Machining Center Opportunistic Maintenance Strategy Using Improved Average Rank Method for Subsystem Reliability Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Reliability Evaluation for Machine Center Subsystems Using the Improved Average Rank Method
- Step 1:
- Use the average rank method to obtain the empirical distribution function.
- Step 2:
- Carry out parameter estimation and obtain the preliminary model.
- Step 3:
- Use the improved average rank method to obtain new rank increments and updated parameters, and obtain the revised model.
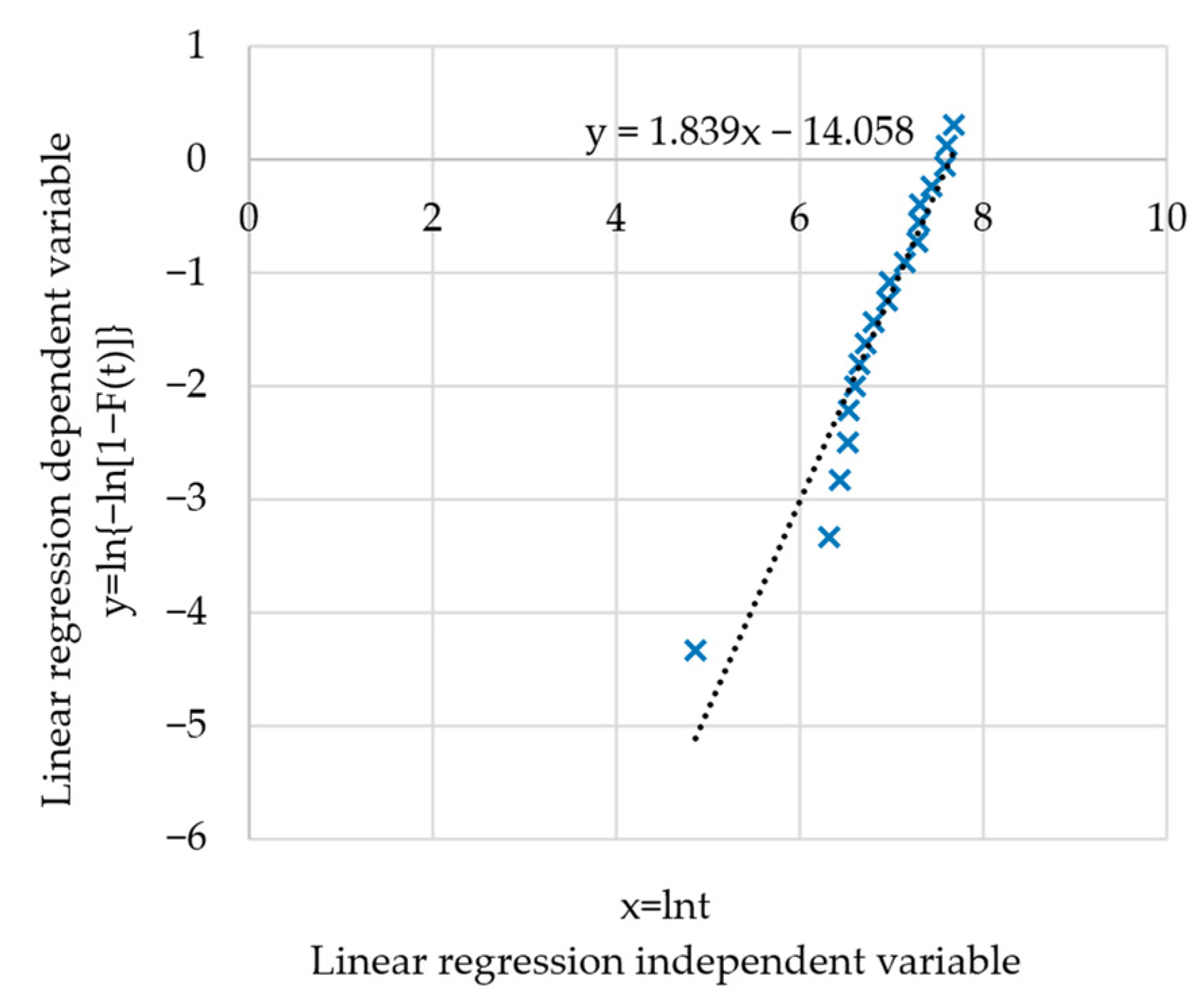
2.1. Average Rank Method
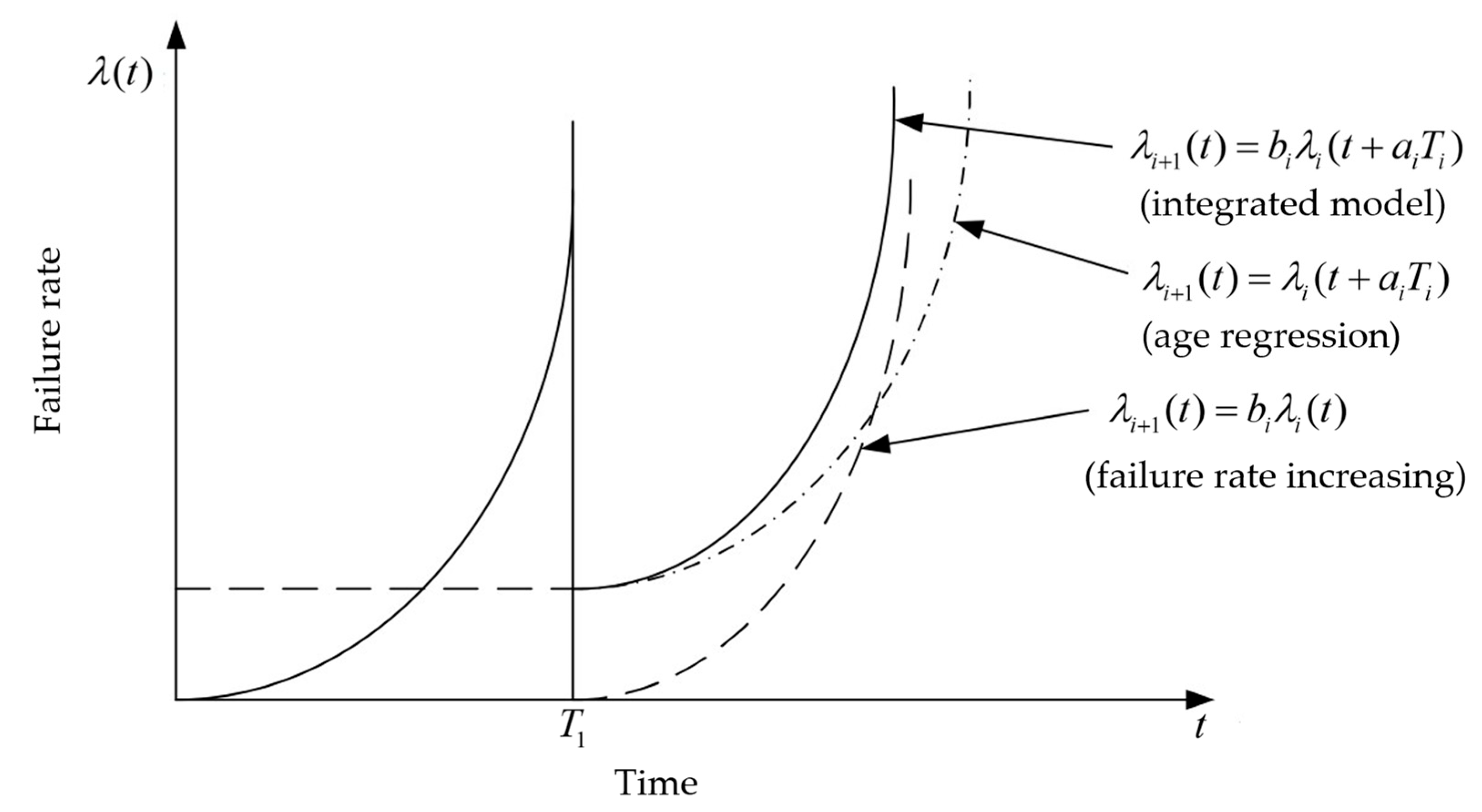
2.2. Reliability Model and Parameter Estimation for Machining Centers
2.3. Improved Average Rank Method
3. Maintenance Strategy
3.1. Subsystem Maintenance Planning
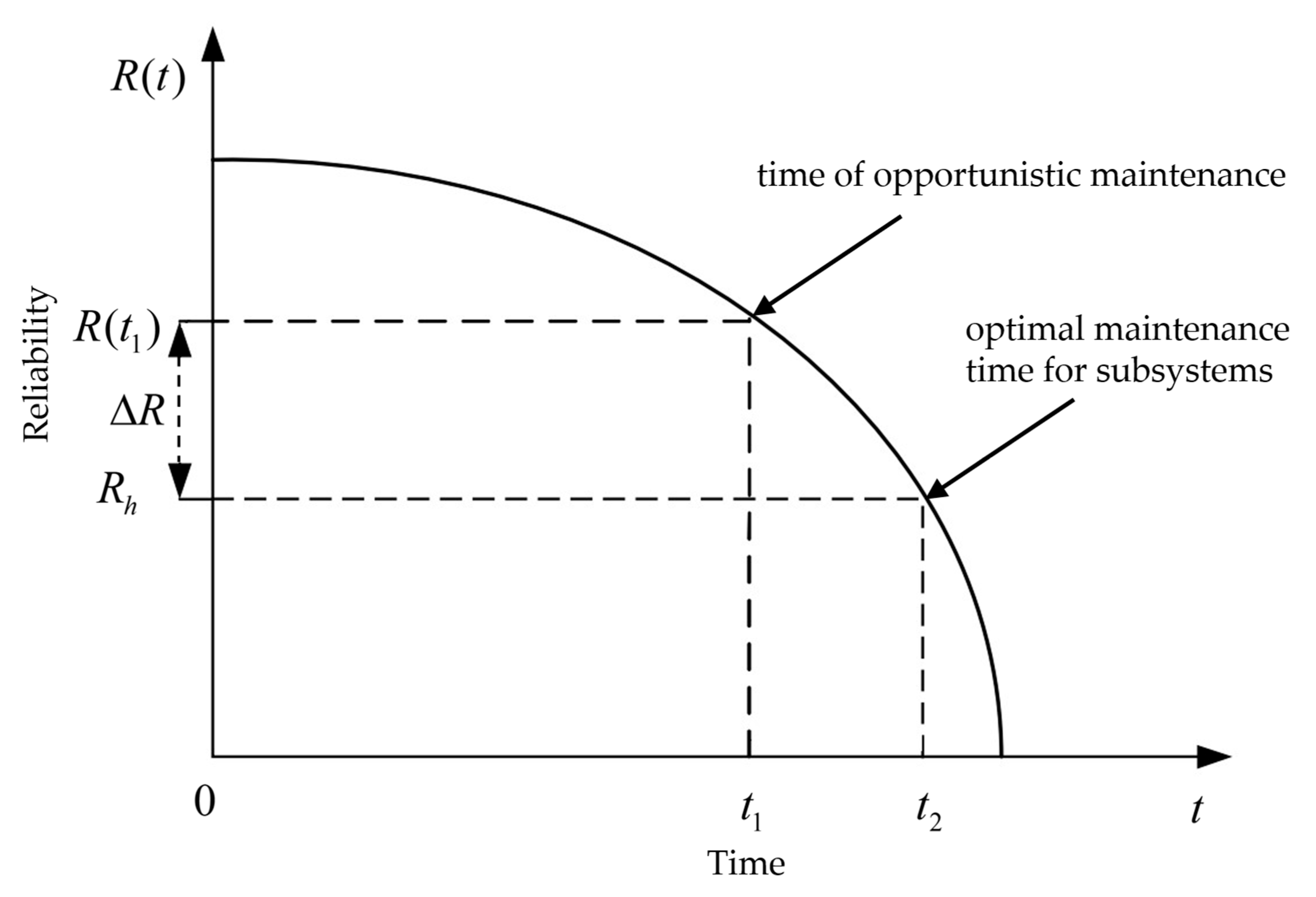
3.2. Opportunistic Maintenance
- is the opportunistic maintenance threshold;
- is the preventive maintenance threshold of the subsystem;
- is the number of shutdowns in the finite operation time of subsystem ;
- is the number of preventive replacements of subsystem ;
- is the number of maintenance cycles of subsystem ;
- is the number of preventive maintenances after the last replacement of subsystem ;
- is the operating time of subsystem in each preventive maintenance cycle, ;
- is the failure rate function of subsystem in the th maintenance cycle, ;
- is the minimum maintenance cost for subsystem in the finite operation time;
- is the minimum maintenance cost of subsystem ;
- is the preventive cost of subsystem in th cycle;
- is the preventive maintenance cost for the th maintenance cycle of subsystem (, meaning that will be counted from the beginning after each replacement);
- is the preventive replacement cost of subsystem ;
- is the indicator, with 1 for the th maintenance cycle of subsystem ending with preventive maintenance, and 2 for the th maintenance cycle of subsystem ending with preventive replacement;
- is the direct maintenance cost for subsystem in the finite operation time;
- is the direct maintenance cost generated by the machining center in the finite operation time;
- is the shutdown time caused by sudden failure of subsystem in the finite operation time;
- is the downtime loss cost caused by sudden failures of the machining center in the finite operation time;
- is the downtime of the th shutdown;
- is the total downtime loss cost caused by preventive maintenance and replacement of the machining center in the finite operation time;
- is the total downtime loss cost of the machining center;
- is the failure risk cost of subsystem in the finite operation time;
- is the failure risk cost of the machining center in the finite operation time;
- is the penalty cost for subsystem due to opportunistic maintenance in the finite operation time;
- is the penalty cost of the machining center in the finite operation time.
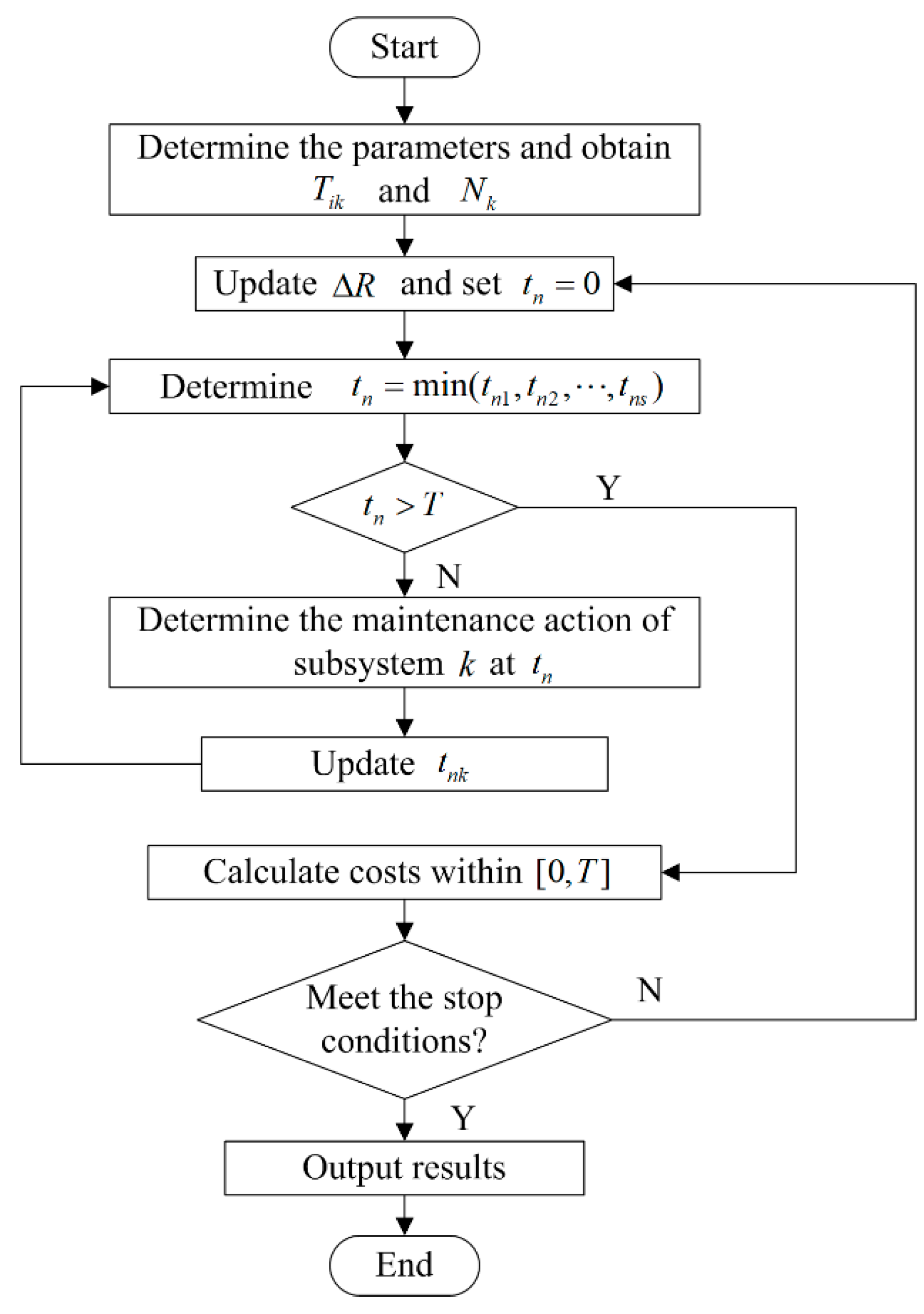
3.3. Solution of Opportunistic Maintenance Model
- Step 1:
- Determine the values of all parameters in the model.
- Step 2:
- Optimize the maintenance plan of the subsystems of the machining center to obtain the optimal maintenance interval and number of maintenance cycles for the subsystems.
- Step 3:
- Determine and record the time of the th shutdown for preventive maintenance or replacement of the machining center. When , .
- Step 4:
- Determine the maintenance action of subsystem at . When , the subsystem does not require preventive maintenance or replacement action at ; when , at the same time and opportunistic maintenance will be performed on subsystem , where is the maintenance cycle number of subsystem at . The maintenance cycle is increased by 1 after preventive maintenance; when , at the same time and an opportunistic preventive replacement will be performed for the subsystem . Then, , and maintenance cycle counting will be restarted.
- Step 5:
- Solve the corresponding time of the th shutdown for preventive maintenance or replacement of the machining center. , whereindicates that subsystem did not undergo preventive maintenance or replacement at , indicates that subsystem performed preventive maintenance at , and indicates that subsystem performed preventive replacement at .
- Step 6:
- Repeat Step 3–Step 5 until .
- Step 7:
- Calculate costs within . Continuously update to minimize costs and record the best .
4. Numerical Example
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.B.; Yang, Z.J.; Cheng, D.B.; Liu, J.X.; Cai, Z.G.; Liu, Y.Z. A New Probability Prediction Method for Key Subsystems of Machining Center. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 411–414, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.T.; Sun, Z.L.; Ren, X.; Yang, Q. Real-Time Reliability Analysis and Optimal Distribution of the Reliability on Five-Axis Machining Center. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 84–85, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Fan, J.-W.; Li, Y. Reliability evaluation method and algorithm for electromechanical product. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2014, 21, 3753–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Guo, J.; Han, W.; Gao, S.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Z. Reliability modeling for failure correlations to a CNC lathe subsystem based on Pagerank Algorithm. Qual. Eng. 2023, 36, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Peng, H.; Yang, Y. Reliability Modeling and Evaluation Method of CNC Grinding Machine Tool. Appl. Sci. 2018, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkash, S.; Tewari, P. Performability analysis for the SPVC line system of leaf spring production plant using probabilistic approach. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2024, 30, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Brownlow, J.D.; Thompson, J.; Brooks, R.G. Bayesian estimation of the mean time between failures of subsystems with different causes using interval-censored system maintenance data. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2024, 40, 3867–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Chattopadhyaya, S. Reliability analysis and failure rate evaluation for critical subsystems of the dragline. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouman, M.A.; Saber, A.S.; Shaat, M.K.; El-Sayed, A.; Torkey, H. A Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Reliability Evaluation of the Reactor Protection System. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 6797–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Z. A machine learning methodology for reliability evaluation of complex chemical production systems. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20374–20384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuryanto, R.; Nurcahyo, R.; Farizal, F. Using Failure And Repair Data For Performance Evaluation of NPK Fertilizer Production Line. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications (ICIEA), Bangkok, Thailand, 16–21 April 2020; pp. 404–408. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, S.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Song, Q. Application of the average rank time method in parameter estimation for fixed-time censoring experiment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechatronics Engineering and Computing Technology (ICMECT), Shanghai, China, 9–10 April 2014; pp. 4146–4150. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Z. Reliability evaluation of protective device based on improved average rank order method. Power Syst. Prot. Control. 2020, 48, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; He, Y.; Lin, Q.; Lu, J. Operational risk-based opportunistic maintenance approach for multi-station manufacturing systems considering machine performance–workpiece quality co-effect. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 262, 111191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, S.; Chen, B.; Chen, F.; An, Y.; Ran, Y.; Zhang, G. Joint optimization of imperfect preventive opportunistic maintenance and spare parts inventory for multi-unit systems considering spare parts reuse. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 261, 111162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, D.-H.; Do, P.; Iung, B. Multi-level opportunistic predictive maintenance for multi-component systems with economic dependence and assembly/disassembly impacts. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 217, 108055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, W. Optimizing opportunistic preventive maintenance strategy for multi-unit system of CNC lathe. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Maintenance Scheduling of Transmission Bays Considering Selective Opportunistic Maintenance Strategy. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Green Energy and Applications (ICGEA), Taiyuan, China, 16–18 March 2019; pp. 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ran, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, F.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, G. Opportunistic maintenance strategy optimization considering imperfect maintenance under hybrid unit-level maintenance strategy. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 185, 109624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, X.; Sun, J. Reliability modeling and maintenance optimization for the two-unit system with preset self-repairing mechanism. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2019, 234, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, H. A preventive, opportunistic maintenance strategy for the catenary system of high-speed railways based on reliability. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2019, 234, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Wu, L. Opportunistic maintenance optimisation for offshore wind farm with considering random wind speed. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 62, 1862–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Rui, X.; Li, S.; Hu, X. An opportunistic maintenance strategy for offshore wind turbine based on accessibility evaluation. Wind. Eng. 2019, 44, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shi, H. Random risk assessment model and risk-based maintenance decisions for natural gas pipelines. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2025, 95, 105591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mahmoodian, M.; Khaloo, A.; Sun, Z. Risk-Cost Optimized Maintenance Strategy for Steel Bridge Subjected to Deterioration. Sustainability 2021, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.F.; Chattopadhyay, G.; Gunawan, I. Development of a Risk-Based Maintenance (RBM) Strategy for Sewerage Pumping Station Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), Macao, 15–18 December 2019; pp. 455–458. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiee, M.; Labib, A.; Maiti, J.; Starr, A. Maintenance strategy selection for multi-component systems using a combined analytic network process and cost-risk criticality model. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2019, 233, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z. Tristage Bargaining Dynamic Game-Based Preventive Maintenance for Electric Multiple Unit. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 3832123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Feng, C.; Chen, W.; Guo, C. Risk-Based Coordination of Maintenance Scheduling and Unit Commitment in Power Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58788–58799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, Z.; Luo, W.; Ma, T.; Huang, H.; Garg, A. A Research on the Combined Maintenance Strategy for Production Line Equipment Based on Mixed Failure Rate. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8856279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.M.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mohammed, A.; Fakhruldeen, H.F.; Hanoon, T.M.; Khurramov, A.; Khalaf, D.H.; Algburi, S. Sustainable strategies for preventive maintenance and replacement in photovoltaic power systems: Enhancing reliability, efficiency, and system economy. Unconv. Resour. 2025, 6, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Subsystem | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Main transmission subsystem | T |
| Feed subsystem | F |
| Hydraulic subsystem | H |
| Lubricating subsystem | L |
| Numerical control subsystem | NC |
| Electrical subsystem | E |
| Cooling subsystem | C |
| Auxiliary subsystem | A |
| Automatic tool changer | ATC |
| Servo subsystem | S |
| TBF/h | Sub- System | TBF/h | Sub- System | TBF/h | Sub- System | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.53 | E | 21 | 730.3 | NC | 41 | 1103.12 | NC |
| 2 | 19.18 | S | 22 | 734.14 | H | 42 | 1129.21 | T |
| 3 | 56.77 | C | 23 | 735.67 | F | 43 | 1139.95 | NC |
| 4 | 92.82 | E | 24 | 742.58 | T | 44 | 1267.29 | H |
| 5 | 129.64 | H | 25 | 772.49 | H | 45 | 1377.75 | F |
| 6 | 331.01 | ATC | 26 | 790.52 | E | 46 | 1378.52 | A |
| 7 | 366.68 | C | 27 | 794.74 | L | 47 | 1451.4 | H |
| 8 | 380.49 | T | 28 | 808.55 | E | 48 | 1472.49 | H |
| 9 | 403.51 | C | 29 | 827.73 | H | 49 | 1488.22 | H |
| 10 | 421.15 | C | 30 | 846.14 | F | 50 | 1544.99 | F |
| 11 | 459.89 | E | 31 | 864.55 | F | 51 | 1693.81 | H |
| 12 | 477.92 | A | 32 | 864.93 | C | 52 | 1877.15 | NC |
| 13 | 515.12 | F | 33 | 882.96 | E | 53 | 1950.79 | H |
| 14 | 551.56 | H | 34 | 882.96 | L | 54 | 1986.85 | H |
| 15 | 610.63 | C | 35 | 901.37 | H | 55 | 2151.01 | H |
| 16 | 623.67 | H | 36 | 932.82 | E | 56 | 2206.25 | E |
| 17 | 625.21 | C | 37 | 991.89 | C | 57 | 2650.79 | T |
| 18 | 680.44 | H | 38 | 1029.48 | C | 58 | 2717.15 | L |
| 19 | 680.44 | F | 39 | 1043.29 | H | |||
| 20 | 684.27 | H | 40 | 1067.45 | H |
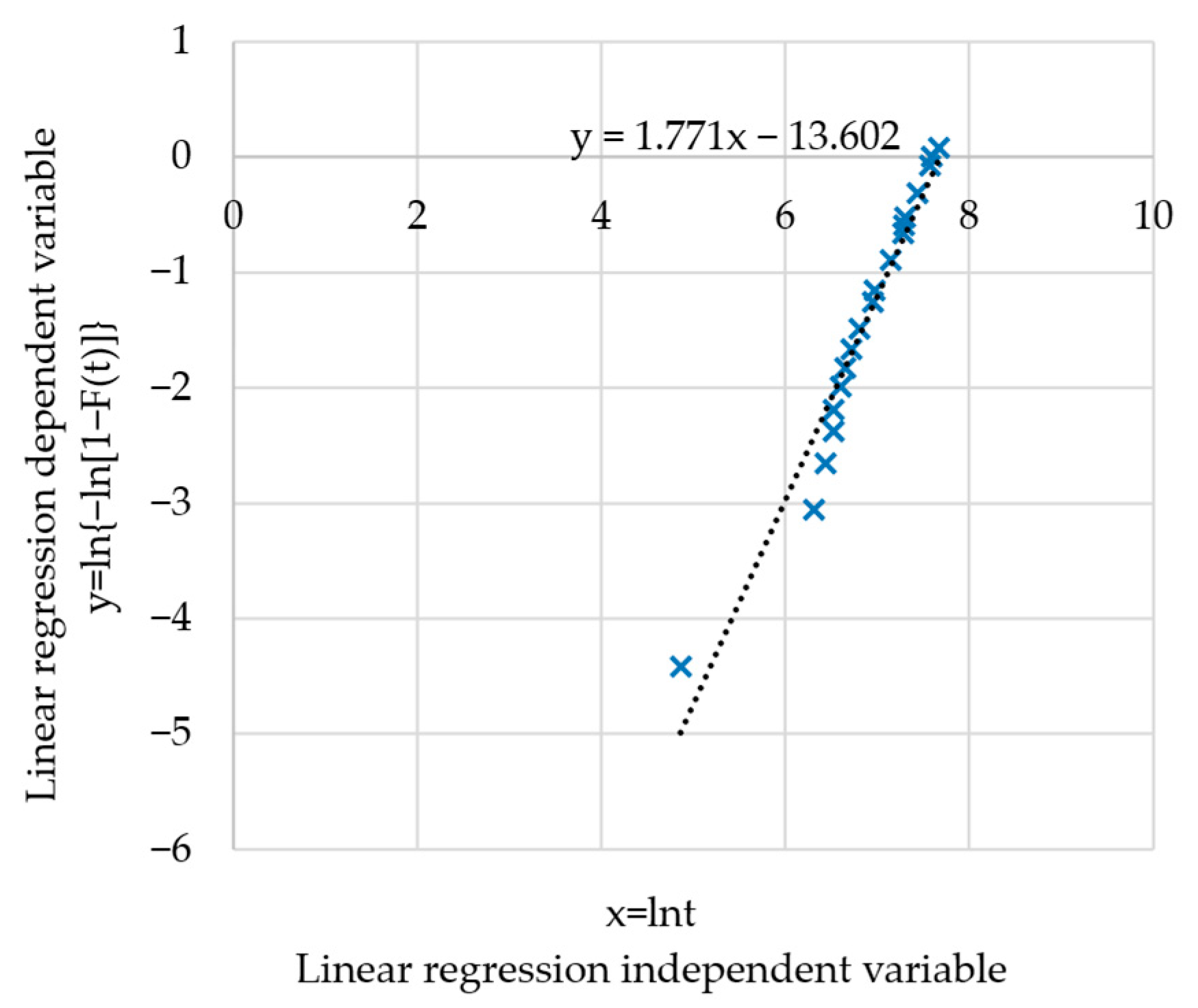
| 5 | 1 | 129.64 | 1.073 | 0.013 |
| 14 | 2 | 551.56 | 2.332 | 0.035 |
| 16 | 3 | 623.67 | 3.620 | 0.057 |
| 18 | 4 | 680.44 | 4.938 | 0.079 |
| 20 | 5 | 684.27 | 6.290 | 0.103 |
| 22 | 6 | 734.14 | 7.677 | 0.126 |
| 25 | 7 | 772.49 | 9.144 | 0.151 |
| 29 | 8 | 827.73 | 10.752 | 0.179 |
| 35 | 9 | 901.37 | 12.682 | 0.212 |
| 39 | 10 | 1043.29 | 14.887 | 0.250 |
| 40 | 11 | 1067.45 | 17.093 | 0.288 |
| 44 | 12 | 1267.29 | 19.712 | 0.332 |
| 47 | 13 | 1451.40 | 22.734 | 0.384 |
| 48 | 14 | 1472.49 | 25.756 | 0.436 |
| 49 | 15 | 1488.22 | 28.779 | 0.488 |
| 51 | 16 | 1693.81 | 32.137 | 0.545 |
| 53 | 17 | 1950.79 | 35.974 | 0.611 |
| 54 | 18 | 1986.85 | 39.812 | 0.677 |
| 55 | 19 | 2151.01 | 43.649 | 0.742 |
| 5 | 1 | 129.64 | 0.024 | 1.024 | 0.012 |
| 14 | 2 | 551.56 | 0.953 | 2.977 | 0.046 |
| 16 | 3 | 623.67 | 0.269 | 4.245 | 0.068 |
| 18 | 4 | 680.44 | 0.245 | 5.490 | 0.089 |
| 20 | 5 | 684.27 | 0.018 | 6.508 | 0.106 |
| 22 | 6 | 734.14 | 0.262 | 7.770 | 0.128 |
| 25 | 7 | 772.49 | 0.237 | 9.006 | 0.149 |
| 29 | 8 | 827.73 | 0.417 | 10.423 | 0.173 |
| 35 | 9 | 901.37 | 0.732 | 12.156 | 0.203 |
| 39 | 10 | 1043.29 | 1.682 | 14.838 | 0.249 |
| 40 | 11 | 1067.45 | 0.295 | 16.133 | 0.271 |
| 44 | 12 | 1267.29 | 2.818 | 19.951 | 0.336 |
| 47 | 13 | 1451.4 | 2.870 | 23.821 | 0.403 |
| 48 | 14 | 1472.49 | 0.328 | 25.148 | 0.425 |
| 49 | 15 | 1488.22 | 0.244 | 26.393 | 0.447 |
| 51 | 16 | 1693.81 | 3.281 | 30.673 | 0.520 |
| 53 | 17 | 1950.79 | 4.080 | 35.754 | 0.607 |
| 54 | 18 | 1986.85 | 0.543 | 37.297 | 0.634 |
| 55 | 19 | 2151.01 | 0.585 | 38.882 | 0.661 |
| Subsystem Symbol | ||
|---|---|---|
| T | 3826.095 | 1.875 |
| F | 2168.142 | 2.6717 |
| H | 2161.748 | 1.7714 |
| L | 2816.645 | 2.6985 |
| NC | 2672.429 | 2.9124 |
| E | 271,521.5 | 0.3857 |
| C | 6254.379 | 0.9874 |
| A | 5647.764 | 1.6973 |
| Cost Parameters | H | A | F | NC | T | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 550 | 850 | 405 | 450 | 1425 | 180 | |
| 380 | 380 | 380 | 380 | 380 | 380 | |
| 30 | 25 | 55 | 65 | 35 | 30 | |
| 10,500 | 6375 | 3050 | 6800 | 15,500 | 3500 | |
| 3.12 | 3.85 | 6.94 | 2.79 | 2.34 | 3 | |
| 6 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 5 | |
| 1.267 | 2.533 | 1.52 | 0.95 | 1.9 | 1.9 | |
| 0.1 | 0.167 | 0.22 | 0.1625 | 0.175 | 0.15 | |
| 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | |
| 8170 | 4010 | 11,044 | 7126 | 12,404 | 5926 | |
| 15,000 | 13,500 | 16,000 | 15,500 | 15,600 | 14,000 |
|
Subsystem Symbols | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | 4 | 0.609 | 1455.009 | 1236.057 | 1049.594 | 896.7964 | |
| A | 4 | 0.497 | 4574.119 | 3890.057 | 3314.518 | 2843.579 | |
| F | 4 | 0.921 | 851.3723 | 726.153 | 607.5688 | 505.635 | |
| NC | 5 | 0.854 | 1428.052 | 1218.195 | 1019.239 | 848.0675 | 707.4946 |
| T | 5 | 0.72 | 2113.055 | 1793.646 | 1517.095 | 1289.705 | 1105.025 |
| L | 4 | 0.855 | 1417.086 | 1208.969 | 1011.509 | 841.5174 |
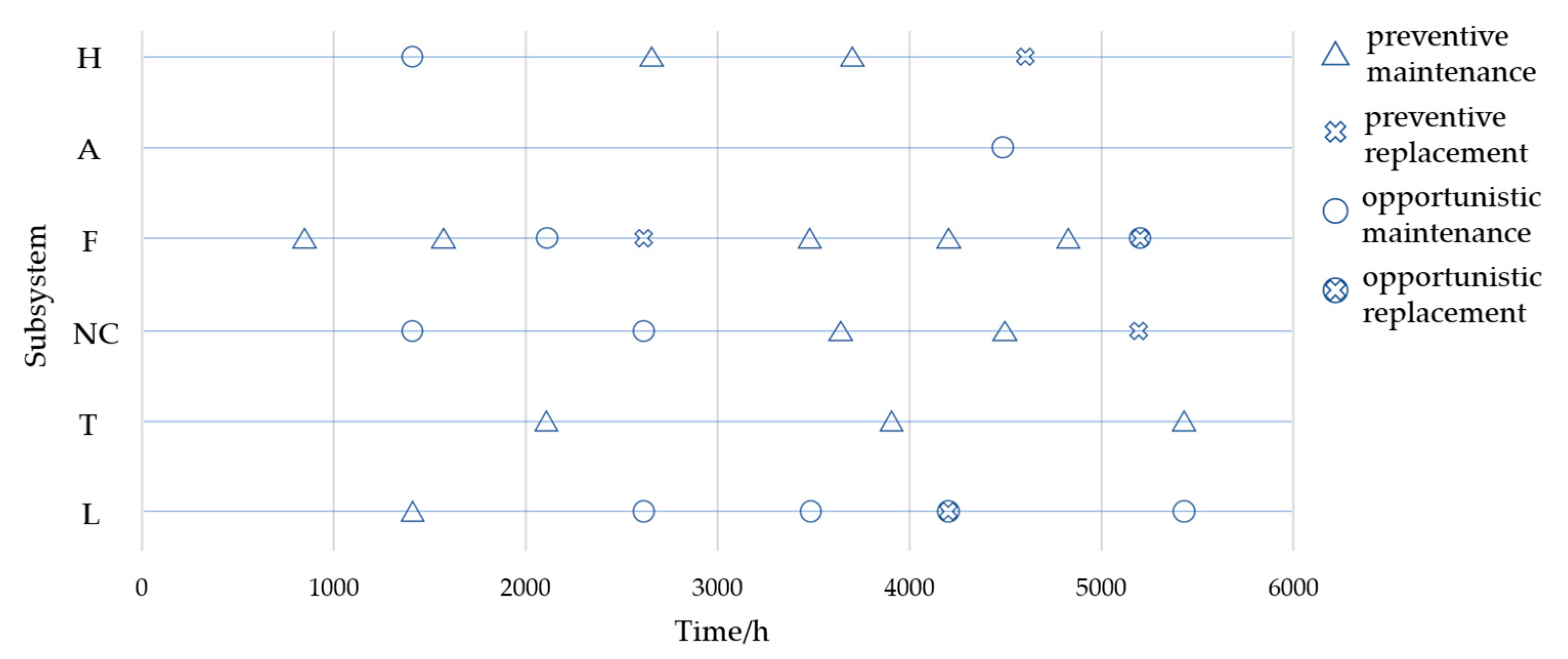
| Time/h | H | A | F | NC | T | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 851 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1417 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| 1579 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2113 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2621 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| 2655 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3479 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 3647 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3706 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3909 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 4208 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 4497 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4605 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4820 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5207 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 5428 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Strategy | Optimal Maintenance Strategy for Subsystems | Opportunistic Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | 108,257 | 100,899 |
| Number of preventive shutdowns | 26 | 16 |
| Preventive downtime | 69 h | 49 h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Song, M.; Wu, W.; Han, F. Machining Center Opportunistic Maintenance Strategy Using Improved Average Rank Method for Subsystem Reliability Modeling. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126944
Zhang Y, Song M, Wu W, Han F. Machining Center Opportunistic Maintenance Strategy Using Improved Average Rank Method for Subsystem Reliability Modeling. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126944
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yingzhi, Minqiao Song, Wei Wu, and Feng Han. 2025. "Machining Center Opportunistic Maintenance Strategy Using Improved Average Rank Method for Subsystem Reliability Modeling" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126944
APA StyleZhang, Y., Song, M., Wu, W., & Han, F. (2025). Machining Center Opportunistic Maintenance Strategy Using Improved Average Rank Method for Subsystem Reliability Modeling. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6944. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126944







