Abstract
Semantic segmentation of human images is a research hotspot in the field of computer vision. At present, the semantic segmentation models based on U-net generally lack the ability to capture the spatial information of images. At the same time, semantic incompatibility exists because the feature maps of encoder and decoder are directly connected in the skip connection stage. In addition, in low light scenes such as at night, it is easy for false segmentation and segmentation accuracy to appear. To solve the above problems, a portrait semantic segmentation method based on dual-modal information complementarity is proposed. The encoder adopts a double branch structure, and uses a SK-ASSP module that can adaptively adjust the convolution weights of different receptor fields to extract features in RGB and gray image modes respectively, and carries out cross-modal information complementarity and feature fusion. A hybrid attention mechanism is used in the jump connection phase to capture both the channel and coordinate context information of the image. Experiments on human matting dataset show that the PA and MIoU coefficients of this algorithm model reach 96.58% and 94.48% respectively, which is better than U-net benchmark model and other mainstream semantic segmentation models.
1. Introduction
Semantic segmentation is one of the main research topics in the field of computer vision, and it is a necessary process for computers to recognize the information features of images from the whole to the pixel level. The core of semantic segmentation is to divide images into non-overlapping sub-blocks with different semantic labels based on the information features of image itself, such as gray distribution between image pixels and image texture [1]. Portrait semantic segmentation is an important part of semantic segmentation. The purpose of portrait semantic segmentation is to separate the portrait semantic region from the complex background information semantic region in the picture- containing portrait, so as to obtain a good portrait boundary [2]. In real life, people transform scenes into images by cameras or other devices, and then segment and label the semantics of objective portrait objects in the images by using algorithms, so as to carry out applications and facilitate people’s lives. A well-trained high-precision portrait segmentation model can also be used as a preprocessing module of the whole portrait intelligent system, avoiding the feature extraction of irrelevant information, such as background, in the subsequent operation, and thus improving the accuracy of the whole system [3]. However, the real portrait image has the characteristics of different target sizes and various background information, which makes the semantic segmentation of portrait quite challenging. First of all, compared with conventional semantic segmentation, the portrait semantic segmentation model needs to face more images with larger target sizes, which tests the generalization of the model and makes it more difficult to guarantee the segmentation details of the model [4]. Meanwhile, the existing model is prone to the phenomena of target portrait loss and background misjudgment in low-light scenes, such as nighttime, due to the fact that the background pixels and target pixels in the portrait image are relatively close to each other, and the segmentation accuracy of the model needs to be improved.
In this paper, in order to solve the above problems, we propose a portrait semantic segmentation model based on dual-modal information complementarity that is in turn based on U-net network. The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- In the encoder stage, we extract image feature based on RGB mode and gray mode: RGB image and grayscale image are simultaneously used as inputs to model encoder, corresponding feature representation is obtained, and feature fusion is carried out. The gray image can be directly converted by RGB image, which avoids the overhead of collecting other modal images in the data set, and realizes the information complementarity and feature extraction in the dual mode. The feature extraction of gray-scale image improves the ability of the model to extract the target figure under low light.
- (2)
- We propose the SK-ASSP (Selective Kernel—Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling) module as a new feature extraction module in the encoder stage: SK-ASSP dynamically adjusts the weight of the void convolution of different receptive fields according to the size of the target in the image through soft attention, thus providing feature extraction capabilities for portrait targets of different sizes. At the same time, SK-ASSP uses edge optimization branch to improve the edge segmentation accuracy of target portrait according to edge feature map.
- (3)
- We propose the mixed-parallel attention mechanism to improve the encoder-decoder connection process: through parallel channel attention module and position attention module, the channel information and location information of input features are captured respectively.
2. Related Works
2.1. Semantic Segmentation Based on CNN
Convolutional neural network (CNN) can automatically learn different mixtures of representational features from training images to perform semantic segmentation of images [5]. On this basis, academics have designed a large number of new efficient semantic segmentation algorithms, of which the semantic segmentation model represented by U-net [6] has now become a popular choice for semantic segmentation as it can perform well on smaller datasets. The structure of U-net is shown in Figure 1, which is mainly divided into three parts: the encoder, the skip connection, and the decoder. In the U-net network, the encoder stageis responsible for the feature extraction of the image, where successive down-sampling operations allow the model to obtain the low-resolution information of the image. The decoder stage is responsible for the reduction of the image feature map, which regains the deep feature information of the image. The hopping connection stage connects the encoder output features with the decoder stage features, which helps the model to effectively fuse the deep and shallow features of the image. The establishment of skip connection can help the model to achieve semantic segmentation at the pixel level, which can provide more fine-grained features for segmentation.
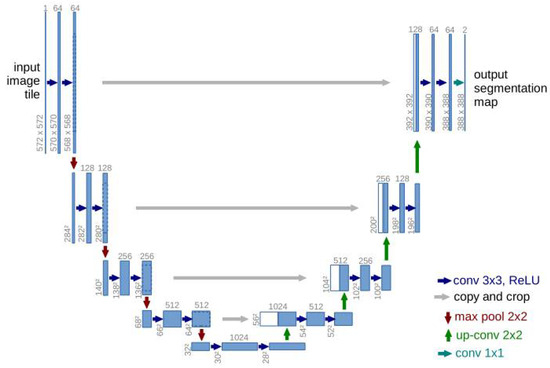
Figure 1.
The network structure of U-net.
However, when U-net is applied to the field of portrait semantic segmentation, the fixed receptive field of the convolutional kernel in the encodermakes the model unable to adaptively adjust the receptive field, which leads to the model being unable to capture the pixel information of the different sizes of portrait targets, resulting in the loss of some of the scale information of the image [7]. To address such problems, Chen et al. [8] proposed the deeplad v3+ model, which better solves the problem of the model failing to capture the information of different scales in the image, and also proposed the Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) module. Among them, the ASPP module parallelizes the void convolution of multiple branches with different expansion rates, to extract multi-scale features of different sizes of sensory fields, which helps the model to better focus on the pixel information of different sizes of target objects in the image [9]. However, deeplad v3+ is not sufficient for the multi-scale connection of feature map [10], and does not pay attention to the semantic gap between the encoder and decoder features, due to the direct connection between the encoder and the decoder, which may lead to poor target edge boundary segmentation accuracy. To address such problems, Oktay et al. [11] proposed Attention U-net, which adds attention coefficients to the down-sampling results and prunes the feature map to reduce the semantic gap by introducing an attention gate in the jump connection stage. While a single attention mechanism lacks the interaction between local feature information and global information, various combinations of attention mechanisms can help the model pay more attention to pixel location information [12]. In this regard, by linking multiple attention mechanisms in the hopping stage, we can obtain the attention weights of feature vectors in multiple dimensions, such as channel or space, so as to give more deep information to the down-sampling results, and thus reduce the semantic gap between the up-sampling results and the down-sampling results [13,14].
2.2. Semantic Segmentation of Cross-Modal
Images in different modalities focus on the different feature information of the image, and scholars believe that using images from multiple modalities for semantic segmentation helps to capture the features extracted from images with different focuses, contributing complementary information and helping to improve the network’s discriminative ability [15]. Zhang et al. [16] proposed that in the dual encoder structure, extracting key information from two modalities, infrared image modality and RGB image modality, before fusing them after passing through the attention module can effectively improve the semantic segmentation of the modeled night scene. ABHINAV et al. [17] introduced a self-supervised model in the segmentation model on the basis of multimodal segmentation, and used the adaptive fusion mechanism to integrate encoder multiple features in the encoder into a single decoder, dynamically adjusting the weights of different modal features in different scenes, and thus improving the generalization of the model in various types of complex scenes. This was based on the above ideas, at the same time, as grayscale images pay more attention to the brightness, structure and shape of the object than RGB images. Therefore, the semantic segmentation model based on RGB and grayscale images in two modalities may be able to effectively solve the problem of poor segmentation accuracy in low-light scenes.
However, on the other hand, if the feature mappings in different modalities of an image are directly summed up, the advantages of multimodal semantic segmentation will not be fully utilized. Accordingly, academics mostly use the attention module to perform feature fusion on the feature mappings in multiple modalities, and then obtain the feature mappings after the information interaction [18]. Wang et al. [19] proposed the MCF module, which extracts the multi-scale spatial information through the spatial context fusion (SCF) block and performs multimodal feature fusion by balancing the channel features through the squeezing learning. Moreover, Li et al. [20] modeled the feature correlation of multiple modalities by introducing a multi-attention mechanism to obtain the feature representation after information interaction.
3. Methods
3.1. Overall Architecture
The model proposed in this paper is mainly divided into three parts: Encoder, Skip connection and Decoder. The structure is shown in Figure 2.
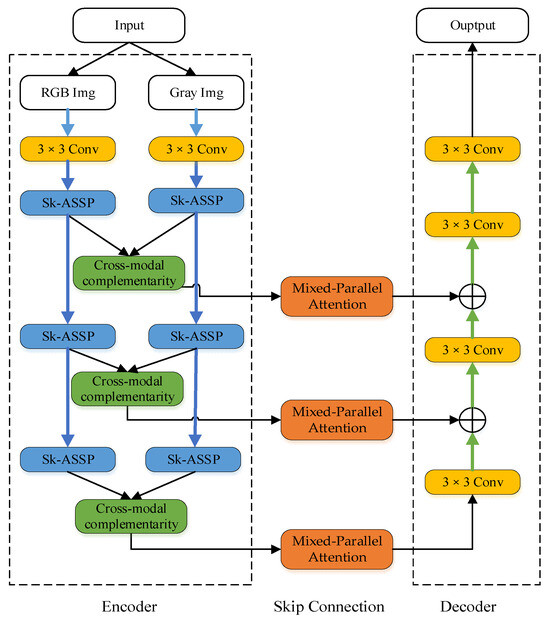
Figure 2.
The network structure of the method in this article.
The encoder part consists of two branches: RGB image input and gray image input. Each image input in two modalities will firstly go through a 3 × 3 convolution to obtain the shallow features in the two modes. After that, three consecutive down-sampling operations are carried out: First, the SK-ASSP module is entered to obtain the feature map under the corresponding mode, and then the output of the two branches of RGB and gray level is entered into the cross-modal complementarity module for feature fusion to obtain the result of this layer of down-sampling. After a total of 3 down-sampling operations, enter the decoder for up-sampling operations.
In the skip connection part, the mixed-parallel attention module is used in this paper. In this module, attention operations are performed simultaneously in channel dimension and coordinate dimension to capture local and global spatial information in features, as well as to mine the context-dependent information of portrait images in space and channel dimension.
In the decoder part, three consecutive up-sampling blocks are used to restore the feature image to the corresponding size. After each up-sampling, the image size becomes larger. In this paper, the original U-Net structure feature graph concatenation operation is changed to pixel-by-pixel addition, which can reduce the dimension. Finally, the output of this model is obtained by a 3 × 3 convolution.
3.2. SK-ASSP Module
We propose the SK-ASSP module in this paper, which consists of adaptive ASSP branch and edge detail optimization branch. Its structure is shown in Figure 3.
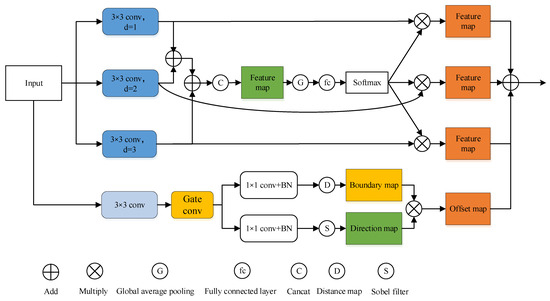
Figure 3.
The structure of the feature SK-ASSP module.
The first half of the adaptive ASSP branch is consistent with the ASSP module, consisting mainly of three parallel computations of atrous convolution with different expansion rates (d = 1, d = 2, d = 3). At the same time, the feature maps obtained using convolution with different expansion rates are added hierarchically before concatenation, thus avoiding the grid problem of extended convolution [21]. The latter part of the adaptive ASSP branch is adaptive weight adjustment based on the ASSP module. Firstly, the feature maps after concatenation are pooled globally, and then aggregated and compressed by fc (fully connected) layer and M vectors (M is the number of cavities convolution in the module, M = 3 in the figure), which are obtained again. Afterward, the weights of each of these three vectors are obtained by softmax operation. Lastly the weights obtained after softmax operation are multiplied with the output of three extended convolution, and the feature map with weight is obtained.
The edge detail optimization branch will first undergo a 3 × 3 convolution to obtain the initial feature map, and then undergo gated convolution to ensure that the edge branch only processes boundary-related information [22]. After that, the new feature map will enter the boundary branch and direction branch. In the boundary branch, after 1 × 1 convolution and BN (Batch Normalization) layer, distance mapping is carried out to calculate the minimum distance from other object semantic types. After all distance maps are aggregated, the model can obtain the final distance map. In the final distance map, all pixels whose distance value is less than the threshold y (the threshold value here is 5, focusing on thinning thin boundaries [23]) are set as boundaries to obtain the corresponding boundary map. On the other hand, the direction branch first goes through a 1 × 1 convolution and BN layer, and then executes the Sobel filter to calculate the corresponding direction mapping (value range 0–360). Each direction points to the inner pixel farthest from the object’s boundary. The whole direction range is divided into m categories (where m is 8 [23]), and the direction of each pixel is assigned to the corresponding category to obtain the corresponding direction mapping. Finally, the maps of the two branches are multiplied to obtain the edge optimization feature map.
Finally, the edge optimization feature map and adaptive ASSP feature map are added to get the final feature map. Adaptive ASSP branches can obtain multi-scale dense spatial information while retaining more fine-grained features, which helps the model to process the output adaptively. The edge optimization branch can effectively solve the problem of blurred edge details in grayscale images [24].
3.3. Cross-Modal Complementarity Module
Different modes of the same image focus on different features. RGB mode focuses on the image’s color and texture features, while gray mode focuses on the image’s brightness, structure and shape features. In order to make the feature maps extracted from the two branches of RGB image and grayscale image complement each other with information, so as to carry out cross-mode feature fusion, this paper makes improvements based on the CMF module (cross model fusion) [25], and proposes the following cross-mode complementary module, whose structure is shown in Figure 4.
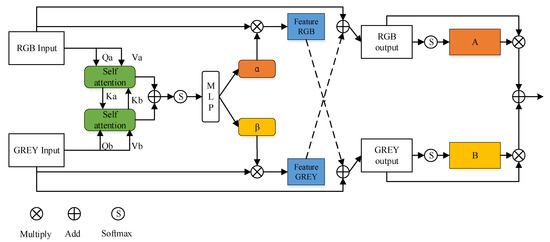
Figure 4.
Structure of Cross-modal complementarity module.
The cross-modal complementary module we use in this paper will first conduct self attention operation on the input of feature map in both RGB and gray image modes. In contrast to the conventional self-attention operation, this self-attention operation uses Q and V of its own mode and K of another mode as inputs, and then carries out the first information interaction to model the correlation of the feature map in the two modes.
Afterwards, in accordance with the original CMF module, the obtained self-attention vector is added and inputted into the multi-layer perceptron MLP after the softmax operation, and the corresponding vectors α, βare obtained respectively, and the inputs of the respective modes are multiplied to obtain a new feature map in the corresponding modes. Then the feature map is added to the input feature of another mode to complete the second information complementation between the corresponding features of the two modes, and two new feature map outputs are obtained. After that, the new feature maps under the two modes are operated by softmax respectively to obtain the corresponding weight matrices αRGB, βGRAY, which can be used to adjust the weights of the two output feature maps. Finally, the results obtained after multiplication are added to obtain the feature map after the complementary information of the two modes.
3.4. Mixed-Parallel Attention Module
By using the mixed-parallel attention mechanism in the skip connection stage, while retaining the long connection structure, more global information can be given to the subsampled results [26], which can be weighted in different dimensions, so as to achieve more accurate extraction of portrait edge details. We use a mixed attention module in this paper, which is mainly composed of channel attention and location attention, to capture the spatial information of images from two levels: channel and coordinate. Its structure is shown in Figure 5. Among them, the upper part is the channel attention module, and the lower part is the position attention module. By learning the weights of different channels, the channel attention mechanism can reduce the response of invalid channels and inhibit the activation of useless features. The location attention mechanism represents the correlation of two positions by modeling any two pixels, so that two pixels with similar characteristics can promote each other and obtain higher weights.
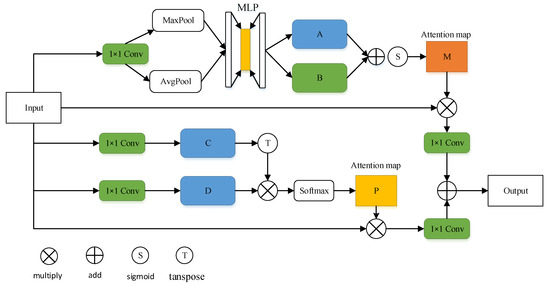
Figure 5.
Hierarchical attention mechanism module.
In the channel attention module, the dimensionality is first reduced by 1 × 1 convolution, and then the input spatial information is aggregated by Avgpool and Maxpool. Afterwards, through the multi-layer perceptron MLP, two spatial context features, representing A and B, are obtained. Finally, the two features are summed element-by-element to merge, and the corresponding channel attention diagram M is calculated, as shown in Equation (1):
where σ represents the sigmoid function, the hidden activation size of multi-layer perceptron, MLP is set to RC/r×1×1(r is the reduction ratio), α_avg and β_max represent the vectors obtained after AvgPool and MaxPool respectively. Finally, the attention map M is multiplied by the input features to get the channel attention feature map.
In the position attention module, for the input features, the dimension reduction operation is carried out first through 1 × 1 convolution, and features C and D. with the same dimensions as the input features. are obtained. Then. feature C is transposed and feature D is multiplied pixel-by-pixel to model the similarity of any two pixels in the feature map, and the corresponding position attention diagram P is calculated, as shown in Equation (2):
where Pij represents the feature similarity between the jth pixel and the ith point in the input feature. N = H × W, where H and W are the height and width of the input feature, respectively. Then, the attention diagram P is multiplied with the input features to get the location attention features. Then the obtained attention map and input features are added together to get the coordinate attention features.
Finally, the two attention feature maps are restored to the input dimension by using 1 × 1 convolution respectively, before the feature fusion is carried out to obtain the output map.
3.5. Loss Function
In order to obtain the context information of the target portrait in the image, we use void convolution in the model encoder phase of this paper. Compared with standard convolution, although it has a larger receptive field, its edge segmentation accuracy will be reduced. Bischke et al. [27] proposed a multi-loss method to enhance the final semantic segmentation results, and used different data functions to constrain the data results in different aspects, achieving a good effect on the output of the constrained model. Inspired by this, the model in this paper optimizes the semantic segmentation results by mixing losses, which means that the output of the model is constrained by two loss functions. The composition of the loss function used in this paper is as follows:
where losspb stands for pixel-based loss, lossdssim stands for Structural Similarity. α and β are bias parameters (where α + β = 1), which is to gradually extract information and perform preliminary evaluation and constraint on the segmented edge information and total precision information.
Pixel-based loss: It is mainly used to compare the pixel-level difference between two images. It can be divided into two parts: the first part is the total amount of information carried by pixels, which is represented by binary cross entropy. The second part, based on the pixel value gap measurement, compares the difference between the segmentation results and the artificially-generated labels in pairs. It is defined as:
where N represents the number of pixels. Sk represents the set of split labels, S represents the set of groundtruth, and Pij represents probabilities. Pij is calculated based on the average of all divided pixel pairs. The pri is between 0 and 1, where 0 means that the segmentation result is opposite to the segmentation label, and 1 means that the segmentation result is exactly correct and each pixel is accurately classified.
ssim: It is mainly used to measure the degree of similarity between the predicted sample and the real sample. Because it takes into account the local neighborhood of each pixel, a higher weight can be assigned to the boundary [28]. It is defined as:
where x and y are denots as pixels of two pictures respectively, μx and μy are the mean values of x and y, and σx and σy are the standard deviations of x and y. C1 is set to 0.022 and C2 is set to 0.042 to prevent the denominator from being 0 [29].
When combined with these two loss functions, the details of the target portrait boundary can be optimized effectively in the segmentation process, thus improving the overall segmentation accuracy of the model.
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Environment
The experiments in this paper are mainly encoded in python3.8, pytorch1.7, Cuda 11.0 environment, and trained on a computer with Intel i7-11700k CPU (Santa Clara, CA, USA), RTX 3070 graphics card (NVIDIA, Santa Clara, CA, USA), and 16 g memory. The adam iterator was selected for training, and the initial learning rate of network parameters was set as 0.01. After several experiments, the bias parameters α and β in the mixed loss function were set to 0.3 and 0.7, batchsize was set to 16, and 100 iterative training sessions were conducted. Freezing training was performed for the first 50 sessions, and freezing was canceled for the last 50 sessions.
4.2. Dataset
Due to the relatively precious portrait data, the available portrait image data is relatively limited. In order to better train the portrait segmentation network, this experiment mainly takes the open portrait data set human matting [30] as the basic data set, and then analyzes 1000 portrait images taken by classroom cameras in the Personalized Guidance Research Based on Cross modal High Order Reasoning Model project. In addition, unified specification cropping (600 × 800 px size) was carried out to complete the construction of the data set.
Since the image in the initial dataset cannot fully simulate the complex background, exposure, weather and other factors in the portrait image in the actual scene, this paper will use data enhancement to expand the data volume, mainly by synthesizing the foreground object in the actual image onto the new background. It mainly includes image color adjustment (contrast adjustment and brightness adjustment) {0.5, 1.5}. Image background replacement (weather effects randomly add {rain, snow, clouds, sunshine} and seasonal background replacement {spring, summer, autumn, winter}). The effect is shown in Figure 6.
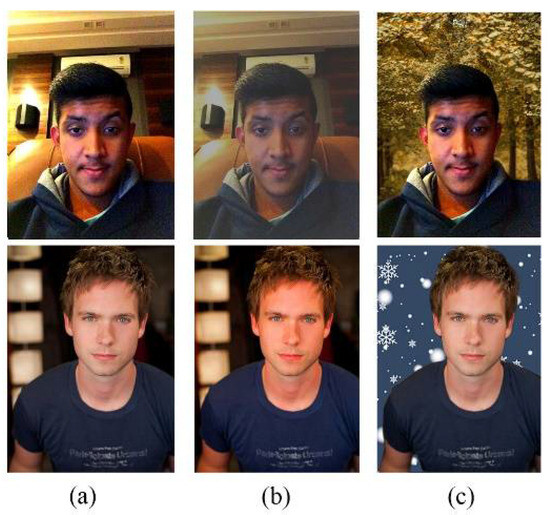

Figure 6.
Samples of data enhancement in this paper. (a) means the original images, (b) means the the color adjustment images, (c) means the background replacement images.
Finally, 6800 data sets were constructed, which were divided according to the partition ratio of 6:2:2, of which 4080 were used as training data sets, 1360 as verification data sets, and 1360 as test data sets.
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
Portrait semantic segmentation can actually be transformed into a binary classification problem between portrait semantic label region and background semantic label region [23]. In this paper, Pixel Accuracy PA (Pixel Accuracy) and MioU (Mean Intersection over Union) index was evaluated. The calculation formula is as follows:
In Formulas (6) and (7), TP represents the true example (that is, the target portrait in the test sample can be accurately predicted into the target portrait), FN represents the false counterexample (that is, the portrait background in the test sample can be accurately predicted into the adult portrait background), FP represents the false positive example (that is, the portrait background in the test sample can be predicted into the target portrait), and FP represents the false positive example (that is, the portrait background in the test sample can be predicted into the target portrait). TN stands for true counterexample (indicating that the portrait background in the test sample can be accurately predicted for the adult portrait background). In Formula (7), K represents the category of classification (2 in this experiment).
4.4. Module Ablation Experiments
4.4.1. Encoder Based Ablation Experiments
In order to verify the effectiveness of the model encoder, using dual branches for modal information complementation and SK-ASSP as a feature extraction module, ablation experiments were carried out, and the following six groups of networks were set up: Network_1 represents the U-net benchmark model. Network_2 represents the model using U-net basic model and encoder adding gray-scale image input. Network_3 represents a model that uses U-net basic model, the encoder adds grayscale image input, and adds cross-modal complementary module for feature fusion. Network_4 represents a model that adds ASSP module on the basis of Network_3 for feature extraction of RGB image and grayscale image. Network_5 represents a model in which the SK-ASSP module is added to the encoder on the basis of Network_3, and the adaptive ASSP branch is used for feature extraction of RGB image and gray image. Network_6 represents a model in which SK-ASSP module is added to encoder on the basis of Network_3, and adaptive ASSP branches and edge optimization branches are used for feature extraction of RGB and gray images. The experimental results are shown in Table 1:

Table 1.
Results of ablation experiment based on Encoder, where 🗸 means that the network contains this module.
According to Table 1, compared with Network_1, Network_2 with grayscale image input increases PA and MIoU by 0.09% and 0.11%, respectively. On the basis of Network_2, Network_3 with the addition of cross-mode complementary module for feature fusion has a more obvious improvement in PA and MIoU by 0.2% and 0.24%, compared with Network_1. Compared with Network_1, Network_4 with ASSP structure has improved both PA and MIoU, which proves that void convolution can effectively improve the segmentation accuracy of the model. Compared with Network_2 in PA and MIoU, Network_5 and Network_6 using SK-ASSP module, which is improved on the basis of ASSP module, have a greater improvement than Network_4. Network_5 has an increase of 0.45% and 0.64% in PA and MIoU compared with Network_4. Network_6 also has 0.2% and 0.32% advantages over Network_4 in PA and MIoU, respectively.
4.4.2. Attention Module Based Ablation Experiments
In order to verify the effectiveness of the hybrid attention module in the jump connection phase, this paper sets up five attention-based networks and conducts ablation experiments. Network_1 represents the U-net benchmark model. Network_2 represents the Attention U-net that introduces the attention gate in the jump connection phase. Network_3 represents the model of U-net with CBAM module added in the skip connection phase [31]. Network_4 represents the model of the mixed attention mechanism used in this paper in the jump connection phase. The experimental results are shown in Table 2:

Table 2.
Results of ablation experiment based on Attention module, where ✓ means that the network contains this module.
According to Table 2, compared with Network_1, Network_2 with the introduction of attention gate increased by 0.52% and 0.96% in PA and MIoU, respectively, and Network_3 with the introduction of CBAM module increased by 0.94% and 1.29% in PA and MIoU compared with Network_1. It is proved that the introduction of the attention mechanism can effectively improve the segmentation accuracy. Compared with Network_3, Network_6 using channel attention and location attention also has an advantage of 0.14% and 0.21% in PA and MIoU, which proves that the mixed attention module used in this paper can improve the accuracy of portrait semantic segmentation more than the CBAM module.
4.4.3. Loss Function Based Ablation Experiments
In this paper, a weighted loss function consisting of pixel-based loss and structural similarity loss is used. In order to verify the validity of the mixed loss function presented in this paper and determine the optimal values of the bias parameters α and β, ablation experiments were conducted. The values of α and β range from 0.1 to 0.9, while the values of α and β are 1. The best results were obtained when α was 0.3 and β was 0.7, as can be seen in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results of the ablation experiment on the mixed loss function.
4.5. Network Comparison Experiment
In this section, in order to evaluate the performance of the model proposed in this paper, it is compared with the evaluation indexes of the algorithm models U-net [5], LinkNet [32], PortraitNet [33], Deeplab v3+ [7] and Trans UNet [34]. The experimental results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Comparison of different segmentation model.
As can be seen from Table 4, the algorithm proposed in this paper performs best on the two segmentation indexes PA and MIoU. Among them, compared with U-net, the benchmark model in this paper, the improvement in PA and MIoU is 2.17% and 3.42%, respectively, which means that the improvement is obvious. Compared with LinkNet, which is improved based on the U-net network and the residual structure in the encoder stage, the model in this paper has a 1.35% and 2.36% improvement in PA and MIoU. Compared with the lightweight model PortraitNet, the proposed model also has advantages of 0.94% and 1.15% in PA and MIoU. Meanwhile, compared with Deeplab v3+, which also uses ASSP module for feature extraction optimization in the encoder stage, the model in this paper can also improve by 0.67% and 0.79% in PA and MIoU. Finally, compared with Trans Unet, with transformer introduced in the encoder stage, the model in this paper can also lead by 0.29% and 0.32% in PA and MIoU. At the same time, the parameter number and average segmentation time of this model are less than that of Trans Unet.
In order to evaluate the segmentation effect of the research model in this paper more intuitively, two groups of images are selected to display the visual effect of the actual results of each model in the above figure. Among them, the second group of experimental images are portrait segmentation images in the low-light scene. The segmentation results are shown in Figure 7.
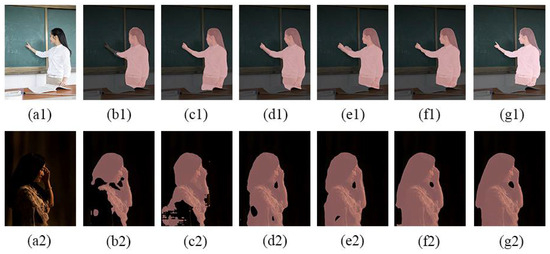
Figure 7.
Segmentation results of different models. a is the original image; b–f is the segmentation effect of U-net, LinkNet, PortraitNet, Deeplab v3+ and Trans UNet; and g is the segmentation effect of this paper’s segmentation model.
It can be seen that the U-net model loses the target portrait in Figure 7(a1,a2). The segmentation effect of LinkNet and PortraitNet is better than that of U-net, but in both Figure 7(c1,d1), at the point of contact between the portrait and the table, some degree of mis-segmentation of the background being categorized as portrait semantics occurs. Still worse, in the low-light scenes of Figure 7(c2,d2), both show the more obvious phenomenon of portraits being misjudged as backgrounds. Deeplab v3+ in Figure 7(e1) has basically completed a good segmentation of portraits, but in the edge details of portraits such as arms, the accuracy still needs to be improved. Meanwhile, in Figure 7(e2) of the low-light scene, there is still a certain phenomenon of portrait loss. In Figure 7(f1,f2), Trans UNet can perform a good segmentation of the target portrait. However, it still appears in the background misjudgment in the lower left corner of the portrait in the dark scene in Figure 7(f2). Compared with other semantic segmentation models, the proposed model in this paper has better segmentation accuracy of edge details, such as the right sleeve and fingers in Figure 7(g1). In Figure 7(g2), in the low-light scene, the portrait preservation is the most complete, and the background discrimination, such as the gap between the arm and the body, is closer to the standard segmentation results than other semantic segmentation models, and the segmentation accuracy is the best.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a new semantic segmentation method based on dual-modal information complementarity that is mainly designed based on the U-net basic model structure. This model uses two modal images, RGB image and gray image, which can solve the problem that the current U-net-based semantic segmentation model has poor segmentation accuracy in the face of different sizes of portrait edges and is prone to mis-segmentation phenomenon in low-light scenarios.
We also propose the SK-ASSP module as a feature extraction module to extract the features of the two modal images respectively. The SK-ASSP module can adaptively adjust the convolutional kernel weights for different sizes of portraits. Meanwhile, direction mapping and distance mapping are used to effectively optimize the edge segmentation accuracy of the portrait. After that, we use the cross-modal complementary module to exchange information on the feature map of the two modes. In the skip connection stage, the encoder and decoder are connected by mixed-parallel attention module, and the feature maps are modeled in channel and coordinate dimensions, and mine the pixel context information of the portrait image in space and channel dimensions.
Based on the above improvements, the model in this paper performs well in the enhanced dataset built under human matting, reaching 96.89% and 95.48% in PA and MIoU, which is a larger improvement than the benchmark model U-net in this paper, in both PA and MioU; at the same time, it has a higher segmentation accuracy than the semantic segmentation models LinkNet, PSPNet, deeplab v3+, and Trans UNet. In the actual image segmentation effect, the model in this paper has a better segmentation effect on the details of portrait edge segmentation, such as fingertips. In the future, we will focus on how to lighten the model by reducing the number of parameters of the model while maintaining the high accuracy of the model, and obtain a portrait semantic segmentation model that is easier to deploy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.F.; methodology, C.T.; software, C.T.; validation, C.T.; resources, G.F.; writing—original draft preparation, C.T.; writing—review and editing, G.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research and the APC was funded by Guangdong Provincial Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project of China, Project Name: Personalized Guidance Research Based on Cross modal High Order Reasoning Model, grant number GD23YJY08.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to contain portrait privacy information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cai, J.L. Research on Image Semantic Segmentation Technology Based on Deep Learning; Guangdong University of Technology: Guangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Research on Portrait Segmentation Based on Deep Learning; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, D.Y. Semantic Segmentation of Road Potholes Based on Deep Learning; Ningxia University: Yinchuan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.L.; Bian, D.W. Algorithm for Portrait Segmentation Combined with MobileNetv2 and Attention Mechanism. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2022, 58, 220–228. [Google Scholar]
- Kuai, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, B.T.; Chen, X.D.; Xue, W.B. Urban vegetation classification based on multi-scale feature perception network for UAV images. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2022, 24, 962–980. [Google Scholar]
- Olaf, R.; Philipp, F.; Thomas, B. U-net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Su, R.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Cheng, C. MSU-Net: Multi-Scale U-Net for 2D Medical Image Segmentation. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 639930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C. Research on Image Semantic Segmentation Algorithm Based on Improved DeepLabv3+. J. Syst. Simul. 2023, 35, 2333–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, A.; Maryam, A.; Mahmood, F. Attention Deeplabv3+: Multi-level Context Attention Mechanism for Skin Lesion Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 251–266. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention U-net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Qiu, K.; Chen, L.; Mei, X.; Hong, L.; Tao, C. SCAttNet: Semantic Segmentation Network with Spatial and Channel Attention Mechanism for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, A.; Lambrou, T.; Ye, X. MDA-Unet: A Multi-Scale Dilated Attention U-Net for Medical Image Segmentation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, D.L.; Ding, H.H. Street Scene Real-Time Semantic Segmentation with Fusion Cross Attention Mechanism [J/OL]. Computer Applications and Software. 2024. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/31.1260.TP.20240112.1654.002 (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Jiao, Y. Multimodal medical image segmentation using multi-scale context-aware network. Neurocomputing 2022, 486, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, R.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Yuan, W.H. Multimodal image semantic segmentation based on attention mechanism. Chin. J. Liq. Cryst. Disp. 2023, 38, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinav, V.; Rohit, M.; Wolfram, B. Self-Supervised Model Adaptation for Multimodal Semantic Segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 1239–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.Q.; Pan, C.; He, L.M.; Xu, Z. Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation Network Based on Multimodal Feature Fusion. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2022, 58, 256–264. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.C.; Gu, N.N.; Xin, J.J.; Wang, S.F. RGB-D Dual Modal Information Complementary Semantic Segmentation Network. J. Comput.-Aided Des. Comput. Graph. 2023, 35, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.Y. Pedestrian Detection and Scene Segmentation Based on Multimodal Image Fusion; Central South University: Changsha, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3141–3149. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.B.; Li, S.; Tian, H.; Yang, X.; Ma, C.; Yu, C. Images semantic segmentation method based on fusion edge optimization. Saf. Coal Mines 2022, 53, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Xie, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. SegFix: Model-Agnostic Boundary Refinement for Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 489–506. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Bai, D.; Lee, J. Real Image Denoising Based on Multi-Scale Residual Dense Block and Cascaded. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 448–449. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Tao, C.; Qiong, L. Complementarity-aware cross-modal feature fusion network for RGB-T semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 131, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.M.; Sima, H.F. A-LinkNet: Semantic segmentation network based on attention and spatial information fusion. Chin. J. Liq. Cryst. Disp. 2022, 37, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischke, B.; Helber, P.; Folz, J.; Borth, D.; Dengel, A. Multi-task learning for segmentation of building footprints with deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1480–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y. Building Extraction Based on U-Net with an Attention Block and Multiple Losses. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Shi, Z.F.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, Z. Improved U-net based on Mixed Loss Function for Liver Medical I-mage Segmentation. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2020, 57, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Ge, T. Semantic human matting. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chaurasia, A.; Culurciello, E. LinkNet: Exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 10–13 December 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.H.; Dong, X.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.L. PortraitNet: Realtime portrait segmentation network for mobile device. Comput. Graph. 2019, 80, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).