Integrated Statistical Analysis and Spatial Modeling of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Sediments in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Geological Setting
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Data Processing
3. Characterization of Hydrate-Bearing Sediments
3.1. Stratigraphic Boundaries
3.2. Gas Hydrate Saturation
3.2.1. Descriptive Statistics
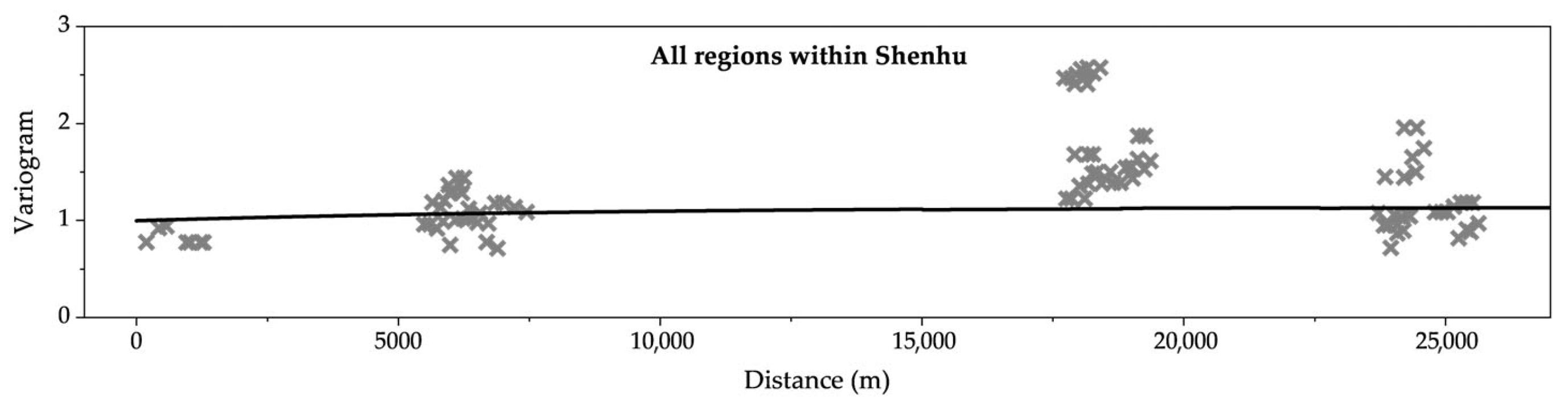
3.2.2. Spatial Variability
3.3. Sediment Properties
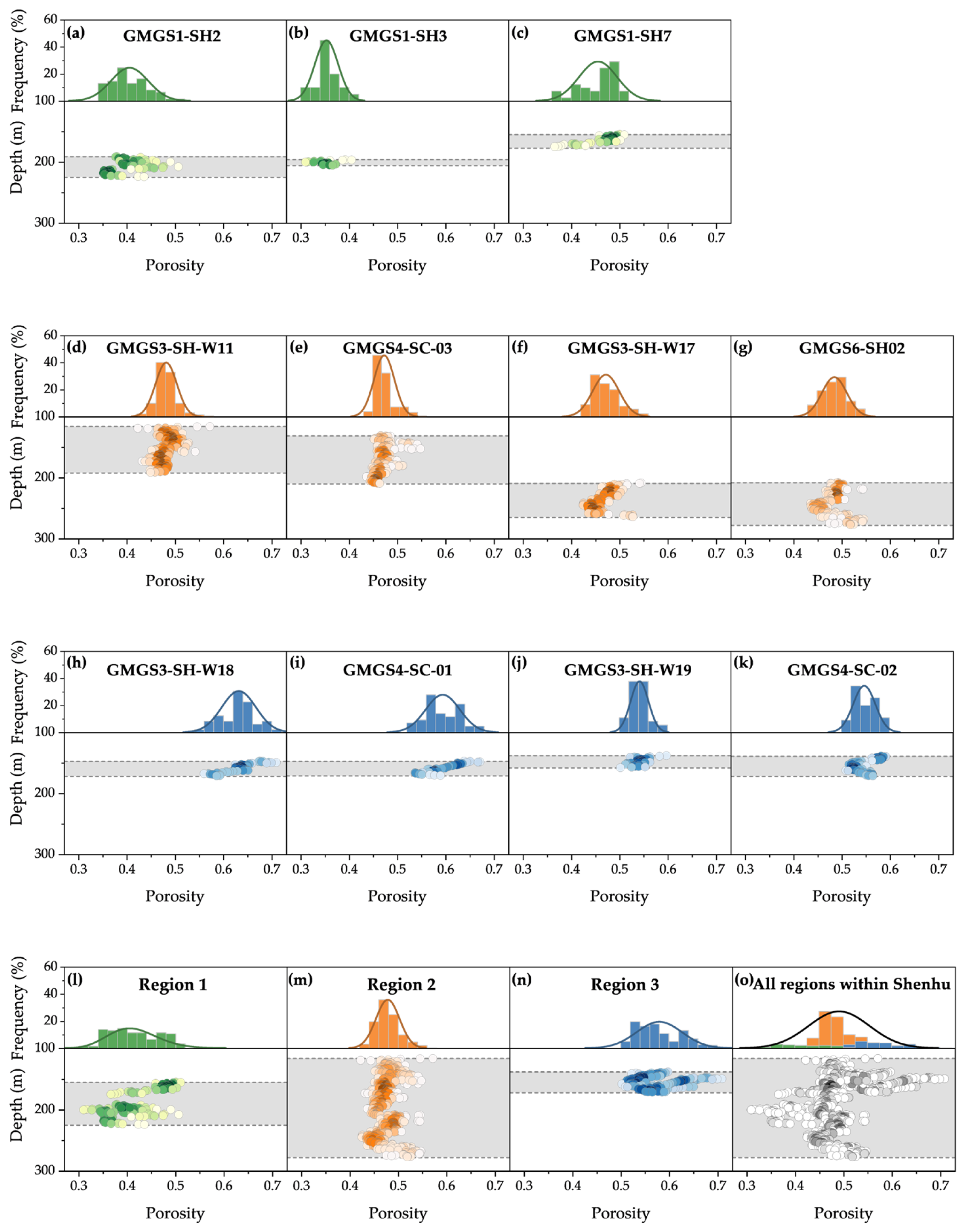
3.3.1. Porosity
3.3.2. Permeability
3.4. Strength Parameters
3.4.1. Logging-Based Estimation
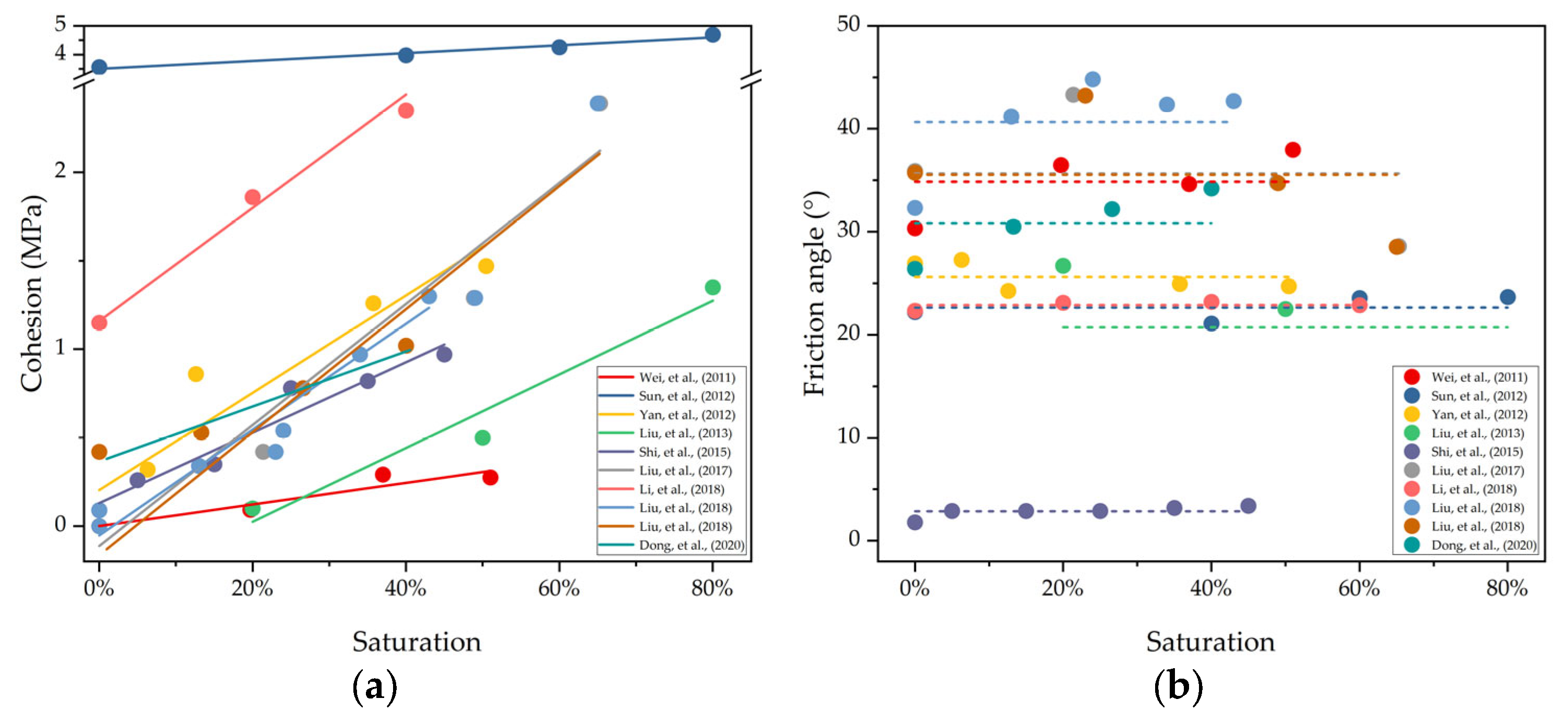
3.4.2. Laboratory Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collett, T. Natural Gas Hydrates—Vast Resource, Uncertain Future; US Geological Survey: Reston, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.Y.; Holland, M.; Schultheiss, P.J. Successful and surprising results for China’s first gas hydrate drilling expedition. Fire Ice Methane Hydrate Newsl. 2007, 7, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, S.; Zhang, M.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Holland, M.; Schultheiss, P. GMGS2 expedition investigates rich and complex gas hydrate environment in the South China Sea. Fire Ice Methane Hydrate Newsl. 2014, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, M.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Holland, M.; Schultheiss, P.; Fu, S.; Sha, Z. Preliminary Results of China’s Third Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition: A Critical Step From Discovery to Development in the South China Sea. Fire Ice Methane Hydrate Newsl. 2015, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Liang, J.; Lei, Y.; Gong, Y.; Xu, H. GMGS4 gas hydrate drilling expedition in the South China Sea. Fire Ice Methane Hydrate Newsl. 2017, 17, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Wei, J.; Liang, J.; Lu, J.; Lu, H. Complex gas hydrate system in a gas chimney, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 104, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.W.; Lu, J.A.; Lu, H.L.; Qiu, H.J.; Liang, J.Q.; Kang, D.J.; Zhan, L.S.; Lu, H.F.; Kuang, Z.G. Coexistence of natural gas hydrate, free gas and water in the gas hydrate system in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. China Geol. 2020, 3, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, J.; Phillips, S.C.; Liang, J.; Deng, W.; Zhong, C.; Meng, D. Insights on gas hydrate formation and growth within an interbedded sand reservoir from well logging at the Qiongdongnan basin, South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2024, 475, 107343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Cook, A.; Ren, J.; Deng, W.; Cao, Y.; Cai, H. A Flat-Lying Transitional Free Gas to Gas Hydrate System in a Sand Layer in the Qiongdongnan Basin of the South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL105744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Ye, J.L.; Qin, X.W.; Qiu, H.J.; Wu, N.Y.; Lu, H.L.; Xie, W.W.; Lu, J.A.; Peng, F.; Xu, Z.Q.; et al. The first offshore natural gas hydrate production test in South China Sea. China Geol. 2018, 1, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.L.; Qin, X.W.; Xie, W.W.; Lu, H.L.; Ma, B.J. Main progress of the second gas hydrate trial production in the South China Sea. Geol. China 2020, 47, 557–568. [Google Scholar]
- Lall, D.; Vishal, V.; Lall, M.V.; Ranjith, P.G. The role of heterogeneity in gas production and the propagation of the dissociation front using thermal stimulation, and huff and puff in gas hydrate reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Xu, T.; Yuan, Y.; Xin, X.; Zhu, H. Optimal design of the field hydrate production test in the offshore India: Insights from the vertically heterogeneous hydrate reservoir model. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 103, 104645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Sun, J.; Ning, F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, N.; Yu, Y. Numerical analysis on gas production from heterogeneous hydrate system in Shenhu area by depressurizing: Effects of hydrate-free interlayers. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 101, 104504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Chang, J.; Qi, X.; Shangguan, S.; Wang, W.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Q.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Numerical simulation on physical composite stimulation and geothermal development performance of hot dry rock: A Case study from Matouying Uplift, China. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 267, 125714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.T.; Zhao, B.; Li, G. Prevention of Potential Hazards Associated with Marine Gas Hydrate Exploitation: A Review. Energies 2018, 11, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ye, J.; Xie, W. Economic Critical Resources for the Industrial Exploitation of Natural Gas Hydrate. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 96, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Hu, M.; Chang, J.; Wang, W.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Shang, S. Explosive fracturing mechanism in low-permeability sandstone-type uranium deposits considering different acidification reactions. Energy 2024, 312, 133676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qian, J.; Sun, L. Geological controls on the occurrence of recently formed highly concentrated gas hydrate accumulations in the Shenhu area, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 116, 104294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Liang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, F.; Wang, F.; Li, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Natural gas hydrate accumulation system in the Shenhu sea area of the northern South China Sea. Nat. Gas Ind. 2020, 40, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Jin, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, J. The characteristics of gas hydrate accumulation and quantitative estimation in the north slope of South China Sea. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 1038–1057. Available online: https://www.scielo.br/j/eagri/a/XRdYQpjHFQSwSCWxT3QtxDv/?format=pdf&lang=pt (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Hassan, W.; Qasim, M.; Alshameri, B.; Shahzad, A.; Khalid, M.H.; Qamar, S.U. Geospatial intelligence in geotechnical engineering: A comprehensive investigation into SPT-N, soil types, and undrained shear strength for enhanced site characterization. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2024, 83, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Q.; Chu, J.; Qi, X.; Wu, S.; Chiam, K. Bayesian evidential learning of soil-rock interface identification using boreholes. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 162, 105638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, T.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Deng, X.; Shi, H. Three-dimensional joint inversion of gravity gradient data based on data space and sparse constrains. Chin. J. Geophys. 2021, 64, 1074–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Wang, Y. Data-driven construction of Three-dimensional subsurface geological models from limited Site-specific boreholes and prior geological knowledge for underground digital twin. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 126, 104493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Fang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Xue, B.; Yang, M.; Wang, N. GPR detection localization of underground structures based on deep learning and reverse time migration. NDT E Int. 2024, 143, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Lee, M.; Guo, Y.; Yang, S.; Liang, J. Gas hydrate saturation from acoustic impedance and resistivity logs in the shenhu area, south china sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lei, Y.; Liang, J.; Holland, M.; Schultheiss, P.; Lu, J. Concentrated Gas Hydrate in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea: Results From Drilling Expeditions GMGS3 & GMGS4. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Gas Hydrates, Denver, CO, USA, 25–30 June 2017; Available online: http://www.geotek.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/YangHollandICGH9.pdf (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Ning, F.; Wu, N.; Li, S.; Zhang, K.; Yu, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Jiang, G.; Sun, C.; Chen, G. Estimation of in-situ mechanical properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments by well logging. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, H.; Peng, L.; Wei, C.; Ning, F. An easy and efficient way to evaluate mechanical properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments: The direct shear test. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 149, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dai, S.; Ning, F.; Peng, L.; Wei, H.; Wei, C. Strength Estimation for Hydrate-Bearing Sediments From Direct Shear Tests of Hydrate-Bearing Sand and Silt. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Liao, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Hu, G.; Liu, L.; Meng, Q. Strength estimation for hydrate-bearing sediments based on triaxial shearing tests. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 184, 106478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, W.J.; Dallimore, S.R.; Collett, T.S.; Jenner, K.A.; Katsube, J.T.; Cranston, R.E.; Wright, J.F.; Nixon, F.M.; Uchida, T. Relation between gas hydrate and physical properties at the Mallik 2L-38 research well in the Mackenzie delta. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 912, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, W.J.; Waite, W.F.; Mason, D.H.; Gilbert, L.Y.; Pecher, I.A. Methane gas hydrate effect on sediment acoustic and strength properties. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2007, 56, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, A.; Haneda, H.; Ogata, Y.; Aoki, K. Mechanical properties of sandy sediment containing marine gas hydrates in deep sea offshore Japan. In Proceedings of the ISOPE Ocean Mining Symposium, Lisbon, Portugal, 1–6 July 2007; pp. 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda, J.; Masui, A.; Konno, Y.; Jin, Y.; Egawa, K.; Kida, M.; Ito, T.; Nagao, J.; Tenma, N. Mechanical behavior of hydrate-bearing pressure-core sediments visualized under triaxial compression. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 66, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, J.; Hyodo, M.; Yoshimoto, N.; Nakata, Y.; Kato, A. Development of high-pressure low-temperature plane strain testing apparatus for methane hydrate-bearing sand. Soils Found. 2013, 53, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, J.; Masui, A.; Tenma, N.; Nagao, J. Triaxial testing system for pressure core analysis using image processing technique. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 114503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamarina, J.; Dai, S.; Terzariol, M.; Jang, J.; Waite, W.; Winters, W.; Nagao, J.; Yoneda, J.; Konno, Y.; Fujii, T.; et al. Hydro-bio-geomechanical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments from Nankai Trough. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 66, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.B.; Liang, J.Q.; Sha, Z.B.; Fu, S.Y. Gas Sources Condition of Gas Hydrate Formation in Shenhu Deep Water Sea Zone. J Southwest Pet. Univ (Sci. Technol. Ed.) 2014, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, T.; Chu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X. The distribution of gas chimney structures in Shenhu area and their influence on gas hydrate accumulation. Mar. Geol. Front. 2015, 31, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, S.; Cartwright, J.; Dong, D. Shallow gas and focused fluid flow systems in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2012, 315, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Collett, T.S.; Lee, M.W.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Wu, S. Geological controls on the occurrence of gas hydrate from core, downhole log, and seismic data in the Shenhu area, South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2014, 357, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, Z.; Luan, Z.; Wang, X.; Xi, S.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Lian, C.; Yan, J. In Situ Raman Detection of Gas Hydrates Exposed on the Seafloor of the South China Sea. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2017, 18, 3700–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Liang, J.; Guo, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Su, P.; Lin, L. Integrated core-log facies analysis and depositional model of the gas hydrate-bearing sediments in the northeastern continental slope, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 86, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Su, M.; Kuang, Z.; Yang, R.; Liang, J.; Wu, N. Canyon-related undulation structures in the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2015, 36, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ye, Y.; Meng, Q.; He, X.; Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, S. The Characteristics of Gas Hydrates Recovered from Shenhu Area in the South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2012, 307, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Q.; Wang, H.B.; Su, X.; Fu, S.Y.; Wang, L.F.; Guo, Y.Q.; Chen, F.; Shang, J.J. Natural gas hydrate formation conditions and the associated controlling factors in the northern slope of the South China Sea. Nat. Gas Ind. 2014, 34, 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, J.; He, J.; Cong, X.; Su, P.; Lin, L.; Liang, J. Differences in natural gas hydrate migration and accumulation between GMGS1 and GMGS3 drilling areas in the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea. Nat. Gas Ind. 2018, 38, 138–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Hutchinson, D.R.; Wu, S.; Yang, S.; Guo, Y. Elevated gas hydrate saturation within silt and silty clay sediments in the Shenhu area, South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makogon, Y.F. Natural gas hydrates—A promising source of energy. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2010, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Xueqin, L.; Huaishan, L.; Zhiliang, Q.; Benjun, M. Research on the Construction of a Petrophysical Model of a Heterogeneous Reservoir in the Hydrate Test Area in the Shenhu Area of the South China Sea (SCS). Geofluids 2021, 2021, 5586118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Fang, Y.; Lu, H.; Lu, H.; Lu, J.; Liang, J.; Yang, S. Distribution and characteristics of natural gas hydrates in the Shenhu Sea Area, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Luo, K.; Liang, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, F.; Su, M.; Fang, Y. Control effect of shallow-burial deepwater deposits on natural gas hydrate accumulation in the Shenhu sea area of the northern South China Sea. Nat. Gas Ind. 2020, 40, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, M.; Collett, T.S. Observed correlation between the depth to base and top of gas hydrate occurrence from review of global drilling data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2017, 18, 2177–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archie, G.E. The Electrical Resistivity Log as an Aid in Determining Some Reservoir Characteristics. Trans. AIME 2003, 146, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Qu, C.; Lu, J. A quantitative evaluation method for the natural gas hydrate reservoir parameters in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. Geoscience 2024, 38, 385–397. [Google Scholar]
- Nazeer, A.; Abbasi, S.A.; Solangi, S.H. Sedimentary facies interpretation of Gamma Ray (GR) log as basic well logs in Central and Lower Indus Basin of Pakistan. Geod. Geodyn. 2016, 7, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Ebinuma, T.; Hideo, N. Estimation of the in-situ permeabilities of nankai trough hydrate bearing sediments from pressure temparature core damplar. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 5–8 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, P.; Tian, H.; Wu, E.; Wei, C. Deformation and failure bahavior of carbon dioxide hydrate-bearing sands with different hydrate contents under triaxial shear tests. Rock Soil Mech. 2011, 32, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cheng, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, Q.; Li, Q. Triaxial compression test on synthetic core sample with simulated hydrate-bearing sediments. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2012, 40, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.T.; Wei, C.F.; Wei, H.Z.; Tian, H.H.; Wu, E.L. Effect of hydrate formation on mechanical strength of hydrate-bearing sand. Yantu Gongcheng Xuebao/Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2012, 34, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Kou, X.Y.; Jiang, M.J.; Xiong, J.H.; Wu, X.F. Triaxial shear strength of synthetic hydrate-bearing sediments. Yantu Gongcheng Xuebao/Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 35, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.H.; Zhang, X.H.; Lu, X.B.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, A.L. Experimental study on the satatic mechanical properties of hydrate-bearing silty-clay in the South China Sea. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2015, 47, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Ansari, U.; Song, B. Establishment and evaluation of strength criterion for clayey silt hydrate-bearing sediments. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2018, 40, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, G.; Chatterjee, S.; Chapman, W.G.; Dugan, B.; Dickens, G.R.; Hirasaki, G.J. Analytical theory relating the depth of the sulfate-methane transition to gas hydrate distribution and saturation. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2011, 12, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, B.; Yang, M.; Song, Y.; Sum, A.K. Methane hydrate phase equilibrium considering dissolved methane concentrations and interfacial geometries from molecular simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2023, 159, 244505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, X.; Zha, R.; Lai, Y.; Yang, T.; Su, P. Pore-Water Geochemical Gradients of Sulfate, Calcium, Magnesium, and Iodide Correlated With Underlying Gas Hydrate Potential: A Case Study of the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 882207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Sha, Z.; Liang, J.; Wu, N.; Qiao, S.; Cong, X. Gas hydrates distribution in the Shenhu area, Northern South China sea: Comparisons between the eight drilling sites with gashydrate petroleum system. Geol. Acta 2016, 14, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, V.I.; Sai, K.S. Process pattern of heterogeneous gas hydrate deposits dissociation. Nauk. Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetu. 2018, 2, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaluk, O.; Sai, K.; Lozynskyi, V.; Petlovanyi, M.; Saik, P. Research into Dissociation Zones of Gas Hydrate Deposits with a Heterogeneous Structure in the Black Sea. Energies 2023, 14, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.J.; Xie, Y.F.; Lu, J.A.; Wang, T.; Liang, J.Q.; Lai, H.F.; Fang, Y.X. Assessment of natural gas hydrate reservoirs at Site GMGS3-W19 in the Shenhu area, South China Sea based on various well logs. China Geol. 2022, 5, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaaks, E.H.; Srivastava, R.M. An Introduction to Applied Geostatistics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, T.W. An Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis, 3rd ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Han, L.; Liu, J.; Jin, J.; Kuang, Z.; Zhou, J. Geophysical characteristics and identification of the coexistence of gas hydrate and free gas. Earth Sci. Front. 2025, 32, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Wang, X.; Collett, T.S.; Guo, Y.; Kang, D.; Jin, J. Downhole log evidence for the coexistence of structure II gas hydrate and free gas below the bottom simulating reflector in the South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, R.; Collett, T.S. Current perspectives on gas hydrate resources. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Song, Y. Analysis of the effect of particle size on permeability in hydrate-bearing porous media using pore network models combined with CT. Fuel 2016, 163, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Su, M.; Qiao, S.; Cong, X.; Su, Z.; Liang, J.; Wu, N. Migration of methane associated with gas hydrates of the Shenhu Area, northern slope of South China Sea. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2015, 36, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Yang, S.X.; Wu, N.Y.; Zhang, G.X.; Liang, J.Q.; Chen, D.F. Controlling factors for gas hydrate occurrence in Shenhu area on the northern slope of the South China Sea. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J. Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Lu, J.; Kang, D.; Ning, F.; Lu, H.; Kuang, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Hu, G.; Wang, J.; et al. Lithological characteristics and hydrocarbon gas sources of gas hydrate-bearing sediments in the Shenhu area, South China Sea: Implications from the W01B and W02B sites. Mar. Geol. 2019, 408, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, H. Research on permeability prediction model of marine fine-grained sandy hydrate reservoirs. China Offshore Oil Gas. 2022, 34, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ci, J.; He, S.; Li, R. Pre-spud study on mechanical stability of wellbore. Nat. Gas Ind. 2006, 44, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- John, I.K.; Tamunobereton-Ari, I.; Horsfall, O.I.; Amakiri, A.R.C. The Effects of Clay Content and Porosity on Acoustic Velocity in clastic Sedimentary Formations, in parts of the Niger Delta, Nigeria. J. Softw. Eng. Simul. 2024, 10, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, P.; Batzle, M.L.; Eastwood, R.L. Relationships between compressional-wave and shear-wave velocities in clastic silicate rocks. Geophysics 1985, 50, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, W.F.; Santamarina, J.C.; Cortes, D.D.; Dugan, B.; Espinoza, D.N.; Germaine, J.; Jang, J.; Jung, J.W.; Kneafsey, T.J.; Shin, H.; et al. Physical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments. Rev. Geophys. 2009, 47, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Tenma, N.; Ogata, Y.; Aoki, K. Effect of Confining Pressure on Mechanical Properties of Sediment Containing Synthetic Methane Hydrate. J. Min. Mater. Process. Inst. Jpn. 2010, 126, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Liao, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. Measurement and assessment of mechanical properties of hydrate-bearing sediments. Mar. Geol. Front. 2020, 36, 34–43. [Google Scholar]

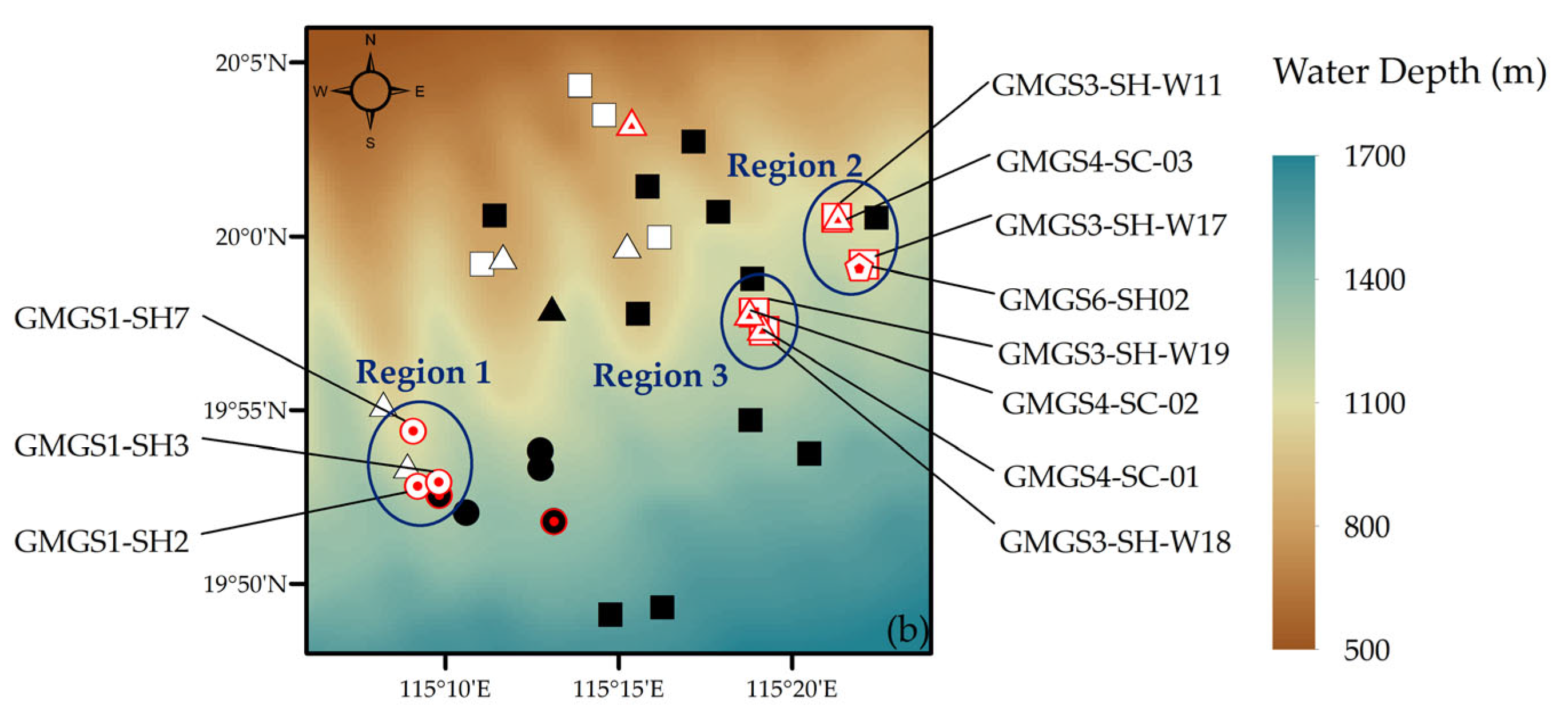
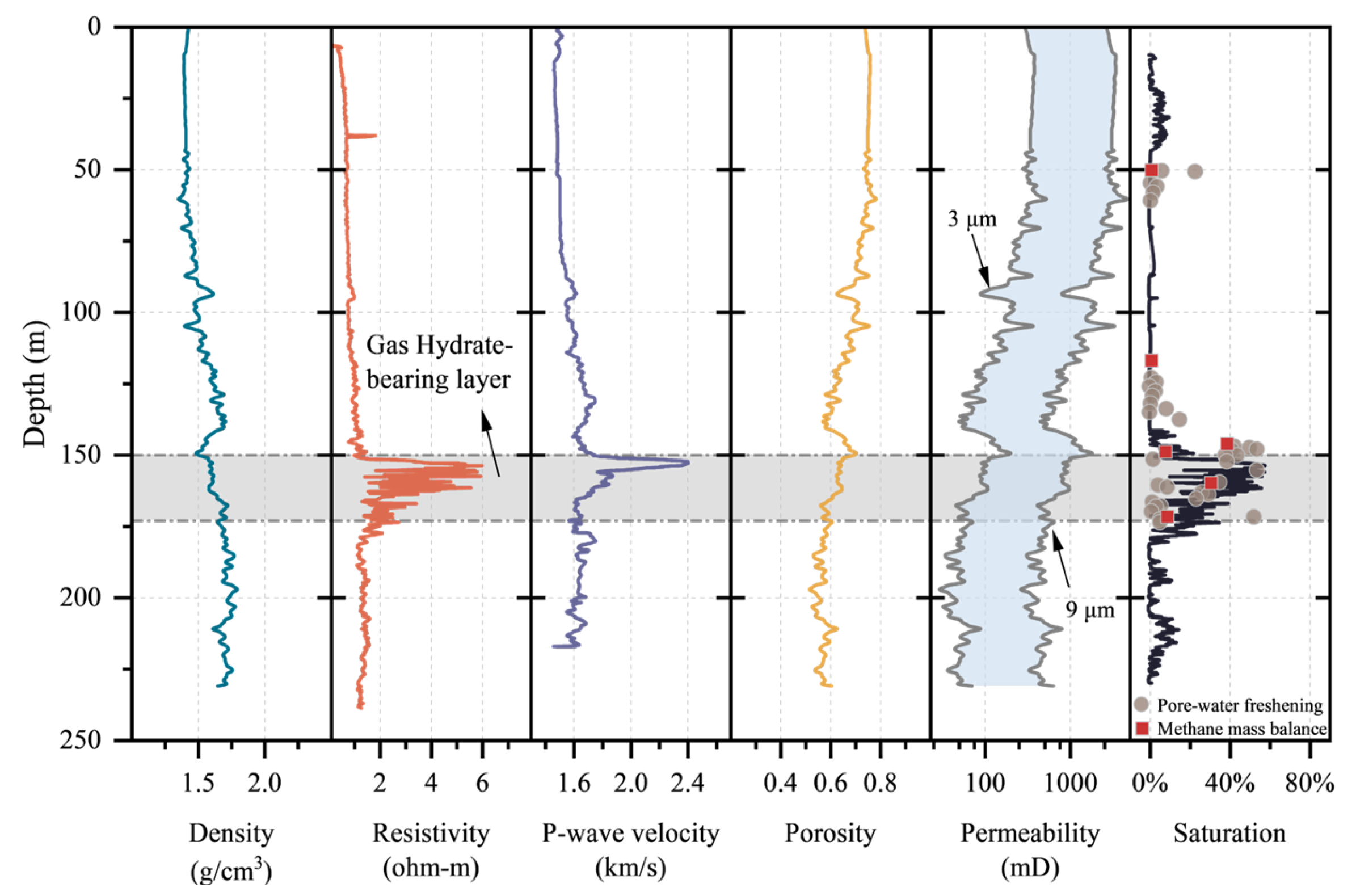
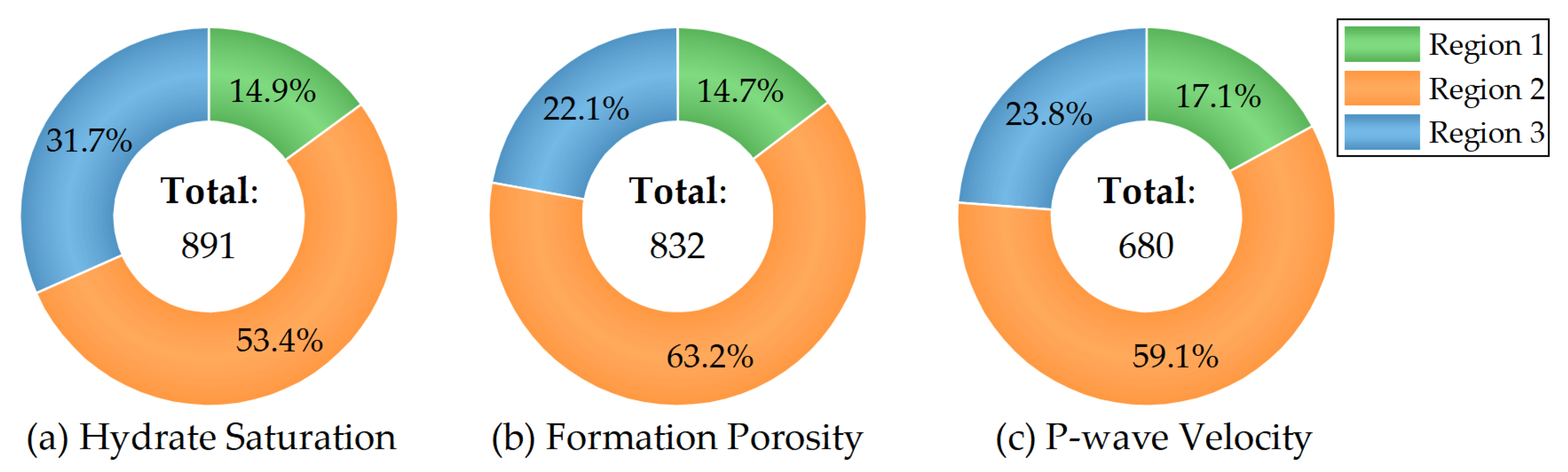
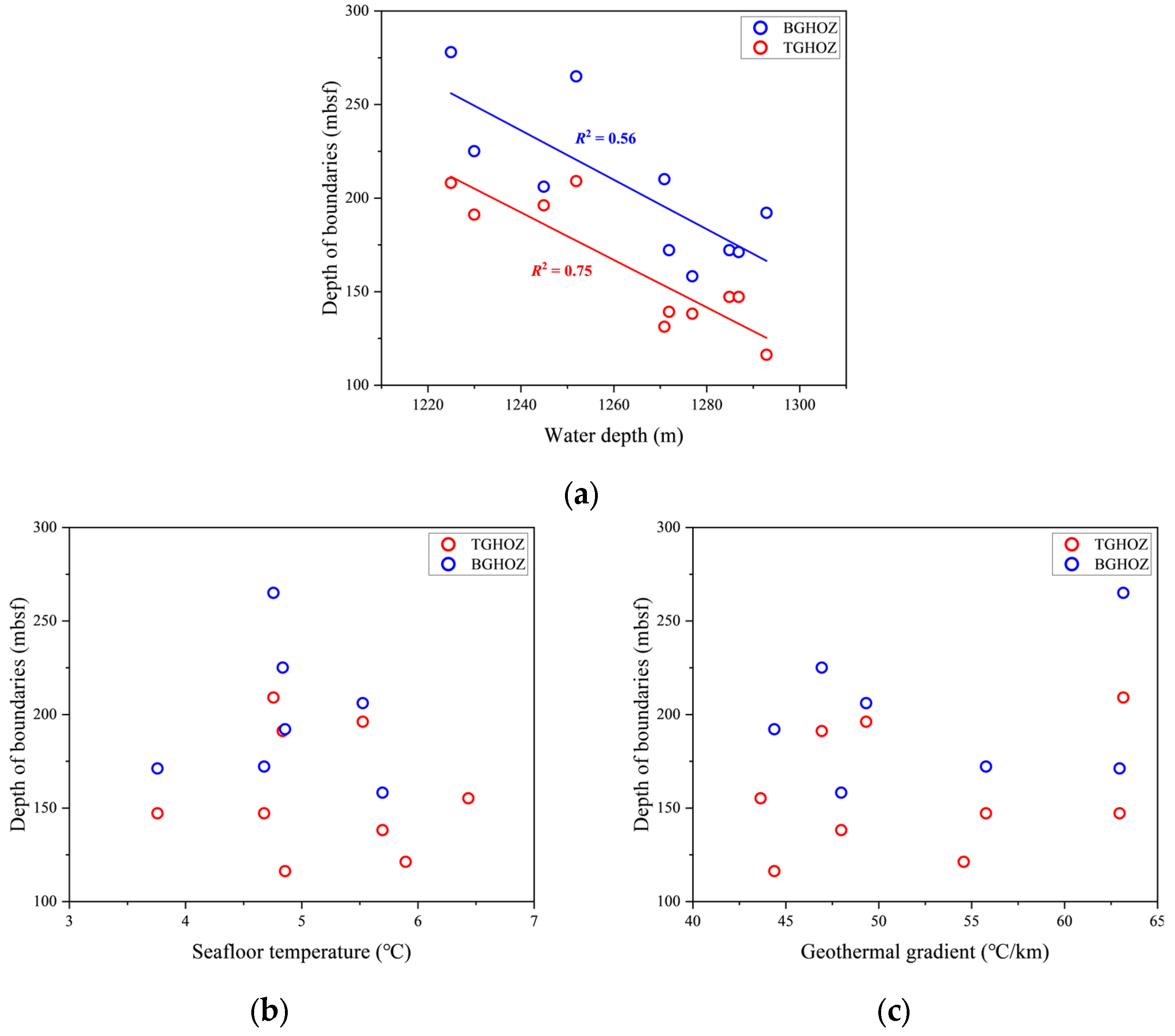
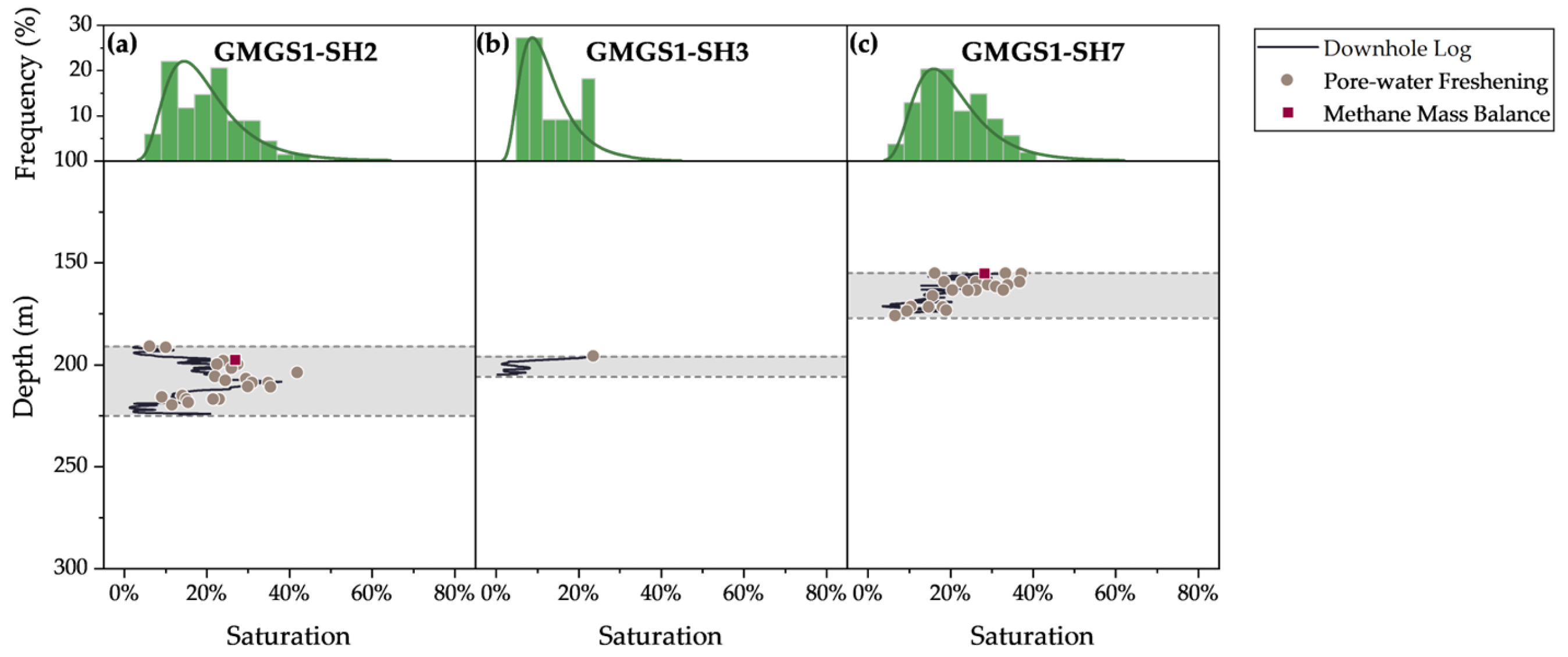
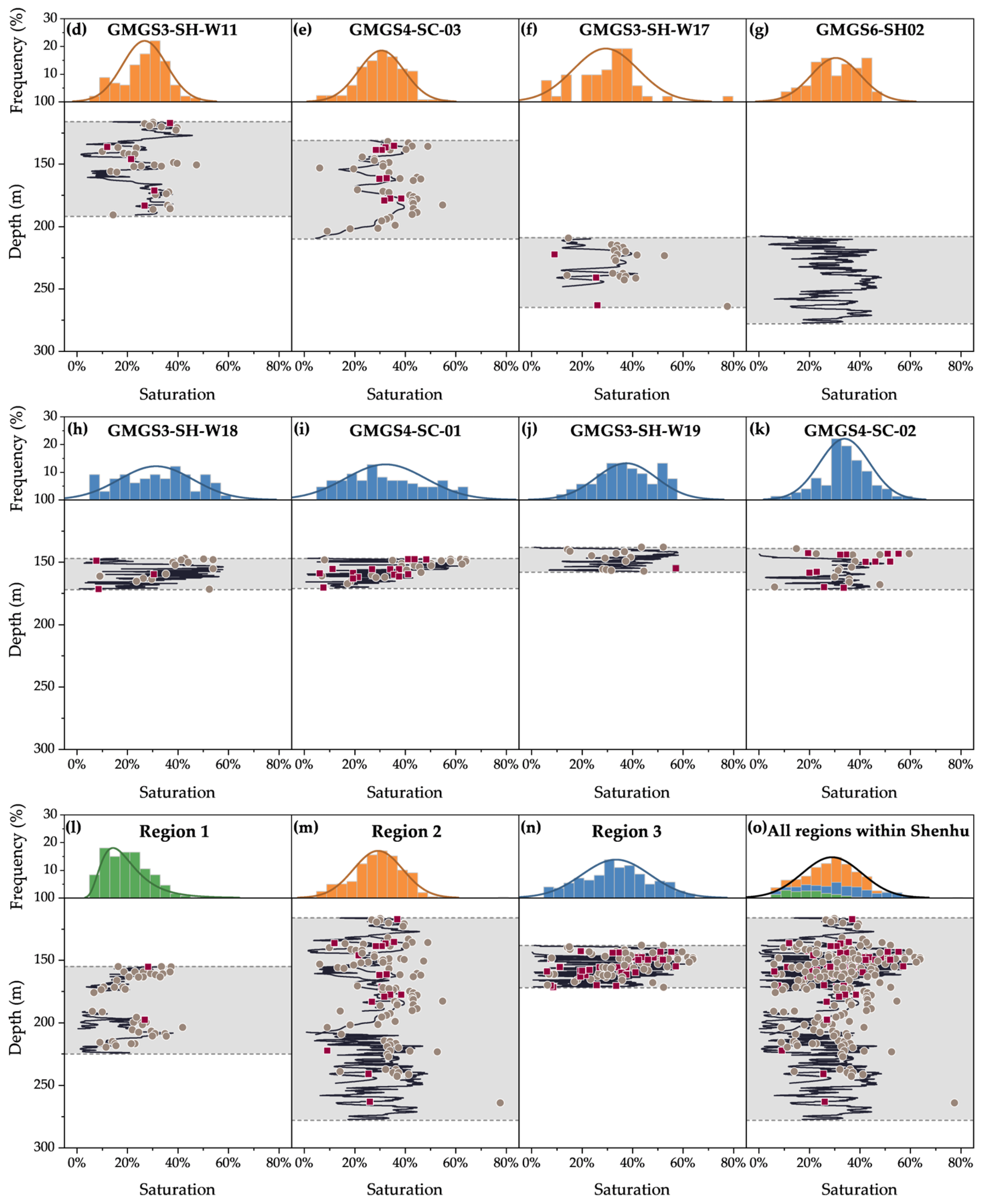

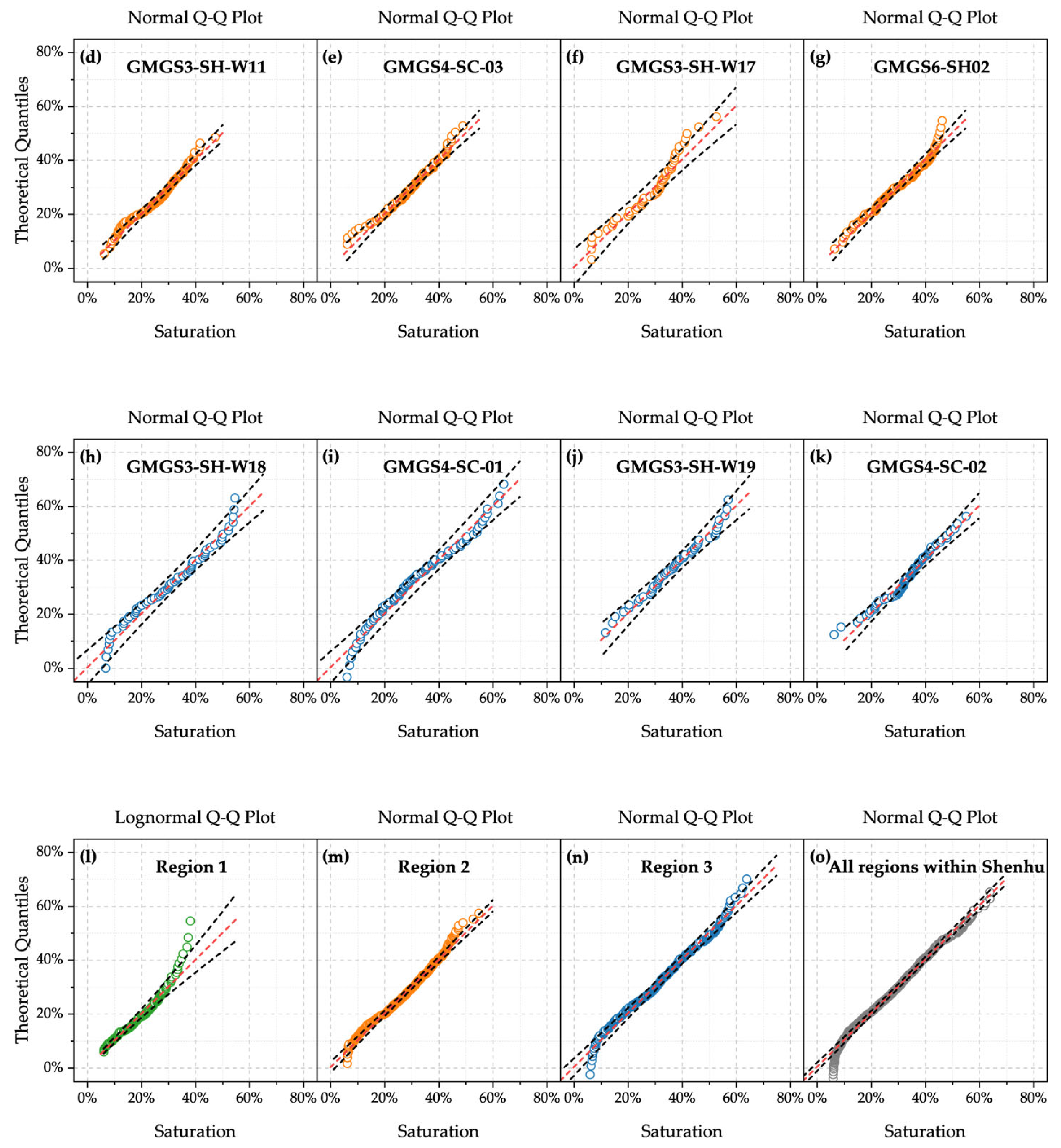
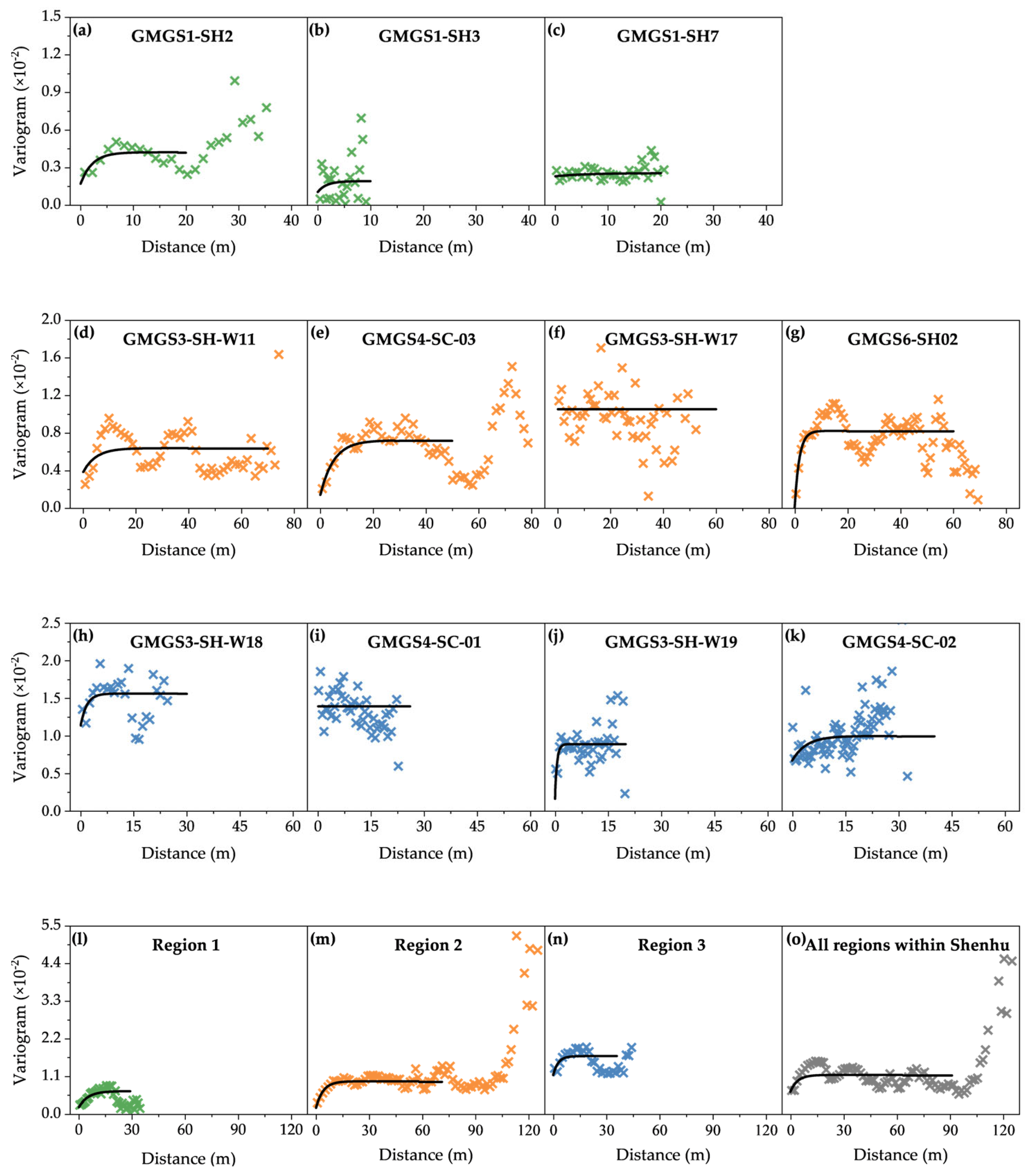

| Site | Expedition | Geothermal Gradient (°C/km) | Seafloor Temperature (°C) | Water Depth (m) | Gas Hydrate-Bearing Layer (mbsf) | Layer Thickness (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH2 | GMGS1 | 46.95 | 4.84 | 1230 | 191–225 | 34 |
| SH3 | 49.34 | 5.53 | 1245 | 196–206 | 10 | |
| SH7 | 43.65 | 6.44 | 1105 | 155–177 | 22 | |
| SH-W11 | GMGS3 | 44.39 | 4.86 | 1293 | 116–192 | 76 |
| SH-W17 | 63.20 | 4.76 | 1252 | 209–265 | 56 | |
| SH-W18 | 55.80 | 4.68 | 1285 | 147–172 | 25 | |
| SH-W19 | 48.00 | 5.70 | 1277 | 138–158 | 20 | |
| SC-01 | GMGS4 | 64.90 | 3.76 | 1287 | 147–171 | 22 |
| SC-02 | 61.20 | - | 1272 | 139–172 | 42 | |
| SC-03 | - | - | 1271 | 131–210 | 79 | |
| SH02 | GMGS6 | - | - | 1225 | 208–278 | 48 |
| No | Host Soil | Hydrate Composition | Test Type | Hydrate Saturation | Cohesion (MPa) | Friction Angle | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sand | Carbon dioxide | CU | 0 | 0 | 30.33° | [60] |
| 19.7% | 0.0924 | 36.48° | |||||
| 37.0% | 0.2914 | 34.63° | |||||
| 51.0% | 0.2754 | 37.96° | |||||
| 2 | sand | Methane | CU | 0 | 3.56 | 22.21° | [61] |
| 40.0% | 3.97 | 21.10° | |||||
| 60.0% | 4.25 | 23.57° | |||||
| 80.0% | 4.69 | 23.67° | |||||
| 3 | sand | Carbon dioxide | CU | 0 | 0 | 26.94° | [62] |
| 6.3% | 0.32 | 27.28° | |||||
| 12.6% | 0.86 | 24.26° | |||||
| 35.8% | 1.26 | 24.94° | |||||
| 50.4% | 1.47 | 24.71° | |||||
| 4 | sand | Tetrahydrofuran | CU | 20.0% | 0.10 | 26.7° | [63] |
| 50.0% | 0.50 | 22.5° | |||||
| 80.0% | 1.35 | 13.0° | |||||
| 5 | silty clay | Tetrahydrofuran | CD | 0 | 0.09 | 1.8° | [64] |
| 5.0% | 0.26 | 2.9° | |||||
| 15.0% | 0.35 | 2.9° | |||||
| 25.0% | 0.78 | 2.9° | |||||
| 35.0% | 0.82 | 3.2° | |||||
| 45.0% | 0.97 | 3.4° | |||||
| 6 | silt | Carbon dioxide | DS | 0 | 0.09 | 35.9° | [30] |
| 21.4% | 0.42 | 43.3° | |||||
| 48.9% | 1.29 | 34.8° | |||||
| 65.3% | 2.39 | 28.6° | |||||
| 7 | clayey silt | Methane | CU | 0 | 1.15 | 22.33° | [65] |
| 20.0% | 1.86 | 23.11° | |||||
| 40.0% | 2.35 | 23.20° | |||||
| 60.0% | 3.12 | 22.88° | |||||
| 8 | sand | Carbon dioxide | DS | 0 | 0 | 32.33° | [31] |
| 13.0% | 0.34 | 41.19° | |||||
| 24.0% | 0.54 | 44.81° | |||||
| 34.0% | 0.97 | 42.34° | |||||
| 43.0% | 1.30 | 42.69° | |||||
| 9 | silt | Carbon dioxide | DS | 0 | 0.09 | 35.74° | |
| 23.0% | 0.42 | 43.21° | |||||
| 49.0% | 1.29 | 34.72° | |||||
| 65.0% | 2.39 | 28.54° | |||||
| 10 | sand | Methane | CU | 0 | 0.42 | 26.4° | [32] |
| 13.3% | 0.53 | 30.5° | |||||
| 26.6% | 0.78 | 32.2° | |||||
| 40.0% | 1.02 | 34.2° |
| Site | Number of Data | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| GMGS1-SH2 | 68 | 19.7% | 8% |
| GMGS1-SH3 | 11 | 12.8% | 7% |
| GMGS1-SH7 | 54 | 20.7% | 8% |
| GMGS3-SH-W11 | 150 | 26.8% | 9% |
| GMGS4-SC-03 | 135 | 30.7% | 9% |
| GMGS3-SH-W17 | 52 | 29.6% | 13% |
| GMGS6-SH02 | 139 | 30.8% | 10% |
| GMGS3-SH-W18 | 66 | 31.4% | 15% |
| GMGS4-SC-01 | 86 | 32.3% | 16% |
| GMGS3-SH-W19 | 53 | 37.7% | 12% |
| GMGS4-SC-02 | 77 | 34.2% | 10% |
| Region 1 | 133 | 19.5% | 8% |
| Region 2 | 476 | 29.4% | 10% |
| Region 3 | 282 | 33.6% | 14% |
| All regions within Shenhu | 891 | 29.2% | 12% |
| Site | Range (m) | Nugget | Partial Sill | Sill | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMGS1-SH2 | 7 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.06 |
| GMGS1-SH3 | 5 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.32 |
| GMGS1-SH7 | 18 | 0.002 | 0.0003 | 0.003 | 0.55 |
| GMGS3-SH-W11 | 15 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.05 |
| GMGS4-SC-03 | 15 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.04 |
| GMGS3-SH-W17 | 8 | 0.011 | 0 | 0.011 | 0.13 |
| GMGS6-SH02 | 5 | 0 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.04 |
| GMGS3-SH-W18 | 5 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 0.14 |
| GMGS4-SC-01 | 10 | 0.014 | 0 | 0.014 | 0.13 |
| GMGS3-SH-W19 | 2 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.09 |
| GMGS4-SC-02 | 12 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.10 |
| Region 1 | 15 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.05 |
| Region 2 | 12 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.06 |
| Region 3 | 8 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.017 | 0.05 |
| All regions within Shenhu | 12 | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.012 | 0.08 |
| Site | Number of Data | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| GMGS1-SH2 | 61 | 0.41 | 0.04 |
| GMGS1-SH3 | 20 | 0.35 | 0.02 |
| GMGS1-SH7 | 41 | 0.46 | 0.04 |
| GMGS3-SH-W11 | 142 | 0.48 | 0.02 |
| GMGS4-SC-03 | 154 | 0.47 | 0.02 |
| GMGS3-SH-W17 | 90 | 0.47 | 0.03 |
| GMGS6-SH02 | 140 | 0.49 | 0.03 |
| GMGS3-SH-W18 | 49 | 0.63 | 0.04 |
| GMGS4-SC-01 | 43 | 0.59 | 0.04 |
| GMGS3-SH-W19 | 37 | 0.54 | 0.02 |
| GMGS4-SC-02 | 55 | 0.55 | 0.02 |
| Region 1 | 122 | 0.41 | 0.05 |
| Region 2 | 526 | 0.48 | 0.02 |
| Region 3 | 184 | 0.58 | 0.05 |
| All regions within Shenhu | 832 | 0.49 | 0.06 |
| Site | Intrinsic Permeability (mD) | Effective Permeability (mD) |
|---|---|---|
| GMGS1-SH2 | 9.9~89.1 | 2.8~25.4 |
| GMGS1-SH3 | 5.1~45.7 | 2.3~20.4 |
| GMGS1-SH7 | 16.7~150.2 | 4.5~65.2 |
| GMGS3-SH-W11 | 20.4~184.0 | 3.6~32.4 |
| GMGS4-SC-03 | 18.5~166.3 | 2.5~22.3 |
| GMGS3-SH-W17 | 18.5~166.3 | 2.7~24.1 |
| GMGS6-SH02 | 22.6~203.5 | 3.0~27.1 |
| GMGS3-SH-W18 | 91.3~821.9 | 11.6~104.6 |
| GMGS4-SC-01 | 61.1~549.8 | 7.3~65.6 |
| GMGS3-SH-W19 | 37.2~334.9 | 3.0~26.7 |
| GMGS4-SC-02 | 41.1~369.7 | 4.3~38.4 |
| Region 1 | 9.9~89.1 | 2.9~25.8 |
| Region 2 | 20.4~184.0 | 3.0~52.6 |
| Region 3 | 55.3~497.7 | 6.0~54.0 |
| All regions within Shenhu | 22.6~203.5 | 3.4~30.3 |
| Site | Number of Data | Cohesion (MPa) | Friction Angle (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Mean | Standard Deviation | ||
| GMGS1-SH2 | 64 | 1.31 | 0.28 | 25.27 | 0.01 |
| GMGS1-SH3 | 18 | 0.88 | 0.22 | 25.28 | 0.01 |
| GMGS1-SH7 | 34 | 1.66 | 0.37 | 25.25 | 0.01 |
| GMGS3-SH-W11 | 89 | 1.27 | 0.37 | 25.27 | 0.01 |
| GMGS4-SC-03 | 82 | 1.53 | 0.28 | 25.26 | 0.01 |
| GMGS3-SH-W17 | 91 | 1.24 | 0.34 | 25.27 | 0.01 |
| GMGS6-SH02 | 140 | 1.31 | 0.47 | 25.27 | 0.02 |
| GMGS3-SH-W18 | 37 | 2.33 | 0.64 | 25.23 | 0.02 |
| GMGS4-SC-01 | 37 | 1.07 | 0.30 | 25.27 | 0.01 |
| GMGS3-SH-W19 | 32 | 1.04 | 0.48 | 25.28 | 0.02 |
| GMGS4-SC-02 | 56 | 1.10 | 0.50 | 25.27 | 0.02 |
| Region 1 | 116 | 1.35 | 0.39 | 25.26 | 0.01 |
| Region 2 | 402 | 1.33 | 0.40 | 25.27 | 0.01 |
| Region 3 | 162 | 1.36 | 0.72 | 25.26 | 0.03 |
| All regions within Shenhu | 680 | 1.34 | 0.49 | 25.26 | 0.02 |
| Reference | Fitting Linear Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| [60] | c = 0.006 × Sh | 0.84 |
| [61] | c = 0.52 + 0.014 × Sh | 0.47 |
| [62] | c = 3.50 + 0.013 × Sh | 0.95 |
| [63] | c = 0.20 + 0.028 × Sh | 0.86 |
| [64] | c = −0.39 + 0.021 × Sh | 0.92 |
| [30] | c = 0.13 + 0.020 × Sh | 0.93 |
| [65] | c = −0.11 + 0.034 × Sh | 0.89 |
| [31] | c = 1.16 + 0.032 × Sh | 0.99 |
| [31] | c = −0.05 + 0.030 × Sh | 0.97 |
| [32] | c = −0.13 + 0.034 × Sh | 0.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Tan, L. Integrated Statistical Analysis and Spatial Modeling of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Sediments in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168857
Feng X, Tan L. Integrated Statistical Analysis and Spatial Modeling of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Sediments in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168857
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xin, and Lin Tan. 2025. "Integrated Statistical Analysis and Spatial Modeling of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Sediments in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168857
APA StyleFeng, X., & Tan, L. (2025). Integrated Statistical Analysis and Spatial Modeling of Gas Hydrate-Bearing Sediments in the Shenhu Area, South China Sea. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168857





