Prediction of Grain Porosity Based on WOA–BPNN and Grain Compression Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Porosity Experiment Determination Method
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Apparatus
2.3. Experimental Principles
2.4. Experimental Program
3. Database
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
4. Modeling Prediction of Grain Porosity
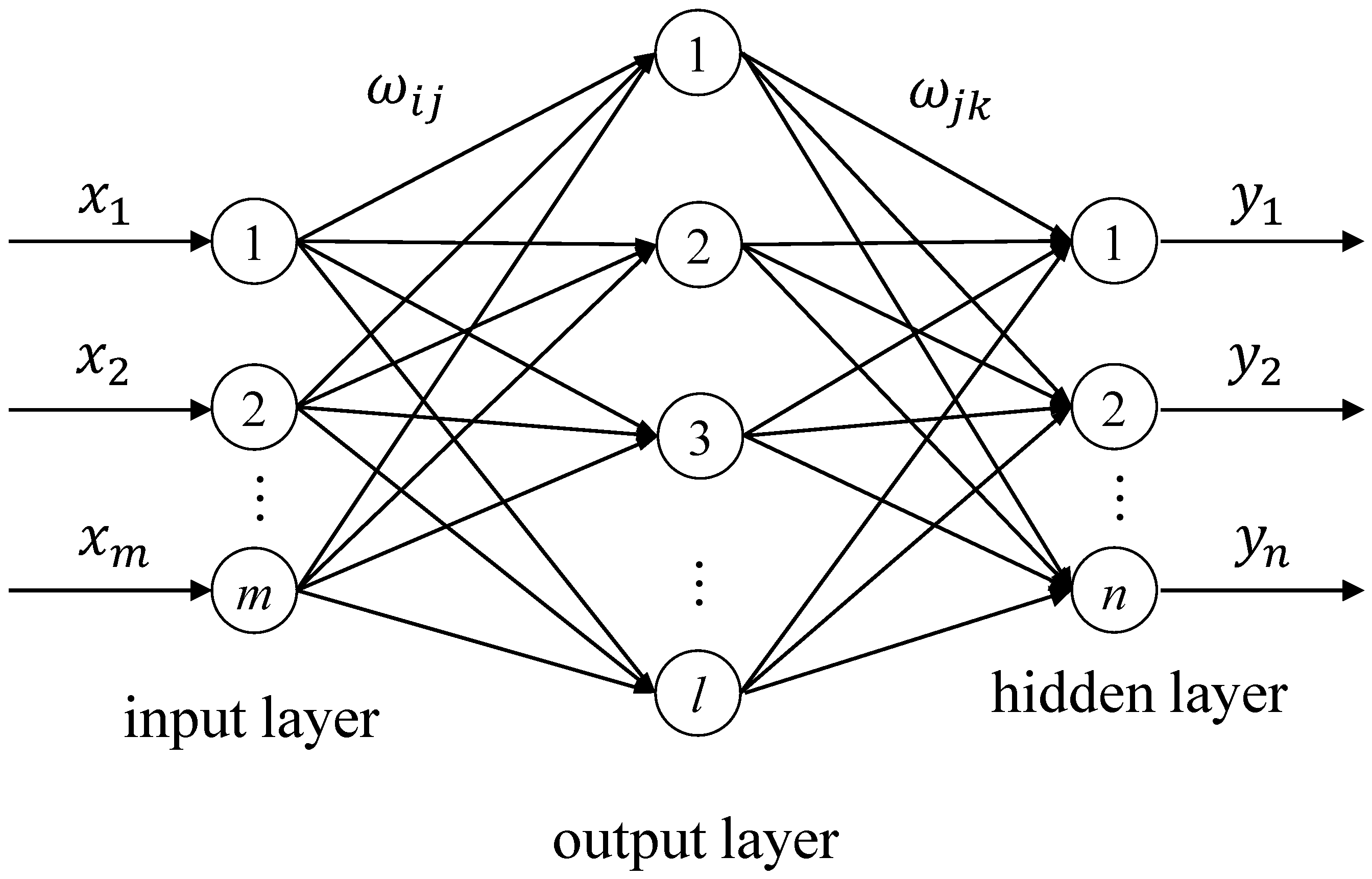
4.1. Back Propagation Neural Network
4.2. Whale Optimization Algorithm
- (1)
- Encircling Prey
- (2)
- Attacking by Bubble Net
- (3)
- Searching for Prey
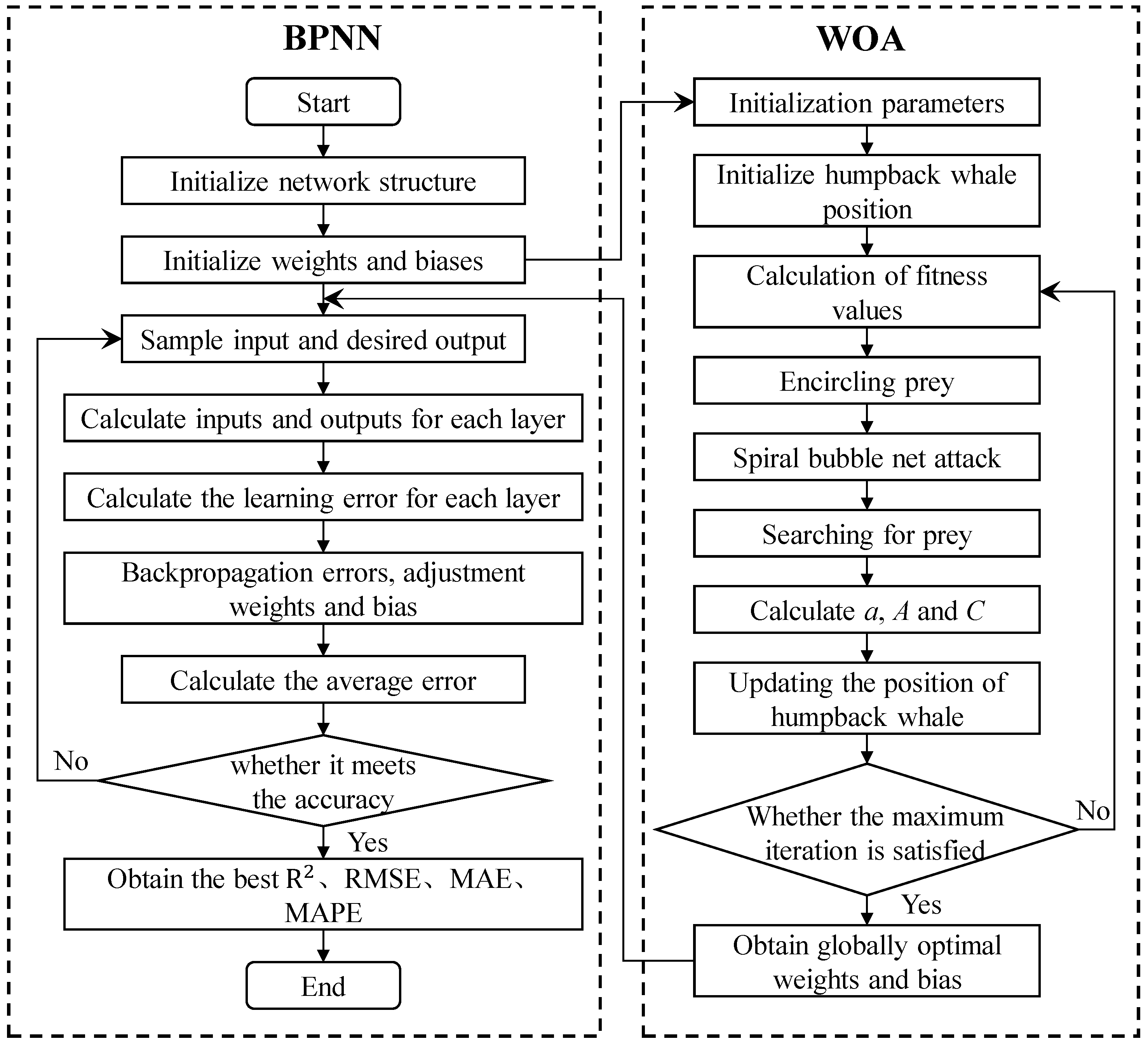
4.3. Construction of Grain Porosity Prediction Model Based on WOA–BPNN
4.4. Model Evaluation Indicators
5. Analysis of Prediction Results
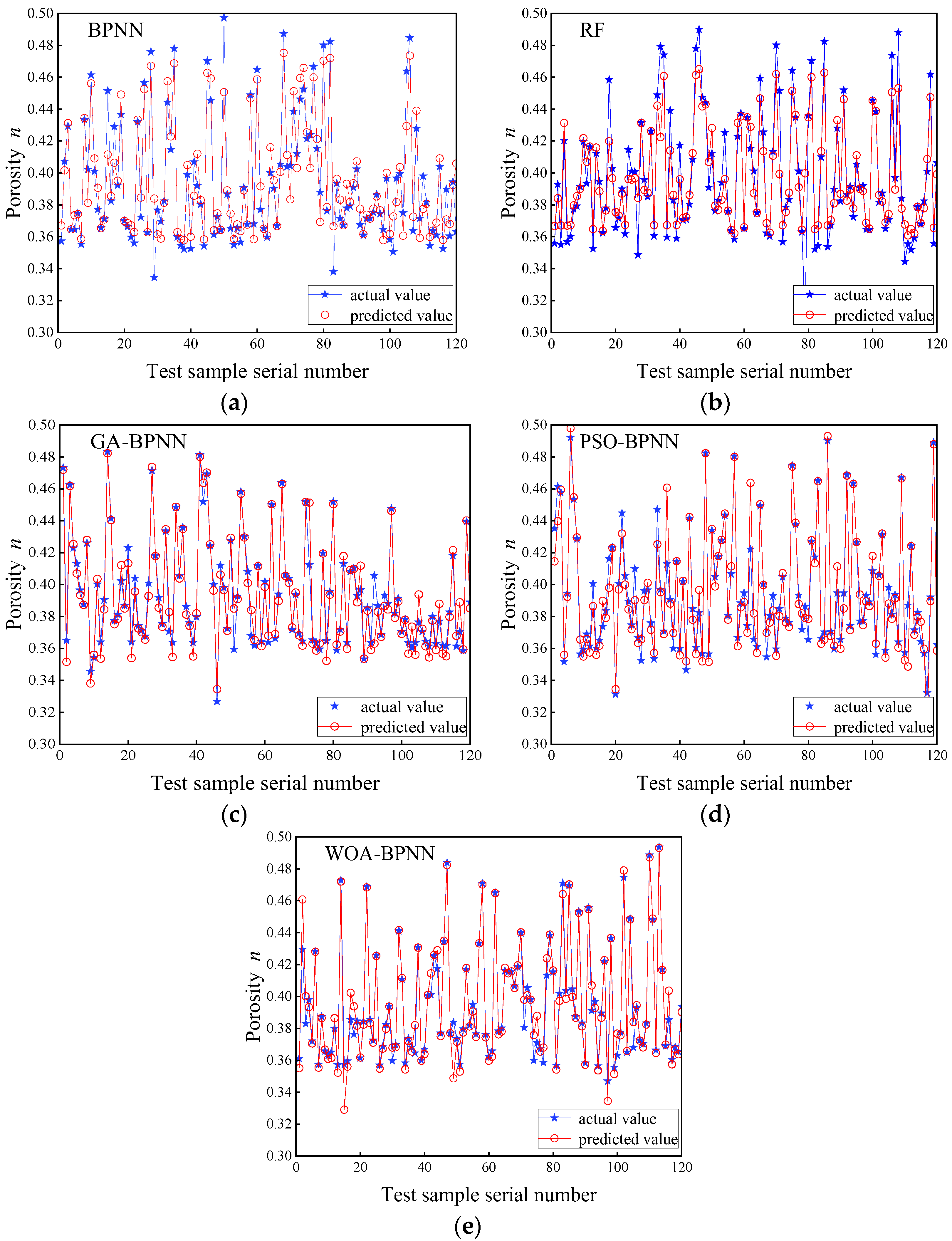
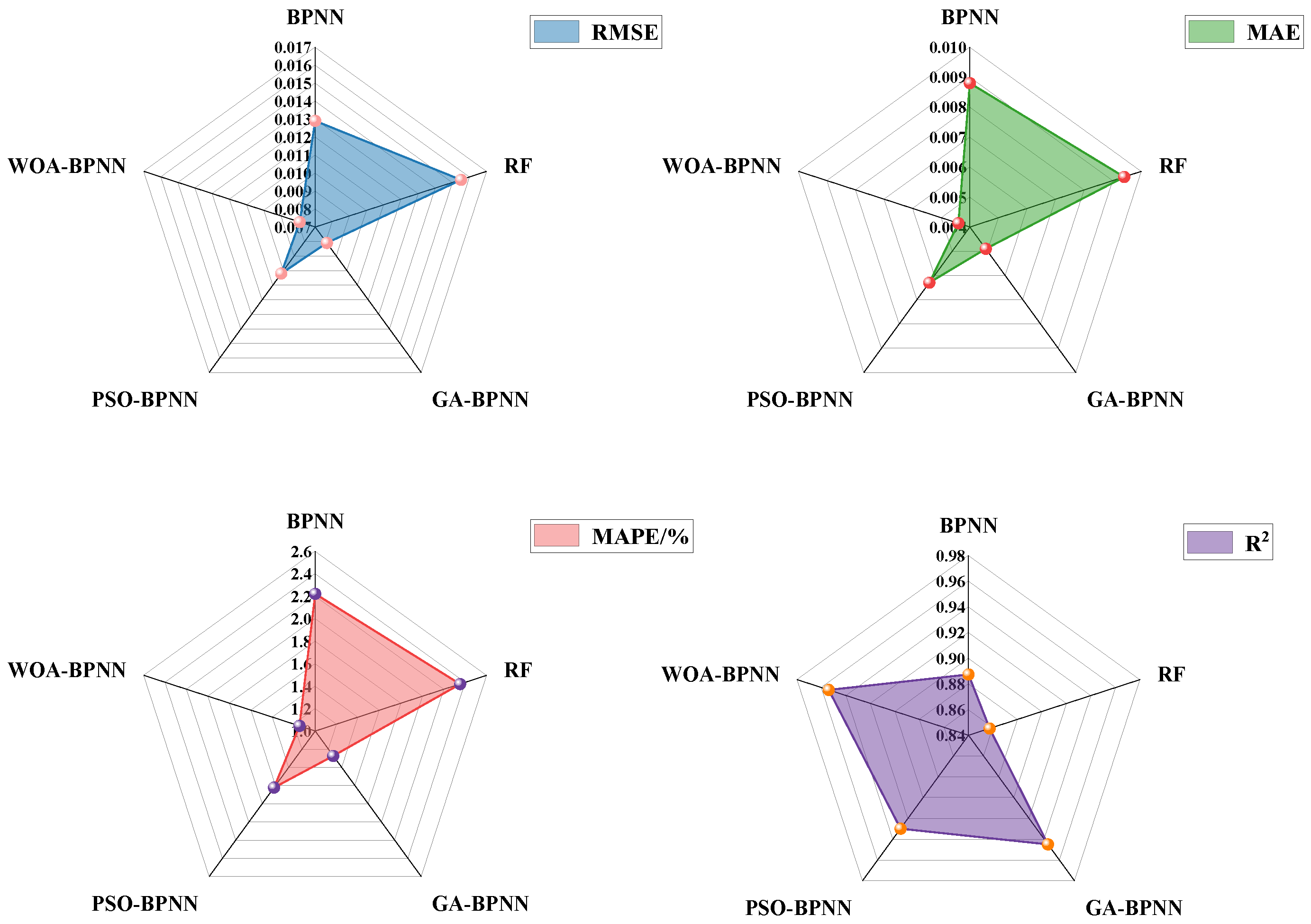
5.1. Comparison of Porosity Prediction Results from Five Machine Learning Models
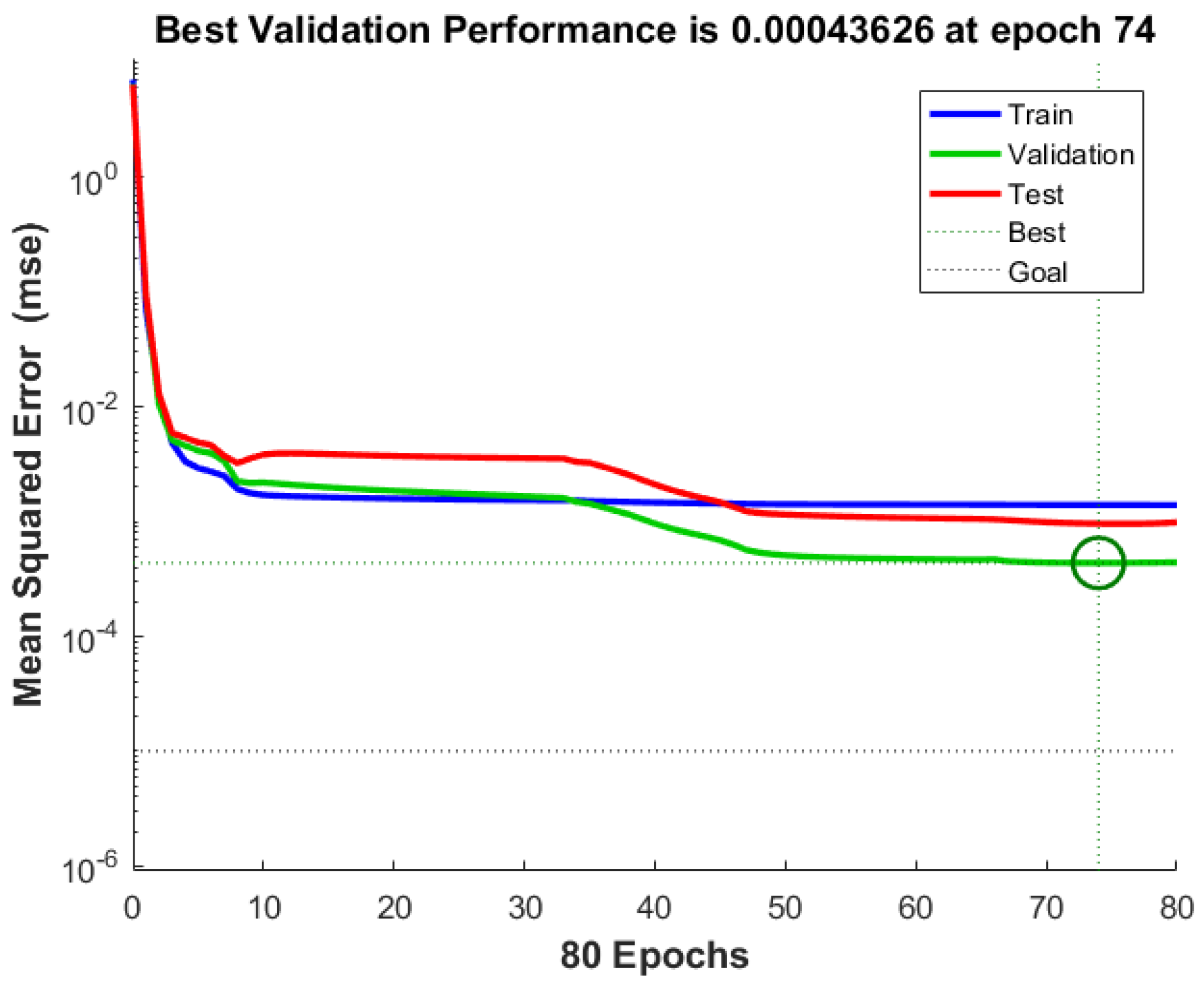
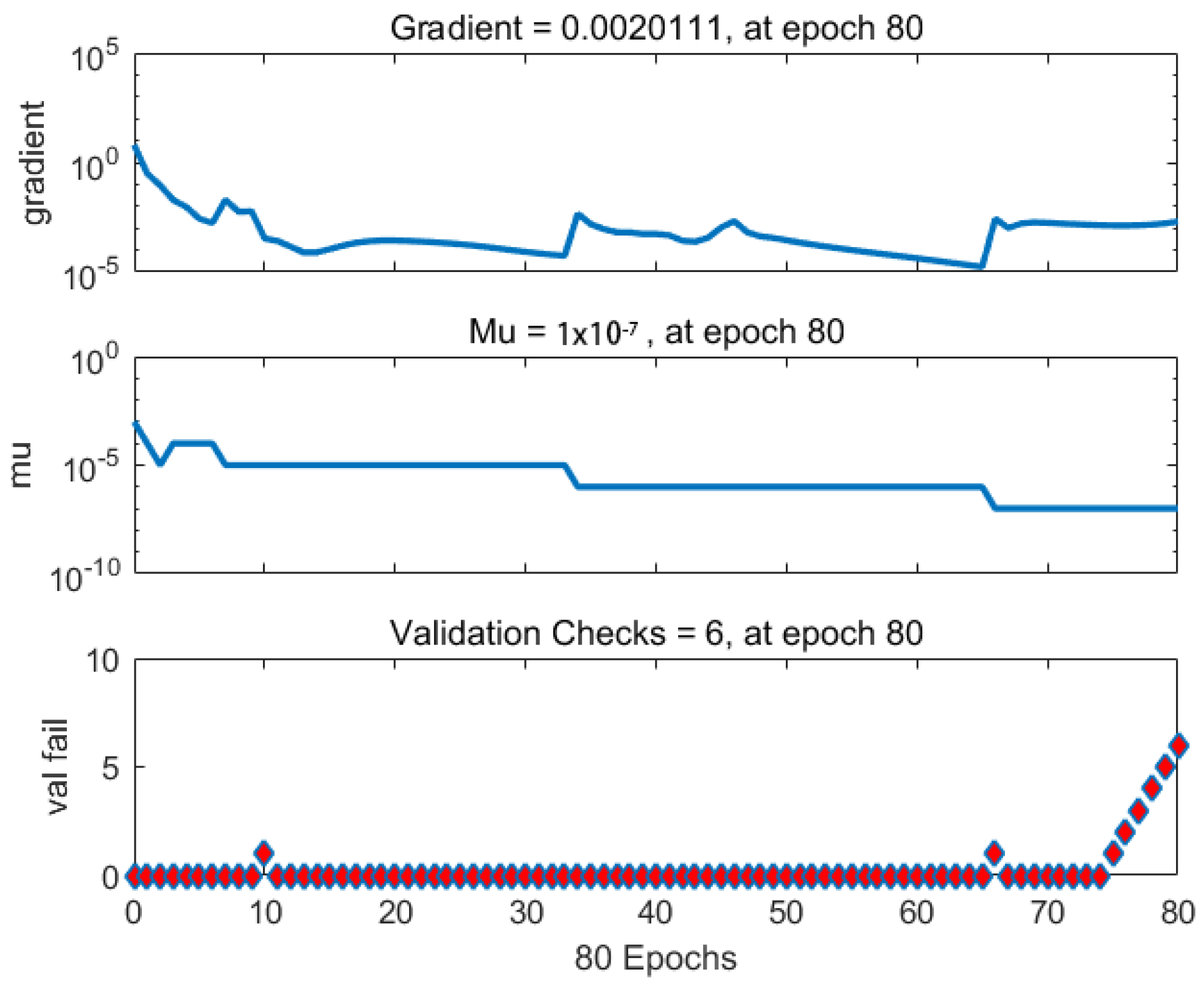
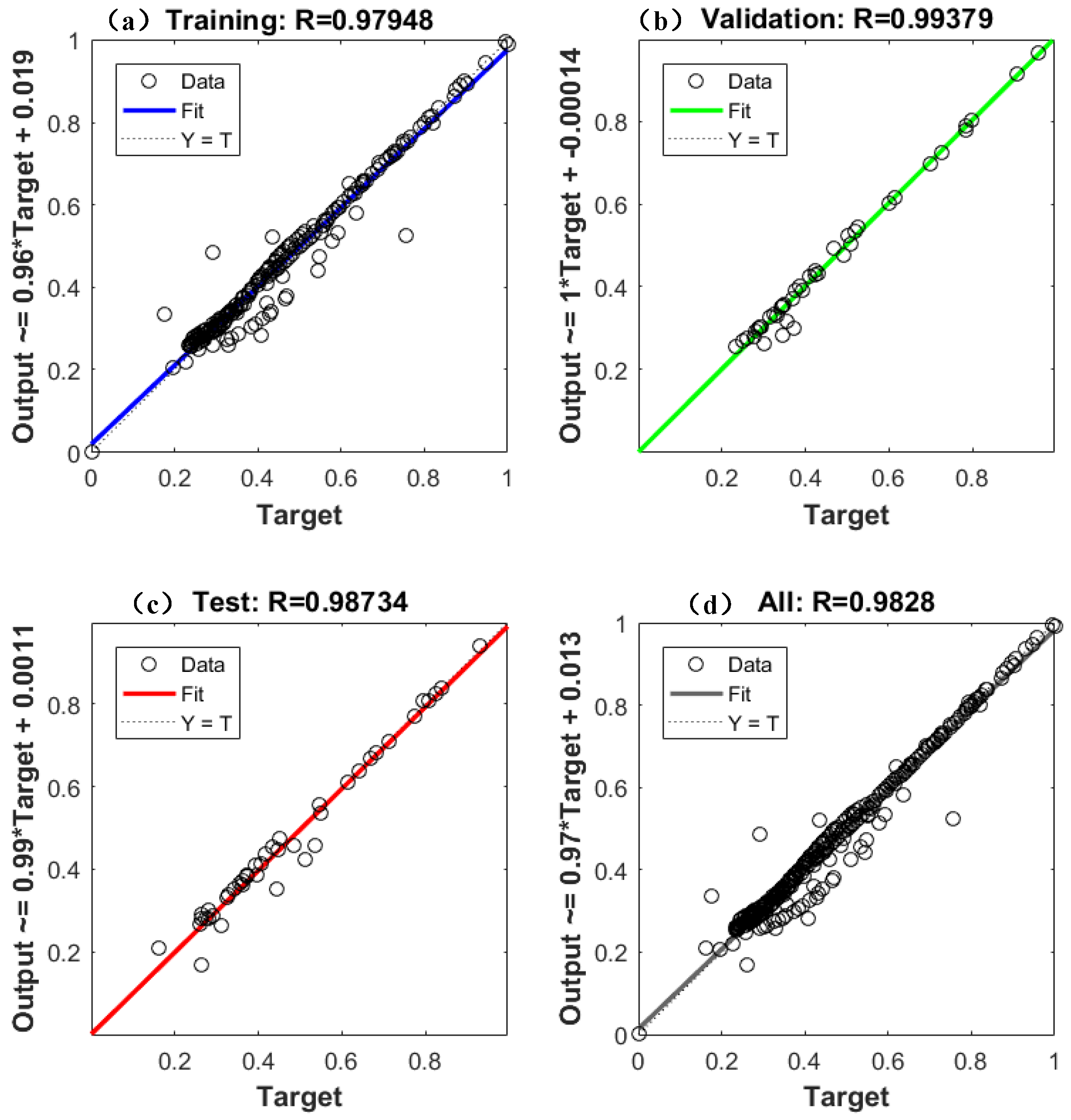
5.2. Performance Evaluation of WOA–BPNN Model for Porosity Prediction
5.3. Experimental Validation of the WOA–BPNN for Porosity Prediction Model
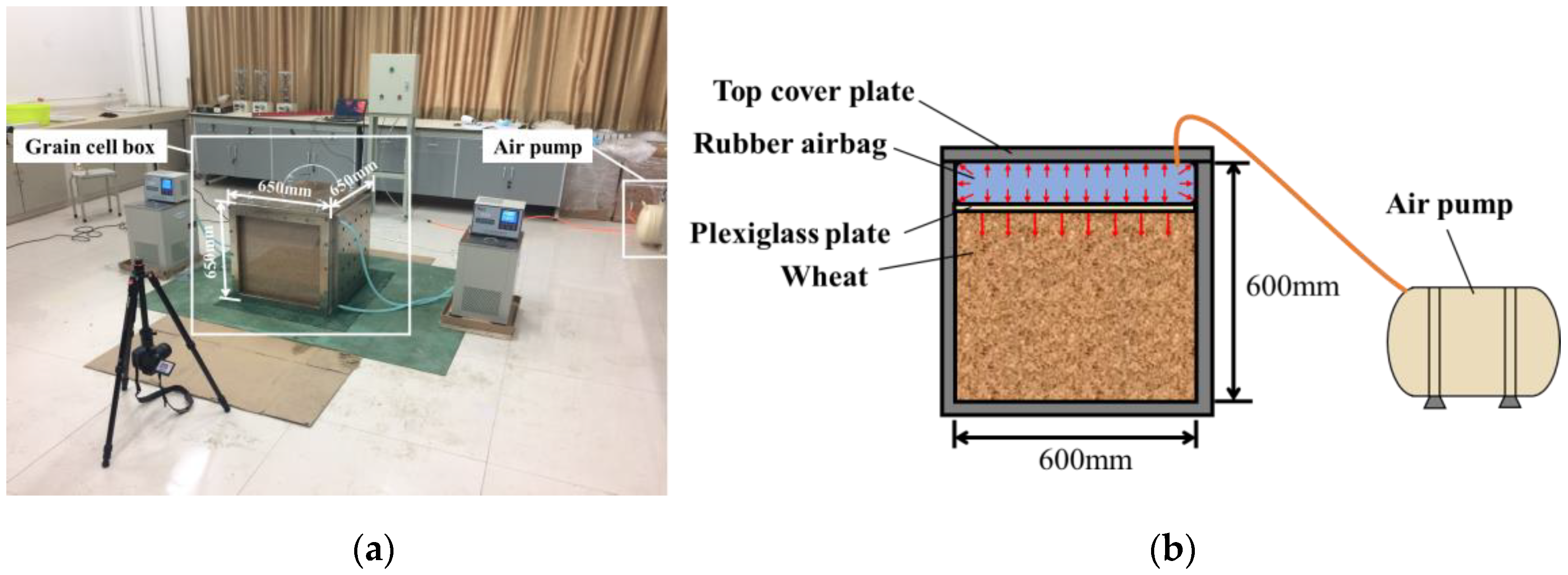
5.3.1. Grain Cell Box Experiment
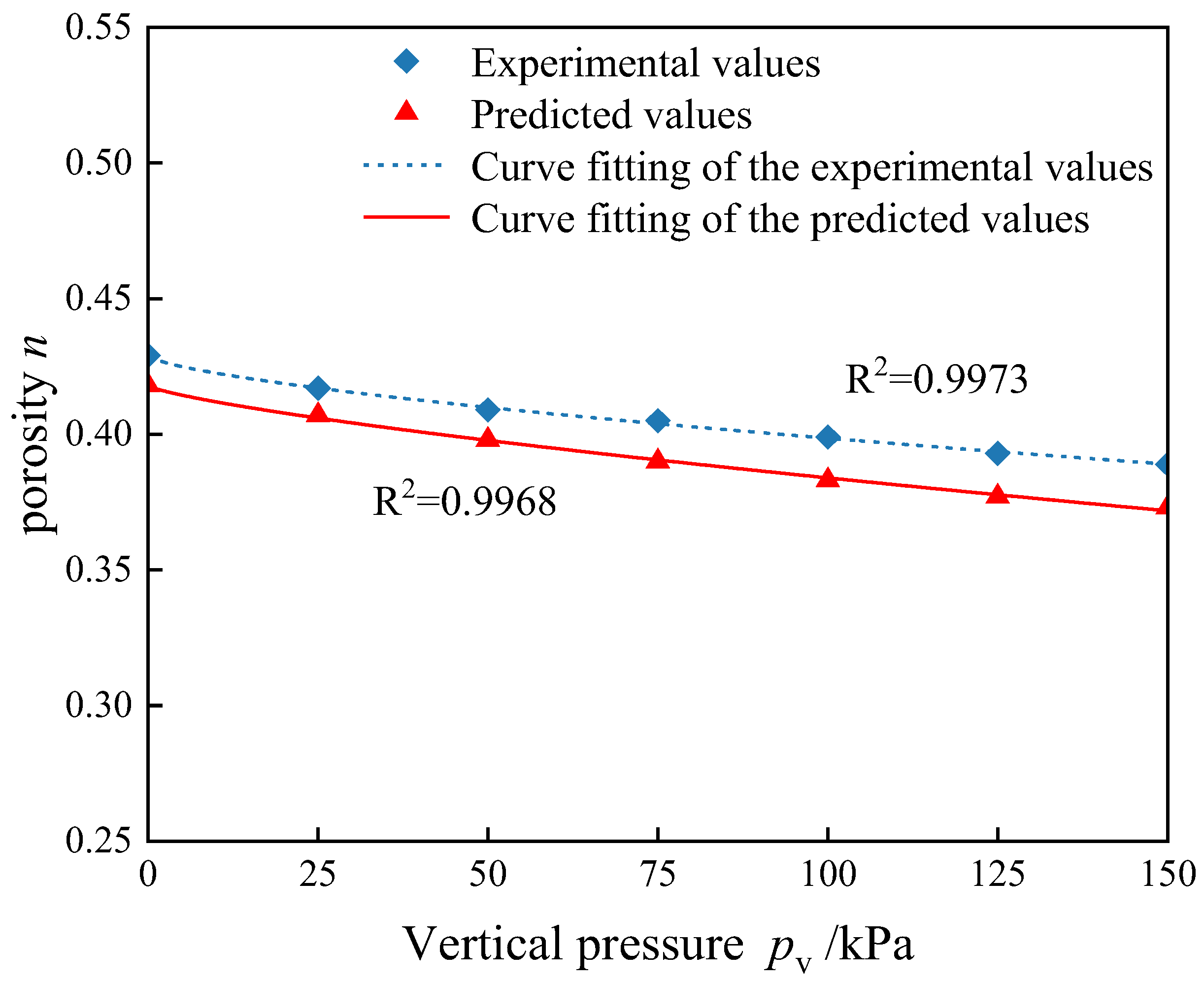
5.3.2. Comparison of Predicted and Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, D.; Kalita, P. Reducing postharvest losses during storage of grain crops to strengthen food security in developing countries. Foods 2017, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.D.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, J.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wu, W.F.; Li, F.J. Interactions of Mutiple Biological Fields in Stored Grain Ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, R.; Zhang, Q. A pore-scale model for predicting resistance to airflow in bulk grain. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 155, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatchatourian, O.A.; Savicki, D.L. Mathematical modelling of airflow in an aerated soya bean store under non-uniform conditions. Biosyst. Eng. 2004, 88, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saki, M.; Siahpoush, S.; Khaz’ali, A.R. A new generalized equation for estimation of sandstone and carbonate permeability from mercury intrusion porosimetry data. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 2637–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahn, L.; Bertier, P.; Seemann, T.; Stanjek, H. Distribution of sorbed water in the pore network of mudstones assessed from physisorption measurements. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 295, 109902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermarck, S.; Juppo, A.M.; Kervinen, L.; Yliruusi, J. Pore structure and surface area of mannitol powder, granules and tablets determined with mercury porosimetry and nitrogen adsorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 46, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.A.; Isaacs, G. Porosity determinations of grains and seeds with an air-comparison pycnometer. Trans. ASAE 1967, 10, 693–0696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Z.; Wang, B. Design and test of porosity testing apparatus for granular materials. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1707, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Karunakaran, C.; Jayas, D.S.; White, N.D.G. X-ray computed tomography image analysis to explain the airflow resistance differences in grain bulks. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 94, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Zheng, D.; Liu, W. Study of the pore structure characteristics of soybean grain piles using image processing technology. Int. Agrophysics 2023, 16, 8519–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Tan, L.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Y. Multiscale and multilayer structural modeling and simulation on drying of grain packing porous media. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 1664–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.; Maier, D.E.; Stroshine, R.L. Three-dimensional transient heat, mass, momentum, and species transfer in the stored grain ecosystem: Part I. Model development and evaluation. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Huang, K.; Wang, F.; Xie, W.; Wei, S.; Yang, D. Simulation of heat and mass transfer in a grain pile on the basis of a 2D irregular pore network. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Proc. 2019, 15, 367–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, M.N.A.; Abdoun, T.; El-Sekelly, W.J. Smart prediction of liquefaction-induced lateral spreading. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, M.N.A.; Shukla, S.K. Geomembranes. Predicting the settlement of geosynthetic-reinforced soil foundations using evolutionary artificial intelligence technique. Geotext. Geomembr. 2021, 49, 1280–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, C.; Zhong, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. Prediction of undrained shear strength using extreme gradient boosting and random forest based on Bayesian optimization. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatti, J.; Grover, K.S. Prediction of compaction parameters for fine-grained soil: Critical comparison of the deep learning and standalone models. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 3010–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xun, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, J. Combining discriminant analysis and neural networks for corn variety identification. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 71, S48–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Gao, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Su, Z. Mildew recognition on maize seed by use of hyperspectral technology. Spectrosc. Lett. 2022, 55, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Mao, S.; Zhang, Y. Forecasting of Grain Pile Temperature From Meteorological Factors Using Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 130721–130733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duysak, H.; Yigit, E. Machine learning based quantity measurement method for grain silos. Measurement 2020, 152, 107279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. Classification of corn kernels grades using image analysis and support vector machine. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 1687814018817642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeymer, J.S.; Guzzo, F.; de Araujo, M.E.V.; Gates, R.S.; Correa, P.C.; Vidigal, M.C.T.R.; Neisse, A.C. Machine learning algorithms to predict the dry matter loss of stored soybean grains (Glycine max L.). J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anami, B.S.; Malvade, N.N.; Palaiah, S. Automated recognition and classification of adulteration levels from bulk paddy grain samples. Inf. Process. Agric. 2019, 6, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASAE S352.2 APR1988 (R2017); Moisture Measurement–Unground Grain and Seeds. ASAE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2017.
- Deshpande, S.D.; Bal, S.; Ojha, T.P. Physical properties of soybean. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1993, 56, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T5498-2013; Code for Inspection of Grain and Oils—Determination of Test Weight. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection, and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB/T5518-2008; Code for Inspection of Grain and Oil—Determination of Relative Density of Grain and Oilseeds. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection, and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
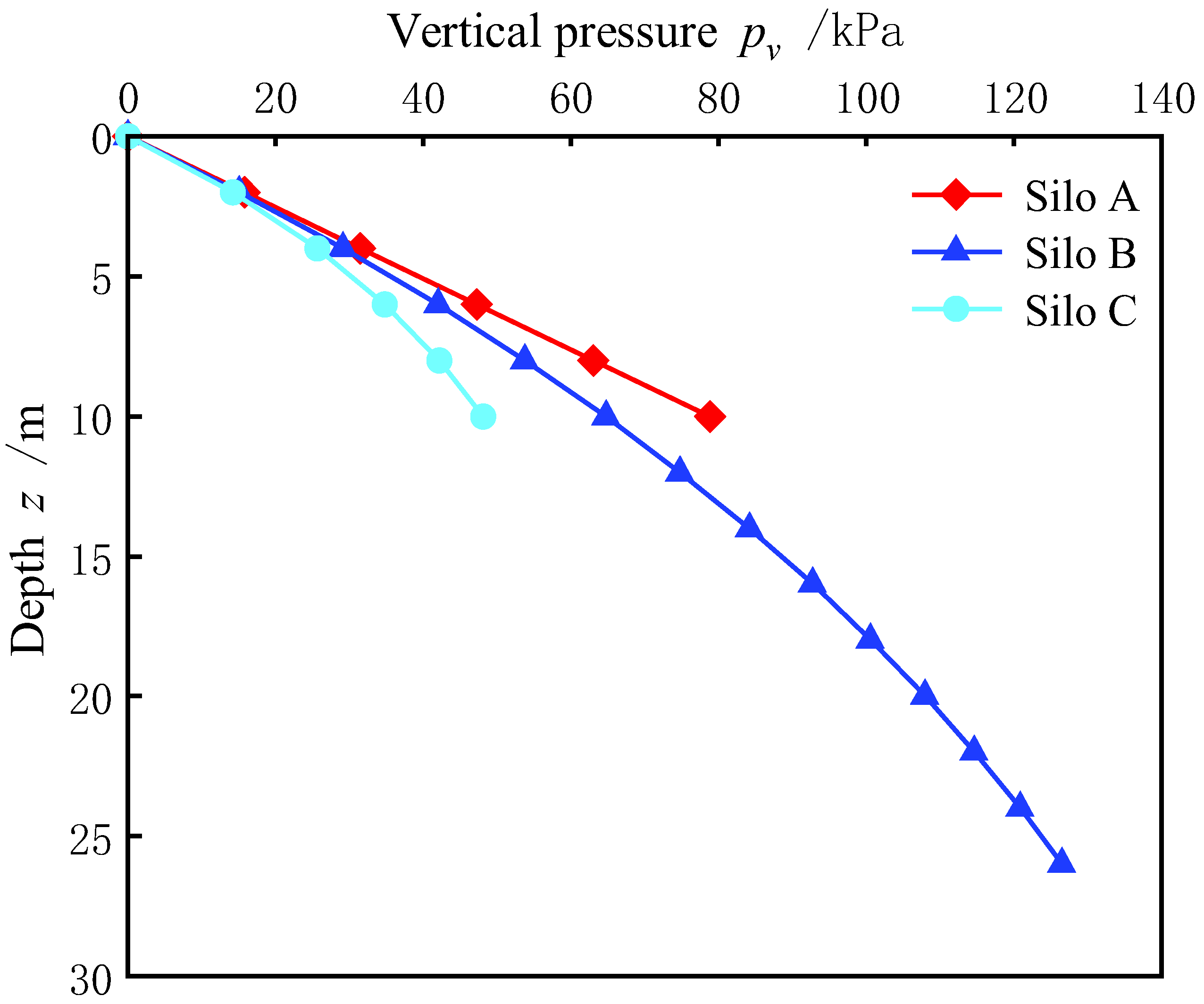
- Talesnick, M.; Horany, H.; Dancygier, A.N.; Karinski, Y.S. Measuring soil pressure on a buried model structure for the validation of quantitative frameworks. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2008, 134, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H. Study on porosity and density of different grains under vertical pressure. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 42, 89–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Z. Element tests and simulation of effects of vertical pressure on compression and mildew of wheat. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50077-2003; Code for Design of Reinforced Concrete Silos. Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Zhang, X. Study on the Pore Parameter of Grain Heap; China Agricultural University: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Test Study on the Porosity of Grain Mass; Henan University of Technology: Zhengzhou, China, 2016. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Yue, L.; Liu, W.; Ge, M. Effect of uniaxial compression on creep behavior and quality of wheat bulk. J. Henan Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 44, 112–116+134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Bi, W.; Jiang, J.; Shi, T. Research on Determination Method and Influencing Factors of Porosity of Wheat Pile. Sci. Technol. Cereals Oils Foods 2021, 29, 187–193. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tang, D.; Tang, W.; Yang, S.; Tang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, F. Agricultural Price Prediction Based on Combined Forecasting Model under Spatial-Temporal Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.H.; Xu, W.H.; Chen, Y.T. Novel back propagation optimization by cuckoo search algorithm. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 878262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Grain Type | Initial Bulk Density /(kg/m3) | Particle Density /(kg/m3) | Grain Length L/mm | Grain Width W/mm | Grain Thickness T/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | 806.8 | 1383.75 | 6.53 | 3.41 | 2.91 |
| Corn | 735.0 | 1256.68 | 11.84 | 8.62 | 4.72 |
| Soybean | 717.1 | 1219.87 | 7.72 | 7.58 | 7.46 |
| Paddy | 599.0 | 1164.49 | 7.38 | 3.07 | 2.13 |
| Grain Type | Initial Moisture Content MC0/% | Actual Moisture Content after Formulation MC/% |
|---|---|---|
| Wheat | 10.70 | 10.70 |
| 11.26 | ||
| 12.89 | ||
| Corn | 11.58 | 11.58 |
| 12.34 | ||
| 13.47 | ||
| Soybean | 10.14 | 8.58 |
| 10.14 | ||
| 13.43 | ||
| Paddy | 12.93 | 11.69 |
| 12.93 | ||
| 14.52 |
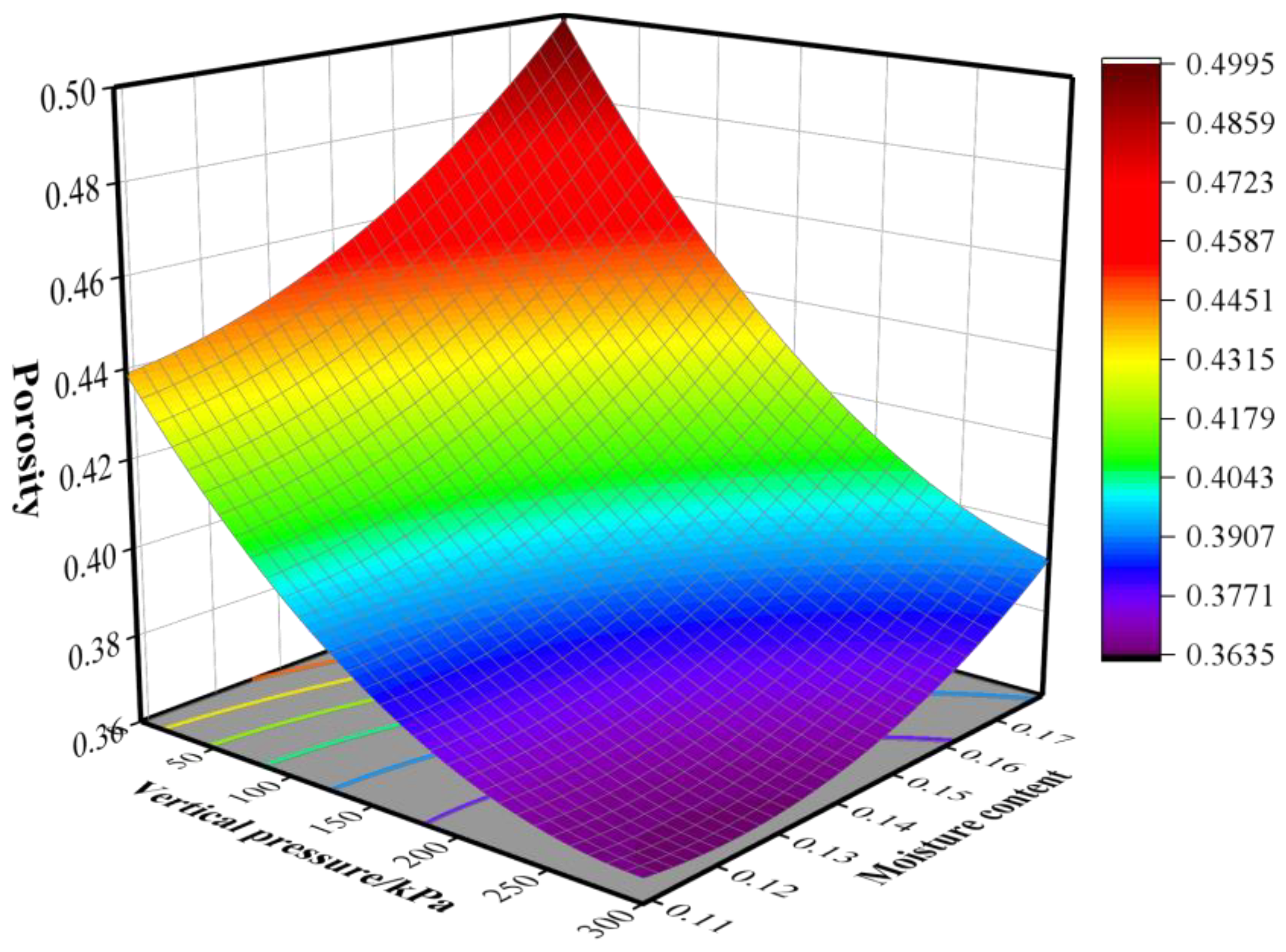
| Grain Types | Moisture Content/% | Vertical Pressure/kPa | Porosity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | 10.70 | 0 | 0.414 |
| Wheat | 10.70 | 21 | 0.405 |
| Wheat | 10.70 | 42 | 0.398 |
| Wheat | 10.70 | 83 | 0.385 |
| Wheat | 10.70 | 125 | 0.377 |
| Corn | 11.58 | 0 | 0.399 |
| Corn | 11.58 | 21 | 0.391 |
| Corn | 11.58 | 42 | 0.384 |
| Corn | 11.58 | 83 | 0.374 |
| Corn | 11.58 | 125 | 0.367 |
| Soybean | 8.58 | 0 | 0.373 |
| Soybean | 8.58 | 21 | 0.363 |
| Soybean | 8.58 | 42 | 0.353 |
| Soybean | 8.58 | 83 | 0.330 |
| Soybean | 8.58 | 125 | 0.306 |
| Paddy | 12.93 | 0 | 0.487 |
| Paddy | 12.93 | 21 | 0.480 |
| Paddy | 12.93 | 42 | 0.474 |
| Paddy | 12.93 | 83 | 0.464 |
| Paddy | 12.93 | 125 | 0.456 |
| Model | Running Time/Second |
|---|---|
| BP | 1.4812 |
| RF | 0.2570 |
| GA–BP | 7.5487 |
| PSO–BP | 4.0655 |
| WOA–BP | 37.6912 |
| Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE | MAPE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPNN | 0.8874 | 0.0129 | 0.0088 | 2.2208 |
| RF | 0.8572 | 0.0155 | 0.0094 | 2.3517 |
| GA–BPNN | 0.9450 | 0.0081 | 0.0049 | 1.2735 |
| PSO–BPNN | 0.9299 | 0.0102 | 0.0063 | 1.6213 |
| WOA–BPNN | 0.9542 | 0.0079 | 0.0044 | 1.1467 |
| Methods for Obtaining Porosity | a | b | n0 | R2 (Curve Fitting) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WOA–BPNN model | −0.0011 | 0.7509 | 0.418 | 0.9968 |
| Grain cell box experiment | −0.0014 | 0.6736 | 0.429 | 0.9973 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, D.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Liu, C. Prediction of Grain Porosity Based on WOA–BPNN and Grain Compression Experiment. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072960
Chen J, Li J, Zheng D, Zheng Q, Zhang J, Wu M, Liu C. Prediction of Grain Porosity Based on WOA–BPNN and Grain Compression Experiment. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(7):2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072960
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiahao, Jiaxin Li, Deqian Zheng, Qianru Zheng, Jiayi Zhang, Meimei Wu, and Chaosai Liu. 2024. "Prediction of Grain Porosity Based on WOA–BPNN and Grain Compression Experiment" Applied Sciences 14, no. 7: 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072960
APA StyleChen, J., Li, J., Zheng, D., Zheng, Q., Zhang, J., Wu, M., & Liu, C. (2024). Prediction of Grain Porosity Based on WOA–BPNN and Grain Compression Experiment. Applied Sciences, 14(7), 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14072960






