Influence of Abrasive Flow Rate and Feed Rate on Jet Lag During Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Beech Plywood
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ma—abrasive mass flow rate of the abrasive particles [kg/s];
- Va—speed of abrasive material exiting the focusing tube [kg/s].
- PDD (Particle Dosing Density) is the abrasive particle density division (the amount of particles necessary to generate a groove of nominal length under specific conditions) [kg/m];
- ma is abrasive mass flow rate [kg/s];
- vf is the traverse speed of water jet movement against material [m/s].
- EDD is the energy density division of abrasive particles (the amount of energy reverted to a unit of the generated groove length) [J/m];
- va is the speed of abrasive coming from the nozzle [kg/s].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Testing of Technical Beech Plywood
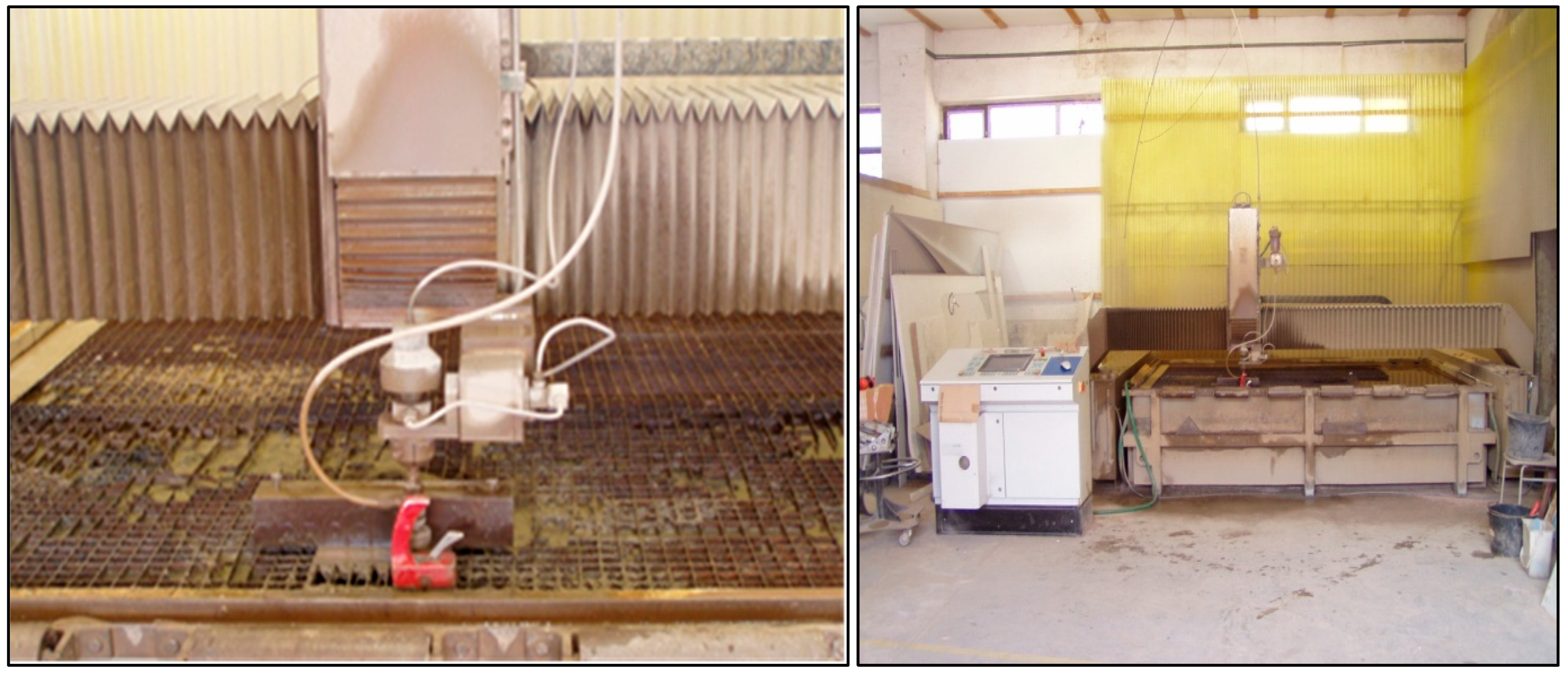
2.2. Parameters of Cutting Process
- Cutting liquid pressure: 400 MPa;
- Abrasive: Australian Garnet GMA (grain composition 80 MESH);
- Abrasive jet diameter: 1 mm;
- Water jet diameter: 0.013 inches = 0.33 mm;
- Electric power input: 37 kW;
- Focusing tube distance above a work piece: 4 mm.
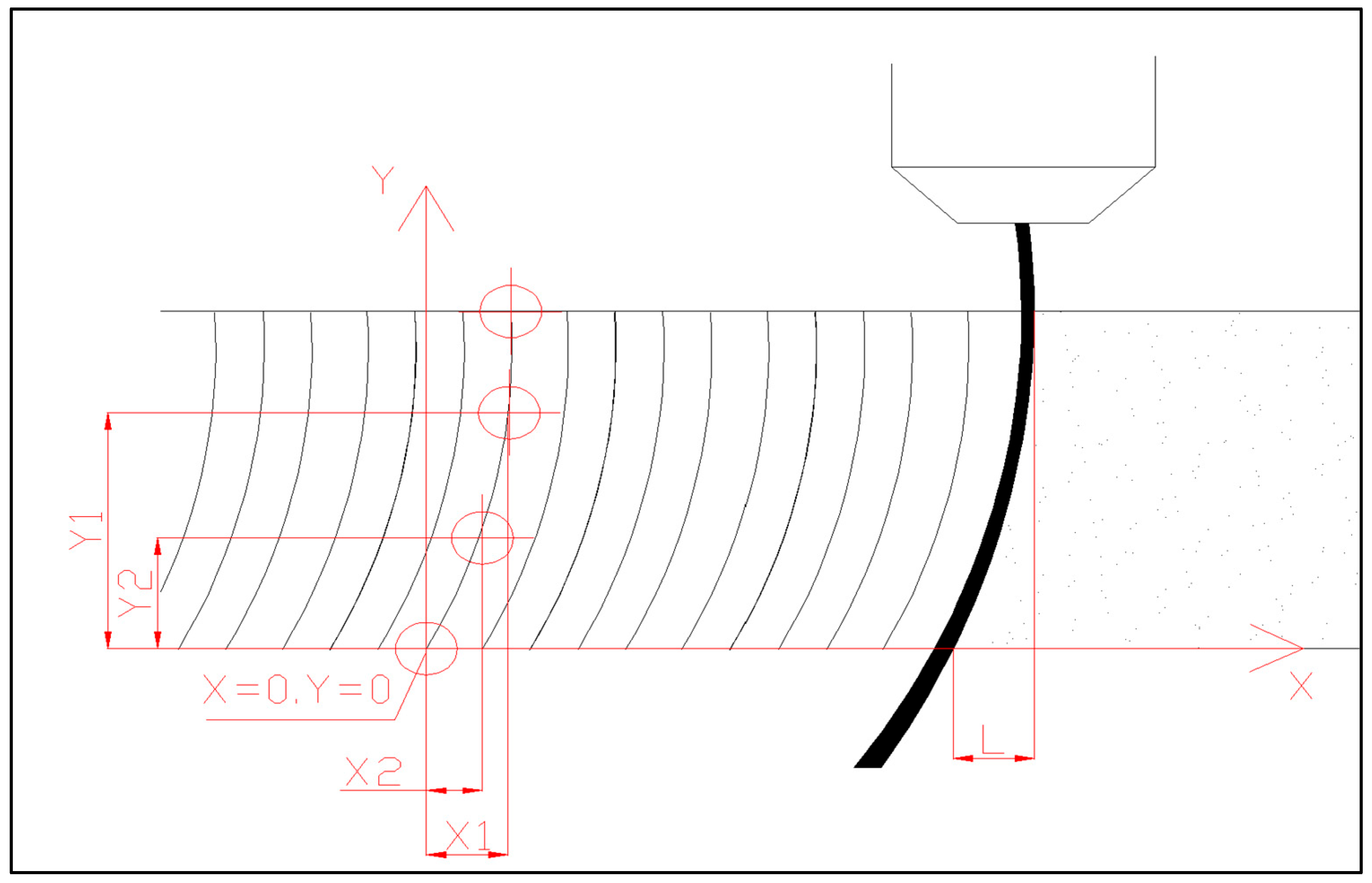
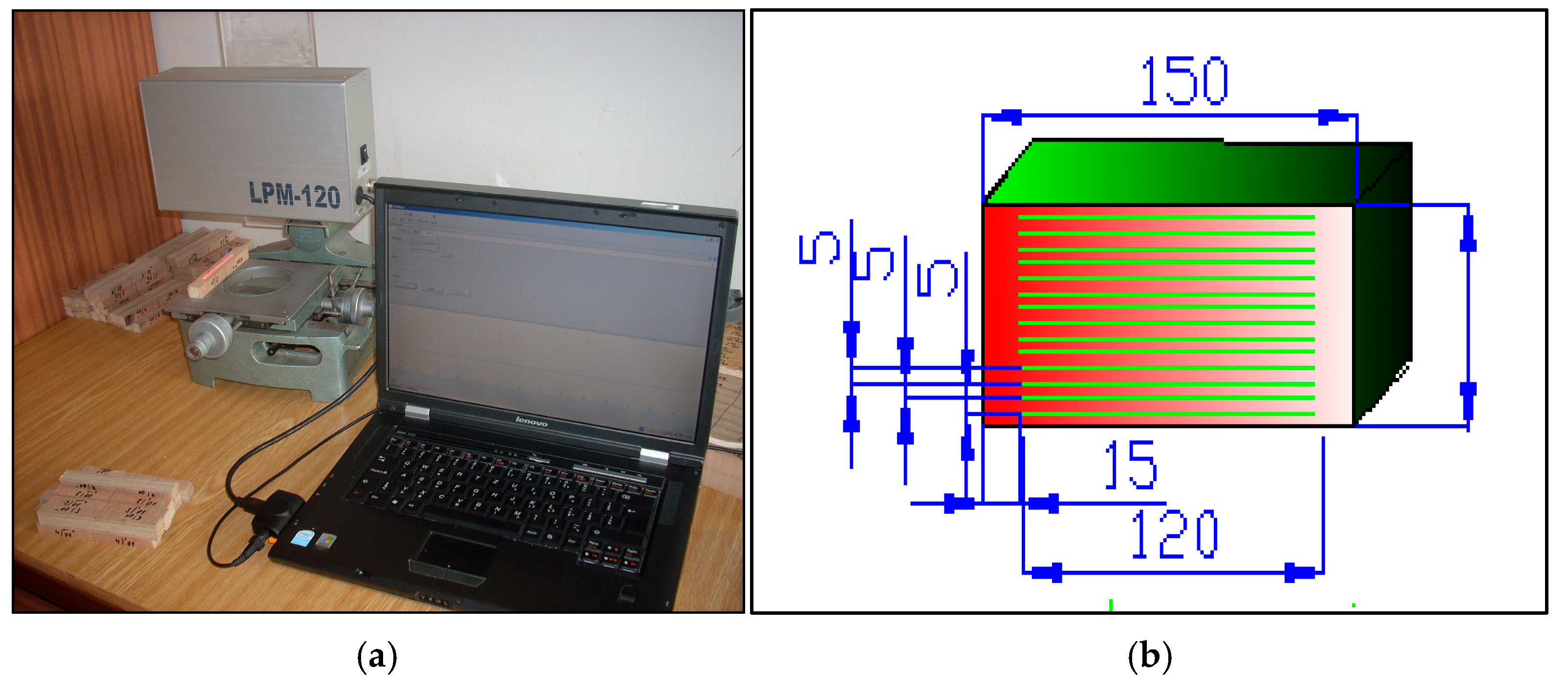
2.3. Methodology of Water Jet Lagging Evaluation
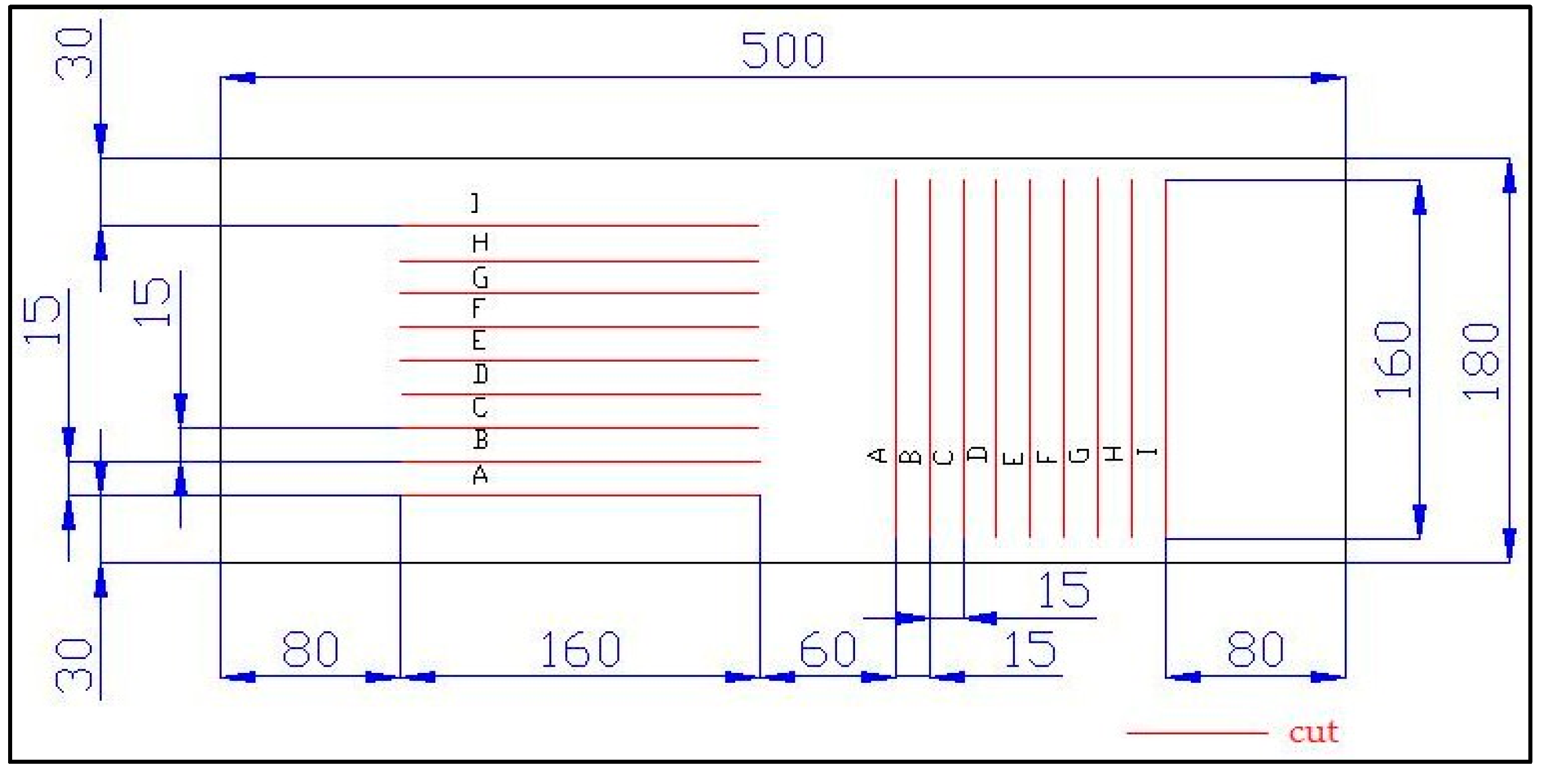
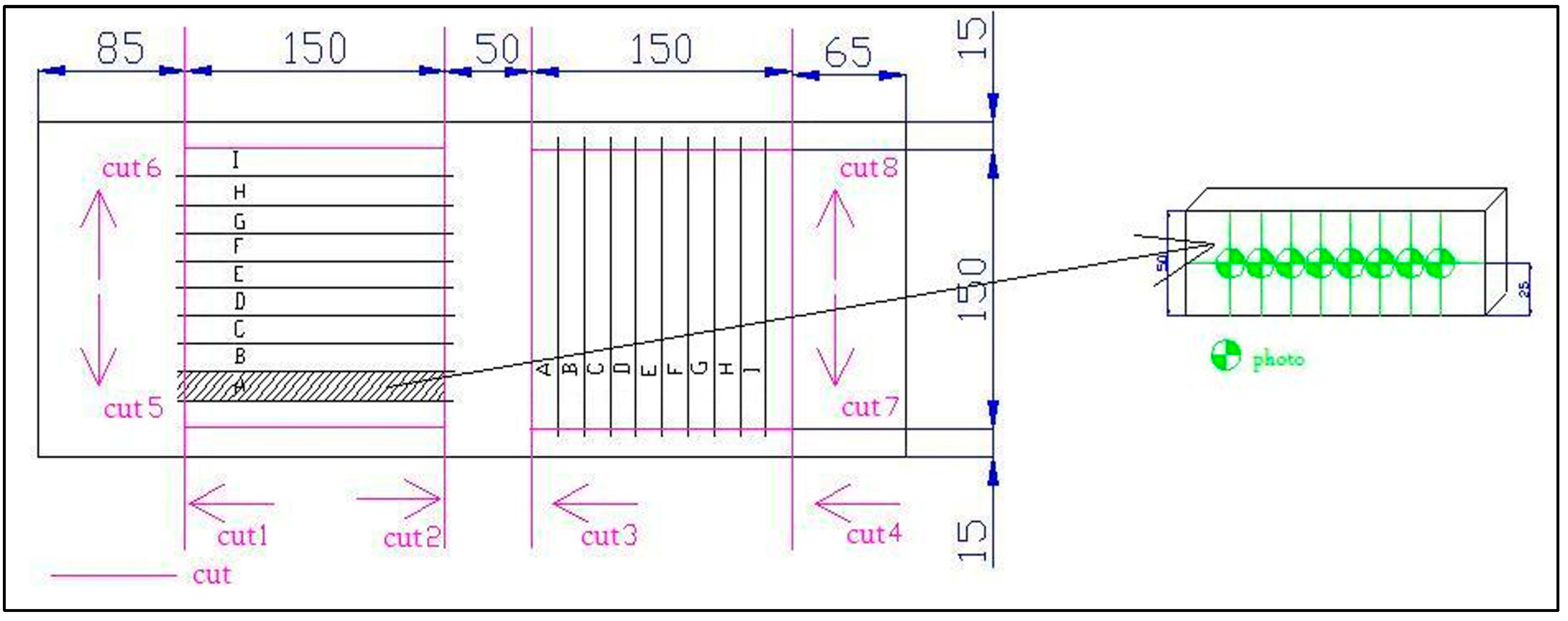
2.4. Working Procedure
- X/Y/L—Real lagging of water jet [mm];
- Xp/Yp/Lp—Proportional dimension of water jet lagging [--];
- a—Real dimension of reference gauge unit [mm];
- ap—proportional dimension of reference gauge unit [--].
- ➢
- All tracks were parallel with lateral edge of a sample;
- ➢
- The first track was 5 mm from lateral edge of the sample;
- ➢
- Every further track was moved by 5 mm;
- ➢
- The last track was 5 mm from opposite lateral edge of the sample;
- ➢
- Tracks were centered in the center of sample length.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Overview of Results
3.2. Effect of Plywood Thickness
3.3. Effect of Traverse Speed in Plywood
3.4. Influence of the Mass Abrasive Flow
3.5. Effect of Cutting Direction in Plywood
3.6. Arithmetic Average Deviations Ra for Plywood
3.7. Final Discussion
4. Conclusions
- Optimizing the Mass Flow Rate of the Abrasive
- Effect on Cut Quality
- Practical Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beer, P. Niekonwencjonalne Narzedzia do Obróbki Drewna; Wydawnictwo Akademii Rolniczej Poznaň: Poznań, Poland, 2007; Volume 74, ISBN 978-83-7160-445-4. [Google Scholar]
- Radomska-Zalas, A. Multi-criteria methods in the optimization of the abrasive waterjet cutting process. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 3130, 020030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusi, N.; Catrawedarma, I.G.N.B.; Gebremariam, M.; Saptaji, K.; Azhari, A. A four-decade of abrasive waterjet processing technology (1980–2023): A scientometric analysis. Manuf. Rev. 2025, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Ma, C.; Gu, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, B. Experimental study on the performance and mechanism of high-pressure abrasive waterjet cutting hard rock. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2024, 42, 3471–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerman, M.; Orbanic, H.; Junkar, M.; Lebar, A. Thermal aspects of ice abrasive water jet technology. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1687814015597619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, S.; Talib, G.A. Abrasive Water Jet Machining of Composites: Empirical and Analytical Modelling; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co., KG: Berlin, Germany, 2024; Volume 275, ISBN 9783111240244 311124024X. [Google Scholar]
- Hlaváčová, I.M.; Geryk, V. Abrasives for water-jet cutting of high-strength and thick hard materials. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatkiewicz, T.; Perec, A.; Radomska-Zalas, A.; Banaszek, K.; Balasz, B. Preliminary studies into cutting of a novel two component 3D-printed stainless steel–polymer composite material by abrasive water jet. Materials 2023, 16, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashish, M. Modeling study of metal cutting with abrasive waterjets. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME 1984, 106, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geskin, E.S.; Chen, W.L.; Chen, S.S.; Hu, F.; Khan, M.E.H.; Kim, S. Investigation of Anatomy of an Abrasive Waterjet. In Proceedings of the 5th American Waterjet Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 29–31 August 1989; pp. 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Kim, T.J. Development of an abrasive waterjet kerf cutting model for brittle materials. In Jet Cutting Technology; Fluid Mechanics and Its Applications; Lichtarowicz, A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; Volume 13, pp. 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engemann Bernd, K. Schneiden mit Laserstrahlung und Wasserstrahl; Ehningen bei Böblinger: Berlin, Germany, 1993; Volume 179, ISBN 3-8169-0748-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, J.; Zhou, G.; Leu, M.C.; Geskin, E. Characteristics of Abrasive Waterjet Generated Surfaces and Effects of Cutting parameters and Structure Vibration. ASME J. Eng. Ind. 1995, 117, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, R.; Yong, Z. Modelling of 3D abrasive waterjet machining, part 1—Theoretical basis. In Jetting Technology; Gee, C., Ed.; Mechanical Engineering Publications Ltd.: Bury St Edmunds, UK; London, UK, 1996; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, Z.; Kovacevic, R. Modelling of 3D abrasive waterjet machining. Part 2—Simulation of machining. In Jetting Technology; Gee, C., Ed.; Mechanical Engineering Publications Ltd.: Bury St Edmunds, UK; London, UK, 1996; pp. 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Krajný, Z. Vodný lúč v Praxi—WJM; EPOS Bratislava: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2001; Volume 384, ISBN 8080570914. [Google Scholar]
- Hashish, M. A Model for Abrasive-Waterjet (AWJ) Machining. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 1989, 111, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.N.; Muthukrishnan, N. Investigation of multiple process parameters in abrasive water jet machining of tiles. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2015, 38, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, Z.; Wen, G.; Yuan, X. Waterjet machining and research developments: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 1257–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, L.; Ericsson, K. Emerging technologies for the production of biojet fuels from wood—Can greenhouse gas emission reductions meet policy requirements? Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 7603–7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascenik, J. Experimental determination of cutting speed influence on cutting surface character in material laser cutting. MM Sci. J. 2016, 3, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Valíček, J.; Hloch, S. Using acoustic sound pressure level for quality prediction of surfaces created by abrasive waterjet. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 48, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maňková, I. Progresívne Technológie; VIENALA: Košice, Slovakia, 2000; Volume 275, ISBN 80-7099-430-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hloch, S.; Valíček, J. Topographical anomaly on surfaces created by abrasive waterjet. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 59, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hreha, P.; Radvanská, A.; Hloch, S.; Peržel, V.; Królczyk, G.; Monková, K. Determination of vibration frequency depending on abrasive mass flow rate during abrasive water jet cutting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 77, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohourkari, I.; Zohoor, M.; Annoni, M. Investigation of the Effects of Machining Parameters on Material Removal Rate in Abrasive Waterjet Turning. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 6, 24203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashish, M. Optimalization Factors in Abrasive Waterjet Machining. J. Eng. Ind. 1991, 113, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepu Kumar, T.N.; Srinivasu, D.S. Understanding and predicting material removal rate in abrasive waterjet milling of kerfs. Manuf. Technol. Today 2023, 22, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Hu, D.; Tang, C.; Lin, P. Modelling and analysis of abrasive water jet cutting front profile. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 114, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, R.; Zhang, X.; Zai, P.; Deng, J. Research Progress in Abrasive Water Jet Processing Technology. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.; Mani, K. Prediction of surface roughness using machine learning approach for abrasive waterjet milling of alumina ceramic. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 119, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L.; Fan, C. Experimental and simulation study on the influence factors of abrasive water jet machining ductile materials. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11840–11857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perec, A. Optimization of Abrasive Water Jet (AWJ) cutting process accuracy. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 225, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perec, A.; Kawecka, E.; Radomska-Zalas, A.; Pude, F. Optimization of abrasive waterjet cutting by using the CODAS method with regard to interdependent processing parameters. Stroj. Vestn.—J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 69, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soori, M.; Arezoo, B. Minimization of surface roughness and residual stress in abrasive water jet cutting of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2024, 238, 1613–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, X.; Wen, Q. Experimental investigation of the distribution patterns of micro-scratches in abrasive waterjet cutting surface. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Fu, L.; Wu, L.; Zuo, W. Research on multiphase flow and nozzle wear in a high-pressure abrasive water jet cutting head. Machines 2023, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelit, H.; Yaman, Ö. Influence of processing parameters on the surface roughness of solid wood cut by abrasive water jet. BioRes 2020, 15, 6135–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valíček, J.; Harničárová, M.; Kušnerová, M.; Palková, Z.; Kopal, I.; Borzan, C.; Czán, A.; Mikuš, R.; Kadnár, M.; Duer, S.; et al. Stress–strain parameter prediction method for AWJ technology from surface topography. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 127, 2617–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, E.; Monno, M.; Semeraro, Q. On the characterisation of surfaces obtained by abrasive water jet machining. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference Jet Cuttting Technology, Rouen, France, 25–27 October 1994; Allen, N.G., Ed.; Mechanical Engineering Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 1994; pp. 177–193. [Google Scholar]
- de la Rosa, S.; Rodríguez-Parada, L.; Ponce, M.B.; Mayuet Ares, P.F. The Abrasive Water Jet Cutting Process of Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Samples Obtained by Additive Manufacturing: A Comparative Analysis. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Miao, X.; Wu, M.; Zhou, P. Study on the process of abrasive water jet cutting for zirconia ceramic tubes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 5555–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wala, T.; Lis, K. Influence of Selected Diagnostic Parameters on the Quality of AWJ Cutting Surface. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2022, 16, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, A.K.; Bhuyan, B.K.; Kumar, S. Perspective study of abrasive water jet machining of composites—A review. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadło, S.; Krajcarz, D.; Młynarczyk, P. A comparison of laser cutting and water-jet cutting. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2014, 66, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, D.B.; Baskey, D.; Rawat, R. Water Jet Cutter: An Efficient Tool for Composite Product Development. 2009. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/reader/11874816 (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Popan, I.A.; Cosma, C.; Popan, A.I.; Bocăneț, V.I.; Bâlc, N. Monitoring Equipment Malfunctions in Composite Material Machining: Acoustic Emission-Based Approach for Abrasive Waterjet Cutting. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perianu, I.A.; Murariu, A.C.; Botila, L.N.; Marin-Corciu, M.; Duma, I.; Baeră, C. Advancements in Abrasive Waterjet Cutting Technologies: A Comprehensive Overview and Future Prospects in the Manufacturing Industry. Key Eng. Mater. 2024, 996, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Advanced Waterjet Technology for Machining Curved and Layered Structures. Curved Layer. Struct. 2019, 6, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cut | Traverse Speed vf = [m/min] | Abrasive Mass Flow ma = [g/min] |
|---|---|---|
| A | 0.6 | 250 |
| B | 0.6 | 350 |
| C | 0.6 | 450 |
| D | 0.4 | 250 |
| E | 0.4 | 350 |
| F | 0.4 | 450 |
| G | 0.2 | 250 |
| H | 0.2 | 350 |
| I | 0.2 | 450 |
| Lagging AWJ (mm) | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Dispersion | F-Test | p-Level of Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 203.9305 | 1 | 203.9305 | 4995.715 | 0.000000 |
| {1} thickness | 29.8266 | 1 | 29.8266 | 730.666 | 0.000000 |
| {2} cutting direction | 0.0008 | 1 | 0.0008 | 0.020 | 0.888127 |
| {3} traverse speed | 1.5739 | 2 | 0.7869 | 19.277 | 0.000000 |
| {4} abrasive flow | 0.3307 | 2 | 0.1653 | 4.050 | 0.019438 |
| thickness * cutting direction | 0.2088 | 1 | 0.2088 | 5.114 | 0.025231 |
| thickness * traverse speed | 1.7062 | 2 | 0.8531 | 20.898 | 0.000000 |
| cutting direction * traverse speed | 0.1372 | 2 | 0.0686 | 1.680 | 0.189994 |
| thickness * abrasive flow | 0.9516 | 2 | 0.4758 | 11.656 | 0.000020 |
| cutting direction * abrasive flow | 1.0787 | 2 | 0.5393 | 13.212 | 0.000005 |
| traverse speed * abrasive flow | 1.0410 | 4 | 0.2603 | 6.376 | 0.000094 |
| thickness * cutting direction * traverse speed | 0.6995 | 2 | 0.3498 | 8.568 | 0.000305 |
| thickness * cutting direction * abrasive flow | 1.1396 | 2 | 0.5698 | 13.959 | 0.000003 |
| thickness * traverse speed * abrasive flow | 0.9075 | 4 | 0.2269 | 5.558 | 0.000345 |
| cutting direction * traverse speed *abrasive flow | 0.8263 | 4 | 0.2066 | 5.061 | 0.000761 |
| 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 | 1.3567 | 4 | 0.3392 | 8.309 | 0.000005 |
| Thickness Material (mm) | Lagging AWJ (µm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value (µm) | Standard Error (µm) | −95.00% (µm) | +95.00% (µm) | |
| 36 | 657.33 | 2.129 | 615.24 | 699.43 |
| 54 | 1471.47 | 2.129 | 1429.37 | 1513.56 |
| Traverse Speed (m/min) | Lagging AWJ (µm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value (µm) | Standard Error (µm) | −95.00% (µm) | +95.00% (µm) | |
| 0.2 | 933.43 | 2.608 | 881.88 | 984.99 |
| 0.4 | 1145.73 | 2.608 | 1094.18 | 1197.29 |
| 0.6 | 1114.03 | 2.608 | 1062.48 | 1165.59 |
| Abrasive Flow (g/min) | AWJ Lagging (µm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value (µm) | Standard Error (µm) | −95.00% (µm) | +95.00% (µm) | |
| 250 | 1067.12 | 2.608 | 1015.56 | 1118.67 |
| 350 | 1010.60 | 2.608 | 959.04 | 1062.16 |
| 450 | 1115.48 | 2.608 | 1063.93 | 1167.04 |
| Cutting Direction | Lagging AWJ (µm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value (µm) | Standard Error (µm) | −95.00% (µm) | +95.00% (µm) | |
| longitudinal | 1066.52 | 2.129 | 1024.43 | 1108.62 |
| transverse | 1062.28 | 2.129 | 1020.18 | 1104.37 |
| Average Arithmetical Deviations of Surface Roughness Ra (μm) | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Variance | F Test | p-Significance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 64,341.63 | 1 | 64,341.63 | 16,232.7 | 0.000000 |
| {1} Feed rate | 14.45 | 2 | 2.616 | 8.35 | 0.000271 |
| {2} Cutting direction | 5.232 | 2 | 2.616 | 10.22 | 0.001453 |
| {3} Abrasive flow | 7.86 | 2 | 2.613 | 9.82 | 0.000458 |
| {4} Thickness | 6.876 | 1 | 2.617 | 10.08 | 0.000345 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kvietková, M.S.; Dvořák, O.; Lin, C.-F.; Jones, D.; Ptáček, P.; Fojtík, R. Influence of Abrasive Flow Rate and Feed Rate on Jet Lag During Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Beech Plywood. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8687. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158687
Kvietková MS, Dvořák O, Lin C-F, Jones D, Ptáček P, Fojtík R. Influence of Abrasive Flow Rate and Feed Rate on Jet Lag During Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Beech Plywood. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(15):8687. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158687
Chicago/Turabian StyleKvietková, Monika Sarvašová, Ondrej Dvořák, Chia-Feng Lin, Dennis Jones, Petr Ptáček, and Roman Fojtík. 2025. "Influence of Abrasive Flow Rate and Feed Rate on Jet Lag During Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Beech Plywood" Applied Sciences 15, no. 15: 8687. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158687
APA StyleKvietková, M. S., Dvořák, O., Lin, C.-F., Jones, D., Ptáček, P., & Fojtík, R. (2025). Influence of Abrasive Flow Rate and Feed Rate on Jet Lag During Abrasive Water Jet Cutting of Beech Plywood. Applied Sciences, 15(15), 8687. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158687






