z4NIzojJj7aUYmbKNMGj06nBzEHnjMPRsZTg41-g1k2iOCQtP58WaZTG9xQZR-26vIM52o=&unipl (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- He, X.D.; Li, T.; Wang, W.Y.; Li, H.Y.; He, F. Photovoltaic panels layout way the influence of the thermal transport of soil water characteristics. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2025, 4, 1–13. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/61.1294.N.20250416.1613.006 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Elamri, Y.; Cheviron, B.; Mange, A.; Dejean, C.; Liron, F.; Belaud, G. Rain concentration and sheltering effect of solar panels on cultivated plots. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Niu, Q.H.; Li, Y.; Zu, R.P.; Wang, J.Z.; Deng, Y.W.; Zhang, J.C.; Su, C.L. Effects of large-scale photovoltaic power station construction on soil bacterial communities in Gonghe Basin. J. Desert Res. 2025, 3, 1–10. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/62.1070.P.20250630.1554.002 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Zuo, Q.; Yang, H.T.; Yang, Y.Y.; Lin, K.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, Y.L. Desert photovoltaic construction models affect the growth characteristics of sand-fixing herbaceous plants through soil moisture. J. Desert Res. 2020, 45, 291–301. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=A2TeIUkP3I3pxVbUXxHi9BdNXopA1BWfVKviGG4Ce3CYAqIykgUkZkBPbq31QKu8a4S6Na8MxUz9e26dUS0zcBqhGZSfU-4AYwFKHagwaFvzi5UJdzZ0uqBCR51WEntOMgaxdDZ91iofKoLrS0iO9s3C0ogisBws25582gY1o1I4qPaIUBbSRIDhcW3bLAXM&uniplatform=NZKPT (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
- Liu, Y.J.; Wang, D.Y.; Chang, X.; An, J.Y.; Mu, R.; Li, X.L.; Xu, T.; Yang, B. Research progress on the impact of Photovoltaic power station construction on the ecological environment in the northwest desert area. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 23, 9–17. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.16843/j.sswc.2024025 (accessed on 11 September 2025). (In Chinese).
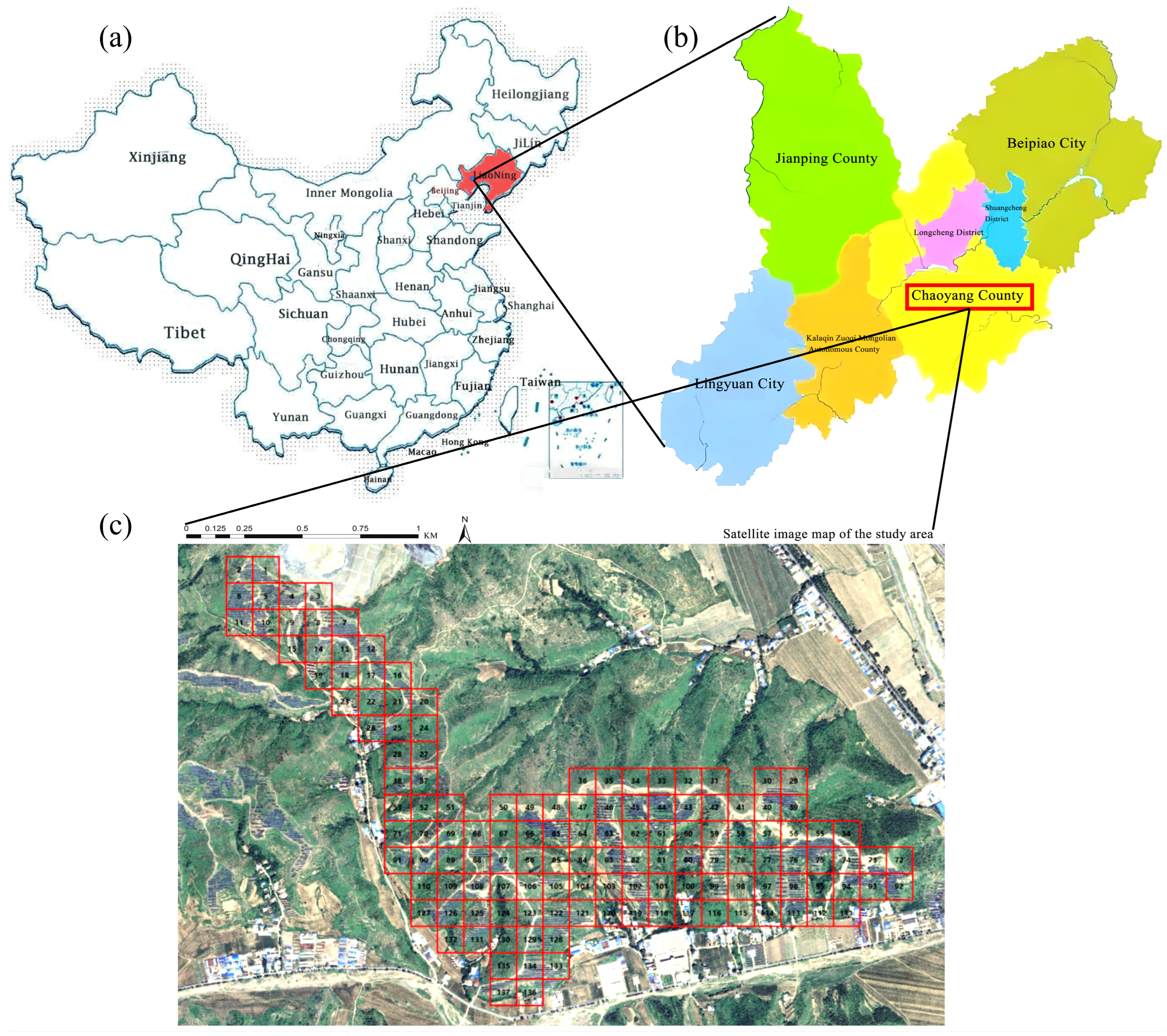


| Determination of Indicators | Methods | Experimental Instruments | Instrument Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total nitrogen (TN) | Kjeldahl Method | DRK-K616 Automatic Kjeldahl Nitrogen Analyzer | Shandong Drickinstruments Co., Ltd., Jinan, China |
| Total phosphorus (TP) | Sodium hydroxide fusion–molybdenum–antimony anticolorimetric method | UV-Vis Spectrophotometer TU-1900 GLLS-JC-059 | Qingdao Optical Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China |
| Total potassium (TK) | Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry | Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectrometer Agilent 5110 ICP-OES GLLS-JC-493 | Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA |
| Organic matter (SOM) | Potassium dichromate external heating method | Analytical Balance (0.0001 g), HH-S Oil Bath, etc. | Changzhou Guohua Electric Appliance Co., Ltd., Changzhou, China |
| Available potassium (AK) | Ammonium acetate extraction–flame photometry | Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer Agilent 280FS GLLS-JC-163 | Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA |
| Available phosphorus (AP) | Sodium bicarbonate extraction–molybdenum-antimony anti-spectrophotometric method | UV-Vis Spectrophotometer TU-1900 GLLS-JC-059 | Qingdao Optical Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China |
| Alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen (AN) | Alkali hydrolysis diffusion method | German Seal AA3 Automated Continuous Flow Analyzer | SEAL Analytical (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| pH | Potentiometry | Ion Meter PXS-270 GLLS-JC-054 | INASE Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Soil bulk density (BD) | Ring knife method | Soil Bulk Density Tester YDRZ-4L | Zhejiang Top Cloud-Agri Technology Co., Ltd., Zhejiang, China |
| Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rate Plot | Number of Soil Physicochemical Properties Test Plots | Number of Vegetation Community Condition Test Plots |
|---|---|---|
| 0% | 18 | 3 |
| 0–5% | 41 | 3 |
| 5–10% | 23 | 3 |
| 10–15% | 21 | 3 |
| 15–20% | 13 | 3 |
| Over 20% | 21 | 3 |
| Control points | 23 | 8 |
| Total | 160 | 26 |
| Indicator | Control Point | 0% | 0–5% | 5–10% | 10–15% | 15–20% | Over 20% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD (g/cm3) | 1.123 | 1.116 | 1.122 | 1.132 | 1.132 | 1.104 | 1.156 |
| TN (g/kg) | 1.8168 | 1.8667 | 1.7565 | 1.7567 | 1.6799 | 1.9875 | 1.6248 |
| TP (%) | 0.037 | 0.031 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.027 | 0.037 | 0.020 |
| TK (g/kg) | 25.532 | 24.267 | 23.918 | 24.309 | 23.819 | 25.578 | 21.083 |
| AN (g/kg) | 0.1684 | 0.1622 | 0.1519 | 0.1643 | 0.1565 | 0.1848 | 0.1339 |
| AK (g/kg) | 0.2384 | 0.2522 | 0.2229 | 0.2159 | 0.2531 | 0.2392 | 0.2138 |
| SOM (g/kg) | 28.950 | 25.931 | 27.888 | 28.509 | 23.648 | 32.886 | 14.465 |
| PH | 7.001 | 6.8678 | 6.8878 | 6.8152 | 6.8681 | 6.9469 | 6.7729 |
| AP (g/kg) | 0.0080 | 0.0079 | 0.0077 | 0.0075 | 0.00895 | 0.0100 | 0.00415 |
| AGB (g) | 409.241 | 432.414 | 380.251 | 379.042 | 377.86 | 482.517 | 297.292 |
| BGB (g) | 4.613 | 4.658 | 4.367 | 4.239 | 4.237 | 5.405 | 2.558 |
| SPI | 4.286 | 4.400 | 3.562 | 3.625 | 3.333 | 4.250 | 2.500 |
| SWI | 1.095 | 1.237 | 0.927 | 0.882 | 0.891 | 1.326 | 0.495 |
| SI | 0.644 | 0.661 | 0.555 | 0.55 | 0.538 | 0.679 | 0.341 |
| PI | 0.767 | 0.861 | 0.738 | 0.753 | 0.731 | 0.928 | 0.35 |
| Indicator | Paired Samples | Mean Values Difference | Standard Error | Significance p | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||||
| BD | 0% vs. over 20% | −0.0398 | 0.0115 | 0.0151 | −0.0755 | −0.0042 |
| 0–5% vs. over 20% | −0.0338 | 0.0096 | 0.0132 | −0.0635 | −0.0040 | |
| 15–20% vs. over 20% | −0.0521 | 0.0127 | 0.0011 | −0.0913 | −0.0130 | |
| SOM | control point vs. over 20% | 13.7881 | 3.9960 | 0.0161 | 1.4240 | 26.1532 |
| 0% vs. over 20% | 10.7690 | 3.3401 | 0.0330 | 0.4320 | 21.1061 | |
| 0–5% vs. over 20% | 12.7260 | 2.7910 | 0.0002 | 4.0910 | 21.3620 | |
| 15–20% vs. over 20% | 18.0150 | 3.6700 | 0.0001 | 6.6580 | 29.3721 | |
| AGB | 15–20% vs. over 20% | 185.226 | 56.9063 | 0.0442 | 2.4444 | 368.007 |
| BGB | 15–20% vs. over 20% | 2.8468 | 0.7035 | 0.0040 | 0.5871 | 5.1060 |
| SPI | control point vs. over 20% | 1.7851 | 0.5350 | 0.0350 | 0.0665 | 3.5049 |
| 0% vs. over 20% | 1.9000 | 0.5729 | 0.0371 | 0.0610 | 3.7400 | |
| 15–20% vs. over 20% | 1.7501 | 0.5229 | 0.0341 | 0.0703 | 3.4301 | |
| SWI | 15–20% vs. over 20% | 0.8315 | 0.2367 | 0.0208 | 0.0711 | 1.5919 |
| PI | 15–20% vs. over 20% | 0.5779 | 0.1728 | 0.0341 | 0.0229 | 1.1329 |
| Genus Name | Plant Name | Plant Latin Name | Genera Count | Species Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitex | Negundo Chastetree | Vitex negundo | 1 | 1 |
| Lespedeza | Korean Lespedeza | Rhamnus aurea | 1 | 2 |
| Shrub Lespedeza | Lespedeza bicolor | |||
| Setaria | Green Bristlegrass | Setaria viridis | 1 | 1 |
| Digitaria | Hairy Crabgrass | Digitaria sanguinalis | 1 | 1 |
| Clematis | Chinese Bushclover | Lespedeza cuneata | 1 | 1 |
| Artemisia | Foetid Wormwood | Artemisia anethifolia | 1 | 2 |
| Sweet Wormwood | Artemisia annua | |||
| Leontopodium | Edelweiss | Leontopodium leontopodioides | 1 | 1 |
| Sanguisorba | Great Burnet | Sanguisorba officinalis | 1 | 1 |
| Dianthus | Chinese Pink | Dianthus chinensis | 1 | 1 |
| Rhamnus | Littleleaf Buckthorn | Rhamnus parvifolia Bunge | 1 | 1 |
| Potentilla | Chinese Cinquefoil | Potentilla chinensis | 1 | 1 |
| Robinia | Black Locust | Robinia pseudoacacia | 1 | 1 |
| Platycladus | Oriental Arborvitae | Platycladus orientalis | 1 | 1 |
| Phragmites | Common Reed | Phragmites australis | 1 | 1 |
| Ulmus | Siberian Elm | Ulmus pumila | 1 | 1 |
| Astragalus | Mongolian Milkvetch | Astragalus membranaceus | 1 | 1 |
| Populus | Black Poplar | Populus nigra | 1 | 1 |
| Kummerowia | Common Lespedeza | Kummerowia striata | 1 | 1 |
| Reynoutria | Japanese Knotweed | Reynoutria japonica | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 19 | 21 |
| Indicator | Control Points | 0% | 0–5% | 5–10% | 10–15% | 15–20% | over 20% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD | −0.2113 | −0.6427 | −0.2729 | 0.3434 | 0.3434 | −1.3823 | 1.8225 |
| TN | 0.2713 | 0.6854 | −0.2297 | −0.2277 | −0.8655 | 1.6891 | −1.3229 |
| TP | 1.0362 | 0.0241 | 0.1928 | 0.1928 | −0.6507 | 1.0362 | −1.8315 |
| TK | 0.9728 | 0.1296 | −0.1030 | 0.1576 | −0.1687 | 1.0032 | −1.9916 |
| AN | 0.52032 | 0.1215 | −0.5354 | 0.2555 | −0.2427 | 1.5678 | −1.6870 |
| AK | 0.2931 | 1.1364 | −0.6562 | −1.0869 | 1.1903 | 0.3393 | −1.2160 |
| SOM | 0.4985 | −0.0186 | 0.3166 | 0.4229 | −0.4096 | 1.1725 | −1.9823 |
| PH | 1.5817 | −0.1589 | 0.1025 | −0.8462 | −0.1549 | 0.8748 | −1.3990 |
| AP | 0.14223 | 0.0869 | −0.0237 | −0.1343 | 0.6677 | 1.2485 | −1.9873 |
| AGB | 0.2653 | 0.6711 | −0.2423 | −0.2635 | −0.2841 | 1.5484 | −1.6949 |
| BGB | 0.3655 | 0.4175 | 0.0812 | −0.0664 | −0.0690 | 1.2806 | −2.0091 |
| SPI | 0.8561 | 1.0250 | −0.2163 | −0.1229 | −0.5554 | 0.8028 | −1.7893 |
| SWI | 0.4215 | 0.9374 | −0.1889 | −0.3524 | −0.3197 | 1.2607 | −1.7585 |
| SI | 0.6695 | 0.8170 | −0.1029 | −0.1463 | −0.2504 | 0.9733 | −1.9602 |
| PI | 0.1873 | 0.6988 | 0.0295 | 0.1112 | −0.0085 | 1.0633 | −2.0815 |
| Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rate | Euclidean Distance from Control Point | Sorted by Similarity to Control Point |
|---|---|---|
| 0% | 2.6474 | 1 |
| 0–5% | 2.9783 | 2 |
| 5–10% | 3.5467 | 4 |
| 10–15% | 3.8948 | 5 |
| 15–20% | 3.2726 | 3 |
| over 20% | 9.1492 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, L.; Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Cui, J.; Liu, X. Effect of Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rate in Mountainous Photovoltaic Power Stations on the Ecological Environment of Mountainous Landscapes. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10068. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810068
Chang L, Dong Y, Liu J, Cui J, Liu X. Effect of Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rate in Mountainous Photovoltaic Power Stations on the Ecological Environment of Mountainous Landscapes. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):10068. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810068
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Le, Yukuan Dong, Jiatong Liu, Juntong Cui, and Xin Liu. 2025. "Effect of Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rate in Mountainous Photovoltaic Power Stations on the Ecological Environment of Mountainous Landscapes" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 10068. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810068
APA StyleChang, L., Dong, Y., Liu, J., Cui, J., & Liu, X. (2025). Effect of Photovoltaic Panel Coverage Rate in Mountainous Photovoltaic Power Stations on the Ecological Environment of Mountainous Landscapes. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 10068. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810068





