The Evolution Mechanism and Stability Prediction of the Wanshuitian Landslide, an Oblique-Dip Slope Wedge Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
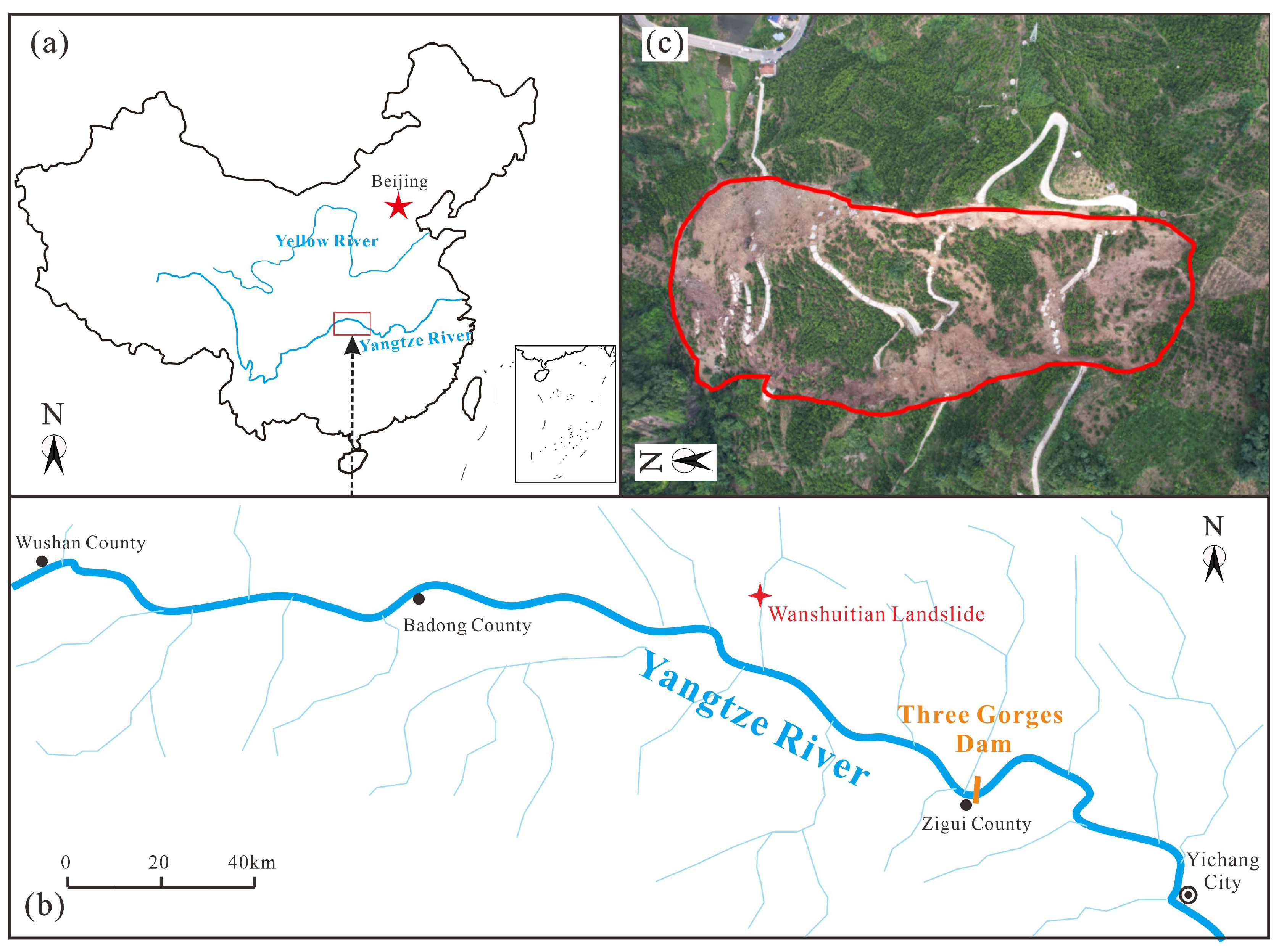
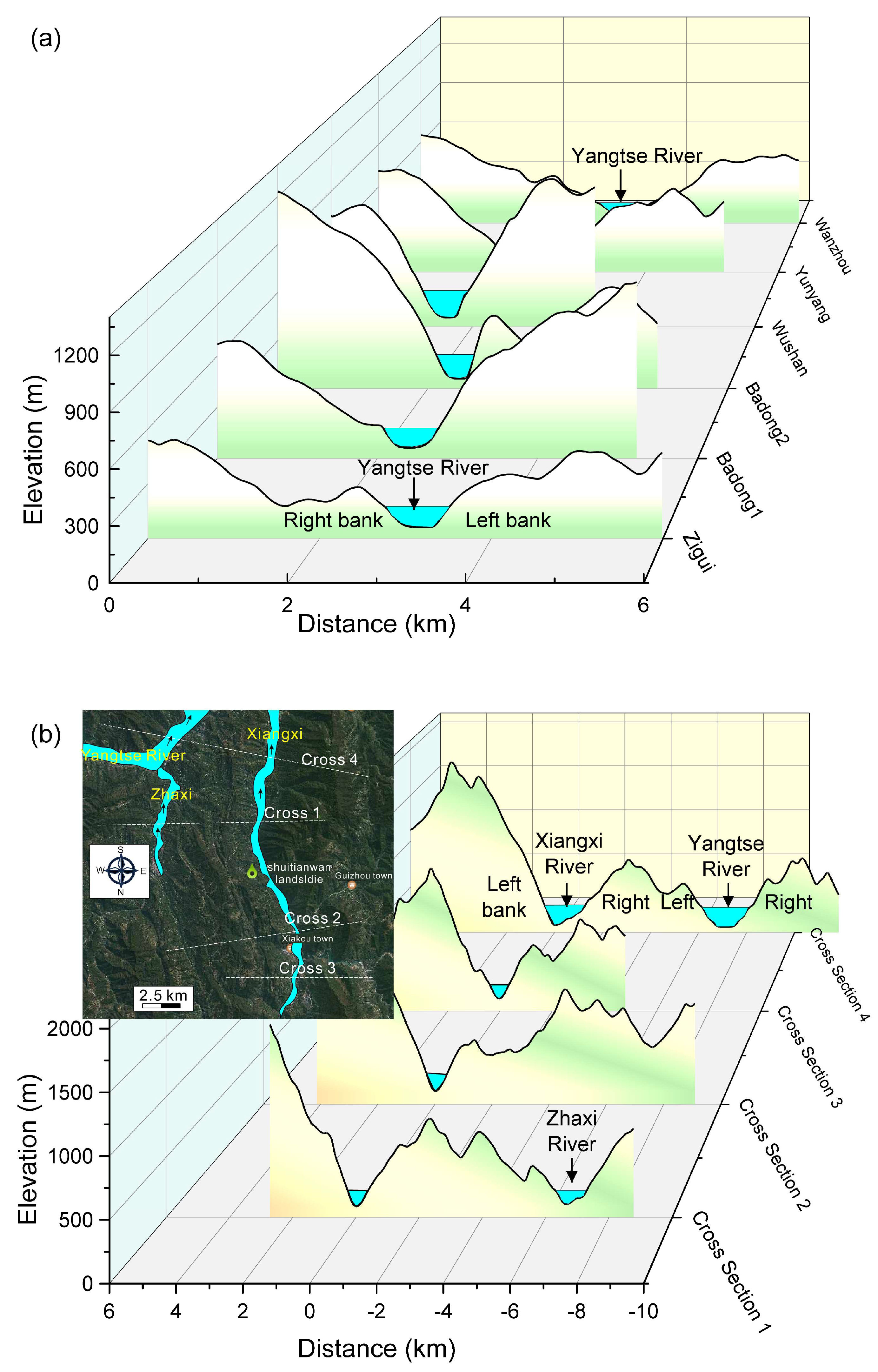
2.1. Geomorphology of Wanshuitian Landslide
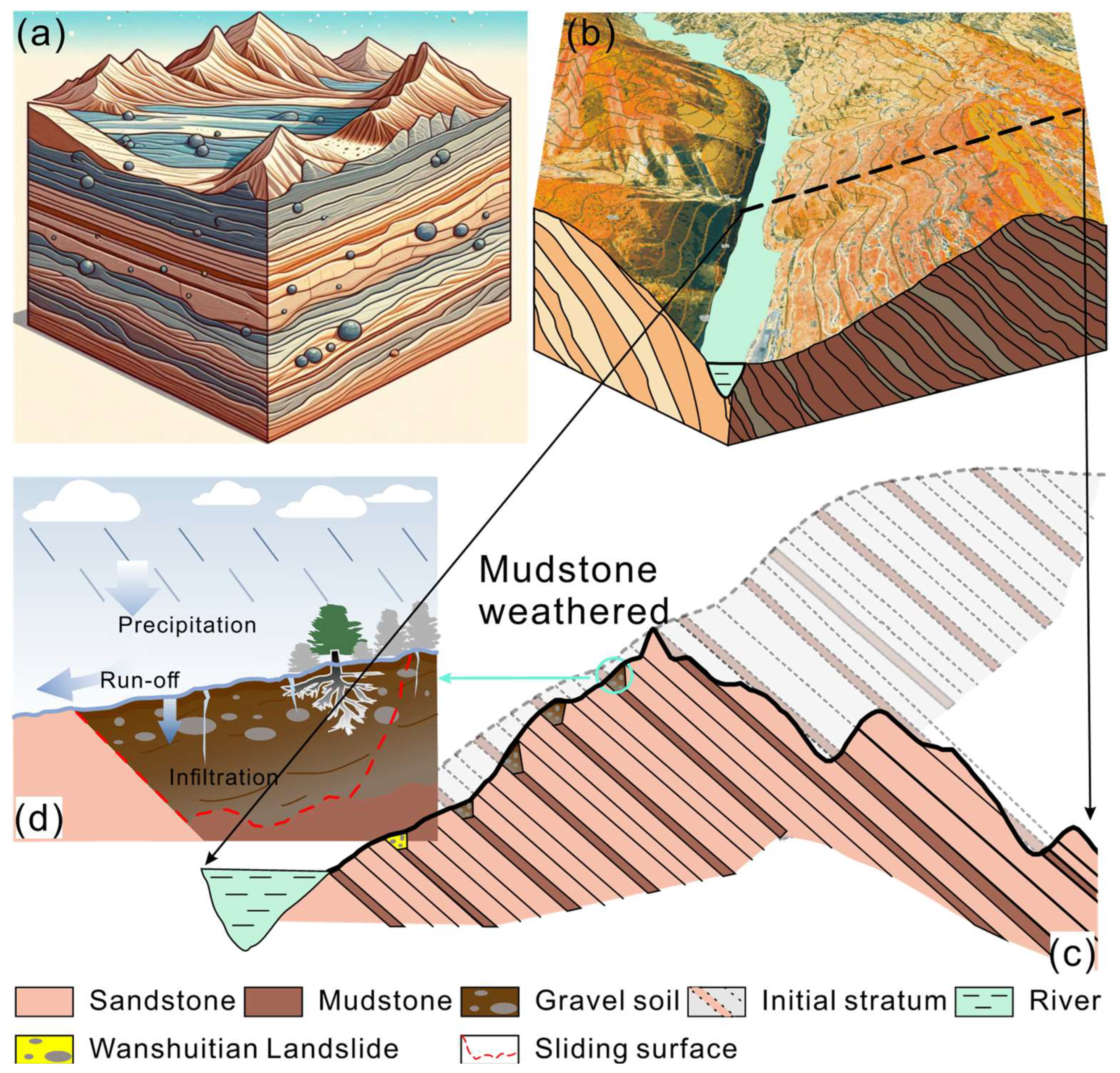
2.2. Geology of Landslide
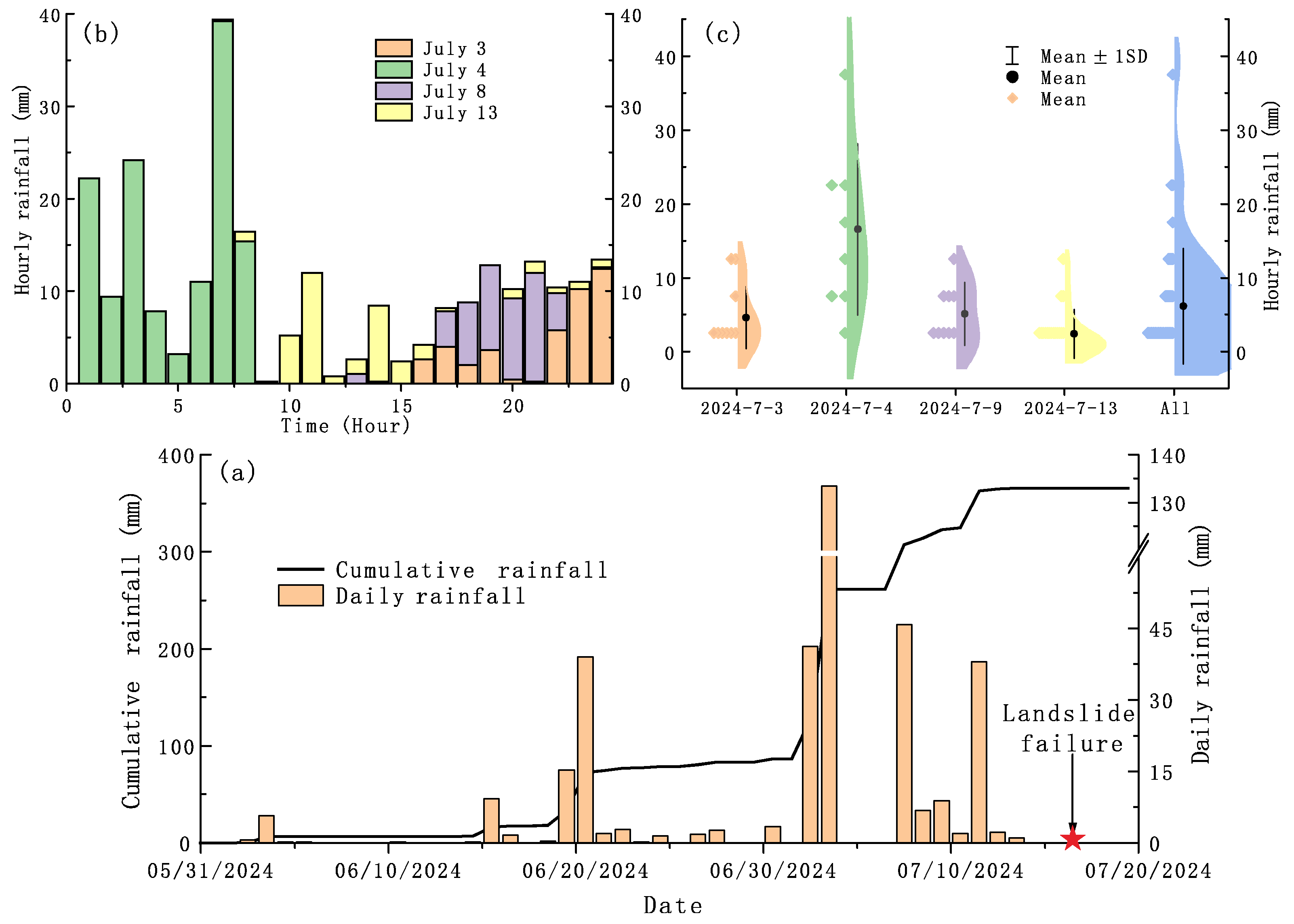
2.3. Rainfall
2.4. Monitoring Methods
3. Results
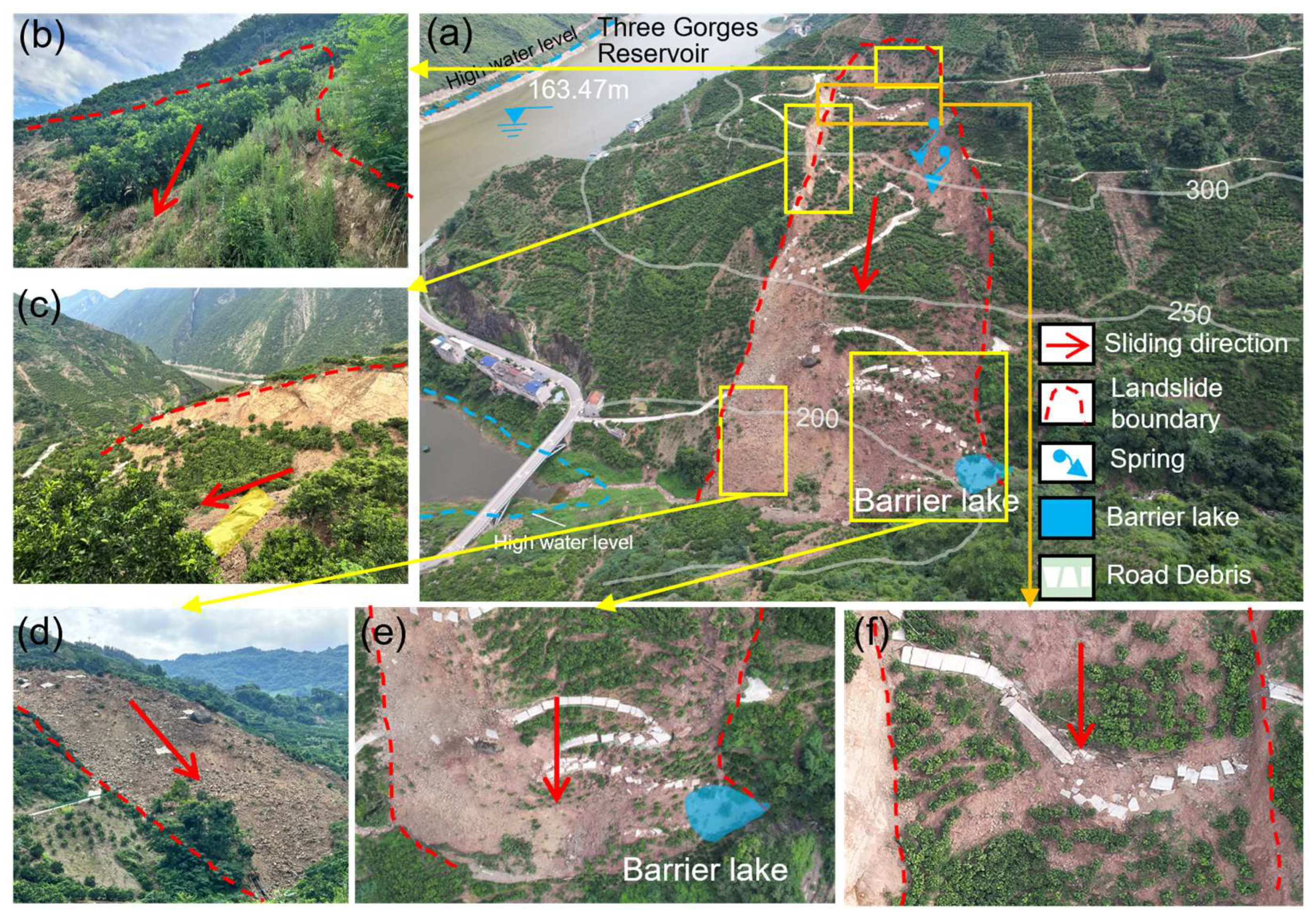
3.1. Deformation Characteristics of Wanshuitian Landslide
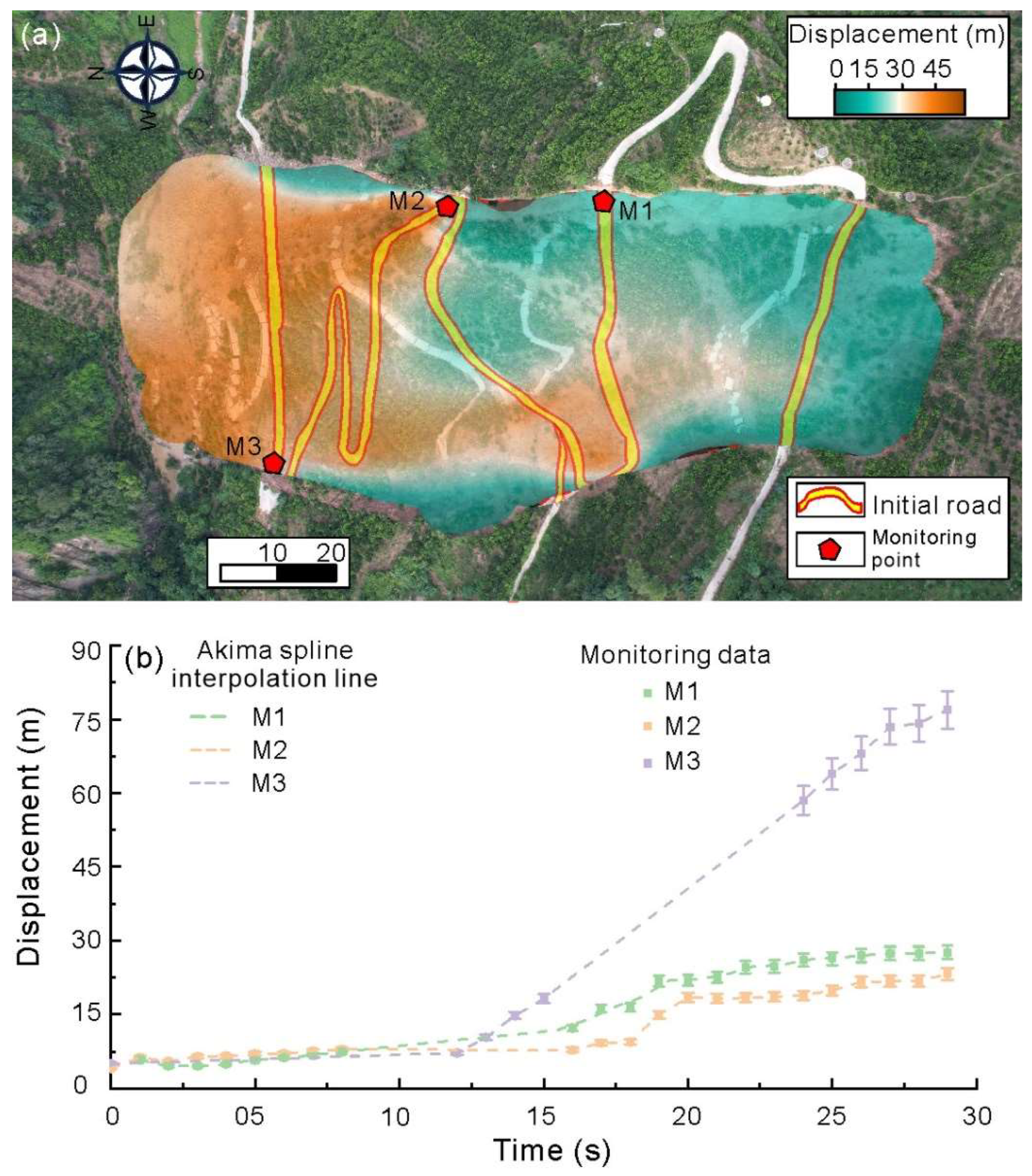
3.2. Displacement of Landslide Surface
3.3. Water Content of Deposit
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolution Mechanism of Landslide
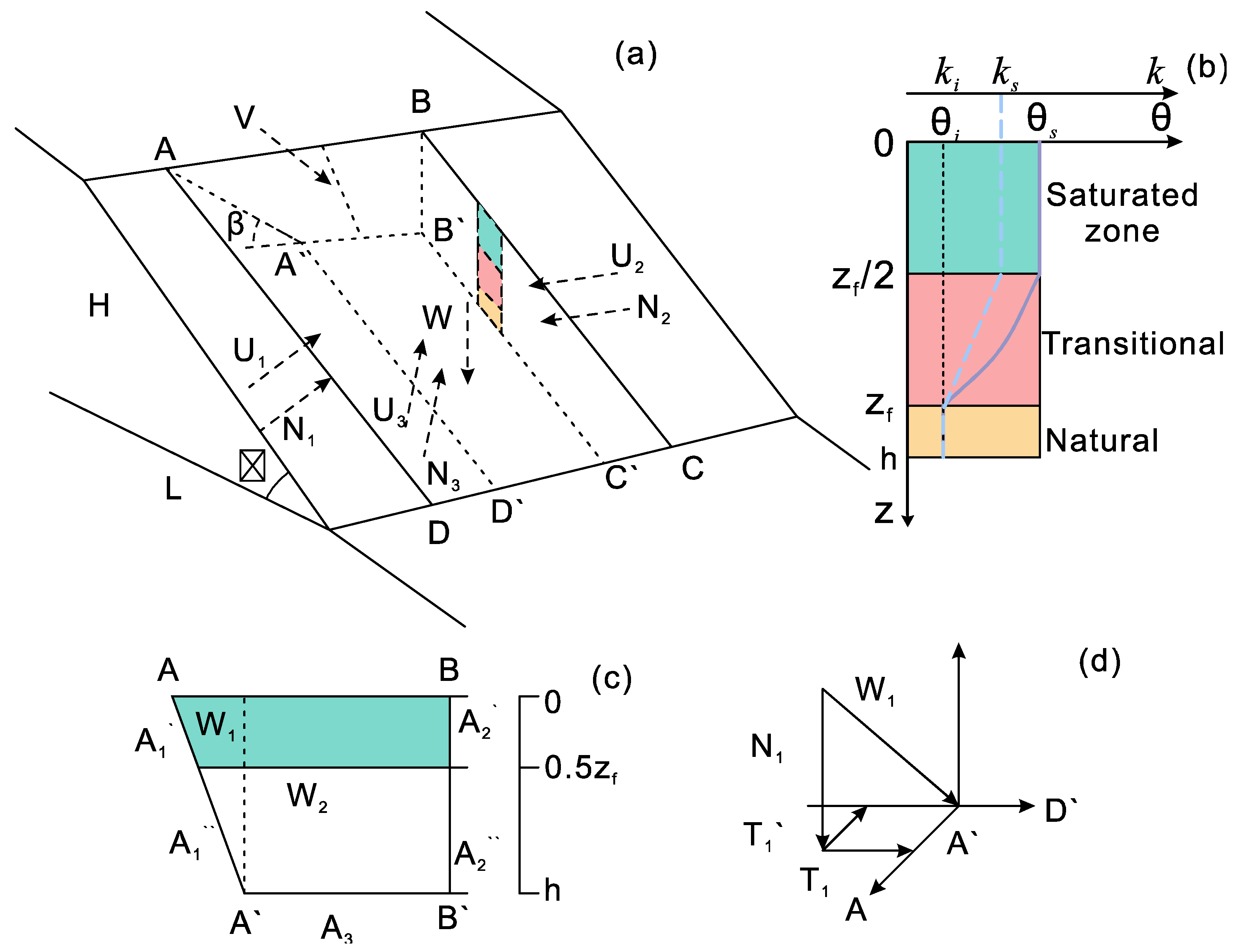
4.2. Stability Prediction of Oblique-Dip Slope Wedge Landslide
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Hong, H.; Chen, W. Regional rainfall-induced landslide hazard warning based on landslide susceptibility mapping and a critical rainfall threshold. Geomorphology 2022, 408, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, M.P.; Kulathilaka, S.A.S.; Robert, D.J.; Zhou, A.; Jayathissa, H.A.G. Risk assessment and management of rainfall-induced landslides in tropical regions: A review. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 2179–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, A.; Sarkar, R.; Pradhan, B.; Segoni, S.; Alamri, A.M. Rainfall induced landslide studies in Indian Himalayan region: A critical review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J. Stability Analysis of the Huasushu Slope Under the Coupling of Reservoir Level Decline and Rainfall. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, R.; Meng, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, H. Effects of changes in soil properties caused by progressive infiltration of rainwater on rainfall-induced landslides. Catena 2023, 233, 107475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Li, Z.; Ye, W.; Peng, T.; Tian, S.; Chen, N.; Huang, N.; Valenzuela, M.S. A small landslide induced a large disaster prior to the heavy rainy season in Jinkouhe, Sichuan, China: Characteristics, mechanism, and lessons. Landslides 2024, 21, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Yan, W.; Yan, C.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Dong, H.; Li, T.; Yu, J.; Zuo, P.; et al. Explainable Machine Learning for Mapping Rainfall-Induced Landslide Thresholds in Italy. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, A.; Poornima, R.; Karthikeyan, G.; Priyatharshini, S.; Thanuja, K.G.; Dhevagi, P. Climate-induced and geophysical disasters and risk reduction management in mountains regions. In Climate Change Adaptation, Risk Management and Sustainable Practices in the Himalaya; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 361–405. [Google Scholar]
- Ponziani, M.; Ponziani, D.; Giorgi, A.; Stevenin, H.; Ratto, S.M. The use of machine learning techniques for a predictive model of debris flows triggered by short intense rainfall. Nat. Hazards 2023, 117, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durukan, S. Evaluation of the Antecedent Saturation and Rainfall Conditions on the Slope Failure Mechanism Triggered by Rainfalls. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Fang, L.; Chang, D.T.T.; Huang, F. Back-analysis of a rainfall-induced landslide case history using deterministic and random limit equilibrium methods. Eng. Geol. 2023, 317, 107055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.T.; Basharat, M.; Ahmed, K.S.; Shahzad, A.; Shah, N.A. Failure mechanism of a massive fault–controlled rainfall–triggered landslide in northern Pakistan. Landslides 2024, 21, 2741–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ai, D.; Huang, W.; Xu, H.; Ma, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, L. Emergency survey and stability analysis of a rainfall-induced soil-rock mixture landslide at Chongqing City, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 774200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Yang, H.; Liang, D.; Chen, L.; Jaboyedoff, M. Step-like displacement prediction and failure mechanism analysis of slow-moving reservoir landslide. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Xing, A.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. Failure and disaster-causing mechanism of a typhoon-induced large landslide in Yongjia, Zhejiang, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 2257–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Dai, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, K.; Tang, J.; Zhang, S. A catastrophic rainfall-induced high landslide, occurred on December 4, 2020, in the Qingliucun mountainous area of Southwest China. Landslides 2023, 20, 2187–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Demisa, M.G.; Han, B.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, Z. A material point method analysis of failure mechanism and kinematic behavior of rainfall-induced landslide. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 13875–13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Hu, H.; Lin, H.; Xie, L. Bedding Slope Destabilization under Rainfall: A Case Study of Zhuquedong Slope in Hunan Province, China. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, B.; Xu, J. Study on deformation and failure mechanism of low-dip red bed slope with soft-hard interbedded structure: A case study of Chishui, China. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 10539–10557. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.Q.; Chen, W.; Long, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, T. Recent rainfall-and excavation-induced bedding rockslide occurring on 22 October 2018 along the Jian-En expressway, Hubei, China. Landslides 2020, 17, 2619–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Shi, W.; Liang, F.; Wang, X. Failure mechanism and evolution of the Jinhaihu landslide in Bijie City, China, on January 3, 2022. Landslides 2022, 19, 2727–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Cui, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, H.; Luo, L.; Zhang, X. Sanxicun landslide: An investigation of progressive failure of a gentle bedding slope. Nat. Hazards 2022, 111, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wei, W.; Zhou, C. A new method for analyzing the stability of rock wedges. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2013, 60, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncone, A.; Pugliese, L.; Parise, A.; Conte, E. Prediction of slow-moving landslide mobility due to rainfall using a two-wedges model. Water 2021, 13, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumsar, H.; Aydan, Ö.; Ulusay, R. Dynamic and static stability assessment of rock slopes against wedge failures. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2000, 33, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Q.; Peng, D.; Zhu, Z.; Li, W.; Wong, H.; Shen, P. Stability analysis of rock wedge slide subjected to groundwater dynamic evolution. Eng. Geol. 2020, 270, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Rodriguez, R.; Sitar, N.; Chacón, J. System reliability approach to rock slope stability. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2006, 43, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambartzumian, R.; Der Kiureghian, A.; Ohaniana, V.; Sukiasiana, H. Multinormal probability by sequential conditioned importance sampling: Theory and application. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 1998, 13, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Der Kiureghian, A. Bounds on system reliability by linear programming. J. Eng. Mech. 2003, 129, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamrakar, N.K.; Singh, J.L.; Bista, K.K.; Maharjan, P. Toppling and wedge failures in Malekhu River area, Malekhu, Central Nepal Lesser Himalaya. Bull. Dep. Geol. 2013, 16, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Xie, J.; Lu, R. Simulation of Seismic Dynamic Response and Post-failure Behavior of Jointed Rock Slope Using Explicit Numerical Manifold Method. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 6921–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ma, W.; Sui, W. Transparent soil model test of a landslide with umbrella-shaped anchors and different slope angles in response to rapid drawdown. Eng. Geol. 2022, 307, 106765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Yan, J.; Gong, W.; Yao, W.; Criss, R.E. Susceptibility of reservoir-induced landslides and strategies for increasing the slope stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area: Zigui Basin as an example. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wasowski, J.; Juang, C.H. Geohazards in the three Gorges Reservoir Area, China–Lessons learned from decades of research. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Criss, R.E.; Fu, Z.; Long, J.; Tan, Q. Evolution characteristics and displacement forecasting model of landslides with stair-step sliding surface along the Xiangxi River, three Gorges Reservoir region, China. Eng. Geol. 2021, 283, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tan, F.; Tang, H.; Zhang, G.; Su, A.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, C. In-situ monitoring platform and preliminary analysis of monitoring data of Majiagou landslide with stabilizing piles. Eng. Geol. 2017, 228, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Kang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z. Experimental study of the influence of wetting and drying cycles on the strength of intact rock samples from a red stratum in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Eng. Geol. 2023, 314, 107013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devitt, D.A.; Smith, S.D. Root channel macropores enhance downward movement of water in a mojave desert ecosystem. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 50, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, S.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Q. Improved Green-Ampt model considering effects of microbial mineralization and vegetation in biological restoration of slopes. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 45, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J. Delay Failure Mechanism of Rainfall-Caused Shallow Landslide. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 2293–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Pugliese, L.; Troncone, A. A simple method for predicting rainfall-induced shallow landslides. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2022, 148, 04022079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Chen, N.; Hu, G.; Han, Z.; Liu, E. Characteristics, mechanisms, and post-disaster lessons of the delayed semi-diagenetic landslide in Hanyuan, Sichuan, China. Landslides 2022, 19, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Xing, K.; Lu, Z.; Peng, B.; Peng, Y.; Guo, F. Comprehensive analysis of July 17, 2024, heavy rainfall-induced landslide at Zigui County in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Landslides 2025, 22, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xia, Z.; Rao, Y.; Chen, H.; Gan, W. Preliminary analysis of Wuyigou landslide on 17 July 2024 in Zigui County, Hubei Province, China. Landslides 2025, 22, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, S.; Luo, X.; Zhu, S.; Wu, L. Animproved Green Ampt model and its experimental verification. J. Eng. Geol. 2023, 31, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Tannant, D.D.; Zhang, G.; Tan, F. Field monitoring and deformation characteristics of a landslide with piles in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Landslides 2018, 15, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value | Picture | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unmanned aerial vehicle (DJI Air 3) | Weight | 6.5 kg |  |
| Size | 830 × 732 × 378 mm | ||
| Load | <3.5 kg | ||
| Accuracy | Horizontal: 1 cm + 1 ppm Vertical: 2 cm + 1 ppm | ||
| Wind resistance capability | 5 scale | ||
| EC-5-type moisture content sensor | Accuracy | 0.1% |  |
| Size | 40 × 15 mm | ||
| Working temperature | −40 °C–50 °C |
| Parameters | α/0 | β/0 | sf/cm | θs/% | θi/% | θr/% | s−1 | s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 20 | 30 | 63.057 | 44 | 11 | 2.3 | 6.4 | |
| Parameters | φ | c | φsat | csat | γ/kNm3 | γsat/kNm3 | ||
| Value | 26 | 31 | 13 | 17 | 19.2 | 19.8 |
| Rainfall Events | Cumulative Rainfall (mm) | Duration (h) | Rainfall Intensity (mm/min) | Cumulative Rainfall Infiltration Depth (m) | Stability Factor (Fos) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 July | 41.2 | 7 | 0.098 | 16.13 | 0.7417 |
| 4 July | 133.4 | 8 | 0.279 | 18.43 | 0.6751 |
| 9 July | 45.8 | 6 | 0.127 | 13.82 | 0.8215 |
| 13 July | 38 | 5 | 0.127 | 11.52 | 0.9177 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, C.; Zhou, C.; Huang, W. The Evolution Mechanism and Stability Prediction of the Wanshuitian Landslide, an Oblique-Dip Slope Wedge Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169194
Xu C, Zhou C, Huang W. The Evolution Mechanism and Stability Prediction of the Wanshuitian Landslide, an Oblique-Dip Slope Wedge Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):9194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169194
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Chu, Chang Zhou, and Wei Huang. 2025. "The Evolution Mechanism and Stability Prediction of the Wanshuitian Landslide, an Oblique-Dip Slope Wedge Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 9194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169194
APA StyleXu, C., Zhou, C., & Huang, W. (2025). The Evolution Mechanism and Stability Prediction of the Wanshuitian Landslide, an Oblique-Dip Slope Wedge Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169194





