Abstract
It can be observed that magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles are increasingly used in bioassay methods. This is due to their stability in aqueous solutions, ease of functionalization, biocompatibility and very low toxicity. Here, we show that the recent discovery of the ability of magnetic nanoparticles to self-assemble into 2D structures of ordered chains may be exploited for bioassays. This would open up the possibility of controlled immobilization of proteins, enzymes, DNA or RNA and other molecular systems on spatially ordered nanostructures. In this work, fluorescein was used as an example. Also shown is the possibility of using Raman spectroscopy to analyze material accumulated on such structures. The observed formation of regularly spaced chains of magnetic nanoparticles takes place during the drying process of a thin layer of magnetic liquid placed on an appropriately prepared low-density polyethylene (LDPE) film.
1. Introduction
Magnetic nanoparticles find numerous applications in the development of new technologies related to environmental protection (pollution reduction, electromagnetic noise shielding/absorption) [1], medicine and biotechnology [2,3,4,5], the pharmaceutical industry [6,7], agriculture [8] and some micro/nanoelectromechanical devices (MEMS/NEMS) [9] or magnetoelectronics [10]. In this study, we limit ourselves to only one type of nanoparticles, magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles, and we show the possibility of using their property to self-assemble into the 2D structure of nanoparticle chains in applications for medical diagnostics, including the form of various types of bioassays. Iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles, due to their biocompatibility and low toxicity, are becoming increasingly used in medical diagnostics and medical treatment. The best-known examples of magnetic nanoparticle applications in this regard relate to the magnetic-hyperthermia method [3,4]. This method takes advantage of the magnetic-nanoparticle’s special property that it can absorb radio-frequency magnetic-field energy, which is then released to the nanoparticle’s surroundings in the form of heat. It is this emitted heat that is used in magnetic-hyperthermia methods to destroy cancer cells. The method of magnetic hyperthermia using iron-oxide nanoparticles has been perfected for many years (for example, see the pioneering paper [11] in 1957, where the effect of magnetic hyperthermia on cancer cells in lymph nodes was studied). Today, it is one of the recognized techniques for destroying cancer cells, which in many cases can be used alongside chemotherapy and conventional irradiation techniques [3].
Another widely known area of magnetic-nanoparticle applications is the use of magnetic nanoparticles in medical imaging. An example is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), where magnetic nanoparticles are used as contrast agents [5]. This applies to very small magnetic nanoparticles with diameters in the order of a few nanometers, such as dextran-stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles of 4.8 to 5.6 nm [5]. These are single-domain nanoparticles in which the heat-power dissipation from the eddy currents can be ignored because it is several orders of magnitude smaller than the heat-power dissipation P from the absorbed electromagnetic radiation [12]. The same applies to magnetic nanoparticles synthesized for magnetic hyperthermia, where they are mainly single-domain iron-oxide nanoparticles with sizes up to 20 nm.
Further areas of medical applications include controlled targeted drug delivery, treatment and diagnostics [2]. For this purpose, magnetic nanoparticles are appropriately functionalized with, among other things, biological components, which gives them additional diagnostic function, and dispensing of the drug to be released [2]. At the same time, the polymer coating of the nanoparticle prevents the agglomeration of magnetic nanoparticles due to magnetic dipole–dipole interactions. The placement of various functional amino and carboxyl groups on the surface of nanoparticles allows us to use them in a new type of immunoassay becoming competitive with conventional ELISA methods. In an earlier publication [13] of two co-authors of this work, it was shown that the presence of magnetic nanoparticles of iron oxide significantly increases the capacity of antibodies to recognize antigens by means of the formation of paratope–epitope-binding complexes. It was explained that the mechanism causing such an effect is a local change in pH in the surrounding nanoparticles. In addition, appropriately dosed use of remote heating of magnetic nanoparticles by an alternating magnetic field permitted control of this pH change. In recent years, antibodies have become a more and more important component of the functionalized nanoparticle surface used in different kinds of bioassays and for targeted drug delivery. In paper [2], there is attached a very broad review of papers on chemical electrobiosensors.
One of the frequently used diagnostic methods is tests involving the analysis of spatial patterns formed from the deposit of a dried layer of body fluids, mucus, etc. These also can act as bioassays, where the reaction of a biofluid to the added chemical components is examined. The stains from dried biofluids carry a great deal of information, e.g., about the emergence of a disease state, a change in the nature of the acidity of the biofluid under study or salt concentration [14]. They often appear in the form of the characteristic shape of the so-called coffee ring [15]. On the other hand, for saliva, tear film or cervical mucus, fern-shaped crystallizing structures appear. They are usually associated with the presence of small salt crystals. An example can be found in [16], where the changes in the fern pattern for cervical mucus to determine the effect of pregnancy status and ovulation, among other things, were presented. A similar discussion can be found for saliva examination [17]. Ferning tests are also used in ophthalmology, and an example of one recent publication in this field is [18]. In such tests, the type of substrate surface may be important. It is easy to find in the literature examples of the stains from drying colloids that correlate with the crystallographic symmetry of the substrate, like the assembly of the collagen layer on the mica surface [19] or the assembly of caffeine crystallites on the mica surface [20]. These results may indicate the need for some standardization for medical diagnostics carried out using the analysis of stains from dried body fluids.
It should be noted that chains of magnetic nanoparticles may also have great potential for biomedical applications. One example of preparing magnetic chains is the method discussed in paper [21], where the self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles into 1D chain structures was stabilized in an external magnetic field and it was combined with simultaneous crystallization of silica using sol–gel processes. Other examples include papers [22,23,24]. Very promising is a method for growth of ganglion neurons by magnetic colloidal nanochains [25]. Other properties of magnetic nanoparticles that are useful for medical applications are their targeted functionalization [26] and their possible use in optical bioassays using surface-plasmon resonance (SPR) [2].
In this paper, the possibility is suggested of using a new type of materials represented by self-assembled magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticle-chain-like structures that may have great potential for controlled immobilization of enzymes and proteins, as well as DNA and RNA molecules. We demonstrate this using fluorescein as an example. At the same time, we show the possibility of chemical analysis of the material collected on such structures using Raman spectroscopy. The arrays of magnetic chains could serve as an analog of ELISA plates working along the magnetic-nanoparticle chains. Thus, some examples of magnetic nanoparticle applications discussed above could be exploited. The possibility of self-assembling magnetic nanoparticles into 2D structures during the drying of a magnetic-liquid droplet on a hydrophobic substrate was shown in our earlier paper [27]. In this case, the stains after the dried droplet formed an array of numerous concentric rings made of magnetic nanoparticles. It should be noted that similar experiments done by other groups were performed for non-magnetic particles [28,29,30].
2. Materials and Methods
The methods presented in this study for obtaining multi-ring structures composed of chains of magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles on a substrate require prior preparation of a stable colloid of such nanoparticles. This implies the need to stabilize the magnetic nanoparticles by applying a suitable non-magnetic coating that separates them from combining into permanent agglomerates due to magnetic dipole–dipole interactions. Such a stabilizing material can be APTES (3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane). The prepared magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles have an average size of 12 nm and have a stabilizing coating up to several nanometers thick. In the magnetic-nanoparticle colloid used for obtaining multi-ring nanoparticle structures, the pH value was approximately 4. At this pH, the zeta-potential value (measured by Zetasizer Ultra Malvern) of the APTES-coated nanoparticles was 38 mV and the average hydrodynamic size was approximately 37 nm. The magnetic dipole–dipole interactions between magnetic nanoparticles in solution were significantly reduced and the nanoparticles exhibited superparamagnetic properties. They agglomerated mainly at the contact line of the drying droplet, where the density of the nanoparticles was increased due to the advective flow towards the contact line caused by the evaporation of the droplet.
2.1. Synthesis of Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
The process involves the dissolution of 3.81 g of in 100 mL of a 0.02 M hydrochloric-acid aqueous solution and dissolving 7.41 g of in 100 mL of distilled water. The resulting solutions were combined in a flask and subjected to stirring at 400 rpm within a nitrogen atmosphere. After about one hour, the speed of the mechanical stirrer was increased to 800 rpm, and 25 mL of a 25% ammonia solution was added dropwise (at a rate of 1 droplet per second). Mixing at 800 rpm was continued for another 30 min. An appropriate volume of the suspension was then extracted. This was followed by a thorough washing procedure with distilled water. During the washing process, the separation of the nanoparticles from the suspension was facilitated by the use of a neodymium magnet. The nanoparticles were left in suspension for the subsequent functionalization step.
2.2. APTES Functionalized Nanoparticles
The process was initiated with a 15 min sonication of a prepared suspension of magnetic nanoparticles within a Falcon 50 mL tube. Next, 4 mL of the suspension was mixed with 36 mL of 99.8% ethanol and the resulting mixture was subjected to an additional 15 min of sonication at a controlled temperature of 67 °C. Subsequently, 0.5 mL of APTES (3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane) was introduced to the ethanol-treated suspension. The mechanical stirrer was activated at 1200 rpm, and the sonication was maintained at a temperature of 67 °C. The process seamlessly transitioned into continued stirring at 1200 rpm. The purpose of this extended processing step was to achieve thorough mixing and promotion of desired chemical interactions within the suspension. The functionalized sample was then washed with 3 cycles of ethanol and 3 cycles of distilled water. The sample was then filled up to a final volume of 25 mL. The resulting nanoparticle concentration was determined to be approximately 2.3 mg/mL.
2.3. Preparation of Magnetic Chain Structures
In a 25 mL volumetric flask, the concentration of APTES-modified magnetic nanoparticles in suspension was lowered and its pH was adjusted to around 4 by adding 2 M HCl solution. Next, 1 L of this prepared suspension was deposited onto a low-density polyethylene (LDPE) film and allowed to dry in ambient conditions. The method requires an asymmetric surface and, therefore, LDPE film was prepared in the stretched form, where a sample width of 1 cm was stretched to 5 cm. The drying time for a 1 L droplet at 20 °C is about one hour. After the droplet dries, a deposit with ring structures of APTES-stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles remains on the LDPE substrate.
2.4. Preparation of Solution Containing Fluorescein
Analytically pure fluorescein sodium salt was dissolved in distilled water to form a solution with a concentration of 10 mg/L. The 1 L droplet of this solution was then placed on a dried-magnetic-liquid-droplet deposit, where the deposit was in the form of an array of ring-shaped chains of magnetic nanoparticles on an LDPE substrate. It took approximately one hour for a droplet of solution containing fluorescein to dry.
2.5. Measurement Characterization
The prepared samples were investigated using various measurement techniques:
- Atomic-force microscopy (AFM) measurements provided by Flex Axiom-Nanosurf to visualize deposits from drying magnetic colloids;
- Optical microscopy provided by Keyence VHX-970F digital microscope;
- Zeta potential for determining stability of magnetic colloids, and dynamic light scattering (DLS) method, where Zetasizer Ultra Malvern was used;
- Raman spectroscopy with the use of the Renishaw InVia Quantor spectrometer to determine the kind of magnetic iron oxides in the magnetic colloids and confirm the presence of fluorescein deposited on a 2D array of ordered chains of magnetic nanoparticles;
- Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with the energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDX), to confirm the size of the coated magnetic nanoparticles and their chemical composition.
For the Raman spectroscopy method, lasers with two different powers corresponding to wavelengths nm and nm were used. Due to luminescence effects in the case of fluorescein, the laser of wavelength nm was selected, which generated Raman spectra with distinct peaks. In the case of LDPE, the laser wavelength nm was used.
3. Results
This section presents the results of an experiment realizing the concept of using a 2D array of rings made of magnetic nanoparticles to capture molecular systems such as proteins, enzymes, DNA or RNA from a droplet of solution with these molecular systems drying on this 2D array. In this work, an example of such a molecular system is fluorescein. The experiment with fluorescein as a marker for the deposition of molecules on magnetic-nanoparticle chains was carried out in three steps:
- (i)
- preparation of a 2D array of magnetic-nanoparticle chains;
- (ii)
- preparing a solution containing fluorescein and placing a droplet of this solution on the substrate with chains of magnetic nanoparticles;
- (iii)
- taking measurements to confirm the presence of fluorescein on the chains of magnetic nanoparticles.
3.1. Preparation of 2D Array of Magnetic-Nanoparticle Chains
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) film was chosen as the substrate, which is hydrophobic, is a non-polar, flexible material and is chemically resistant to both acidic and basic solutions. It is commonly used for packaging and as an insulating material but is also of increasing importance in biomedical applications [31]. However, another hydrophobic substrate with axial asymmetry, e.g., with a parallel-fiber structure, can be used. In the case of thin LDPE film, such an asymmetry is obtained by stretching the film in one direction—say, the x-direction, as shown in Figure 1a,b. In the examples shown, 1 cm of the film has been stretched to 5 cm. The process of self-assembling magnetic nanoparticles on an unstretched film is very random and the ring structures are very fuzzy. The method of preparing a multi-ring structure of magnetic nanoparticles [27] has been extended to include the ability to remove the core (the spot in the center part of the droplet deposit in Figure 1c) formed from excess magnetic nanoparticles in the drying droplet, so that only chains of nanoparticles remain on the substrate (Figure 1d). In addition, Figure 1e shows the possibility of preparing rectilinear chains of magnetic nanoparticles. It should be noted that the removal of the excess magnetic liquid in the drying droplet can be done at any time. For this purpose, this excess can be removed with a pipette or perilstatic pump (the methods used in this work) and suitable hygroscopic material. The time needed for the formation of subsequent nanoparticle chains as the magnetic-liquid droplet dries is several seconds (see also [27]) under ambient conditions.
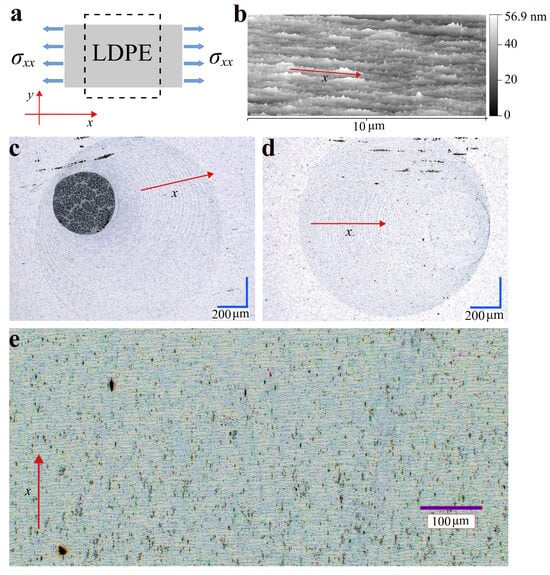
Figure 1.
2D printing of spatial structures from magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles functionalized with APTES on a thin film of LDPE: (a) Schematic showing the preparation of the LDPE substrate for the sample by stretching it in the x-direction. (b) AFM image of the surface of the stretched LDPE. (c) Typical optical-microscopy image of a multi-ring magnetic-nanoparticle deposit formed by a drying droplet of magnetic colloid with a circular stain inside. (d) Analogous to (c) but the circular stain has not been created, due to a different printing procedure involving the removal of excess magnetic colloid during the final stage of the droplet drying process. (e) Optical-microscope image of the magnetic nanoparticle deposit in the form of a structure of evenly spaced rectilinear chains. Note: images of spatial nanostructures obtained by optical microscopy are visible due to the light-scattering phenomenon, as are numerous dark spots caused by the irregularities inside the LDPE.
Figure 2 shows AFM images with details of the topography of the magnetic-nanoparticle chain arrangement in the 2D structure, and TEM-microscopy images enriched with elemental analysis of the prepared magnetic nanoparticles. The nanoparticles were coated with APTES. Elemental composition analysis was performed on a copper grid with the help of the EDX method.
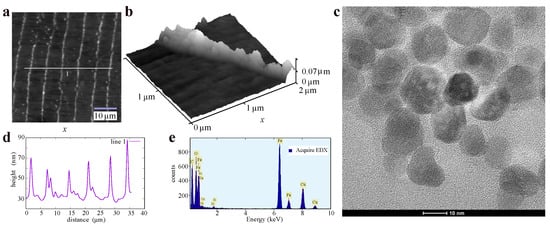
Figure 2.
Topography of the multi-ring structure of magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles on LDPE thin film: (a) AFM image of an LDPE fragment coated with chains of magnetic nanoparticles using the methods in Figure 1, where white line 1 indicates the path along which the heights of the magnetic nanowires were measured. (b) AFM image of a fragment of a single nanowire. (c) TEM image of APTES-functionalized magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles. (d) surface topography of LDPE along line 1 from panel (a). (e) EDX spectrum by TEM microscopy showing elemental composition for the area with magnetic nanoparticles (c) placed on a copper grid (method of measurement).
The formation of elongated structures from nanoparticles is a result of the mechanism of the coffee-ring phenomenon [15]. It usually means the appearance of a single-ring or several-rings structure of precipitate from the material of the drying colloid droplet. In this work, the phenomenon concerns a magnetic colloid droplet drying on a hydrophobic substrate, where during drying the droplet’s contact line shrinks while agglomerating magnetic nanoparticles on it, which slows down this shrinking by interacting with the substrate, so that the growing agglomerates take on a ring shape consistent with that of the contact line and pin the contact line to the substrate. Then, the process of diffusive sliding of the contact line of the droplet through the growing rings of nanoparticles begins, and the angle of the droplet decreases until the configuration of the contact line is no longer energetically convenient (the minimum Gibbs-free-energy condition is no longer satisfied) and the contact line jumps to a new position, where the angle of the droplet at the contact line increases again. The process of forming a ring of nanoparticles then repeats. The coated magnetic nanoparticles should not be too large because they must be able to flow to the edge of the droplet, due to the loss of droplet mass caused by the droplet evaporation. The placement of the colloid droplets can be automated and, for this purpose, for example, the extruder of a 3D printer can be used. However, the presence of too many droplets of magnetic liquid next to each other significantly alters the conditions of their drying (the drying time significantly increases), and over large areas the drying conditions become inhomogeneous.
There are several parameters by which the density of rings present in the deposit of a dried magnetic-liquid droplet can be controlled under the same environmental conditions of temperature, pressure and humidity. These are: (1) the concentration of magnetic nanoparticles in the colloid, (2) the salt concentration in the solution and (3) the magnitude of a magnetic-field gradient, which can be applied under the sample or above the sample. In Figure 3, panels (a) and (b) show the effect of magnetic-nanoparticle concentration. The solution with a suspension of nanoparticles should be stable and sonicated long enough. On the other hand, panels (c) and (d) in Figure 3 show the effect of a concentration of NaCl salts on the resulting droplet deposit. Panels (e) and (f) in Figure 3 show the droplet deposit when, for the same concentration of magnetic nanoparticles, the droplets dry without the presence of a magnetic field and when a field gradient is applied. In the latter case, the magnetic field above the sample and below the sample can be further controlled. The effect of magnetic-field gradients on the formation of multiple-ring structures was discussed in [27].
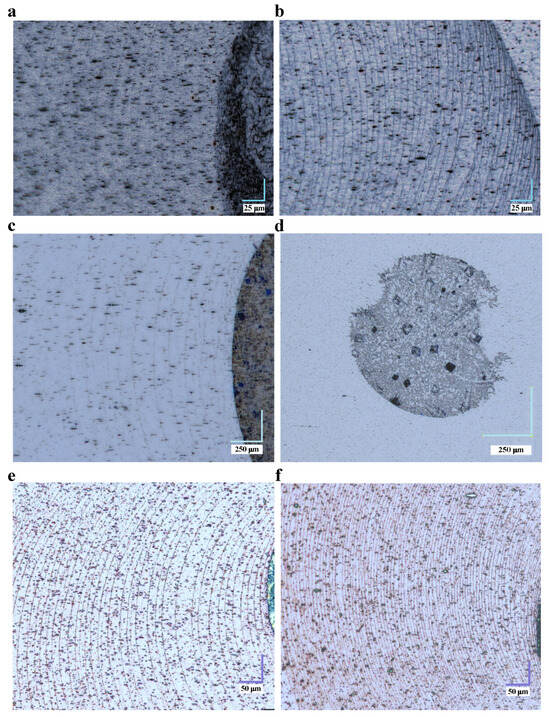
Figure 3.
Optical-microscopy images of the stains from a droplet of magnetic liquid dried on a stretched LDPE film for different parameters: (a) For the concentration 0.012 mg/mL of magnetic nanoparticles at zero concentration of NaCl salt. (b) The same as in (a) but for the nanoparticle concentration 0.045 mg/mL. (c) For the magnetic nanoparticle concentration 0.045 mg/mL at the concentration of NaCl salt equal to 0.2 mM. (d) The same as in (c) but for the salt concentration of 20 mM. (e,f) For different values of the external magnetic-field gradient for the same magnetic-nanoparticle concentration 0.045 mg/mL, respectively, in the absence of a magnetic field and when the droplet dries in the presence of a neodymium magnet (the residual magnetic-flux density T) placed at a distance of 2.5 mm below the LDPE film.
3.2. Deposition of Fluorescein on Magnetic Chains
In all of the above cases, magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles are functionalized with APTES, but even at the stage of formation of 2D structures of the deposit, additional functionalization is possible. For possible use in bioassays, the easier method is to coat the already-existing 2D ring structure on the dry substrate. Figure 4 shows the effect of fluorescein deposition on part of the magnetic-nanoparticle chains after drying a droplet with fluorescein, which has been placed on a substrate with a 2D array of magnetic-nanoparticle chains. The fluorescein luminescence clearly shows the area where the droplet with fluorescein dried.
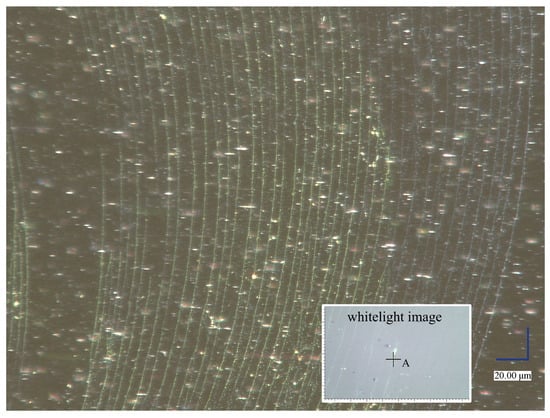
Figure 4.
Fluorescence effect under white light from optical microscopy of fluorescein-coated magnetic-nanoparticle chains. The fluorescein comes from a dried droplet of a solution containing fluorescein laid on a substrate with chains of magnetic nanoparticles. The inset in light color is an optical-microscope image from a Raman spectrometer on which point A is marked for Raman spectroscopy analysis.
Figure 5a shows fragments of Raman spectra for pure fluorescein, LDPE film and a chain of magnetic nanoparticles coated with fluorescein. These fragments correspond to the Raman shift range from 200–1000 cm−1 where the spectrum for LDPE in Figure 5b is flattened. These results confirm the presence of fluorescein on the magnetic-nanoparticle chains.
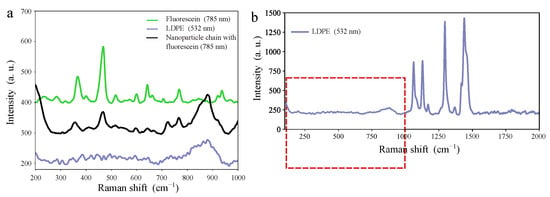
Figure 5.
Plots of Raman spectra for pure fluorescein, LDPE film and a fluorescein-coated magnetic-nanoparticle chain, the latter measured at point A marked in Figure 4: (a) Fragments of the Raman spectra in the range of values 200–1000 cm−1 are shown. (b) The full Raman spectrum of LDPE, the red-framed section of which is shown in panel (a). Because of the fluorescence effect, a laser with wavelength nm was used for fluorescein. For LDPE, the wavelength nm was used.
4. Discussion
The presented results of using the ordered 2D structure of the magnetic-nanoparticle chains to capture fluorescein from a drying droplet of a solution containing fluorescein may suggest the possibility of extending this method to other molecular systems, such as proteins, enzymes and others. In this work, fluorescein acted only as a marker for the deposition of molecules on nanostructures, but it shows the possibility of testing the chemical reactions of the materials under study at multiple points simultaneously. At the same time, the example of the application of Raman spectroscopy shown in the paper demonstrates the possibility of analyzing the results of these chemical reactions. Moreover, magnetic nanoparticles can further catalyze such reactions by locally changing the pH or further functionalizing their surfaces. Iron-oxide nanoparticles can acquire a pH-dependent electric charge on their surface when they come into contact with an aqueous solution. Similar to other metal oxides, both magnetic and non-magnetic, there is a specific value of pH that is called the point of zero charge (PZC), at which the sum of all positive and negative surface charges equals zero. The charge is positive for pH < PZC and negative for pH > PZC. In this work, the PZC of iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles is around 6.2. If we denote the change in pH at the surface of the nanoparticles by pH = pH0 − pH, where pH0 represents the surface-pH value, then pH defines the surface electric potential as the following:
where F is the Faraday’s constant, T is the temperature and R is the gas constant. This electric potential depends on the fraction of protonated and deprotonated hydroxyl groups present on the nanoparticle surface. The resulting change in pH could be used to control certain chemical reactions directly on the magnetic-nanoparticle chains. It should be added that the linear part of is the well-known form of the Nernst potential [32]:
The greater the pH deviation from PZC, the greater will be the change in pH around the nanoparticles (Equation (1)). Depending on the pH value of the solution, the presence of nanoparticles will lower the pH value or increase it in their immediate vicinity. Referring to paper [13] on catalyzing antibody–antigen reactions with magnetic nanoparticles, the catalytic capabilities of magnetic-nanoparticle chains can be extended by using alternating magnetic fields at radio frequencies. Once the energy of the alternating magnetic field absorbed by magnetic nanoparticles is released to the surrounding nanoparticles in the form of heat it can affect the pH level. In [12] it was shown, using the example of the silica-magnetic-nanoparticles interface, that such a process may lead to increased deprotonation in the surroundings of the nanoparticles.
This work mainly focuses on ordered chains of magnetic nanoparticles in the form of concentric rings. However, noteworthy are rectilinear magnetic nanowires (as in panel (e) of Figure 3), which could enrich electrophoresis techniques by being able to add magnetic-field effects on separation in nano and microfluidics. It should be noted that magnetic nanoparticles are intensively used in immunoassays, due to their stability and ability to functionalize [2].
5. Conclusions
Using fluorescein as an example, the concept of trapping molecular systems from a thin layer of solution laid on a substrate with a two-dimensional array of separated chains of magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles present is demonstrated. Due to the ability to easily functionalize the surface of iron-oxide nanoparticles, this method may have great potential for biomedical applications. The formation of the magnetic-nanoparticle chains itself is the result of the self-assembling of the nanoparticles into ring-shaped deposits as the magnetic colloid droplet placed on a suitably prepared surface dries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R.D. and M.M.; methodology, M.R.D.; validation, A.D., M.R.D., M.M., W.W., S.M. and I.S.; investigation, M.R.D., A.D., M.M. and W.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M. and M.R.D.; writing—review and editing, M.R.D., M.M., A.D., W.W., S.M. and I.S.; visualization, M.R.D., M.M. and W.W.; supervision, M.R.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Polish Ministry of Education and Science under the program “Regional Initiative of Excellence” in 2019–2023, funding amount 11 936 596.10 PLN, grant number No. 003/RID/2018/.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AFM | atomic-force microscopy |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| EDX | energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane |
| LDPE | low-density polyethylene |
| SPR | surface-plasmon resonance |
| rpm | rotations per minute |
| PZC | point of zero charge |
References
- Hussain, S.; Youngs, I.J.; Ford, I.J. The electromagnetic properties of nanoparticle colloids at radio and microwave frequencies. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materón, E.M.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Carr, O.; Joshi, N.; Picciani, P.H.S.; Dalmaschio, C.J.; Davis; Shimizu, F.F.M. Magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 6, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustini, A.J.; Petryk, A.A.; Cassim, S.M.; Tate, J.A.; Baker, I.; Hoopes, P.J. Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia in cancer treatment. Nano Life 2010, 1, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, G.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tiwari, S.; Shi, K.; et al. Comprehensive understanding of magnetic hyperthermia for improving antitumor therapeutic efficacy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3793–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.L.; Fan, H.M. Advances in magnetic nanoparticle-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 12531–12542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stueber, D.D.; Villanova, J.; Aponte, I.; Xiao, Z.; Colvin, V.L. Magnetic nanoparticles in biology and medicine: Past, present, and future trends. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, L.H.; Arias, J.L.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Design and Characterization, Toxicity and Biocompatibility, Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5818–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, M.; Ma, C.; Hao, Y.; Guo, J.; Rui, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, T.; et al. Nanoparticles as a Potential iron fertilizer for peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 815. [Google Scholar]
- Zahn, M. Magnetic fluid and nanoparticle applications to nanotechnology. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2001, 3, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo, D.; Tostado-Blázquez, G.; Baran, D. Flexible Electronics: Status, Challenges and Opportunities. Front. Electron. 2020, 1, 594003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, R.K.; Medal, R.; Shorey, W.D.; Hanselman, R.C.; Parrott, J.C.; Taylor, C.B. Selective inductive heating of lymph nodes. Ann. Surg. 1957, 146, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolak, W.; Kolomeisky, A.B.; Dudek, M.R.; Marć, M.; Najder-Kozdrowska, L. Enhancing silica surface deprotonation by using magnetic nanoparticles as heating agents. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 465001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleczko, J.; Defort, A.; Kozioł, J.J.; Nguyen, T.T.; Mirończyk, A.; Zapotoczny, B.; Nowak-Jary, J.; Gronczewska, E.; Marć, M.; Dudek, M.R. Limitation of tuning the antibody-antigen reaction by changing the value of pH and its consequence for hyperthermia. J. Biochem. 2016, 159, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreón, Y.J.P.; Gómez-López, M.L.; Díaz-Hernández, O.; Vazquez-Vergara, P.; Moctezuma, R.E.; Saniger, J.M.; González-Gutiérrez, J. Patterns in dried droplets to detect unfolded BSA. Sensors 2022, 22, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, R.D.; Bakajin, O.; Dupont, T.F.; Huber, G.; Nagel, S.R.; Witten, T.A. Capillary flow as the cause of ring stains from dried liquid drops. Nature 1977, 389, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisman, A. The fern reaction of cervical mucus. Canad. Med. Ass. J. 1964, 91, 805–807. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, B.S.; Pushpaja, M.; Siva Kumar, A.V.; Maruthy, K.N. Does the salivary fern pattern determine fertile period in reproductive female? Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 8, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmali, A.M.; Purslow, C.; Murphy, P.J. The tear ferning test: A simple clinical technique to evaluate the ocular tear film. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2014, 97, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leow, W.W.; Hwang, W. Epitaxially guided assembly of collagen layers on mica surfaces. Langmuir 2011, 27, 10907–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röthel, C.; Radziown, M.; Resel, R.; Zimmer, A.; Simbrunner, C.; Werzer, O. Complex behavior of caffeine crystallites on muscovite mica surfaces. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 4563–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, S.; Makovec, D. Magnetic assembly of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle clusters into nanochains and nanobundles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9700–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Hao, N.; Zhang, J.X.J.; Hoopes, P.J.; Shubitidze, F.; Chen, Z. Fabrication of monodisperse magnetic nanorods for improving hyperthermia efficacy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potrč, T.; Kralj, S.; Nemec, S.; Kocbek, P.; Kreft, M.E. The shape anisotropy of magnetic nanoparticles: An approach to cell-type selective and enhanced internalization. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Feng, H.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Hu, C.; Yan, X.; Yang, H.; Song, J. Spatiotemporally Controlled Formation and Rotation of Magnetic Nanochains In Vivo for Precise Mechanotherapy of Tumors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202213319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, R. Controllable growth of spiral ganglion neurons by magnetic colloidal nanochains. Nano Today 2022, 44, 101507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstad, E.; Textora, M.; Reimhult, E. Stabilization and functionalization of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2819–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marć, M.; Wolak, W.; Drzewiński, A.; Dudek, M.R. Coffee-ring formation through the use of the multi-ring mechanism guided by the self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, J.R.; Sefiane, K.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on contact line stick-slip behavior of volatile drops. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 8860–8866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askounis, A.; Orejon, D.; Koutsos, V.; Sefiane, K.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Nanoparticle deposits near the contact line of pinned volatile droplets: Size and shape revealed by atomic force microscopy. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-O.; Pack, M.; Rokoni, A.; Kaneelil, P.; Sun, Y. The EECT of particle wettability on the stick-slip motion of the contact line. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 9599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Cui, B.; Duan, X. Preparation and applications of linear low-density polyethylene. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2229, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, I.; Attard, P. Surface charge of silver iodide and several metal oxides, are all surfaces nernstian? J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2000, 227, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).