Parallelization of Rainbow Tables Generation Using Message Passing Interface: A Study on NTLMv2, MD5, SHA-256 and SHA-512 Cryptographic Hash Functions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Cryptographic Hash Functions, Their Properties and Attacks
2.2. Evolution of Cryptanalytic Time-Memory Trade-Offs
2.3. Parallel Computing Methods for Rainbow Tables Generation
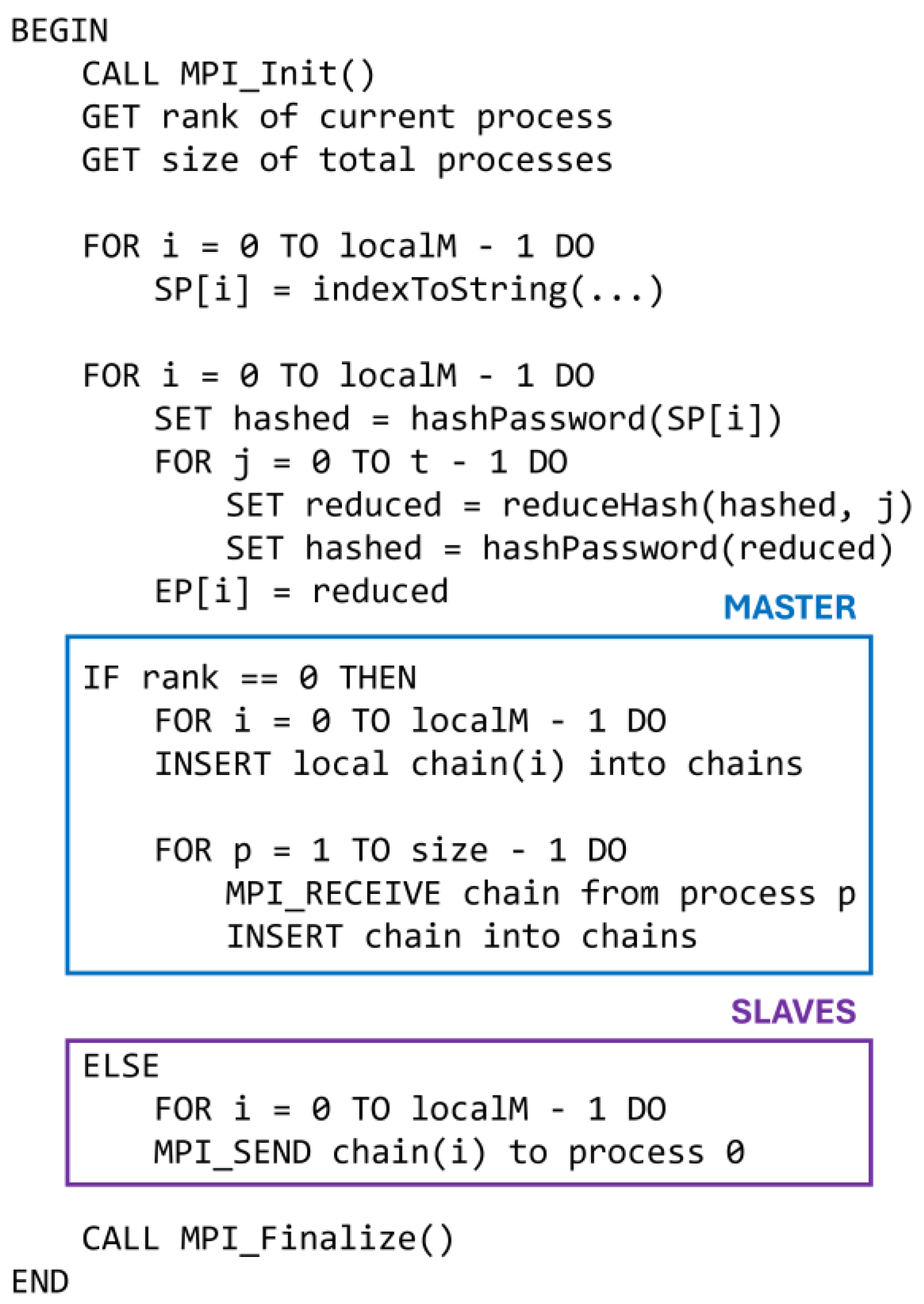
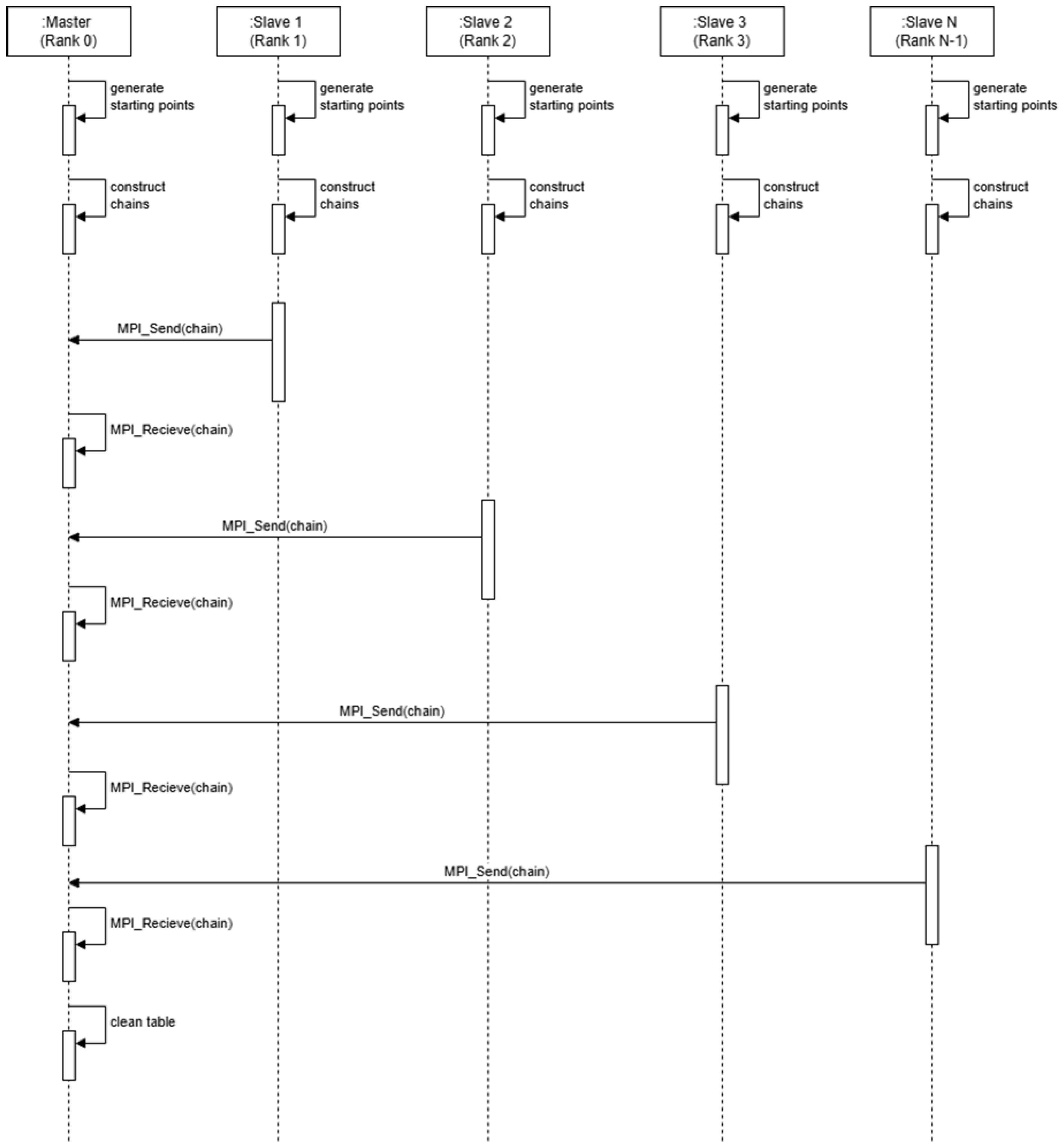
3. Proposed Method
4. Results and Discussion
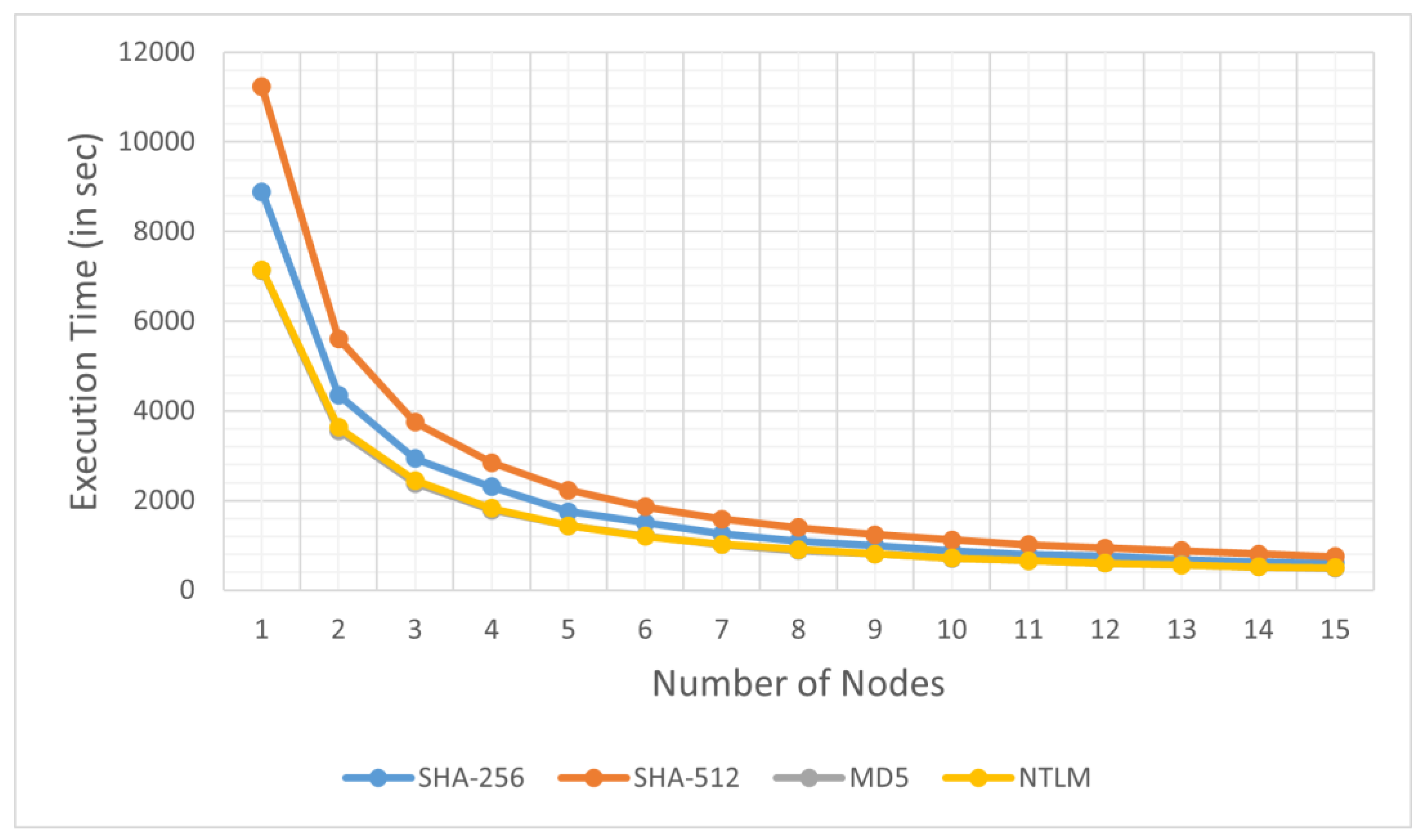
4.1. The Influence of Hash Functions on the Parallel Performance
4.2. The Influence of Chain Count on the Execution Time
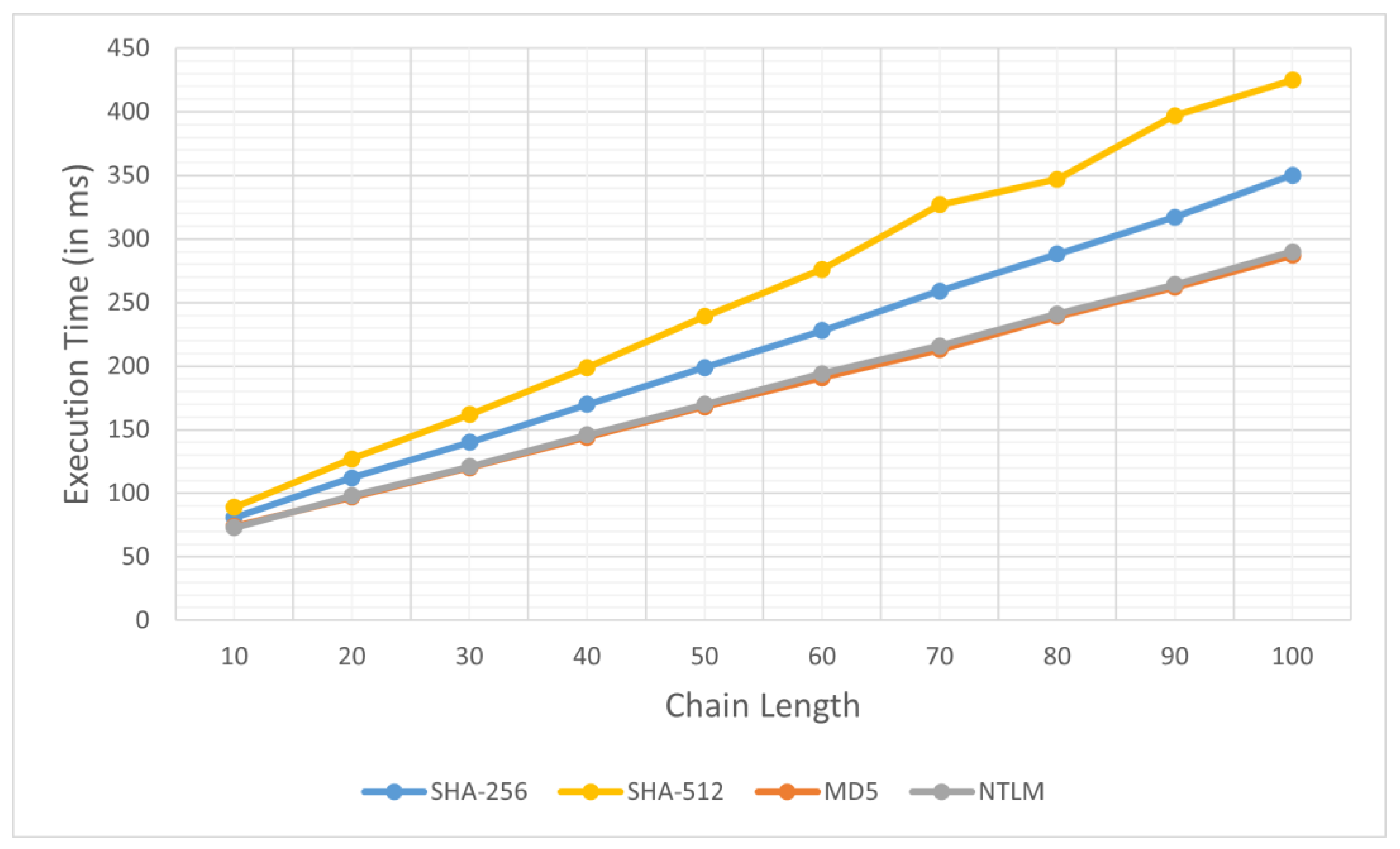
4.3. The Influence of Chain Length on the Execution Time
4.4. The Impact of the Internal Characteristics of the Cryptographic Hash Functions on the Performance of Parallel Rainbow Tables Generation
4.5. Comparative Analysis
5. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonneau, J.; Herley, C.; Van Oorschot, P.C.; Stajano, F. The Quest to Replace Passwords: A Framework for Comparative Evaluation of Web Authentication Schemes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–23 May 2012; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 553–567. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, A.J.; Vanstone, S.A.; Van Oorschot, P.C. Handbook of Applied Cryptography, 1st ed.; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; ISBN 0849385237. [Google Scholar]
- Horálek, J.; Holík, F.; Horák, O.; Petr, L.; Sobeslav, V. Analysis of the Use of Rainbow Tables to Break Hash. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 32, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosnjak, L.; Sres, J.; Brumen, B. Brute-Force and Dictionary Attack on Hashed Real-World Passwords. In Proceedings of the 2018 41st International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics, MIPRO 2018—Proceedings, Opatija, Croatia, 21–25 May 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1161–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Delaune, S.; Jacquemard, F. A Theory of Dictionary Attacks and Its Complexity. In Proceedings of the Computer Security Foundations Workshop, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 30 June 2004; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 17, pp. 2–15. [Google Scholar]
- Oechslin, P. Making a Faster Cryptanalytic Time-Memory Trade-Off. In Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO 2003; LNCS; Boneh, D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 2729, pp. 617–630. [Google Scholar]
- Hellman, M. A Cryptanalytic Time-Memory Trade-Off. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1980, 26, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kačeniauskas, A.; Rutschmann, P. Parallel FEM Software for CFD Problems. Informatica 2004, 15, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kačeniauskas, A.; Kačianauskas, R.; Maknickas, A.; Markauskas, D. Computation and Visualization of Discrete Particle Systems on GLite-Based Grid. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2011, 42, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khazraji, S.H.A.A. Using Parallel Computing to Implement Security Attack. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. 2015, 13, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Meganathan, N. What Is the Effectiveness of Salt and Pepper in Preventing Rainbow Table Attacks in Modern Password Hashing Algorithms? Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2024, 9, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosaaen, K. LM Hash Cracking—Rainbow Tables vs GPU Brute Force. Available online: https://www.netspi.com/blog/technical-blog/network-pentesting/lm-hash-cracking-rainbow-tables-vs-gpu-brute-force/ (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Pabico, J.P. A Framework for a Multiagent-Based Scheduling of Parallel Jobs. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisenko, A.B.; Gorlatch, S. Parallel MPI-Implementation of the Branch-and-Bound Algorithm for Optimal Selection of Production Equipment. Bull. Tambov. State Tech. Univ. 2016, 22, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, H. Hans Peter Luhn and the Birth of the Hashing Algorithm. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/hans-peter-luhn-and-the-birth-of-the-hashing-algorithm (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Pacevič, R.; Kačeniauskas, A. Hash Functions and GPU Algorithm of Infinite Grid Method for Contact Search. Inf. Technol. Control 2022, 51, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Liu, Z.; Tong, R.; Manocha, D. PSCC: Parallel Self-Collision Culling with Spatial Hashing on GPUs. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 2018, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, D.; Lai, X.; Yu, H. Collisions for Hash Functions MD4, MD5, HAVAL-128 and RIPEMD. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2004, 2004/199. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, M.; Sotirov, A.; Appelbaum, J.; Lenstra, A.; Molnar, D.; Osvik, D.A.; de Weger, B. Short Chosen-Prefix Collisions for MD5 and the Creation of a Rogue CA Certificate. In Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO 2009; LNCS; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 5677, pp. 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, T.; Liu, F.; Feng, D. Fast Collision Attack on MD5. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2013, 2013/170. [Google Scholar]
- Nkouankou, A.; Clarice, F.; Abel, W.; Ndoundam, R. Pre-Image Attack of the MD5 Hash Function by Proportional Logic. Int. J. Res. Innov. Appl. Sci. 2022, 7, 2454–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Lai, X. Preimage Attacks on Reduced DHA-256. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2009, 2009/552. [Google Scholar]
- Dobbertin, H. The First Two Rounds of MD4 Are Not One-Way. In Fast Software Encryption; LNCS; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 1372, pp. 284–292. [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey, J.; Schneier, B. Second Preimages on N-Bit Hash Functions for Much Less than 2n Work. In Advances in Cryptology—EUROCRYPT 2005; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 3494, pp. 474–490. [Google Scholar]
- Sulak, F.; Koçak, O.; Saygı, E.; Öğünç, M.; Bozdemır, B. A Second Pre-Image Attack and a Collision Attack to Cryptographic Hash Function Lux. Commun. Fac. Sci. Univ. Ank. Ser. A1 Math. Stat. 2017, 66, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, E.; Bouillaguet, C.; Dunkelman, O.; Fouque, P.-A.; Hoch, J.; Kelsey, J.; Shamir, A.; Zimmer, S. New Second-Preimage Attacks on Hash Functions. J. Cryptol. 2016, 29, 657–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D. Cryptography and Data Security; Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1982; ISBN 0201101505. [Google Scholar]
- Avoine, G.; Junod, P.; Oechslin, P. Characterization and Improvement of Time-Memory Trade-Off Based on Perfect Tables. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2008, 11, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avoine, G.; Carpent, X. Optimal Storage for Rainbow Tables. In Proceedings of the Information Security and Cryptology—ICISC 2013, LNCS, Seoul, Korea, 27–29 November 2013; Lee, H.-S., Dong-Guk, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 8565, pp. 144–157. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, L.J.; Ye, T.J.; Ling, G.G.; Balachandran, V. QIris: Quantum Implementation of Rainbow Table Attacks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.07032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dat, T.N.; Iwai, K.; Matsubara, T.; Kurokawa, T. Implementation of High Speed Rainbow Table Generation Using Keccak Hashing Algorithm on GPU. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th NAFOSTED Conference on Information and Computer Science (NICS), Hanoi, Vietnam, 12–13 December 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Seo, J.; Hong, J.; Park, K.; Kim, S. High-speed Parallel Implementations of the Rainbow Method Based on Perfect Tables in a Heterogeneous System. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2015, 45, 837–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhu, W.; Chen, J.; Yao, S.; Hsu, C.F.; Xiong, G. High-Speed Implementation of Rainbow Table Method on Heterogeneous Multi-Device Architecture. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 143, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenderi, M.; Pnevmatikatos, D.; Papaefstathiou, I.; Manifavas, C. Breaking the GSM A5/1 Cryptography Algorithm with Rainbow Tables and High-End FPGAS. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Oslo, Norway, 29–31 August 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 747–753. [Google Scholar]
- Papantonakis, P.; Pnevmatikatos, D.; Papaefstathiou, I.; Manifavas, C. Fast, FPGA-Based Rainbow Table Creation for Attacking Encrypted Mobile Communications. In Proceedings of the 2013 23rd International Conference on Field programmable Logic and Applications, Porto, Portugal, 2–4 September 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Theocharoulis, K.; Papaefstathiou, I.; Manifavas, C. Implementing Rainbow Tables in High-End FPGAs for Super-Fast Password Cracking. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, Milan, Italy, 31 August–2 September 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Sykes, E.R.; Skoczen, W. An Improved Parallel Implementation of RainbowCrack Using MPI. J. Comput. Sci. 2014, 5, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avoine, G.; Carpent, X.; Leblanc-Albarel, D. Stairway to Rainbow. In Proceedings of the ACM Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 10–14 July 2023; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 286–299. [Google Scholar]
- Avoine, G.; Carpent, X.; Leblanc-Albarel, D. Precomputation for Rainbow Tables Has Never Been so Fast. In Proceedings of the 26th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Darmstadt, Germany, 4–8 October 2021; pp. 215–234. [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard Jørgensen, M. Free Rainbow Tables: Distributed Rainbow Table Project. Available online: https://freerainbowtables.com/ (accessed on 2 November 2024).
- Vaideeswaran, N. NTLM Explained. Available online: https://www.crowdstrike.com/en-us/cybersecurity-101/identity-protection/windows-ntlm/ (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Adusumilli, S. Testing a Legacy Application with Zero Documentation. Available online: https://www.cigniti.com/blog/testing-a-legacy-application-with-zero-documentation/ (accessed on 26 June 2025).


| Nodes Count | SHA-256 | SHA-512 | MD5 | NTLMv2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1.957 | 2.008 | 1.983 | 1.972 |
| 3 | 2.967 | 2.968 | 2.850 | 2.983 |
| 4 | 3.945 | 3.968 | 3.868 | 3.967 |
| 5 | 4.965 | 5.017 | 4.923 | 4.979 |
| 6 | 5.934 | 5.952 | 5.966 | 6.016 |
| 7 | 6.886 | 7.037 | 6.834 | 7.078 |
| 8 | 7.934 | 8.050 | 7.910 | 8.112 |
| 9 | 9.012 | 9.024 | 8.691 | 9.025 |
| 10 | 9.864 | 10.081 | 9.915 | 9.890 |
| 11 | 11.060 | 11.079 | 10.830 | 11.107 |
| 12 | 11.774 | 12.032 | 11.733 | 12.237 |
| 13 | 12.807 | 12.862 | 12.800 | 13.127 |
| 14 | 14.038 | 13.987 | 13.803 | 14.156 |
| 15 | 14.897 | 14.920 | 14.666 | 15.041 |
| Nodes Count | SHA-256 | SHA-512 | MD5 | NTLMv2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2.045 | 2.001 | 2.007 | 1.970 |
| 3 | 3.029 | 2.997 | 2.998 | 2.924 |
| 4 | 3.857 | 3.953 | 3.996 | 3.921 |
| 5 | 5.073 | 5.035 | 4.981 | 4.984 |
| 6 | 5.925 | 6.030 | 5.895 | 5.981 |
| 7 | 7.104 | 7.075 | 7.021 | 6.973 |
| 8 | 8.146 | 8.037 | 8.070 | 7.854 |
| 9 | 8.959 | 9.077 | 8.884 | 8.835 |
| 10 | 10.134 | 10.034 | 10.047 | 9.983 |
| 11 | 11.222 | 11.095 | 10.875 | 10.813 |
| 12 | 11.679 | 11.983 | 11.870 | 11.953 |
| 13 | 13.147 | 12.745 | 12.626 | 12.856 |
| 14 | 14.063 | 13.983 | 13.692 | 13.799 |
| 15 | 14.715 | 15.012 | 14.618 | 14.154 |
| Hash Function | Digest Size | Block Size | Number of Rounds |
|---|---|---|---|
| SHA-256 | 256 bits (32 bytes) | 512 bits (64 bytes) | 64 rounds |
| SHA-512 | 512 bits (64 bytes) | 1024 bits (128 bytes) | 80 rounds |
| MD5 | 128 bits (16 bytes) | 512 bits (64 bytes) | 64 rounds |
| NTLMv2 | 128 bits (16 bytes) | No fixed block size (based on MD4) | 3 rounds |
| Aspect | Our Work (This Paper) | Sykes et al. [37] | Al-Khazraji [10] | Avoine et al. [38] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Problem Addressed | High inter-process communication | Long time required to generate rainbow tables and search them | Long time required to generate rainbow tables | Inefficiency in the precomputation phase of rainbow tables related with chain discarding |
| Parallelization Model | Modified master-slave (start points generated independently) | Not mentioned | Classic master-slave (master assigns tasks to slaves) | Not mentioned |
| Number of Computing Nodes/CPU Cores Used | 15 nodes | 32 CPU cores | 201 nodes (1 master, 200 slaves) | 5 nodes on a personal computer |
| Performance Improvement | Near-linear speedup (efficiency: 95–99%) | Significant reduction in execution time (from 6 years to around 6 days) | Significant reduction in execution time (from 7.14 days to 46.45 min) | 2.56 times faster |
| Execution Time | 41.73 min | ~6 days | ~46.45 min | Not mentioned |
| Handling of Chain Merges | Master process filters out merged chains to maintain a clean non-perfect table | No mention of merges | No mention of merges | Merged chains are recycled |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vainer, M.; Kačeniauskas, A.; Goranin, N. Parallelization of Rainbow Tables Generation Using Message Passing Interface: A Study on NTLMv2, MD5, SHA-256 and SHA-512 Cryptographic Hash Functions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158152
Vainer M, Kačeniauskas A, Goranin N. Parallelization of Rainbow Tables Generation Using Message Passing Interface: A Study on NTLMv2, MD5, SHA-256 and SHA-512 Cryptographic Hash Functions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(15):8152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158152
Chicago/Turabian StyleVainer, Mark, Arnas Kačeniauskas, and Nikolaj Goranin. 2025. "Parallelization of Rainbow Tables Generation Using Message Passing Interface: A Study on NTLMv2, MD5, SHA-256 and SHA-512 Cryptographic Hash Functions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 15: 8152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158152
APA StyleVainer, M., Kačeniauskas, A., & Goranin, N. (2025). Parallelization of Rainbow Tables Generation Using Message Passing Interface: A Study on NTLMv2, MD5, SHA-256 and SHA-512 Cryptographic Hash Functions. Applied Sciences, 15(15), 8152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158152









