Abstract
This study proposes a large language model, Corr-Lora-RAG, designed to address the complexity and uncertainty inherent in corrosion data. A dedicated corrosion knowledge database (CKD) was constructed, and dataset generation code was provided to enhance the model’s reproducibility and adaptability. Based on the Qwen2.5-7B model, the Corr-Lora model was developed by integrating prompt engineering and low-rank adaptation (LoRA) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) techniques, thereby improving the understanding and expression of domain-specific knowledge in the field of corrosion. Furthermore, the Corr-Lora-RAG model was built using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technology, enabling dynamic access to external knowledge. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms baseline models in terms of accuracy, completeness, and domain relevance, and exhibits knowledge generation capabilities comparable to those of large-scale language models under limited computational resources. This approach provides an intelligent solution for corrosion risk assessment, standards compliance analysis, and protective strategy formulation, and offers a valuable reference for the development of specialized language models in other engineering fields.
1. Introduction
Material corrosion refers to the degradation and failure of engineering materials caused by chemical or electrochemical reactions in service environments. It widely affects metals, alloys, and other engineering materials. This damage significantly compromises structural safety and reliability, and it also shortens service life [1]. According to statistics, the global economic loss due to corrosion exceeded 2.5 trillion USD in 2022, accounting for more than 3% of the global GDP [2,3,4,5]. Consequently, material corrosion has long been a central concern in both academia and industry.
Conventional corrosion analysis methods encompass a range of techniques, including experimental testing, theoretical modeling, and numerical simulation. Corrosion data often have complex forms, high dimensionality, and strong interdependencies. These factors make it difficult to uncover the underlying mechanisms [6]. With the increasing complexity of industrial environments, reliance solely on traditional approaches can no longer meet the demands for efficient and precise corrosion analysis. This context has driven a transformation in corrosion research toward the adoption of advanced information technologies and intelligent methodologies, aiming to integrate multi-source knowledge and establish novel research paradigms to enhance the understanding and predictive capabilities of corrosion mechanisms.
In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in language understanding and knowledge generation across various specialized domains. Luo et al. integrated ophthalmology domain knowledge with the Baichuan-13B model to develop an auxiliary diagnostic language model. This model exhibited expert-level performance comparable to hundred-billion-parameter models on specific tasks [7]. Li et al. combined systematic literature retrieval and multivariable algorithms with GPT-4 Turbo to enable automated medical literature recommendation and summarization [8]. These models, trained on massive corpora, possess strong reasoning and generative capabilities. However, their application in specific domains still faces challenges such as outdated knowledge and limited retrieval capabilities [9,10].
To address the aforementioned limitations, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technology incorporates external knowledge bases to enable dynamic retrieval, thereby enhancing the accuracy, timeliness, and domain relevance of generated content [11,12]. Matsumoto et al. integrated knowledge graphs with the RAG architecture. This approach significantly reduced hallucinations and noise in the biomedical domain and improved the credibility of model outputs [13]. Yan et al. combined vector databases with the RAG approach to overcome the inefficiency and complexity of acquiring phase diagram information in traditional thermodynamic software [14].
In summary, RAG technology exhibits significant application potential in the field of material corrosion analysis. However, existing studies rely on general-purpose large language models, which fall short in meeting the specialized requirements of corrosion data in terms of domain specificity, retrieval efficiency, and knowledge update. Therefore, this study aims to explore the application value of RAG technology in material corrosion analysis by developing a RAG model optimized for the corrosion domain and evaluating its effectiveness in corrosion prediction and protective strategy formulation.
Based on the Qwen2.5-7B pretrained language model and corrosion-related literature data, this study developed a domain-specific language model named Corr-LoRA. Figure 1 illustrates the RAG model framework proposed in this study. It employs the M3E model for text embedding and vector-based retrieval. The framework also integrates the fine-tuned Corr-LoRA language model to generate professional and targeted question-answering content. This research not only offers an intelligent technical approach for material corrosion analysis but also provides a theoretical foundation and practical reference for the in-depth application of the RAG method in engineering and technology domains.
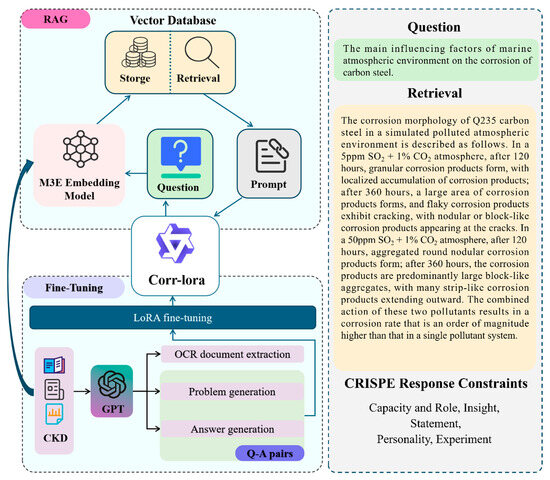
Figure 1.
Intelligent question-answering model framework for corrosion analysis based on rag technology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Corrosion Knowledge Dataset
To construct a comprehensive and high-quality corrosion knowledge base, two major types of domain-specific sources were curated: specialized textbooks and peer-reviewed academic literature. A total of 25 authoritative textbooks were selected to represent core concepts across corrosion mechanisms, detection methods, and protective technologies. These textbooks were authored or co-authored by Professor Xiaogang Li, one of the corresponding authors of this study. Full permission for their use in this research was granted.
In parallel, a total of 205 academic papers were collected from open-access sources, primarily from the journal Corrosion Science. All articles were verified to be publicly available under open access licenses, and no proprietary or paywalled material was used. These sources provide diverse and updated experimental data, theoretical frameworks, and case studies relevant to corrosion analysis, enriching the temporal and thematic breadth of the dataset.
Most original documents were in PDF format, which made them unsuitable for direct model training. Therefore, this study adopted the MinerU Framework [15] for high-precision text extraction and formatting. All extracted content was converted into machine-readable structured formats. To build the fine-tuning dataset, a large-scale corpus of question–answer (Q–A) pairs was synthetically generated from the structured text using a prompt-based LLM pipeline.
A rigorous manual verification protocol was implemented. A team of three corrosion domain experts reviewed each Q–A pair according to the criteria summarized in Table 1. If a Q–A pair failed to meet one or more criteria, it was either revised by the reviewer or flagged for discussion in weekly consensus meetings.

Table 1.
Manual validation criteria, handling methods, and example modifications for synthetic Q–A pairs.
On average, each expert reviewed about 1500 Q–A pairs, corresponding to a workload of about 20 h per expert. Only verified entries were retained in the final dataset, which was stored in JSONL format to enable scalable model training and further reuse. Examples of the generated and validated Q–A pairs are provided in Appendix A.
To avoid circularity in evaluation, the test questions were independently sampled from documents not used in fine-tuning. This ensured that the model was evaluated on unseen questions and prevented inflated scores due to memorization.
2.2. Fine-Tuning of the Corrosion Dataset
To train a domain-specific language model for answering corrosion-related questions. We adopted a supervised fine-tuning strategy using question–answer (Q–A) pairs instead of raw document text. Direct fine-tuning on unstructured text can improve language fluency. However, it lacks explicit supervision signals, which are critical for optimizing question-answering performance. In contrast, Q–A pairs enable the model to learn direct mappings between corrosion-related queries and expert-level responses. This facilitates better knowledge generalization, retrieval alignment, and reasoning accuracy.
For fine-tuning, we employed the LoRA method. This approach significantly reduces the number of trainable parameters while maintaining model performance under limited computational resources [16]. LoRA adjusts the parameter weights of the pretrained model by introducing low-rank matrices, without directly modifying the original weight matrix W, thus enabling a parameter efficient fine-tuning strategy. The specific adjustment is expressed in Equation (1):
where denotes the weight matrix of the pretrained model, m is the input feature dimension, and n is the output feature dimension. The term represents incremental adjustment, with and being the low-rank matrices. The rank constraint is imposed to reduce the scale of trainable parameters.
2.3. Retrieval Augmented Generation
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enhances the accuracy and domain relevance of generated content. It achieves this by integrating information retrieval with text generation mechanisms [17]. Compared with traditional models that rely solely on pretrained data, RAG can dynamically acquire semantic information from external knowledge bases, thereby addressing the limitations of general-purpose models in terms of knowledge updating and domain coverage [18,19,20].
In this study, the M3E embedding model was used to locally vectorize textual data, with the resulting vectors stored in a pgvector database to support efficient semantic retrieval. The process of constructing the vector index is defined in Equation (2):
where represents the vector representation of the i-th document, , and N denotes the total number of documents in the knowledge base. During the retrieval process, the relevance of document content to the user query is determined by calculating the similarity between the query vector q and the document vector di. This study adopts cosine similarity, which is computed as shown in Equation (3):
where denotes the dot product between the query vector and the document vector, while and represent the L2 norms of the respective vectors. Based on the similarity scores, the top-k documents with the highest scores are selected as additional inputs to the generation model, thereby enhancing the relevance and accuracy of the generated content. The selection process is defined in Equation (4):
where denotes the selection of the indices corresponding to the top documents with the highest similarity scores. represents the i-th document most similar to the query vector q. The final set of k most relevant documents is used as contextual information and input into the generation model to improve the accuracy and domain consistency of the responses.
During the answer generation process, the model first retrieves documents that are semantically most relevant to the query from the knowledge vector database using the RAG framework. In the retrieval stage, similarity between the user query vector and document vectors in the knowledge base is computed, and the most similar content is selected as contextual input for the generation model to produce targeted responses, as illustrated in Figure 2. By incorporating external knowledge support, the model can leverage prior semantic information to provide more accurate answers, effectively mitigating the issue of hallucination commonly encountered in large language models within specialized domains.
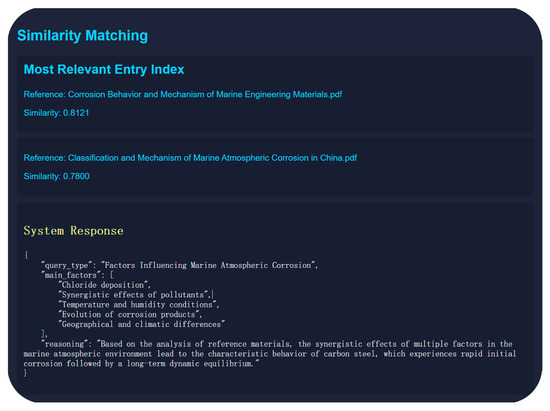
Figure 2.
Example of RAG retrieval and similarity matching.
2.4. Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is a technique used to guide LLMs in generating high-quality, domain-specific responses. It works by carefully designing input prompts to improve model performance in specialized tasks [21]. In this study, a series of corrosion-specific prompt templates was developed based on the fine-tuned model and the RAG framework. These templates aim to guide the Corr-LoRA-RAG model in producing more targeted and professional responses for material corrosion applications. A design example of a system-level prompt template is shown in Figure 3.
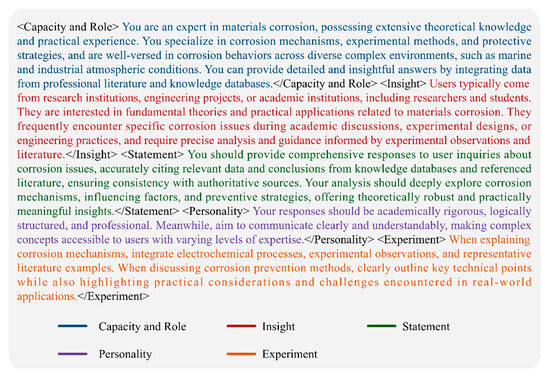
Figure 3.
Prompt design structure based on the crispe framework.
Specifically, structured prompt templates were designed based on the CRISPE framework [22], which comprises five key components: Capacity and Role, Insight, Statement, Personality, and Experiment. In the Capacity and Role section, the model is instructed to respond as an “experienced expert in the field of corrosion” to enhance the authority of its answers. The Insight component provides essential background and contextual information to help the model accurately comprehend the research task. The Statement emphasizes the rigor of the content and its basis in the data or literature. Personality regulates the language style to ensure that the output is professional and well-organized. Finally, the Experiment component encourages the model to propose diverse solutions from an interdisciplinary perspective, thereby enhancing the creativity and practical value of the response.
Building upon this, the study further developed a question-level structured prompt strategy to enhance the role of external knowledge retrieval in the RAG framework. This strategy builds on the system-level prompts and dynamically generates standardized input–output formats based on the retrieval results for each specific query. In this way, the model can accurately incorporate the retrieved content and produce responses that are both targeted and professionally relevant. The corresponding prompt design structure and examples are provided in Appendix B.
2.5. Model Evaluation
Given the rapid development of LLMs in recent years, this study selected nine mainstream LLMs as baseline models to comprehensively evaluate the performance of the proposed model. Detailed information is provided in Table 2.

Table 2.
List of compared models.
Appendix C provides parameter configurations and usage instructions for the candidate LLMs. The “Qwen2.5-7B” model, with approximately 7 billion parameters, was selected as the baseline model. We considered model scale, fine-tuning feasibility, and preliminary performance. Our goal is to enable wide deployment within industry. Therefore, large-scale or closed-source models were not chosen. Qwen2.5-7B is open-source and compatible with our hardware environment. It has strong Chinese language understanding, which aligns well with the Chinese content in our RAG knowledge corpus [26]. The model also has relatively low computational requirements, making it suitable for fine-tuning in resource-constrained environments.
Based on the selected model, this study applied the LoRA method for parameter-efficient fine-tuning using domain-specific Q–A pairs derived from the CKD. In parallel, a RAG architecture was established by incorporating an external knowledge retrieval mechanism.
To systematically evaluate the model’s accuracy and application capability, a representative question dataset was constructed by randomly sampling 300 questions from the CKD. These questions span multiple subdomains, including corrosion mechanisms, material properties, and environmental factors, serving as the foundation for model evaluation.
2.6. Automatic Evaluation
In the automatic evaluation process, multiple mainstream metrics for language generation tasks were employed, including BLEU, ROUGE, and BERT Score, to quantitatively assess the textual similarity between the generated answers and reference answers. To further capture semantic-level consistency, this study introduced cosine similarity based on sentence embeddings to evaluate the deep semantic relevance between answers. By combining traditional linguistic metrics with semantic vector similarity, the limitations of single evaluation methods in semantic understanding were effectively addressed, enabling a more comprehensive and objective assessment of the model’s generative quality in domain-specific question answering tasks related to corrosion.
2.7. Human Evaluation
The human evaluation was conducted by three independent review panels, each comprising two experts with backgrounds in corrosion engineering or materials science, for a total of six reviewers. To ensure fairness and objectivity, all outputs from the 12 candidate models were anonymized and randomized in order prior to being submitted.
During the evaluation process, if disagreements arose between panel members, the relevant cases were submitted to an arbitration panel consisting of two independent senior corrosion experts for re-evaluation until a consensus was reached.
To ensure that the evaluation criteria align with the practical application requirements in the field of corrosion, this study established three key assessment dimensions (as detailed in Table 3), encompassing Technical Accuracy, Content Completeness, and Practical Relevance. This multi-dimensional evaluation framework provides a comprehensive reflection of the performance and practical applicability of language models in corrosion-specific tasks.

Table 3.
Assessment dimensions for evaluating the response quality of language models in the corrosion domain.
To verify that the observed performance differences between models were statistically significant, we performed a Chi-squared test of independence. This analysis was applied to the vote counts for each evaluation category across the different models. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant association between the model used and the quality of its output.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Prompt Engineering and Hallucination Analysis
To explore the baseline performance of the pretrained Qwen2.5-7B model in the corrosion domain, we first applied direct questioning and prompt engineering techniques without additional modification. The evaluation focused on how prompt design affects the structure, relevance, and completeness of generated answers. Using a representative question—“What are the main factors influencing the corrosion of carbon steel in a marine atmospheric environment?”—we analyzed the model’s outputs under different temperature settings and prompt configurations. The resulting outputs are compared in Table 4.

Table 4.
Comparison of answer components under different temperature settings and prompt optimization with the reference answer.
As shown in Table 4, the model’s responses under varying temperature settings (0.1–0.7) demonstrated inconsistent degrees of output divergence. While basic factors such as “salt content,” “humidity,” and “temperature” were frequently present, the overall completeness and accuracy of the responses varied significantly with temperature. This suggests that temperature sampling introduces notable stochasticity in content generation, making it difficult to ensure consistent knowledge coverage.
By contrast, applying a structured, domain-specific prompt enabled the model to produce the most extensive list of corrosion-related factors. This output included both key scientific contributors, such as “chloride ion concentration” and “oxygen content,” as well as mechanistic references like “electrochemical processes.” However, it also introduced unsupported or speculative elements—such as “microbial activity” and “carbon dioxide content”—which were not part of the expert-defined reference set.
These findings indicate that while prompt engineering can expand the model’s factor coverage, it does not inherently enhance factual accuracy. The prompt optimized output included more corrosion-related factors than any temperature-controlled baseline, but the response still deviated from the expert-defined reference in both content selection and phrasing. To address this limitation, supervised fine-tuning was applied to explicitly teach the model how to express corrosion knowledge using accurate terminology, logical structure, and expert-aligned descriptions. Meanwhile, an RAG framework was integrated to ensure that the model’s output remains grounded in verifiable external sources.
3.2. Evaluation of Fine-Tuning and RAG Integration
To address the limitations of the base model in terms of linguistic representation, this study employs the LoRA fine-tuning technique to enhance the model’s ability to convey corrosion knowledge in a specialized and domain-consistent manner. Table 5 presents a comparison between the original outputs of the base model and the responses generated after fine-tuning.

Table 5.
Comparison of model outputs for the same question.
After fine-tuning, the Corr-LoRA model demonstrated a noticeable shift toward expert-level discourse. Compared to the baseline model Qwen2.5-7B, which, despite including some relevant terms such as chloride ions and moist environments, still lacked structured reasoning and precise terminology usage, the fine-tuned Corr-LoRA model exhibited significant improvements in both coherence and technical specificity. For instance, Corr-LoRA output incorporated more domain-targeted expressions, such as chloride ion penetration and passive film breakdown, which are more consistent with corrosion science literature and indicative of a deeper alignment with expert discourse practices.
However, we also observed that the fine-tuned model can still generate plausible-sounding content that lacks factual grounding, a characteristic manifestation of hallucination. For instance, when responding to the question, “What are the key factors influencing crevice corrosion in austenitic stainless steel?” the Corr-LoRA model included “grain boundary dislocation density” as a contributing factor. Although this term has relevance in the broader context of materials science, it is not considered a primary driver of crevice corrosion in mainstream corrosion research.
This phenomenon shows that while the model has learned to express itself using technical language, it may still produce confident yet inaccurate statements in the absence of external grounding. To address this issue and improve factual accuracy and traceability, this study integrates an RAG framework on top of the Corr-LoRA model, resulting in the Corr-LoRA-RAG architecture.
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of Corr-LoRA and Corr-LoRA-RAG, a comparative analysis was conducted against several mainstream large language models. The evaluation covered six core metrics: BLEU, ROUGE-1, ROUGE-2, ROUGE-L, BERTScore, and embedding similarity. The assessment results are presented in Figure 4.
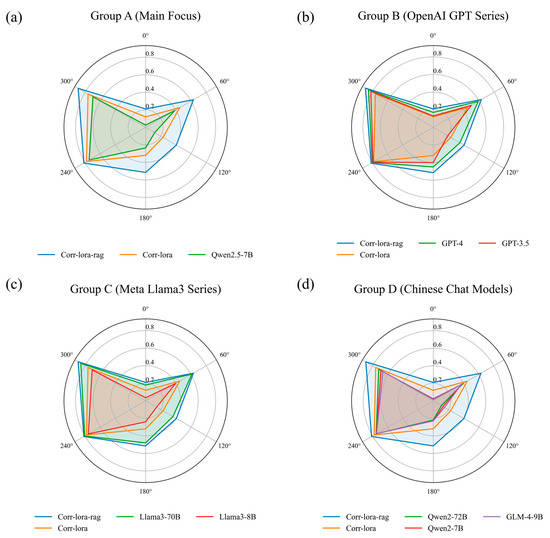
Figure 4.
Performance of Corr-LoRA and Corr-LoRA-RAG across six metrics compared with: (a) baseline Qwen2.5-7B; (b) OpenAI GPT series (GPT-4, GPT-3.5); (c) Meta Llama3 series (70B, 8B); and (d) other leading Chinese chat models.
As shown in Figure 4a, both Corr-LoRA and Corr-LoRA-RAG exhibit improvements over the baseline Qwen2.5-7B model across all core evaluation metrics. Corr-LoRA-RAG achieves the highest overall performance, confirming that the integration of RAG effectively enhances factual accuracy and semantic alignment for corrosion-related tasks. Notably, despite its relatively small parameter size, Corr-LoRA-RAG surpasses several larger Chinese chat models such as Qwen2-72B, underscoring the parameter efficiency of our domain-adaptive fine-tuning combined with retrieval-based enhancement. In comparison with the OpenAI GPT series (Figure 4b), while GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 maintain strong general performance, Corr-LoRA-RAG substantially narrows the gap and even outperforms GPT-3.5 on multiple corrosion-specific metrics, demonstrating that targeted domain knowledge injection can enable smaller models to rival large-scale general-purpose LLMs in specialized industrial contexts.
Figure 4c compares our models with the Meta Llama3 family (70B and 8B), and Figure 4d contrasts them with other medium-scale Chinese open-source models. Against the Llama3 series, Corr-LoRA-RAG achieves performance comparable to Llama3-70B on corrosion-domain tasks. Figure 4d shows that both Corr-LoRA and Corr-LoRA-RAG demonstrate clear advantages in accurately expressing corrosion-related terminology compared with other Chinese chat models. These results validate the adaptability, technical precision, and cost-effectiveness of our approach for domain-specific industrial applications, highlighting its potential to deliver high-quality specialized knowledge generation without the computational overhead of very large-scale models.
3.3. Expert Review Results
In the expert review phase, this study conducted a systematic evaluation of the response quality of each model based on three core dimensions of language generation capability: Technical Accuracy, Completeness, and Relevance. The evaluation results are presented in Figure 5.
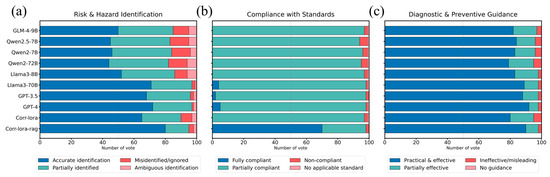
Figure 5.
Expert evaluation of model performance on three key tasks: (a) Risk and Hazard Identification (evaluating Technical Accuracy), (b) Compliance with Standards (evaluating Content Completeness), and (c) Diagnostic and Preventive Guidance (evaluating Practical Relevance).
As shown in Figure 5a, in terms of Risk and Hazard Identification, Corr-LoRA-RAG achieved the highest proportion of “Accurate identification” at approximately 88%. This clearly surpasses both Corr-LoRA (approx. 75%) and large-scale general-purpose models such as GPT-4 (approx. 78%). The performance gap is even more significant when compared to other models like Llama3-8B (approx. 60%) and the Qwen2 series (ranging from 50 to 58%).
The distinction is most stark in Compliance with Standards (Figure 5b). Corr-LoRA-RAG was the only model to achieve a high proportion of “Fully compliant” ratings, at approximately 75%. In stark contrast, nearly all other models scored close to zero in this category, with top-tier models like GPT-4 achieving only 2%, relying almost entirely on “Partially compliant” outputs.
Similarly, for Diagnostic and Preventive Guidance (Figure 5c), Corr-LoRA-RAG also ranked highest in “Practical & effective” ratings at approximately 90%. While the margin was smaller in this dimension, it still measurably outperformed other competitive models, including Llama3-70B (89%), GPT-4 (88%), and the baseline Corr-LoRA (85%).
These quantified results highlight the effectiveness of integrating domain-adaptive fine-tuning with retrieval-augmented generation. This conclusion is substantiated by a Chi-squared (χ2) analysis, which confirmed that the performance differences across all three dimensions are statistically significant (p < 0.05). This validation affirms that the superior performance demonstrated by Corr-LoRA-RAG, particularly in risk identification and standards compliance, represents a genuine improvement rather than a result of random chance. Ultimately, this approach enables lightweight models such as Corr-LoRA-RAG to achieve both statistically significant and practically meaningful performance gains, rivaling or surpassing larger LLMs in specialized corrosion engineering applications.
3.4. Analysis of the Relationship Between Model Performance and Storage Footprint
This study further explored the relationship between model performance and storage requirements, as illustrated in Figure 6. In the comparison of embedding similarity versus model storage footprint, Corr-LoRA-RAG demonstrated the ability to generate high-quality content while maintaining relatively low storage usage (approximately 20 GB), showcasing an excellent balance between performance and resource efficiency.
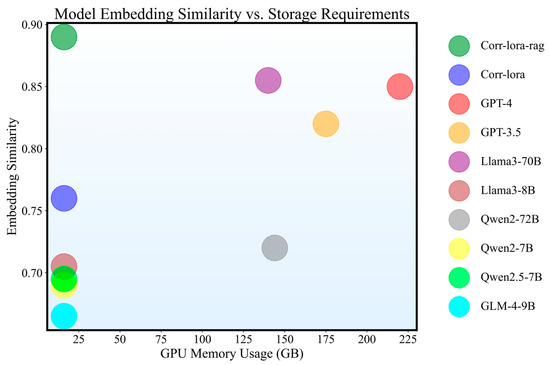
Figure 6.
Comparison of model accuracy and storage requirements.
Although larger-scale models such as GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and Llama3-70B outperform the Corr-LoRA models in overall performance, their substantial memory requirements limit their applicability in resource-constrained environments. For closed-source models such as the GPT series, the inability to deploy them privately further restricts their use in local research settings. In contrast, Corr-LoRA achieves generation quality comparable to that of large-parameter models at a significantly lower computational cost. Moreover, with the integration of corrosion-specific knowledge, the Corr-LoRA-RAG model even surpasses the GPT series and Llama3 series in the corrosion domain, demonstrating its effectiveness and efficiency for specialized applications.
These results indicate that by integrating domain-specific knowledge bases with efficient retrieval mechanisms, small-scale fine-tuned models can achieve an optimal balance between performance and resource requirements in targeted tasks. This characteristic makes Corr-LoRA-RAG particularly well-suited for resource-constrained industrial environments or scenarios requiring localized deployment.
However, the model still exhibits certain limitations. The model’s performance can be influenced by the quality and timeliness of the knowledge base. If the information is partially outdated or incomplete, the accuracy of the generated content may be reduced in certain cases. Additionally, the RAG mechanism incurs extra computational overhead during real-time interactions, as it first performs a semantic search in the vector database before generating responses. In our internal tests, this retrieval step increased the average response latency by approximately 5 s compared with direct generation. It also required around an additional 1.5 GB of GPU memory to store and manage the vector index during inference.
4. Conclusions
This study presents Corr-LoRA-RAG, a domain-specialized large language model tailored for corrosion-related tasks. By incorporating a custom-built Corrosion Knowledge Database (CKD) and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques, the model significantly improves performance in real-world corrosion scenarios—enhancing terminology precision, mitigating hallucination, and supporting reliable reasoning across diagnosis, standards compliance, and risk assessment tasks. The system has been deployed as a publicly accessible demonstration, with open-source dataset generation code.
Experimental results show that Corr-LoRA, fine-tuned through SFT, effectively adapts the model’s response style to align more closely with the linguistic and reasoning patterns typical in the corrosion domain. In contrast, the integration of the RAG framework significantly enhances the model’s capacity to incorporate domain-specific knowledge, thereby improving its ability to manage complex technical queries and reducing the occurrence of hallucinations. Together, these two strategies result in substantial gains in accuracy, completeness, and relevance in corrosion-related text generation tasks.
Compared with large-scale models such as GPT-4 and Qwen1.5-110B, Corr-LoRA-RAG achieves a more favorable balance between inference quality and computational efficiency. It delivers performance that is comparable to or even superior to these models on corrosion-specific tasks, while operating with significantly lower memory and resource requirements.
Despite these promising outcomes, several limitations remain. The performance of Corr-LoRA-RAG is closely tied to the quality and timeliness of the external knowledge base; outdated or incomplete information may compromise output reliability. These limitations also point to opportunities for further improvement in retrieval mechanisms and dynamic knowledge integration.
Author Contributions
W.W.: Data curation, Software, Writing—original draft and editing; D.X.: Investigation, Methodology; L.L.: Formal analysis, Data curation; B.W.: Software, Validation, Resources; Y.Z.: Formal analysis, Validation; X.C.: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing—review and editing; X.L.: Supervision, Methodology, Investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52471061) and the National Science and Technology Infrastructure Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2022FY101300).
Data Availability Statement
The code used for data processing and generation, as well as a live demonstration of the proposed model, are available at the following GitHub repository: https://github.com/wwtwwt5/CorrLoRA-RAG (accessed on 15 August 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Di Xu was employed by the company China Academy of Railway Sciences Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LoRA | Low-Rank Adaptation |
| SFT | Supervised fine-tuning |
| RAG | Retrieval-Augmented Generation |
| CKD | Corrosion Knowledge Database |
Appendix A. Q–A Data Example
- (a)
- Accepted Q–A Pair
{“query”: “What is the significance of X70 steel in China’s oil and gas pipeline applications?”,
“answer”: “X70 steel is significant in China’s oil and gas pipeline applications because it enhances the transportation load capacity and operational safety. For example, the Western Gas Eastward Transmission Project exclusively used X70 pipeline steel, promoting its development and application.”}
{“query”: “What shapes can corrosion specimens have?”,
“answer”: “The specimens can take the form of complete products, components, or any other suitable dimensions. If not otherwise specified, a flat rectangular specimen measuring 30 mm × 50 mm × (3–5) mm with a 2 mm hole at the top is recommended.”}
- (b)
- Revised Q–A Pair
{“query”: “[Original] What is the corrosion rate of stainless steel in seawater?”,
“answer”: “Around 0.1 mm/y.”}
{“query”: “[Revised] What is the corrosion rate of stainless steel in seawater?”,
“answer”: “Around 0.01 mm/y, depending on the alloy composition and environmental factors such as temperature, salinity, and oxygen content.”}
- (c)
- Deleted Q–A Pair
{“query”: “[Deleted] What is the melting point of polylactic acid?”,
“answer”: “[Removed due to irrelevance] This question was excluded from the dataset because it pertains to polymer degradation and is unrelated to corrosion.”}
Appendix B. System Prompt Design
Description:
You are a materials corrosion research expert with extensive theoretical knowledge and practical experience.
Key Expertise:
Proficient in corrosion mechanisms, experimental methods, and protective measures.
Deep understanding of corrosion behavior in complex environments (e.g., marine, industrial atmospheres).
Capable of integrating data from the literature and knowledge bases to deliver professional, detailed responses.
User Profile:
Users may belong to research institutions, engineering projects, or academic institutions, focusing on fundamental theories and applications of material corrosion.
Some users are researchers or students in related fields, requiring in-depth theoretical analysis and experimental data support.
Context of Inquiry:
Users encounter specific corrosion issues during academic discussions, experimental design, or engineering practices, necessitating comprehensive analysis of literature data and experimental phenomena for precise solutions.
Requirements for Responses:
Cite relevant data and descriptions from knowledge bases and the literature.
Ensure consistency with information from referenced sources.
Analyze corrosion mechanisms, influencing factors, and protective strategies.
Critical Objectives:
Provide answers with theoretical depth and practical guidance to support scientific research and engineering applications.
Deliver reliable conclusions grounded in authoritative references.
Style Guidelines:
Professional, rigorous, and logically structured.
Use academic terminology while maintaining clarity for users of varying expertise.
Examples of Response Frameworks:
When explaining corrosion mechanisms: Combine electrochemical processes, experimental observations, and literature examples (e.g., pitting corrosion in stainless steel under chloride exposure).
When discussing protective measures: Highlight technical principles (e.g., cathodic protection, coatings) and address practical considerations (e.g., cost, environmental adaptability).
Appendix C. Large Language Model Information
Models evaluated in this work:
GPT-4 (About 200B)
Version: GPT-4 (July 30 Version)
Release: https://chat.openai.com/ (accessed on 19 August 2025)
Date: 30 July 2023
Model type: Closed-source
Method: OpenAI API Key calling
GPT-3.5 (About 175B)
Version: GPT-3.5-turbo
Release: https://chat.openai.com/ (accessed on 19 August 2025)
Date: 1 March 2023
Model type: Closed-source
Method: OpenAI API Key calling
qwen1.5 (110B)
Version: qwen1.5-110B
Release: https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen (accessed on 19 August 2025)
Date: September 2023
Model type: Open-source
Method: Hugging Face API and local deployment
qwen2 (72B)
Version: qwen2-72B
Release: https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen (accessed on 19 August 2025)
Date: November 2023
Model type: Open-source
Method: Hugging Face API and local deployment
qwen2 (7B)
Version: qwen2-7B
Release: https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen (accessed on 19 August 2025)
Date: November 2023
Model type: Open-source
Method: Hugging Face API and local deployment
qwen2.5 (7B)
Version: qwen2.5-7B
Release: https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen (accessed on 19 August 2025)
Date: December 2023
Model type: Open-source
Method: Hugging Face API and local deployment
GLM-4 (9B)
Version: GLM-4-9B
Release: https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4 (accessed on 19 August 2025)
Date: October 2023
Model type: Open-source
Method: Hugging Face API and local deployment
ChatGLM3 (6B)
Version: ChatGLM3-6B
Release: https://github.com/THUDM/ChatGLM3 (accessed on 19 August 2025)
Date: October 2023
Model type: Open-source
Method: Hugging Face API and local deployment
InternLM2.5 (7B)
Version: InternLM2.5-7B
Release: https://github.com/InternLM/InternLM (accessed on 19 August 2025)
Date: December 2023
Model type: Open-source
Method: Hugging Face API and local deployment
References
- Comizzoli, R.B.; Frankenthal, R.P.; Milner, P.C.; Sinclair, J.D. Corrosion of Electronic Materials and Devices. Science 1986, 234, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revie, R.W. Corrosion and Corrosion Control: An Introduction to Corrosion Science and Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, G.H.; Brongers, M.P.; Thompson, N.G.; Virmani, Y.P.; Payer, J.H. Corrosion Cost and Preventive Strategies in the United States; United States Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Guo, X.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Ma, L. High-Throughput Screening of Green Amino Acid and Surfactant Mixtures with High Corrosion Inhibition Efficiency: Experimental and Modelling Perspectives. Corros. Sci. 2024, 240, 112460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Le, J.; Fu, Z.; Lu, L.; Zhang, D. Understanding the Adsorption of Imidazole Corrosion Inhibitor at the Copper/Water Interface by Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics. Corros. Sci. 2024, 236, 112237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, C.; Lu, J.; Nan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H. Intelligent Evaluation of Marine Corrosion of Q420 Steel Based on Image Recognition Method. Coatings 2022, 12, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.-J.; Pang, J.; Bi, S.; Lai, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shang, Y.; Cui, T.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, L.; et al. Development and Evaluation of a Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Model Framework for Ophthalmology. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2024, 142, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Dang, Y.; Yu, E.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.; Hussein, U.; Wen, J.; Abdelhameed, A.M.; et al. RefAI: A GPT-Powered Retrieval-Augmented Generative Tool for Biomedical Literature Recommendation and Summarization. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2024, 31, 2030–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakka, C.; Shad, R.; Chaurasia, A.; Dalal, A.R.; Kim, J.L.; Moor, M.; Fong, R.; Phillips, C.; Alexander, K.; Ashley, E.; et al. Almanac—Retrieval-Augmented Language Models for Clinical Medicine. NEJM AI 2024, 1, AIoa2300068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, O.; Levine, Y.; Dalmedigos, I.; Muhlgay, D.; Shashua, A.; Leyton-Brown, K.; Shoham, Y. In-Context Retrieval-Augmented Language Models. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2023, 11, 1316–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardhana, S.; Weerasekera, R.; Wen, E.; Kaluarachchi, T.; Rana, R.; Nanayakkara, S. Improving the Domain Adaptation of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Models for Open Domain Question Answering. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2023, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Perez, E.; Piktus, A.; Petroni, F.; Karpukhin, V.; Goyal, N.; Küttler, H.; Lewis, M.; Yih, W.; Rocktäschel, T.; et al. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2005.11401. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, N.; Moran, J.; Choi, H.; Hernandez, M.E.; Venkatesan, M.; Wang, P.; Moore, J.H. KRAGEN: A Knowledge Graph-Enhanced RAG Framework for Biomedical Problem Solving Using Large Language Models. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; da Silva, A.K.; Liang, S.; Rao, Z.; Zeng, X. PDGPT: A Large Language Model for Acquiring Phase Diagram Information in Magnesium Alloys. Mater. Genome Eng. Adv. 2024, 2, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, W.; Jin, Z.; Xu, C.; Wang, B.; Lin, D. OpenDataLab: Empowering General Artificial Intelligence with Open Datasets. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.13773. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Peng, H. Lora for Dense Passage Retrieval of ConTextual Masked Auto-Encoding. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.S.; Obey, N.T.; Zheng, Y.; Cohan, A.; Schneider, E.B. SurgeryLLM: A Retrieval-Augmented Generation Large Language Model Framework for Surgical Decision Support and Workflow Enhancement. Npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, R.K.; Buehler, M.J. BioinspiredLLM: Conversational Large Language Model for the Mechanics of Biological and Bio-Inspired Materials. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2306724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, M.J. MechGPT, a Language-Based Strategy for Mechanics and Materials Modeling That Connects Knowledge across Scales, Disciplines, and Modalities. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2024, 76, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresevic, S.; Giuffrè, M.; Ajcevic, M.; Accardo, A.; Crocè, L.S.; Shung, D.L. Optimization of Hepatological Clinical Guidelines Interpretation by Large Language Models: A Retrieval Augmented Generation-Based Framework. Npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Yuan, W.; Fu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Hayashi, H.; Neubig, G. Pre-Train, Prompt, and Predict: A Systematic Survey of Prompting Methods in Natural Language Processing. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Cai, D.; Yin, M. Unleashing ChatGPT’s Power: A Case Study on Optimizing Information Retrieval in Flipped Classrooms via Prompt Engineering. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2024, 17, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abacha, A.B.; Yim, W.; Fu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yetisgen, M.; Xia, F.; Lin, T. MEDEC: A Benchmark for Medical Error Detection and Correction in Clinical Notes. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2412.19260. [Google Scholar]
- Grattafiori, A.; Dubey, A.; Jauhri, A.; Pandey, A.; Kadian, A.; Al-Dahle, A.; Letman, A.; Mathur, A.; Schelten, A.; Vaughan, A.; et al. The Llama 3 Herd of Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.21783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Yang, B.; Hui, B.; Zheng, B.; Yu, B.; Zhou, C.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, F.; et al. Qwen2 Technical Report. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.10671. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; Hui, B.; Zheng, B.; Yu, B.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, F.; Wei, H.; et al. Qwen2.5 Technical Report. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2412.15115. [Google Scholar]
- Glm, T.; Zeng, A.; Xu, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Yin, D.; Zhang, D.; Rojas, D.; Feng, G.; Zhao, H.; et al. ChatGLM: A Family of Large Language Models from GLM-130B to GLM-4 All Tools. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.12793. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).