Two-Line Element Outlier and Space Event Detection Method Based on Multi-Strategy Genetic Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
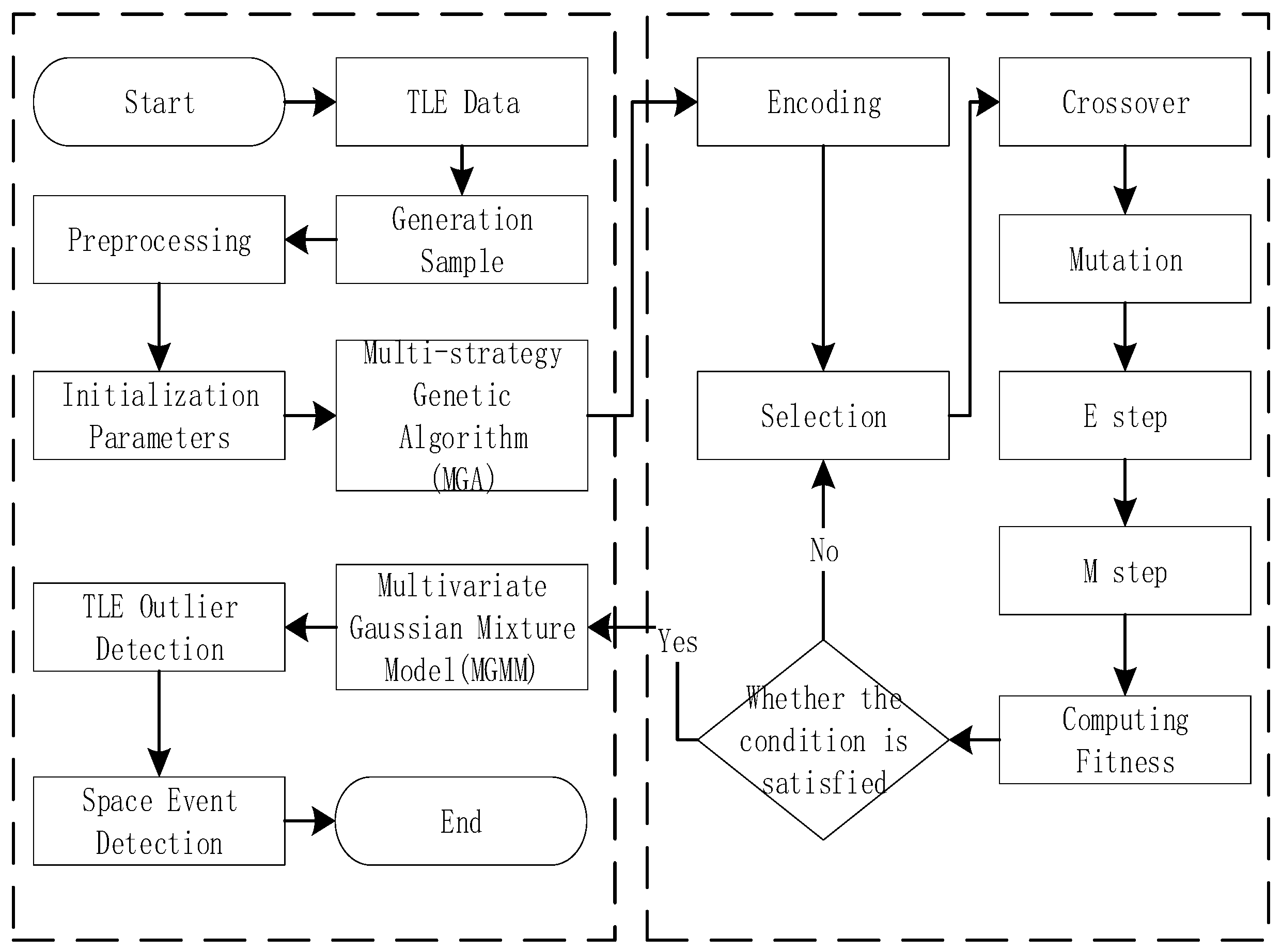
2. Method
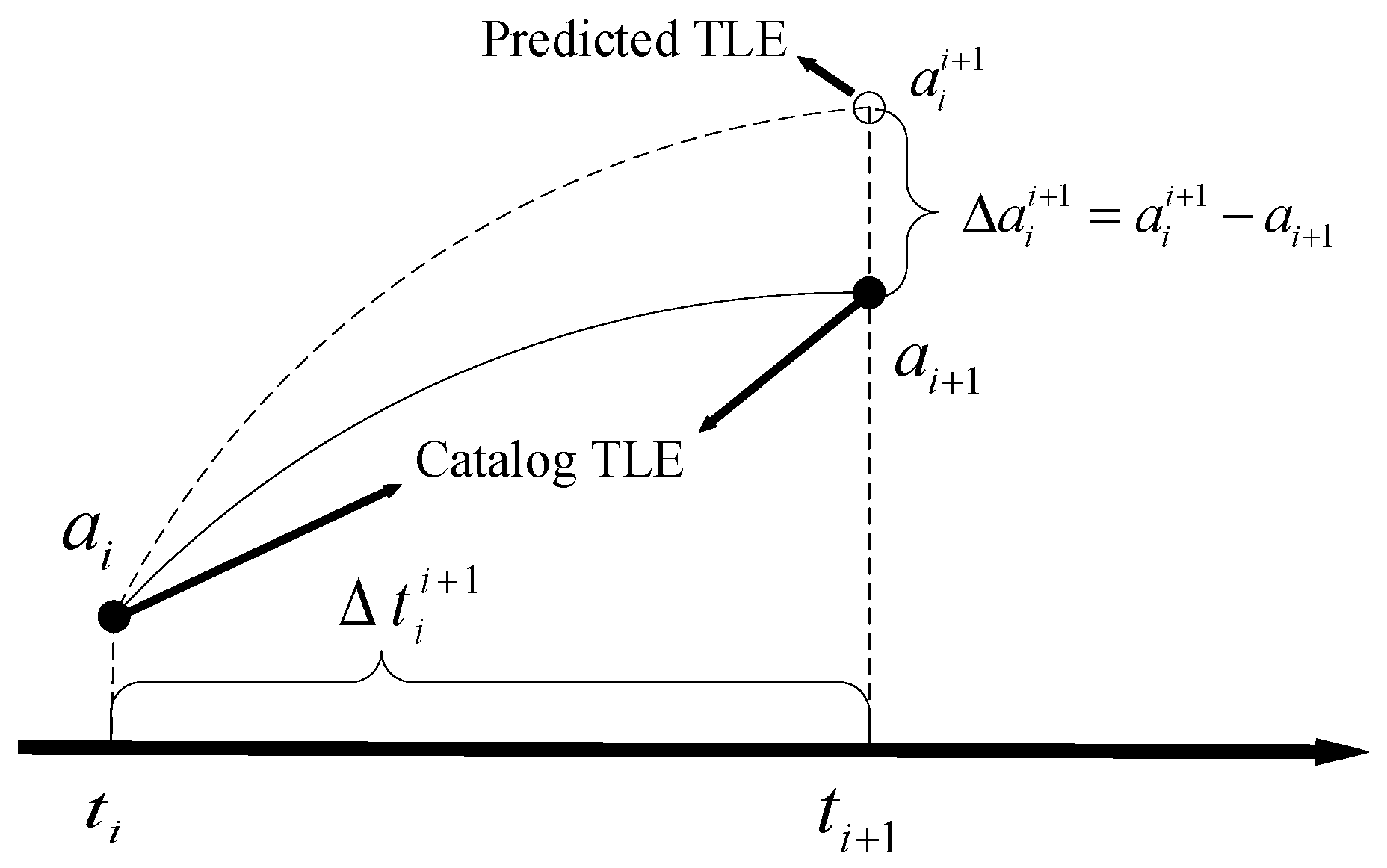
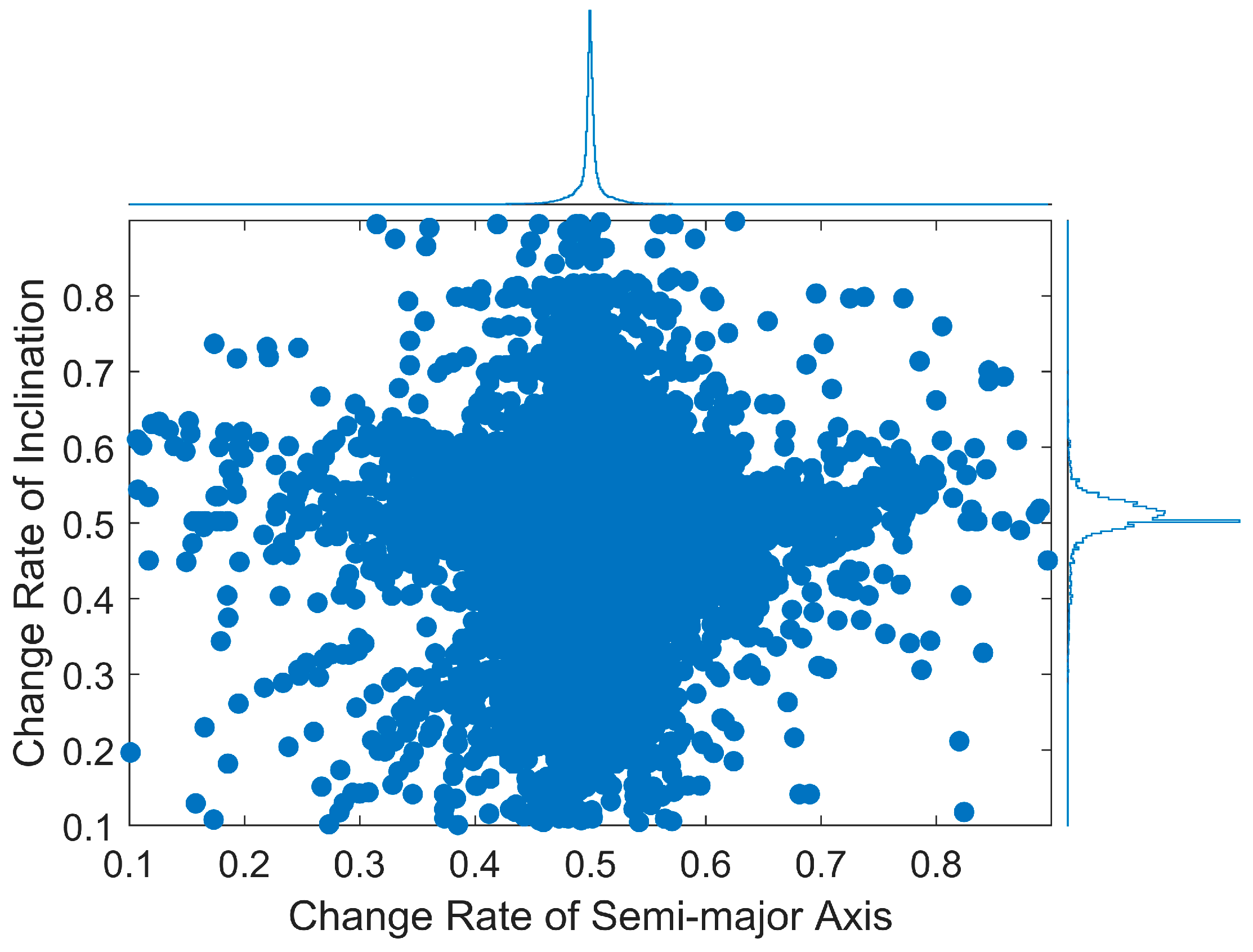
2.1. Sample Data Generation
2.2. Loss Function
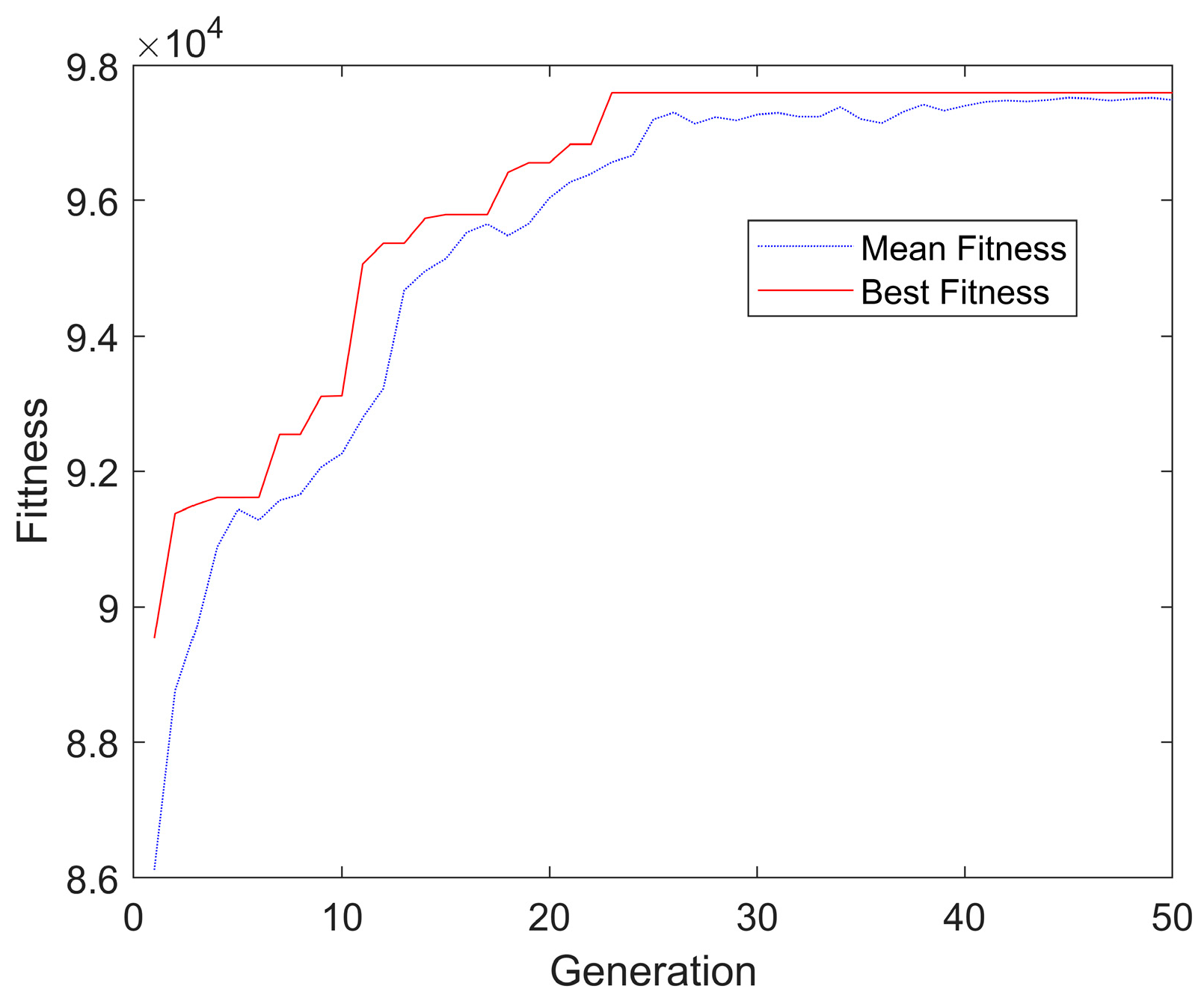
2.3. Multi-Strategy Genetic Algorithm
2.3.1. Chaotic Initialization Strategy
2.3.2. Posterior Probability Penalty
2.3.3. Iterative Local Optimization
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
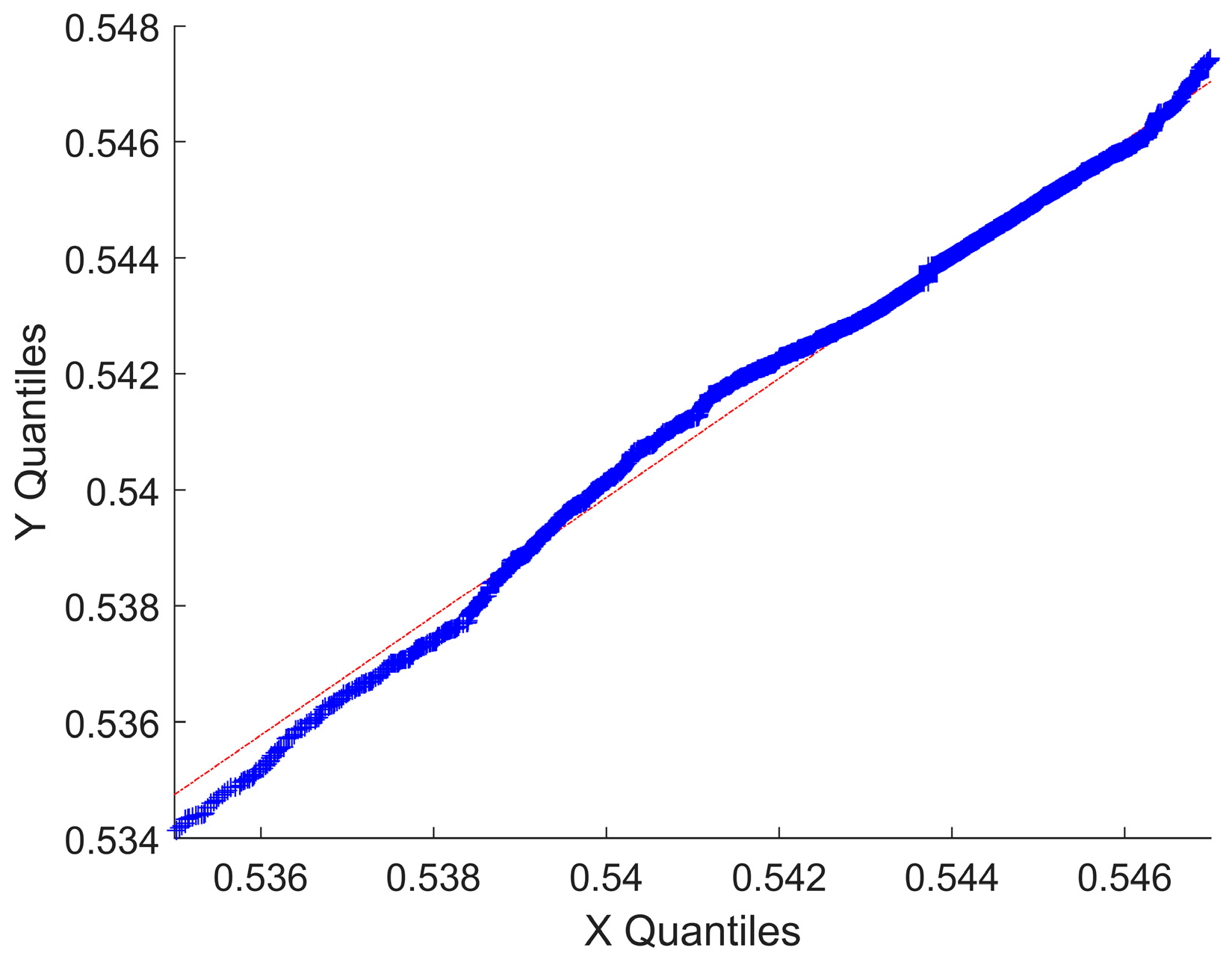
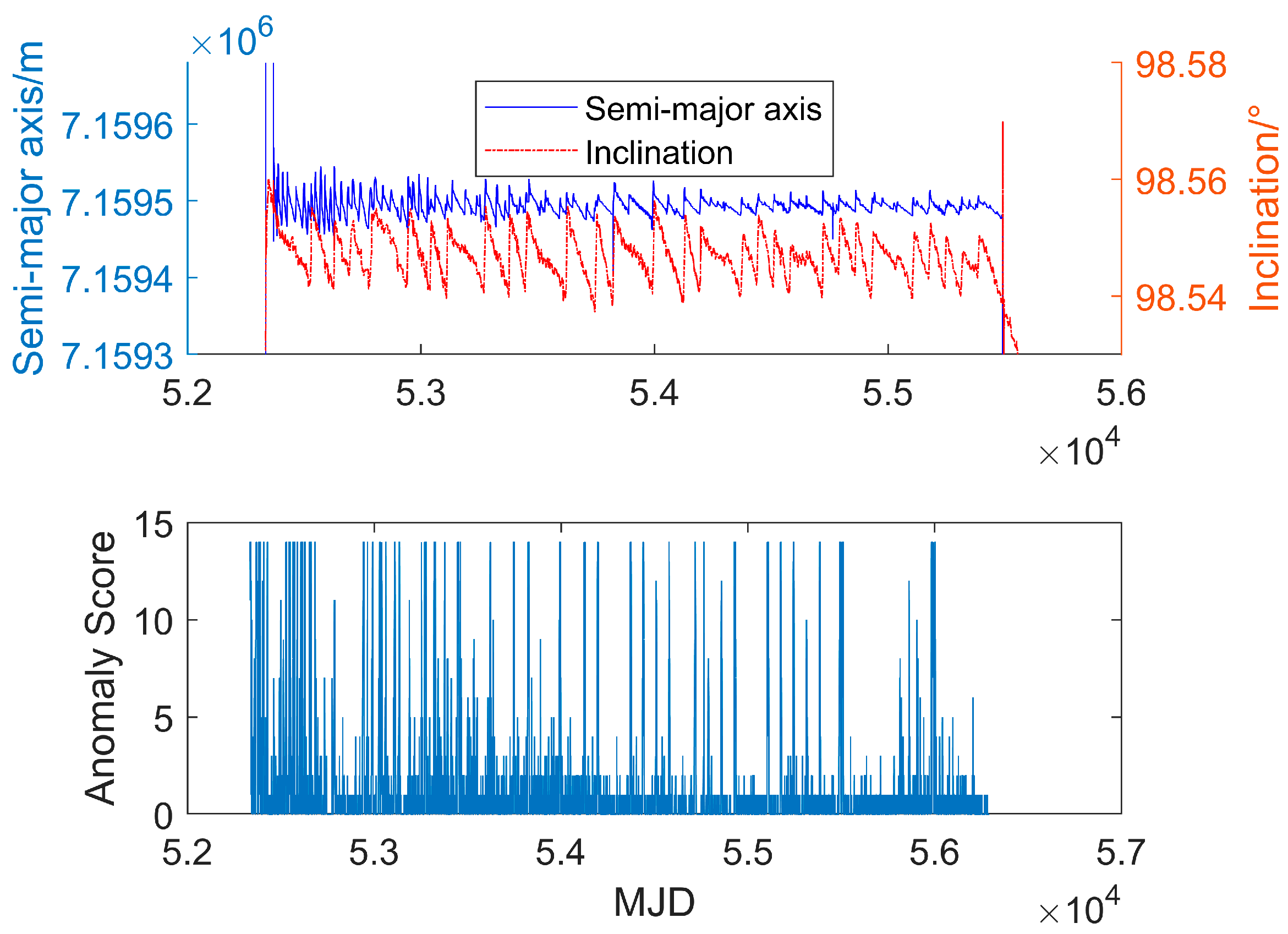
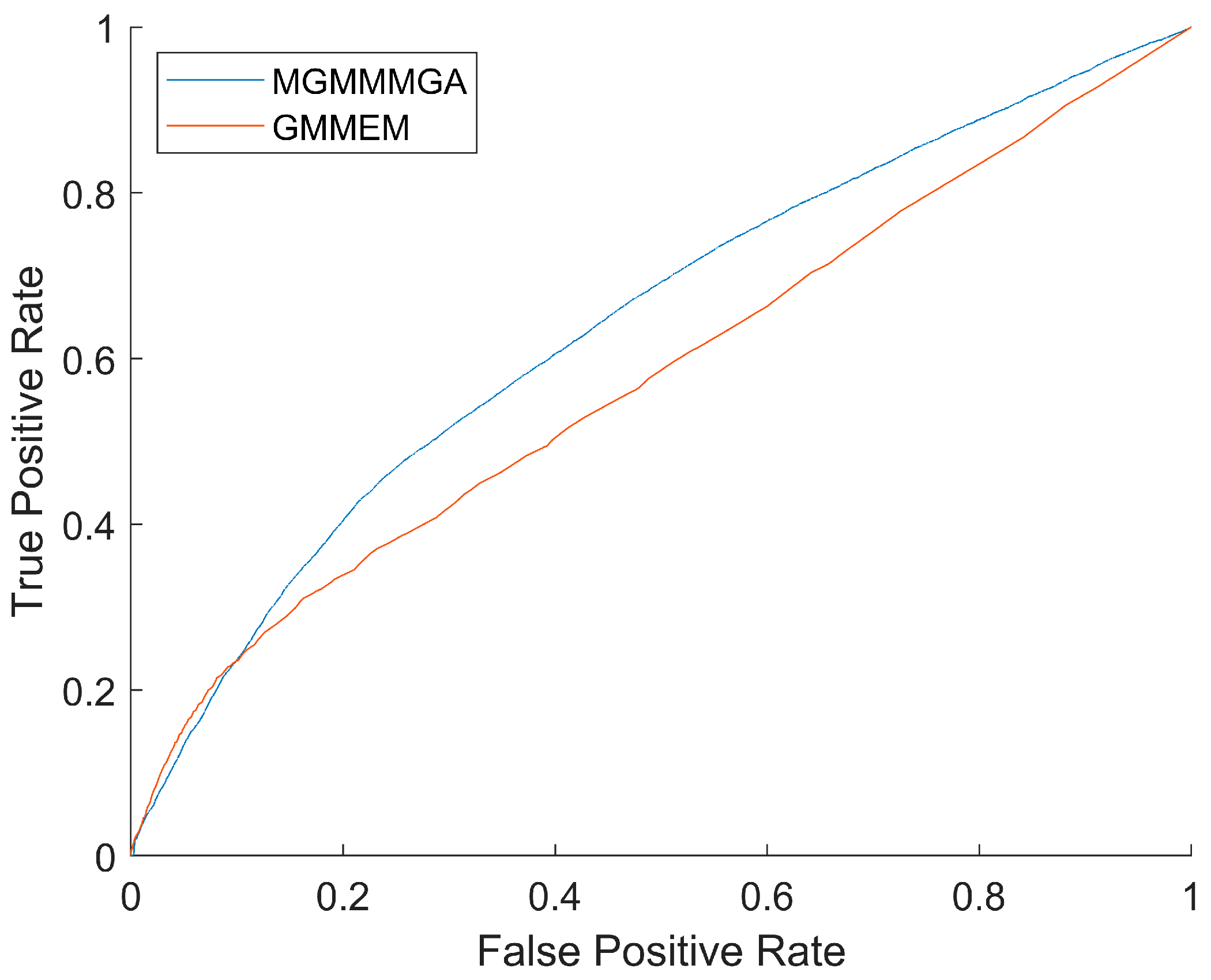
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Space-Track.org. Available online: https://www.Space-Track.Org (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Kang, Z.; Sun, J.; Chen, L. Improved Initial Orbit Determination Based on the Gooding Method of Low Earth Orbit Space Debris Using Space-Based Observations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z. Space Target Tracking with the HRRP Characteristic-Aided Filter via Space-Based Radar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, P., Jr. Prospects for Improving the Space Catalog. In Proceedings of the Space Programs and Technologies Conference, Huntsville, AL, USA, 24–26 September 1996; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Valley City, ND, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kelecy, T.; Hall, D.; Hamada, K.; Stocker, M.D. Satellite Maneuver Detection Using Two-Line Element (TLE) Data. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 12–15 September 2007; p. 16. [Google Scholar]
- Swartz, R.; Coggi, J.; McNeill, J. A Swift SIFT for Satellite Event Detection. In Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–5 August 2010; p. 7527. [Google Scholar]
- Patera, R.P. Space Event Detection Method. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2008, 45, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, K.; Chen, L. New Manoeuvre Detection Method Based on Historical Orbital Data for Low Earth Orbit Satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.D.; Wang, R.L.; Wang, J. A Simple and Valid Analysis Method for Orbit Anomaly Detection. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, L. Historical-Orbital-Data-Based Method for Monitoring the Operational Status of Satellites in Low Earth Orbit. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 151, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukundan, A.; Wang, H.-C. Simplified Approach to Detect Satellite Maneuvers Using TLE Data and Simplified Perturbation Model Utilizing Orbital Element Variation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmens, S.; Krag, H. Two-Line-Elements-Based Maneuver Detection Methods for Satellites in Low Earth Orbit. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2014, 37, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, A.; Escribano, G.; Escobar, D. Satellite Maneuver Detection with Optical Survey Observations. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference (AMOS), Maui, HI, USA, 15–18 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kovář, P.; Puričer, P.; Kovářová, K. Study of the Two-Line Element Accuracy by 1U CubeSat with a GPS Receiver. Sensors 2022, 22, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, T.; Xu, M.; Xing, N. An Unsupervised Anomaly Detection Approach for Spacecraft Based on Normal Behavior Clustering. In Proceedings of the 2012 Fifth International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Zhangjiajie, China, 12–14 January 2012; pp. 478–481. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, X.; Peng, H.; Chen, G.; Shen, D.; Blasch, E.; Sheaff, C.B. Gaussian-Binary Classification for Resident Space Object Maneuver Detection. Acta Astronaut. 2021, 187, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, F. A Machine Learning Method for the Orbit State Classification of Large LEO Constellation Satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 1644–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Horwood, J.T.; Aristoff, J.M.; Murray-Krezan, J. Athena: A Data-Driven Anomaly Detection and Space Object Classification Tool for SSA. In Proceedings of the 26th AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Napa, CA, USA, 14–18 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abay, R.; Gehly, S.; Balage, S.; Brown, M.; Boyce, R. Maneuver Detection of Space Objects Using Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, Maui, HI, USA, 11–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.; Sheaff, C.; Guo, M.; Blasch, E.; Pham, K.; Chen, G. Enhanced GANs for Satellite Behavior Discovery. Sens. Syst. Space Appl. XIII 2020, 11422, 110–121. [Google Scholar]
- Najari, N.; Berlemont, S.; Lefebvre, G.; Duffner, S.; Garcia, C. RADON: Robust Autoencoder for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 14th International Conference on Security of Information and Networks (SIN), Edinburgh, UK, 15–17 December 2021; Volume 1, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.; Sheaff, C.; Lu, J.; Chen, G.; Blasch, E.; Pham, K. Adaptive Markov Inference Game Optimization (AMIGO) for Rapid Discovery of Satellite Behaviors. Sens. Syst. Space Appl. XII 2019, 11017, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, S.; Lee, S.; Shin, Y.; Lee, M.S.; Jung, O.; Chung, D.; Woo, S.S. Detecting Anomalies in Space Using Multivariate Convolutional LSTM with Mixtures of Probabilistic PCA. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 2123–2133. [Google Scholar]
- Mortlock, T.; Kassas, Z.M. Assessing Machine Learning for LEO Satellite Orbit Determination in Simultaneous Tracking and Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Aerospace Conference (50100), Big Sky, MT, USA, 6–13 March 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Li, K.; Chen, L. Maneuver Detection Method Based on Probability Distribution Fitting of the Prediction Error. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2019, 56, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Deguine, B.; Garmier, R.; Revelin, B. Two Line Element Accuracy Assessment Based on a Mixture of Gaussian Laws. In Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit, Keystone, CO, USA, 21–24 August 2006; p. 6518. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Barnes, D.; Martinez-Murcia, F.J.; Ramírez, J.; Górriz, J.M.; Salas-Gonzalez, D. Expectation–Maximization Algorithm for Finite Mixture of α-Stable Distributions. Neurocomputing 2020, 413, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-F.; Tsai, C.-M.; Chen, C.-H.; Wong, Y.-H.; Fang, Y.-C.; Wen, C.-C.; Lee, H.-Y.; Le, H.-T.; Chang, S.-H.; Liao, H.-Y. Optical Design and Optimization with Genetic Algorithm for High-Resolution Optics Applied to Underwater Remote-Sensing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Gao, L.; Li, Y. A Modified Genetic Algorithm with New Encoding and Decoding Methods for Integrated Process Planning and Scheduling Problem. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 4429–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Isa, N.A.M.; Lim, W.H.; Ang, K.M. Differential Evolution with Modified Initialization Scheme Using Chaotic Oppositional Based Learning Strategy. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 11835–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimipour, B.; Li, X.; Qin, A.K. A Review of Population Initialization Techniques for Evolutionary Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Beijing, China, 6–11 July 2014; pp. 2585–2592. [Google Scholar]
- de Menezes, D.Q.F.; Prata, D.M.; Secchi, A.R.; Pinto, J.C. A Review on Robust M-Estimators for Regression Analysis. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2021, 147, 107254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Becker, D.; Hobiger, T. Stochastic Modeling with Robust Kalman Filter for Real-Time Kinematic GPS Single-Frequency Positioning. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Fan, J.; Li, J.; Li, B. Research on Robust Adaptive RTK Positioning of Low-Cost Smart Terminals. Sensors 2024, 24, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Kutterer, H.; Zeng, W.; Li, D. On Robust Estimation of the Gauss–Markov Model with a Singular Covariance Matrix. Measurement 2023, 223, 113834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Li, B.; Deng, Y.; Tang, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, J. MMDL-Net: Multi-Band Multi-Label Remote Sensing Image Classification Model. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, L.; Vasile, M. Intelligent Decision Support for Collision Avoidance Manoeuvre Planning under Uncertainty. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 2627–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, N.; Opromolla, R.; Fasano, G. Machine Learning-Based Approach for Ballistic Coefficient Estimation of Resident Space Objects in LEO. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 5007–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NORAD ID | Mass [kg] | Launch Date | Period [min] | Apogee [km] | Perigee [km] | Inclination [°] | TLE Quantity | Events Quantity | TLE Time Span |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27386 | 8100 | March 2002 | 100 | 791 | 785 | 98.6 | 11,896 | 177 | 2003–2010 |
| 36508 | 720 | April 2010 | 99 | 732 | 718 | 92 | 8630 | 179 | 2010–2023 |
| 41240 | 553 | January 2016 | 112 | 1343 | 1331 | 66 | 7235 | 47 | 2016–2023 |
| 41335 | 1250 | February 2016 | 101 | 806 | 802 | 99 | 10,788 | 73 | 2016–2023 |
| 43476 | 600 | May 2018 | 94 | 491 | 470 | 89 | 4139 | 39 | 2018–2023 |
| 43477 | 600 | May 2018 | 94 | 491 | 470 | 89 | 4134 | 39 | 2018–2023 |
| 37781 | 1500 | August 2011 | 103 | 917 | 902 | 99 | 12,805 | 58 | 2011–2023 |
| 39086 | 400 | February 2013 | 101 | 785 | 782 | 99 | 7039 | 63 | 2013–2023 |
| NORAD ID | Maneuvers | MGMMMGA | GMM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | F1 | Precision | Recall | F1 | ||
| 27386 | 177 | 93.1% | 91.0% | 92.0% | 97.7% | 73.4% | 83.9% |
| 36508 | 179 | 99.3% | 84.3% | 91.2% | 99.2% | 67.6% | 80.4% |
| 41240 | 47 | 92.2% | 100.0% | 95.9% | 85.5% | 100.0% | 92.2% |
| 41335 | 73 | 83.9% | 100.0% | 91.3% | 100.0% | 68.5% | 81.3% |
| 43476 | 39 | 84.2% | 82.1% | 83.1% | 56.5% | 33.3% | 41.9% |
| 73477 | 39 | 80.6% | 74.4% | 77.3% | 56.7% | 43.6% | 49.3% |
| 37781 | 58 | 89.2% | 100.0% | 94.3% | 46.0% | 100.0% | 63.0% |
| 39086 | 63 | 94.2% | 77.8% | 85.2% | 96.2% | 39.7% | 56.2% |
| Total | 675 | 91.7% | 88.9% | 90.3% | 81.6% | 68.3% | 74.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; He, Z. Two-Line Element Outlier and Space Event Detection Method Based on Multi-Strategy Genetic Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093729
Zhang H, Zhao C, He Z. Two-Line Element Outlier and Space Event Detection Method Based on Multi-Strategy Genetic Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(9):3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093729
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haoyue, Chunmei Zhao, and Zhengbin He. 2024. "Two-Line Element Outlier and Space Event Detection Method Based on Multi-Strategy Genetic Algorithm" Applied Sciences 14, no. 9: 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093729
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhao, C., & He, Z. (2024). Two-Line Element Outlier and Space Event Detection Method Based on Multi-Strategy Genetic Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 14(9), 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14093729






