Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption in W-Type Ba-Hexaferrites: Role of Composition and Grain Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, X.; He, J.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Xue, H. Laminated magnetic graphene with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, X.; Song, C.; Han, M.; Xu, H.; Duan, W.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L. Self-Assembly Core–Shell Graphene-Bridged Hollow MXenes Spheres 3D Foam with Ultrahigh Specific EM Absorption Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Gui, X.; Yao, L.; Hu, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Mei, H.; Tang, Z. Ultrathin, Lightweight, and Flexible CNT Buckypaper Enhanced Using MXenes for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; He, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, D.; Xia, L.; Huang, X.; Zhong, B. Facile fabrication of graphene/g-C3N4 for electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Wang, L.; Dai, Y.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Deng, Z. Construction of 1D heterogeneous PPy@FeCo@PPy nanotubes with broadband and strong electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1001, 175030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Fan, T. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous carbon/Co nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 013110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Kong, L.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Travitzky, N.; Greil, P. Electromagnetic properties of Si–C–N based ceramics and composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 326–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Qin, G.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X. Constructing flake-like ternary rare earth Pr3Si2C2 ceramic on SiC whiskers to enhance electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cao, Q.; Bi, H.; Liang, C.; Yuan, K.; She, W.; Yang, Y.; Che, R. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 Microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño-Castellanos, P.; Guerrero, F.; Romaguera-Barcelay, Y.; Goveia-Alcaide, E.; Cotta, E.A.; Leyet, Y.; Anglada-Riveira, J.; Padrón-Hernández, E.; Peña-Garcia, R. Effect of La3+ cation solubility on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of barium hexaferrite. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 8236–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, F.Z.; Siddiqui, J.J.; Ali, K.; Arshad, H.; Mudsar, M.; Ijaz, A. Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of W-type nanoferrite in X and Ku band. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 2278–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Lee, T.-W.; Kang, Y.-M. Tunable and broad-band electromagnetic wave absorption using W-type Hexaferrites in 1–40 GHz range. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 962, 171060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotgering, F.K.; Vromans, P.H.G.M.; Huyberts, M.A.H. Permanent-magnet material obtained by sintering the hexagonal ferrite W = BaFe18O27. J. Appl. Phys. 1980, 51, 5913–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadizadeh, A.R.; Ebrahimi, S.A.S.; Masoudpanah, S.M. Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of ZnCo-substituted W-type strontium hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 382, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collomb, A.; Mignot, J.P. The Ba(Sr)Mn2Fe16O27 W-type Hexagonal Ferrites as Permanent Magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1987, 69, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoek, J.L. Dispersion and absorption in magnetic ferrites at frequencies above one Mc/s. Physica 1948, 14, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwell, J. Magnetic Properties of Materials; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1971; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.B.; Li, Z.W.; Liu, L.; Huang, R.; Abshinova, M.; Yang, Z.H.; Tang, C.B.; Tan, P.K.; Deng, C.R.; Matitsine, S. Recent progress in some composite materials and structures for specific electromagnetic applications. Int. Mater. Rev. 2013, 58, 203–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Xu, B.; Suo, H.; Wu, F.; Xiang, S.; Zhao, M. Microwave absorptive behavior of ZnCo- substituted W-type Ba hexaferrite nanocrystalline composite material. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 212, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, I.M.; Irfan, M.; Naheed, F.; Akhtar, M.N.; Rasool, R.T.; Ashraf, G.A.; Gulbadan, S.; Khan, M.A. Dielectric, physicochemical, and reflection loss features of Gd-substituted W-type hexaferrites for microwave absorption application. Appl. Phys. A. 2024, 130, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, X. Absorption Band Tunable La-Sr Co-Doped BaCo2-W Type Hexaferrites. Materials 2023, 16, 5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, N. Microstructure and microwave electromagnetic properties of Dy3+-doped W-type hexaferrites. Rare Met. 2011, 30, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudasar, M.; Xu, Z.H.; Lian, S.Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, X. Featuring heterogeneous composite of W-type hexagonal ferrite with 2D vanadium carbide MXene for wideband microwave absorption. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 2699–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Chen, L.F.; Ong, C.K. High-frequency magnetic properties of W-type barium-ferrite BaZn2−xCoxFe16O27 composites. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 5918–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Suetake, K. Application of Ferrite to Electromagnetic Wave Absorber and Its Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1971, 19, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-E.; Kang, Y.-M. Electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of Ni-Zn ferrite powder–epoxy composites in GHz range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 513, 167075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gao, Y.; Tan, G.; Man, Q.; Wang, Z. Comparative study of microwave absorption properties of Ni–Zn ferrites obtained from different synthesis technologies. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 22896–22905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Han, Q.; Wei, S.; Liu, K.; He, X.; Sun, R.; et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Mn0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 powders synthesized by high-temperature mechanochemical method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 2024, 302, 117243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-K.; Yu, P.-Y.; Kang, Y.-M. Electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of SrFe12−2xCoxTixO19 hexaferrite–CNT–epoxy composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 537, 168235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-U.; Kang, Y.-M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Properties of M12+–M24+ Substituted M-Type Sr-Hexaferrites. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.J.; Choi, J.R.; Lee, S.-B.; Lee, J.I.; Lee, H. Frequency tunable Ni–Ti-substituted Ba–M hexaferrite for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption in 8.2–75 GHz range. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 976, 173019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; You, J.-H.; Bon, C.Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Yoo, S.-I. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Zn-substituted SrW-type hexaferrite composites in the Ku-band. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 7571–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.-H.; You, J.-Y.; Kang, Y.-M. Synthesis, characterization, and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Sr3Co2Fe24O41 hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 550, 169051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Yang, R.-B.; Jeong, W.H.; Manh, D.H.; Phan, T.-L.; Lee, B.W. Enhanced microwave absorption features of Ba3Co2Fe24O41 hexaferrite by high lanthanium doping concentration. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 105, 4122–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dubey, D.P.; Shannigrahi, S.; Chatterjee, R. Complex permittivity, permeability, magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of Ni2+ substituted mechanically milled U-type hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 774, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Zhang, K.; Gong, L.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, J. Electromagnetic wave absorption enhancement of double-layer structural absorbers based on carbon nanofibers and hollow Co2Y hexaferrite microfibers. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 814, 152302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ji, Y.; Mu, C.; Huo, Y.; Xiang, J.; Nie, A.; Xue, T.; Zhai, K.; Liu, Z.; Wen, F. Well-controlled Core-shell structures based on Fe3O4 nanospheres coated by polyaniline for highly efficient microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 591, 153176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhong, S.; Yu, M.; Wang, C. A simple method for preparing flaky FeSiAl for low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 574, 170676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
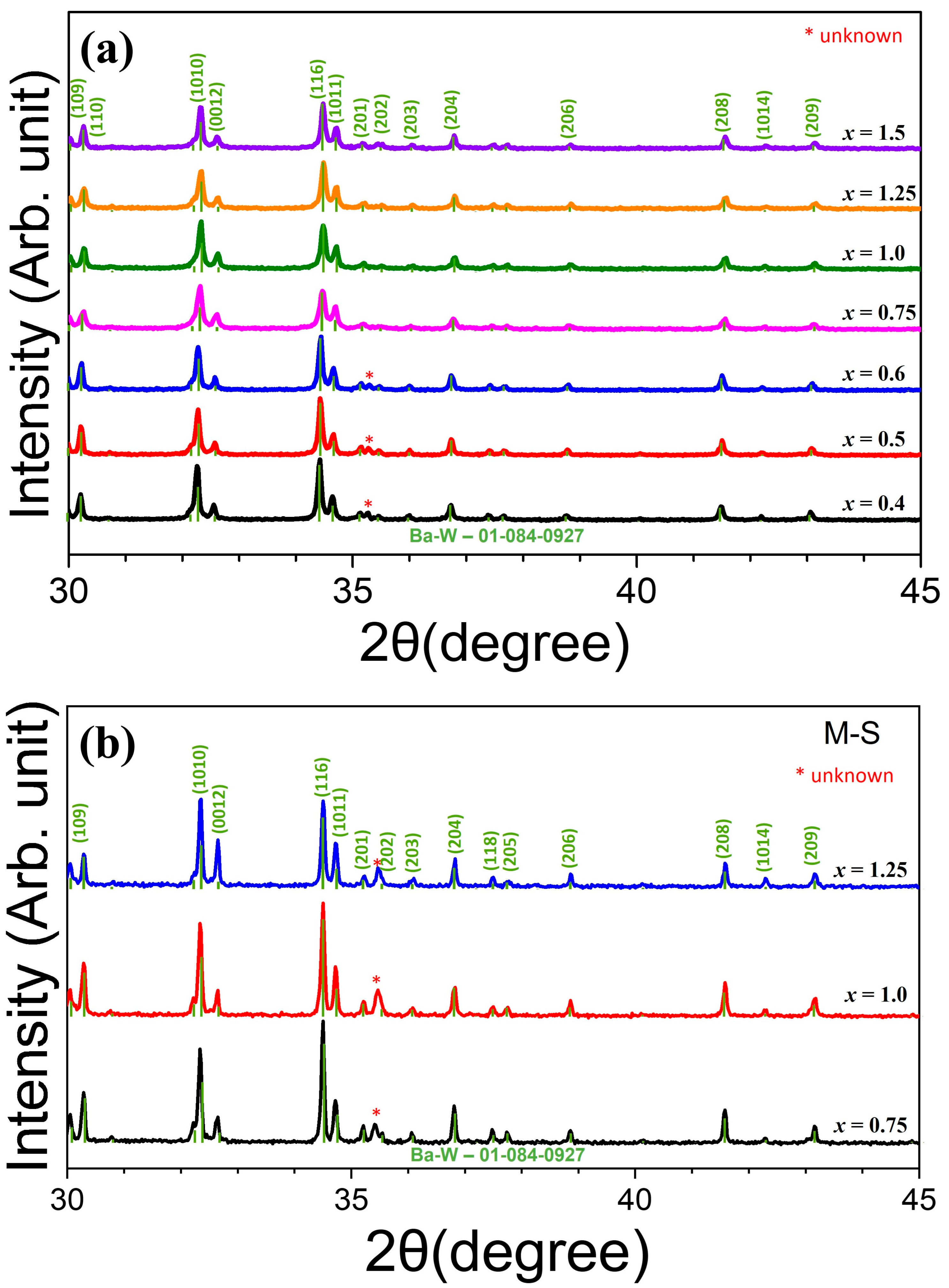
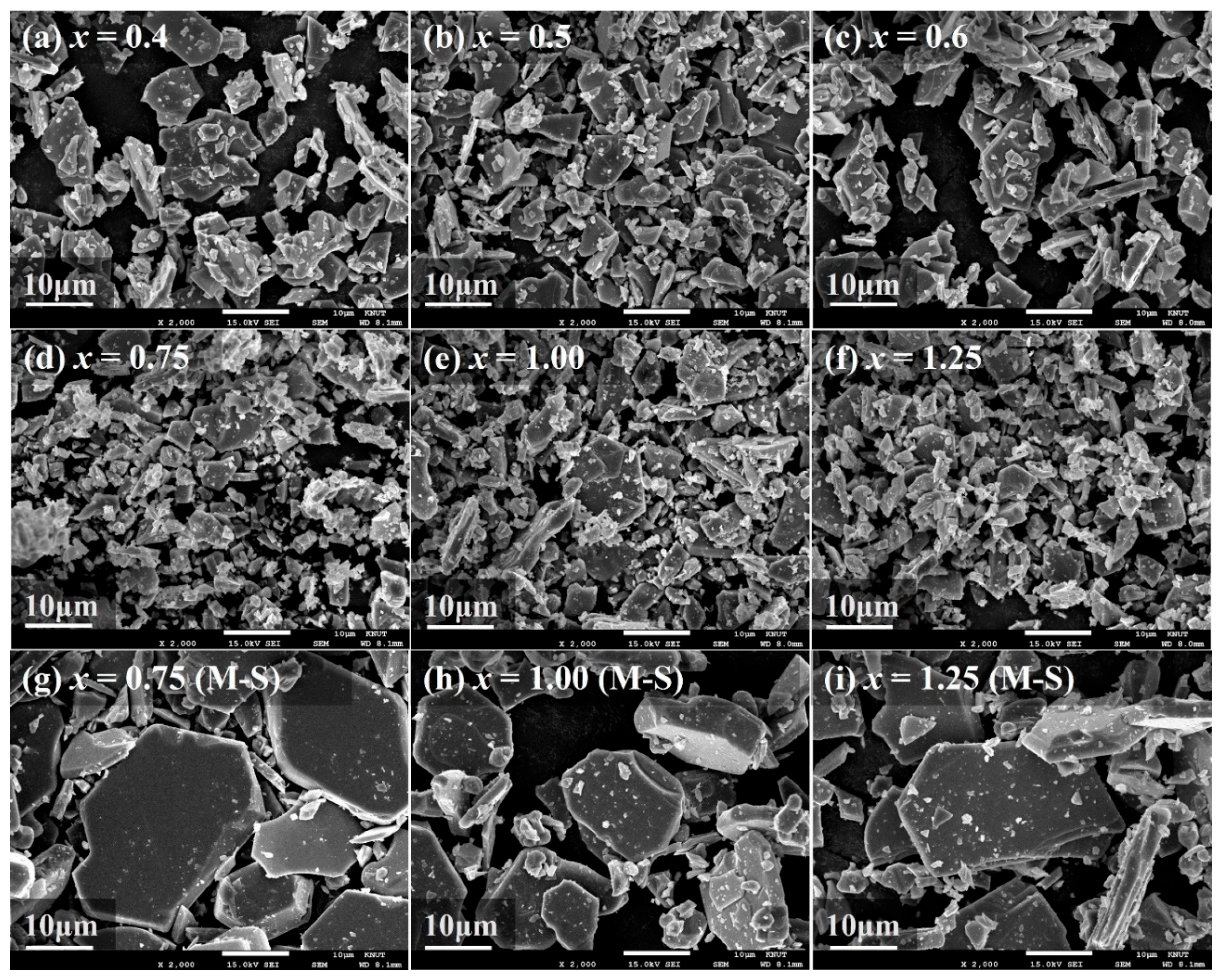
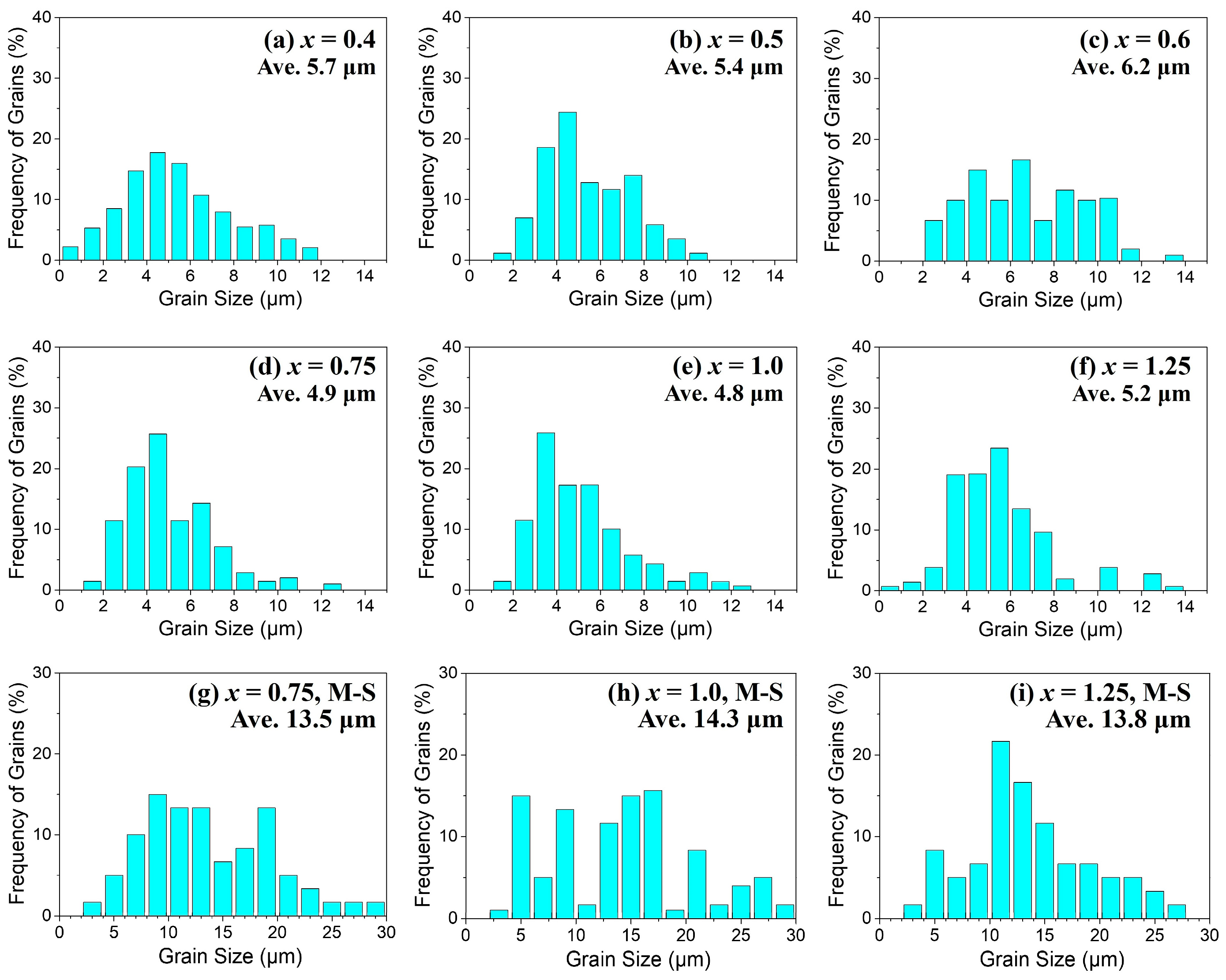
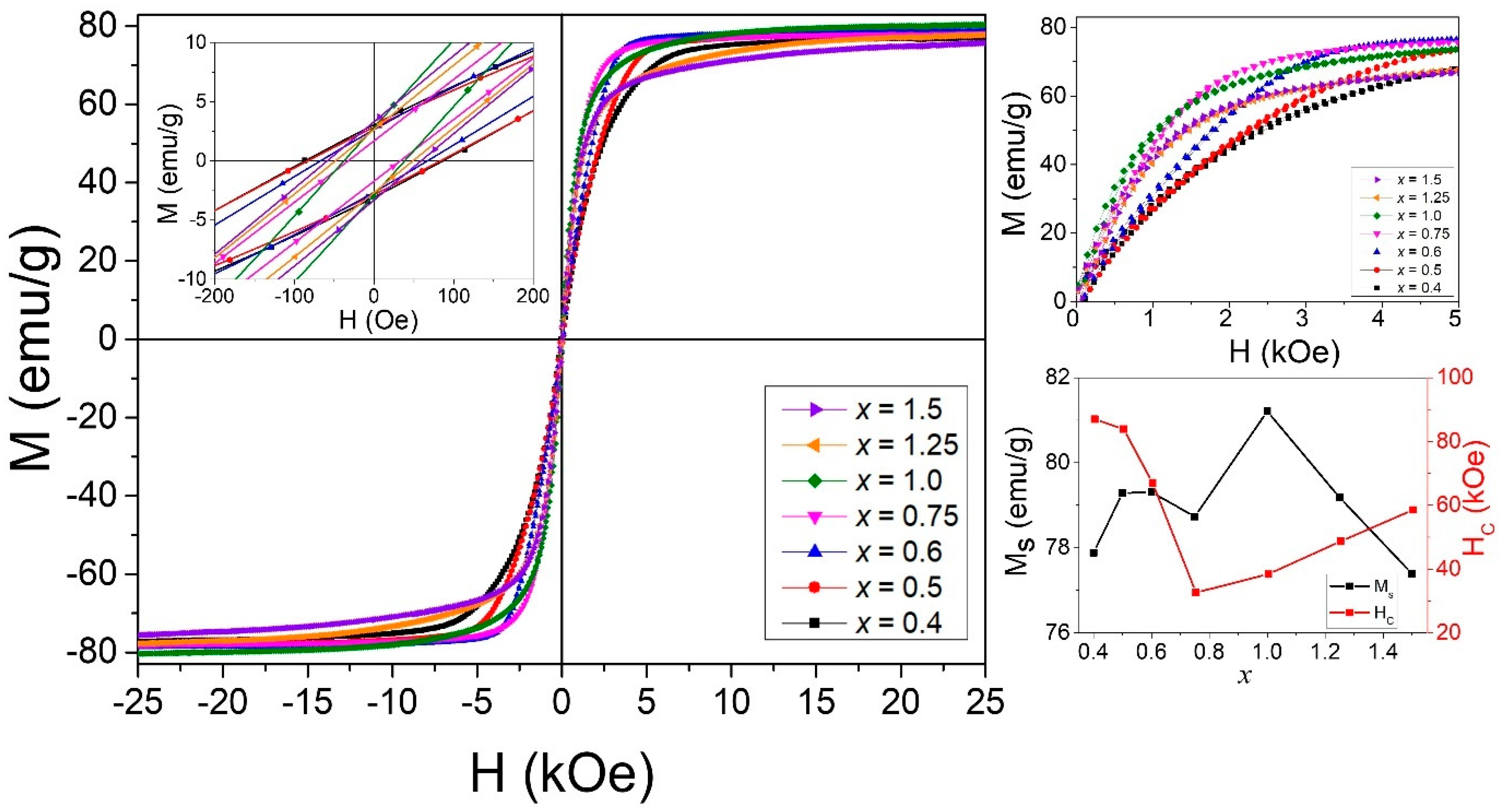
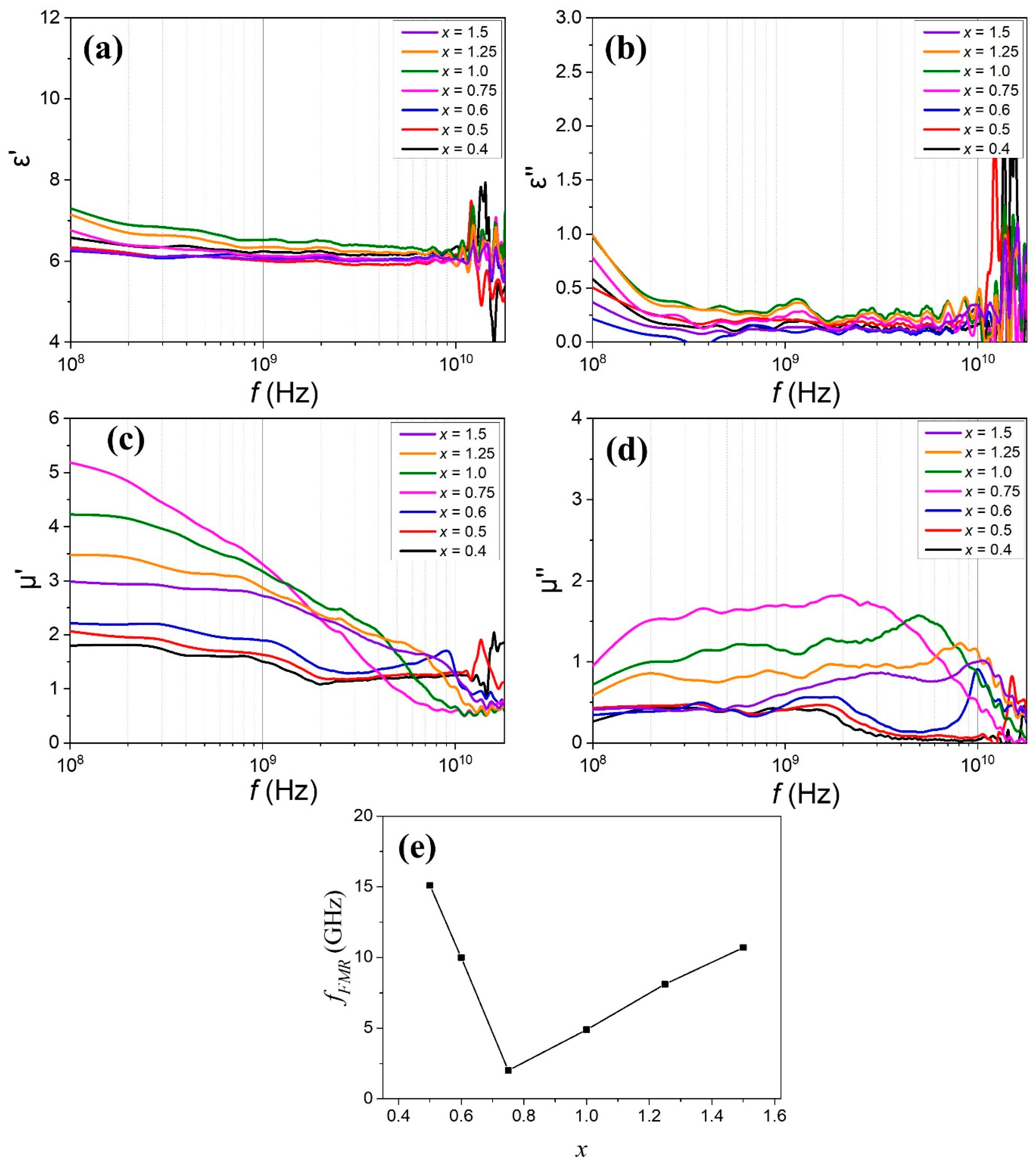
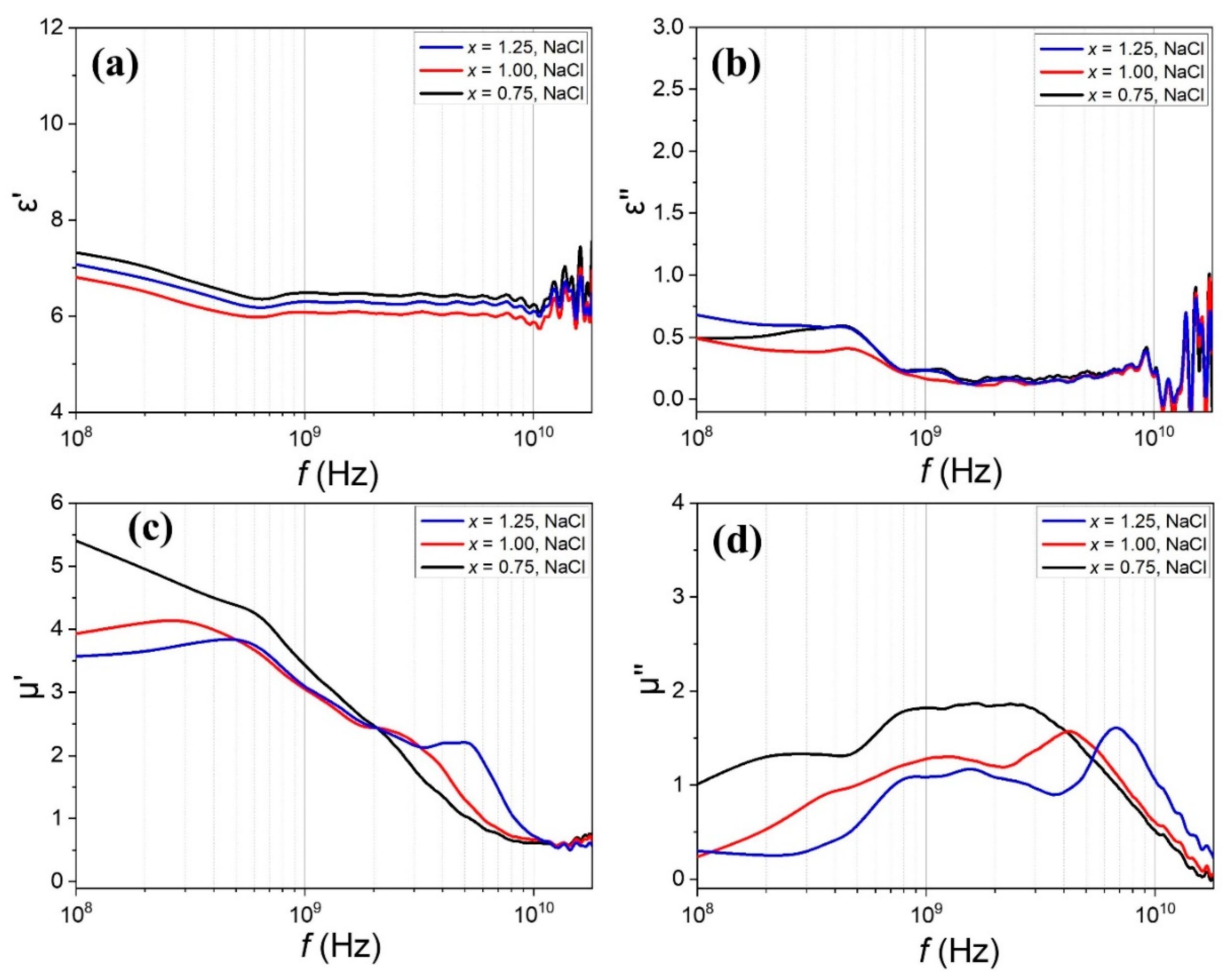
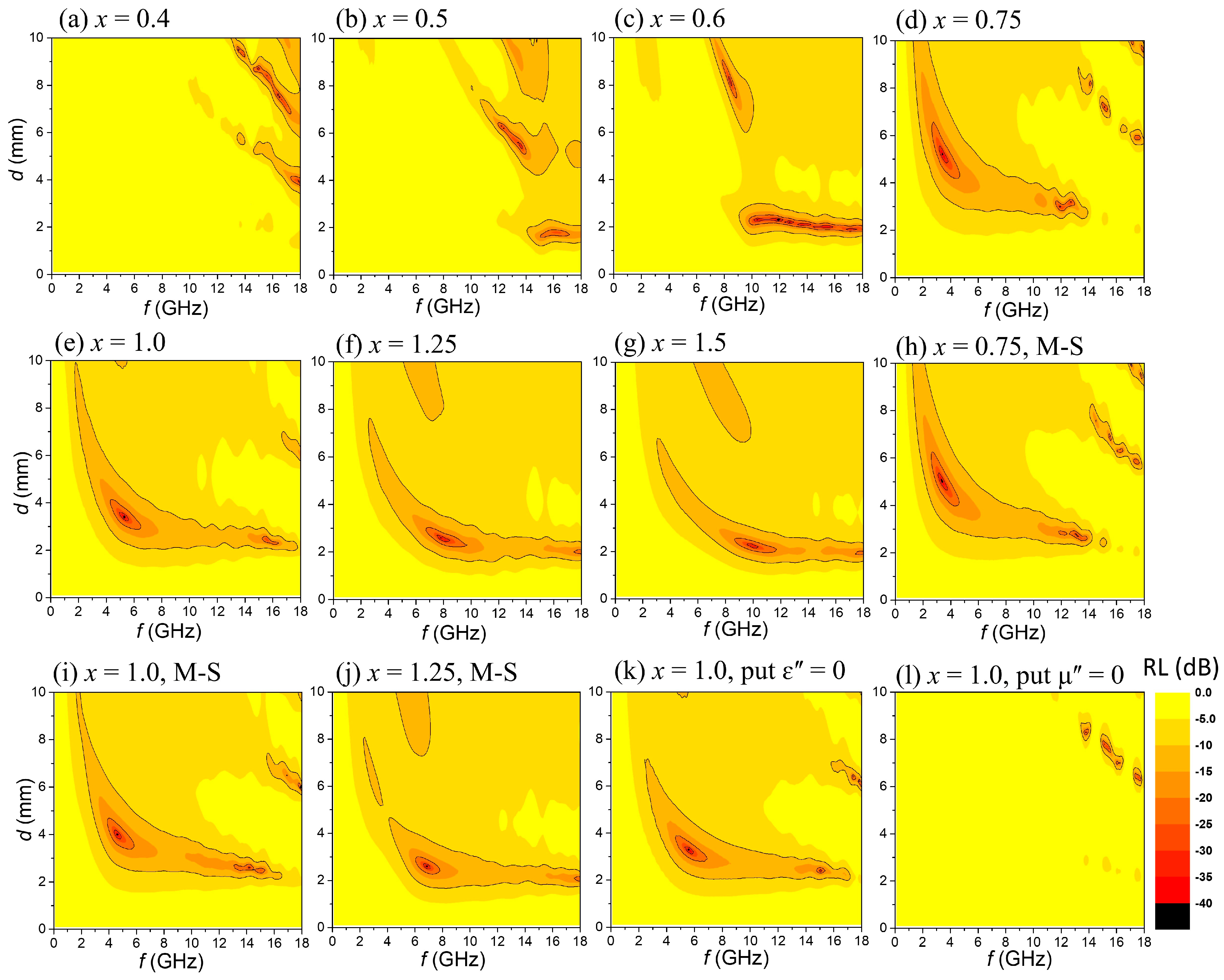
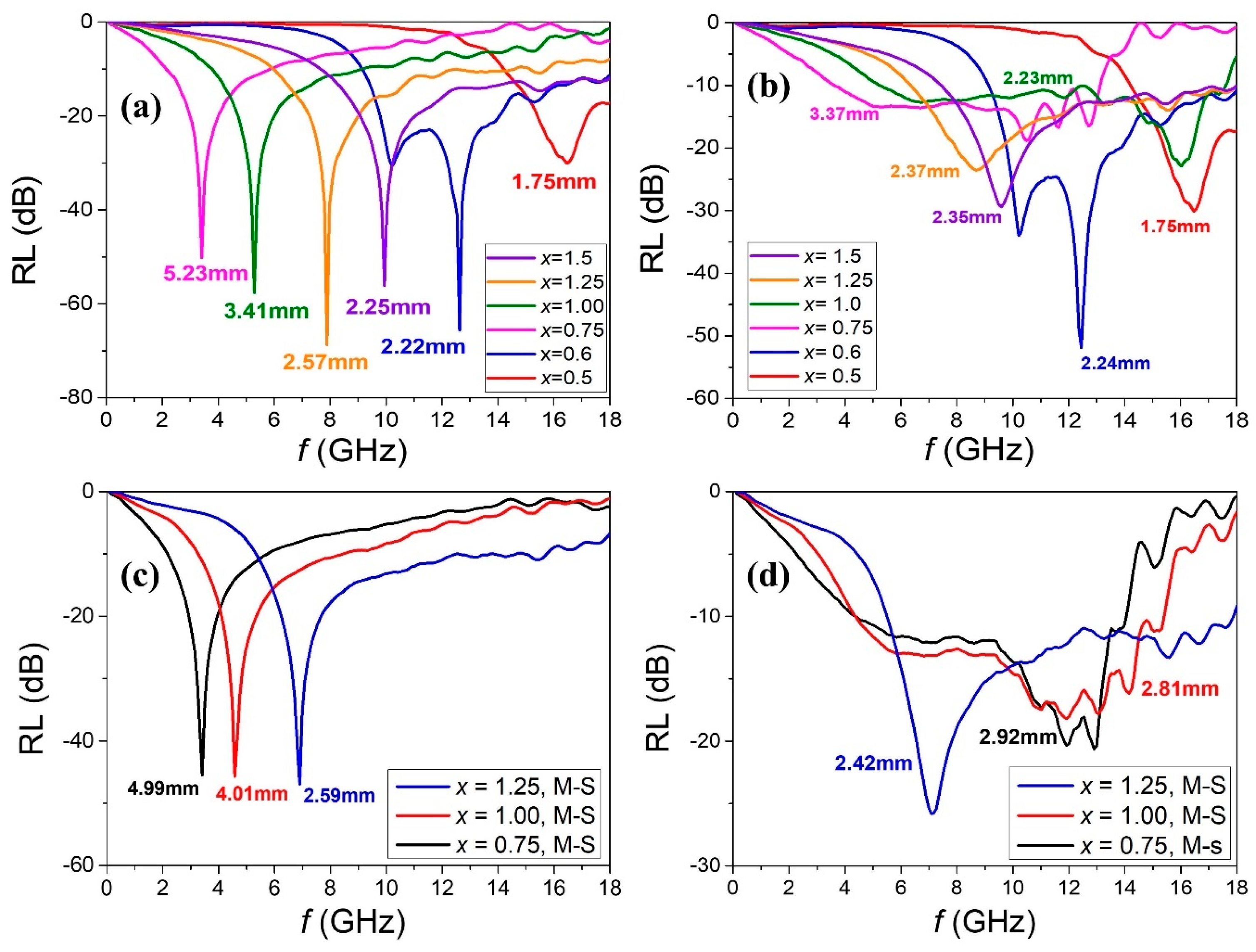
| Composition | x | a (Å) | c (Å) | Vol. (Å3) | MS (emu/g) | HC (Oe) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaZn2−xCoxW (non M-S) | 0.4 | 5.913 | 32.97 | 998.3 | 77.08 | 86.98 |
| 0.5 | 5.910 | 32.98 | 997.5 | 78.44 | 83.89 | |
| 0.6 | 5.910 | 32.96 | 997.1 | 78.77 | 67.01 | |
| 0.75 | 5.904 | 32.94 | 994.3 | 78.06 | 32.64 | |
| 1.00 | 5.903 | 32.90 | 993.5 | 80.34 | 38.42 | |
| 1.25 | 5.902 | 32.92 | 993.1 | 77.77 | 48.69 | |
| 1.50 | 5.902 | 32.91 | 992.8 | 75.64 | 58.56 | |
| BaZn2−xCoxW (M-S) | 0.75 | 5.898 | 32.91 | 991.3 | - | - |
| 1.00 | 5.987 | 32.91 | 991.2 | - | - | |
| 1.25 | 5.898 | 32.89 | 990.9 | - | - |
| Composition | x | fFMR (GHz) | fRLmin (GHz) | RLmin (dB) | dRLmin (mm) | Δfwb (GHz) | dwb (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaZn2−xCoxW | 0.4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 0.5 | 15.1 | 16.5 | −30.9 | 1.75 | >3.82 14.18–18(+) | 1.75 | |
| 0.6 | 9.99 | 12.6 | −65.7 | 2.22 | >8.92 9.08–18(+) | 2.24 | |
| 0.75 | 2.01 | 3.41 | −50.3 | 5.23 | 9.58 3.59–13.17 | 3.37 | |
| 1.0 | 4.89 | 5.29 | −57.8 | 3.41 | 12.52 5.12–17.64 | 2.33 | |
| 1.25 | 8.11 | 7.89 | −69.0 | 2.57 | >11.68 6.32–18(+) | 2.37 | |
| 1.5 | 10.7 | 9.94 | −56.2 | 2.25 | >10.54 7.46–18(+) | 2.35 | |
| BaZn2−xCoxW (M-S) | 0.75 | 1.87 | 3.42 | −46.1 | 4.99 | 9.77 4.32–14.09 | 2.92 |
| 1.0 | 4.13 | 4.61 | −46.5 | 4.01 | 11.09 4.36–15.45 | 2.81 | |
| 1.25 | 6.75 | 2.59 | −47.7 | 2.59 | 12.37 5.48–17.85 | 2.42 |
| Materials | fFMR (GHz) | dRLmin (mm) | RLmin (dB) | fRLmin (GHz) | f-Range (RL < −10 dB) | Δf (GHz) | Ref. # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-ZnFe2O4 | 1.45 | 5.6 | −63 | 2.9 | 2.5–3.5 | 1.0 | [26] |
| 1.45 | 3.1 | −37 | 12.6 | 4.0–13.0 | 9.0 | [26] | |
| - | 3.7 | −42 | - | 2.9–11.9 | 9.0 | [27] | |
| Mn-ZnFe2O4 | - | 4.3 | −44 | 6.2 | 4.6–7.5 | 2.9 | [28] |
| - | 7.6 | −21 | 3.8 | 2.3–5.3 | 3.0 | [28] | |
| Co-Ti SrM | 6.4 | 3.1 | −42 | 6.4 | 5.1–9.1 | 4.0 | [29] |
| 8.2 | 2.7 | −40 | 8.5 | 6.7–13.3 | 6.6 | [29] | |
| 15.0 | 1.5 | −30 | 13.5 | 11.8–18.0(+) | 6.2+ | [29] | |
| Zn-Zr SrM | 8.3 | 2.7 | −45 | 8.8 | 7.5–14.7 | 7.2 | [30] |
| 10.8 | 2.0 | −39 | 11.8 | 10.2–18.0(+) | 7.8+ | [30] | |
| Ni-Ti BaM | - | 0.9 | −52 | 29.5 | 34.8–44.9 | 10.1 | [31] |
| SrZn2W | - | 1.9 | −66 | 11.3 | 9.7–13.4 | 3.7 | [32] |
| Sr0.75Ca0.25Zn2−xCoxW | 8.2 | 2.6 | −38 | 7.6 | 7.1–18.0(+) | 10.9 | [12] |
| Sr3Co2Z | 2.9 | 4.7 | −51 | 3.1 | 2.2–7.8 | 8.7 | [33] |
| Ba3−xLaxCo2Z | - | 3.5 | −47 | 3.5 | 3.7–13.7 | 10.0 | [34] |
| (Ba0.7Bi0.2)4(Co1−xNix)2U | 10.1 | 1.9 | −39 | 11.0 | - | 6.3 | [35] |
| 13.2 | 1.9 | −44 | 11.3 | - | 8.6 | [35] | |
| Co2Y | - | 3.0 | −15 | 11.3 | 10.2–17.3 | 7.1 | [36] |
| Carbon nanofiber | - | 1.3 | −22 | 17.5 | 9.8–18(+) | 8.2+ | [36] |
| Fe3O4@PANI | - | 1.6 | −56 | 17.3 | 12.6–18 | 5.4 | [37] |
| FeSiAl | - | 2.7 | −21 | - | 9.0–14.2 | 5.2 | [38] |
| BaZn0.75Co1.25W | 8.1 | 2.6 | −69 | 7.89 | 6.32–18(+) | 11.7 | this work |
| BaZn1.0Co1.0W | 4.89 | 4.89 | −58 | 5.29 | 5.12–17.64 | 12.5 | this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, J.-H.; Kang, Y.-M. Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption in W-Type Ba-Hexaferrites: Role of Composition and Grain Growth. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210631
Heo J-H, Kang Y-M. Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption in W-Type Ba-Hexaferrites: Role of Composition and Grain Growth. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(22):10631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210631
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Jae-Hee, and Young-Min Kang. 2024. "Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption in W-Type Ba-Hexaferrites: Role of Composition and Grain Growth" Applied Sciences 14, no. 22: 10631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210631
APA StyleHeo, J.-H., & Kang, Y.-M. (2024). Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption in W-Type Ba-Hexaferrites: Role of Composition and Grain Growth. Applied Sciences, 14(22), 10631. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210631







