Microseismic Velocity Inversion Based on Deep Learning and Data Augmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Velocity Inversion and Network Architecture
2.2. Data Augmentation
2.3. Loss Functions and Quantitative Metrics
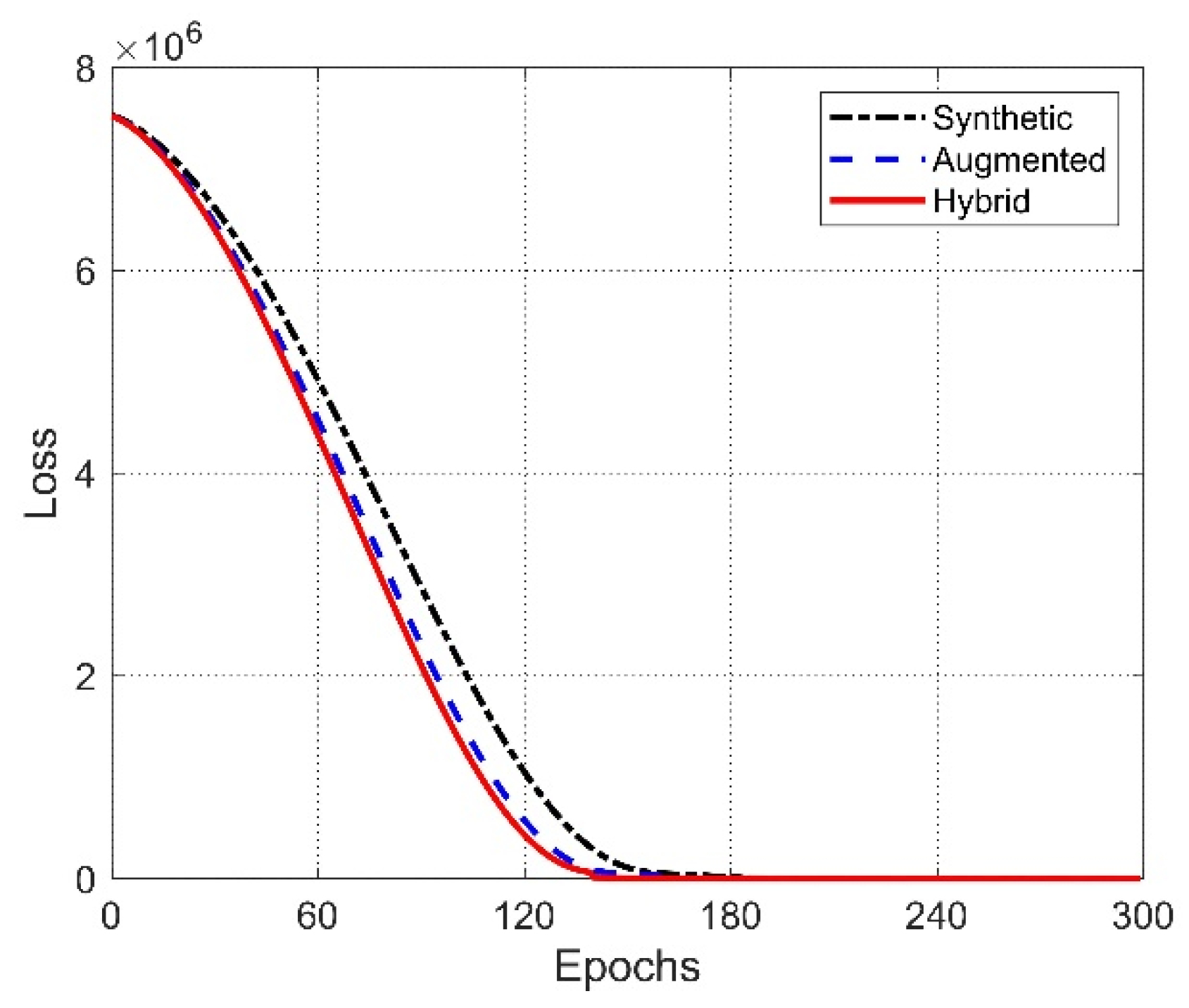
2.4. Training Procedure
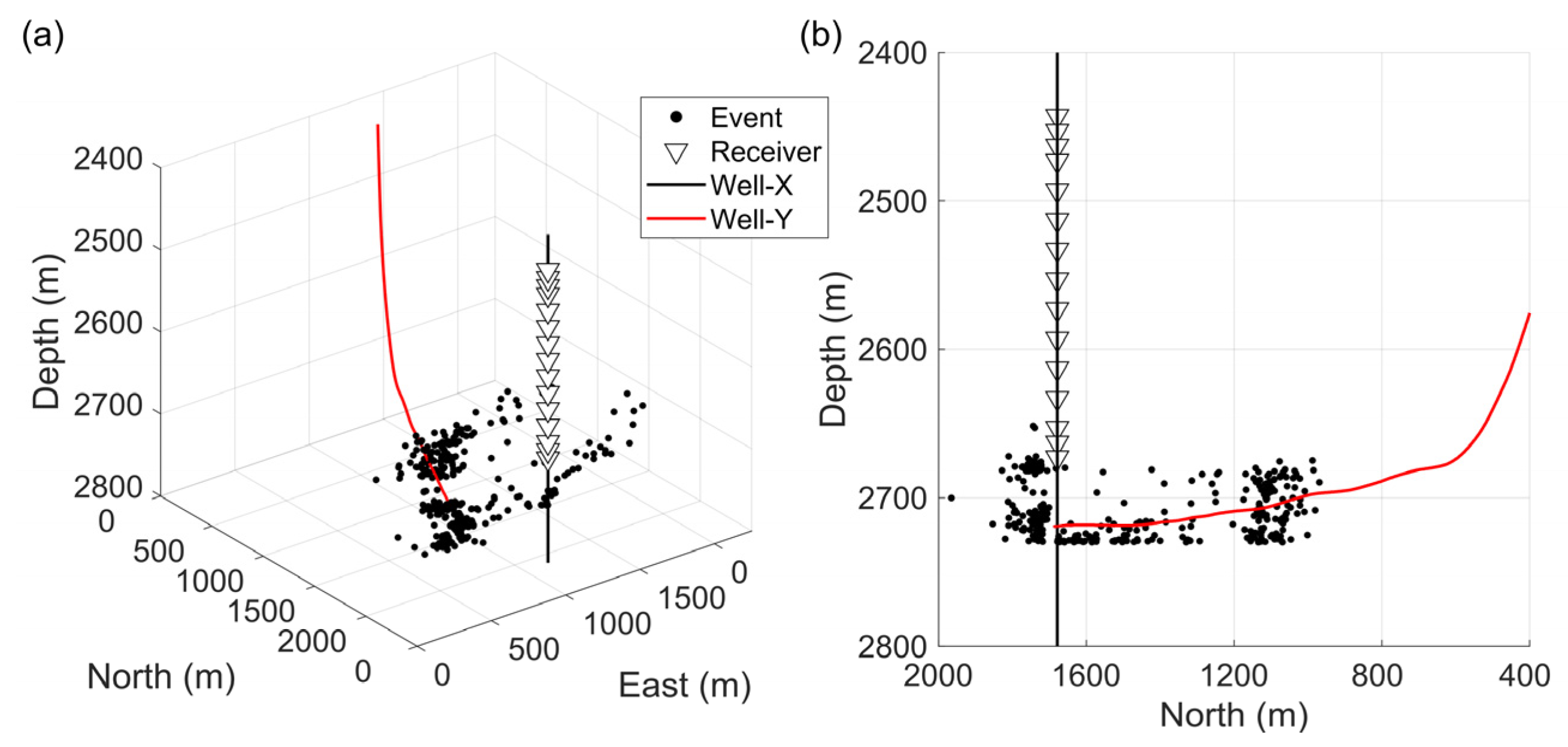
3. Data
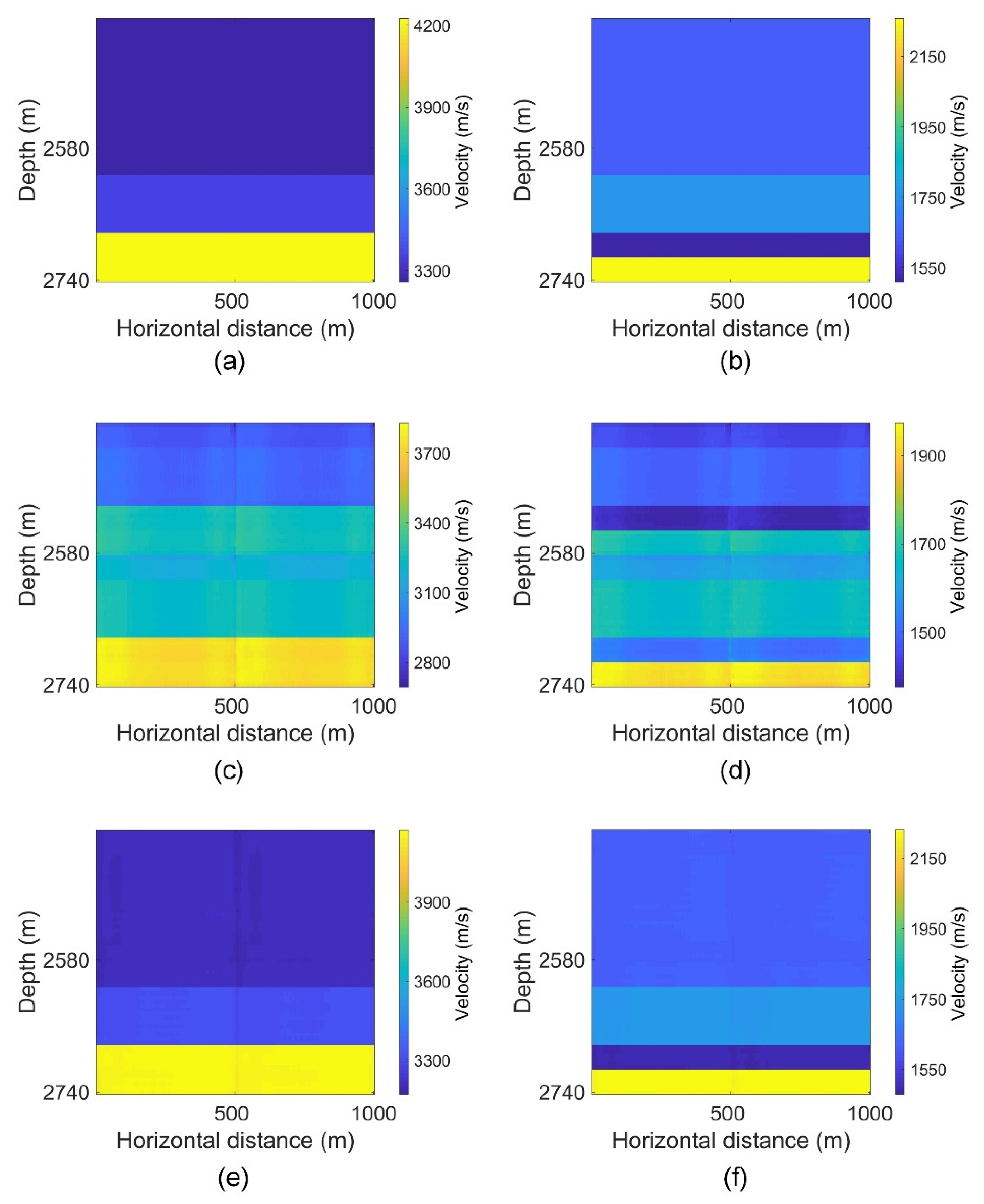
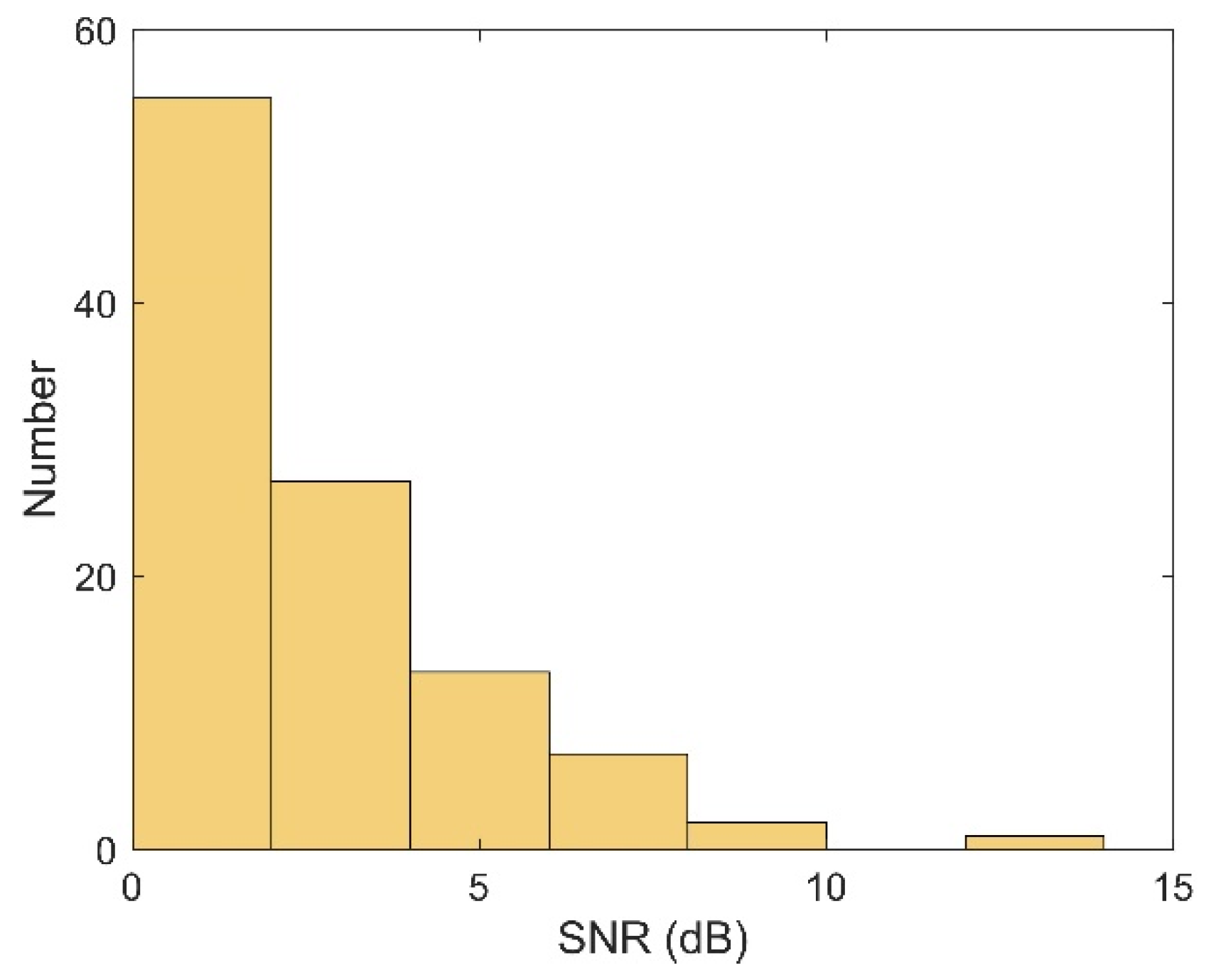
4. Result
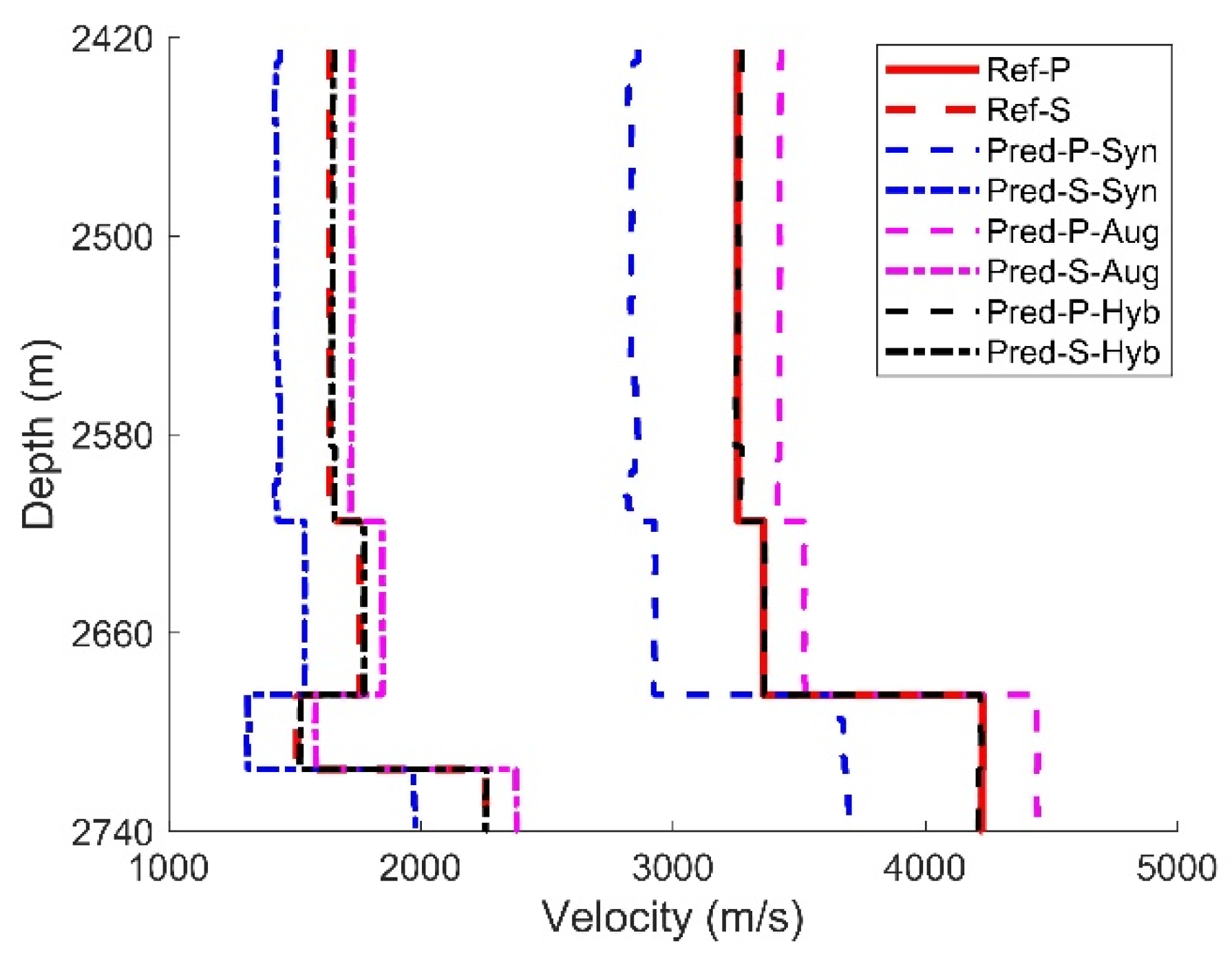
4.1. Single-Stage Examples
4.2. Robustness Testing
4.3. Multi-Stage Examples
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eaton, D.W. Passive Seismic Monitoring of Induced Seismicity: Fundamental Principles and Application to Energy Technologies, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-107-14525-2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Tan, J.; Wood, D.A.; Zhao, Z.; Becker, D.; Lyu, Q.; Shu, B.; Chen, H. A Review of the Current Status of Induced Seismicity Monitoring for Hydraulic Fracturing in Unconventional Tight Oil and Gas Reservoirs. Fuel 2019, 242, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-B.; Chen, H.-C.; Niu, F.-L.; Du, Y.-J. Master Event Based Backazimuth Estimation and Its Application to Downhole Microseismic Monitoring. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 2675–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tan, J.; Tan, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhao, Z. Chapter Eight: Microseismic Analysis to Aid Gas Reservoir Characterization. In Sustainable Natural Gas Reservoir and Production Engineering; Wood, D.A., Cai, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 219–242. [Google Scholar]
- Tomassi, A.; Milli, S.; Tentori, D. Synthetic Seismic Forward Modeling of a High-Frequency Depositional Sequence: The Example of the Tiber Depositional Sequence (Central Italy). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansky, J.; Plicka, V.; Eisner, L. Feasibility of Joint 1D Velocity Model and Event Location Inversion by the Neighbourhood Algorithm. Geophys. Prospect. 2010, 58, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tan, J.; Schwarz, B.; Staněk, F.; Poiata, N.; Shi, P.; Diekmann, L.; Eisner, L.; Gajewski, D. Recent Advances and Challenges of Waveform-based Seismic Location Methods at Multiple Scales. Rev. Geophys. 2020, 58, e2019RG000667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warpinski, N.R.; Sullivan, R.B.; Uhl, J.E.; Waltman, C.K.; Machovoe, S.R. Improved Microseismic Fracture Mapping Using Perforation Timing Measurements for Velocity Calibration. SPE J. 2005, 10, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, D.; Quirein, J.A.; Cornish, B.E.Q.; Quinn, D.; Warpinski, N.R. Velocity Calibration for Microseismic Monitoring: A Very Fast Simulated Annealing (VFSA) Approach for Joint-Objective Optimization. Geophysics 2009, 74, WCB47–WCB55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; He, C.; Mao, Z. Microseismic Velocity Model Inversion and Source Location: The Use of Neighborhood Algorithm and Master Station Method. Geophysics 2018, 83, 1JA-Z18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igonin, N.; Innanen, K.A. Analysis of Simultaneous Velocity and Source Parameter Updates in Microseismic FWI. In Proceedings of the SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2018, Anaheim, CA, USA, 27 August 2018; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2018; pp. 1033–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Alkhalifah, T. Microseismic Imaging Using a Source Function Independent Full Waveform Inversion Method. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 214, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virieux, J.; Operto, S. An Overview of Full-Waveform Inversion in Exploration Geophysics. Geophysics 2009, 74, WCC1–WCC26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitton, A.; Díaz, E. Attenuating Crosstalk Noise with Simultaneous Source Full Waveform Inversion. Geophys. Prospect. 2012, 60, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Beroza, G.C. Deep-Learning Seismology. Science 2022, 377, eabm4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anikiev, D.; Birnie, C.; bin Waheed, U.; Alkhalifah, T.; Gu, C.; Verschuur, D.J.; Eisner, L. Machine Learning in Microseismic Monitoring. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 239, 104371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, C.; Pazzi, V.; Zou, Y.; Casagli, N. Microseismic Signal Denoising and Separation Based on Fully Convolutional Encoder–Decoder Network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Qin, G.; Li, H. Research on Automatic Classification of Coal Mine Microseismic Events Based on Data Enhancement and FCN-LSTM Network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Ran, X.; Xu, W.; Yan, W.; Li, T.; Dai, K.; Wan, J.; Lin, Y.; Tong, K. Fine Classification Method for Massive Microseismic Signals Based on Short-Time Fourier Transform and Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Li, F.; Gao, J. Microseismic First-Arrival Picking Using Fine-Tuning Feature Pyramid Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 7505105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, T.; Qi, J.; Wang, S.-X. SegNet-Based First-Break Picking via Seismic Waveform Classification Directly from Shot Gathers with Sparsely Distributed Traces. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Leng, J.; Dong, Y.; Yu, Z.; Hu, T.; He, C. Phase Arrival Picking for Bridging Multi-Source Downhole Microseismic Data Using Deep Transfer Learning. J. Geophys. Eng. 2022, 19, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamriew, D.; Dorhjie, D.B.; Bogoedov, D.; Pevzner, R.; Maltsev, E.; Charara, M.; Pissarenko, D.; Koroteev, D. Microseismic Monitoring and Analysis Using Cutting-Edge Technology: A Key Enabler for Reservoir Characterization. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamriew, D.; Pevzner, R.; Maltsev, E.; Pissarenko, D. Deep Neural Networks for Detection and Location of Microseismic Events and Velocity Model Inversion from Microseismic Data Acquired by Distributed Acoustic Sensing Array. Sensors 2021, 21, 6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araya-Polo, M.; Jennings, J.; Adler, A.; Dahlke, T. Deep-Learning Tomography. Lead. Edge 2018, 37, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ma, J. Deep-Learning Inversion: A next-Generation Seismic Velocity Model Building Method. Geophysics 2019, 84, R583–R599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamriew, D.; Charara, M.; Pissarenko, D. Joint Event Location and Velocity Model Update in Real-Time for Downhole Microseismic Monitoring: A Deep Learning Approach. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 158, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, J.; Shang, X.; Huang, W. Microseismic Data-Direct Velocity Modeling Method Based on a Modified Attention U-Net Architecture. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, P.; Yang, J.; Xu, W.; Tong, S. Compensating Low-Frequency Signals for Prestack Seismic Data and Its Applications in Full-Waveform Inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5920814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Q.; Lin, Y. Enhancing Data-Driven Seismic Inversion Using Physics-Guided Spatiotemporal Data Augmentation. In Proceedings of the First International Meeting for Applied Geoscience & Energy Expanded Abstracts, Denver, CO, USA, 1 September 2021; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2021; pp. 1395–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhalifah, T.; Wang, H.; Ovcharenko, O. MLReal: Bridging the Gap between Training on Synthetic Data and Real Data Applications in Machine Learning. Artif. Intell. Geosci. 2022, 3, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Si, X.; Bi, Z.; Yang, J.; Gao, H.; Xie, D.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J. Sensing Prior Constraints in Deep Neural Networks for Solving Exploration Geophysical Problems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2219573120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. ISBN 978-3-319-24573-7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.-B.; Si, H.-J.; Wu, X.-M.; Yan, S.-S. A Comparison of Deep Learning Methods for Seismic Impedance Inversion. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Li, M. Empirical Evaluation of Rectified Activations in Convolutional Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00853. [Google Scholar]
- Glorot, X.; Bordes, A.; Bengio, Y. Domain Adaptation for Large-Scale Sentiment Classification: A Deep Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-11), Bellevue, WA, USA, 28 June–2 July 2011; pp. 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Alkhalifah, T. Direct Microseismic Event Location and Characterization from Passive Seismic Data Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Geophysics 2021, 86, KS109–KS121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y. Data-Driven Seismic Waveform Inversion: A Study on the Robustness and Generalization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6900–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, Z.; Pan, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, D. Deep Learning with Adaptive Attention for Seismic Velocity Inversion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, B.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, P. Deep-Learning Inversion of Seismic Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2135–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Cui, H. Improved Threshold Denoising Method Based on Wavelet Transform. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC 2015), Sousse, Tunisia, 18–20 December 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar]



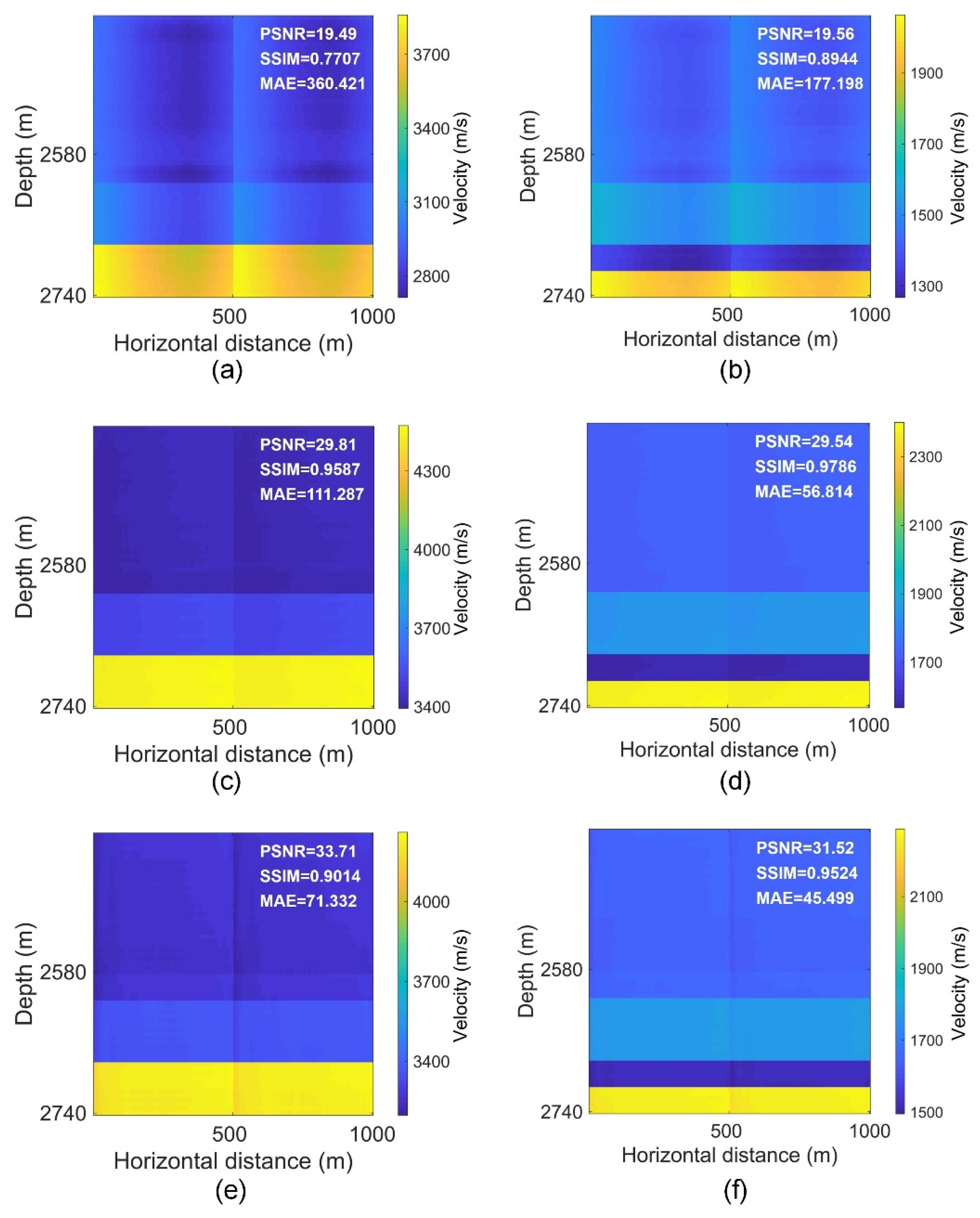

| Training Dataset | Phase | PSNR | SSIM | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic | P | 19.88 | 0.7097 | 272.243 |
| S | 19.92 | 0.8139 | 133.958 | |
| Augmented | P | 27.90 | 0.8644 | 113.514 |
| S | 27.71 | 0.8912 | 57.431 | |
| Hybrid | P | 30.04 | 0.8591 | 93.143 |
| S | 29.60 | 0.8911 | 48.308 |
| Training Dataset | Phase | PSNR | SSIM | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic | P | 18.75 | 0.7094 | 314.843 |
| S | 19.16 | 0.7209 | 155.461 | |
| Augmented | P | 21.50 | 0.7030 | 228.985 |
| S | 17.89 | 0.6759 | 152.441 | |
| Hybrid | P | 22.24 | 0.7478 | 221.382 |
| S | 18.46 | 0.6369 | 165.114 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Zeng, X.; Pan, X.; Peng, L.; Tan, Y.; Liu, J. Microseismic Velocity Inversion Based on Deep Learning and Data Augmentation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052194
Li L, Zeng X, Pan X, Peng L, Tan Y, Liu J. Microseismic Velocity Inversion Based on Deep Learning and Data Augmentation. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(5):2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052194
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lei, Xiaobao Zeng, Xinpeng Pan, Ling Peng, Yuyang Tan, and Jianxin Liu. 2024. "Microseismic Velocity Inversion Based on Deep Learning and Data Augmentation" Applied Sciences 14, no. 5: 2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052194
APA StyleLi, L., Zeng, X., Pan, X., Peng, L., Tan, Y., & Liu, J. (2024). Microseismic Velocity Inversion Based on Deep Learning and Data Augmentation. Applied Sciences, 14(5), 2194. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052194







