Statistical Properties of SIS Processes with Heterogeneous Nodal Recovery Rates in Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
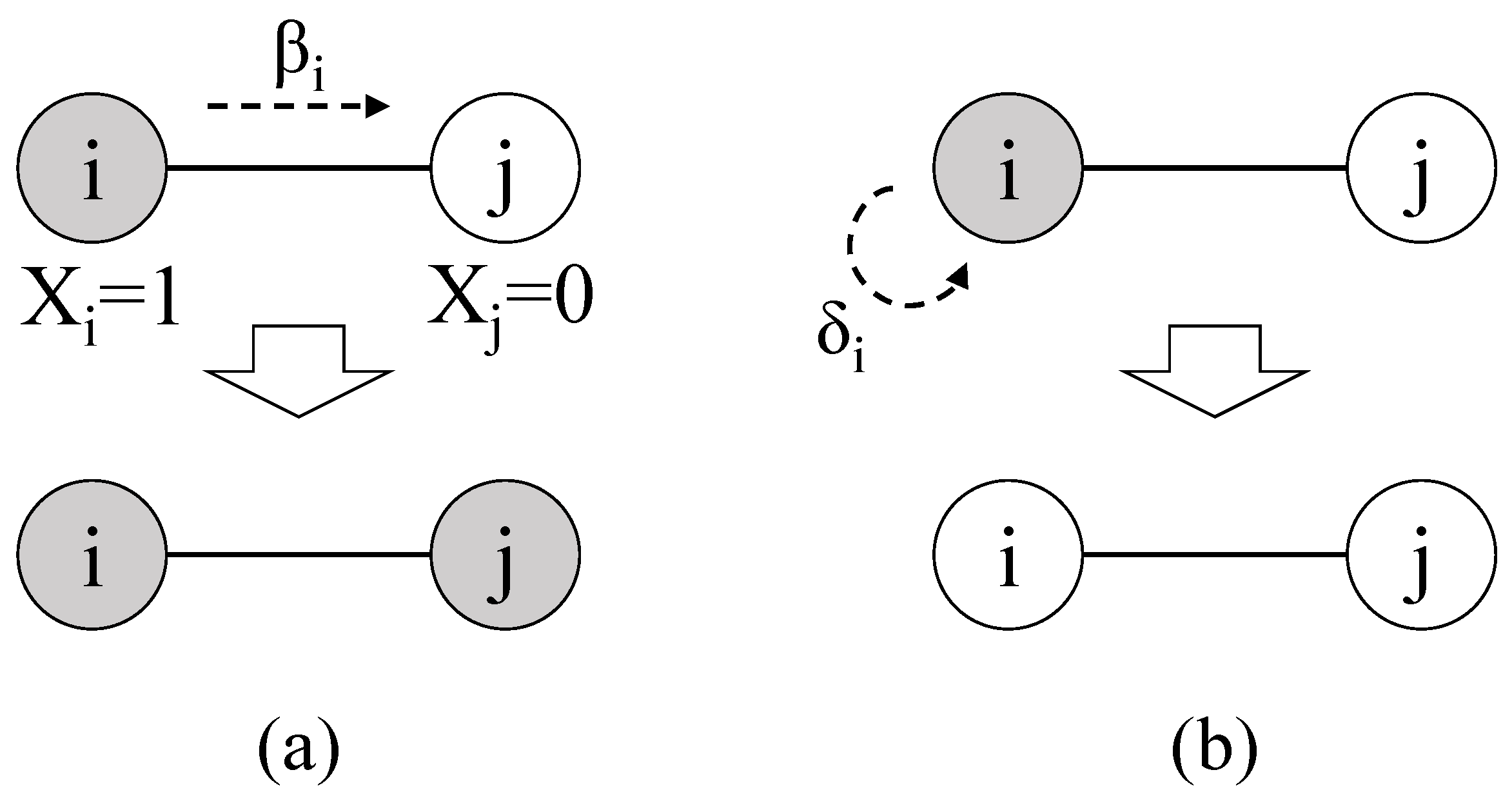
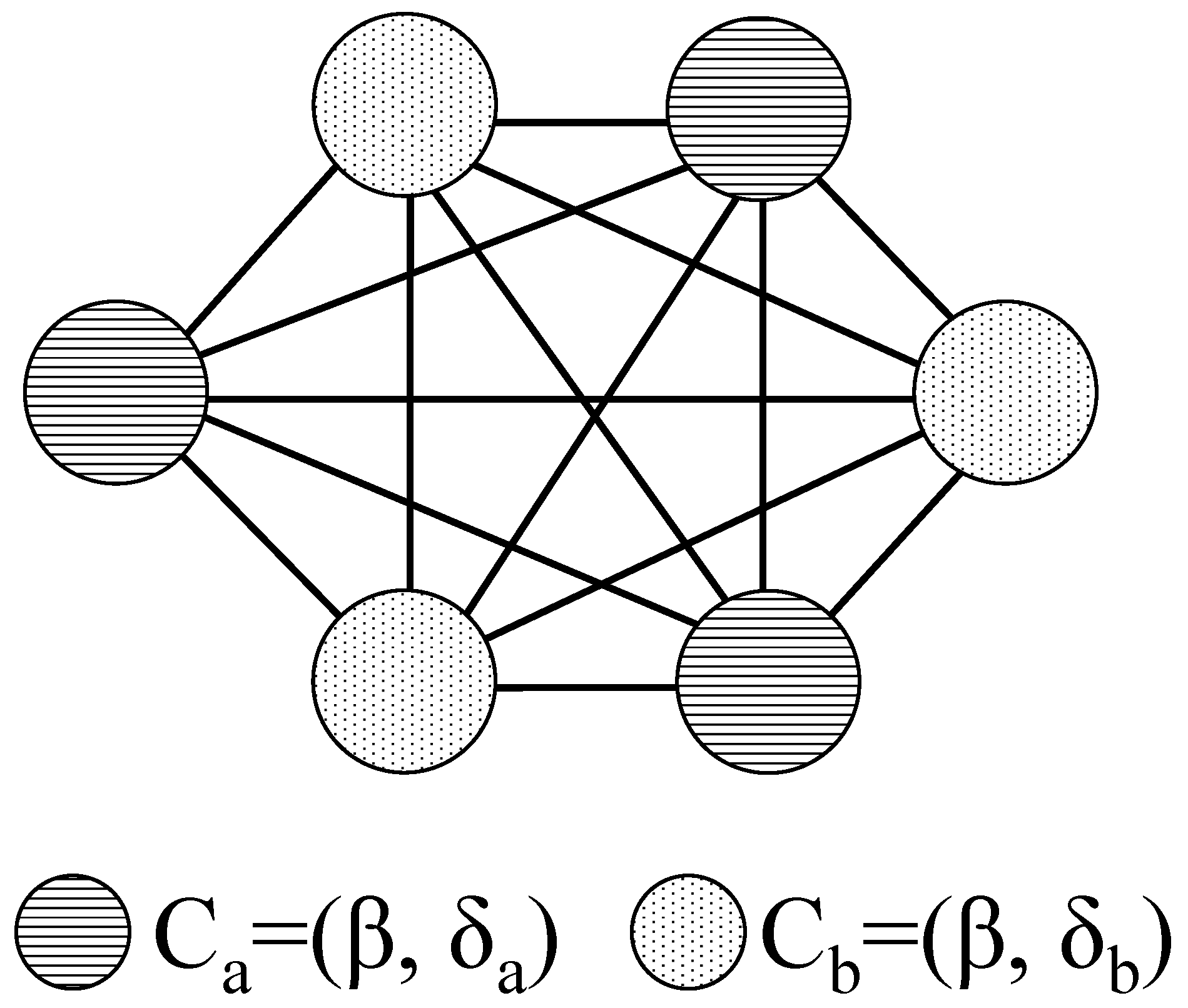
3.1. Notation and Model
3.2. Mean Value and Variance of Steady-State Infection Fraction
3.3. Bounds on Steady-State Infection
3.4. Simulation Method
4. Results
4.1. Time Evolution and Steady State
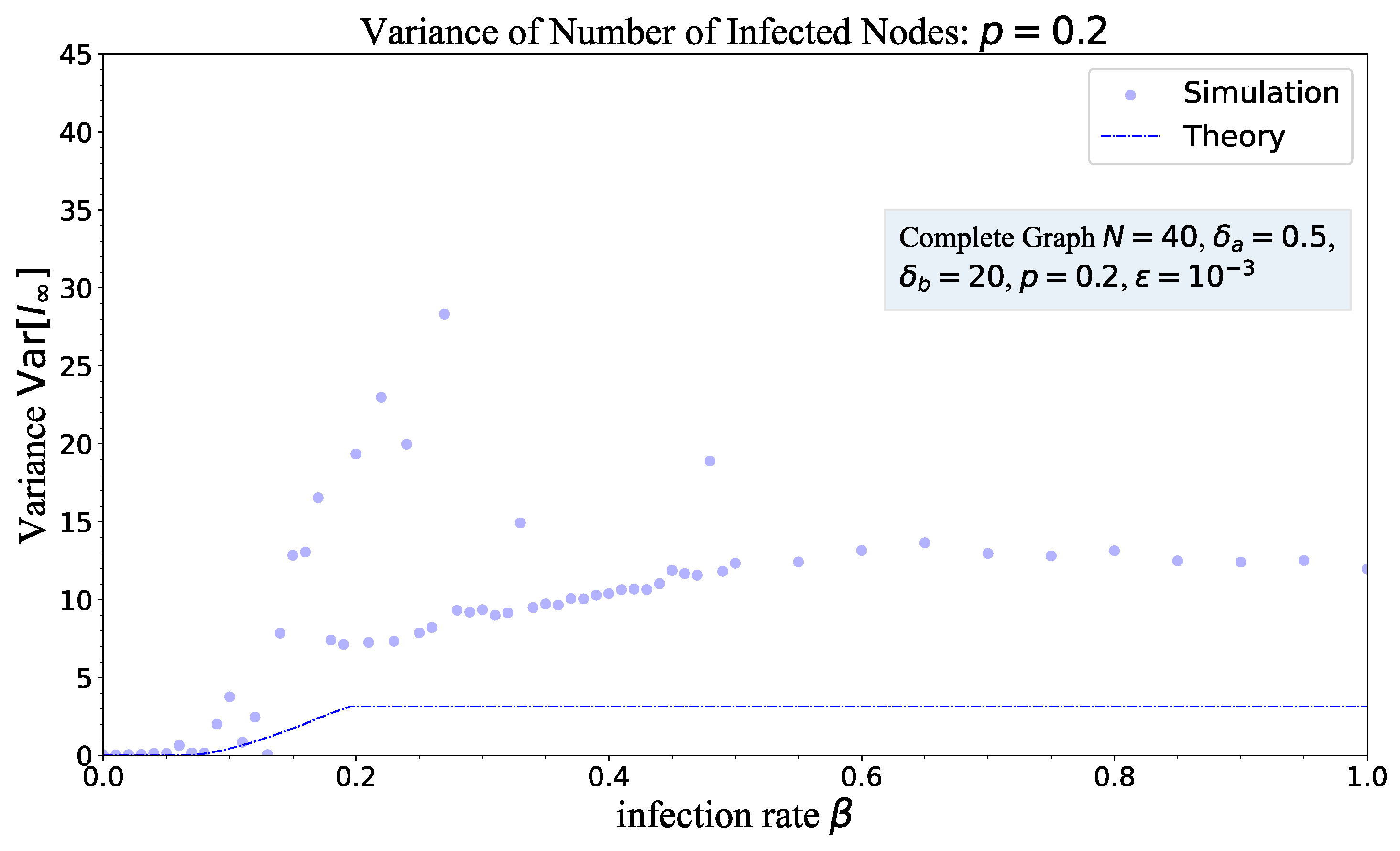
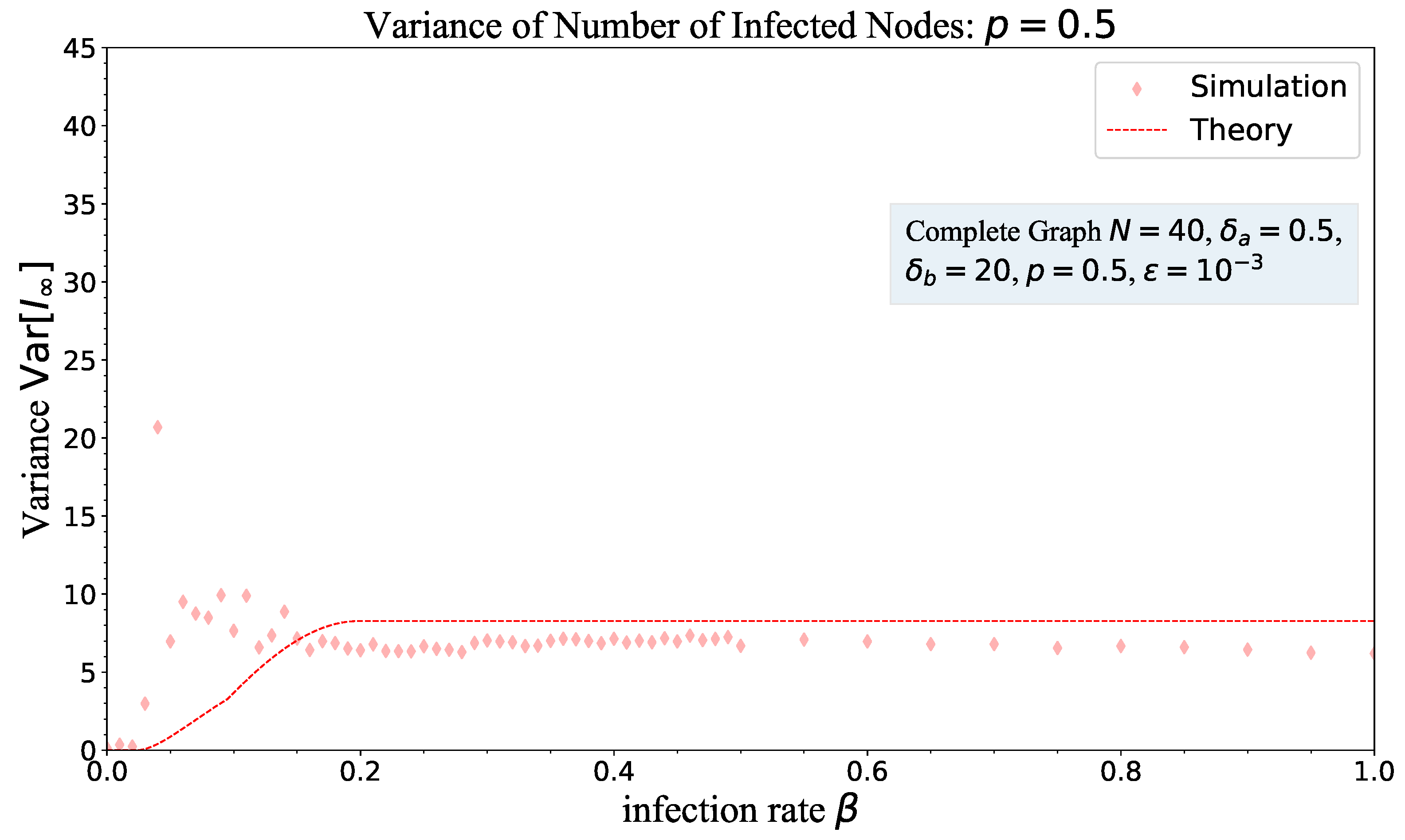
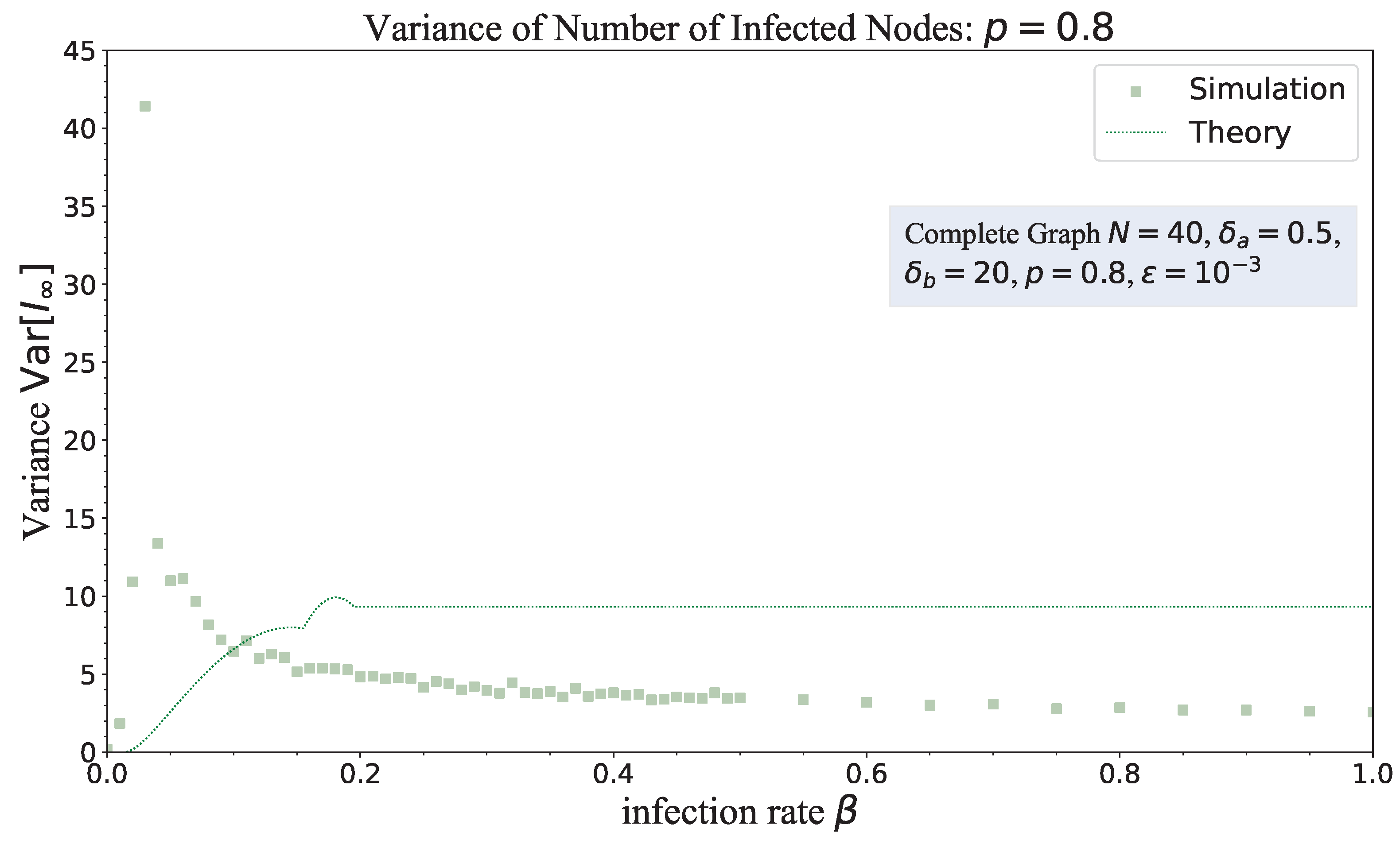
4.2. Variance of Steady-State Infection Fraction
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SIS | Susceptible–infected–susceptible |
| NIMFA | N-intertwined mean-field approximation |
| HNIMFA | Heterogeneous N-intertwined mean-field approximation |
| NDN | Named data networking |
Appendix A. Proof of Lemma 1
Appendix B. Proof of Lemma 2
Appendix C. Proof of Lemma 3
References
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic dynamics and endemic states in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 63, 066117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Castellano, C.; Van Mieghem, P.; Vespignani, A. Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 925–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianconi, G. Multilayer Networks: Structure and Function; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Arruda, G.F.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Moreno, Y. Fundamentals of spreading processes in single and multilayer complex networks. Phys. Rep. 2018, 756, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, S.; Perc, M.; Ghosh, D. Dynamics on higher-order networks: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Arruda, G.F.; Aleta, A.; Moreno, Y. Contagion dynamics on higher-order networks. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2024, 6, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomovski, I.; Basnarkov, L.; Abazi, A. Discrete-Time Non-Markovian SEIS Model on Complex Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnarkov, L.; Tomovski, I.; Sandev, T.; Kocarev, L. Non-Markovian SIR epidemic spreading model of COVID-19. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 160, 112286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Lin, Z.; Yin, Q.; Tang, M.; Guan, S.; Boguñá, M. Non-Markovian epidemic spreading on temporal networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 173, 113664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.A.; Tapper, A.; Simon, P.L.; Mann, R.P. Micro-scale foundation with error quantification for the approximation of dynamics on networks. Commun. Phys. 2022, 5, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.H.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Ferreira, S.C. Accuracy of discrete- and continuous-time mean-field theories for epidemic processes on complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2024, 110, 014302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Message passing methods on complex networks. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2023, 479, 20220774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, E.; Machado, D.; Lage-Castellanos, A. Dynamics of epidemics from cavity master equations: Susceptible-infectious-susceptible models. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 105, 024308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cator, E.; Van Mieghem, P. Susceptible-infected-susceptible epidemics on the complete graph and the star graph: Exact analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 012811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Guo, D.; Quan, W. Analyzing NDN NACK on Interest Flooding Attack via SIS Epidemic Model. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 1862–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mieghem, P.; Omic, J.; Kooij, R. Virus Spread in Networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2009, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Leskovec, J.; Faloutsos, C. Epidemic thresholds in real networks. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2008, 10, 1:1–1:26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omic, J.; Van Mieghem, P. Epidemic Spreading in Networks–Variance of the Number of Infected Nodes; Technical Report report20090707; Quantum and Computer Engineering Department, Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Van Mieghem, P.; Omic, J. In-homogeneous Virus Spread in Networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1306.2588. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, L.; Yin, H.; Guo, D.; Lyu, Y. Heterogeneous Malware Spread Process in Star Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems Workshops (ICDCSW), Atlanta, GA, USA, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Liu, F.; Jardón-Kojakhmetov, H.; Cao, M. Discrete-time layered-network epidemics model with time-varying transition rates and multiple resources. Automatica 2024, 159, 111303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliara, R.; Leonard, N.E. Adaptive Susceptibility and Heterogeneity in Contagion Models on Networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2021, 66, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Feng, M. Impact of time-dependent infection rate and self-isolation awareness on networked epidemic propagation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 15653–15669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Liu, G.; Jin, Z. Stochastic dynamics of an SIS epidemic on networks. J. Math. Biol. 2022, 84, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Jiao, L.; Jiao, J.; Meng, K. Variance of the Infection Number of Heterogeneous Malware Spread in Network. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mieghem, P. Performance Analysis of Communications Networks and Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Mieghem, P.; Cator, E. Epidemics in networks with nodal self-infection and the epidemic threshold. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 016116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; van de Bovenkamp, R.; Van Mieghem, P. Susceptible-infected-susceptible model: A comparison of N-intertwined and heterogeneous mean-field approximations. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 026116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cator, E.; Van Mieghem, P. Second-order mean-field susceptible-infected-susceptible epidemic threshold. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 056111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, X.F.; Guo, D. High-Order Mean-Field Approximations for Adaptive Susceptible-Infected-Susceptible Model in Finite-Size Networks. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6637761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, D.; Jiao, L.; Feng, W. Statistical Properties of SIS Processes with Heterogeneous Nodal Recovery Rates in Networks. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219987
Guo D, Jiao L, Feng W. Statistical Properties of SIS Processes with Heterogeneous Nodal Recovery Rates in Networks. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(21):9987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219987
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Dongchao, Libo Jiao, and Wendi Feng. 2024. "Statistical Properties of SIS Processes with Heterogeneous Nodal Recovery Rates in Networks" Applied Sciences 14, no. 21: 9987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219987
APA StyleGuo, D., Jiao, L., & Feng, W. (2024). Statistical Properties of SIS Processes with Heterogeneous Nodal Recovery Rates in Networks. Applied Sciences, 14(21), 9987. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14219987





