Review of Advances in Active Impulsive Noise Control with Focus on Adaptive Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fractional Lower-Order Power-Based Algorithms
2.1. p-Power Algorithms
2.2. Other Algorithms
3. Non-Linear Transformation-Based Algorithms
3.1. Threshold Method
3.2. Logarithmic Transformation and Trigonometric Transformation
4. Other Transformation Algorithms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guicking, D. On the invention of active noise control by Paul Lueg. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 87, 2251–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J.C. Active Adaptive Sound Control in A Duct: A Computer Simulation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 70, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, R.; Zhou, Z.; Hsu, Y. Adaptive Filtering of Stable Processes for Active Attenuation of Impulsive Noise; ICASSP: Detroit, MI, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Fast stable normalised least-mean fourth algorithm. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 1276–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Q.; Yu, Y.; Gao, S.B.; Zeng, X.P.; He, Z.Y. A new normalized LMAT algorithm and its performance analysis. Signal Process. 2014, 105, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T.; Mitsuhashi, W. Robust Adaptive Algorithm for Active Noise Control of Impulsive Noise; ICASSP: Taipei, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamasco, M.; Piroddi, L. Active Noise Control of Impulsive Noise Using Online Estimation of an Alpha-Stable Model; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, M.T.; Mitsuhashi, W. Improving robustness of filtered-x least mean p-power algorithm for active attenuation of standard symmetric-α-stable impulsive noise. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T.; Nishihara, A. Data-reusing-based filtered-reference adaptive algorithms for active control of impulsive noise sources. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 92, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T. A time-varying normalized step-size based generalized fractional moment adaptive algorithm and its application to ANC of impulsive sources. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 155, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lu, L.; Yu, Y.; de Lamare, R.C.; Liu, Z. FxlogRLP: The Filtered-X Logarithmic Recursive Least P-Power Algorithm; SSP: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.H.; John, M.V. Tracking analysis of the sign algorithm in nonstationary environments. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 1990, 12, 2046–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, V.; Cho, S. Improved convergence analysis of stochastic gradient adaptive filters using the sign algorithm. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 1987, 35, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Zheng, Y.R.; Benesty, J. An affine projection sign algorithm robust against impulsive interferences. IEEE Signal Process Lett. 2010, 17, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, H. An Efficient Memory-improved proportionate affine projection sign algorithm based on l0-norm for sparse system identification. Adv. Intell. 2014, 277, 509–518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.B.; Wang, G.; Liao, X.F. Modified memory-improved proportionate affine projection sign algorithm based on correntropy induced metric for sparse system identification. Electron. Lett. 2018, 54, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lee, T.; Wu, B. A variable step-size sign algorithm for channel estimation. Signal Process. 2014, 102, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Zhao, J.H.; Qu, H.; Chen, B.D. A correntropy inspired variable step-size sign algorithm against impulsive noises. Signal Process. 2017, 141, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Chang, J.H.; Nam, S.W. Affine projection sign algorithm with l1 minimization-based variable step-size. Signal Process. 2014, 105, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ni, J. Variable step-size weighted zero-attracting sign algorithm. Signal Process. 2020, 172, 107542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Ni, J.; Chen, J. A family of normalized dual sign algorithms. DSP 2021, 110, 102954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.; Avlonitis, A. A robust mixed-norm adaptive filter algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1997, 4, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulis, E.V.; Stathaki, T. A normalized robust mixed-norm adaptive algorithm for system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2004, 11, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.C.; Zhao, H.Q. Filtered-x generalized mixed norm (FXGMN) algorithm for active noise control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 107, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, H. Adaptive Volterra filter with continuous lp-norm using a logarithmic cost for nonlinear active noise control. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 364, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayyani, H. Continuous mixed p-norm adaptive algorithm for system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P.X.; Zhang, L.J.; Meng, D.J.; Pi, X.F. An active impulsive noise control algorithm with self-p-normalized method. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 186, 108428. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Kuo, S.M.; Meng, G. Adaptive algorithm for active control of impulsive noise. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 291, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T.; Mitsuhashi, W. Improving performance of FxLMS algorithm for active noise control of impulsive noise. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 327, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, M.; Della Rossa, F.; Piroddi, L. Active Noise Control of Impulsive Noise with Selective Outlier Elimination; ACC: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 4171–4176. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, V.; Santhiyakumari, N. An active noise control system for impulsive noise using soft threshold FxLMS algorithm with harmonic mean step size. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 109, 2263–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chan, S.C.; Ho, K.L. New sequential partial-update least mean M-estimate algorithms for robust adaptive system identification in impulsive noise. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4455–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qiu, X. An M-estimator based algorithm for active impulse-like noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T. An adaptive algorithm, based on modified tanh non-linearity and fractional processing, for impulsive active noise control systems. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2018, 37, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.H.; Li, M.F.; Lim, T.C. Enhanced filtered-x least mean mestimate algorithm for active impulsive noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 90, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; He, H.; Qiu, X. An active impulsive noise control algorithm with logarithmic transformation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 19, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.V.; Panda, G. A robust filtered-s LMS algorithm for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, M.O.; Vanli, N.D.; Kozat, S.S. A novel family of adaptive filtering algorithms based on the logarithmic cost. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2014, 62, 4411–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, H.; Chen, B. Improved variable forgetting factor recursive algorithm based on the logarithmic cost for Volterra system identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2016, 63, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.L.; Narwaria, M. Lorentzian based adaptive filters for impulsive noise environments. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.; Zeb, A.; Yasir Umair, M.; Iyas, D.; Sheikh, S.A. Less complex solutions for active noise control of impulsive noise. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2020, 102, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Xiong, K.; Iu, H.H.; Chi, K.T. Logarithmic hyperbolic cosine adaptive filter and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2021, 51, 2512–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Bhattacharjee, S.S.; George, N.V. A family of logarithmic hyperbolic cosine spline nonlinear adaptive filters. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 178, 07973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Li, W.; Yu, Y.; de Lamare Rodrigo, C. Robust spline adaptive filtering based on accelerated gradient learning: Design and performance analysis. Signal Process. 2021, 183, 107965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Park, P.; Newcomb, R.W. A normalized least mean squares algorithm with a step-size scaler against impulsive measurement noise. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2013, 60, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yang, X.M. Behavior of the LMS algorithm with hyperbolic secant cost. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 1943–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.Y.; Chen, S.M.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Lin, D.Y.; Shen, M.L.; Wang, S.Y. Generalized Hyperbolic Tangent Based Random Fourier Conjugate Gradient Filter for Nonlinear Active Noise Control. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2023, 31, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Zhao, H.Q.; He, X.Q.; Shu, Z.L.; Chen, B.D. Cascaded Random Fourier Filter for Robust Nonlinear Active Noise Control. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2022, 30, 2188–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Y. An enhanced normalized step-size algorithm based on adjustable nonlinear transformation function for active control of impulsive noise. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 176, 107853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Li, Y.S.; Zakharov, Y.V.; Xue, W.; Qi, J.W. Constrained least lncosh adaptive filtering algorithm. Signal Process. 2021, 183, 108044. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Pandey, R.; Bhattacharjee, S.S.; George, N.V. Exponential Hyperbolic Cosine Robust Adaptive Filters for Audio Signal Processing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 28, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, S.; Albu, F.; Chandrasekar, A. Robust Exponential Hyperbolic Sine Adaptive Filter for Impulsive Noise Environments. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 5149–5153. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.; Cheng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Biswal, B. Robust adaptive filtering algorithms based on (inverse) hyperbolic sine function. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, 0258155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Pokharel, P.P.; Principe, J.C. Correntropy: Properties and applications in non-Gaussian signal processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 5286–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Principe, J.C. Using Correntropy as a Cost Function in Linear Adaptive Filters; IJCNN: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2009; pp. 2950–2955. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Lei, X.; Liang, J.; Zheng, N.N.; Príncipe, J.C. Steady-state mean-square error analysis for adaptive filtering under the maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 880–884. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Xing, L.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, N.N.; Príncipe, J.C. Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 64, 3376–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, H. Active impulsive noise control using maximum correntropy with adaptive kernel size. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 87, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, G.; Dai, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, H.B. Affine projection mixed-norm algorithms for robust filtering. Signal Process. 2021, 187, 108153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.A. Generalized maximum correntropy algorithm with affine projection for robust filtering under impulsive-noise environments. Signal Process. 2020, 172, 107524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Qu, H.; Chen, B.; Principe, J.C. A Switch Kernel Width Method of Correntropy for Channel Estimation; IJCNN: Killarney, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, E.L.; Xia, B.Y.; Li, E.; Wang, T.T. An efficient algorithm for impulsive active noise control using maximum correntropy with conjugate gradient. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 188, 108511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xing, L.; Xu, B.; Zhao, H.Q.; Zheng, N.N.; Príncipe, J.C. Kernel risk-sensitive loss: Definition, properties and application to robust adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 2888–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Huang, X.; Wang, S. Minimum kernel risk sensitive mean p-power loss algorithms and their performance analysis. DSP 2020, 104, 102797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Dong, F.; Wang, S. Robust constrained minimum mixture kernel risk-sensitive loss algorithm for adaptive filtering. DSP 2020, 107, 102859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S. Maximum versoria criterion-based robust adaptive filtering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 64, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, K.; Xu, J. Convex combination of the FxAPV algorithm for active impulsive noise control. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 181, 109443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.B.; Chao, L.; Chen, S.M.; Ge, P.Y.; Cao, Y.T. Active control of impulsive noise based on a modified convex combination algorithm. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 186, 108438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, S.; Albu, F.; Chandrasekar, A. Steady state mean square analysis of standard maximum versoria criterion based adaptive algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S. A family of robust adaptive filtering algorithms based on sigmoid cost. Signal Process. 2018, 149, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrhman, O.M.; Sen, L. Robust adaptive filtering algorithms based on the half-quadratic criterion. Signal Process. 2023, 202, 108775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Pandey, R.; Bora, S.S.; George, N.V. A Robust Family of Algorithms for Adaptive Filtering Based on the Arctangent Framework. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 1967–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
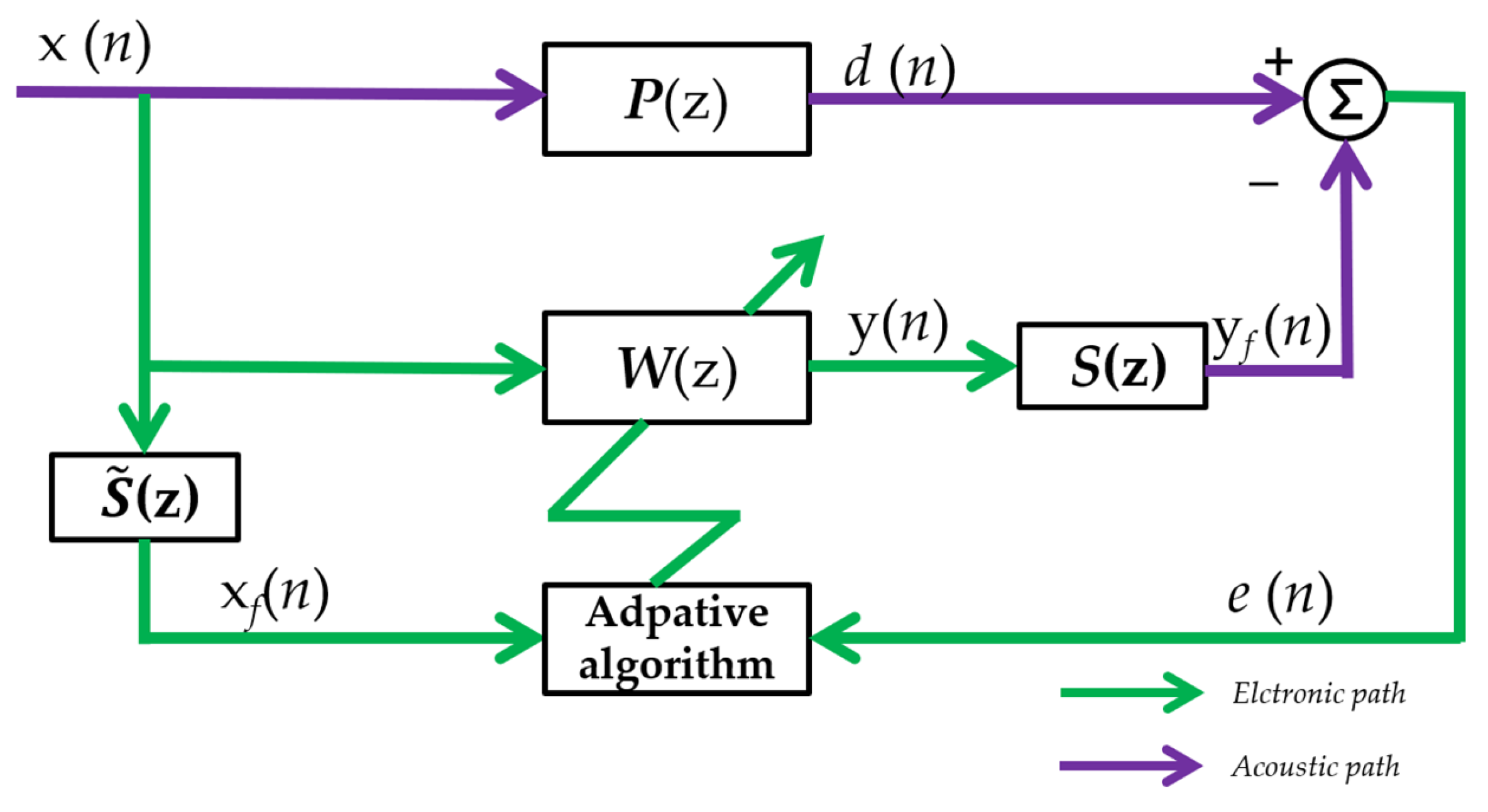
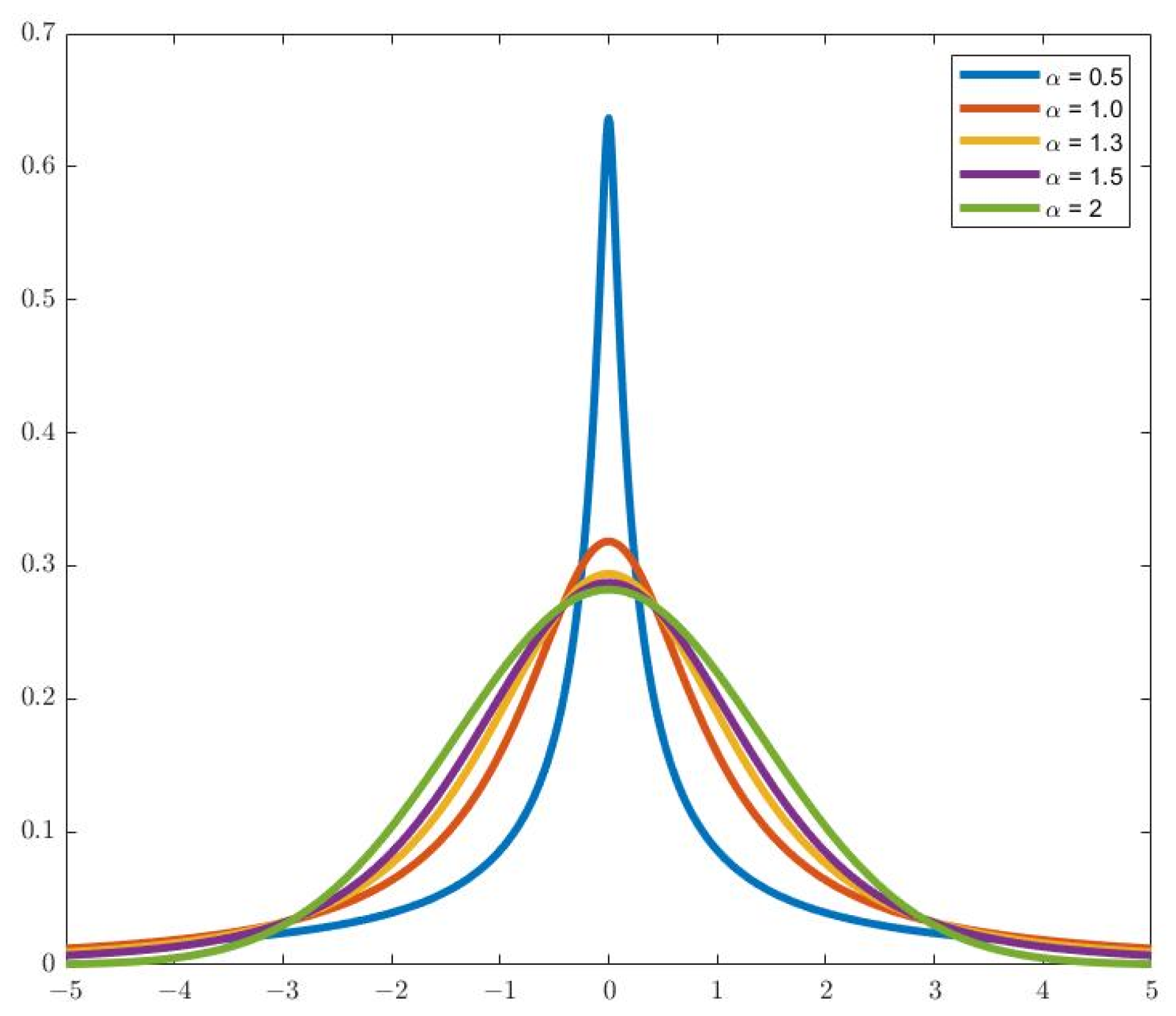
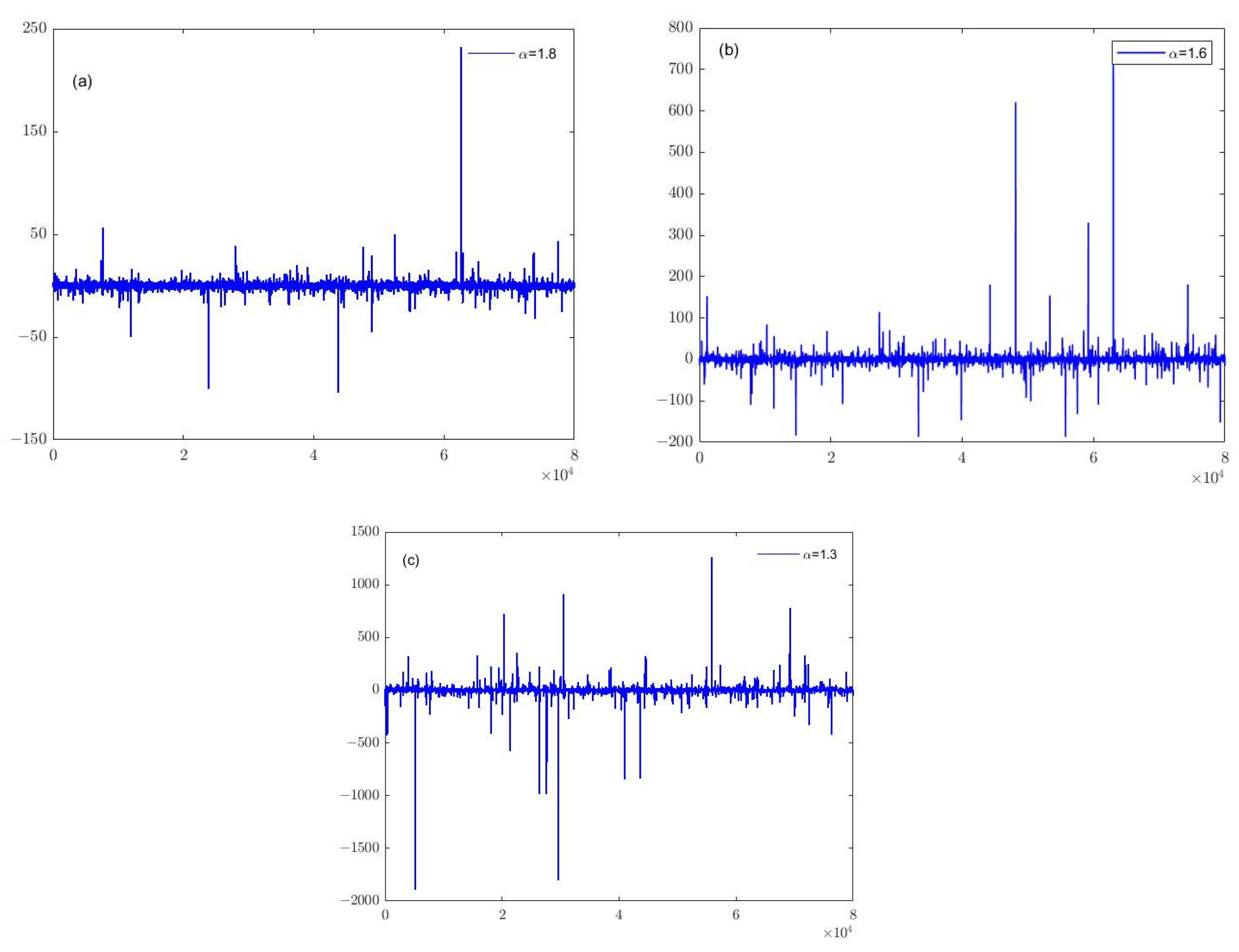
| Characteristics | Active Noise Reduction | Passive Noise Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time | Faster response and adaptation | Relatively slower response |
| Adaptability | Automatically adjusts parameters | Typically lacks adaptability |
| Effective Noise Reduction | Effectively suppresses various types of noise | Limited effectiveness in handling complex noise patterns |
| Power Consumption | Requires additional power | Relatively lower power consumption |
| Complexity | Algorithm and hardware | Material or structure Relatively simple implementation |
| Cost Function | References | |
|---|---|---|
| [3,4] | ||
| [5] | ||
| [6,7] | ||
| [8,9] | ||
| [10] | ||
| [11] |
| Cost Function | References | |
|---|---|---|
| [12,13,19] | ||
| [14,15] | ||
| [17] | ||
| [18] | ||
| [19] | ||
| [20] | ||
| [24] | ||
| [25] | ||
| [26] | ||
| [27] |
| Cost Function | Reference | |
|---|---|---|
| [29] | ||
| [30] | ||
| [31] | ||
| [32] | ||
| [33] | ||
| [34] | ||
| [35] |
| Cost Function | References | |
|---|---|---|
| [36] | ||
| [37] | ||
| [38] | ||
| [39] | ||
| [40] | ||
| [41,42,43,44,50] | ||
| [45] | ||
| [46] | ||
| [47] | ||
| [48] | ||
| [49] | ||
| (p = 2) | [51] | |
| [52] | ||
| [53] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Lei, Z. Review of Advances in Active Impulsive Noise Control with Focus on Adaptive Algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031218
Liu Y, Lei Z. Review of Advances in Active Impulsive Noise Control with Focus on Adaptive Algorithms. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(3):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031218
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yan, and Zhichun Lei. 2024. "Review of Advances in Active Impulsive Noise Control with Focus on Adaptive Algorithms" Applied Sciences 14, no. 3: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031218
APA StyleLiu, Y., & Lei, Z. (2024). Review of Advances in Active Impulsive Noise Control with Focus on Adaptive Algorithms. Applied Sciences, 14(3), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14031218





