Single-Shot Time-Lapse Target-Oriented Velocity Inversion Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
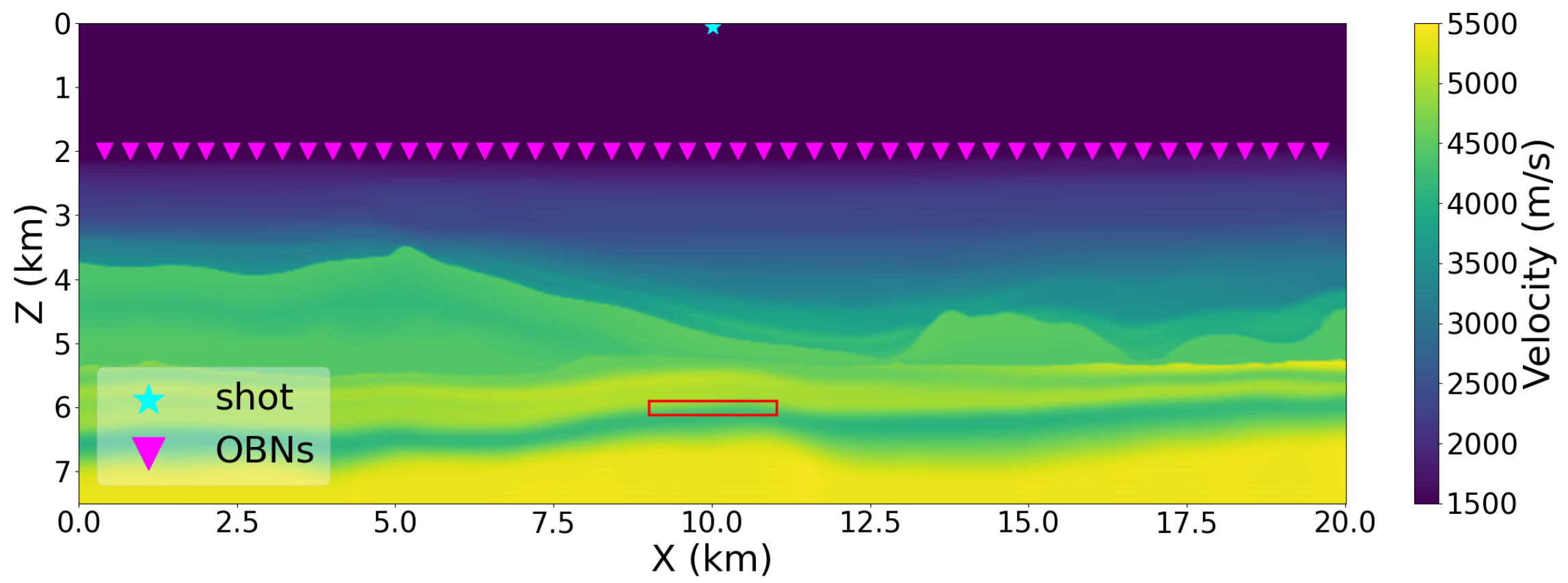
2.1. Synthetic Modeling
2.2. Reservoir Simulation
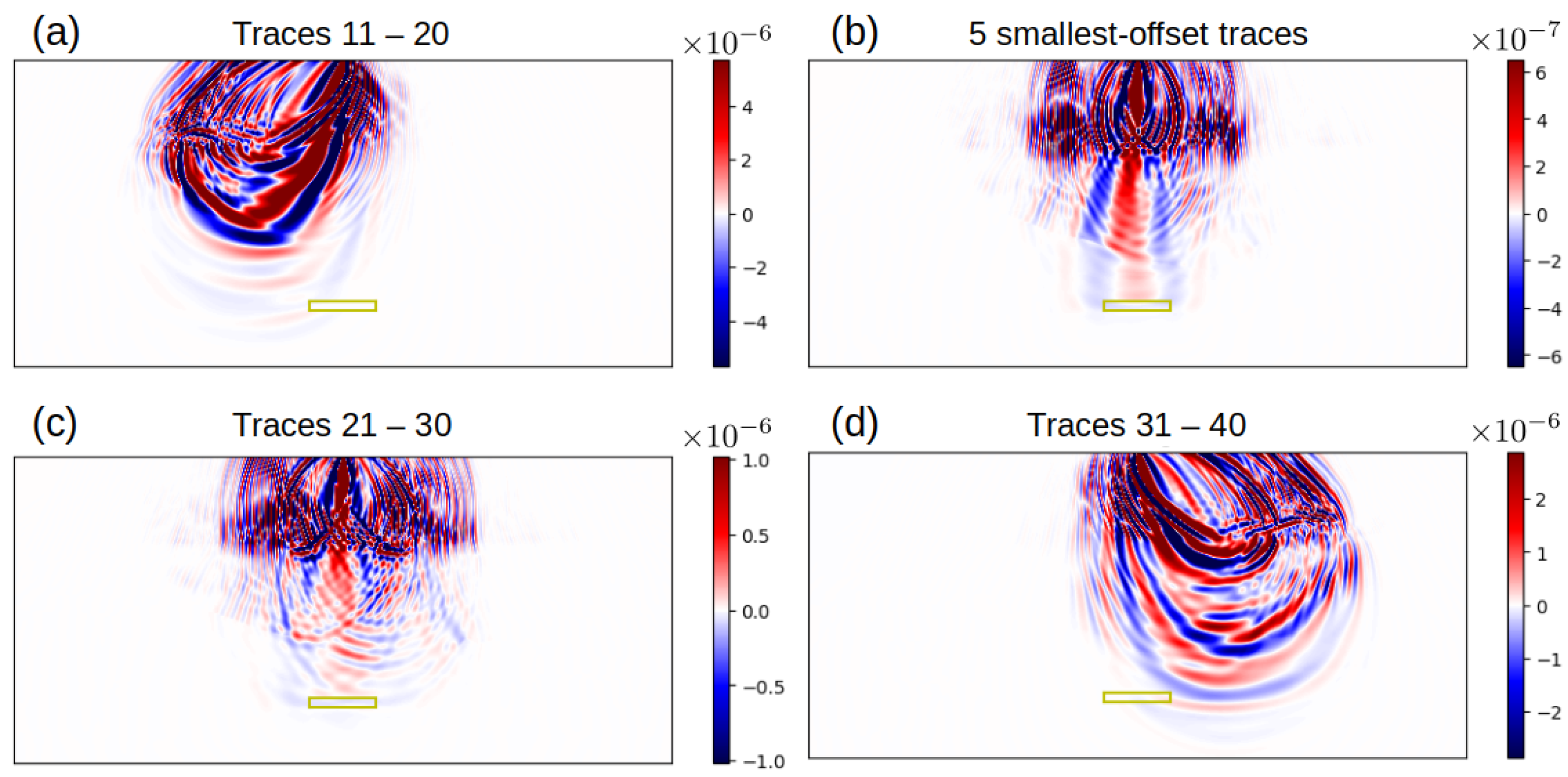
2.3. Illumination Study
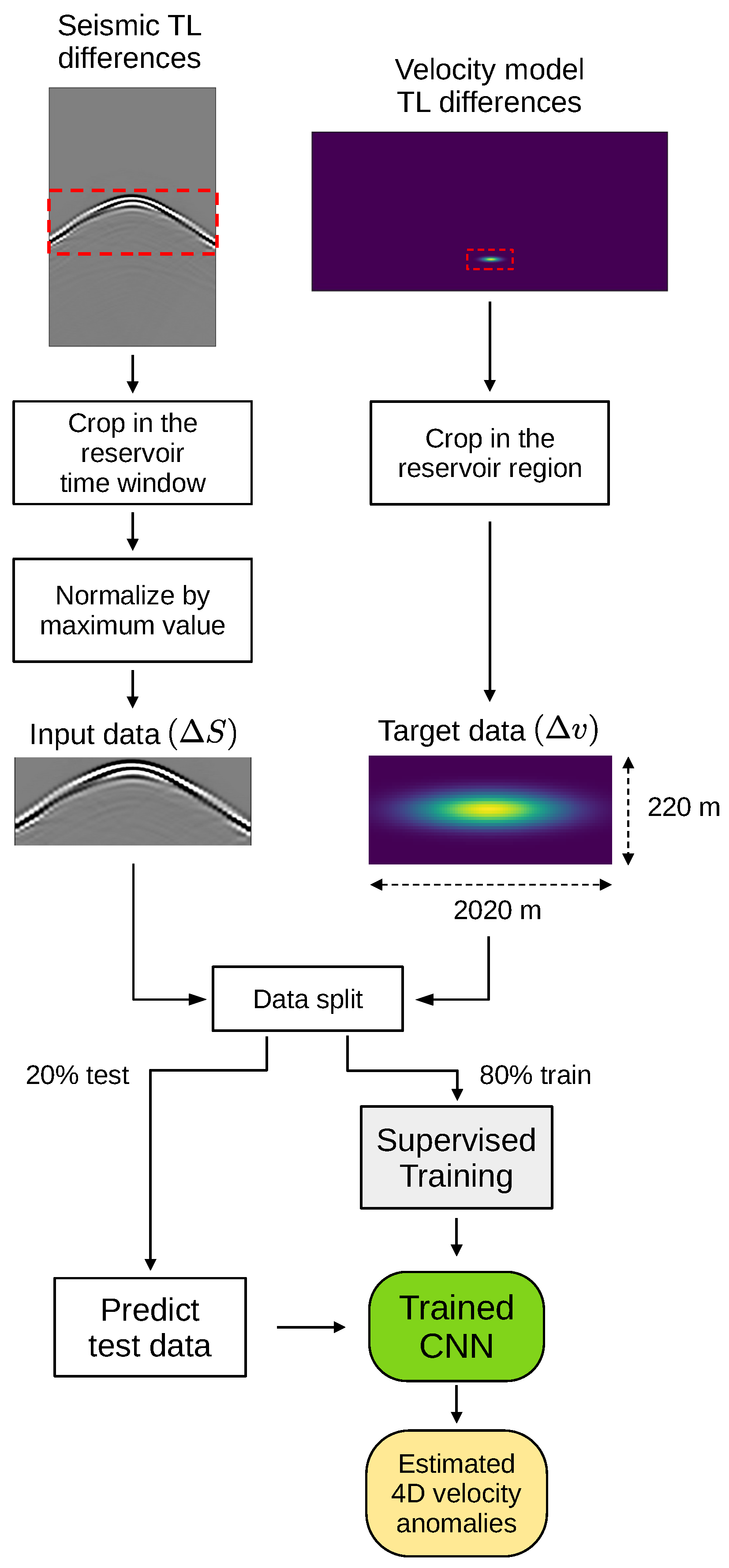
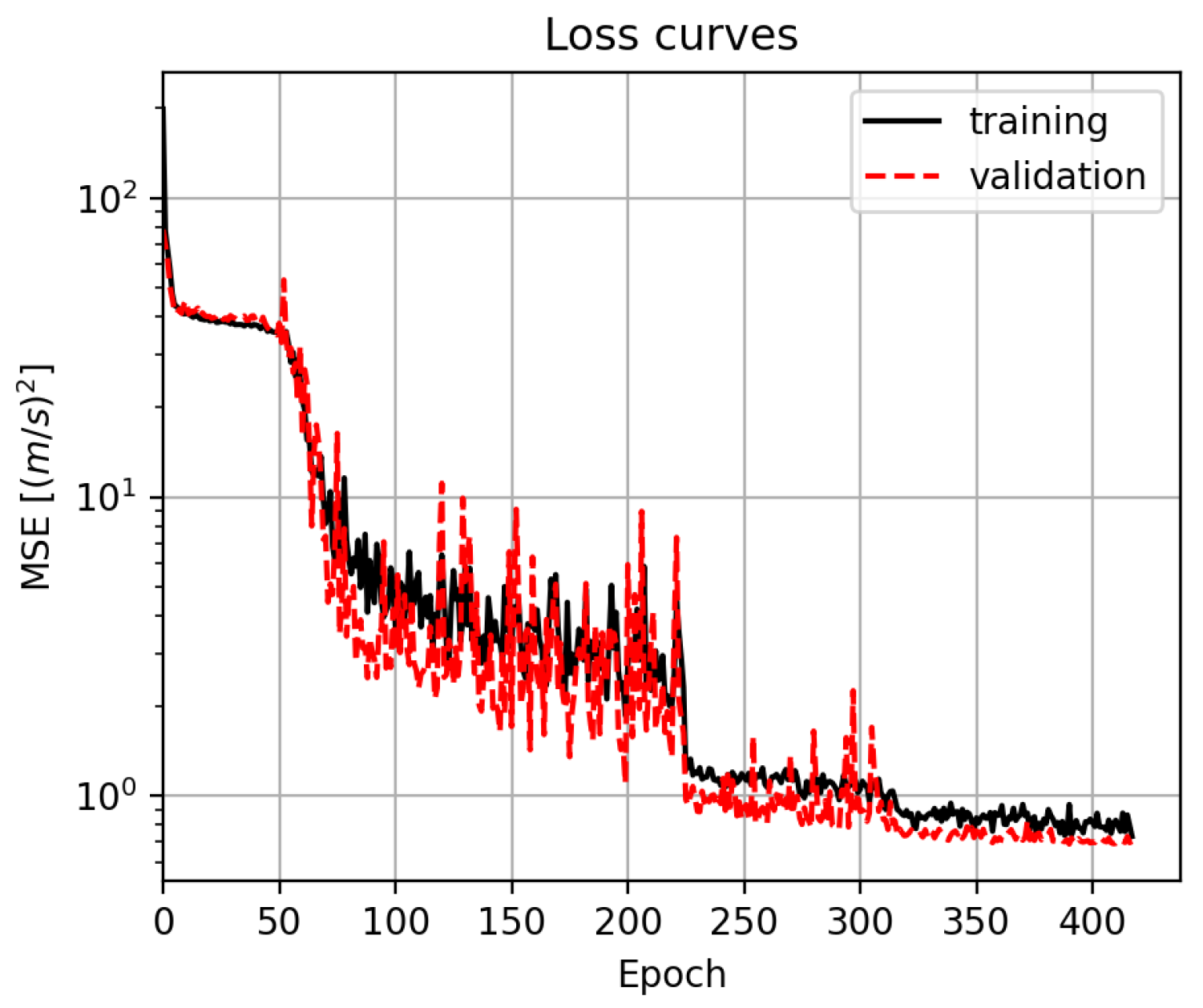
2.4. Machine Learning Training and Testing
3. Results
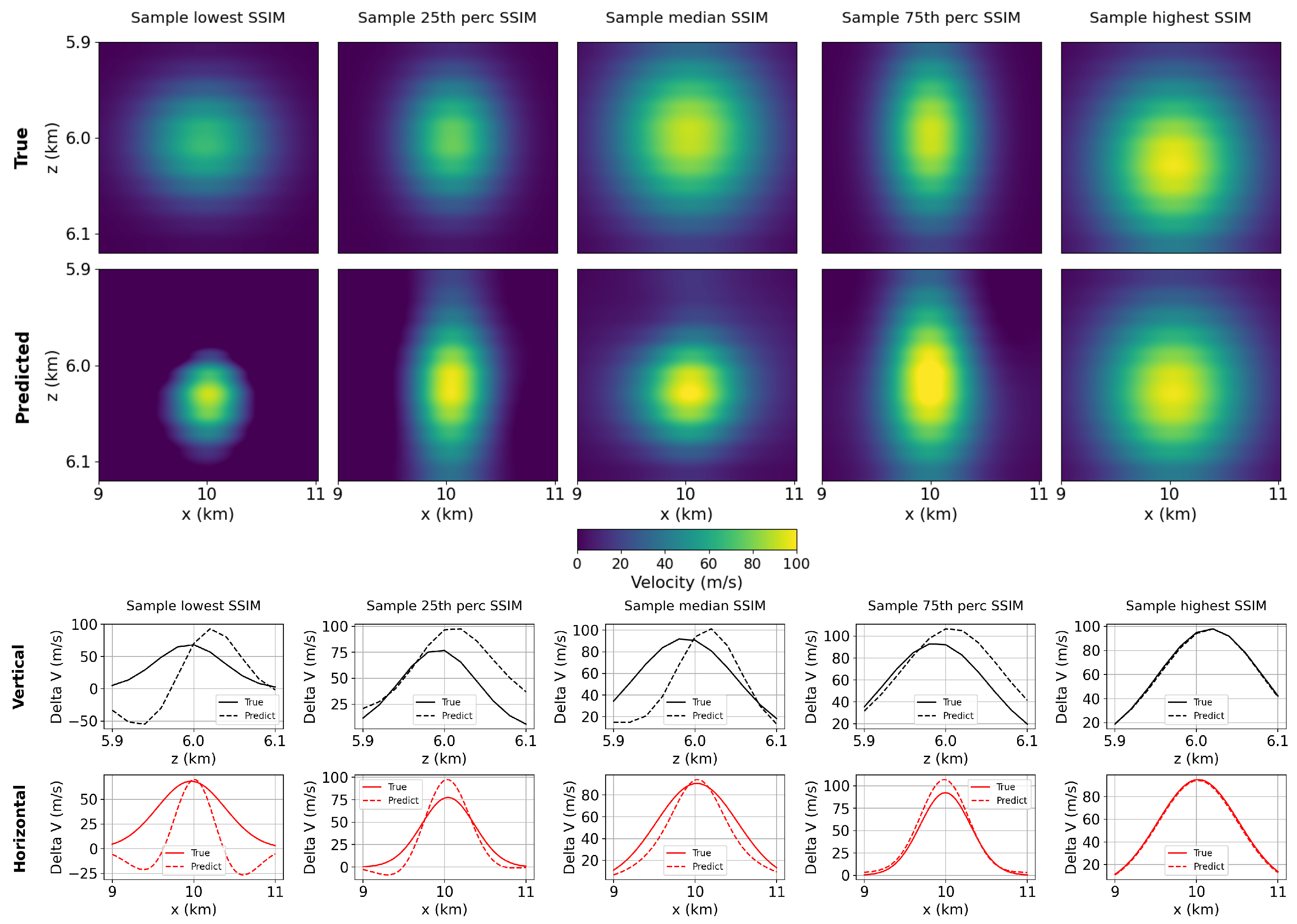
3.1. Inversion for Perfect Repeatability
3.2. Inversion in Non-Repeatability Scenarios
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnston, D.H. Practical Applications of Time-Lapse Seismic Data; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.K.T.; Nam, M.J.; Park, C. A review on time-lapse seismic data processing and interpretation. Geosci. J. 2015, 19, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Dowell, N.; Fennell, P.; Shah, N.; Maitland, G. The role of CO2 capture and utilization in mitigating climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldakheel, M.; Pevzner, R.; Gurevich, B.; Glubokovskikh, S. Seismic characterization of CO2 storage driven by time-lapse images of a prior injection using the artificial neural network. Interpretation 2021, 9, T911–T925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Roy, B. Time-lapse reservoir property change estimation from seismic using machine learning. Lead. Edge 2017, 36, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.B.; Si, H.J.; Wu, X.M.; Yan, S.S. A comparison of deep learning methods for seismic impedance inversion. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, A.; Kazei, V.; Sun, B.; Alkhalifah, T. Time-lapse data matching using a recurrent neural network approach. Geophysics 2022, 87, V405–V417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, A.; Smith, R.; Nivlet, P.; Bakulin, A.; Alkhalifah, T. Time-lapse seismic cross-equalization using temporal convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the SEG/AAPG/SEPM First International Meeting for Applied Geoscience & Energy, Denver, CO, USA, 26 September–1 October 2021; pp. 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Yuan, S.; Hatchell, P.; Vila, J.; Wang, K. Estimation of time-lapse timeshifts using machine learning. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2020; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2020; pp. 3724–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.C.F.; Corso, G.; Nascimento, H.A.D.; Souza, S.X.; Araújo, J.M.; Barros, T. Estimation of Water Velocity and Receiver Position Changes in Time-Lapse Seismic Using Machine Learning. Braz. J. Geophys. 2024, 42, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollmann, K.; Soriano-Vargas, A.; Almeida, F.; Davolio, A.; Schiozer, D.J.; Rocha, A. Convolutional Neural Network Formulation to Compare 4-D Seismic and Reservoir Simulation Models. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 3052–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Araujo, M.; Lopez, J.; Wang, K.; Kumar, G. Machine learning to reduce cycle time for time-lapse seismic data assimilation into reservoir management. Interpretation 2019, 7, SE123–SE130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Zhong, Z.; Sun, A.; Fomel, S. Time-lapse seismic data inversion for estimating reservoir parameters using deep learning. Interpretation 2022, 10, T167–T179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramsch, J.S.; Christensen, A.N.; MacBeth, C.; Lüthje, M. Deep Unsupervised 4-D Seismic 3-D Time-Shift Estimation With Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte, G.; MacBeth, C. A Physics-Based Loss Function to Constrain Neural Network Inversion of 4D Seismic Data. In Proceedings of the 82nd EAGE Annual Conference & Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 October 2021; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 2021, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Alkhalifah, T.; Guo, Q. Target-oriented time-lapse waveform inversion using deep learning-assisted regularization. Geophysics 2021, 86, R485–R495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.; Seol, S.; Byun, J. Machine Learning-Based Time-Lapse 1d Seismic Full-Waveform Inversion with Efficient Training Data Generation in a Carbon Capture and Storage Monitoring. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 238, 212852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O. Seismic Data Analysis: Processing, Inversion, and Interpretation of Seismic Data; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Seismic Inversion: Theory and Applications; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.; Duarte, E.F.; Almeida, W.; Ferreira, M.; Moura, F.A.; de Araújo, J.M. Target-oriented inversion using the patched Green’s function method. Geophysics 2021, 86, R811–R823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.; Neto, F.; Cabrera, M.; Cooke, S.; Grandi, S.; Roehl, D. Refraction seismic for pre-salt reservoir characterization and monitoring. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2020; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2020; pp. 2365–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypriano, L.; Yu, Z.; Ferreira, D.; Huard, B.; Pereira, R.; Jouno, F.; Khalil, A.; Urasaki, E.; Cruz, N.; Yin, A.; et al. OBN for pre-salt imaging and reservoir monitoring—Potential and road ahead. In Proceedings of the 16th International Congress of the Brazilian Geophysical Society, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 19–22 August 2019; Volume 318. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Seismic ray tracing in anisotropic media: A modified Newton algorithm for solving highly nonlinear systems. Geophysics 2014, 79, T1–T7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.Z.; Koltun, V. An Empirical Evaluation of Generic Convolutional and Recurrent Networks for Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01271v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géron, A. Hands-on Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras & TensorFlow, 3rd ed.; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.M. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.; Sheikh, H.; Simoncelli, E. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickett, J.E.; Lumley, D.E. Cross-equalization data processing for time-lapse seismic reservoir monitoring: A case study from the Gulf of Mexico. Geophysics 2001, 66, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, D.; Adams, D.C.; Meadows, M.; Cole, S.; Wright, R. 4D seismic data processing issues and examples. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2003; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2003; pp. 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickett, J.; Lumley, D.E. A cross-equalization processing flow for off-the-shelf 4D seismic data. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 1998; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1998; pp. 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, D. Dynamic warping of seismic images. Geophysics 2013, 78, S105–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte, G.; Dramsch, J.; Amini, H.; MacBeth, C. Keynote 5: Informing neural networks with fluid flow consistent property correlations: A 4D seismic inversion application. In Third EAGE Workshop on Practical Reservoir Monitoring; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 2021, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramsch, J.; Corte, G.; Amini, H.; Lüthje, M.; MacBeth, C. Deep Learning Application for 4D Pressure Saturation Inversion Compared to Bayesian Inversion on North Sea Data. In Proceedings of the Second EAGE Workshop Practical Reservoir Monitoring 2019, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1–4 April 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rincon, K.; Araújo, R.C.F.; Galvão, M.M.; Xavier-de-Souza, S.; de Araújo, J.M.; Barros, T.; Corso, G. Single-Shot Time-Lapse Target-Oriented Velocity Inversion Using Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142110047
Rincon K, Araújo RCF, Galvão MM, Xavier-de-Souza S, de Araújo JM, Barros T, Corso G. Single-Shot Time-Lapse Target-Oriented Velocity Inversion Using Machine Learning. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(21):10047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142110047
Chicago/Turabian StyleRincon, Katerine, Ramon C. F. Araújo, Moisés M. Galvão, Samuel Xavier-de-Souza, João M. de Araújo, Tiago Barros, and Gilberto Corso. 2024. "Single-Shot Time-Lapse Target-Oriented Velocity Inversion Using Machine Learning" Applied Sciences 14, no. 21: 10047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142110047
APA StyleRincon, K., Araújo, R. C. F., Galvão, M. M., Xavier-de-Souza, S., de Araújo, J. M., Barros, T., & Corso, G. (2024). Single-Shot Time-Lapse Target-Oriented Velocity Inversion Using Machine Learning. Applied Sciences, 14(21), 10047. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142110047






