Exploring High-Order Skeleton Correlations with Physical and Non-Physical Connection for Action Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Firstly, this paper proposes a spatio-temporal hypergraph modeling method of human skeleton correlation. This method focuses on the inherent physical connections and non-physically connected relationships among human skeletons. For different actions, different weights are assigned to different vertex in the hypergraph, which highlights the regions that have a significant impact on human action.
- Secondly, this paper proposes an adaptive multi-channel spatio-temporal hypergraph neural network (AMC-STHGNN). The network captures the high-order correlation among human skeletons, and the features of different data channels are adaptively fused, making full use of the complementarity and diversity among three types of features.
- Finally, our proposed method is tested on two public datasets and shows a superior performance, effectively enhancing the ability of environmental perception and action analysis.
2. Related Work
2.1. Action Recognition Based on Skeleton
2.2. Hypergraph Neural Networks
3. Hypergraph Theory
4. The Proposed Method
4.1. Pipeline Overview
4.2. Spatio-Temporal Hypergraph Modeling of Human Skeleton Correlation
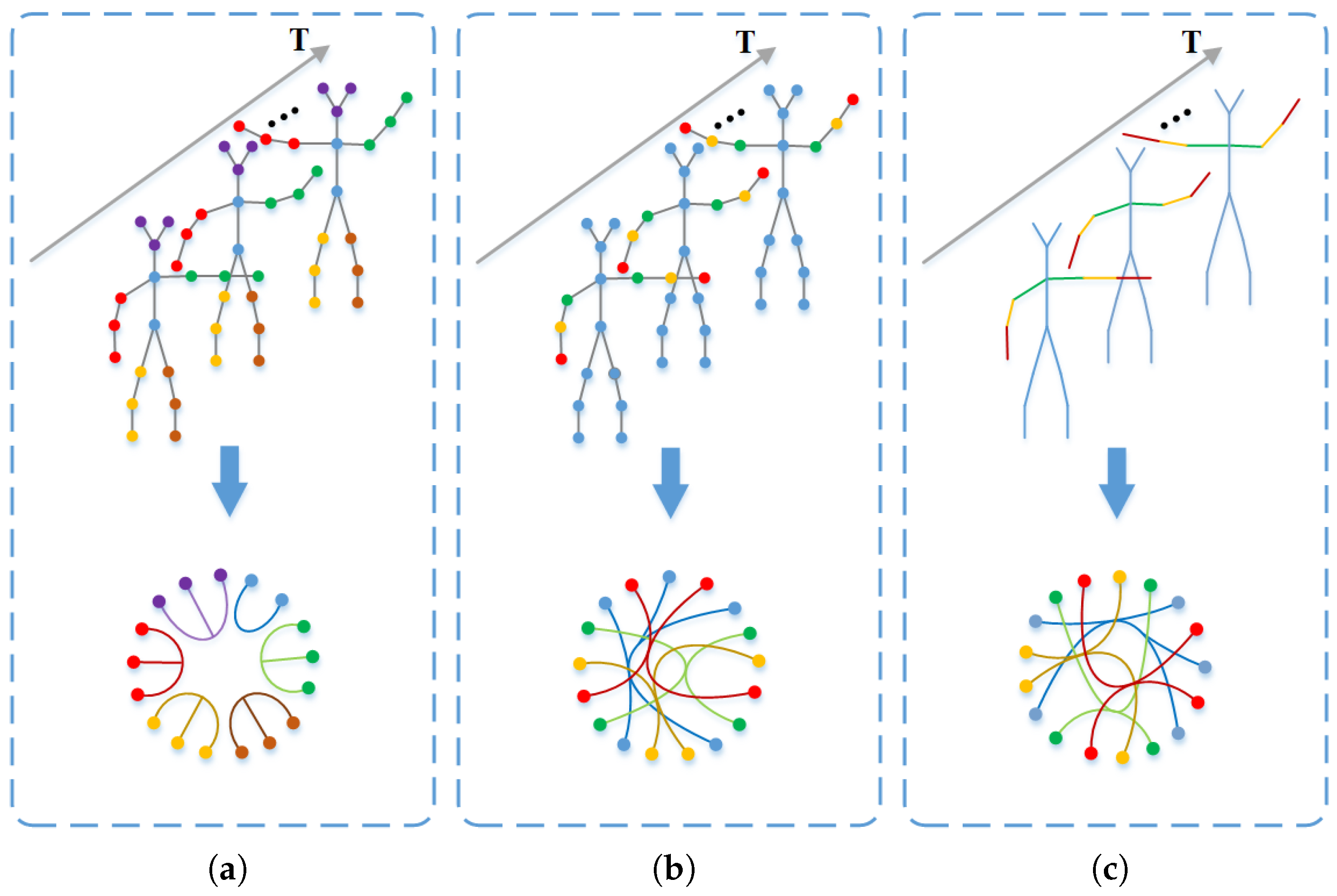
4.2.1. Physically Connected Joint Spatio-Temporal Hypergraph
4.2.2. Non-Physically Connected Joint Spatio-Temporal Hypergraph
4.2.3. Non-Physically Connected Bone Spatio-Temporal Hypergraph
4.3. Adaptive Multi-Channel Spatio-Temporal Hypergraph Neural Network
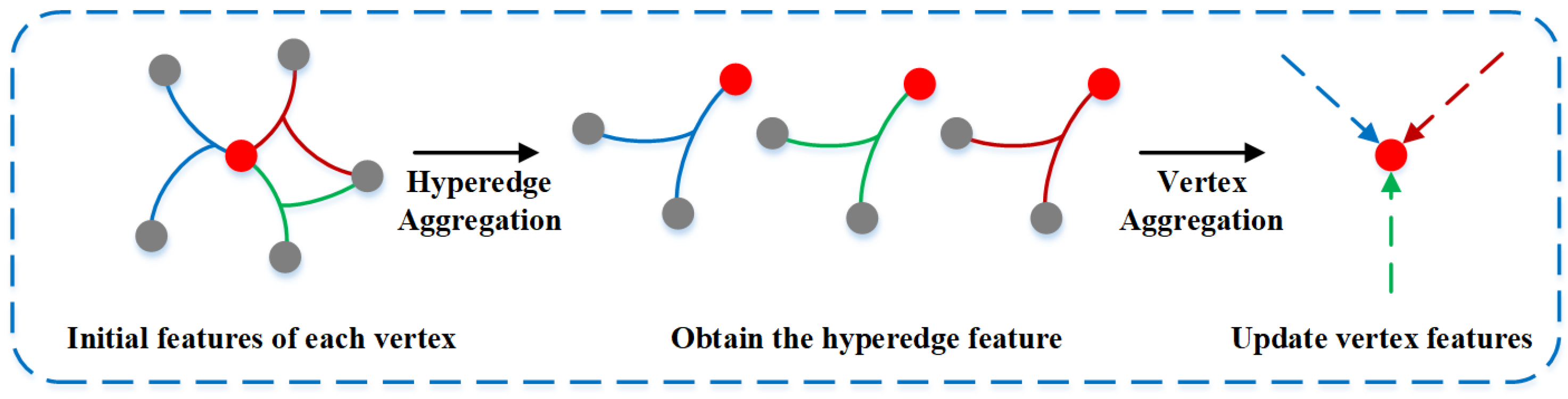
4.3.1. Hypergraph Convolution Module Based on Spatio-Temporal Information
4.3.2. Multi-Feature Fusion Module Based on Cross-Channel Attention Mechanism
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
5.1. Dataset
5.2. Experimental Settings
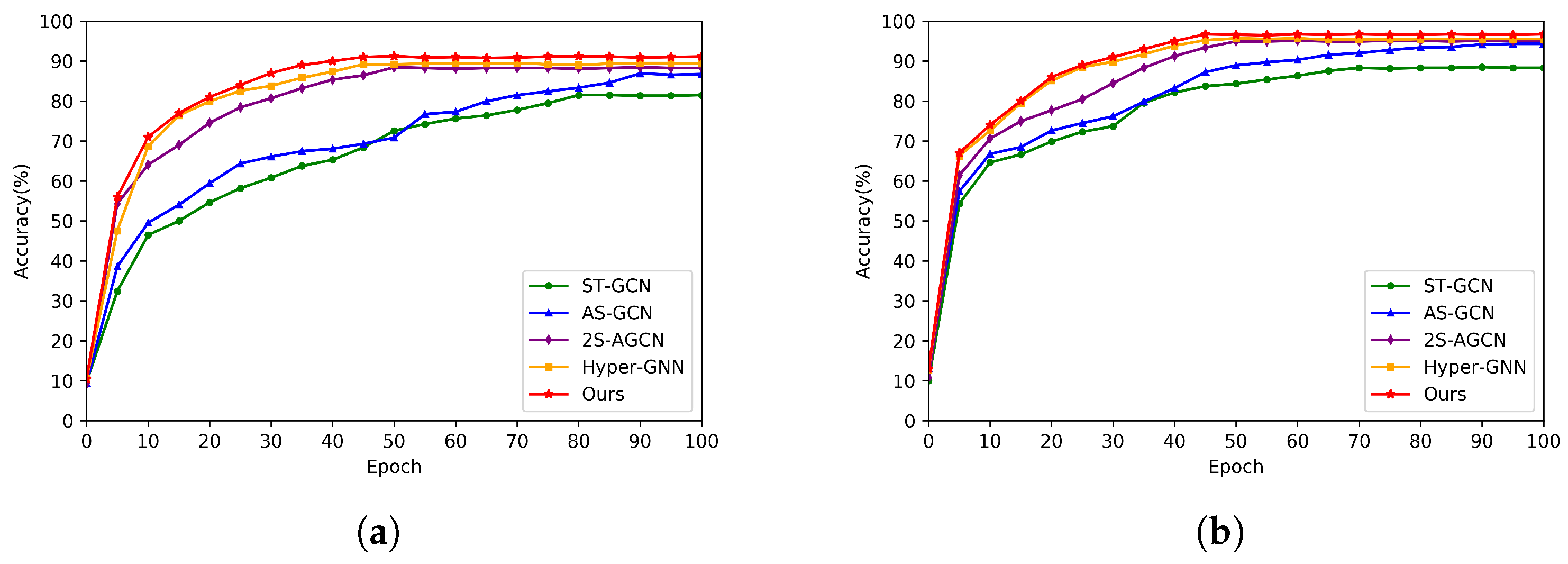
5.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
5.4. Ablation Experiments
5.4.1. Different Channel Data Channels
5.4.2. Different Neural Network Structures
5.4.3. Different Multi-Channel Fusion Modules
5.5. Visualization
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, N.; Wu, Z.; Cheung, Y.m.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, B. A survey of human action recognition and posture prediction. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 973–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jiang, C.; Wu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Jing, X.; Mu, J. Wi-Fi sensing for joint gesture recognition and human identification from few samples in human-computer interaction. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2022, 40, 2193–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallel, M.; Havard, V.; Dupuis, Y.; Baudry, D. Digital twin of an industrial workstation: A novel method of an auto-labeled data generator using virtual reality for human action recognition in the context of human–robot collaboration. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 118, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, A.B.; Zagrouba, E. Abnormal behavior recognition for intelligent video surveillance systems: A review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 91, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ma, N.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Yao, Y.; Chen, L. Attention Mechanism Based on Improved Spatial-Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks for Traffic Police Gesture Recognition. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. 2022, 36, 2256001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Shu, X.; Zhang, J.; Dai, G.; Song, Y. Spatiotemporal Decouple-and-Squeeze Contrastive Learning for Semisupervised Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Sun, Z.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Jia, K. Global spatio-temporal synergistic topology learning for skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 140, 109540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhao, X.; Du, S.; Zou, C. Hypergraph Learning: Methods and Practices. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 2548–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ma, N.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Y. Survey of Hypergraph Neural Networks and Its Application to Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Beijing, China, 27–28 August 2022; pp. 387–398. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Ye, F.; Zhong, Q.; Xie, D. Topology-aware convolutional neural network for efficient skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 28 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 2866–2874. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade-Ambriz, Y.A.; Ledesma, S.; Ibarra-Manzano, M.A.; Oros-Flores, M.I.; Almanza-Ojeda, D.L. Human activity recognition using temporal convolutional neural network architecture. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 191, 116287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, C.; Li, B.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W. Channel-wise topology refinement graph convolution for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 13359–13368. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, C.; Wang, L. Constructing Stronger and Faster Baselines for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 1474–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; You, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, R.; Gao, Y. Hypergraph neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HA, USA, 29–31 January 2019; Volume 33, pp. 3558–3565. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Wei, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cao, J.; Gao, Y. Dynamic Hypergraph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; pp. 2635–2641. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, F.; Torr, P.H. Hypergraph convolution and hypergraph attention. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 110, 107637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ji, S.; Ji, R. HGNN+: General Hypergraph Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 3181–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhao, X.; Ji, R.; Gao, Y. Inductive Multi-Hypergraph Learning and Its Application on View-Based 3D Object Classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 5957–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, N.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Sun, J. Hypergraph-induced convolutional networks for visual classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 30, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, H.; Luo, Y.; Hu, C. Informed Patch Enhanced HyperGCN for skeleton-based action recognition. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, Y. Dynamic Spatial-temporal Hypergraph Convolutional Network for Skeleton-based Action Recognition. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.08689. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Geng, Y.; Xie, X.; Keuper, M. Hypergraph transformer for skeleton-based action recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.09590. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Wu, X. Visual classification by ℓ1-hypergraph modeling. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2015, 27, 2564–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Ying, S.; Gao, Y. Deep Hypergraph Structure Learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.12547. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Huang, J.; Schölkopf, B. Learning with hypergraphs: Clustering, classification, and embedding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2006, 19, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Wan, H.; Li, P.; Zhao, X.; Ma, N.; Gao, Y. Exploring High-Order Spatio–Temporal Correlations From Skeleton for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 949–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Guan, Y.; Dai, R. Convolutional gated recurrent units for medical relation classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Madrid, Spain, 3–6 December 2018; pp. 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahroudy, A.; Liu, J.; Ng, T.T.; Wang, G. Ntu rgb+ d: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1010–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, W.; Carreira, J.; Simonyan, K.; Zhang, B.; Hillier, C.; Vijayanarasimhan, S.; Viola, F.; Green, T.; Back, T.; Natsev, P.; et al. The kinetics human action video dataset. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.06950. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 12026–12035. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HA, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7291–7299. [Google Scholar]
- Vemulapalli, R.; Arrate, F.; Chellappa, R. Human action recognition by representing 3d skeletons as points in a lie group. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shahroudy, A.; Xu, D.; Wang, G. Spatio-temporal lstm with trust gates for 3d human action recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 816–833. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Lan, C.; Xing, J.; Zeng, W.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. View adaptive recurrent neural networks for high performance human action recognition from skeleton data. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2117–2126. [Google Scholar]
- Si, C.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. An attention enhanced graph convolutional lstm network for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1227–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Soo Kim, T.; Reiter, A. Interpretable 3d human action analysis with temporal convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhong, Q.; Xie, D.; Pu, S. Co-occurrence feature learning from skeleton data for action recognition and detection with hierarchical aggregation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.06055. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Lan, C.; Xing, J.; Zeng, W.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. View adaptive neural networks for high performance skeleton-based human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 1963–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Skeleton-based action recognition with multi-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 9532–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Chen, W.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Skeleton-based action recognition with shift graph convolutional network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, T.; Yu, M. Hypergraph neural network for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 2263–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Lv, P.; Yang, X.; Xu, M. Dynamic hypergraph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.10570. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, G.; Xu, X.; Ji, Y.; Shen, F. Selective hypergraph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Newark, NJ, USA, 27–30 June 2022; pp. 518–526. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Xiao, C.; Liu, S.; Qin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X. Single-skeleton and dual-skeleton hypergraph convolution neural networks for skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing: 28th International Conference, ICONIP 2021, Sanur, Bali, Indonesia, 8–12 December 2021; pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, B.; Gavves, E.; Oramas, J.M.; Ghodrati, A.; Tuytelaars, T. Modeling video evolution for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 5378–5387. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q. Symbiotic graph neural networks for 3d skeleton-based human action recognition and motion prediction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3316–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Li, D.; He, W.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Future vehicles: Interactive wheeled robots. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 156101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ma, N.; Gao, Y. Future vehicles: Learnable wheeled robots. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 193201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Type | Method | NTU RGB+D 60 | Kinetics-Skeleton | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS (%) | CV (%) | TOP-1 (%) | TOP-5 (%) | ||
| Handcraft feature based | Lie Group [32] | 50.1 | 82.5 | - | - |
| Feature Enc [46] | - | - | 14.9 | 25.8 | |
| RNN based | ST-LSTM [33] | 69.2 | 77.7 | - | - |
| VA-LSTM [34] | 79.4 | 87.6 | - | - | |
| AGC-LSTM [35] | 89.2 | 95.0 | - | - | |
| Deep LSTM [28] | - | - | 16.4 | 35.3 | |
| CNN based | TCN [36] | 74.3 | 83.1 | 20.3 | 40.0 |
| HCN [37] | 86.5 | 91.1 | - | - | |
| VA-CNN [38] | 88.7 | 94.3 | - | - | |
| Ta-CNN+ [10] | 90.7 | 95.1 | - | - | |
| GCN based | ST-GCN [39] | 81.5 | 88.3 | 30.7 | 52.8 |
| 2S-AGCN [30] | 88.5 | 95.1 | 36.1 | 58.7 | |
| MS-AAGCN [40] | 90.0 | 96.2 | 37.8 | 61.0 | |
| Shift-GCN [41] | 90.7 | 96.5 | - | - | |
| Sym-GNN [47] | - | - | 37.2 | 58.1 | |
| HGNN based | Hyper-GCN(3S) [42] | 89.5 | 95.7 | 37.1 | 60.0 |
| DHGCN [43] | 90.7 | 96.0 | 37.7 | 60.6 | |
| Selective-HCN [44] | 90.8 | 96.6 | 38.0 | 61.1 | |
| SD-HGCN [45] | 90.9 | 96.7 | 37.4 | 60.5 | |
| Ours | 91.2 | 96.7 | 39.1 | 61.3 | |
| Hypergraph Construction Method | Input Data | NTU RGB+D 60 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCJ | N-PCJ | N-PCB | Joint | Bone | CS (%) | CV (%) |
| √ | √ | 88.6 | 94.0 | |||
| √ | √ | 88.7 | 93.8 | |||
| √ | √ | 89.2 | 94.2 | |||
| √ | √ | √ | 90.7 | 95.4 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 90.3 | 95.2 | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 91.7 | 96.7 |
| Method | NTU RGB+D 60 | |
|---|---|---|
| CS (%) | CV (%) | |
| Only temporal convolution blocks | 81.2 | 86.3 |
| Only spatial convolution blocks | 82.1 | 87.7 |
| Temporal convolution blocks + spatial convolution blocks | 91.2 | 96.7 |
| Method | NTU RGB+D 60 | |
|---|---|---|
| CS (%) | CV (%) | |
| Coequal fusion method | 88.4 | 93.2 |
| Multi-feature fusion module based on cross-channel attention mechanism | 91.2 | 96.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Ma, N.; Wu, Z. Exploring High-Order Skeleton Correlations with Physical and Non-Physical Connection for Action Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093832
Wang C, Ma N, Wu Z. Exploring High-Order Skeleton Correlations with Physical and Non-Physical Connection for Action Recognition. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(9):3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093832
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cheng, Nan Ma, and Zhixuan Wu. 2024. "Exploring High-Order Skeleton Correlations with Physical and Non-Physical Connection for Action Recognition" Applied Sciences 14, no. 9: 3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093832
APA StyleWang, C., Ma, N., & Wu, Z. (2024). Exploring High-Order Skeleton Correlations with Physical and Non-Physical Connection for Action Recognition. Applied Sciences, 14(9), 3832. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093832







