Relationship-Based Ambient Detection for Concrete Pouring Verification: Improving Detection Accuracy in Complex Construction Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Research Framework
2.2. Data Collection and Annotation
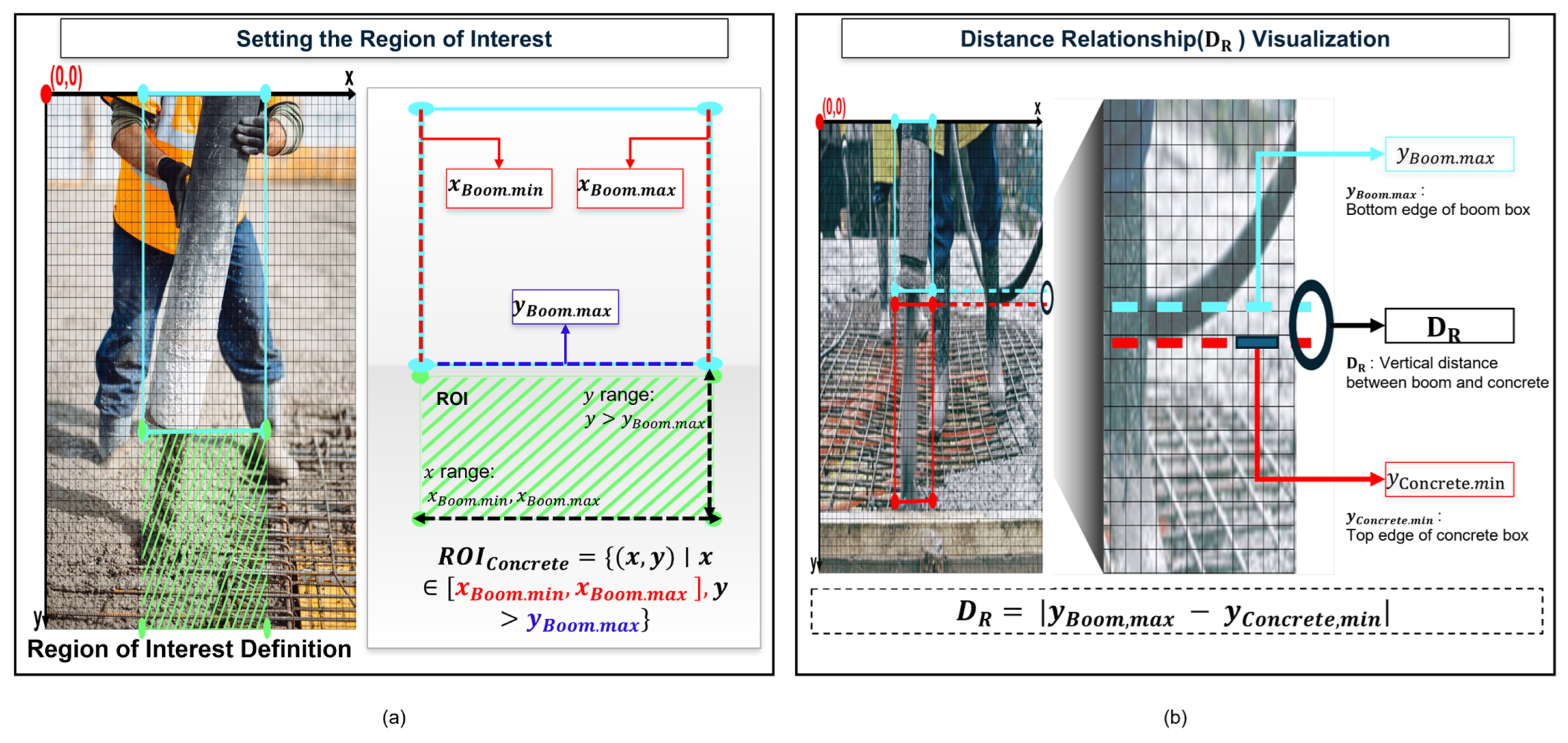
2.3. ROI Definition Using Boom Detection
2.4. Relationship-Based Weight Analysis
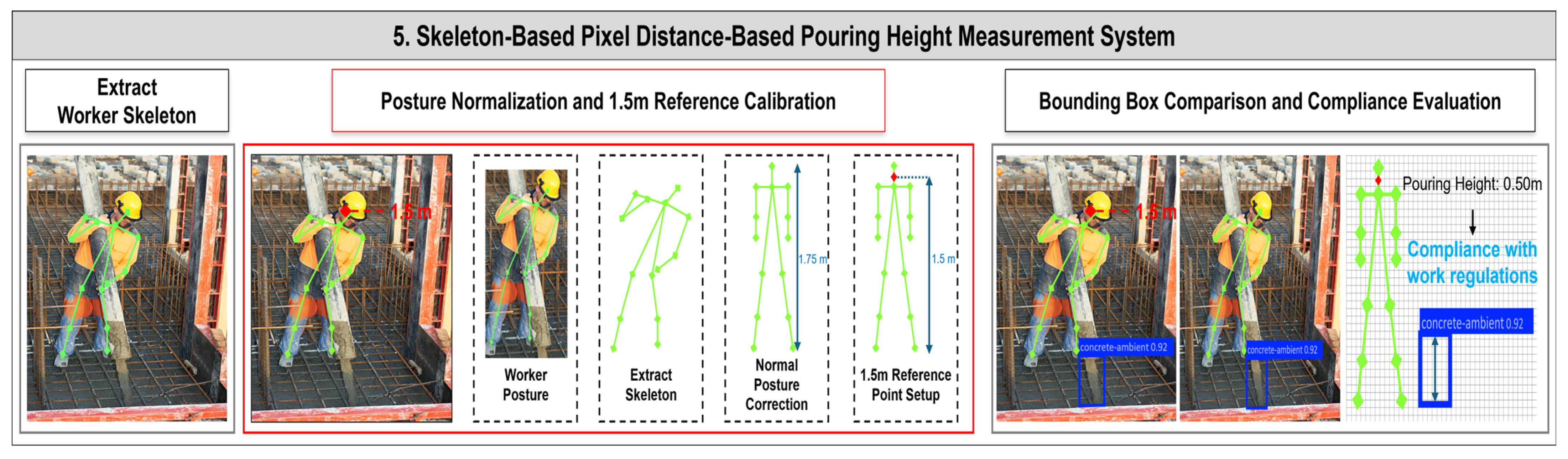
2.5. Pouring Height Measurement System
2.6. Model Training and Optimization
3. Results
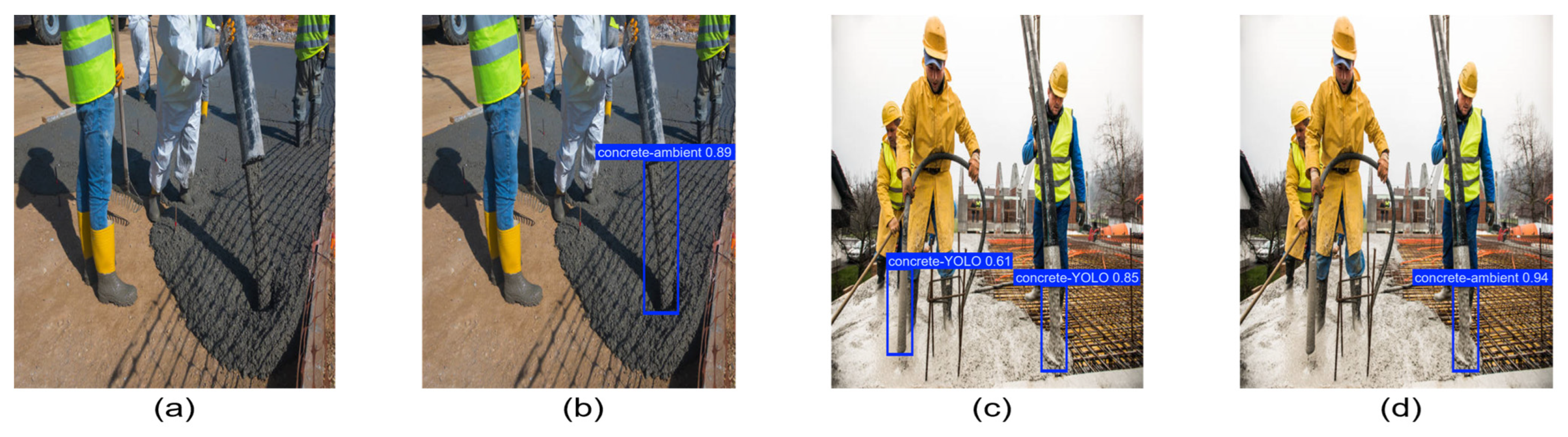
3.1. Comparative Performance Analysis
3.2. Qualitative Analysis and Statistical Significance Analysis
3.3. Ablation Study by Relationship Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Comprehesive Analysis of Object Recognition Performance
4.2. Contributions and Limitations
4.3. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, B.; Hwang, S.; Kim, H. The Feasibility of Information-Entropy-Based Behavioral Analysis for Detecting Environmental Barriers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Kim, H. Two-Step k-Means Clustering Based Information Entropy for Detecting Environmental Barriers Using Wearable Sensor. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H. Feasibility of DRNN for Identifying Built Environment Barriers to Walkability Using Wearable Sensor Data from Pedestrians’ Gait. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Cho, G.; Kim, H. Performance Analysis of Wearable Robotic Exoskeleton in Construction Tasks: Productivity and Motion Stability Assessment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, M.; Hwang, S. Small Object Detection (SOD) System for Comprehensive Construction Site Safety Monitoring. Autom. Constr. 2023, 156, 105103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, J.; Shen, F. Automated Construction Site Monitoring Based on Improved YOLOv8-Seg Instance Segmentation Algorithm. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 139082–139096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, B.; Wong, J.K.-W.; Fini, A.A.F.; Smith, P. Computer Vision-Based Interior Construction Progress Monitoring: A Literature Review and Future Research Directions. Autom. Constr. 2021, 127, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Meng, Q.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, X. Review on the Developments of Structure, Construction Automation, and Monitoring of Intelligent Construction. Buildings 2022, 12, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schutter, G.; Bartos, P.J.M.; Domone, P.J.G.; Gibbs, J. Self Compacting Concrete; Whittles Publishing: Dunbeath, UK, 2008; ISBN 978-1904445302. Available online: http://ndl.ethernet.edu.et/bitstream/123456789/75013/1/89.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Howes, R.; Hadi, M.N.; South, W. Concrete Strength Reduction Due to over Compaction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Lin, L.; Chen, K.; Antwi-Afari, M.F.; Chen, L. Digital Technology for Quality Management in Construction: A Review and Future Research Directions. Dev. Built Environ. 2022, 12, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Onstein, E.; La Rosa, A.D. A Semantic Approach for Automated Rule Compliance Checking in Construction Industry. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 129648–129660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieyan, A.; Sarvari, H.; Chan, D.W. Identifying and Evaluating the Essential Factors Affecting the Incidence of Site Accidents Caused by Human Errors in Industrial Parks Construction Projects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wilde, A.; Menzel, K.; Sheikh, M.Z.; Kuznetsov, B. Computer Vision for Construction Progress Monitoring: A Real-Time Object Detection Approach. In Proceedings of the Working Conference on Virtual Enterprises; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 660–672. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Huang, M.M.; Jiang, S.; Wang, C.; Wu, M. Unmanned Aircraft Path Planning for Construction Safety Inspections. Autom. Constr. 2023, 154, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussamadin, R.; Jansson, G.; Mukkavaara, J. Digital Quality Control System—A Tool for Reliable on-Site Inspection and Documentation. Buildings 2023, 13, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Radanovic, M.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.; Fang, Y.; Khoshelham, K.; Palaniswami, M.; Ngo, T. Real-Time Monitoring of Construction Sites: Sensors, Methods, and Applications. Autom. Constr. 2022, 136, 104099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Chen, F. An Effective Monitoring Method of Dynamic Compaction Construction Quality Based on Time Series Modeling. Measurement 2024, 224, 113930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.A.S.; Neto, A.P.D.F.; Fernandino, R.M.A.; Carvalho, R.F.; Fernandes, A.L.; Guimaraes, F.G. Automated Monitoring of Construction Sites of Electric Power Substations Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19195–19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanti, M.Z.; Cho, C.-S.; de Soto, B.G.; Byon, Y.-J.; Yeun, C.Y.; Kim, T.Y. Real-Time Monitoring of Work-at-Height Safety Hazards in Construction Sites Using Drones and Deep Learning. J. Saf. Res. 2022, 83, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.W.; Bameri, F.; Ahmadian Fard Fini, A.; Maghrebi, M. Tracking Indoor Construction Progress by Deep-Learning-Based Analysis of Site Surveillance Video. Constr. Innov. 2025, 25, 461–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Fan, Q.; Shao, Y. Deep Learning-Based Rebar Detection and Instance Segmentation in Images. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2025, 65, 103224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, H. Time-Series Image-Based Automated Monitoring Framework for Visible Facilities: Focusing on Installation and Retention Period. Sensors 2025, 25, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Hong, S.; Choi, B.; Ham, Y.; Kim, H. Integrating Text Parsing and Object Detection for Automated Monitoring of Finishing Works in Construction Projects. Autom. Constr. 2025, 174, 106139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Miao, Y.; Zheng, J. A YOLO-Based Intelligent Detection Algorithm for Risk Assess-Ment of Construction Sites. J. Intell. Constr. 2024, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, R.; Hu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, G. Multi-Task Intelligent Monitoring of Construction Safety Based on Computer Vision. Buildings 2024, 14, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tao, M. FE-YOLO: A Lightweight Model for Construction Waste Detection Based on Improved YOLOv8 Model. Buildings 2024, 14, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, J.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y. Detection Method for Safety Helmet Wearing on Construction Sites Based on UAV Images and YOLOv8. Buildings 2025, 15, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Abisado, M.B. Lightweight Construction Safety Behavior Detection Model Based on Improved YOLOv8. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.; Hoque, R. Construction Site Risk Reduction via YOLOv8: Detection of PPE, Masks, and Heavy Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Computing, Applications and Systems (COMPAS), Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh, 25–26 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Seth, Y.; Sivagami, M. Enhanced YOLOv8 Object Detection Model for Construction Worker Safety Using Image Transformations. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 10582–10594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Jain, A.; Sharma, V.; Girdhar, P. PPE Detection for Construction Site Safety Leveraging YOLOv8. 2024. SSRN 4923318, 2024. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=4923318 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Alzubi, K.M.; Alaloul, W.S.; Malkawi, A.B.; Al Salaheen, M.; Qureshi, A.H.; Musarat, M.A. Automated Monitoring Technologies and Construction Productivity Enhancement: Building Projects Case. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 102042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarat, M.A.; Khan, A.M.; Alaloul, W.S.; Blas, N.; Ayub, S. Automated Monitoring Innovations for Efficient and Safe Construction Practices. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, I.; Asadi, K.; Ramshankar, H.; Han, K.; Albert, A. Real-Time Vision-Based Worker Localization & Hazard Detection for Construction. Autom. Constr. 2021, 121, 103448. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W. Construction of Interactive Construction Progress and Quality Monitoring System Based on Image Processing. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Telecommunications and Power Electronics (TELEPE), Frankfurt, Germany, 29–31 May 2024; pp. 601–607. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.-W.; Kang, K.-S.; Son, B.-S.; Ryu, H.-G. Extraction of Workers and Heavy Equipment and Muliti-Object Tracking Using Surveillance System in Construction Sites. J. Korea Inst. Build. Constr. 2021, 21, 397–408. [Google Scholar]
- Son, H.; Kim, C. Integrated Worker Detection and Tracking for the Safe Operation of Construction Machinery. Autom. Constr. 2021, 126, 103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, D.; Zhang, S.; Su, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, J. GSO-YOLO: Global Stability Optimization YOLO for Construction Site Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.00906. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.00906 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Lv, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Guo, N. Road Scene Multi-Object Detection Algorithm Based on CMS-YOLO. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 121190–121201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X. Multi-Object Detection Method in Construction Machinery Swarm Operations Based on the Improved YOLOv4 Model. Sensors 2022, 22, 7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhou, X.; Shi, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, G. GeoIoU-SEA-YOLO: An Advanced Model for Detecting Unsafe Behaviors on Construction Sites. Sensors 2025, 25, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. YOLOv11: An Overview of the Key Architectural Enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar]
- Terven, J.; Córdova-Esparza, D.-M.; Romero-González, J.-A. A Comprehensive Review of Yolo Architectures in Computer Vision: From Yolov1 to Yolov8 and Yolo-Nas. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1680–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, C.; Chang, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, X.; Sham, C.-W. A More Compact Object Detector Head Network with Feature Enhancement and Relational Reasoning. Neurocomputing 2022, 499, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, H. Object Detection with a Dynamic Interactive Network Based on Relational Graph Routing. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 165, 112119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, D.; Puneeth, B.; Venkatesh, K.S. Ambiguous Boundary Uncertainty Reduction in Single Stage Detector Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Machine Intelligence (CVMI), Prayagraj, India, 19–20 October 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mekled, A.S.; Abdennadher, S.; Shehata, O.M. Performance Evaluation of YOLO Models in Varying Conditions: A Study on Object Detection and Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Computer and Applications (ICCA), Cairo, Egypt, 17–19 December 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, G.; Zhou, W.; Liu, M.; Xu, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Ju, Y. An Empirical Study of the Convolution Neural Networks Based Detection on Object with Ambiguous Boundary in Remote Sensing Imagery—A Case of Potential Loess Landslide. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ren, J. MFL-YOLO: An Object Detection Model for Damaged Traffic Signs. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.06750. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.06750 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Lin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y. YOLO-DA: An Efficient YOLO-Based Detector for Remote Sensing Object Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 6008705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-Y.; Lee, M.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Lee, T.-S. Yolo-Ore: A Deep Learning-Aided Object Recognition Approach for Radar Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 72, 5715–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Cao, G.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F. ViT-YOLO: Transformer-Based YOLO for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2799–2808. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Bak, J.; Park, S. Small and Overlapping Worker Detection at Construction Sites. Autom. Constr. 2023, 151, 104856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouardirhi, Z.; Mahmoudi, S.A.; Zbakh, M. Enhancing Object Detection in Smart Video Surveillance: A Survey of Occlusion-Handling Approaches. Electronics 2024, 13, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yu, X.; Xiong, S. Robust Skeleton-Based AI for Automatic Multi-Person Fall Detection on Construction Sites with Occlusions. Autom. Constr. 2025, 175, 106216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C. Head-Integrated Detecting Method for Workers under Complex Construction Scenarios. Buildings 2024, 14, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, X.; Cai, Y.; Xiao, G. Learning a Layout Transfer Network for Context Aware Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 4209–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, C.; Xie, H.; Zhu, M.; Tie, M.; Chen, J. Global Context Aware RCNN for Object Detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 11627–11639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ren, H.; Ye, X.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, H.; Nan, Y.; Sun, M.; Ren, X.; Huo, H. Object Detection from UAV Thermal Infrared Images and Videos Using YOLO Models. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, C.; Chen, A.P.S.; Christanto, H.J. Recognizing Similar Musical Instruments with YOLO Models. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-C.; Wang, C.-J.; Wen, C.-K.; Tzou, S.-J. Multi-Person Pose Estimation Using Thermal Images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 174964–174971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H. Lightweight Open Pose Based Body Posture Estimation for Badminton Players. For. Chem. Rev. 2022, 339–350. Available online: http://forestchemicalsreview.com/index.php/JFCR/article/view/923 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- OpenPose’s Evaluation in The Video Traditional Martial Arts Presentation. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8905243 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Wang, X.; Han, C.; Huang, L.; Nie, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Li, M. AG-Yolo: Attention-Guided Yolo for Efficient Remote Sensing Oriented Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ye, L. Enhanced Semantic Feature Pyramid Network for Small Object Detection. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2023, 113, 116919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, X.; Chaturvedi, K.; Braytee, A.; Li, J.; Prasad, M. Detecting Human Falls in Poor Lighting: Object Detection and Tracking Approach for Indoor Safety. Electronics 2023, 12, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, B.; Ahmadian Fard Fini, A.; Wong, J.K.W.; Smith, P. A Deep Learning-Based Approach to Facilitate the as-Built State Recognition of Indoor Construction Works. Constr. Innov. 2024, 24, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Hashmi, K.A.; Pagani, A.; Liwicki, M.; Stricker, D.; Afzal, M.Z. Survey and Performance Analysis of Deep Learning Based Object Detection in Challenging Environments. Sensors 2021, 21, 5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afif, M.; Said, Y.; Ayachi, R.; Hleili, M. An End-to-End Object Detection System in Indoor Environments Using Lightweight Neural Network. Trait. Signal 2024, 41, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, B.; Wong, J.K.W.; Fini, A.A.F.; Smith, P.; Thengane, V. Deep Learning-Based Computer Vision in Project Management: Automating Indoor Construction Progress Monitoring. Proj. Leadersh. Soc. 2024, 5, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjepandić, J.; Sommer, M. Object Recognition Methods in a Built Environment. In DigiTwin: An Approach for Production Process Optimization in a Built Environment; Stjepandić, J., Sommer, M., Denkena, B., Eds.; Springer Series in Advanced Manufacturing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 103–134. ISBN 978-3-030-77538-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Peng, W.; Li, C. Accurate Detection of the Workers and Machinery in Construction Sites Considering the Occlusions. In International Conference on Neural Computing for Advanced Applications; Zhang, H., Ke, Y., Wu, Z., Hao, T., Zhang, Z., Meng, W., Mu, Y., Eds.; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2023; Volume 1869, pp. 546–560. ISBN 978-981-9958-43-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Peng, W.; Tian, C.; Li, C. A Vision-Based Approach for Detecting Occluded Objects in Construction Sites. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 10825–10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, L.; Zhang, G.K.; Wu, S. Using Context-Guided Data Augmentation, Lightweight CNN, and Proximity Detection Techniques to Improve Site Safety Monitoring under Occlusion Conditions. Saf. Sci. 2023, 158, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Seo, S. Automatic Detection of Construction Workers’ Helmet Wear Based on Lightweight Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qian, S.; Tan, C. Automated Bridge Crack Detection Method Based on Lightweight Vision Models. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 1639–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, S.; Luo, N.; Xu, M. A New High-Precision and Lightweight Detection Model for Illegal Construction Objects Based on Deep Learning. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2024, 29, 1002–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoph, B.; Cubuk, E.D.; Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.-Y.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning Data Augmentation Strategies for Object Detection. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12372, pp. 566–583. ISBN 978-3-030-58582-2. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Chen, C.; Xiao, B.; Seo, J. Vision-Based Detection Method for Construction Site Monitoring by Integrating Data Augmentation and Semisupervised Learning. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2024, 150, 04024027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, K.M.; Louis, J. Times-Series Data Augmentation and Deep Learning for Construction Equipment Activity Recognition. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2019, 42, 100944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Seong, J.; Jung, H.-J. Optimal Domain Adaptive Object Detection with Self-Training and Adversarial-Based Approach for Construction Site Monitoring. Autom. Constr. 2024, 158, 105244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, S. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Crack Detection. Autom. Constr. 2023, 153, 104939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, M.; Kim, T.; Lee, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, H. Domain Adaptation Through Weak and Self-Supervision for Small Object Segmentation in Construction Site Monitoring. SSRN 5200114, 2025. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=5200114 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Heslinga, F.G.; Ruis, F.; Ballan, L.; van Leeuwen, M.C.; Masini, B.; van Woerden, J.E.; den Hollander, R.J.; Berndsen, M.; Baan, J.; Dijk, J. Leveraging Temporal Context in Deep Learning Methodology for Small Object Detection. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence for Security and Defence Applications, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 17 October 2023; Volume 12742, pp. 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.-C.; Jang, H. A Study on the Web Building Assistant System Using GUI Object Detection and Large Language Model. In Proceedings of the Annual Symposium of KIPS 2024 (ASK 2024 Spring Conference), Pyeongchang, Republic of Korea, 23–25 May 2024; KIPS: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2024; pp. 830–833. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, H.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Guo, R. AutoRepo: A General Framework for Multimodal LLM-Based Automated Construction Reporting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, E.; Muley, S.; Wang, C. Automatic Construction Accident Report Analysis Using Large Language Models (LLMs). J. Intell. Constr. 2025, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, X. Applications of Natural Language Processing in Construction. Autom. Constr. 2022, 136, 104169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z. Natural Language Processing for Smart Construction: Current Status and Future Directions. Autom. Constr. 2022, 134, 104059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Number of Correctly Recognized Images | Accuracy (%) | F1-Score (%) | Misdetection Rate (%) | Complete Failure Rate (%) | Processing Time (ms/image) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yolov11 Object Detection | 188/232 | 81.03 | 89.52 | 6.03 | 12.93 | 45 |
| Ambient Detection | 216/232 | 93.10 | 96.43 | 1.72 | 5.17 | 65 |
| Category | Description | Number of Images |
|---|---|---|
| A | Both YOLOv11 and Ambient Detection succeeded | 180 |
| B | YOLOv11 succeeded, Ambient Detection failed | 8 |
| C | Ambient Detection succeeded, YOLOv11 failed | 36 |
| D | Both YOLOv11 and Ambient Detection failed | 8 |
| Total | 232 |
| Configuration | Detection Success | Success Rate (%) | Total Failures | Misdetections | Complete Failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 216/232 | 93.10 | 16 | 4 | 12 | |
| 206/232 | 88.79 | 26 | 6 | 20 | |
| 203/232 | 87.50 | 29 | 7 | 22 | |
| 187/232 | 80.60 | 45 | 11 | 34 | |
| only | 190/232 | 81.90 | 42 | 10 | 32 |
| only | 175/232 | 75.43 | 57 | 14 | 43 |
| only | 178/232 | 76.72 | 54 | 14 | 40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Kim, H. Relationship-Based Ambient Detection for Concrete Pouring Verification: Improving Detection Accuracy in Complex Construction Environments. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6499. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126499
Yang S, Kim H. Relationship-Based Ambient Detection for Concrete Pouring Verification: Improving Detection Accuracy in Complex Construction Environments. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6499. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126499
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Seungwon, and Hyunsoo Kim. 2025. "Relationship-Based Ambient Detection for Concrete Pouring Verification: Improving Detection Accuracy in Complex Construction Environments" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6499. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126499
APA StyleYang, S., & Kim, H. (2025). Relationship-Based Ambient Detection for Concrete Pouring Verification: Improving Detection Accuracy in Complex Construction Environments. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6499. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126499







