Preparation and Characterization of High-Strength and High-Modulus Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Hydroxyapatite/Carbon Fiber/Polyetheretherketone Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Main Raw Materials
2.2. Main Instruments and Equipment
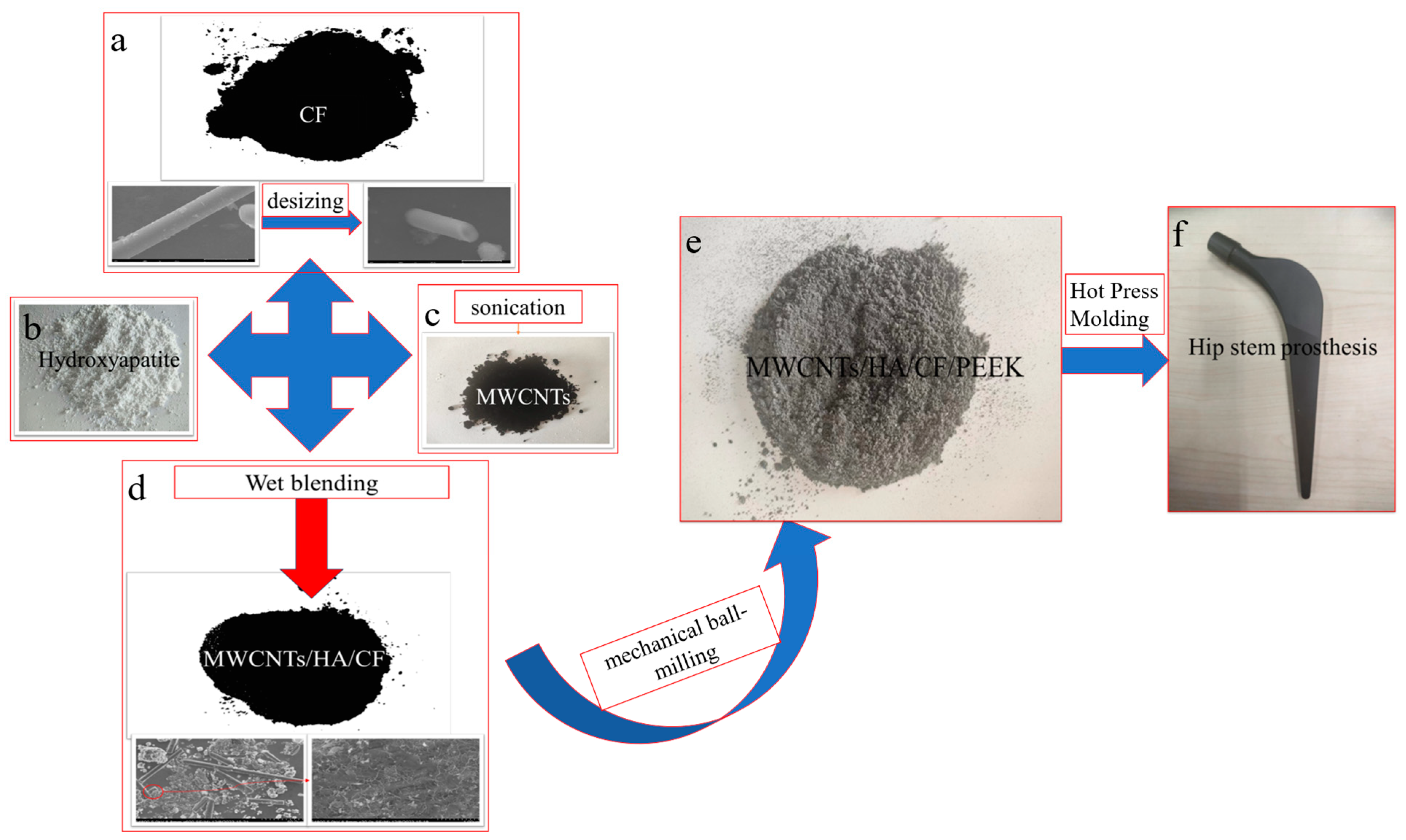
2.3. Sample Preparation of Composite Material
2.3.1. Preparation of MWCNT Dispersions
2.3.2. Premixing of Composite Materials
2.3.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Characterization of Composite Materials
2.4.1. Performance Testing and Structural Characterization of Ternary Composites
2.4.2. Quaternary Composite Material Performance Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composite Material Performance Testing
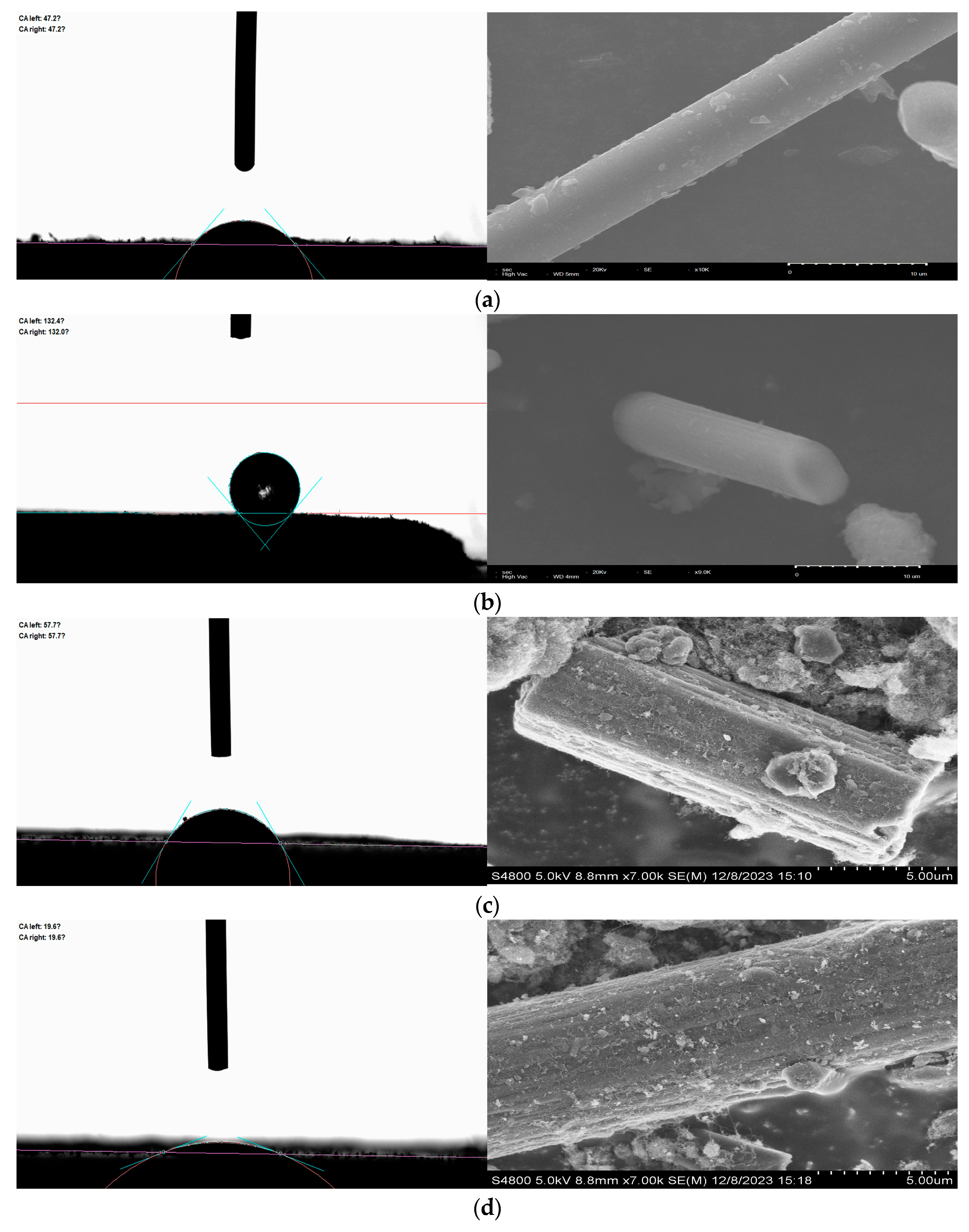
3.1.1. SEM and Contact Angle Testing
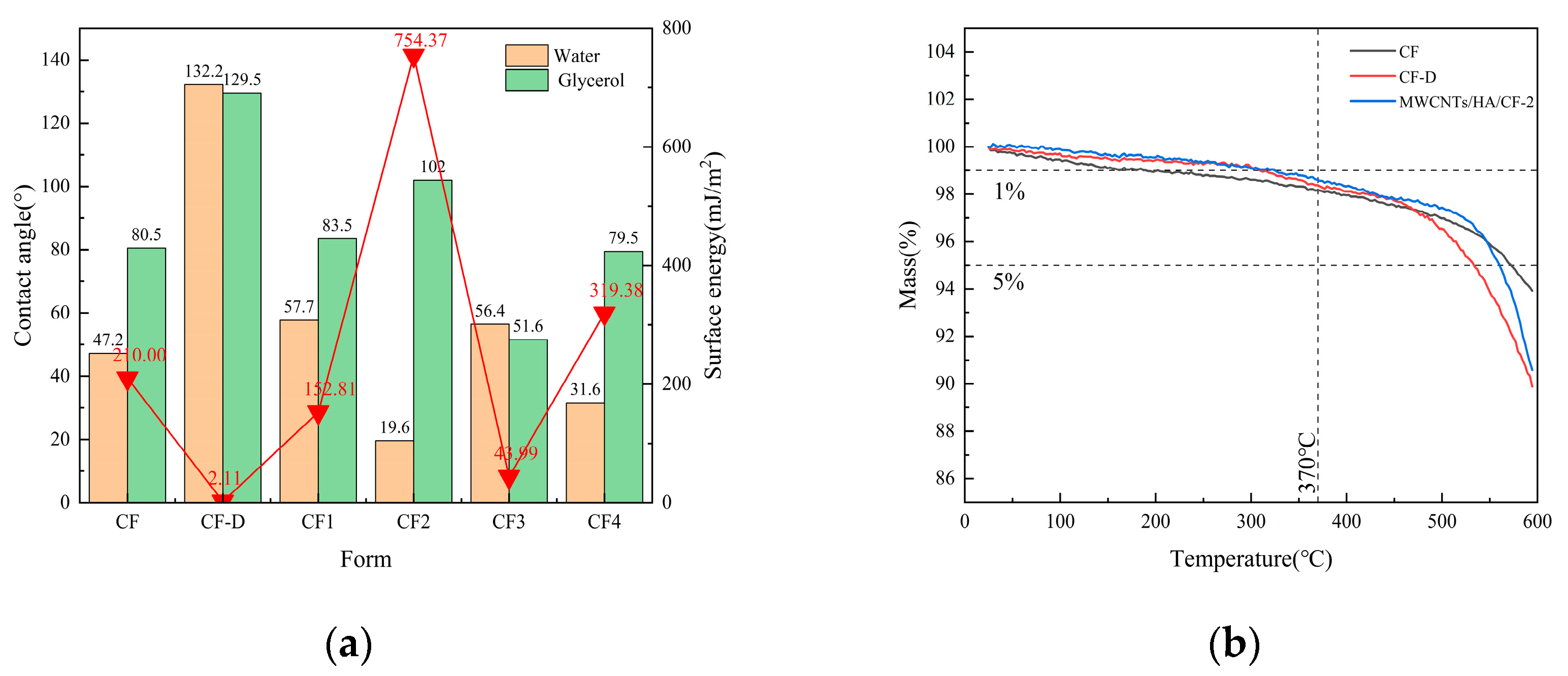
3.1.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.2. Testing of Mechanical Properties of Composite Materials
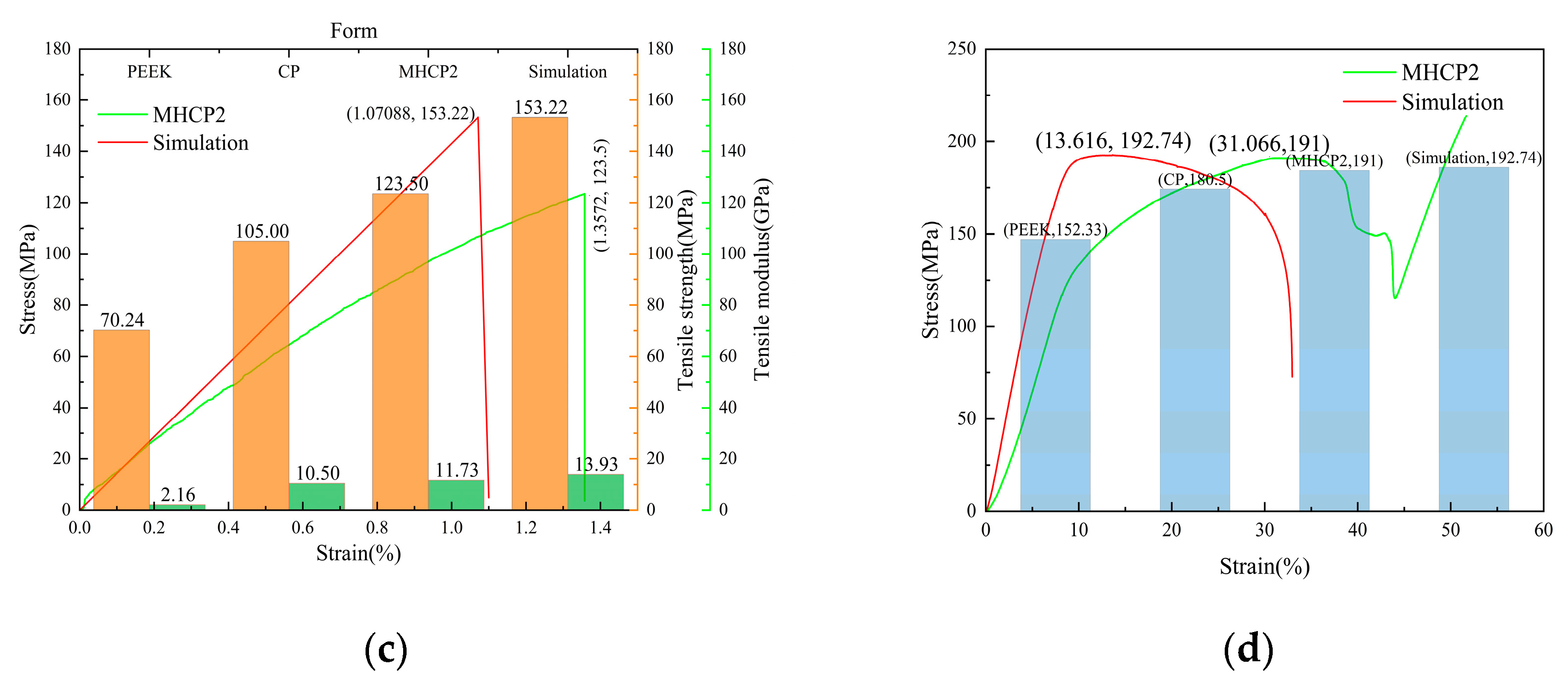
3.2.1. Tensile Properties
3.2.2. Compression Property
3.2.3. Density
3.2.4. Friction and Wear Experiment
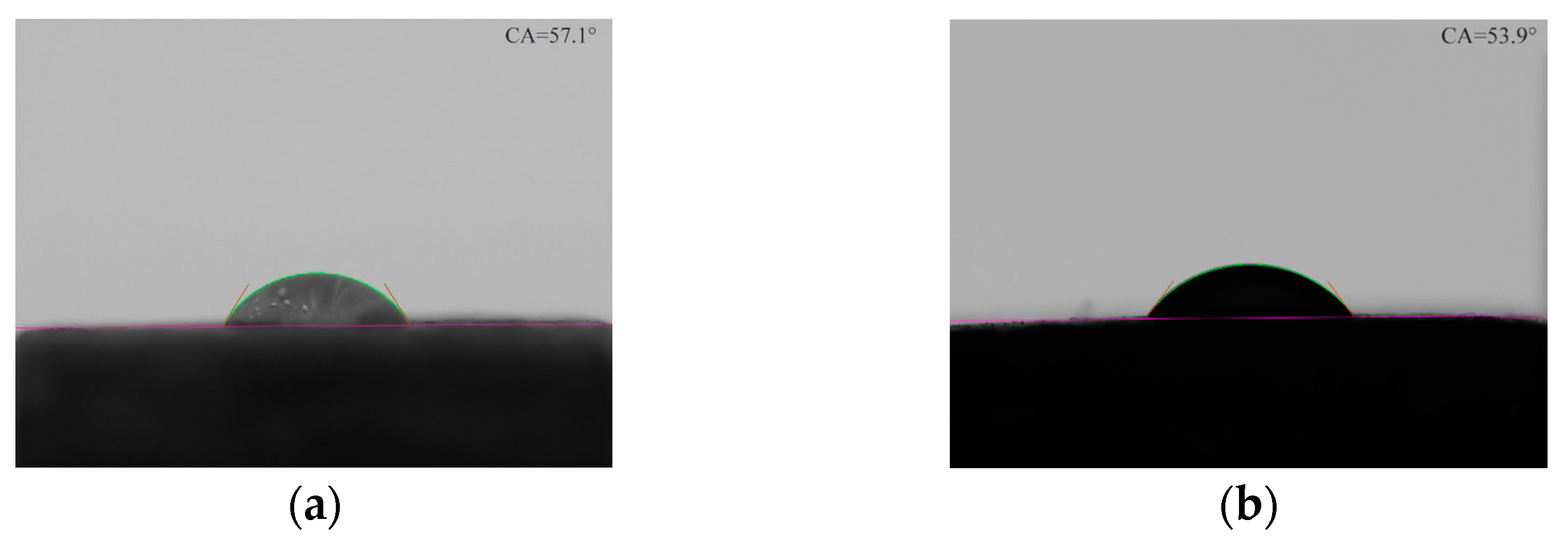
3.2.5. Contact Angle Test
4. Conclusions
- Due to the addition of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and nanohydroxyapatite, the surface energy of the ternary composites increases, the contact angle decreases, and the hydrophilicity is enhanced. The CF2 composites exhibited better heat resistance than the original carbon fibers. The de-sized carbon fibers were prepared to meet the requirements of the hot compression molding process. Additionally, the surface roughness of the carbon fiber in the CF2 composites increased.
- The MHCP2 composite tensile strength was 123.5 MPa, which was 17.62% higher than the CP tensile strength and 75.82% higher than pure PEEK. The MHCP2 elastic modulus was 11.73 GPa, which is close to that of human cortical bone. The compressive strength of the MHCP2 composite was 191 MPa, which was 5.82% higher than the compressive strength of CP and 25.39% higher than pure PEEK. Reducing the friction coefficient and density of the composite material can reduce energy loss and wear, resulting in characteristics such as light weight, high strength, and high elastic modulus. The hydrophilicity of the tetrameric composite material was improved, consequently leading to faster absorption or spreading of liquid onto the solid surface.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mbogori, M.; Vaish, A.; Vaishya, R.; Haleem, A.; Javaid, M. Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone (PEEK) in orthopaedic practice—A current concept review. J. Orthop. Res. 2022, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Prakash, C.; Ramakrishna, S. 3D printing of polyether-ether-ketone for biomedical applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 114, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Wen, J.; Qian, S.; Cao, H.L.; Ning, C.Q.; Pan, X.X.; Jiang, X.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Chu, P.K. Enhanced osteointegration on tantalum-implanted polyetheretherketone surface with bone-like elastic modulus. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häger, A.M.; Davies, M. Short-fibre reinforced, high-temperature resistant polymers for a wide field of tribological applications. J. Compos. Mater. 1993, 8, 107–157. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, D.N.; Rachchh, N.V. Graphene and its application in thermoplastic polymers as nano-filler—A review. Polymer 2022, 240, 124486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, I.S.; Lee, M.H.; Choi, H.H.; Lee, S.; Chon, J.W.; Chung, D.J.; Park, J.H.; Jho, J.Y. Mechanical properties and bioactivity of Polyetheretherketone/Hydroxyapatite/Carbon fiber composite prepared by the mechanofusion process. Polymers 2021, 13, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.L.; Luo, Y.X.; Chen, C.Y.; Dong, Z.J.; Jiang, G.M.; Chen, F.X.; Ma, P.B. Mechanical Enhancement of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymers: From Interfacial Regulating Strategies to Advanced Processing Technologies. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 142, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, J.D.; Yu, L. Blending strategy to modify PEEK-based orthopedic implants. Compos. B Eng. 2023, 250, 110427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Liang, Q.; Tang, B. Mechanical properties and cytotoxicity of hierarchical carbon fiber-reinforced poly (ether-ether-ketone) composites used as implant materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 89, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Han, X.; Gao, W.J.; Li, Y.L.; Yu, W.Q.; Yang, S.H.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Shi, R.N.; Zhou, Y.M.; et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of different types of carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone: A comparative study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 135, 105472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.A.M.; Ge, D.T.; Yang, L.L.; Zhou, J.F.; Liu, M.X.; Yu, M.H.; Zhu, S. Highly boosting the interlaminar shear strength of CF/PEEK composites via introduction of PEKK onto activated CF. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 112, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Xing, T.; Tang, B.; Chen, W.Y. Mechanical properties and osteogenesis of CFR-PEEK composite with interface strengthening by graphene oxide for implant application. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 148, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Liu, P.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Xin, J.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Zou, X.S.; Mei, X.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, S.K. Strategies to improve bioactive and antibacterial properties of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for use as orthopedic implants. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 16, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.Z.; Li, Y.C.; Tjong, S.C. Polyetheretherketone and its composites for bone replacement and regeneration. Polymers 2020, 12, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Xu, C.P.; Luque, R. Development and characterization of novel poly (ether ether ketone)/ZnO bionanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3065–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, U.; Padhan, M.; Bijwe, J. Carbon nanotubes-a powerful nano-filler for enhancing the performance properties of polyetherketoneketone composites and adhesives. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 210, 108813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.Q.; Zhou, J.Y.; Shi, Q.H. Research progress on enhancement mechanism and mechanical properties of FRP composites reinforced with graphene and carbon nanotubes. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 64, 541–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khallaf, R.M.; Emam, A.N.; Mostafa, A.A.; Nassif, M.S.; Hussein, T.S. Strength and bioactivity of PEEK composites containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes and bioactive glass. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 144, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puértolas, J.A.; Castro, M.; Morris, J.A.; Ríos, R.; Ansón-Casaos, A. Tribological and mechanical properties of graphene nanoplatelet/PEEK composites. Carbon 2019, 141, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.L.; Chen, M.; Bai, J.X.; Xu, Y.Z.; Wang, M.; Geng, D.C.; Pan, G.Q. Recent advances in orthopedic polyetheretherketone biomaterials: Material fabrication and biofunction establishment. Smart Mater. Med. 2022, 3, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.M.; Chen, X.C.; Guo, Z.J.; Qiu, X.T.; Yang, Y.T.; Su, C.L.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y.B.; Sun, D.; Zhang, L. Super tough graphene oxide reinforced polyetheretherketone for potential hard tissue repair applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 174, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhou, P.; Liu, X.C.; Wang, L.X.; Xiong, X.L.; Tang, Z.H.; Wei, J.; Wei, S.C. Preparation, characterization, cellular response and in vivo osseointegration of polyetheretherketone/nano-hydroxyapatite/carbon fiber ternary biocomposite. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 136, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.F.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H.C.; Zhang, L.F.; Xiong, C.D. Preparation and properties of multiwalled carbon nanotubes/hydroxyapatite/polyetheretherketone ternary nanocomplexes. Plast. Ind. 2018, 46, 113–116, 123. [Google Scholar]

| Form | Mass Fraction (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNTs | HA | CF | PEEK | |
| CP | 0 | 0 | 30 | 70 |
| CDP | 0 | 0 | 30 | 70 |
| MHCP1 | 6 | 0 | 30 | 64 |
| MHCP2 | 6 | 6 | 24 | 64 |
| MHCP3 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 64 |
| MHCP4 | 6 | 18 | 12 | 64 |
| Form | Contact Angle (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Glycerol | ||
| CF | 47.2 | 80.5 | 210.00 |
| CF-D | 132.2 | 129.5 | 2.11 |
| CF1 | 57.7 | 83.5 | 152.81 |
| CF2 | 19.6 | 102 | 754.37 |
| CF3 | 56.4 | 51.6 | 43.99 |
| CF4 | 31.6 | 79.5 | 319.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhu, S.; Wu, S.; Wei, B.; Yang, G. Preparation and Characterization of High-Strength and High-Modulus Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Hydroxyapatite/Carbon Fiber/Polyetheretherketone Composites. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051723
Liu L, Zhang Y, Ma S, Zhu S, Wu S, Wei B, Yang G. Preparation and Characterization of High-Strength and High-Modulus Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Hydroxyapatite/Carbon Fiber/Polyetheretherketone Composites. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(5):1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051723
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lijian, Yongkang Zhang, Shaobo Ma, Shouxiao Zhu, Shuxuan Wu, Bin Wei, and Guang Yang. 2024. "Preparation and Characterization of High-Strength and High-Modulus Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Hydroxyapatite/Carbon Fiber/Polyetheretherketone Composites" Applied Sciences 14, no. 5: 1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051723
APA StyleLiu, L., Zhang, Y., Ma, S., Zhu, S., Wu, S., Wei, B., & Yang, G. (2024). Preparation and Characterization of High-Strength and High-Modulus Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Hydroxyapatite/Carbon Fiber/Polyetheretherketone Composites. Applied Sciences, 14(5), 1723. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051723





