New Approach to Effective Dry Grinding of Materials by Controlling Grinding Media Actions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Conducting a mathematical model for the description of the grinding process and predict the efficiency of the proposed approach;
- (2)
- Developing the design of the experimental apparatus reproducing the proposed approach;
- (3)
- Conducting experimental investigations of the proposed approach.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Description of the Grinding Process
- Case 1: The grinding process is conducted as a result of two- and one-sided grinding media actions in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively (using Equation (13)).
- Case 2: The grinding process is conducted as a result of one- and two-sided grinding media actions in the horizontal and vertical directions (using Equation (14)).
2.2. Experimental Investigation of the New Mill Design
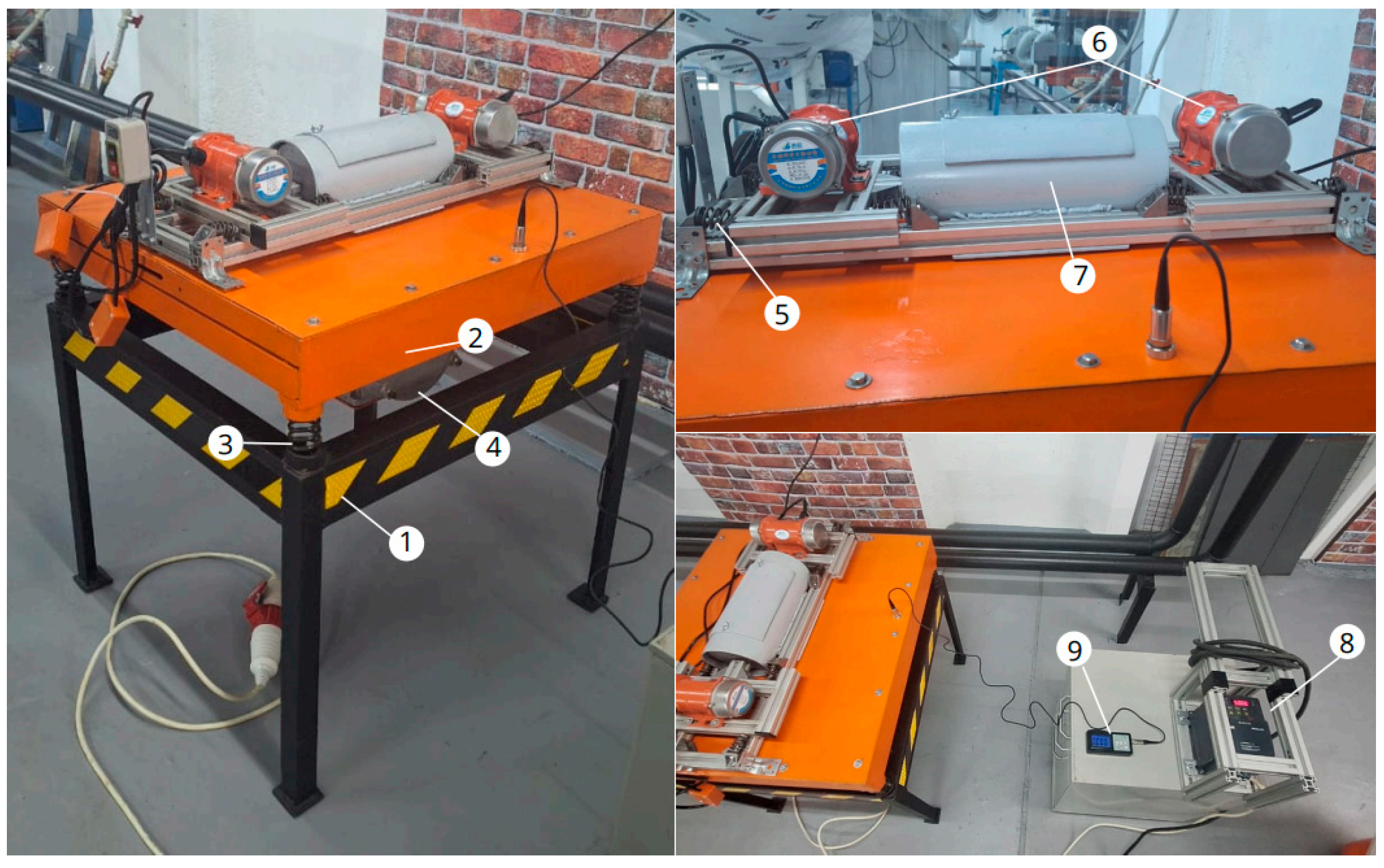
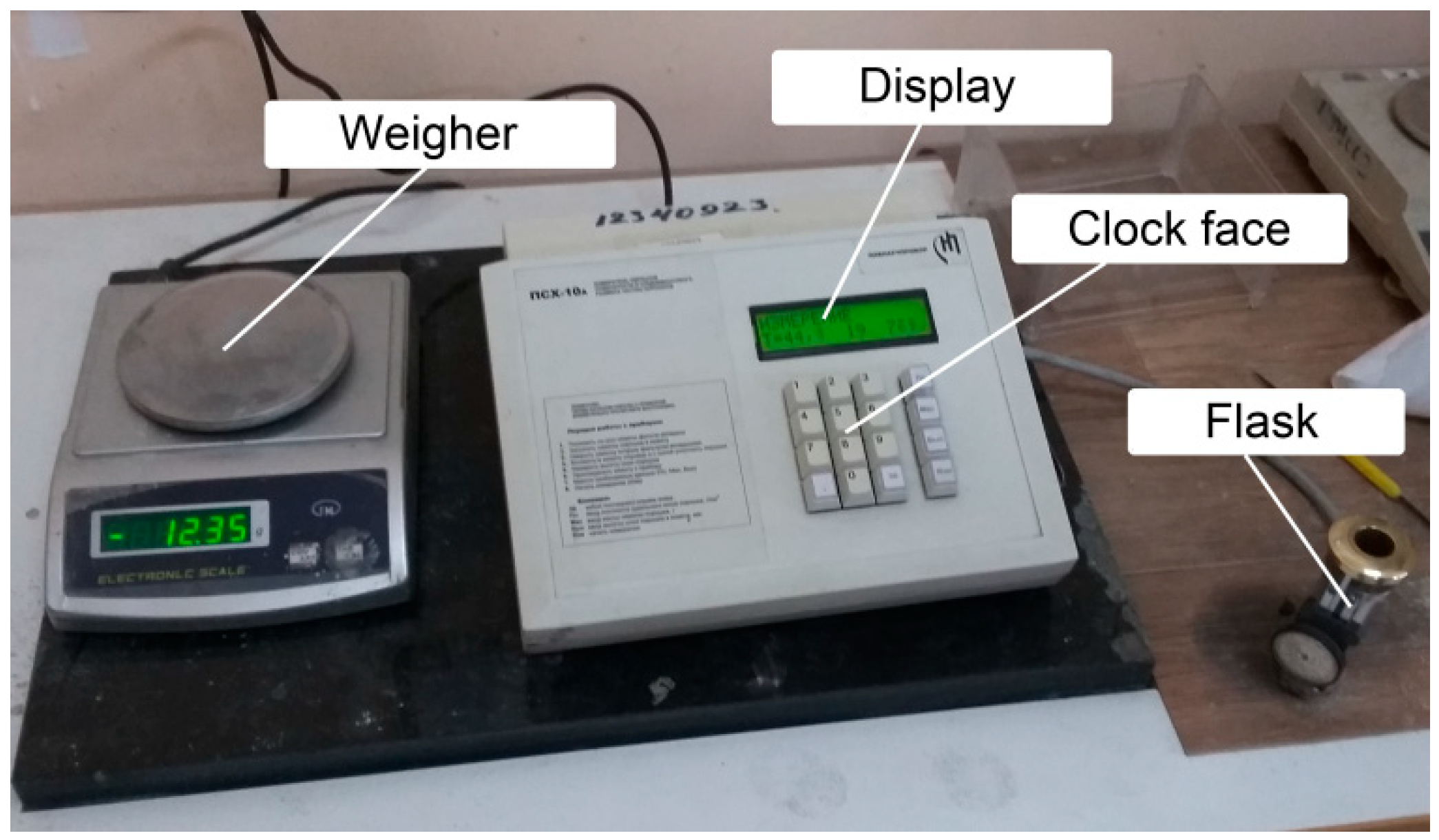
2.2.1. Description of Experimental Apparatus
2.2.2. Description of Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
- The limited power of the drive motor restricted the maximum torque, which prevented the testing of harder or highly compressed materials under realistic industrial conditions.
- The dimensions of the grinding chamber constrained the size of input materials, which may limit the scalability and generalizability of the obtained results.
- The absence of a cooling system during operation may have led to uncontrolled temperature increases, potentially affecting the material properties and grinding efficiency.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, W.; Gui, X.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, R.; Meng, W.; Luo, M. Study on the unequal-probability comminution of spodumene and feldspar during the grinding process of lithium ore. Powder Technol. 2023, 418, 118776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussayev, M.; Sherov, K.; Taskarina, A.; Sherov, A.; Gabdyssalik, R.; Buzauova, T.; Ainabekova, S. Chip formation during thermal friction turn milling. J. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2021, 19, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherov, К.; Ainabekova, S.; Kuanov, I.; Myrzakhme, B.; Bekzhanov, Y.; Gabdyssalik, R.; Mazdubay, A.; Kamarov, A.; Sherov, A. Research of temperature distribution in the process of thermo-frictional cutting of titanium alloy ti-5553. J. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2021, 20, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.; Xie, M.; Ran, Y. Evaluation of Different Particle Size Reduction Techniques in Application of Formulation Preparation. Asian J. Appl. Sci. 2016, 4, 803–809. [Google Scholar]
- Möller, M.F.; Peppersack, C.; Kwade, A. Milling efficiency and wear behavior of silicon grinding media in autogenous stirred media milling. Miner. Eng. 2024, 214, 108785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Yang, X.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Zhu, P.; Yang, J. Study on the Population Balance Dynamics Simulation of Grinding under Impact Crushing. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraio, D.; Villoria, J.; Ingram, A.; Alexiadis, A.; Stitt, E.H.; Marigo, M. Validation of a Discrete Element Method (DEM) Model of the Grinding Media Dynamics within an Attritor Mill Using Positron Emission Particle Tracking (PEPT) Measurements. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołosiewicz-Głąb, M.; Pięta, P.; Foszcz, D.; Ogonowski, S.; Niedoba, T. Grinding Kinetics Adjustment of Copper Ore Grinding in an Innovative Electromagnetic Mill. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aziz, F.A.; Masruroh; Fauzy, A.I.M.; Sakti, S.P.; Santjojo, D.J.D.H. Rotational speed effect of the planetary ball milling on the particle size and crystal structure of CaMnO3 as a thermoelectric material. In Proceedings of the II International Scientific and Practical Symposium “Materials Science and Technology” (MST-II-2022); AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, A.; Aissat, S. Analyzing the influence of lifter design and ball mill speed on grinding performance, particle behavior and contact forces. Mech. Ind. 2023, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, K.; Liang, D.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, Z. Effect of ball milling speed on the quality of Al2O3 stripped graphene in a wet milling medium. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 17171–17177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekaj, P.; Cieplok, G. Experimental tests of the antiresonance vibratory mill of a sectional movement trajectory. Open Eng. 2021, 11, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliang, T.; Bo, C.; Xianzhou, S.; Haonan, J.; Yijiang, L.; Zhaohua, W. Experimental study on the influence of rotational speed on grinding efficiency for the vertical stirred mill. Minerals 2024, 14, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Xie, Q. Analysis and optimization of the milling performance of an industry-scale VSM via numerical simulations. Materials 2023, 16, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megret, A.; Vitry, V.; Delaunois, F. High-energy ball milling of WC-10Co: Effect of the milling medium and speed on the mechanical properties. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 104, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Uematsu, T.; Shiomi, H.; Osaki, K.; Ishihara, S.; Kano, J. Prediction of power of a vibration rod mill during cellulose decrystallization processing by DEM. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 3717–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaya, B.; Toroglu, I.; Bilen, M. Studying the effect of different operation parameters on the grinding energy efficiency in laboratory stirred mill. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 4517–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.; Pinkney, S.; Blackburn, S.; Rowson, N.A. Spatial distributions of media kinetic energy as measured by positron emission particle tracking in a vertically stirred media mill. Miner. Eng. 2016, 98, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, O.; Benzer, H.; Enderle, U. The effects of chamber and rotor design on dry horizontal stirred mill performance. Miner. Eng. 2014, 69, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilden, M.M.; Powell, M.S.; Yahyaei, M. An improved method for grinding mill filling measurement and the estimation of load volume and mass. Miner. Eng. 2021, 160, 106638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasundara, C.T.; Yang, R.Y.; Yu, A.B.; Rubenstein, J. Effect of disc rotation and media loading on particle flow and grinding performance in a horizontal stirred mill. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 96, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, T.; Rhymer, D.; Werner, D.; Ingram, A.; Windows-Yule, C.R.K. Investigating the impact of impeller geometry for a stirred mill using the discrete element method: Effect of pin number and thickness. Powder Technol. 2023, 428, 118810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhaffez, G.S.; Ahmed, A.A.; Haitham, M.A. Effect of grinding media on the milling efficiency of a ball mill. Min.-Geol.-Pet. Eng. Bull. 2022, 38, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomach, P. The influence of the grinding media diameter on grinding efficiency in a vibratory ball mill. Materials 2024, 17, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankosa, M.J.; Adel, G.T.; Yoon, R.H. Effect of media size in stirred ball mill grinding of coal. Powder Technol. 1986, 49, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, B.; Jafari, M.; Parian, M.; Rosenkranz, J.; Chehreh Chelgani, S. Study on the impacts of media shapes on the performance of tumbling mills–A review. Miner. Eng. 2020, 157, 106490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnott, M.D.; Cleary, P.W.; Morrison, R.D. Is media shape important for grinding performance in stirred mills? Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigereyev, S.; Guryanov, G. New method for increase in product fineness in stirred mills. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2019, 19, 768–778. [Google Scholar]
- Baigereyev, S.; Guryanov, G.; Suleimenov, A.; Abdeyev, B.; Kim, V. New method for materials comminution using grinding balls. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. 2023, 17, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeev, B.; Baigereyev, S.; Guryanov, G. Generalized dynamic theory of a solid particle grinding by pulse-force compression with two non-deformable balls. PNRPU Mech. Bull. 2018, 4, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

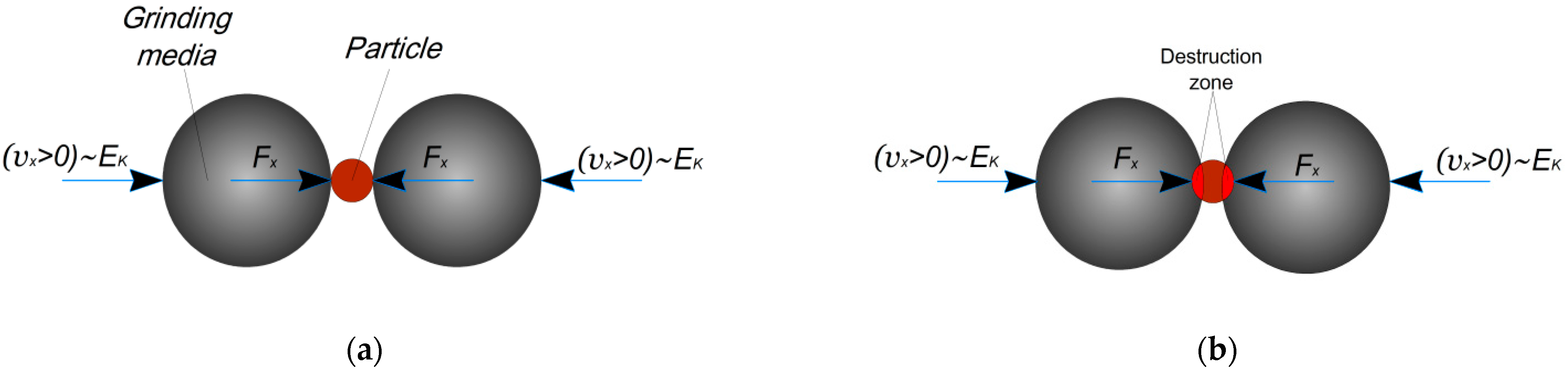





| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Mill parameters | ||
| Amplitude in horizontal direction | 4 mm | |
| Oscillation frequency in horizontal direction | 50 Hz | |
| Amplitude in vertical direction | 2 mm | |
| Oscillation frequency in vertical direction | 50 Hz | |
| Material parameters (sand) | ||
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.27 | |
| Elastic modulus | ||
| Initial size (diameter) of the particle | 100 µm | |
| Ultimate stress | 1.15 MPa | |
| Grinding media parameters | ||
| Grinding media density (steel) | ||
| Diameter of the grinding media | 10 mm | |
| Parameters | Case 1 | Case 2 |
|---|---|---|
| mm/s | mm/s | |
| µm | µm |
| Case | Description | Experimental Data | Theoretical Data | Difference, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximal Product Fineness | Maximal Processing Time | Maximal Product Fineness | |||
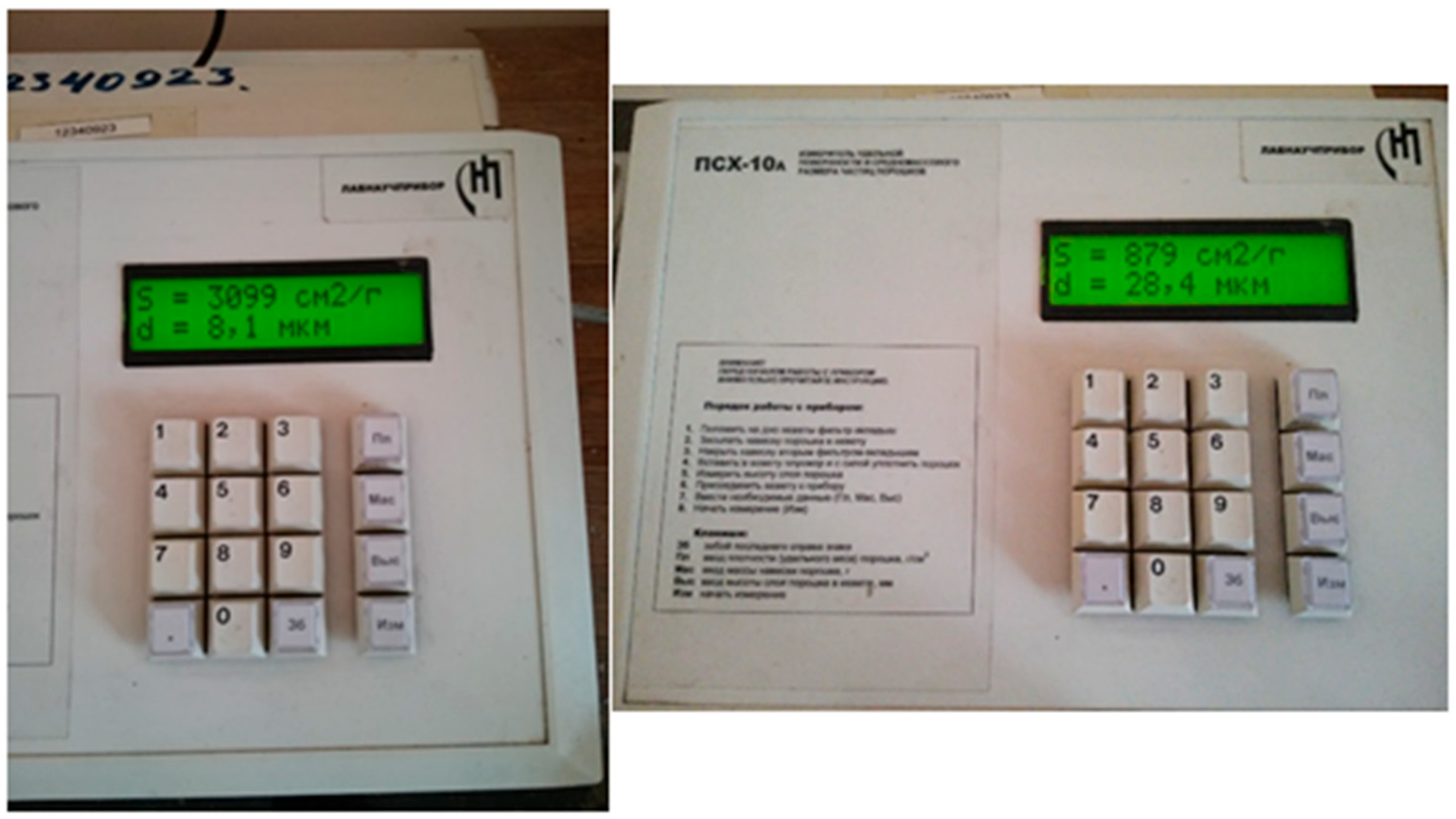
| 1 | Both of the unbalanced vibrators for the creation of the horizontal vibrational actions are activated; the vibrating table drive is activated | 8.1 µm | 12 | 7.3 µm | 10.96% |
| 2 | One of the unbalanced vibrators for the creation of the horizontal vibrational actions is activated, and the other one is not activated; the vibrating table drive is activated | 28.4 µm | 17 | 27.7 µm | 2.53% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baigereyev, S.; Guryanov, G.; Suleimenov, A.; Abdeyev, B. New Approach to Effective Dry Grinding of Materials by Controlling Grinding Media Actions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7713. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147713
Baigereyev S, Guryanov G, Suleimenov A, Abdeyev B. New Approach to Effective Dry Grinding of Materials by Controlling Grinding Media Actions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7713. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147713
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaigereyev, Samat, Georgiy Guryanov, Ansagan Suleimenov, and Boris Abdeyev. 2025. "New Approach to Effective Dry Grinding of Materials by Controlling Grinding Media Actions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7713. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147713
APA StyleBaigereyev, S., Guryanov, G., Suleimenov, A., & Abdeyev, B. (2025). New Approach to Effective Dry Grinding of Materials by Controlling Grinding Media Actions. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7713. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147713






