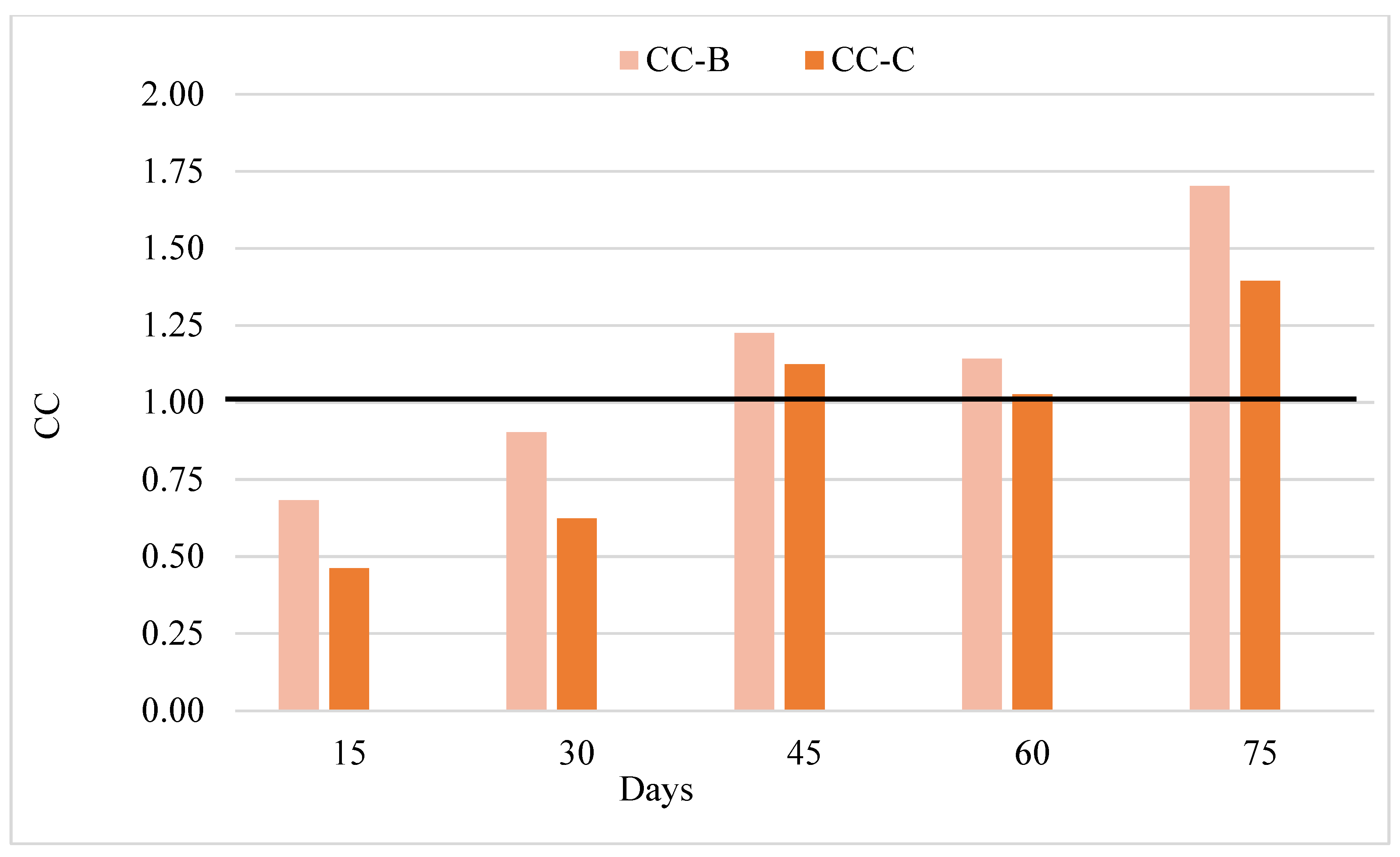Abstract
The use of Mediterranean euryhaline fish and halophytes in aquaponics presents a sustainable and alternative approach to food production. The present study investigates the effect of compensatory growth on sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and Baltic prawn (Palaemon adspersus) co-cultivated with the halophytic glasswort (Salicornia europaea). Three autonomous systems were established, each containing forty-five sea bass, nine Baltic prawns, and eight glasswort plants, with different feeding regimes for each treatment: (i) daily feeding (treatment A), (ii) three days of feeding per week followed by four days of fasting (treatment B), and (iii) feeding for seven days followed by seven days of fasting (treatment C). The growth performance of the fish was significantly higher in treatment B. Conversely, the feed conversion ratio (FCR) was notably higher in treatment A. As for the prawns, their final body weight and length were similar across all treatments. The glasswort plants also demonstrated significantly improved growth in treatment B. These results indicate that the incorporation of feeding and fasting cycles can be an effective feed management strategy for polyculture aquaponic systems. Additionally, food deprivation had a positive impact on the growth performance of both glasswort and prawns.
1. Introduction
Aquaponics represents a unified system that integrates hydroponic cultivation with recirculating aquaculture [1]. This integration offers several advantages, including shared initial setup, operational, and infrastructure costs. It also facilitates the removal of waste nutrients and water from the recirculating tanks through the plants, thereby conserving water and reducing environmental waste discharge. Additionally, it enhances profitability by allowing for the simultaneous production of two or more marketable crops [2]. The plants are fed with the excrement or waste of the aquatic animals, thereby assisting in the purification of the water that returns to the fish [3]. This technology is emerging as a promising approach for sustainable organic crop production and a highly efficient method for optimizing water utilization and addressing the challenge of limited arable land [4]. In aquaponics using brackish water, halophytes (glasswort, rock samphire etc.) play a significant role [5]. Similarly, euryhaline fish species native to the Mediterranean, such as sea bream (Sparus aurata, Linnaeus, 1758) or sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, Linnaeus, 1758), can be utilized [6,7].
So far, aquaponics systems are usually used for freshwater cultivation, but they can also be designed for marine fish or prawn species [8,9]. In this case, the use of euryhaline species is proposed, as they can adapt to a wide range of salinities [10], allowing the cultivation of a greater number of plants that would otherwise be limited [11]. In this respect, salt-tolerant halophytes are promising candidates for saltwater aquaponics [10]. Glasswort (Salicornia europaea, Linnaeus 1753) is a succulent, annual, halophytic plant that exhibits a cylindrical growth pattern with regular branching [12]. The plant is devoid of leaves; the internodes comprise a photosynthetic outer cortex encasing a central pith. At the conclusion of the growing season, each green internode produces six flowers in two cyme clusters of three each, with each flower setting one seed [13].
The Baltic prawn (Palaemon adspersus, Rathke, 1837) is a species that is widely distributed in protected brackish waters. It can be found in bays, lagoons, and estuaries in the eastern Atlantic, Baltic, Mediterranean, Black Sea, Caspian, and Aral Sea, as well as in Atlantic Canada [14]. Baltic prawns are utilized as live food for aquaculture [15], though they are predominantly employed as live bait for commercial, artisanal, and sport fisheries [16]. The commercial cultivation of these shrimp could classify them as one of the most promising species for Greek aquaculture.
World aquaculture production reached a new record of 130.9 million tons in 2022, with Europe contributing 3.53 million tons [17]. Sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, Linnaeus, 1758) is the most important fish species farmed in the Mediterranean. In Greece, the production of sea bass in 2021 was 54,000 tons [18]. Sea bass are optimal for brackish water aquaponics as they are euryhaline species and can tolerate a wide range of salinities [5,7,19].
Compensatory growth is an innovative method of reducing the cost of feed and maintaining the growth of farmed organisms [20]. In rearing experiments using the compensation growth technique, greater growth has been observed in fish that were deprived of food compared to fish that were fed daily [21]. With total or partial food deprivation, excessive lipid accumulation by fish is reduced [22]. This leads to increased growth rates and the optimization of food consumption by organisms [23,24].
This work is significant in that it demonstrates the beneficial impact of growth compensation on the cultivation of two or more organisms in closed aquaponics systems. This approach is being employed for the first time with this specific combination of organisms and for the second time in an aquaponic system (Mitsopoulos et al., 2024). According to the international literature, it has been utilized in RAS but not in aquaponics systems.
The objective of the present study is threefold. Firstly, to identify a method of simultaneous cultivation that has a reduced environmental impact, reduced usage of water resources, and a minimal requirement for additional feed, in order to optimize the growth of farmed organisms. Secondly, to determine whether this method can optimize the growth of farmed organisms of animal and plant origin. Thirdly, to assess the environmental impact and resource usage associated with this method of cultivation.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the impact of fasting and refeeding on the growth performance of sea bass (D. labrax) and Baltic prawn (P. adspersus) in a brackish water polyculture aquaponics system co-cultivated with glasswort (S. europaea). This study investigates whether the compensatory growth of the fish affects the performance of glasswort in a polyculture aquaponics system.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design—Animal and Plant Procurement
The present study was conducted in the Aquaculture Laboratory of the Department of Aquaculture, Faculty of Agricultural Sciences, University of Thessaly, Greece. All experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines set forth in the EU Directive 2010/63/EU on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. This research was carried out by scientists holding qualifications at levels A–D, as defined by the Federation of European Laboratory Animal Science Associations (FELASA). The experimental protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Region of Thessaly, Directorate of Veterinary Medicine, Department of Animal Welfare-Pharmaceuticals-Veterinary Applications (approval number 112841/23-03-2022). The experiment was conducted at the registered experimental facility (EL-43 BIO/exp-01) of the Aquaculture Laboratory of the Department of Fish and Aquatic Environment of the University of Thessaly.
Nine small-scale autonomous aquaponic systems were constructed. These systems functioned as integrated polyculture aquaponic systems where sea bass (D. labrax) and glasswort (S. europaea) were co-cultured for 75 days under 12 g/kg salinity. Fish were supplied to the laboratory by a local nursery facility (Avramar SA, Managouli, West Greece). Baltic prawn (P. adspersus) was caught with a beach seining net from the Mesolonghi–Etoliko lagoon (38.387° N 21.358° E). The adaptation period for European sea bass, Baltic prawn, and glasswort at the experimental salinity (12 g/kg) was 30 days, and it took place gradually in a 100 L aquarium and consisted of salinity reduced by 5 g/kg once a week (5, 7, 10, 24). Fish were fed a 1.8 mm commercial diet (ZOONOMI SA, GREECE) during adaptation. Glasswort (S. europaea) plants were collected from the Evros River Delta (Greece). After collection, the plants were transported to the laboratory, and a 30-day adaptation period to a salinity increase schedule of 3 units every five days took place (24).
After the adaptation period of the European sea bass and Baltic prawn to the experimental salinity, 135 sea bass juveniles (45 individuals/treatment) with an average body weight of 3.39 ± 0.22 g and an average body length of 7.02 ± 0.28 cm and 27 Baltic prawns (9 individuals/treatment) with an average body weight of 1.21 ± 0.20 g and an average body length of 3.34 ± 0.44 cm were divided into three NFT aquaponics systems. Moreover, 24 glasswort plants (8 plants/NFT hydroponic bed) were placed in each hydroponic NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) pipe. The experiment lasted for 75 days.
2.2. Rearing System and Conditions
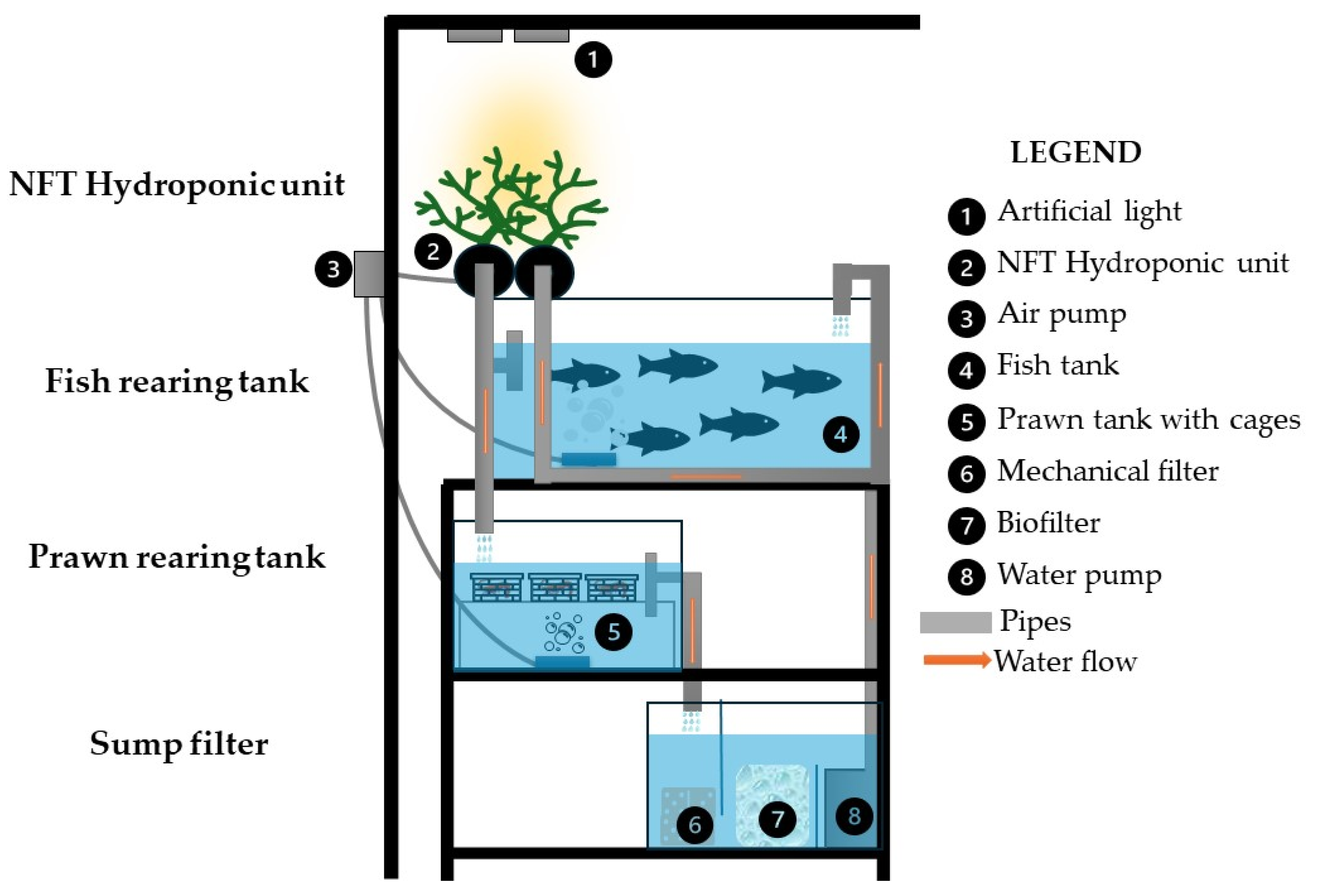
Three stand-alone recirculating aquaponics systems (NFT) with a total volume of 222 liters were constructed for the experiment. Each aquarium system consisted of three rectangular fish tanks (40 × 35 × 26 cm) with a volume of 36.4 L, one rectangular shrimp rearing tank (40 × 35 × 30 cm) with a total volume of 42 L (Figure 1), two cylindrical-shaped hydroponic tanks (growth bed—NFT) consisting of a PVC pipe (113 cm high and 10 cm in diameter) with a total volume of 17.8 L, and a sump-type upflow and downflow filter with a total volume of 53.6 L. Water flowed continuously through the NFT so that the roots of the plants in the growth bed were in constant contact with the nutrient solution (water), creating a thin “film” 0.08 cm to 0.3 cm deep that was in contact with the aerated water. The effluent from the fish tank and hydroponic growth bed was gravity-fed into the shrimp tank and then into the mechanical filter (which consists of a porous sponge that collects fish feces and uneaten food).
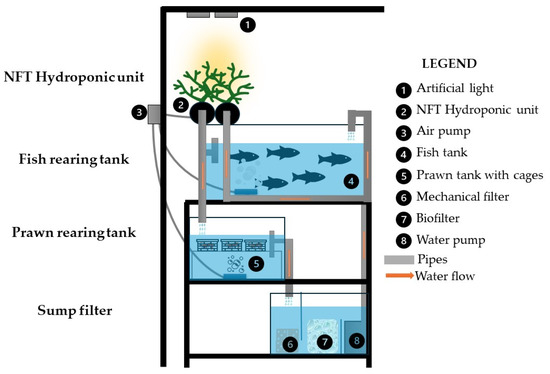
Figure 1.
Side view of a self-contained aquaponic unit.
The water flow was designed to follow a gravity trajectory [1] from the NFT hydroponic culture (at the highest point of the system) to the shrimp rearing tank (at the middle point of the system) and into the biofilter of the well. The sump-type filter consists of three distinct sections: the mechanical, biological, and pump compartment. The mechanical filter contained a porous sponge. The mechanical filter was used for the purpose of capturing uneaten food and fish feces. The filter media of the biological filter had a surface area of 360 cm2 and consisted of 3 L biological balls (Aquamedit, Ø 19 mm, with specific surface area (SSA) cm2/cm3 and density 0.92 g/cm3) and 3 L ceramic ring media (Sera-Siporax, Ø 15 mm, with SSA 1000 cm2/cm3 and porosity < 1%). Water was pumped through the filter bed and fish tank at a ratio of 80% to 20%, respectively, using a pump (OCEAN RUNNER 1200) set at 2.02 cm3/min, resulting in a filtration rate of 2.24 cm3/min. The water renewal rate was less than 5%, which can be attributed to two primary factors: water evaporation and the purification processes inherent in the aquaculture system. The aquaculture system was configured to undergo eight circulation cycles per hour.
Finally, a 400-Watt LED lamp was placed 45 cm from the surface of the NFT hydroponics units in each aquaponics system to provide uniform lighting to the plants. Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) was maintained at 500–600 μmol m−2 s−1. A photoperiod of 14 h of light and 10 h of darkness was used.
2.3. Feed Intake and Utilization
The feeding program for all treatments began after the fish had been transferred to the breeding tanks of the individual aquaponics systems. The sea bass were fed the experimental diet (45.61% crude protein, 19.45% crude fat, and 23.03 MJ/kg energy). The feed was administered ad libitum [22] by hand at 09:00, 13:00, and 17:00. During feeding, the behavior of the fish and prawns was observed and recorded daily. The experiment lasted 75 days. For the first 37 days, the feeding schedule for the three dietary treatments was as follows: (i) treatment A—daily feeding (0 days fasting); (ii) treatment B—three days feeding per week followed by four days fasting; and (iii) treatment C—seven days feeding per week followed by seven days fasting. After the 37 days, all fish in all dietary treatments were fed daily for another 38 days.
The feed was weighed on a daily basis with a precision balance (CAS. MWP-300 H) and stored at 4 °C. At 15-day intervals, the fish were anesthetized by the use of 0.20 mg/L MSS 222 (Syndel) in order to re-calculate feed intake and utilization. The cleaning of fish tanks was performed on a daily basis, and any uneaten food and fecal matter were removed using a siphon.
The daily feed intake was calculated for all treatments by siphoning and separating the uneaten food and collected feces before the first meal. The uneaten food and feces were separated in a plankton net with a mesh size of 0.5–0.2 mm. The sample was meticulously rinsed with deionized water to eliminate residual matter, weighed, and then placed in an oven set at 105 °C for 24 h, in accordance with the methodology described by [25]. The food intake was calculated in accordance with the following equation, as described by [5]:
The leaching factor represents the estimated quantity of food provided during two consecutive meals. It is calculated from a preweighed quantity of 10 pellets placed in the water for 24 h, after which they are reweighed. The formula employed for this calculation is that described by [26]:
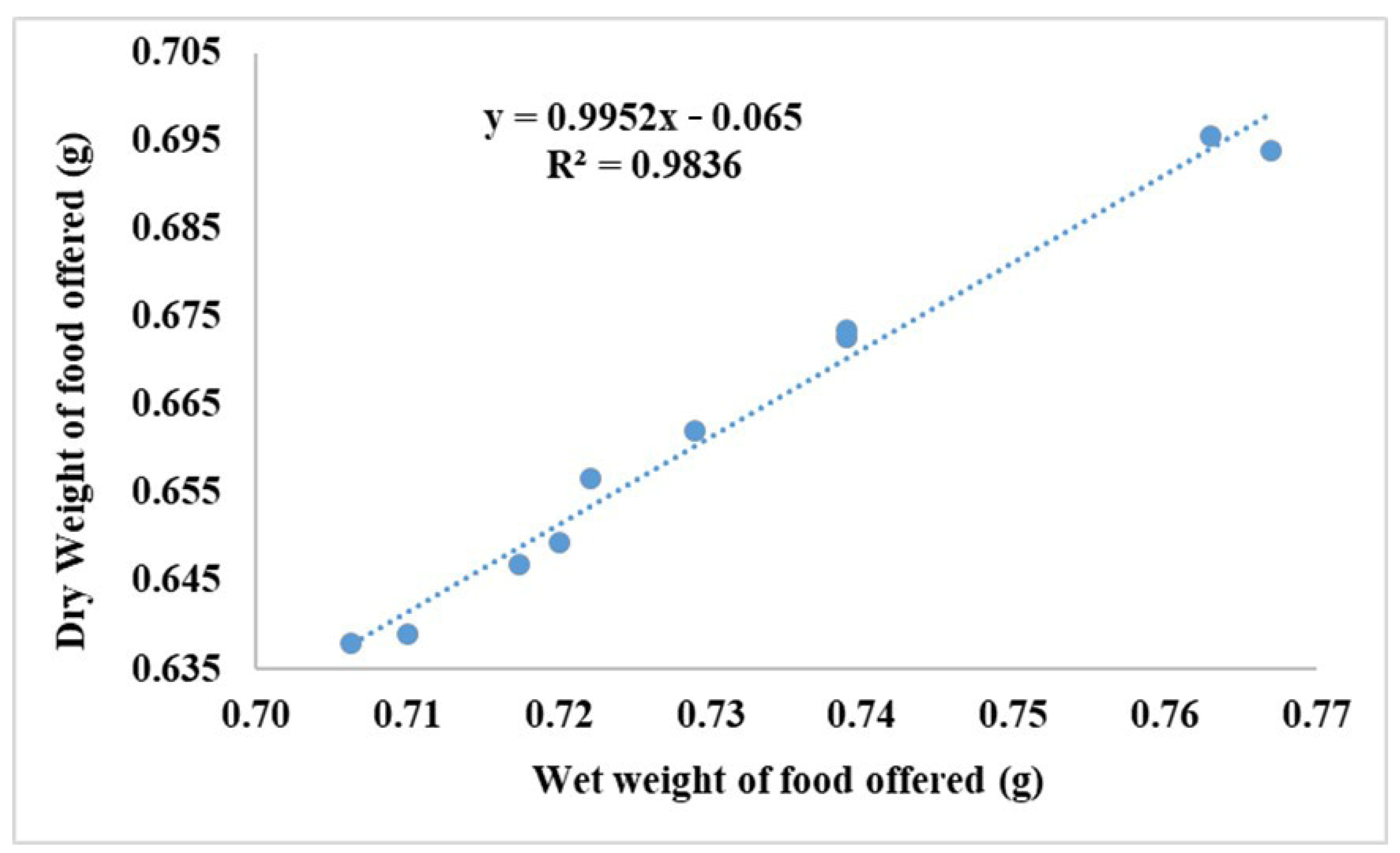
A linear regression (Figure 2) was employed to ascertain the correlation between the wet and dry weight of the feed provided:
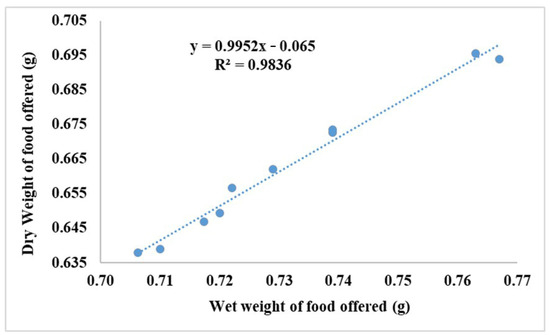
Figure 2.
Food dry and wet weight correlation during the 75 days of this study.
2.4. Water Quality Criteria
The oxygen saturation of the water in both aquaponics systems was, as is typical of aquaponics systems, at a mean value of 7.7 mg/L through an air stone (10.0 × 4.1 × 3.1 cm). The concentration of dissolved oxygen was determined on a daily basis using a multiparameter device (HACK-LANGE, Berlin, Germany, HQ 40 d). The temperature of the water in both aquaponics systems was maintained at 20 ± 0.5 °C throughout the course of the experiment. The concentration of total ammonia (TAN), nitrite (NO2−) and nitrate ions (NO3−), and phosphate ions (PO43−) and the pH were determined at seven-day intervals using test kits [27].
2.5. Photosynthetic Pigment Content
The concentration of photochemical pigments in glasswort was determined through spectrophotometric analysis following the extraction of these compounds with acetone. A branch sample of the plant was randomly selected and taken, with a mass between 0.6 and 1.0 g. Subsequently, the sample was divided into smaller pieces and combined with acetone (80%) and calcium carbonate (0.5 g) using a mortar and pestle. Subsequently, the homogenate was then transferred to a centrifuge tube and mixed with 0.5 g of sand. Subsequently, the samples were subjected to centrifugation at 4000 rpm for a period of 20 min. The absorbance was determined at 720, 663, 646, and 470 nm by the use of a double-beam spectrophotometer (SHIMADZU UV 1900 UV-VIS Spectrophotometer, Duisburg, Germany). Chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoid concentrations were calculated by the Lichtenthaler and Wellburn [28] equations.
2.6. Sampling—Chemical Analysis
At the outset of the experiment, 40 fish samples and 40 plant samples were obtained for the purpose of conducting a chemical analysis of the white muscle of the fish and the plant tissue, respectively. The total weight and length of the fish and prawns were measured at 15-day intervals using a ruler and an electronic balance (CAS MWP-300 H). The initial and final biomass of S. europea was calculated at the start and the end of this study by weighting the aerial part after drying at 75 °C for 24 h.
A bath with anesthetic MS 222, 0.20 g/L, was used to anesthetize the fish and prawns in order to measure their morphometric characteristics. A bath with an overdose of the same anesthetic was used for fish euthanasia.
To ascertain the nutritional composition of the white muscle meat of fish, an approximate analysis was conducted in accordance with the methodologies delineated by the AOAC [29]. To ascertain the moisture content of the fish samples, the constant weight of the samples was measured following their drying in an oven at 105 °C. The crude protein content was determined by Kjeldahl analysis (nitrogen × 6.25; Behr Labor-Technik, Germany), and the crude fat content was determined by exhaustive Soxhlet extraction with petroleum ether (40–60 °C, BP) on a Soxtec system (Gerhard, Germany). The ash content was determined by dry ashing in porcelain crucibles in a muffle furnace at 600 °C for a period of 12 h. All of the aforementioned parameters are expressed as a percentage of the dry weight of the sample.
2.7. Nutritional and Plant Growth Indices
In order to evaluate the comprehensive performance of the entire system, data pertaining to fish growth and dietary intake were meticulously gathered and analyzed. To estimate the growth rate of the entire population of fish in the tank, five fish were randomly selected from the culture aquarium, and their length and body weight were measured. Furthermore, the growth of the fish was monitored over time, from day 0 to day 75, which marked the conclusion of the experiment.
At the final stage of the experiment, the nutrient indices and survival rate of the two cultivated species, along with the growth performance of the plants, were calculated using the equations described in previous studies [5,7,30,31]. The following equations were employed to analyze the data:
Weight Gain (WG), g/fish = FBW − IBW
Specific Growth Rate (SGR), %/days = 100 × (lnFBW − lnIBW)/days
Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) = feed intake (g)/wet weight gain (g)
Protein Efficiency Ratio (PER) = weight gain (g)protein intake (g)
Fulton Factor (K), g/cm3 = 100 × FBW (g)/FBL3 (cm)
Nitrogen Retention (NR), g*N/ABW*days = (FBW * FBN – IBW × FBN)/(Nd × FI)
Lipid Retention (LR), % = 100 × lipid gain(g)/lipid intake (g)
Compensation coefficient (CC) = ΔΤ/ΔC
ΔΤ was the average weight gain (g) in the treatment group tanks divided by the number of feeding days, and ΔC was the average weight gain (g) in the control group tanks divided by the number of feeding days; thus, CC > 1.0 would indicate compensation [32].
Where ABW = ((IBW + FBW)/2), IBW and FBW are the initial and final weight, IBN and FBN are the initial and final body nitrogen content, and Το Nd is the nitrogen content in food.
where IBWp and FBWp are the initial and the final prawn weights.
Prawn Weight Gain (WGp), g/prawn = FBWp − IBWp
Prawn Specific Growth Rate (SGRp), %/days = 100 * (lnFBWp − lnIBWp)/days
The following equations of plant growth performance indices were used [30]:
Height Gain (LG), cm = FH − IH
Biomass Gain (BG), g = FB − IB
Branch Gain (BrG) = FBr − IBr
Yield kg/m2 = FW/Grow bed area
IH and FH are the initial and final height of glasswort, IB and FB are the initial and final weight of the plant, and IBr and FBr are the initial and final number of glasswort branches.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The values are presented as mean values ± standard error. The mean values of all variables were subjected to a Kolmogorov–Smirnov test and a Levene test to ascertain their normality and homogeneity of variances, respectively. The comparison of means was conducted using one-way ANOVA, which was deemed statistically significant at p = 0.05. Subsequently, the Tukey post hoc test was employed when significant differences were identified. In cases where the prerequisites for ANOVA were not satisfied, a non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test was employed [33]. The statistical analyses were performed using the IBM SPSS Statistics software, version 28.
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality
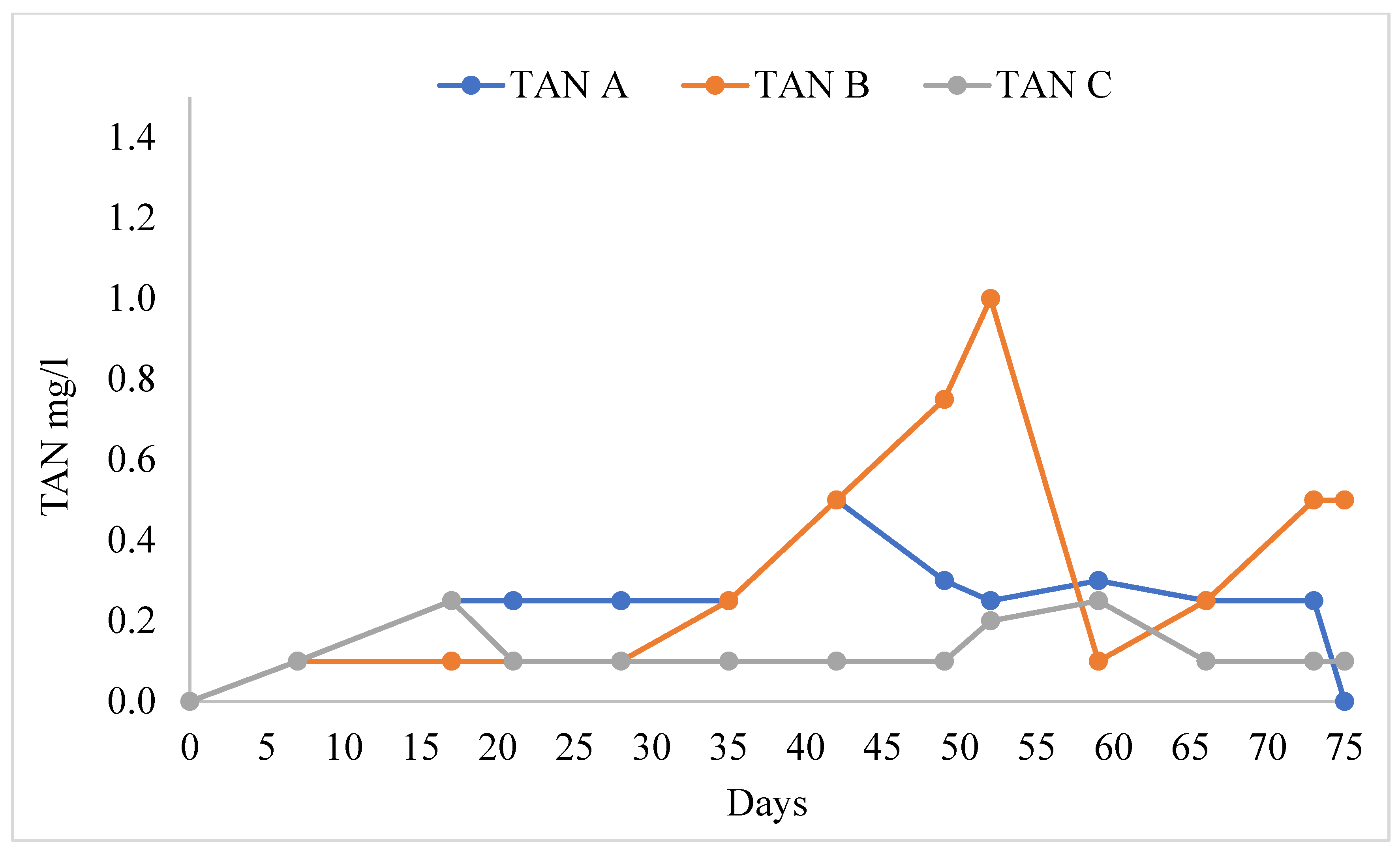
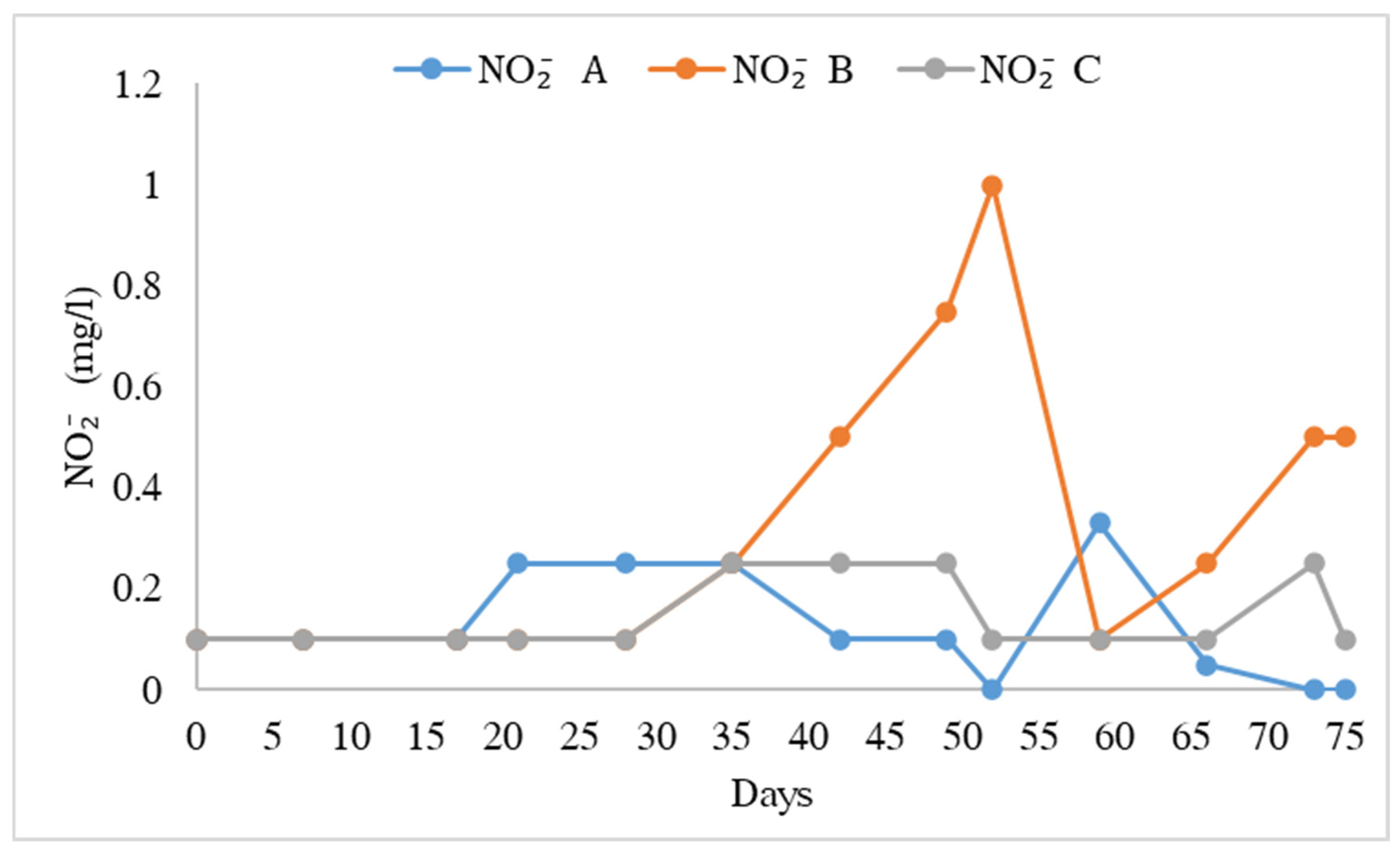
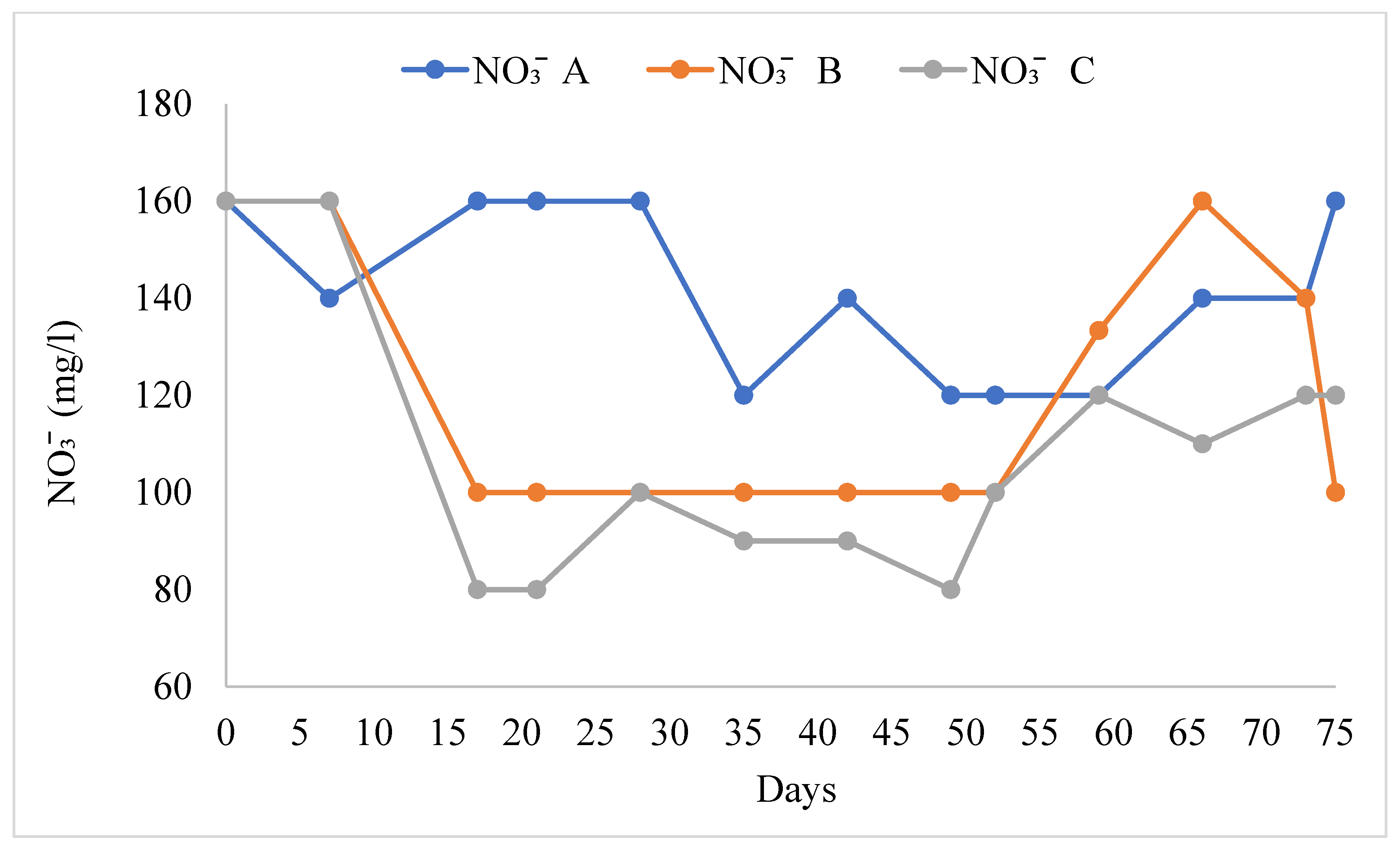
The water quality variables in the different treatments are shown in Table 1. The pH values ranged from 8.09 ± 0.07 to 8.21 ± 0.06. There were no significant differences in pH in all treatments (F = 0.614, F0.05 = 0.547). TAN (Figure 3) was significantly higher in treatment B than in treatments A and C (F = 3.87, F0.05 = 0.30). Nitrites (NO2−) were significantly higher in treatment B than in treatments A and C, and the mean value of nitrite was lower (Figure 4, F = 4.407, F0.05 = 0.019). Nitrate ions (NO3−) in the biofilter (Figure 5) were significantly higher in treatment A than in treatments B and C (F = 6.28, F0.05 = 0.005) with a range from 141.54 ± 4.78 mg/L to 108.46 ± 7.58 mg/L. Nitrate ions (NO3-in) in the fish tank were significantly higher in treatment A than in treatments B and C (F = 4.41, F0.05 = 0.019). In addition, nitrate ions (NO3-out) in the hydroponic unit were significantly higher in treatment A than in treatments B and C (F = 6.49, F = 0.004) and ranged from 111.92 ± 5.82 to 84.62 ± 4.02 (Table 1).

Table 1.
Water chemical parameters of the trial throughout the experiment (75 days).
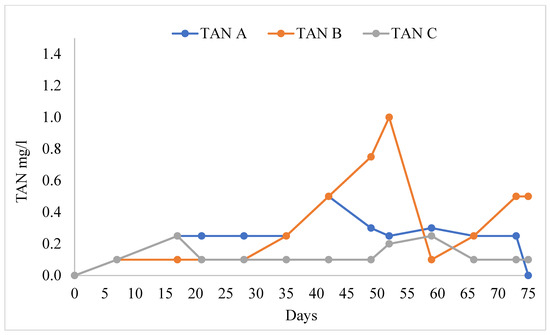
Figure 3.
Concentration of total ammonium during the experimental process.
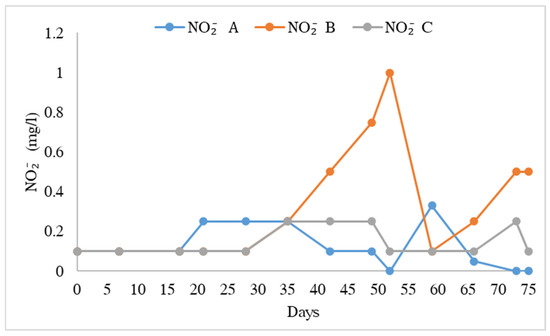
Figure 4.
Concentration of nitrite ions during the experimental process.
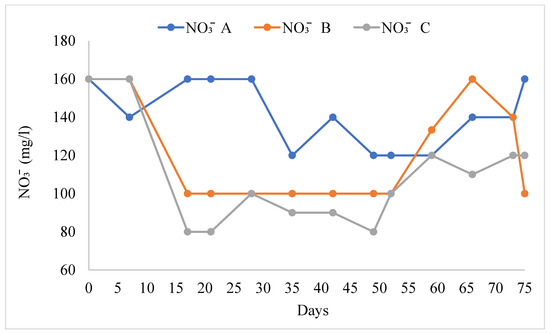
Figure 5.
Concentration of nitrate ions during the experimental process.
3.2. Fish, Prawn, and Plant Growth Performance Indices
The growth performance, feed conversion, and morphometric parameters of the sea bass and prawns in the three treatments for a culture period of 75 days are shown in Table 2. At the beginning of this study, the initial mean body weight (IBW) and initial body length (IBL) were similar between treatments (F = 0.000, F0.05 = 1.000 and F = 0.003, F0.05 = 0.997, respectively). For sea basses, the mean final body weight (FBW) was significantly higher in treatment B than in treatments A and C, which were lower (Table 2; F = 63.099, F0.05 < 0.01). The final body length (FBL) was significantly higher in treatment C than in treatments A and B, which were lower (F = 259.19, F0.05 < 0.01). Weight gain (WG) (F = 63.099, F0.05 < 0.01) and SGR were significantly lower in treatments A and C (F = 21.921, F0.05 < 0.01) than in treatment B. Survival rates (S) ranged from 84.45% to 93.33%, with significantly higher rates in treatment B (ANOVA, p < 0.05) than the other two treatments. The FCR was significantly higher in treatment A than in treatments B and C (F = 59.304, F < 0.01). The PER values were significantly higher in treatment B than in treatments A and C (63.099, F0.05 < 0.01). In contrast, the nitrogen retention (NR) (F = 45.141, F0.05 < 0.01) values were significantly lower in treatment A, while lipid retention (LR) was lower in treatment B (F = 1.981, F0.05 < 0.01), indicating lower lipid storage in fish muscle. The Fulton Factor was the same between treatments (Table 2; F = 0.071, F0.05 = 0.931).

Table 2.
European sea bass and prawn growth performance, feed utilization, and morphometrics throughout 75 days of this study in the integrated brackish aquaponic system.
For prawns, the final weight (FBWp, g) (F = 1.402, F0.05 = 0.269) and final length (FBLp, cm) (F = 7.724, F0.05 = 0.003) were similar between treatments (Table 2). SGRp (%/days) (F = 5.049, F0.05 = 0.017), prawn weight gain (WGp, g) (F = 8.854, F0.05 = 0.002), prawn Fulton Factor (Kp, g/cm3) (F = 0.603, F0.05 = 0.555), and prawn survival showed statistically significant differences between treatments (Table 2).
The proximate composition (Table 3) of the white muscle tissue of sea bass individuals from the study trials of fasting and refeeding is shown in Table 3. The moisture of the sea bass muscle at the end of this study was significantly lower in treatment A than in treatment C (F = 27.96, F0.05 = 0.001). The protein content of the sea bass muscle was also significantly higher in treatments B and C than in treatment A, while the ash content was higher in treatments B and C (F = 35.82, F0.05 = 0.001). The total lipid content was significantly lower in treatment B than in treatments A and C. In addition, the energy content of the muscles was significantly higher in treatments A and C than in treatment B (F = 12.24, F0.05 = 0.001).

Table 3.
Approximate analysis of the muscle of European sea bass at the end of cultivation (75 days) in the polyculture aquaponic systems.
To express the compensatory growth in a numerical sense, the compensation coefficient (CC) was calculated (Figure 6). Treatments B and C showed no compensation tendency during the first 30 days of the trial (CC < 1). Both treatments showed compensation tendency from day 45 and until the end of the experiment (CC > 1). At the end of the trial, the CC values of groups Β and C were 1.70 and 1.39, respectively.
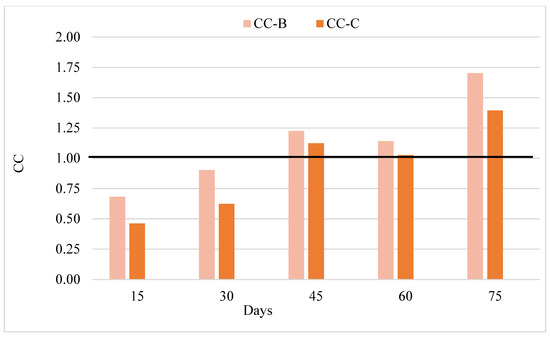
Figure 6.
Changes in compensation coefficient of European sea bass juveniles fed according to different feeding frequencies for 75 days.
Glasswort growth performance, photosynthetic pigments, and chemical composition at the end of the cultivation period (75 days) are represented in Table 4. The plants’ initial heights and initial biomass at the beginning of the experiment were similar (Table 4, F = 0.229, F0.05 = 0.797) in all treatments. All groups of glassworts had similar final biomass and final branches (F = 0.707, F0.05 = 0.505). The final height was higher in treatment B. Glasswort yield was significantly higher in treatment B than in treatments A and C (F = 8.256, F0.05 = 0.001). By the end of the experiment, chlorophyll a was found to be significantly lower in treatment B than in the other two treatments (F = 5.610, F = 0.013), while chlorophyll b and carotenoids were similar for all treatments (Table 4, F = 0.430, F0.05 = 0.658). The nitrogen content of the plant branches exhibited statistically significant differences between the experimental treatments, with the highest concentration observed in treatment B in comparison to the other two treatments. The ash content of the glasswort branches exhibited a statistically significant difference, with the highest value observed in treatment C. The moisture content of the plant demonstrated statistically significant variations, with the lowest value noted in treatment A.

Table 4.
Glasswort growth performance, photosynthetic pigments, and content at the end of the cultivation period (75 days).
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Quality
Throughout the experimental process, the levels of water quality indicators such as total alkalinity (TAN) and nitrate (NO2−) were maintained at minimal levels. Significant differences were observed between the treatments (ANOVA, p <0.05). The mean nitrate values at the control site, situated at the outlet of the hydroponic subsystem (NO3−out), were found to be lower than those at the control site within the fish tank (NO3−in). This indicates that the plants were absorbing nutrients from the water. However, the water quality parameters remained within the optimal limits for both the aquaculture [34] and hydroponic systems [1]. This study demonstrated that compensatory growth can effectively reduce ammonia levels [35]. The increased nitrate ions were utilized by the plants for nutritional and growth purposes [1].
Ammonia serves as a suitable source of nutrients for plants, particularly when nitrate levels are low. However, plants absorb significantly more nitrate when ammonia levels increase [36]. Buzby and Lin [37] observed that in an aquaponic system with fresh water, where lettuce was cultivated, the retention efficiency of ammonia (NH4+/NH3) was superior to that of nitrate ions. In the present study, ammonia levels were maintained at a consistently low level throughout the experimental period, with the maximum value occurring in treatment B. This suggests that ammonia was oxidized to nitrite and nitrate ions more effectively in treatment C, which supports the uptake and growth of glasswort plants. Ref. [38] reported nitrate ion levels of 116.71 ± 17.57 mg/L and ammonia levels of 0.2 ± 0.02 mg/L, in a glasswort culture experiment conducted with marine aquaculture wastewater.
In the present study, the nitrate ion levels at the control point, where water exits the hydroponic subsystems (NO3−out), indicated the efficient operation of the coupled aquarium system and the oxidizing capacity of the filter [5]. When sea bass and rock samphire were grown in a brackish aquaponic system at three different salinities (8 g/kg, 14 g/kg, 20 g/kg), lower levels of nitrate ions were measured. Specifically, levels were found to be between 93.94 ± 7.81 mg/L and 119.81 ± 7.36 mg/L [35]. Moreover, ref. [5] observed significantly lower nitrate concentrations, ranging from 76.4 to 77.2 mg/L, in a recirculating brackish aquaponic system that co-cultivated bass and prawns at salinities of 8 g/kg and 14 g/kg, respectively.
In the present study, the pH values remained consistent across the various experimental treatments. For optimal nutrient uptake, plants require a pH level between 5.5 and 6.5 [39]. Bacteria are most likely to flourish in a pH range of 7.0 to 8.0, whereas the optimal pH for aquaculture is between 6.5 and 8.5 [39]. It can thus be posited that the optimal pH range for aquaculture is 6.5 to 7.0. When pH values exceed 7.0, the solubility of phosphorus and other nutrients may be diminished [40].
4.2. Fish Growth Performance
Previous studies [41,42] examined a similar feeding pattern. According to Ziegelbecker et al. [42], when Acipenser dabryanus (Dumeril, 1869) was subjected for 28 days to zero, three, and seven days of fasting per week, followed by 14 days of refeeding, the final weights of fish subjected to zero or three days of fasting were similar. The same results reported by Wu et al. [41] for Tropheus sp. Over a study period of 80 weeks, fish were subjected to zero or four days of fasting per week for 20 weeks (followed by 60 weeks of refeeding); at the end of the study, the body size of the fish was similar. This feeding trial was based on the results of these studies [41,42].
The results of the fish growth performance study indicated a significant impact of fasting on compensatory growth. The sea bass subjected to fasting treatments (B and C) demonstrated superior growth and total compensatory growth compared to the fish that were provided with daily nourishment (A). It is crucial to consider the impact of refeeding on compensatory growth. In instances of complete compensation, starved fish ultimately attain the same size and age as their continuously fed counterparts [43,44].
The findings of this study are at odds with those of Jobling [44] for Gadus morhua, where weight did not demonstrate a compensatory effect at the end of the three weeks of refeeding. In the present study, fish grown in a multi-culture aquaponic system and fed according to the treatment B protocol exhibited the highest weight gain (WG, g) and the highest specific growth rate (SGR, %/days) (ANOVA, p > 0.05).
The survival rate of the fish at the conclusion of the experiment ranged from 93.3% to 84.5%, a figure that was significantly lower than the survival rates reported by [45] for Acanthopagrus latus (Houttuyn, 1782) (96.7–100%) and Sparidentex hasta (Munro, 1948) (83–96%). The Fulton condition factor (K), which serves as an indicator of fish well-being, demonstrated no statistically significant differences between treatments (ANOVA, p > 0.05), indicating that short-term food deprivation does not exert a considerable impact on fish welfare. Subsequently, the Fulton condition factor value at the conclusion of the 75-day growing period was compared with values obtained from other studies. The value obtained in this study was found to be lower than the K value reported for Atlantic cod (K: 1.31 ± 0.11 g/cm3, 1.27 ± 0.11 g/cm3, and 1.22 ± 0.11 g/cm3) when one-, two-, and three-week fasting periods were followed by a one-week refeeding program [44]. Ref. [45] reported higher K values (1.1 to 1.4 g/cm3) for A. latus subjected to a two-week refeeding period. The Fulton Factor (K) serves as a verification method for the level of energy reserves and the health status of the fish. Fluctuations in its value may be indicative of alterations in the nutritional status of the fish [46].
It has been reported that fasting can induce oxidative stress in fish, which in turn results in a reduction in stored antioxidants and nutrients [47]. Protein degradation can be increased in order to provide amino acids for vital body functions [47]. Moreover, the findings indicated that sea bass cultivated in a brackish water aquaponic system and nourished in accordance with the feeding protocol of treatments B and C demonstrated a markedly elevated mean final weight in comparison to the values observed in treatment A (daily feeding).
The findings of the present study are consistent with those of [48], where it was observed that gilthead seabream with an initial mean weight of 5.85 ± 0.54 g reached a mean final weight of 27.08 ± 0.8 g after eight days of feeding followed by two days of fasting. It was reported that the grey mullet exhibited a four times increment in mean final weight when starved for 5 and 20 days [48]. Other studies have indicated that species such as Salmo salar (Linnaeus, 1758), Aristichthys nobilis (Richardson, 1845), Gasterosteus aculeatus (Linnaeus, 1758) and Acipenser dabryanus (Duméril, 1869) achieve the same mean weight as those subjected to a program of fasting and refeeding [41,49,50,51]. A number of fish species, including the gilthead seabream [48], sturgeon [41], and salmon [52], have been observed to exhibit accelerated growth following a period of starvation and subsequent refeeding. Furthermore, the findings of the present study indicated a markedly elevated specific growth rate (SGR) and weight gain (WG) in sea bass subjected to treatments B and C, in comparison to treatment A. The study reported in [53] documented that rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum, 1792) exhibited an analogous specific growth rate (SGR) under 2 (SGR: 2%/d), 4 (SGR: 2.2%/d), 8 (SGR: 1.7%/d), and 14 (SGR: 1.7%/d) days of fasting in comparison to fish subjected to no fasting (SGR: 2.1%/d).
Nutrient digestibility and, consequently, the specific growth rate are influenced by a number of factors, including food intake, fish size, and water temperature. In compensatory growth experiments, a number of mechanisms have been identified as playing a role, including hyperphagia [21], the optimization of metabolic rate [54], protein biosynthesis [55], the adaptability of the endocrine system during restricted feeding, a reduction in the basal metabolic rate, and an improvement in the feed conversion ratio (FCR) [45].
The feed conversion ratio (FCR) was found to be significantly higher in treatment A than in treatments B and C (ANOVA, p < 0.05). Turkmen et al. [56] reported a lower feed conversion ratio (FCR) for sea bass, with a range of 1.0 ± 0.04 to 1.2 ± 0.75. Yılmaz and Eroldoğan [57] reported hyperplasia when juvenile gilthead seabream were subjected to two periods of fasting (1 day fasting, 3 days refeeding and 1 day fasting, 5 days refeeding). Compensatory growth feeding leads to hyperphagia. A reduction in food transit through the digestive tract has been observed to result in hyperphagia. Hyperphagia in animals allows the same or higher total food intake as an individual with no food restriction, thereby reaching the same size [58].
The protein efficiency ratio (PER) demonstrated notable discrepancies among the experimental treatments (ANOVA, p < 0.05), suggesting that the sea bass were influenced by the dietary regimen implemented throughout the investigation. Ref. [43] also observed similar results, with PER values differing between the control and starvation treatments. In contrast, ref. [59] reported that there was no significant difference in the PER values between the control and the 7-day fasting treatments. However, in the feeding regimen applied for longer fasting periods (2, 3, and 4 weeks), the PER values demonstrated a decline as the number of fasting days increased.
Significant differences were observed in lipid retention (LR) among the treatments (ANOVA, p < 0.05), with the highest value observed in treatment A and the lowest in treatment B. These findings are comparable to those reported by [6,31]. Specifically, ref. [6] shows that seabreams and sea bass that were fed daily without starvation showed a higher LR than fish that were subjected to 4 or 7 days of starvation. Ref. [31] reported that in fish fed with the lowest protein content diet (30%), the LR values ranged from 34.3 ± 1.57% to 77 ± 3.22%. Diplodus puntazzo (Walbaum, 1792) exhibited higher LR values. During periods of food deprivation, energy consumption is reduced due to a decrease in the fish’s locomotor activity. During the rearing period, the reduction in activity contributes to compensatory growth in the fish, with available energy being allocated to this process. In fish species such as the sea bass (D. labrax), rainbow trout [60], and tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, Linnaeus, 175862) [61] that are in a state of starvation, lipids are broken down at a faster rate than other nutrients. Modifications in lipid levels manifest prior to and throughout the period of compensatory growth. Increased lipid retention may lead to lipid accumulation in the liver, muscle, and viscera [62]. In the results, the fact that treatment B resulted in the lowest lipid retention, in conjunction with the fact that fish in that treatment showed increased FBW and decreased FCR, leads to the conclusion that the lipids were used for fish growth.
The analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed a significant difference in nitrogen retention (NR) among treatment A and treatments B and C (p < 0.05). In juvenile D. puntazzo, the NR values ranged from 23.4 to 30.2, indicating a lower nitrogen retention capacity than that observed in the present study [63]. Significant differences were observed in the levels of protein, fat, ash, and energy among the various treatments (ANOVA, p < 0.05). The biochemical composition of the fish body was found to be influenced by the feeding regime employed in order to achieve compensatory growth [20]. However, the total lipid content was lower in treatment B than in other treatments. Similarly, previous studies have reported that a reduction in crude lipids is a result of fasting [64].
Treatments B and C exhibited compensation trends during the intermediate phases of this study, specifically after 45 days of experimentation, with compensation coefficients exceeding 1 (CC > 1). Group C, which was subjected to a prolonged period of fasting, demonstrated a compensatory growth trend until the conclusion of the trial, with a CC value greater than 1. Similarly, it has been reported that Coregonus lavaretus (Linnaeus, 1758) exhibited elevated CC values following fasting regimens [65]. In their study on compensatory growth in perch fish, ref. [23] found that the three-day fed and fasted one and six-day fed and fasted one treatment improved compensatory abilities and partially compensated for growth (CC > 1). In addition to the aforementioned studies, the duration of fasting in the present study demonstrated an impact on the compensation factor.
4.3. Prawn Growth Performance
The survival of prawns at the end of the experimental rearing period exhibited a range of values, from 88.9% to 77.8%, and was superior to the survival demonstrated by [66] for the same species (86.7% to 53.3%), with an initial body weight of 0.50 ± 0.01 g.
Moreover, the results demonstrate a markedly diminished specific growth rate (SGR) and weight gain (WG) in treatment B, in comparison to treatments A and C. This indicates that a seven-day fasting period had a beneficial impact on shrimp growth. In a related study, ref. [67] observed weight gain per unit time (WGp) values that were lower than those observed in the present experiment when rearing the same species, Palaemon elegans (Martin & Rathke, 1837). Moreover, ref. [66] conducted a feeding experiment with the same shrimp species as the present study, feeding them insect meal, and observed SGRp values that were lower than those observed in the present study.
Additionally, the prawns’ Fulton Factor (Kp, g/cm3) was found to be greater in the fasting treatments (B and C), indicating that short-term fasting does not affect prawn welfare.
4.4. Plant Growth Performance
Glasswort (S. europaea) is a halophytic plant that is particularly well suited to growth in saline environments. Halophytes employ a range of processes and metabolic adaptations that enable them to flourish in a diverse array of soil salinities, spanning the low levels characteristic of agricultural soils to the exceedingly high levels prevalent in coastal ecosystems [68]. The responses of different species to salinity levels vary, and the optimal level of salinity for growth is dependent on both genotype and environmental conditions. A number of halophytes are capable of attaining optimal growth under conditions of mild to moderate salinity, due to the presence of established physiological adaptations [69]. Additionally, glasswort is included in this category, exhibiting optimal growth at salinities between 12 and 25 g/kg. However, growth is negatively impacted when salinities fall below or exceed this range, for instance, at 0.55 and 72 g/kg [70]. Similarly, ref. [71] determined that glasswort exhibits optimal growth at salinities of 10–22 g/kg. Therefore, the salinity levels utilized in this study are within the optimal range for glasswort growth. The application of fish treatments resulted in notable impacts on the growth parameters of the plants.
Notably, the glasswort cultivated with treatment B exhibited a greater height than the other two treatments. This increase in height can be attributed, at least in part, to the elevated levels of nitrate in the recycled water. In a greenhouse study conducted by De Souza et al. [72] on the related species Salicornia neei (Alonso & Crespo, 1817), a similar number of branches was observed along with slightly taller plants than those in our study, despite the plants being subjected to a salinity of 11 g/kg. With regard to productivity, the yield observed in treatment B (42.38 ± 5.66 kg/m2) was found to be significantly higher than the yields reported by [73] for the related species Sarcocornia ambigua in co-culture with Pacific white shrimp at a salinity of 16 g/kg.
The enhanced growth of plants in treatment B can be attributed to the higher nitrogen content observed in their branches, which exhibited statistically significant differences compared to the other treatments, with treatment B showing the highest values. The nitrogen levels measured in this study indicate that S. europaea is a valuable source of protein. Similar nitrogen contents have been reported in S. europaea by [74] and in Arthrocnemum macrostachyum (Koch, 1853) by [75].
Moreover, treatments A and B exhibited markedly diminished ash content in comparison to treatment C. The total ash content observed in this study was significantly lower than the values reported by [74] for the same species (31.2%). A distinctive trait of halophytes is the accumulation of minerals in plant tissues, which is indicated by a high ash content.
Regarding photosynthetic pigments, the findings revealed significantly elevated levels of chlorophyll A. The chlorophyll A findings were higher than those of [70]. The concentrations of chlorophyll B and carotenoids exhibited no discernible variation across the various treatments. The observed decreases in chlorophyll content are consistent with the findings of [70] at salinity levels exceeding 400 mM NaCl. Additionally, [76] observed that the chlorophyll and carotenoid content of cultivated glasswort is lower than that of glasswort harvested in the field.
5. Conclusions
This study is the first investigation of the compensatory growth effects on the growth and survival of European sea bass, Baltic prawn, and glasswort in a brackish aquaponic system. The findings indicate that the cultivation of glasswort in a brackish water polyculture aquaponic system is advantageous, as it effectively absorbs the nutrients produced by the European sea bass and prawns within the system. The impact of compensatory growth was found to be significantly advantageous for the growth performance of the European sea bass and glasswort, in comparison to the control.
The aquaponics system allows for the conservation of water and nutrients by utilizing areas that are unsuitable for other food production techniques, thereby promoting local food production and creating new business opportunities. The compensatory growth observed in this study, when combined with the aforementioned benefits of aquaponics, demonstrates that providing nutrients at a specific frequency can lead to the high growth of animal organisms while simultaneously reducing the production of metabolic waste products. This allows for optimal plant growth.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.M., N.V., P.B. and E.M.; methodology, I.M., N.V., A.P. and E.M.; software, I.M., N.V. and E.M.; validation, N.V., P.B. and E.M.; formal analysis, I.M., N.V., E.L., P.B. and E.M.; research, I.M., N.V., E.L., P.B. and E.M.; sources, I.M., N.V., P.B. and E.M.; data curation, I.M., N.V., P.B., E.L. and E.M.; initial draft writing—preparation, I.M., N.V., P.B., E.L. and E.M.; writing—revising and editing, I.M., N.V., P.B., E.L. and E.M.; visualization, I.M., N.V., P.B., E.L. and E.M.; supervision, N.V., P.B., E.L. and E.M.; project management, N.V., P.B. and E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All experimental procedures were conducted according to the guidelines of EU Directive 2010/63/EU regarding the protection of animals used for scientific purposes and were applied by FELASA-accredited scientists (functions A–D). The Ethics Committee of the Region of Thessaly, Veterinary Directorate, Department of Animal Protection-Medicines-Veterinary Applications, approved the experimental protocol. The experiment was conducted at the registered experimental facility (EL-43 BIO/exp-01) of the Laboratory of Aquaculture, Department of Ichthyology and Aquatic Environments, University of Thessaly.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to AVRAMAR SA for the generous sponsorship of the sea bass (D. labrax).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Somerville, C.; Cohen, M.; Pantanella, E.; Stankus, A.; Lovatelli, A. Small-scale aquaponic food production: Integrated fish and plant farming. FAO Fish. Aquac. Tech. Pap. 2014, 589, I. [Google Scholar]
- Diver, S.; Rinehart, L. Aquaponics-Integration of Hydroponics with Aquaculture; Attra: Butte, MT, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, P.; Guo, R.; Jin, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y. Evaluation and analysis of water quality of marine aquaculture area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Zheng, Y. Energy-saving techniques in urban aquaponics farms by optimizing equipment operating scheme. Aquaculture 2024, 587, 740873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahos, N.; Berillis, P.; Levizou, E.; Patsea, E.; Panteli, N.; Demertzioglou, M.; Morfesis, K.; Voudouri, G.; Krigas, N.; Kormas, K.; et al. Investigating Salinity Effects in Brackish Aquaponics Systems: Evidencing the Co-Cultivation of the Halophyte Crithmum maritimum with the Euryhaline Sparus aurata. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsopoulos, I.; Kontou, I.G.; Babouklis, K.; Vlahos, N.; Berillis, P.; Levizou, E.; Mente, E. Starvation and re-feeding of Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) and European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) co-cultured with glasswort (Salicornia europaea) in a polyculture aquaponic system. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulou, P.; Berillis, P.; Levizou, E.; Sakellariou-Makrantonaki, M.; Kormas, A.K.; Angelaki, A.; Kapsis, P.; Vlahos, N.; Mente, E. Basil and Nile tilapia production in a small scale aquaponic system. J. Fish. Sci. 2018, 12, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Baganz, G.F.M.; Timpe, A.; Baganz, D.; Staaks, G.; Hunger, B.; Kloas, W.; Lohrberg, F. City or hinterland–site potentials for upscaled aquaponics in a Berlin case study. npj Urban Sustain. 2022, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzen, B.; Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Moheimani, N.; Burnell, G.M. Aquaponics: Alternative types and approaches. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems: Combined Aquaculture and Hydroponic Production Technologies for the Future; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 301–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Bibbiani, C.; Fierro-Sañudo, J.F.; Maibam, C.; Incrocci, L.; Pardossi, A.; Fronte, B. Selection of marine fish for integrated multi-trophic aquaponic production in the Mediterranean area using DEXi multi-criteria analysis. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccinelli, M.; Fierro-Sañudo, J.F.; Bibbiani, C.; Fronte, B.; Maibam, C.; Dubois, T.; Pardossi, A.; Incrocci, L.; Rossi, L. Multi-Criteria DEXi Analysis for the Selection of Crop Species for Saltwater Aquaponics. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.E. A Review of Structure in Several North Carolina Salt Marsh Plants; Reimold, R.J., Queen, W.H., Eds.; Ecology of Halophytes; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 307–344. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, A.M. Effects of competition, disturbance, and herbivory on Salicornia europaea. Ecology 1987, 68, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ortegón, E.; Sargent, P.; Pohle, G.; Martinez-Lage, A. The Baltic prawn Palaemon adspersus Rathke, 1837 (Decapoda, Caridea, Palaemonidae): First record, possible establishment, and illustrated key of the subfamily Palaemoninae in northwest Atlantic waters. Aquat. Invasions 2014, 10, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janas, U.; Spicer, J.I. Seasonal and temperature effects on osmoregulation by the invasive prawn Palaemon elegans Rathke, 1837 in the Baltic Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2010, 6, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glamuzina, B.; Pešić, A.; Joksimović, A.; Glamuzina, L.; Matić-Skoko, S.; Conides, A.; Klaoudatos, D.; Zacharaki, P. Observations on the increase of wild gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata abundance, in the eastern Adriatic Sea: Problems and opportunities. Int. Aquat. Res. 2014, 6, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Brief to The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024; Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation of Greek Maricultures. Annual Report 2023. Available online: https://fishfromgreece.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/HAPO_AR23_WEB-NEW.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Rubio, V.C.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J.; Madrid, J.A. Effects of salinity on food intake and macronutrient selection in European sea bass. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 85, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylord, T.G.; Gatlin, D.M. Dietary protein and energy modifications to maximize compensatory growth of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 2001, 194, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Al-Asgah, N.; Al-Ogaily, S.; Ali, S. Effect of feeding different levels of alfalfa meal on the growth performance and body composition of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings. Asian Fish. Sci. 2003, 16, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorakis, K.; Alexis, M. Effects of fasting on the meat quality and fat deposition of commercial-size farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata, L.) fed different dietary regimes. Aquac. Nutr. 2005, 11, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, J.; Koskela, J.; Pirhonen, J. The effect of the length of repeated feed deprivation between single meals on compensatory growth of pikeperch Sander lucioperca. Aquaculture 2009, 296, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Pasquet, A.; Aubin, J.; Nahon, S.; Lecocq, T. When more is more: Taking advantage of species diversity to move towards sustainable aquaculture. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 767–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahos, N.; Levizou, E.; Patsea, E.; Tasiou, K.; Berillis, P.; Antonopoulou, E.; Bekiari, V.; Martou, N.; Morfesis, K.; Lazari, D.; et al. Salinity affects the efficiency of a brackish aquaponics system of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and rock samphire (Crithmum maritimum). Aquaculture 2023, 571, 739493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland, S.; Grisdale-Helland, B.; Nerland, S. A simple method for the measurement of daily feed intake of groups of fish in tanks. Aquaculture 1996, 139, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddicoat, M.I.; Tibhitts, S.; Butler, E.I. The determination of ammonia in seawater. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1975, 20, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 16th ed.; AOAC INTERNATIONAL: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Endut, A.; Jusoh, A.; Ali, N.; Nik, W.B.W.; Hassan, A. A study on the optimal hydraulic loading rate and plant ratios in recirculation aquaponic system. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karapanagiotidis, I.T.; Kyritsi, S.; Dretaki-Stamou, G.; Psofakis, P.; Neofytou, M.C.; Mente, E.; Vlahos, N.; Karalazos, V. The effect of different dietary protein levels on growth performance and nutrient utilization of snarpsnout sea bream (Diplodus puntazzo). Aquac. Res. 2021, 53, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaklı, A.; Taşbozan, O. The effects of different cycles of starvation and refeeding on growth and body composition on europaean sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Turkish J. Fish Aquat. 2015, 15, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Prentice-Hall: London, UK, 1999; p. 718. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.S. Handbook for aquaculture water quality. In Handbook for Aquaculture Water Quality; USDA ARS: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 439. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Choudhury, T.G.; Mandal, S. Compensatory growth in fishes a boon to aquaculture. Aquac. Eur. 2012, 37, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Ji, W.; Castell, J.D.; O’Dor, R. The nutritional value of dietary n-3 and n-6 fatty acids for the Chinese prawn (Penaeus chinensis). Aquaculture 1993, 118, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzby, K.M.; Lin, L.-S. Scaling aquaponic systems: Balancing plant uptake with fish output. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 63, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinta, R. Effectiveness of Halophytic Plants in the Treatment of Marine Aquaculture Wastewater; Bangor University: Bangor, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, H.Y.; Robaina, L.; Pirhonen, J.; Mente, E.; Domínguez, D.; Parisi, G. Fish Welfare in aquaponic systems: Its relation to water quality with an emphasis on feed and faeces—A review. Water 2017, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, R.V.; Simonne, E.H.; White, J.M.; Lamb, E.M. Reconciling water parameters impacting nitrification in aquaponics: The pH levels. Proc. Fla. State Hortic. Soc. 2004, 117, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Lai, J.-S.; Liu, Y.; Song, M.-J.; Gong, Q.; Long, Z.-H. Effects of starvation and refeeding on growth performance, appetite, growth hormone–insulin-like growth factor axis levels and digestive function of Acipenser dabryanus. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 126, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegelbecker, A.; Sefc, K.M. Growth, body condition and contest performance after early-life food restriction in a long-lived tropical fish. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 10904–10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.Z.; Jauncey, K. Evaluation of mixed feeding schedules with respect to compensatory growth and body composition in African catfish Clarias gariepinus. Aquac. Nutr. 2004, 10, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, M. Are compensatory growth and catch-up growth two sides of the same coin? Aquac. Int. 2010, 18, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, S.; Oujifard, A.; Mozanzadeh, M.T.; Safari, O. Compensatory growth, antioxidant capacity and digestive enzyme activities of Sobaity (Sparidentex hasta) and yellowfin seabreams (Acanthopagrus latus) subjected to ration restriction. Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 2448–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goede, R.W. Organismic indices and an autopsy-based assessment as indicators of health and condition of fish. Am. Fish. Soc. Symp. 1990, 8, 93–108. [Google Scholar]
- Krogdahl, Å.; Bakke-McKellep, A.M. Fasting and refeeding cause rapid changes in intestinal tissue mass and digestive enzyme capacities of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2005, 141, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroldoğan, O.T.; Taşbozan, O.; Tabakoğlu, S. Effects of restricted feeding regimes on growth and feed utilization of juvenile gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2008, 39, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, A.; Metcalfe, N.B. Social status, access to food, and compensatory growth in juvenile Atlantic salmon. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 58, 1331–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P. Gut contents of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) and the processing and digestion of algal cells in the alimentary canal. Aquaculture 2001, 195, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cui, Y.; Ali, M.; Wootton, R.J. Comparison of compensatory growth responses of juvenile three-spined stickleback and minnow following similar food deprivation protocols. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 58, 1149–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvas, M.; Nilsson, J.; Vågseth, T.; Nola, V.; Fjelldal, P.G.; Hansen, T.J.; Oppedal, F.; Stien, L.H.; Folkedal, O. Full compensatory growth before harvest and no impact on fish welfare in Atlantic salmon after an 8-week fasting period. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikki, J.; Pirhonen, J.; Jobling, M.; Karjalainen, J. Compensatory growth in juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), held individually. Aquaculture 2004, 235, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Lajonchère, L.; Ibarra-Castro, L. Aquaculture species selection method applied to marine fish in the Caribbean. Aquaculture 2013, 408, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, J.C.; Blake, R.W. The effect of feed cycling and ration level on the compensatory growth response in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus my kiss. J. Fish Biol. 1990, 37, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, S.; Eroldoğan, O.T.; Yılmaz, H.A.; Ölçülü, A.; Inan, G.A.K.; Erçen, Z.; Tekelioğlu, N. Compensatory growth response of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) under cycled starvation and restricted feeding rate. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, H.A.; Eroldogan, O.T. Combined effects of cycled starvation and feeding frequency on growth and oxygen consumption of gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2011, 42, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Mandal, S.C.; Bhagabati, S.K.; Akhtar, M.S.; Singh, S.K. Important live food organisms and their role in aquaculture. Front. Aquac. 2012, 5, 69–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.H.; Park, B.H.; Lee, S.-M. Effect of feeding ratio on growth and body composition of juvenile olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus fed extruded pellets during the summer season. Aquaculture 2006, 251, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezierska, B.; Hazel, J.R.; Gerking, S.D. Lipid mobilization during starvation in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson, with attention to fatty acids. J. Fish Biol. 1982, 21, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Watanabe, T. Studies on nutritive-value of dietary lipids in fish. Effects of starvation and environmental-temperature on proximate and fatty-acid compositions of tilapia-nilotica. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1984, 50, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.; Corraze, G.; Pérez-Jiménez, A.; Larroquet, L.; Cluzeaud, M.; Panserat, S.; Oliva-Teles, A. Dietary carbohydrate and lipid source affect cholesterol metabolism of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, F.; Peres, H.; Guerreiro, I.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Oliva-Teles, A. Dietary protein requirement of sharpsnout sea bream (Diplodus puntazzo, Cetti 1777) juveniles. Aquaculture 2012, 356, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, H.; Santos, S.; Oliva-Teles, A. Lack of compensatory growth response in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles following starvation and subsequent refeeding. Aquaculture 2011, 318, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Känkänen, M.; Pirhonen, J. The effect of intermittent feeding on feed intake and compensatory growth of whitefish Coregonus lavaretus L. Aquaculture 2009, 288, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastoraki, M.; Vlahos, N.; Patsea, E.; Chatzifotis, S.; Mente, E.; Antonopoulou, E. The effect of insect meal as a feed ingredient on survival, growth, and metabolic and antioxidant response of juvenile prawn Palaemon adspersus (Rathke, 1837). Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 3551–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, J.; Bureau, D.P.; Andrade, J.P. Effects of binder type and binder addition on the growth of juvenile Palaemonetes varians and Palaemon elegans (Crustacea: Palaemonidae). Aquac. Int. 2008, 16, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Priyam, M.; Siddik, M.A.; Kumar, N.; Mishra, P.K.; Gupta, K.K.; Sarkar, B.; Sharma, T.R.; Pattanayak, A. Immunomodulation by dietary supplements: A preventive health strategy for sustainable aquaculture of tropical freshwater fish, Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822). Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 2364–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Biswas, G.; Ghoshal, T.; Kailasam, M.; Christina, L.; Vijayan, K. Current knowledge on the biology, captive breeding and aquaculture of the brackishwater catfish, Mystus gulio (Hamilton, 1822): A review. Aquaculture 2019, 499, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Pérez, S.; Rajabi Dehnavi, A.; Leszczyński, K.; Lubińska-Mielińska, S.; Ludwiczak, A.; Pierni, A. Salicornia europaea L. Functional traits indicate its optimum growth. Plants 2022, 11, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozema, J.; Schat, H. Salt tolerance of halophytes, research questions reviewed in the perspective of saline agriculture. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, M.M.; Mendes, C.R.; Doncato, K.B.; Badiale-Furlong, E.; Costa, C.S. Growth, phenolics, photosynthetic pigments, and antioxidant response of two new genotypes of sea asparagus (Salicornia neei Lag.) to salinity under greenhouse and field conditions. Agriculture 2018, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, I.; Carneiro, R.F.S.; do Nascimento Vieira, F.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Fett, R.; de Oliveira Costa, A.C.; Magallon-Barajas, F.J.; Seiffert, W.Q. Aquaponic production of Sarcocornia ambigua and pacific white shrimp in biofloc system at different salinities. Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, A.; Mariottini, G.; Gabriele, M.; Longo, V.; Souid, A.; Dauvergne, X.; Magné, C.; Foggi, G.; Conte, G.; Santin, M.; et al. Nutritional Composition and Bioactivity of Salicornia europaea L. Plants Grown in Monoculture or Intercropped with Tomato Plants in Salt-Affected Soils. Acta Hortic. 2022, 8, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreira, L.; Resek, E.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Rocha, M.I.; Pereira, H.; Bandarra, N.; da Silva, M.M.; Varela, J.; Custódio, L. Halophytes: Gourmet food with nutritional health benefits? J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 59, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winicov, I.; Bastola, D.R. Salt tolerance in crop plants: New approaches through tissue culture and gene regulation. Acta Physiol. Plant. 1997, 19, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).