Multivariate Analysis and Geostatistics of the Physicochemical Quality Waters Study from the Complex Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aneho (Southern Togo)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
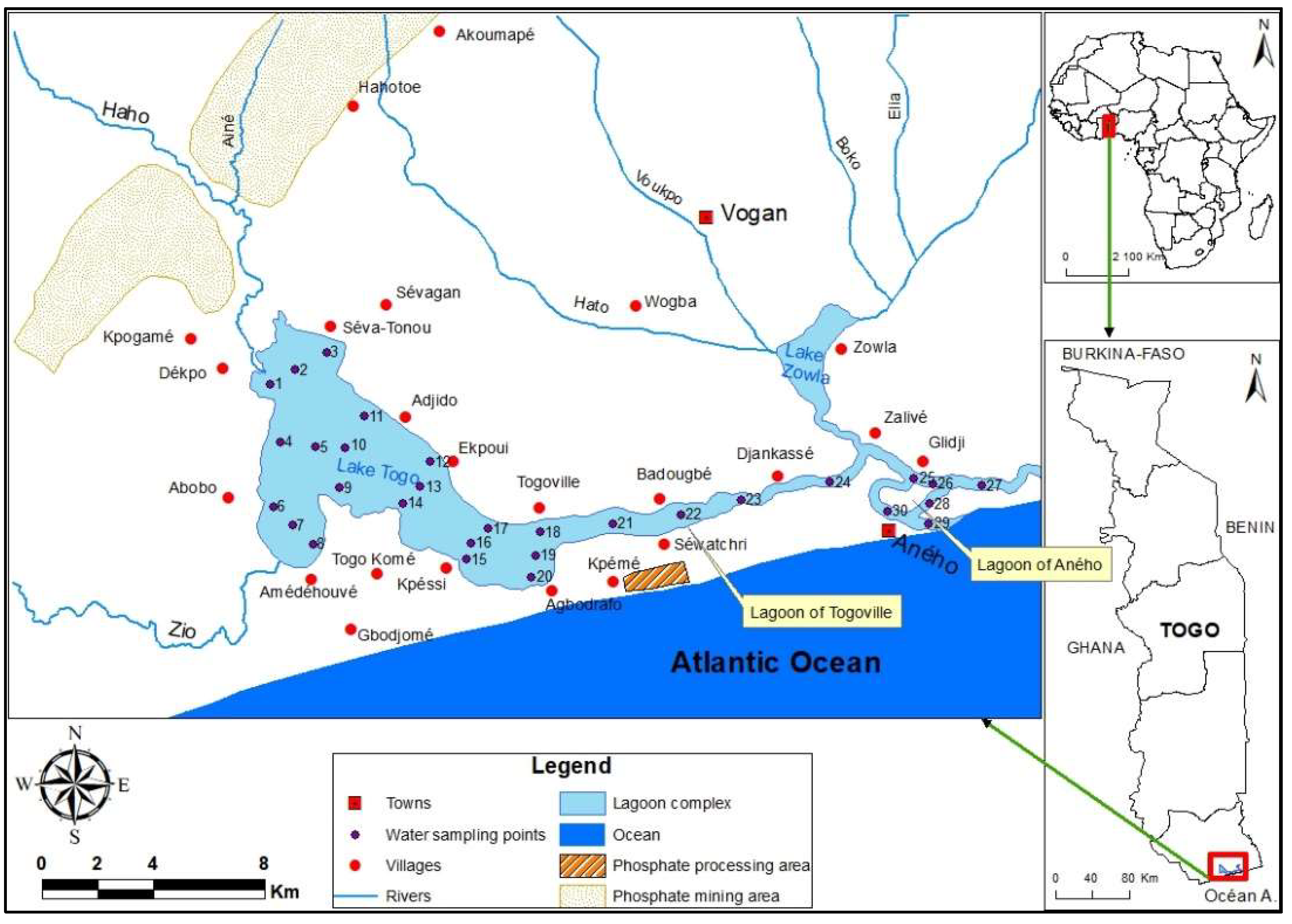
2.1. Description of the Studied Zone
2.2. Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Quality Control
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Mapping
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters of Waters
3.2. Trace Element Concentrations in Water
3.3. Multivariate Analysis of Physicochemical Quality of the Waters
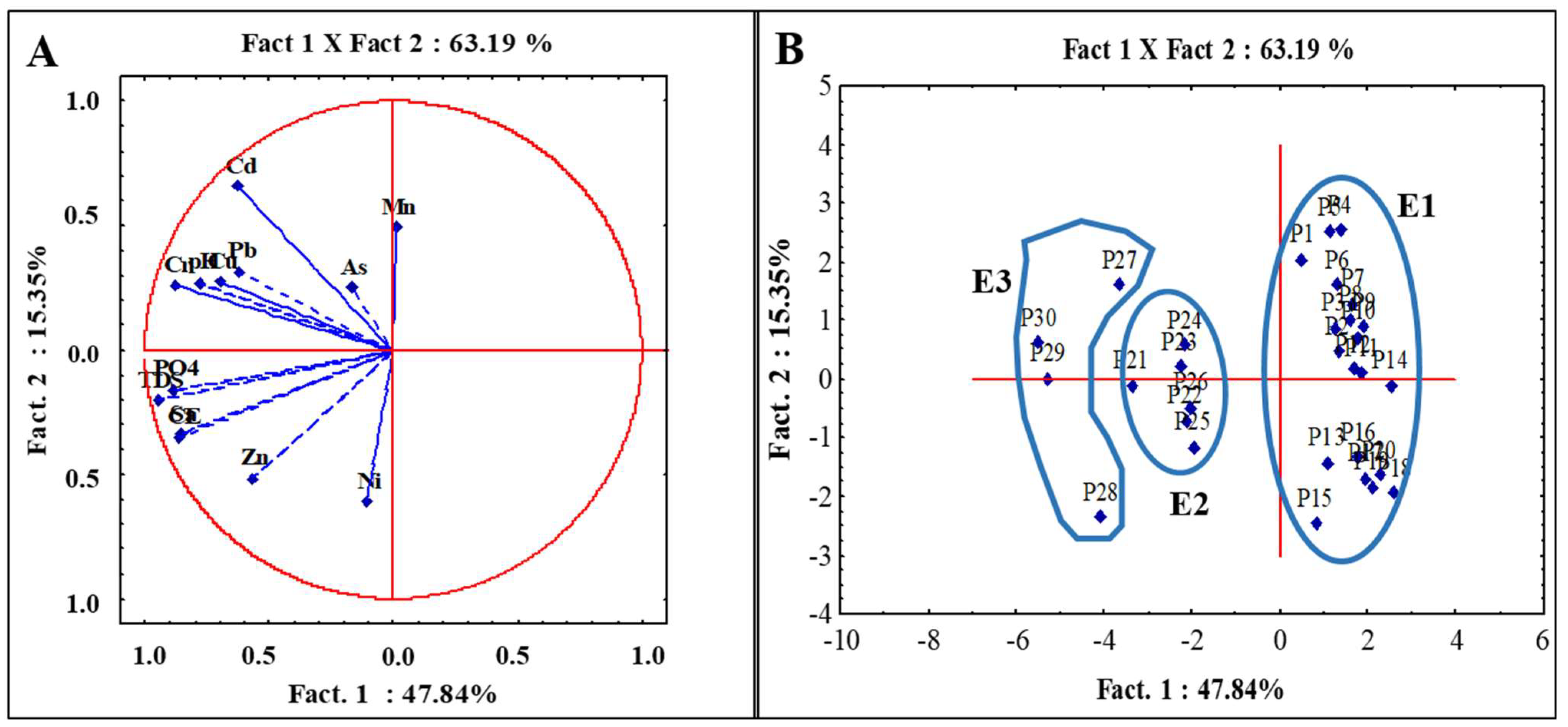
3.3.1. Correlation and Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
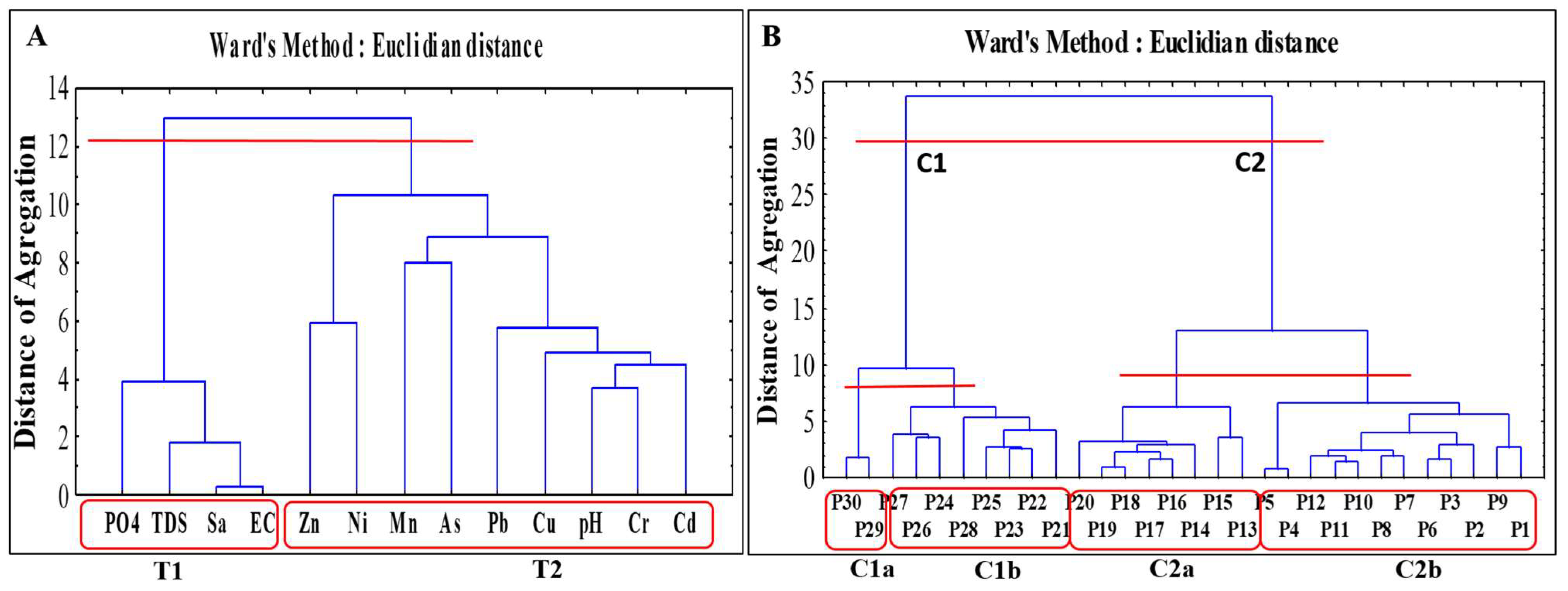
3.3.2. Cluster Analysis (CA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacquiod, S.; Cyriaque, V.; Riber, L.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Gillan, D.C.; Wattiez, R.; Sørensen, S.J. Long-term industrial metal contamination unexpectedly shaped diversity and activity response of sediment microbiome. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, F.; Meng, F.; Jiang, L.; Li, G.; Zhou, R. Assessment of metal contamination in estuarine surface sediments from Dongying City, China: Use of a modified ecological risk index. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y. Study of heavy metal pollution, ecological risk and source apportionment in the surface water and sediments of the Jiangsu coastal region, China: A case study of the Sheyang Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souri, A.; Niyogi, S.; Naji, A. Distribution, source apportionment, bioavailability and ecological risks of metals in reef sediments and corals of the Persian Gulf (Iran): Khark Island, Chirouyeh, and Hendorabi Island. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badassan, T.E.E.; Avumadi, A.M.D.; Ouro-Sama, K.; Gnandi, K.; Jean-Dupuy, S.J.L.; Probst, A. Geochemical composition of the Lomé Lagoon sediments, Togo: Seasonal and spatial variations of major, trace and rare earth element concentrations. Water 2020, 12, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouro-Sama, K.; Solitoke, H.D.; Tanouayi, G.; Lazar, I.M.; Bran, P.; Nadejde, M.; Badassan, T.E.-E.; Ahoudi, H.; Nyametso, A.Y.; Gnandi, K.; et al. Spatial and seasonal variation of trace elements contamination in the sediments of a tropical lagoon system: The Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aného complex (southern Togo). Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solitoke, H.D.; Afiademanyo, K.M.; Ouro-Sama, K.; Tanouayi, G.; Badassan, T.E.-E.; Gnandi, K. Human Health Risks Associated with Trace Element Contamination of Crassostrea gasar (Dautzenberg, 1891) from Lake Zowla-Aného Lagoon Hydrosystem (Southern Togo). J. Environ. Pollut. Hum. Health 2021, 9, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- French, A.D.; Ragg, N.L.C.; Ericson, J.A.; Goodwin, E.; McDougall, D.R.; Mohammadi, A.; Vignier, J. Balancing essential and non-essential metal bioavailability during hatchery rearing of Greenshell mussel (Perna canaliculus) larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hounkpè, J.B.; Kélomè, N.C.; Adèchina, R.; Lawani, R.N. Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments at the lake of Ahémé in southern of Benin (West Africa). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 4369–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pape, O. Essential Coastal Fish Habitats: Identifying Them, Understanding How They Work and Monitoring Their Quality to Better Manage and Sustain Exploited Marine Resources. Habilitation Thesis, University of Western Brittany, Brest, France, 2005. Available online: https://halieutique.institut-agro.fr/files/fichiers/pdf/743.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Ramsar Convention, Ramsar Handbooks for the Wise Use of Wetlands, 4th ed., Handbook 12: Coastal Zone Management. Available online: https://www.ramsar.org/sites/default/files/documents/pdf/lib/hbk4-01fr.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Harley, C.D.G.; Randall Hughes, A.; Hultgren, K.M.; Miner, B.G.; Sorte, C.J.B.; Thornber, C.S.; Rodriguez, L.F.; Tomanek, L.; Williams, S.L. The impacts of climate change in coastal marine systems. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, S. Coastal Urbanization: Spaces, Landscapes and Representations. Territories at the City-Sea Interface. Habilitation Thesis, University of Western Brittany, Brest, France, 2019. Available online: https://theses.hal.science/tel-02350064v1 (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Gning, N. Trophic Ecology of Juveniles of Four Fish Species in the Reverse Estuary of Sine-Saloum (Senegal): Influence of Contrasting Salinity Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Montpellier II, Montpellier, France, 2008. Available online: https://horizon.documentation.ird.fr/exl-doc/pleins_textes/divers11-03/010047104.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Beiras, R.; His, E. Effects of dissolved mercury on embryogenesis, survival, growth and metamorphosis of Crassostrea gigas oyster larvae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 113, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.C.; Fukushima, T. Metals in aquatic ecosystems: Mechanisms of uptake, accumulation and release-ecotoxicological perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1999, 56, 385–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquel, M.G. The Effects of Heavy Metals on the Environment and Health, Parliamentary Office for the Evaluation of Scientific and Technological Choices. Report 261, Paris, France, 2001. Available online: https://www.senat.fr/rap/l00-261/l00-261_mono.html (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Mai, H.; Cachot, J.; Brune, J.; Geffard, O.; Belles, A.; Budzinski, H.; Morin, B. Embryotoxic and genotoxic effects of heavy metals and pesticides on early life stages of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastami, K.D.; Afkhami, M.; Mohammadizadeh, M.; Ehsanpour, M.; Chambari, S.; Aghaei, S.; Esmaeilzadeh, M.; Neyestani, M.R.; Lagzaee, F.; Baniamam, M. Bioaccumulation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments and mullet Liza klunzingeri in the northern part of the Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 94, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smita Achary, M.; Satpathy, K.K.; Panigrahi, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Padhi, R.K.; Biswas, S.; Prabhu, R.K.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Panigrahy, R.C. Concentration of heavy metals in the food chain components of the nearshore coastal waters of Kalpakkam, south east coast of India. Food Control 2017, 72, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouro-Sama, K.; Afiademanyo, K.M.; Solitoke, H.D.; Tanouayi, G.; Badassan, T.E.-E.; Adje, K.; Agbere, S.; Gnandi, K. Trace elements in mollusks, crustaceans and fish commonly consumed by the catfish Chrysichthys nigrodigitatus Lacépède, 1803 from the Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aného hydrosystem (Southern Togo). J. Environ. Prot. 2021, 12, 1185–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouro-Sama, K.; Afiademanyo, K.M.; Solitoke, H.D.; Tanouayi, G.; Agbere, S.; Badassan, T.E.-E.; Adje, K.; Gnandi, K. Consumption of the Silver Catfish Chrysichthys nigrodigitatus Lacépède, 1803 from the Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aného Hydrosystem (Southern Togo): Risks to Human Health. Haya Saudi J. Life Sci. 2021, 6, 284–294. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, H.F.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Po-Hsun, C. GIS for the assessment of the groundwater recharge potential zone. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Laiq, M.; Nabi, M. Geostatistical analysis and multivariate assessment of groundwater quality. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Multivariate methods. In Analytical Chemistry; Kellner, R., Mermet, J.M., Otto, M., Widmer, H.M., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Agyemang, V.O. Application of geostatistical techniques in the assessment of groundwater contamination in the Afigya Kwabre District of Ghana. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, M.G.; Battaloglu, R.; Ilhan, S. Heavy metal sources in Sultan Marsh and its neighborhood, Kayseri, Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y. Spatial distribution, bioavailability, and health risk assessment of soil Hg in Wuhu urban area, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 179, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbarpour, M.R.; Goorzadi, M.; Vahabzade, G. Spatial variability of heavy metals in surficial sediments: Tajan River Watershed, Iran. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2013, 1–2, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, S. Spatial distribution, source identification and affecting factors of heavy metals contamination in urban–suburban soils of Lishui city, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.; van der Meer, F.; van Ruitenbeek, F.; van der Werff, H.; de Smeth, B.; Kim, K. Mapping of heavy metal pollution in stream sediments using combined geochemistry, field spectroscopy, and hyperspectral remote sensing: A case study of the Rodalquilar mining area, SE Spain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3222–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaaks, E.H.; Srivastava, R.M. An Introduction to Applied Geostatistics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; 561p. [Google Scholar]
- Gnandi, K.; Tchangbedji, G.; Baba, G.; Kili, K.; Abbé, K.D. The impact of phosphate mine tailings on the bioaccumulation of heavy metals in marine fish and crustaceans from the coastal zone of Togo. Int. J. Mine Water Environ. 2006, 25, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North-South Environement. Réduction des Rejets des Mines de Phosphates du Togo Dans le GCLME, Projet de Démonstration du Togo; Rapport final; United Nations Industrial Development Organization/North-South Environment (ONUDI/NSE): Vienna, Austria, 2007; p. 138. [Google Scholar]
- Gnandi, K. Cadmium et Autres Polluants Inorganiques Dans Les Sols et Sédiments de la Region Côtière du Togo: Une Etude Géochimique. Ph.D. Thesis, University d’Erlangen-Nurenberg, Erlangen, Germany, 1998; p. 165. [Google Scholar]
- Gnandi, K.; Tobschall, H.J. Heavy metals distribution of soils around mining sites of cadmium-rich marine sedimentary phosphorites of Kpogame and Hahotoe (Southern Togo). Environ. Geol. 2002, 41, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnandi, K.; Rezaie, B.; Edorh, A. The geochemical characterization of mine effluents from the phosphorite processing plant of Kpémé (southern Togo). Mine Water Environ. 2009, 28, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, B. Study of Some Hydrological and Hydrochemical Characteristics of the Lagoon System of Lake Togo Years 1981 and 1982; ORSTOM: Marseille, France, 1983; p. 134. [Google Scholar]
- Millet, B. Hydrology and Hydrochemistry of a Tropical Lagoon Environment: Lake Togo. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD), Paris, France, 1986. Available online: https://horizon.documentation.ird.fr/exl-doc/pleins_textes/pleins_textes_7/divers2/21095.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Rodier, J.; Legube, B.; Merlet, N.; Brunet, R. Water Analysis: Natural Waters, Wastewater, Seawater, 9th ed.; Dunod: Paris, France, 2009; p. 1579. [Google Scholar]
- Bastami, K.D.; Bagheri, H.; Haghparast, S.; Soltani, F.; Hamzehpoor, A.; Bastami, M.D. Geochemical and geo-statistical assessment of selected heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Gorgan Bay. Iran Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, P.; Yu, W.; Shen, Z.; Feng, C. Spatial variation, environmental assessment and source identification of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, M.A.; Wani, J.; Bhat, M.; Kirmani, N.; Wani, Z.M.; Bhat, S.N. Mapping of soil micronutrients in kashmir agricultural landscape using ordinary kriging and indicator approach. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2013, 41, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nshimiyimana, F.-X.; Faciu, M.-E.; El Blidi, S.; El Abidi, A.; Soulaymani, A.; Fekhaoui, M.; Lazar, G. Seasonal influence and risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in groundwater, Arjaat village, Morocco. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2016, 15, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouro-Sama, K.; Solitoke, H.D.; Tanouayi, G.; Badassan, T.E.-E.; Ahoudi, H.; Nyametso, A.Y.; Gnandi, K. Spatio-temporal variation of the physicochemical parameters of waters from the hydrosystem Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aného (South-East of Togo). J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2018, 5, 164–178. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi-Zanjani, A.; Saeedi, M. Metal pollution assessment and multivariate analysis in sediment of Anzali international wetland. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1791–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arain, M.B.; Ullah, I.; Niaz, A.; Shah, N.; Shah, A.; Hussain, Z.; Tariq, M.; Afridi, H.I.; Baig, J.A.; Kazi, T.G. Evaluation of water quality parameters in drinking water of district Bannu, Pakistan: Multivariate study. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2014, 3–4, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summary of Regulatory Values or Chemical Substances in Force in Water, Air and Foodstuffs in France. Available online: https://www.ineris.fr/fr/conception-cahier-charges-etudes-zones (accessed on 22 February 2025).
- Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality Third Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda Volume 1 Recommendations. World Health Organization (WHO) Chronicle. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/204411/9789241547611_eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization (WHO) Chronicle. 2011. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/44584/9789241548151_eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Chapman, D.; Kimstach, V. Selection of Water Quality Variables, Water Quality and Assesments-A Guide to Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring; Chapman, D., Ed.; E and FN Spon: London, UK, 1996; pp. 56–133. [Google Scholar]
- Ouro-Sama, K.; Tanouayi, G.; Solitoke, H.D.; Badassan, T.E.-E.; Ahoudi, H.; Nyametso, A.Y.; Gnandi, K. Seasonal variation, quality and typology of waters’ abiotic parameters of a tropical lagoon: The hydrosystem Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aného (South-East of Togo). Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2018, 24, 656–673. [Google Scholar]
- Issola, Y.; Kouassi, A.M.; Dongui, B.; Biemi, J. Caractéristiques physico-chimiques d’une lagune côtière tropicale: Lagune de Fresco (Côte d’Ivoire). Afr. Sci. 2008, 4, 368–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidance on the Site-Specific Application of the Canadian Water Quality Guidelines: Procedures for Establishing Numerical Water Quality Objectives. Available online: https://ccme.ca/fr/res/recommandations-pour-la-qualit-des-eaux-au-canada-procdures-dtablissement-dobjectifs-numriques-de-qualit-de-leaufr.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Gnandi, K. Les déchets miniers phosphatés, sources de la pollution marine au Togo. J. Rech. Sci. Univ. Lomé 2003, 7, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, P.Y.D.; Flicoteaux, R.; Affaton, P.; Seddoh, K.; Tairou, M.S.; Johnson, A.K.C. Le Continental terminal du bassin côtier du togolais: Un témoin d’altération pédogénétique sous climat tropical depuis l’oligocène supérieur. Afr. Geosci. Rev. 2006, 13, 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, P.Y.D.; Affaton, P.; Salaj, J.; Johnson, A.K.C.; Seddoh, K. Biozonation des formations sédimentaires du bassin côtier du Togo (Afrique de l’ouest). Rev. Ivoirienne Sci. Technol. 2013, 21, 45–73. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.K.C.; Da Costa, Y.D. Le passage Paléocène-Eocène dans les bassins sédimentaires côtiers du golfe du Benin: Togo Benin et Nigeria. Rev. Ivoirienne Sci. Technol. 2008, 11, 193–205. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.K.; Rat, P.; Lang, J. Le bassin sédimentaire à phosphate du Togo (Maastrichtien-Eocène): Stratigraphie, environnements et évolution. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2000, 30, 153–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnandi, K.; Tobschall, H.J. Heavy metal release from phosphorite tailings into seawater: A simulated laboratory study. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 236, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slansky, M. Géologie Des Phosphates Sédimentaire; BRGM Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières: Paris, France, 1980; p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel, H. Über die Cadmiumverteilung in den Phosphoritlagerstätten von Kpogamé/Hahotoé. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universtät Erlangen-Nuremberg, Erlangen, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- FD T90-523-3, NF EN ISO 5667-3; Water Quality—Sampling—Part 3: Preservation and Handling of Water Samples. Association Francaise de Normalisation: La Plaine Saint-Denis, France, 2013.
- NF T90-112; Water Quality—Determination of Eight Metallic Elements (Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Ag, Pb) by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry—Direct and After Complexing and Extraction Determination Methods. Association Francaise de Normalisation: La Plaine Saint-Denis, France, 1998.
- ISO 5961:1994; Water Quality—Determination of Cadmium by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994.
- NF EN 1233; Water Quality—Determination of Chromium—Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Methods. European Standards Organizations: Brussels, Belgium, 1996.
- NF EN ISO 11969; Water Quality—Determination of Arsenic—Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Method (Hydride Technique). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Cambardella, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Novak, J.M.; Parkin, T.B.; Karlen, D.L.; Turco, R.F.; Konopka, A.E. Field scale variability of soil properties in Central Iowa Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garry, B. Étude des Processus D’écoulements de la Zone non Saturée Pour la Modélisation des Aquifères Karstiques: Expérimentation Hydrodynamique et Hydrochimique sur les Sites du Laboratoire Souterrain à Bas Bruit (LSBB) de Rustrel et de Fontaine de Vaucluse. Ph.D. Thesis, Université d’Avignon, Avignon, France, 2007; p. 206. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, M.T. Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater in the Blue Nile Basin, eastern Sudan, using conventional and multivariate techniques. Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceloux, D.G. Chromium. Journal of Toxicology. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 173–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lauwerys, R.R. Chrome. Toxicologie Industrielle et Intoxications Professionnelles; Masson: Moulineaux, France, 1999; pp. 188–198. [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso, T.F. Chromium as an industrial carcinogen: Part 1. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1997, 31, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, D.; Saas, B.M.; Moore, D.A. Chromium(III) hydrolysis constants solubility of chromium hydroxide. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaprara, E.; Kazakis, N.; Simeonidis, K.; Colesa, S.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Samaras, P.; Mitrakas, M. Occurrence of Cr(VI) in drinking water of Greece and relation to the geological background. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 281, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouro-Sama, K.; Solitoke, H.D.; Tanouayi, G.; Lazar, I.M.; Bran, P.; Nadejde, M.; Ahoudi, H.; Badassan, T.E.-E.; Nyametso, A.Y.; Gnandi, K.; et al. Spatial and seasonal variation of trace elements contamination level of the waters from the hydrosystem Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aného (South of Togo). SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
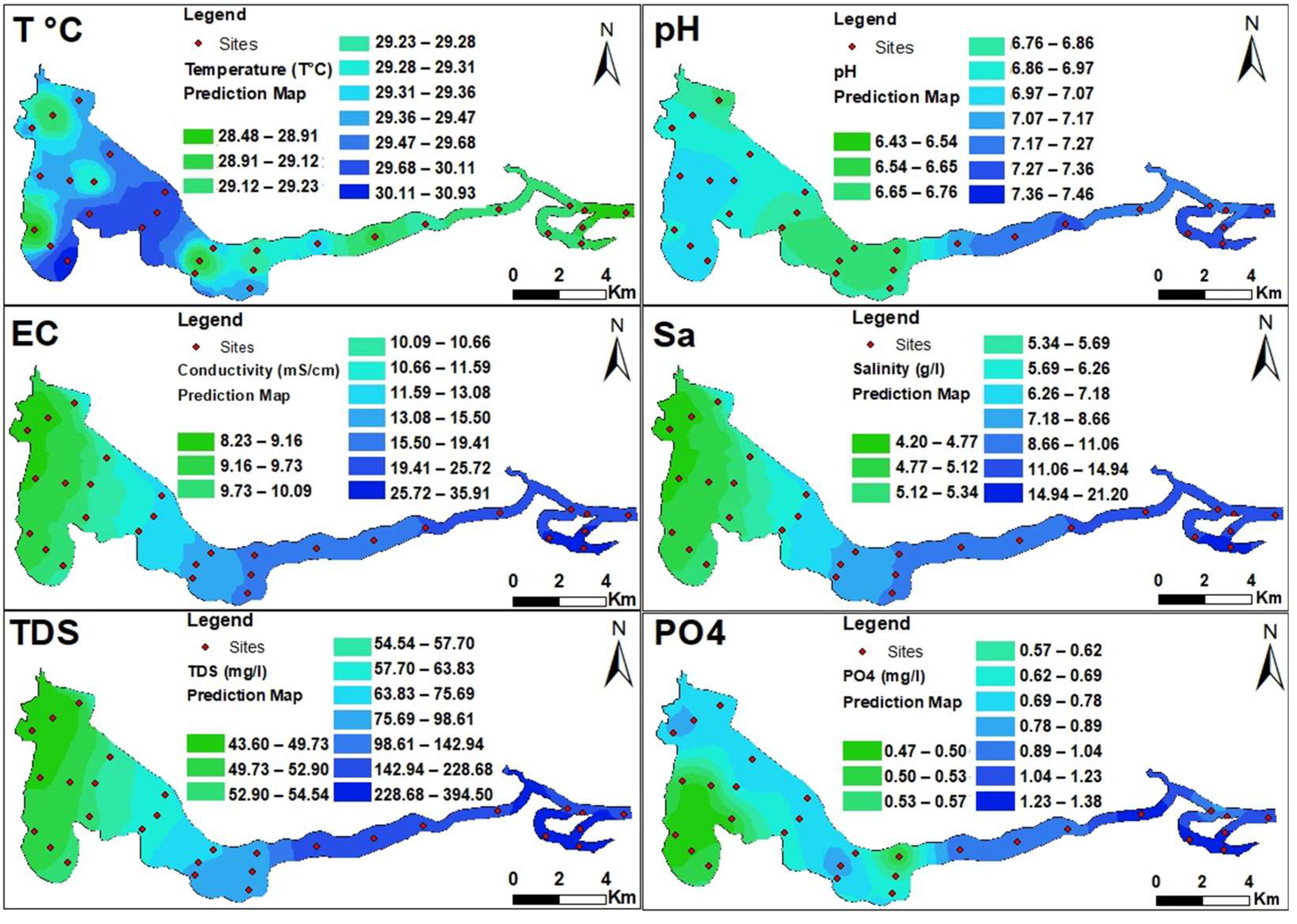
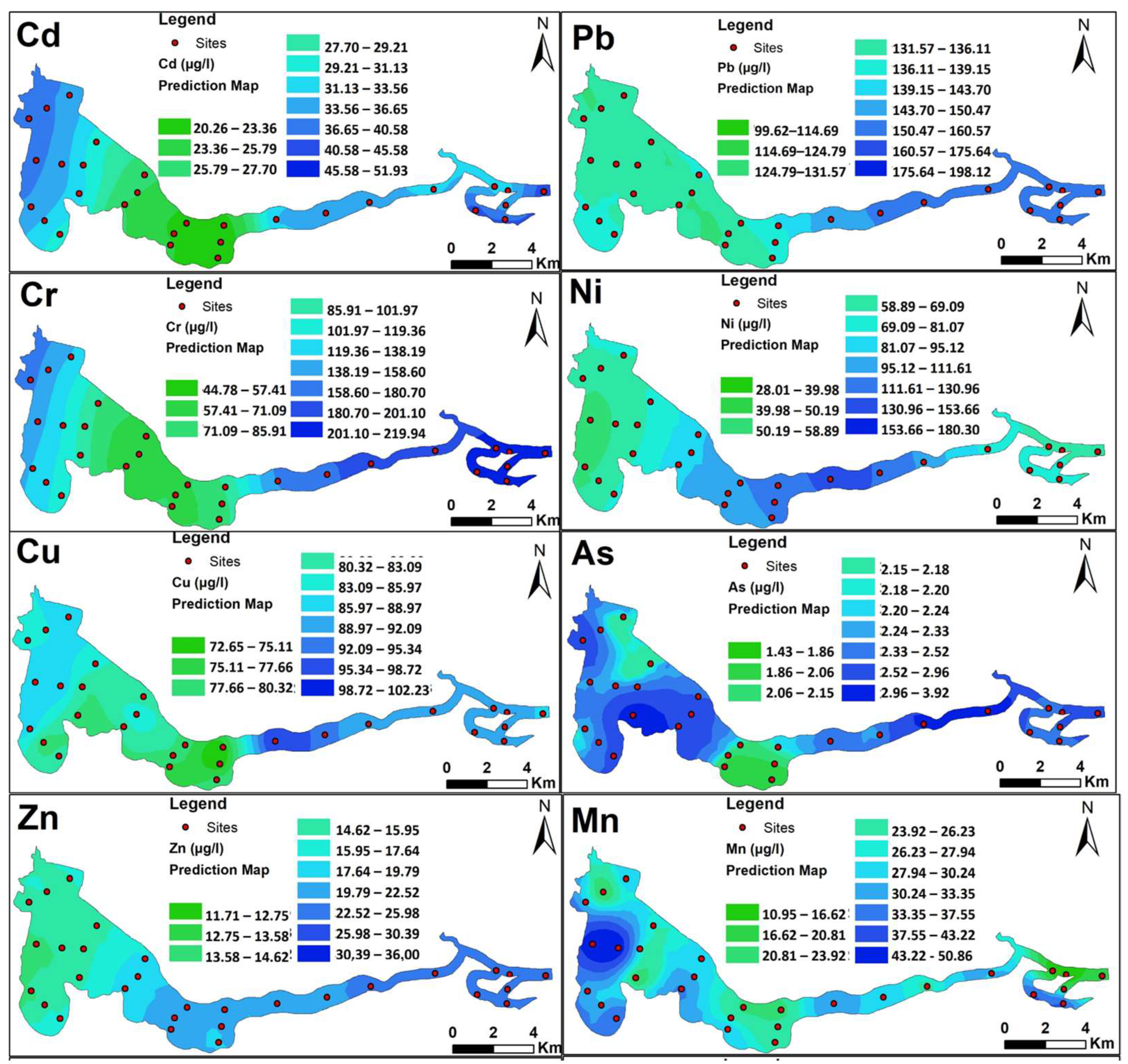
| Statistical Parameters | Physicochemical Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T°C | pH | EC | Sa | PO43− | |
| Minimum | 28.49 | 6.43 | 8.24 | 4.20 | 0.48 |
| Maximum | 30.94 | 7.46 | 35.91 | 21.20 | 1.38 |
| Average | 29.33 | 6.99 | 15.51 | 8.52 | 0.80 |
| Median | 29.27 | 7.01 | 14.30 | 7.93 | 0.74 |
| SD * | 0.48 | 0.29 | 7.38 | 4.41 | 0.28 |
| CV * | 1.64 | 4.21 | 47.54 | 51.82 | 34.63 |
| Skewness | 1.16 | −0.27 | 1.51 | 1.57 | 0.86 |
| Kurtosis | 3.26 | −0.71 | 1.94 | 2.25 | −0.17 |
| 1st quartile | 29.03 | 6.79 | 9.86 | 5.10 | 0.58 |
| 3rd quartile | 29.50 | 7.22 | 18.80 | 10.49 | 0.94 |
| Standards WHO * | 25 | 6.5–9.5 | 0.18–1 | 0.3–0.5 | 0.5–0.9 |
| Physico-Chemical | Semivariogram Models and Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | = SD (%) | Range (km) | ME * | RMSE * | |||
| T°C | Exponential | 0.00 | 0.236 | 0.00 | 0.025 | −0.018 | 0.45 |
| pH | Spherical | 0.023 | 0.103 | 22.33 | 0.159 | −0.005 | 0.22 |
| EC | Spherical | 5.74 | 75.847 | 7.57 | 0.242 | 0.122 | 3.09 |
| Sa | Spherical | 1.99 | 27.528 | 7.22 | 0.242 | 0.069 | 1.88 |
| TDS | Gaussian | 1844.93 | 19,449.50 | 9.48 | 0.242 | 1.033 | 48.07 |
| PO4 | Exponential | 0.004 | 0.018 | 21.79 | 0.024 | −0.009 | 0.137 |
| Statistical Parameters | Trace Elements (µg/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Pb | Cr | Ni | Cu | As | Zn | Mn | |
| Minimum | 20.26 | 99.62 | 44.78 | 28.01 | 72.70 | 1.43 | 11.71 | 10.95 |
| Maximum | 51.93 | 198.12 | 219.94 | 180.30 | 102.20 | 3.92 | 36.00 | 50.86 |
| Average | 31.96 | 141.63 | 133.02 | 83.28 | 85.12 | 2.46 | 19.63 | 28.75 |
| Median | 30.15 | 141.31 | 132.51 | 79.11 | 86.67 | 2.23 | 17.09 | 28.63 |
| SD * | 8.37 | 21.15 | 56.75 | 33.41 | 6.72 | 0.58 | 6.53 | 8.87 |
| CV * | 26.19 | 14.93 | 42.66 | 40.11 | 7.90 | 23.77 | 33.26 | 30.84 |
| Skewness | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.16 | 0.79 | 0.11 | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.58 |
| Kurtosis | 0.04 | 0.88 | −1.44 | 0.96 | 0.00 | 0.46 | −0.17 | 1.11 |
| 1st quartile | 26.15 | 126.56 | 77.15 | 55.51 | 79.19 | 2.08 | 14.26 | 23.39 |
| 3rd quartile | 37.07 | 154.24 | 189.59 | 109.57 | 89.70 | 2.89 | 24.07 | 31.73 |
| Guidelines WHO * | 3 | 10 | 50 | 70 | 2000 | 10 | 3000 | 400 |
| Trace Elements | Semivariogram Models and Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | = SD (%) | Range (km) | ME * | RMSE * | |||
| Cd | Gaussian | 33.43 | 66.78 | 50.06 | 0.14 | 0.004 | 1.05 |
| Pb | Stable | 248.62 | 529.66 | 46.94 | 0.24 | 0.001 | 1.17 |
| Cr | Exponential | 99.25 | 4475.17 | 2.22 | 0.22 | −0.018 | 0.64 |
| Ni | Stable | 447.82 | 1454.77 | 30.78 | 0.12 | 0.017 | 1.07 |
| Cu | Exponential | 0.21 | 78.50 | 0.27 | 0.17 | −0.02 | 1.23 |
| As | Stable | 0.17 | 0.21 | 81.90 | 0.02 | −0.001 | 1.06 |
| Zn | Spherical | 28.46 | 39.54 | 71.97% | 0.07 | −0.002 | 5.78 |
| Mn | Exponential | 0.28 | 99.63 | 0.28 | 0.02 | 0.004 | 0.83 |
| Cd | Pb | Cr | Ni | Cu | As | Zn | Mn | pH | EC | Sa | TDS | PO4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pb | 0.61 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cr | 0.71 | 0.57 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ni | −0.27 | 0.01 | −0.12 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cu | 0.56 | 0.47 | 0.73 | 0.11 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| As | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.23 | −0.07 | 0.20 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Zn | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Mn | 0.30 | 0.04 | −0.05 | −0.04 | 0.17 | −0.11 | −0.29 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| pH | 0.65 | 0.44 | 0.76 | −0.03 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| EC | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.62 | 0.20 | 0.37 | −0.01 | 0.52 | −0.06 | 0.56 | 1 | - | - | - |
| Sa | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.61 | 0.18 | 0.36 | −0.03 | 0.50 | −0.05 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 1 | - | - |
| TDS | 0.44 | 0.48 | 0.76 | 0.17 | 0.56 | 0.09 | 0.53 | −0.05 | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 1 | - |
| PO4 | 0.43 | 0.48 | 0.71 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.22 | 0.53 | −0.12 | 0.58 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 1 |
| Parameters | Factorial Axes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | |
| TDS | −0.95 | −0.20 | −0.10 |
| PO4 | −0.89 | −0.16 | 0.09 |
| Cr | −0.88 | 0.26 | 0.14 |
| EC | −0.86 | −0.35 | −0.19 |
| Sa | −0.86 | −0.34 | −0.21 |
| pH | −0.79 | 0.27 | −0.13 |
| Cu | −0.70 | 0.28 | 0.07 |
| Pb | −0.62 | 0.32 | 0.18 |
| Zn | −0.57 | −0.51 | 0.18 |
| Cd | −0.63 | 0.66 | −0.08 |
| Ni | −0.11 | −0.61 | −0.10 |
| Mn | 0.01 | 0.49 | −0.66 |
| As | −0.17 | 0.25 | 0.76 |
| Eigenvalues | 6.22 | 2.00 | 1.23 |
| % Total variance | 47.84 | 15.35 | 9.42 |
| % Cumulative variance | 47.84 | 63.19 | 72.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouro-Sama, K.; Solitoke, H.D.; Tanouayi, G.; Barsan, N.; Mosnegutu, E.; Agbere, S.; Badanaro, F.; Nedeff, V.; Gnandi, K.; Nedeff, F.-M.; et al. Multivariate Analysis and Geostatistics of the Physicochemical Quality Waters Study from the Complex Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aneho (Southern Togo). Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7940. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147940
Ouro-Sama K, Solitoke HD, Tanouayi G, Barsan N, Mosnegutu E, Agbere S, Badanaro F, Nedeff V, Gnandi K, Nedeff F-M, et al. Multivariate Analysis and Geostatistics of the Physicochemical Quality Waters Study from the Complex Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aneho (Southern Togo). Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7940. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147940
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuro-Sama, Kamilou, Hodabalo Dheoulaba Solitoke, Gnon Tanouayi, Narcis Barsan, Emilian Mosnegutu, Sadikou Agbere, Fègbawè Badanaro, Valentin Nedeff, Kissao Gnandi, Florin-Marian Nedeff, and et al. 2025. "Multivariate Analysis and Geostatistics of the Physicochemical Quality Waters Study from the Complex Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aneho (Southern Togo)" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7940. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147940
APA StyleOuro-Sama, K., Solitoke, H. D., Tanouayi, G., Barsan, N., Mosnegutu, E., Agbere, S., Badanaro, F., Nedeff, V., Gnandi, K., Nedeff, F.-M., Panainte-Lehadus, M., & Chitimus, D. (2025). Multivariate Analysis and Geostatistics of the Physicochemical Quality Waters Study from the Complex Lake Togo-Lagoon of Aneho (Southern Togo). Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7940. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147940









