Coal Dust and Methane as a Hazard in Coal Preparation Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
- geological characteristics of the coal seam and the properties of the coal mined (location, mineral composition, hardness, degree of coalification, etc.),
- mining method, run-of-mine haulage method to the coal preparation plant (type of machinery and equipment for mining and loading, modes and means of transport),
- technology adopted for the preparation of coal in the preparation plant (beneficiation methods, type of machinery and equipment),
- Physical properties of the dust, such as particle size and dispersibility.
- -
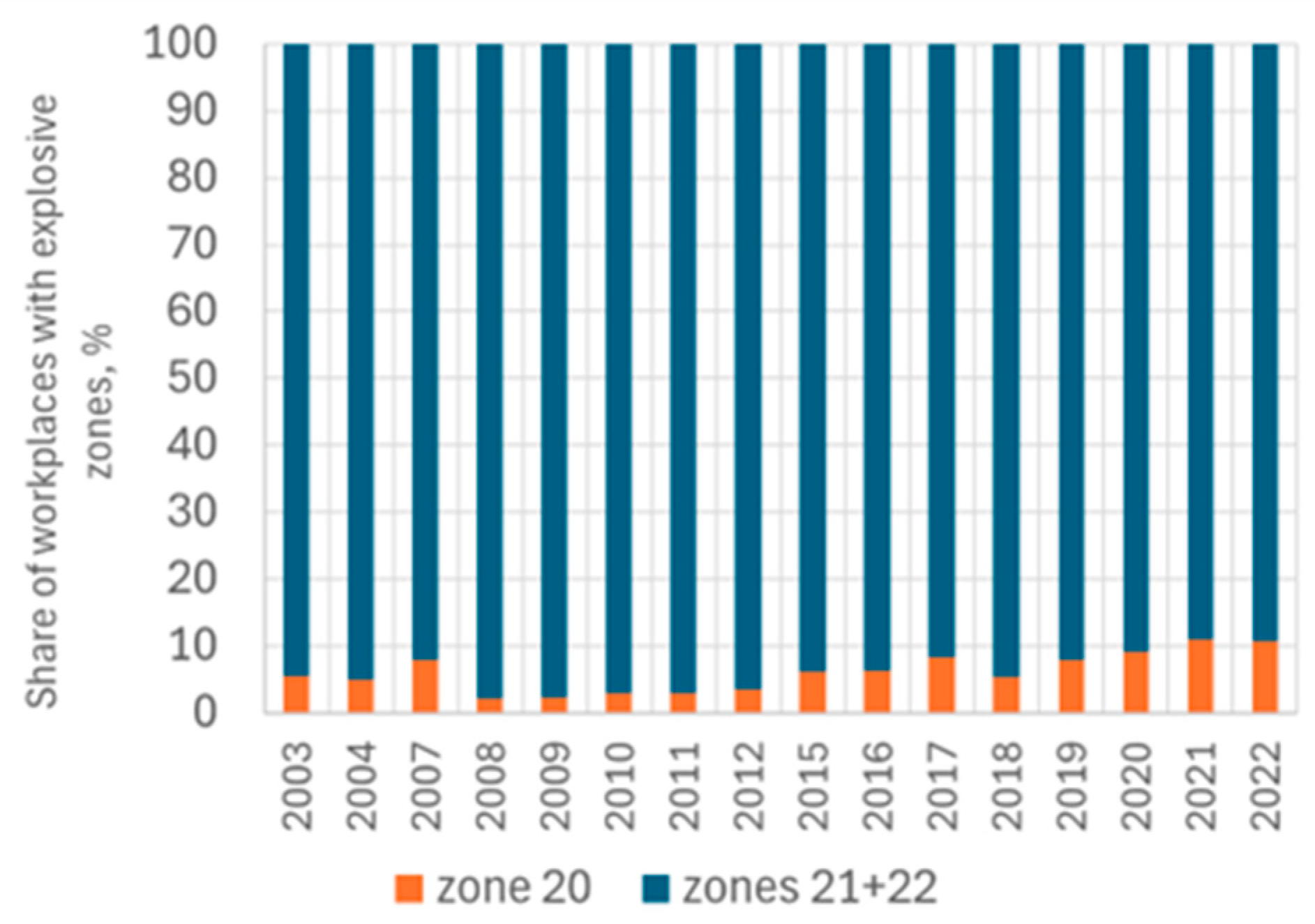
- zone 20—a place in which an explosive dust atmosphere, in the form of a cloud of dust in air, is present continuously, or for long periods or frequently,
- -
- zone 21—a place in which an explosive dust atmosphere, in the form of a cloud of dust in air, is likely to occur in normal operation occasionally,
- -
- zone 22—area in which an explosive dust atmosphere, in the form of a cloud of combustible dust in air, is not likely to occur in normal operation but, if it does occur, will persist for a short period only.
2. Coal Dust Control in Hard Coal Preparation Plants
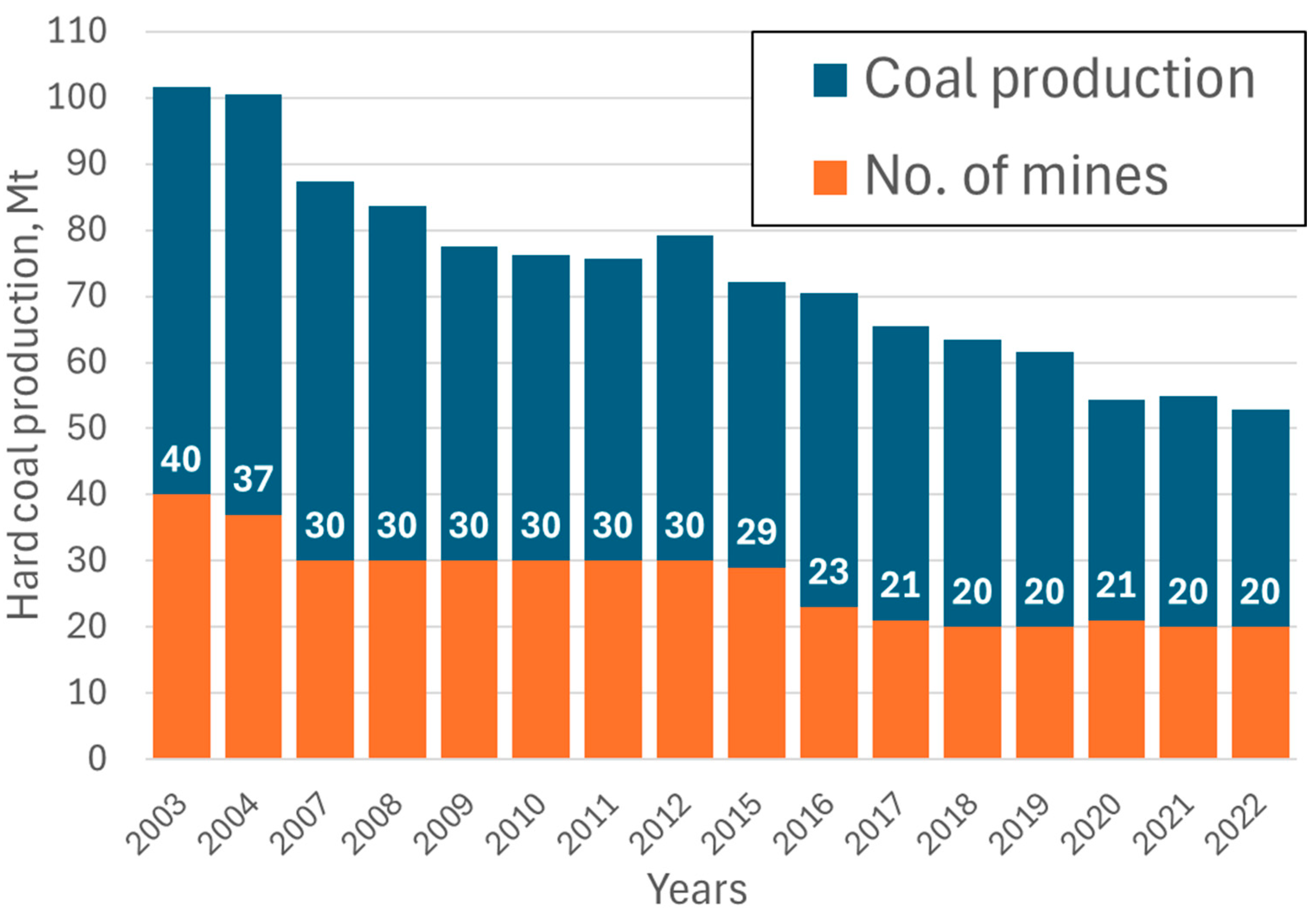
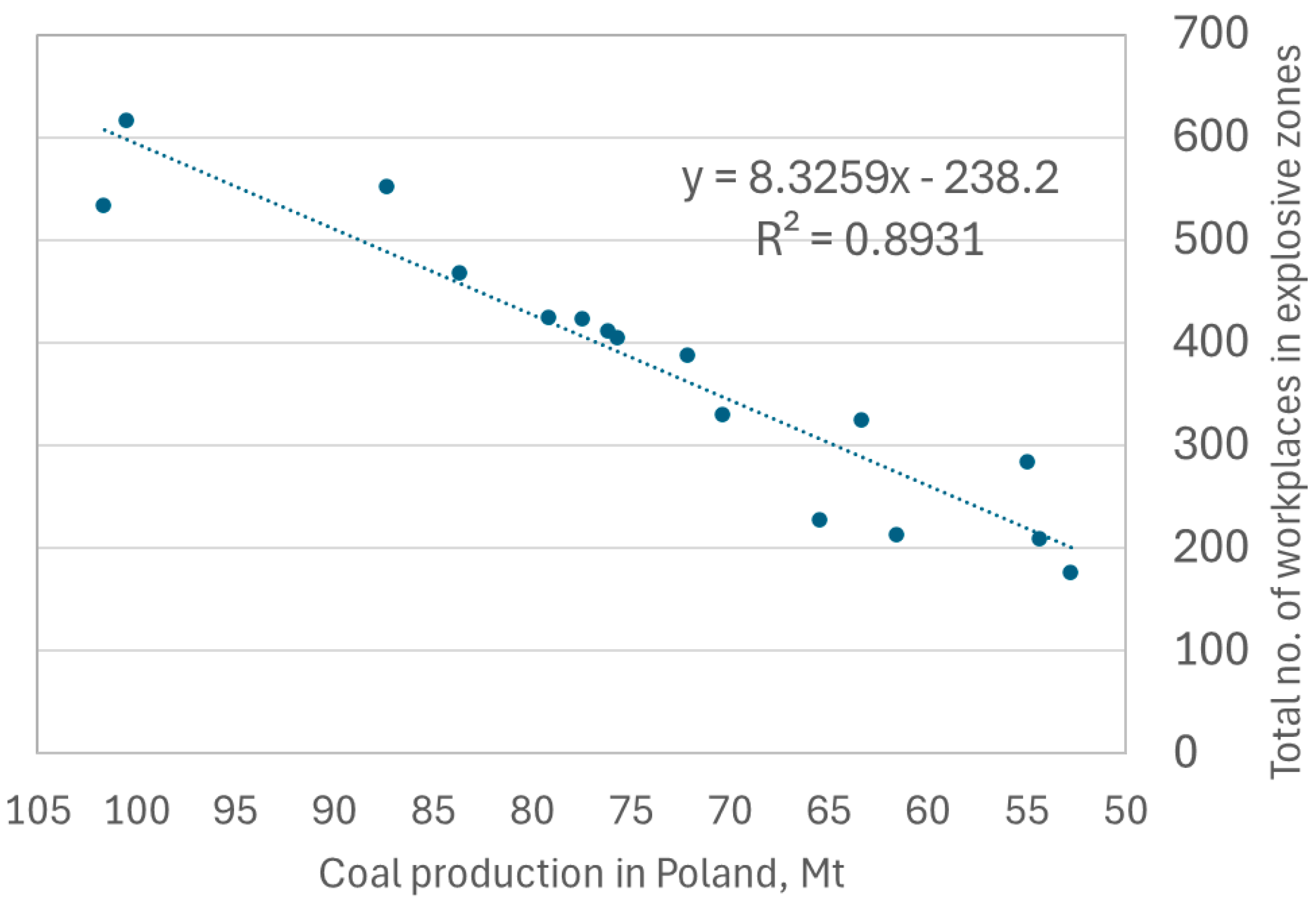
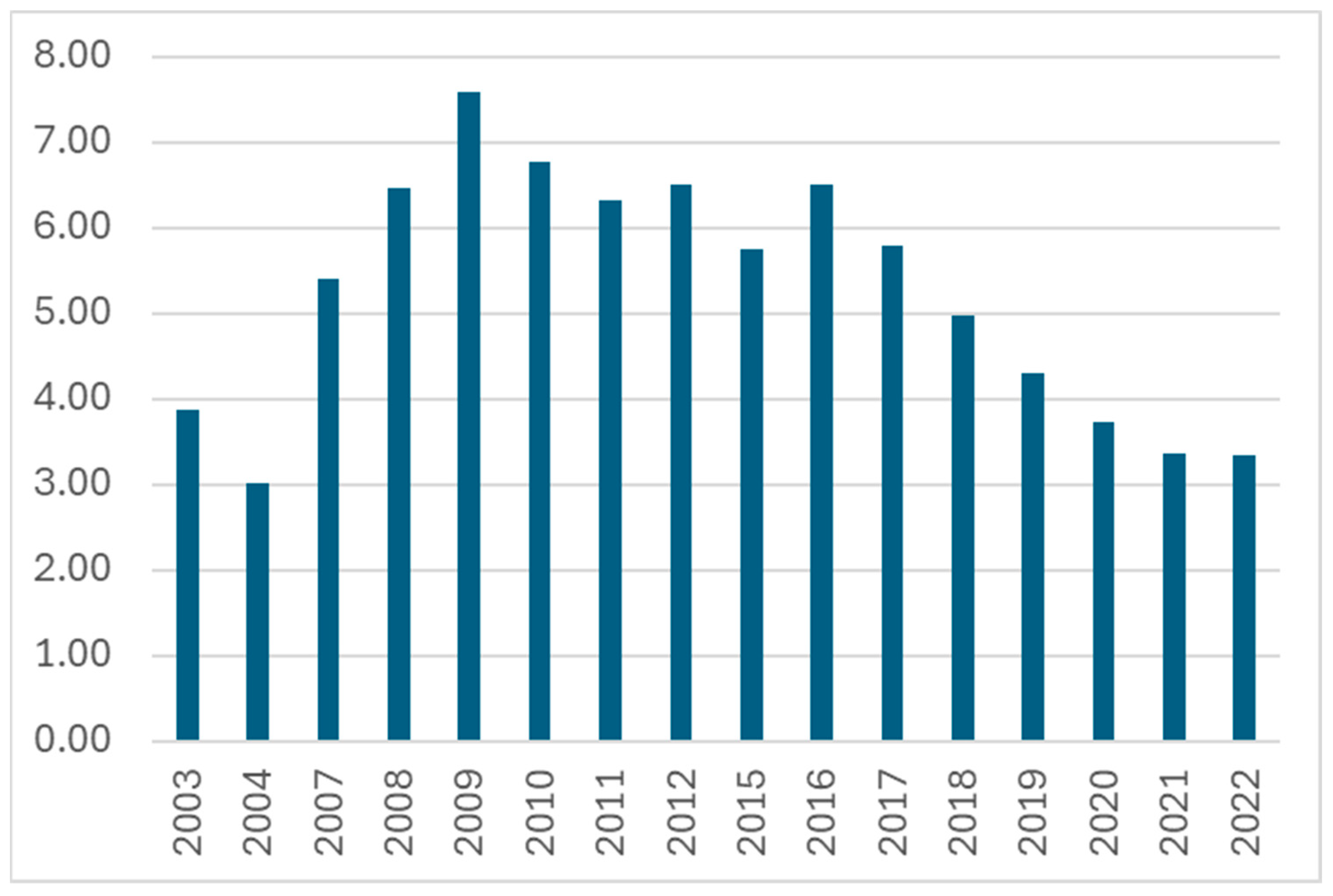
3. Indexes for Coal Dust and Methane Hazards Estimation in Hard Coal Preparation Plants
| Year | Coal Production, Million Mg | No. of Workplaces in Zone 20 | No. of Workplaces in Zone 21 + 22 | No. of Workplaces in MAC | No. of Workplaces in Zone 2 Methane Explosive Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 101.7 | 30 | 504 | 395 | 240 |
| 2004 | 100.5 | 30 | 587 | 303 | 325 |
| 2007 | 87.4 | 44 | 508 | 472 | 225 |
| 2008 | 83.7 | 10 | 458 | 541 | 274 |
| 2009 | 77.5 | 10 | 414 | 588 | 225 |
| 2010 | 76.2 | 12 | 400 | 516 | 232 |
| 2011 | 75.7 | 12 | 393 | 478 | 351 |
| 2012 | 79.2 | 15 | 410 | 516 | 279 |
| 2015 | 72.2 | 24 | 364 | 415 | 280 |
| 2016 | 70.4 | 21 | 309 | 458 | 251 |
| 2017 | 65.5 | 19 | 309 | 380 | 352 |
| 2018 | 63.4 | 17 | 308 | 315 | 217 |
| 2019 | 61.6 | 17 | 196 | 265 | 219 |
| 2020 | 54.4 | 19 | 190 | 203 | 237 |
| 2021 | 55.0 | 31 | 253 | 185 | 259 |
| 2022 | 52.8 | 19 | 157 | 177 | 282 |
| No data available for years 2005, 2006, 2013, and 2014. | |||||
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Further Recommendations
Future Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chunmiao, Y.; Chang, L.; Gang, L. Coal Dust Explosion Prevention and Protection Based on Inherent Safety. Procedia Eng. 2011, 26, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divers, E.F.; Cecala, A.B. Dust Control in Coal Preparation and Mineral Processing Plants; Bureau of Mines: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Attfield, M.; Castranova, V.; Hale, J.M.; Suarthana, E.; Thomas, K.C.; Wang, M.L. Coal Mine Dust Exposures and Associated Health Outcomes; a Review of Information Published since 1995. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2011–172. 2011. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2011-172/pdfs/2011-172.pdf (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- Jiang, J.; Wang, P.; Pei, Y.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.; He, Y. Preparation and Performance Analysis of a Coking Coal Dust Suppressant Spray. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prostański, D. Experimental Study of Coal Dust Deposition in Mine Workings with the Use of Empirical Models. J. Sustain. Min. 2015, 14, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60079-10-2; Explosive Atmospheres—Part 10-2: Classification of Areas—Explosive Dust Atmospheres. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Pracy i Polityki Społecznej. Rozporządzenie Ministra Pracy i Polityki Społecznej z dnia 6 czerwca 2014 r. w sprawie najwyższych dopuszczalnych stężeń i natężeń czynników szkodliwych dla zdrowia w środowisku pracy; Dz. U. 2014, poz. 817. Regulation of the Minister of Labor and Social Policy. Regulation of the Minister of Labor and Social Policy of June 6, 2014, on the maximum allowable concentrations and intensities of harmful factors for health in the work environment; Journal of Laws 2014, item 817.
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Pracy i Polityki Społecznej. Rozporządzenie Ministra Pracy i Polityki Społecznej w sprawie najwyższych dopuszczalnych stężeń i natężeń czynników szkodliwych dla zdrowia w środowisku pracy; Dz. U. 2018, poz. 1286. (Regulation of the Minister of Labor and Social Policy. Regulation of the Minister of Labor and Social Policy on the maximum allowable concentrations and intensities of harmful factors for health in the work environment; Journal of Laws 2018, item 1286.).
- Rahimi, E.; Shekarian, Y.; Shekarian, N.; Roghanchi, P. Investigation of Respirable Coal Mine Dust (RCMD) and Respirable Crystalline Silica (RCS) in the U.S. Underground and Surface Coal Mines. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, S. The Impacts of Coal Dust on Miners’ Health: A Review. Environ. Res. 2020, 190, 109849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, L.H.T.; Cohen, R.A. Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis and Other Mining-Related Lung Disease: New Manifestations of Illness in an Age-Old Occupation. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocek, P.; Mocek, K. Health Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Industrial Dust in Preparation Plants of Hard Coal Mines. Sci. J. Marit. Univ. Szczec. 2022, 72, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józef Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2003; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2004; ISBN 978-83-65503-.
- Makówka, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2022; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2023; ISBN 978-83-65503-53-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lutyński, A. Zwalczanie Zagrożeń Wywoływanych Przez Metan, pył i Hałas w Zakładach Przeróbki Mechanicznej Kopalń Węgla Kamiennego; Innowacyjne Techniki i Technologie Mechanizacyjne; Instytut Techniki Górniczej KOMAG: Gliwice, Poland, 2017; ISBN 978-83-65593-03-0. [Google Scholar]
- Prostański, D.; Vargová, M. Installation Optimization of Air-and-Water Sprinklers at Belt Conveyor Transfer Points in the Aspect of Ventilation Air Dust Reduction Efficiency. EBSCOhost. Available online: https://openurl.ebsco.com/contentitem/gcd:135672923?sid=ebsco:plink:crawler&id=ebsco:gcd:135672923 (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Lutyński, A.; Prostański, D. Zwalczanie Zagrożenia Wywoływanego Pyłem w Zakładach Przeróbki Mechanicznej Kopalń Węgla Kamiennego. Inżynieria Górnicza 2017, 3–4, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bałaga, D.; Siegmund, M. Systemy Do Redukcji Zapylenia w Zak\ladach Przeróbczych. Masz. Górnicze 2015, 33, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jedziniak, M. Malogabarytowe Urządzenie Odpylające. Masz. Górnicze 2013, 31, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Górniczy, W.U. Stan Bezpieczeństwa i Higieny Pracy w Górnictwie; State Mining Authority (Wyższy Urząd Górniczy): Katowice, Poland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ocena Stanu Bezpieczeństwa Pracy. Ratownictwa Górniczego Oraz Bezpieczeństwa Powszechnego w Związku z Działalnością Górniczo-Geologiczną w 2022 Roku; State Mining Authority (Wyższy Urząd Górniczy): Katowice, Poland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Coal Production and Consumption Statistics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Coal_production_and_consumption_statistics (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- Kabiesz, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2020; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2021; ISBN 978-83-65503-32-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kabiesz, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2019; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2020; ISBN 978-83-65503-28-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kabiesz, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2018; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2019; ISBN 978-83-65503-16-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kabiesz, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2017; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2018; ISBN 978-83-65503-. [Google Scholar]
- Kabiesz, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2016; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2017; ISBN 978-83-65503-. [Google Scholar]
- Kabiesz, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2015; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2016; ISBN 978-83-65503-. [Google Scholar]
- Kabiesz, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2012; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2013; ISBN 978-83-65503-. [Google Scholar]
- Kabiesz, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2011; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2012; ISBN 978-83-65503-. [Google Scholar]
- Kabiesz, J. Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2010; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2011; ISBN 978-83-65503-. [Google Scholar]
- Józef Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2004; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2005; ISBN 978-83-65503-.
- Józef Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2007; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2008; ISBN 978-83-65503-.
- Józef Raport Roczny o Stanie Podstawowych Zagrożeń Naturalnych i Technicznych w Górnictwie Węgla Kamiennego w Roku 2009; Główny Instytut Górnictwa: Katowice, Poland, 2010; ISBN 978-83-65503-.
- Coal Production and Consumption up in 2022—Products Eurostat News—Eurostat. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/products-eurostat-news/w/ddn-20230622-2 (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- Eurostat. Europe 2020 Indicators—Climate Change and Energy. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Europe_2020_indicators_-_climate_change_and_energy (accessed on 23 October 2017).
- Dong, X.; Yang, Z.; Guo, L.; Gao, Y. Assessment of the Explosion Accident Risk in Non-Coal Mining by Hasse Diagram Technique. Processes 2023, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J. Risk Assessment of Unsafe Acts in Coal Mine Gas Explosion Accidents Based on HFACS-GE and Bayesian Networks. Processes 2023, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Hua, Y.; Guo, L. Study on Dust Control Technology and Parameters for a Coal Washing Plant Screening Workshop Based on CFD Technology of Positive-Negative Pressure Dust Removal Systems. Powder Technol. 2024, 448, 120250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarver, E.; Keleş, Ç.; Afrouz, S.G. Particle Size and Mineralogy Distributions in Respirable Dust Samples from 25 US Underground Coal Mines. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2021, 247, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dust Fraction | Silica Content in Dust, % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <2 | 2 to 10 | 10 to 50 | >50 | |
| Inhalable (<100 µm) | 10 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Respirable (<7 µm) | - | 2 | 1 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lutyński, A.; Lutyński, M. Coal Dust and Methane as a Hazard in Coal Preparation Plants. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311433
Lutyński A, Lutyński M. Coal Dust and Methane as a Hazard in Coal Preparation Plants. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(23):11433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311433
Chicago/Turabian StyleLutyński, Aleksander, and Marcin Lutyński. 2024. "Coal Dust and Methane as a Hazard in Coal Preparation Plants" Applied Sciences 14, no. 23: 11433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311433
APA StyleLutyński, A., & Lutyński, M. (2024). Coal Dust and Methane as a Hazard in Coal Preparation Plants. Applied Sciences, 14(23), 11433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311433








