Abstract
Polyamines are essential biological compounds that play crucial roles in various physiological processes, including cardiovascular function. This study explored polyamine levels in peripheral blood cells and plasma from patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and chronic heart failure (CHF), aiming to assess their value as biomarkers for cardiac diseases. A total of 129 individuals participated, comprising healthy controls and patients diagnosed with AMI or CHF. Polyamine concentrations were measured and analysed alongside standard clinical and biochemical markers of cardiac diseases. The results showed distinct patterns of polyamine alteration in AMI patients; putrescine levels were reduced in mononuclear cells, while isoamylamine levels were elevated in erythrocytes and plasma. In contrast, CHF patients had consistently low levels of all measured polyamines in erythrocytes and plasma, accompanied by high isoamylamine levels. Statistical analyses revealed significant correlations between polyamine levels and clinical indicators such as left ventricular ejection fraction, diastolic blood pressure, and troponin. Discriminant function analysis effectively distinguished between the control, AMI, and CHF groups based on their polyamine profiles. These findings suggest that an altered polyamine metabolism is associated with cardiovascular disease and support the potential of blood polyamine profiling as a non-invasive diagnostic and monitoring tool. Further research is warranted.
1. Introduction
Polyamines are found in all living cells and play crucial roles in numerous biological functions in the organism. These biological compounds are synthesised endogenously: ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), the first enzyme in polyamine biosynthesis, converts ornithine into putrescine, which is subsequently metabolised into spermidine and spermine. Catabolic enzymes and membrane transport mechanisms regulate intracellular polyamine homeostasis [1].
Polyamines exert acute effects on the heart, modulating physiological properties such as chronotropism and inotropism via direct interaction with the rat [2] and human [3] cardiac β-adrenoceptor system and as mediators of cardiotonic agents [4,5,6], as demonstrated in experimental models and cultured human cardiomyocyte studies. Polyamines are also involved in mechanisms related to the cardioprotective effect of ischaemic preconditioning, as it is associated with an upregulation of ODC and an inhibition of spermidine/spermine acetyltransferase. Furthermore, it is abolished by inhibiting ODC activity [7]. In addition, spermine conferred cardiomyocyte protection when administered before ischaemia/reperfusion injury is induced [8,9], and spermidine also showed cardioprotection [10].
Polyamines have been linked to more than just protective influences on the heart. An increase in polyamine synthesis [11] or a decrease in polyamine catabolism has been implicated in cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial damage in response to several hormonal and trophic stimuli in experimental models [12,13,14,15,16]; some of the effects can be pharmacologically counteracted. In patients with chronic heart failure (CHF), elevated ODC activity detected in cardiac tissue is positively associated with left atrium dilation. However, cardiac polyamine levels are not related to clinical hypertrophy parameters such as septum and left ventricular wall size; on the contrary, spermidine has been positively correlated with cardiac output [17].
The positive relationship between spermidine and cardiac output aligns with the findings of epidemiological studies in which high spermidine intake has been associated with a cardioprotective effect [18,19]. In several models, spermidine supplementation produces cardioprotection and extends the lifespan in mice [10]. Lifespan enhancement was previously reported in various experimental models [20]. The proposed mechanisms include the stimulation of autophagy, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects [1], and improving the contractile function of cardiomyocytes [21].
Polyamine levels in cardiac tissue may be an independent biological marker of cardiac damage and function in humans. However, this method is not feasible in clinical settings, and it is more practical to search for biomarkers in peripheral blood. In this sense, plasma levels have revealed that a decrease in ornithine is associated with the protective mechanisms of remote ischaemic preconditioning, which protects the myocardium from ischaemia–reperfusion injury [22], which has been proposed as a biomarker of ischaemic cardiomyopathy [23]. In addition, serum polyamines have shown prognostic value in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and cardiovascular events [24].
Isoamylamine has been discovered in human cardiac tissue from patients with CHF [17]. In mammals, it has been reported that mouse kidneys express a specific decarboxylase of leucine-forming isoamylamine [25,26]. This primary amine acts as a metabolic intermediate in the degradation of leucine, is a by-product of microbial activity, and is found in fermented foods [27,28]. However, its sources and potential biological role in mammals are poorly understood.
In healthy individuals, the levels of polyamines in peripheral blood cells are more sensitive to age-related changes than measurements made in whole blood [29]. This difference may be because the polyamine level within cells is tightly regulated, while the levels in plasma or serum are more susceptible to enzymatic metabolism.
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS), which includes non-ST-elevation ACS (non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) and unstable angina) and ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), is a high-incidence clinical condition and a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide [30]. AMI is a significant contributor to CHF, a condition characterised by high morbidity and mortality rates. The initial acute-phase response to AMI involves immune system activation (releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines and growth factors) and neurohormonal activation (catecholamines and the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system [RAAS]) to maintain blood pressure and perfusion, although cardiac remodelling may occur over time [30]. In addition, the inflammatory response can extend myocardial necrosis and impact long-term prognosis, as it contributes to the structural and functional changes that accompany heart failure, as observed in CHF [31,32].
When heart cells die, they release molecules such as high-sensitivity cardiac troponin and the less selective creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). High-sensitivity cardiac troponin serves as a blood marker that facilitates ACS diagnosis [30]. Identifying new biomarkers could improve both the diagnosis and prognosis of cardiovascular diseases.
Considering the link between polyamines and isoamylamine on cardiovascular health, this study aims to determine whether measuring these amine levels in peripheral blood cells—erythrocytes and mononuclear cells in particular—can provide additional insights complementing previous measurements taken in plasma or serum. Cellular homeostasis is tightly regulated and can be disrupted by various pathological conditions, depending on the cell types involved [1]. Additionally, changes in polyamine levels within cells appear to be more sensitive than those observed in whole blood [29].
Our objective is to measure the levels of polyamines and isoamylamine in peripheral blood cells and plasma from patients who have suffered AMI or CHF, as well as in a control group, using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Furthermore, we aim to explore the potential of these amine levels as supplementary biological markers that correlate with clinical parameters in patients with AMI or CHF.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
An observational study was conducted involving 43 patients (30 males and 13 females) and 86 volunteers who comprised the control group (44 males and 42 females), with all participants aged between 39 and 88. Due to the limited sample size of the case group, a higher control-to-case ratio was implemented to improve statistical power. This resulted in an overall control-to-case ratio of approximately 2:1, with a ratio of about 3:1 for patients with myocardial infarction (MI) and around 5:1 for patients with congestive heart failure (CHF). To match the age of the CHF patients, who were 58 years and older, a subgroup of 46 participants from the control group was formed to discard the age effect on amine levels in CHF patients. The control-to-case ratio was approximately 3:1.
Patients were recruited consecutively, from February 2016 to December 2019, without bias toward sex, from the Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias in Spain. This group included individuals diagnosed with AMI upon admission to the Coronary Care Unit and those suffering from CHF who were attending cardiology follow-ups, with at least 5 years of evolution. The control group was selected from healthy blood donors at the Centro Comunitario de Sangre y Tejidos de Asturias, specifically those aged up to 65 years. Participants were included if they had no known diseases and were not undergoing any pharmacological treatments. Additionally, older adults were recruited from medical consultations, provided they had no cardiovascular, renal, respiratory, or metabolic diseases.
This study was explained to the participants, who signed an informed consent form to collect 4.5 mL blood samples in tubes containing EDTA to prevent clotting. Blood samples were collected on the first day of admission to the Coronary Care Unit for patients with MI. For patients with CHF, samples were taken on the day of their follow-up appointment. The data used for the clinical analysis were collected on the same date as the blood sample collection in both groups.
This study received approval from the Comité de Ética de la Investigación del Principado de Asturias (Spain) (CElmPA 28/10; 90/17; 277/18; 28/19) and adhered to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
The variables considered in this study included age, sex, and biogenic amines in peripheral blood samples, which were determined using HPLC. The presence of cardiovascular disease, AMI, or CHF was also examined. Additionally, clinical and analytical parameters, including heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), left interventricular septum measurements, and left atrial diameter as assessed by 2D echocardiography, were analysed for possible correlations with the determined polyamines. Biochemical data (Table 1) for each patient were collected on the same date as the blood samples for polyamine determination.

Table 1.
Characteristics and clinical and analytical data of participants. The quantitative variables are expressed as medians (with percentiles 25–75).
Heart failure (HF) was classified in accordance with 2021 European Society of Cardiology Guidelines [32], based on the value of the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in HF with preserved EF (HFpEF), LVEF > 50%, HF with mildly reduced EF (HFmrEF), LVEF 40–49%), and HF with reduced EF (HFrEF), LVEF < 40%.
2.2. Separation of Cells and Plasma from Peripheral Blood
Blood samples were collected between 8:30 and 11:00 a.m. and transported to the laboratory within an hour for the separation of blood cells and plasma. The separation was performed using Ficoll, in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol (GE Healthcare Ficoll-Paque PLUS, from Sigma-Aldrich, Madrid, Spain). Cell counts were determined using a Neubauer counting chamber. Subsequently, aliquots of mononuclear cells, erythrocytes, and plasma were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until they were needed to determine the amines.
2.3. Determination of Polyamines via HPLC
The amine level in the samples was determined using a pre-column derivatisation method [33]. For the analysis, 300 μL of Milli-Q water was added to the whole pellet of mononuclear cells, and 250 μL was added to a 50 μL aliquot of erythrocytes. A total of 450 μL of the plasma samples was collected. These samples were then homogenised and treated with perchloric acid to achieve a final concentration of 15.8%, followed by incubation for 10 min at 4 °C.
The extracts were then centrifuged at 10,000× g for 30 min at 4 °C; later, 0.2 mL of the supernatant was collected, and the standard concentration (1.25 μL of a concentration of 1 mM) was added. The sample was neutralised with 0.3 mL of a saturated solution of NaHCO3, and the samples were dansylated overnight (~16 h) with 0.5 mL of a solution containing 5 mg/mL of dansyl chloride in acetone. The next day, 0.1 mL of 100 mg/mL proline was added for 30 min; then, 0.5 mL of toluene was added. Finally, 0.4 mL of the organic phase was removed and dried under a nitrogen atmosphere at 42 °C in a thermoblock (Techne Dri-Block DB3, Cambridge, UK) and then resuspended in 0.2 mL of acetonitrile (VWR, Rosny-sous-Bois-cedex, France).
The HPLC was a Shimadzu Prominence (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) using a C18 (2.5 μm, 3.0 × 75 mm) reverse-phase column (XBridge, Waters, Milford, MA, USA) at room temperature between 21 and 23 °C and equipped with two LC-20AD pumps, a fluorescence detector (RF-20A), a SIL-20AD HT autosampler injector at 4 °C, and a DGU-20A3 degasser (all from Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The binary gradient used a flow rate of 0.55 mL/minute as follows: 0–0.5 min, 0% B; 0.5–10 min, 75% B; 10–11.30 min, 75% B; and 11.3–11.50 min, 0% B. Solvent A was 45% acetonitrile, and solvent B was 100% acetonitrile. The injection volume was 5 μL.
The duration of the chromatogram was 14 min. The identification of the compounds was performed using their retention time in minutes (standard: 5.88; N-acetyl putrescine: 1.56; N-acetyl spermidine: 6.11; isoamylamine: 7.04; putrescine: 7.38; N-acetyl spermine: 9.41; spermidine: 10.38; spermine: 12.41) and a wavelength of excitation of 365 nm and emission of 510 nm. All measurements were made using the Shimadzu LCsolution Version 1.25 software. The data analysed were the means of duplicate injections. The biogenic amines were quantified using 1,3-Diamino-2-hydroxypropane as an internal standard. The amines were expressed as nmol or pmol per mg of protein. The protein content was determined using the Bradford method by taking 50 μL of the homogenised sample.
2.4. Chemicals
The following chemicals were used: putrescine (tetramethylenediamine dihydrochloride), spermidine (N-(3-aminopropyl)-1,4-butanediamine), spermine (N,N′-bis (3-aminopropyl)-1,4-butanediamine), N-acetyl putrescine (N-(4-aminobutyl) acetamide hydrochloride), N-acetyl spermidine (N8-acetylspermidine dihydrochloride), N-acetyl spermine (N1-acetylspermine trihydrochloride), and isoamylamine (isopentylamine: 1-amino-3-methylbutane). These were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Madrid, Spain). The compounds were dissolved in purified water with a 10–15 MΩ·cm resistance.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Non-parametric statistics were used due to violations of normality. Box-and-whisker plots were used to show the concentrations of biogenic amines across the groups of control and diseases. Statistical significance was calculated using the Kruskal–Wallis test (pairwise comparison p-values adjusted by the Bonferroni correction for multiple tests). The Mann–Whitney test analysed the differences between two independent groups (p-values adjusted by Bonferroni correction). Discriminant function analysis was undertaken to determine the difference between the control group and those with AMI and CHF.
Spearman’s rank correlation (rs) was utilised to assess the association between variables. Multiple regression analysis was performed to explore the relationship between the dependent variable and the polyamines and isoamylamine determined in blood cells and plasma as potential predictor variables.
A significance level of p ≤ 0.05 was applied across all analyses. All statistical computations were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0 (BM, Armonk, NY, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Description of Participants
A total of 129 individuals participated in this study, comprising 74 males (57.4%) and 55 females (42.6%). Their ages ranged from 39 to 88 years, with a median age of 60 years (59 years for males and 61 years for females); the observed differences due to sex were not significant. Among these participants, 24 individuals had AMI, with ages ranging from 39 to 87 years. This AMI group included 20 males and 5 females, with a median age of 58 years (60 years for males and 58 years for females); the observed differences due to sex were not significant. In addition, 18 participants had been diagnosed with CHF and were aged between 58 and 82 years. This group comprised 10 males and 8 females, with a median age of 69.5 years (68 years for males and 69.5 years for females); the observed differences due to sex were not significant. The control group comprised 44 males and 42 females, with ages ranging from 39 to 88 years. The median age for this group was 59 years (57 years for males and 60.5 years for females); the Mann–Whitney test revealed that the differences in their ages were significant. The Kruskal–Wallis test revealed that differences in the ages of the participants were significant (p < 0.01), with the patients with CHF being older than participants in the control group (p < 0.01) and the patients with AMI (p = 0.012); this was adjusted using the Bonferroni correction for multiple tests. The subgroup of control participants, matched for age to patients with CHF, comprised 20 males and 26 females, with a median age of 63.5 years (59 years for males and 61 years for females, with no significant differences); the Mann–Whitney test revealed no significant differences in age compared to CHF patients (Table 1).
3.2. Clinical Data on the Patients
General clinical data specific for the pathology of the patients were registered, including cardiac damage in AMI patients and structural changes and heart function in CHF patients (Table 1). The patients with AMI stayed in the Coronary Care Unit an average of 2.6 (standard error: 0.52) days, and the total number of days in the hospital was 8.3 (standard error: 1.3).
3.3. Correlation Between Polyamine Levels in Peripheral Blood Cells and Plasma
In the control group, Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (rs) analysis showed that in mononuclear cells, putrescine was significantly and positively correlated with spermidine, spermine, N-acetyl putrescine, and N-acetyl spermidine; spermidine was significantly and positively correlated with spermine, N-acetyl putrescine, and N-acetyl spermidine; and spermine was positively correlated with N-acetyl putrescine, and N-acetyl spermidine. In erythrocytes, putrescine was significantly and positively correlated with spermine, N-acetyl putrescine, and N-acetyl spermidine; spermidine was significantly and positively correlated with spermine and N-acetyl spermidine. In plasma, putrescine was significantly and positively correlated with spermine and N-acetyl putrescine (Table 2).

Table 2.
Significant Spearman correlation coefficients (rs) between polyamines in the peripheral blood cells and plasma of the different groups.
In the AMI group, the putrescine level in mononuclear cells was significantly and positively correlated with spermidine, as was spermidine with spermine. In erythrocytes, putrescine was significantly correlated with spermidine, N-acetyl putrescine, and N-acetyl spermidine; spermidine was correlated with spermine and N-acetyl putrescine. In plasma, putrescine was significantly and positively correlated with spermidine and N-acetyl spermidine; spermidine was significantly and positively correlated with spermine (Table 2).
In the CHF group, putrescine in mononuclear cells was significantly and positively correlated with spermidine and N-acetyl putrescine. In erythrocytes, putrescine was significantly correlated with spermidine, spermine, N-acetyl putrescine, and N-acetyl spermidine; spermidine was correlated with spermine, N-acetyl putrescine, and N-acetyl spermidine; and spermine was correlated with N-acetyl putrescine and N-acetyl spermidine. In plasma, putrescine was significantly and positively correlated with spermine and N-acetyl spermidine; spermidine was significantly and positively correlated with spermine (Table 2).
3.4. Discriminant Function Analysis of Participants in the Control Group and Patients with AMI and CHF Based on the Amine Levels Measured in Blood Cells and Plasma
Discriminant function analysis revealed two discriminant functions. The first explained 66.3% of the variance (canonical R2 = 0.64), while the second explained 33.7% (canonical R2 = 0.48). In combination, these discriminant functions significantly differentiated the three groups (Ʌ = 0.19, χ2[10] = 157.12, p < 0.001). Removing the first function revealed that the second function also significantly differentiated the three groups (Ʌ = 0.52, χ2[4] = 60.76, p < 0.05). The correlations between the outcomes and the discriminant functions revealed that isoamylamine in plasma and erythrocytes correlated strongly and fairly evenly with the first function (r = 0.78 and r = 0.7, respectively) but less so with the second (r = −0.42 and −0.35, respectively). N-acetyl putrescine in plasma, isoamylamine in mononuclear cells, and spermidine in erythrocytes correlated more strongly with the second function (r = 0.65, r = −0.51, and r = 0.39, respectively) than with the first function (r = 0.28, r = −0.16, and r = 0.23, respectively). The classification model achieved a prediction accuracy rate of 100% for the control group, 83.3% for patients with AMI, and 88.9% for those with CHF. The discriminant function plot shows that both functions differentiated the groups of subjects analysed (Figure 1).
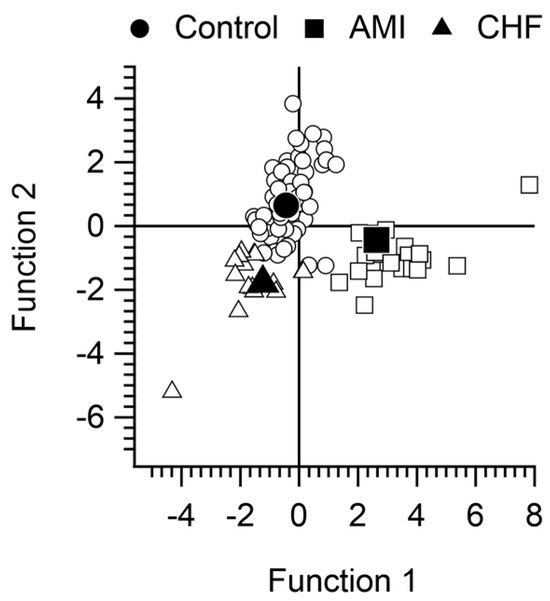
Figure 1.
Discriminant function analysis of control subjects, patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), and those with chronic heart failure (CHF).
3.5. Polyamine Levels in Peripheral Blood Cells and Plasma for Patients and the Control Group
Comparing the polyamine levels in mononuclear cells between the control group and patients with AMI and CHF patients, the Kruskal–Wallis test revealed significant differences between the groups for putrescine and isoamylamine (p < 0.001). Pairwise comparisons indicated lower putrescine levels in patients with AMI than the controls (p < 0.001) and CHF patients (p = 0.04) and higher isoamylamine levels in CHF patients than in the control group (p < 0.001) and AMI patients (p = 0.018). The comparison of the control subgroup matched for age with the CHF patient group showed the same significant differences for these amines as the control group using the Mann–Whitney test. No significant differences were found for the remaining amines examined in the blood cells and plasma (Figure 2; Supplementary Table S1).
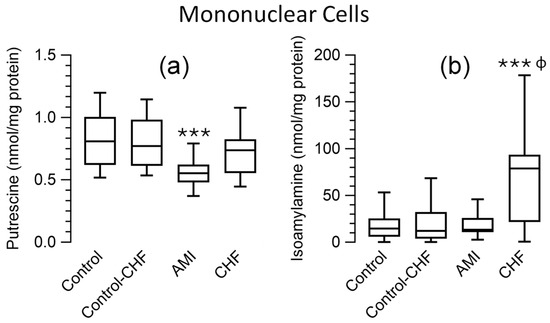
Figure 2.
Box-and-whisker plots showing the levels (pmol/mg of protein) of putrescine (a) and isoamylamine (b) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from the control group and from patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or chronic heart failure (CHF). Control–CHF: Control subgroup matched for age with CHF patients. *** p ≤ 0.001 compared to the control group, ɸ p ≤ 0.05 compared to the patients with AMI using the Kruskal–Wallis test.
Regarding polyamine levels in erythrocytes (Figure 3; Supplementary Table S1) and plasma (Figure 4; Supplementary Table S1), the Kruskal–Wallis test showed significant differences between the groups (p < 0.001) for putrescine, spermidine, spermine, N-acetyl putrescine, and N-acetyl spermidine. Pairwise comparisons revealed that the levels of all these amines were significantly lower in patients with CHF than in the control group (p < 0.001). No significant differences were observed when comparing the AMI patients to the control group. Regarding isoamylamine, the levels were higher in erythrocytes (Figure 3) and plasma (Figure 4) in patients with AMI than control groups or patients with CHF. The statistical significance of the levels of these amines in the erythrocytes and plasma of the control subgroup matched for age with the CHF group compared to CHF patients showed the same p-value using the Mann–Whitney test as the control group.
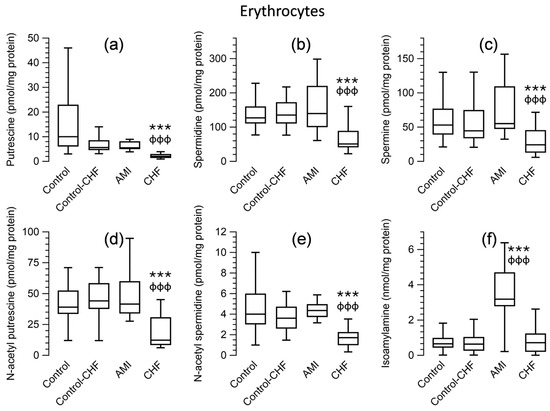
Figure 3.
Box-and-whisker plots showing the levels of putrescine (a), spermidine (b), spermine (c), N-acetyl putrescine (d), N-acetyl spermidine (e) (pmol/mg of protein), and isoamylamine (f) (nmol/mg of protein) in peripheral blood erythrocytes from the control group and from patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or chronic heart failure (CHF). Control–CHF: Control subgroup matched for age with CHF patients. *** p ≤ 0.001 compared to the control group and ɸɸɸ p ≤ 0.001 compared to patients with AMI vs. CHF using the Kruskal–Wallis test.
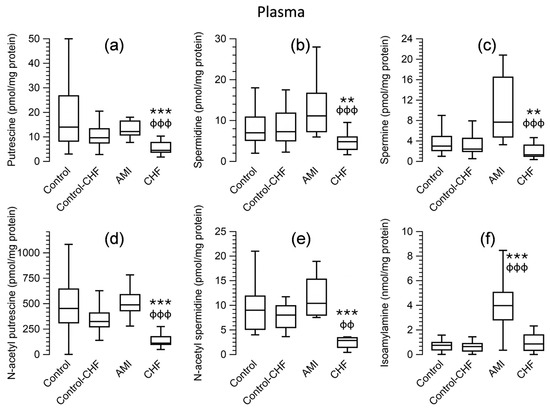
Figure 4.
Box-and-whisker plots showing the levels of putrescine (a), spermidine (b), spermine (c), N-acetyl putrescine (d), N-acetyl spermidine (e) (pmol/mg of protein), and isoamylamine (f) (nmol/mg of protein) in peripheral blood plasma from the control group and from patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or chronic heart failure (CHF). Control–CHF: Control subgroup matched for age with CHF patients. ** p ≤ 0.01 and *** p ≤ 0.001 compared to the control group; ɸɸ p ≤ 0.01 and ɸɸɸ p ≤ 0.001 compared to patients with AMI vs. CHF using the Kruskal–Wallis test.
The AMI group included 5 NSTEMI and 20 STEMI patients. The Mann–Whitney test revealed no significant differences in their polyamine levels; thus, they were treated as a unique group.
3.6. Correlation Between Polyamines in Peripheral Blood Cells and Plasma and the Clinical and Analytical Parameters of the Patients
In patients with AMI, diastolic pressure showed a positive correlation with putrescine levels in mononuclear cells (rs = 0.431, p = 0.035, n = 24). LVEF also exhibited a positive correlation with putrescine (rs = 0.438, p = 0.032, n = 24), spermine (rs = 0.456, p = 0.025, n = 24), and isoamylamine levels in mononuclear cells (rs = 0.412, p = 0.045, n = 24). In addition, LVEF correlated positively with isoamylamine levels in erythrocytes (rs = 0.509, p = 0.011, n = 24). In patients with AMI, in terms of cardiac damage markers, troponin levels were negatively correlated with the plasma spermine-to-spermidine ratio (rs = −0.538, p = 0.008, n = 24), as well as with plasma isoamylamine levels (rs = −0.459, p = 0.024, n = 24). Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels were positively correlated with N-acetyl putrescine levels in mononuclear cells (rs = 0.733, p = 0.016, n = 10) and negatively correlated with plasma isoamylamine levels (rs = −0.709, p = 0.022, n = 10). The other markers of cardiac damage were correlated among them. Alanine aminotransferase positively correlated to N-acetyl spermidine in erythrocytes (rs = 0.475, p = 0.04, n = 19) and to spermine in plasma erythrocytes (rs = −0.665, p < 0.001, n = 22); the aspartate aminotransferase-to-alanine aminotransferase ratio positively correlated to N-acetyl putrescine in mononuclear cells (rs = 0.646, p = 0.009, n = 15), but no significant correlation was observed for aspartate aminotransferase.
The days of stay in the Coronary Care Unit among patients with AMI were negatively correlated with the levels of putrescine (rs = −0.474, p = 0.022, n = 23) and spermine (rs = −0.485, p = 0.019, n = 23) in mononuclear cells. The total days of hospitalisation correlated negatively with spermine levels (rs = −0.599, p = 0.002, n = 24) in mononuclear cells.
In patients with CHF, LVEF exhibited a positive correlation with plasma spermidine levels (rs = 0.503, p = 0.033, n = 18).
3.7. Lineal Regression Analysis of Clinical Parameters of Patients with AMI and CHF as Dependent Variables and Polyamines as Predictor Variables
Multiple regression analysis was undertaken to predict clinically relevant variables in patients with AMI and CHF, with cardiac damage or structural or functional changes included as dependent variables and polyamines and isoamylamine as independent variables or predictors. The results show that determining polyamine and isoamylamine in peripheral blood cells with different models could predict LVEF in 66.6% of patients with AMI and 86% of patients with CHF. In patients with CHF, the models could predict 51.2% of the heart rate and 55% of the septum size (Table 3). Other dependent variables analysed were not predicted.

Table 3.
Multiple regression analysis with coefficients of constants and model of independent variables to predict left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in patients with acute myocardial infarction and chronic heart failure and septum size in patients with chronic heart failure.
4. Discussion
The results of this study showed that there are specific changes in the homeostasis of polyamines and isoamylamine in the blood cells and plasma of patients suffering from AMI and CHF, and these changes correlate differently with the tissue damage markers and haemodynamic clinical parameters of the patients. This is the first study to provide data on the association of the remarkably lower levels of polyamines and isoamylamine in blood cells and plasma related to ventricular function in CHF patients.
Polyamine homeostasis is tightly regulated within cells and is modified in pathological situations. In cardiac disease, alterations in polyamine metabolism have been described in experimental heart models and human cardiac tissue in association with anatomical and functional parameters of the heart. These changes may be biological markers in the pathophysiology of cardiac disease. However, there are limitations, as obtaining human cardiac tissue is not feasible. In this study, we focused on analysing data on readily available cells from patients to determine whether potential changes in their polyamine metabolism can be linked to cardiac damage or function in AMI or CHF, which may have clinical implications. Peripheral blood is one of the most accessible sources for obtaining cells, which are broadly categorised into two distinct types: erythrocytes and mononuclear cells. In addition, blood cells may be subjected to stimulatory stress mediators that account for the cardiac pathologies studied.
Using the control group as a reference, the determination of polyamine levels in blood cells and the analysis of the data reveal physiological correlations between polyamine synthesis (putrescine, spermidine, and spermine) and catabolism (N-acetyl putrescine and N-acetyl spermine). Based on these two processes, there are variations in the correlations between different polyamines in the blood cells of patients with AMI and CHF. A discriminant function analysis revealed three well-differentiated groups: the control group, patients with AMI, and patients with CHF. This finding highlights specific alterations in polyamine and isoamylamine metabolism associated with different cardiac conditions. Our analysis encompassed the following: isoamylamine levels in mononuclear cells, erythrocytes, and plasma; spermidine levels in erythrocytes; and N-acetyl putrescine levels in plasma.
When comparing the control and patient groups, significant differences in median polyamine levels and isoamylamine levels were observed across blood cells and plasma. Patients with AMI, with no differences between NSTEMI and STEMI, exhibited low putrescine levels in mononuclear cells and elevated isoamylamine levels in erythrocytes and plasma. In contrast, in CHF patients, all the polyamines analysed in erythrocytes and plasma were diminished, with elevated isoamylamine levels in erythrocytes. Patients with CHF were older than participants in the other groups; notably, it has been reported that there is typically a significant decrease in putrescine levels in erythrocytes and plasma during the sixth decade of life [29]. An age effect was invalidated by comparing the amines in the different samples with a control group of the same age range, which revealed equally significant decreases in all samples. Therefore, alterations in the homeostasis of polyamines accompany underlying AMI and CHF.
The findings of variations in the blood and plasma isoamylamine levels—isoamylamine is a primary amine—are interesting and novel. Isoamylamine has been discovered in human cardiac tissue from patients with CHF [17], and as seen in our study, it is equally present in human peripheral blood cells and plasma. Therefore, it may play a role.
In addition to observing varying intracellular and plasma levels between the different groups, establishing potential clinical significance was also explored. Specifically, in patients with AMI, we calculated the correlation between amine levels, heart function, and biological markers of cardiac damage, and the correlation between heart function and levels of atrial natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) was calculated in CHF patients.
In patients with AMI, putrescine levels in mononuclear cells were positively associated with arterial diastolic pressure. Regarding LVEF, a positive correlation was established between isoamylamine levels in erythrocytes and putrescine, spermine, and isoamylamine levels in mononuclear cells. The intracellular levels of these amines may be related to the stress that occurs after AMI, leading to an activation of the sympathetic nervous system and the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system [34]. The mediators of these systems may stimulate all types of cells, whether they have receptors for their recognition. Thus, in addition to their known effect on the cardiovascular system, they may act on mononuclear cells and erythrocytes, as these cells express adrenergic [35,36,37] and angiotensin receptors [38,39]. Therefore, there may be a link between the neurohumoral system and intracellular polyamine metabolism. It has been reported that the activation of β-adrenoceptors [11,40] and angiotensin II receptors [41] increases intracellular polyamines in cardiac cells, which might be involved in cardiac remodelling [11,42]. Furthermore, additional polyamine synthesis, at least in the heart, is associated with left atria dilation in patients with CHF, which corresponds to ODC activity [17]. Conversely, polyamines may interact with rat [2] and human β-adrenoceptors [3] to increase cAMP, leading to putrescine inducing a chronotropic and cardiotonic effect in isolated rat atria [2].
Therefore, it seems that the pro-inflammatory and neurohumoral responses triggered in individuals with AMI simultaneously affect polyamine metabolism in blood cells and plasma; this has potential diagnostic and prognostic value.
Another interesting finding is that the plasma spermine-to-spermidine ratio in patients with AMI is inversely correlated with troponin plasma levels. These data may indicate that a positive spermine balance is associated with minor cardiac damage. This hypothesis aligns with the cardioprotective effects reported in various forms of cardiac injury and dysfunction [43,44,45], as well as the more thoroughly researched links between spermidine [10,45] and the immune system [46]. Plasma isoamylamine levels might also be a marker of cardiac damage, as they were inversely correlated with troponin and LDH levels. In contrast, N-acetyl putrescine is positively correlated with LDH. These findings may have predictive value, since serum LDH levels have been associated with cardiac dysfunction after AMI [47].
The study results for patients with CHF indicate a positive correlation between plasma spermidine levels and LVEF. This finding is consistent with previous studies that have reported a positive correlation between spermidine levels in human cardiac tissue and LVEF and heart rate [17]. As mentioned earlier, the spermidine plasma levels in the CHF patients in this study were lower than those in the control and AMI groups. Although the relationship observed between these variables indicates a potential functional effect, it should not be interpreted as a causal relationship. Nonetheless, it would be interesting to investigate whether increasing the polyamine levels in blood cells and plasma could, in parallel, act as a cardioprotective agent that improves ventricular function, as indicated by spermidine supplementation in experimental models [10]. A limitation here is that spermidine-rich foods do not significantly increase blood spermidine levels in humans [48,49]; hence, it may be necessary to employ a different strategy.
The linear regression analysis showed significant models with combinations of polyamines and isoamylamine determined in blood cells and plasma, which could have a predictive value on the clinical parameters of the patients, mainly for CHF.
In addition to β-adrenoceptors and angiotensin II receptors, the functional and structural effects of polyamines and isoamylamine may also be elicited through the interaction of nonolfactory trace amine-associated receptors (TAARs) in the heart and blood cells Multiple TAARs are expressed in various organs throughout the body. TAAR1 and—less significantly—TAAR3 are expressed in the heart [50]. Putrescine, spermidine, spermine, and isoamylamine bind to TAAR1 and isoamylamine binds to TAAR3 [51]. These amines are located intracellularly. However, in the case of cardiac cell damage, they may be released locally and produce effects without increasing plasma levels, which could be metabolised; thus, the changes may not be evident.
Different peripheral mononuclear cells express several TAARs (TAAR1, TAAR2, TAAR5, TAAR6, TAAR8, and TAAR9) [51]. The potential activation of these receptors and the changes in polyamine levels described earlier may lead to an alteration in immune function in patients with either AMI or CHF, which may also play a role in heart remodelling. The erythrocyte amine levels for all the amines measured were significantly low in patients with CHF, which may alter cell integrity and function; no TAARs were reported in these cells.
While this study yielded valuable results, it has limitations. These include patient selection based on convenience rather than randomisation, as well as a potentially small sample size, especially among patients with NSTEMI.
5. Conclusions
These findings indicate that polyamines measured in cells and plasma can be biomarkers for these cardiac diseases. It should be noted that these pathologies are temporally distinct: in AMI, the analysis referred to the first day of the patients’ stay in the Coronary Care Unit, while changes in CHF are long-term, with at least 5 years of evolution. Furthermore, our findings may complement previous studies with findings indicating that polyamines present in serum, plasma, and whole peripheral blood can be valuable indicators for prognosis in patients after AMI, at least regarding ventricular function and the days spent in the Coronary Care Unit and on overall hospitalisation. However, further research is needed to explore the prognostic value of these findings in patients with cardiac disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app15126456/s1; Table S1: Amine levels (nmol or pmol/mg of protein) in samples of peripheral blood cells and plasma, presented as medians (percentiles 25–75).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M.R., B.C. and M.S.; Methodology, J.M.R., L.S., B.C., E.B.-A. and I.R.-U.; Formal analysis, L.S. and B.C.; Investigation, J.M.R., L.S., B.C., E.B.-A., I.R.-U. and M.S.; Resources, E.B.-A. and I.R.-U.; Data curation, M.S.; Writing—original draft, J.M.R., B.C. and M.S.; Writing—review & editing, L.S., E.B.-A. and I.R.-U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by a Grant from Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria del Principado de Asturias (ISPA) (Convocatoria Intramural para el Fomento de Proyectos de Investigación 2018), Spain.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Principality of Asturias, Spain (references: CElmPA 28/10; 90/17; 277/18; 28/19).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the health personnel and donors of the Centro Comunitario de Sangre y Tejidos de Asturias (Spain) for their generous donation of blood samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Schibalski, R.S.; Shulha, A.S.; Tsao, B.P.; Palygin, O.; Ilatovskaya, D.V. The role of polyamine metabolism in cellular function and physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2024, 327, C341–C356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordallo, C.; Cantabrana, B.; Velasco, L.; Secades, L.; Meana, C.; Méndez, M.; Bordallo, J.; Sánchez, M. Putrescine modulation of acute activation of the β-adrenergic system in the left atrium of rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 598, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meana, C.; Bordallo, J.; Bordallo, C.; Suarez, L.; Cantabrana, B.; Sanchez, M. Functional effects of polyamines via activation of human beta1- and beta2-adrenoceptors stably expressed in CHO cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2010, 62, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, L.; Secades, L.; Bordallo, C.; Bordallo, J.; de Boto, M.J.; Rubin, J.M.; Hidalgo, A.; Cantabrana, B.; Sanchez, M. Role of putrescine on androgen-elicited positive inotropism in the left atrium of rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2008, 52, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordallo, C.; Rubin, J.M.; Varona, A.B.; Cantabrana, B.; Hidalgo, A.; Sanchez, M. Increases in ornithine decarboxylase activity in the positive inotropism induced by androgens in isolated left atrium of the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 422, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.; Secades, L.; Bordallo, C.; Meana, C.; Rubin, J.M.; Cantabrana, B.; Bordallo, J. Role of polyamines and cAMP-dependent mechanisms on 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone-elicited functional effects in isolated right atria of rat. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 54, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Xue, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Lu, F.; Li, H.; Bai, S.; Lin, Y.; et al. Exercise training preserves ischemic preconditioning in aged rat hearts by restoring the myocardial polyamine pool. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 457429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murry, C.E.; Jennings, R.B.; Reimer, K.A. Preconditioning with ischemia: A delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 1986, 74, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Peng, X.; Shao, H.; Li, H.; Bai, S.; Xu, C. Exogenous spermine inhibits hypoxia/ischemia-induced myocardial apoptosis via regulation of mitochondrial permeability transition pore and associated pathways. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, T.; Abdellatif, M.; Schroeder, S.; Primessnig, U.; Stekovic, S.; Pendl, T.; Harger, A.; Schipke, J.; Zimmermann, A.; Schmidt, A.; et al. Cardioprotection and lifespan extension by the natural polyamine spermidine. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantz, L.M.; Feith, D.J.; Pegg, A.E. Targeted overexpression of ornithine decarboxylase enhances beta-adrenergic agonist-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Biochem. J. 2001, 358, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamigni, F.; Stefanelli, C.; Guarnieri, C.; Caldarera, C.M. Modulation of ornithine decarboxylase activity and ornithine decarboxylase-antizyme complex in rat heart by hormone and putrescine treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 882, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipnis, U.R.; He, G.Y.; Li, S.; Campbell, G.; Boor, P.J. Attenuation of isoproterenol-mediated myocardial injury in rat by an inhibitor of polyamine synthesis. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2000, 9, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, M.J.; Russell, D.H. Polyamine biogenesis in left ventricle of the rat heart after aortic constriction. Am. J. Physiol. 1972, 222, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cubria, J.C.; Reguera, R.; Balana-Fouce, R.; Ordonez, C.; Ordonez, D. Polyamine-mediated heart hypertrophy induced by clenbuterol in the mouse. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1998, 50, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldarera, C.M.; Casti, A.; Rossoni, C.; Visioli, O. Polyamines and noradrenaline following myocardial hypertrophy. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1971, 3, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meana, C.; Rubin, J.M.; Bordallo, C.; Suarez, L.; Bordallo, J.; Sanchez, M. Correlation between endogenous polyamines in human cardiac tissues and clinical parameters in patients with heart failure. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Baek, Y.; Lee, S. Dietary polyamine intake lowers the risk of all-cause and cardiovascular disease-related mortality: Follow-up of the Korean National health and nutrition Examination survey 2007–2015. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 119, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, K.; Kano, Y.; Chiba, F. Food polyamine and cardiovascular disease--an epidemiological study. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2012, 4, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, T.; Knauer, H.; Schauer, A.; Büttner, S.; Ruckenstuhl, C.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Ring, J.; Schroeder, S.; Magnes, C.; Antonacci, L.; et al. Induction of autophagy by spermidine promotes longevity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.P.; Patel, J.R.; Marton, L.J.; Moss, R.L. Polyamines decrease Ca(2+) sensitivity of tension and increase rates of activation in skinned cardiac myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H1383–H1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao de la Barca, J.M.; Bakhta, O.; Kalakech, H.; Simard, G.; Tamareille, S.; Catros, V.; Callebert, J.; Gadras, C.; Tessier, L.; Reynier, P.; et al. Metabolic Signature of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Involving a Cocktail of Amino Acids and Biogenic Amines. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.; Liu, C.; Mehta, A.; Ko, Y.A.; Tahhan, A.S.; Dhindsa, D.S.; Uppal, K.; Jones, D.P.; Butler, J.; Morris, A.A.; et al. N8-Acetylspermidine: A Polyamine Biomarker in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy With Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Yin, L.; Xu, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, J. Association of Serum Polyamines with Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Chronic Kidney Disease. Cardiorenal Med. 2025, 15, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertos, A.; Ramos-Molina, B.; Cerezo, D.; López-Contreras, A.J.; Peñafiel, R. The mouse Gm853 gene encodes a novel enzyme: Leucine decarboxylase. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ŞahutoĞlu, A.S. Comparative modelling of a novel enzyme: Mus musculus leucine decarboxylase. Turk. J. Chem. 2020, 44, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbès-Paus, C.; Pochet, S.; Helinck, S.; Veisseire, P.; Bord, C.; Lebecque, A.; Coton, M.; Desmasures, N.; Coton, E.; Irlinger, F.; et al. Impact of Gram-negative bacteria in interaction with a complex microbial consortium on biogenic amine content and sensory characteristics of an uncooked pressed cheese. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coton, M.; Delbés-Paus, C.; Irlinger, F.; Desmasures, N.; Le Fleche, A.; Stahl, V.; Montel, M.C.; Coton, E. Diversity and assessment of potential risk factors of Gram-negative isolates associated with French cheeses. Food Microbiol. 2012, 29, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Suárez, L.; Banda, G.; Barreiro-Alonso, E.; Rodríguez-Uña, I.; Rubín, J.M.; Cantabrana, B. Age-associated polyamines in peripheral blood cells and plasma in 20 to 70 years of age subjects. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.A.; Rossello, X.; Coughlan, J.J.; Barbato, E.; Berry, C.; Chieffo, A.; Claeys, M.J.; Dan, G.A.; Dweck, M.R.; Galbraith, M.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3720–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, A.; Sammartino, A.M.; Papp, Z.; von Haehling, S.; Biegus, J.; Ponikowski, P.; Adamo, M.; Falco, L.; Lombardi, C.M.; Pagnesi, M.; et al. 2024 update in heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2025, 12, 8–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 4–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, M.I.; Legaz, M.E. High performance liquid chromatography of the dansyl derivatives of putrescine, spermidine, and spermine. Plant Physiol. 1988, 87, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygin, D.; Wanner, N.; Rose, J.A.; Naga Prasad, S.V.; Tang, W.H.W.; Erzurum, S.; Asosingh, K. Relative quantification of beta-adrenergic receptor in peripheral blood cells using flow cytometry. Cytom. Part A J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2018, 93, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bree, F.; Gault, I.; d’Athis, P.; Tillement, J.P. Beta adrenoceptors of human red blood cells, determination of their subtypes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1984, 33, 4045–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horga, J.F.; Gisbert, J.; De Agustín, J.C.; Hernández, M.; Zapater, P. A beta-2-adrenergic receptor activates adenylate cyclase in human erythrocyte membranes at physiological calcium plasma concentrations. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2000, 26, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Terao, S.; Vital, S.A.; Rodrigues, S.F.; Yilmaz, G.; Granger, D.N. Role of blood cell-associated angiotensin II type 1 receptors in the cerebral microvascular response to ischemic stroke during angiotensin-induced hypertension. Exp. Transl. Stroke Med. 2011, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, H.; Suzuki, H.; Maruyama, T.; Saruta, T. Gene expression of angiotensin II receptor in blood cells of Cushing’s syndrome. Hypertension 1995, 26, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipnis, U.R.; Frasier-Scott, K.; Skiera, C. Isoprenaline induced changes in ornithine decarboxylase activity and polyamine content in regions of the rat heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 1989, 23, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Irimajiri, O.; Nakano, T.; Mizokami, T.; Ogawa, K.; Sanjo, J.; Yamada, H.; Sasaki, H.; Isogai, Y. Effect of captopril on isoproterenol-induced myocardial ornithine decarboxylase activity. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1991, 23, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.C.; Hata, J.A.; Shah, A.S.; Glower, D.D.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Koch, W.J. Preservation of myocardial beta-adrenergic receptor signaling delays the development of heart failure after myocardial infarction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5428–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Yang, W.; Jiang, D.; Tao, K.; Dong, A.; Cheng, H. Spermine ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion injury in cardiomyocytes via regulation of autophagy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Shao, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, B.; Li, S.; Xu, C.; Wei, C. Exogenous spermine attenuates myocardial fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Chai, N.; Chen, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Shi, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Spermine and spermidine reversed age-related cardiac deterioration in rats. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 64793–64808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Sun, M.; Liang, X.; Che, B.; Wang, N.; Shi, L.; Fan, Y. Spermine Regulates Immune and Signal Transduction Dysfunction in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 740493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kang, K.; Chen, S.; Su, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, L.; Lin, X.; Peng, F.; Lin, J.; Chai, D. High serum lactate dehydrogenase as a predictor of cardiac insufficiency at follow-up in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2024, 117, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, K.; Uemura, T.; Sanayama, H.; Igarashi, K.; Fukui, T. Polyamine-Rich Diet Elevates Blood Spermine Levels and Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Status: An Interventional Study. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senekowitsch, S.; Wietkamp, E.; Grimm, M.; Schmelter, F.; Schick, P.; Kordowski, A.; Sina, C.; Otzen, H.; Weitschies, W.; Smollich, M. High-Dose Spermidine Supplementation Does Not Increase Spermidine Levels in Blood Plasma and Saliva of Healthy Adults: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Pharmacokinetic and Metabolomic Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainetdinov, R.R.; Hoener, M.C.; Berry, M.D. Trace Amines and Their Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 549–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberles, S.D.; Buck, L.B. A second class of chemosensory receptors in the olfactory epithelium. Nature 2006, 442, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseenko, V.I.; Apryatina, V.A.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Apryatin, S.A. Trace Amine-Associated Receptors’ Role in Immune System Functions. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).