Theory of Refraction, Ray–Wave Tilt, Hidden Momentum, and Apparent Topological Phases in Isotropy-Broken Materials Based on Electromagnetism of Moving Media
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
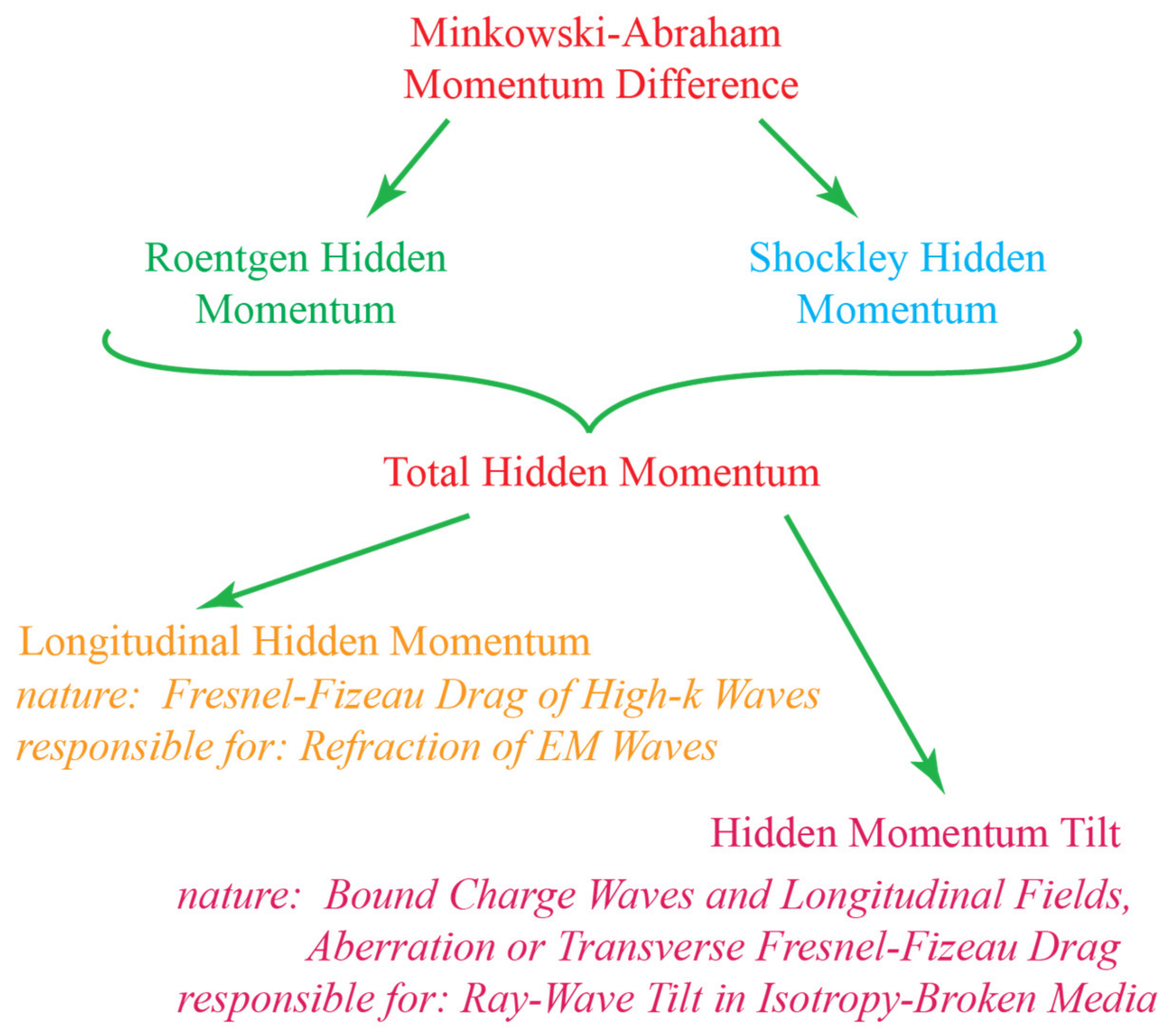
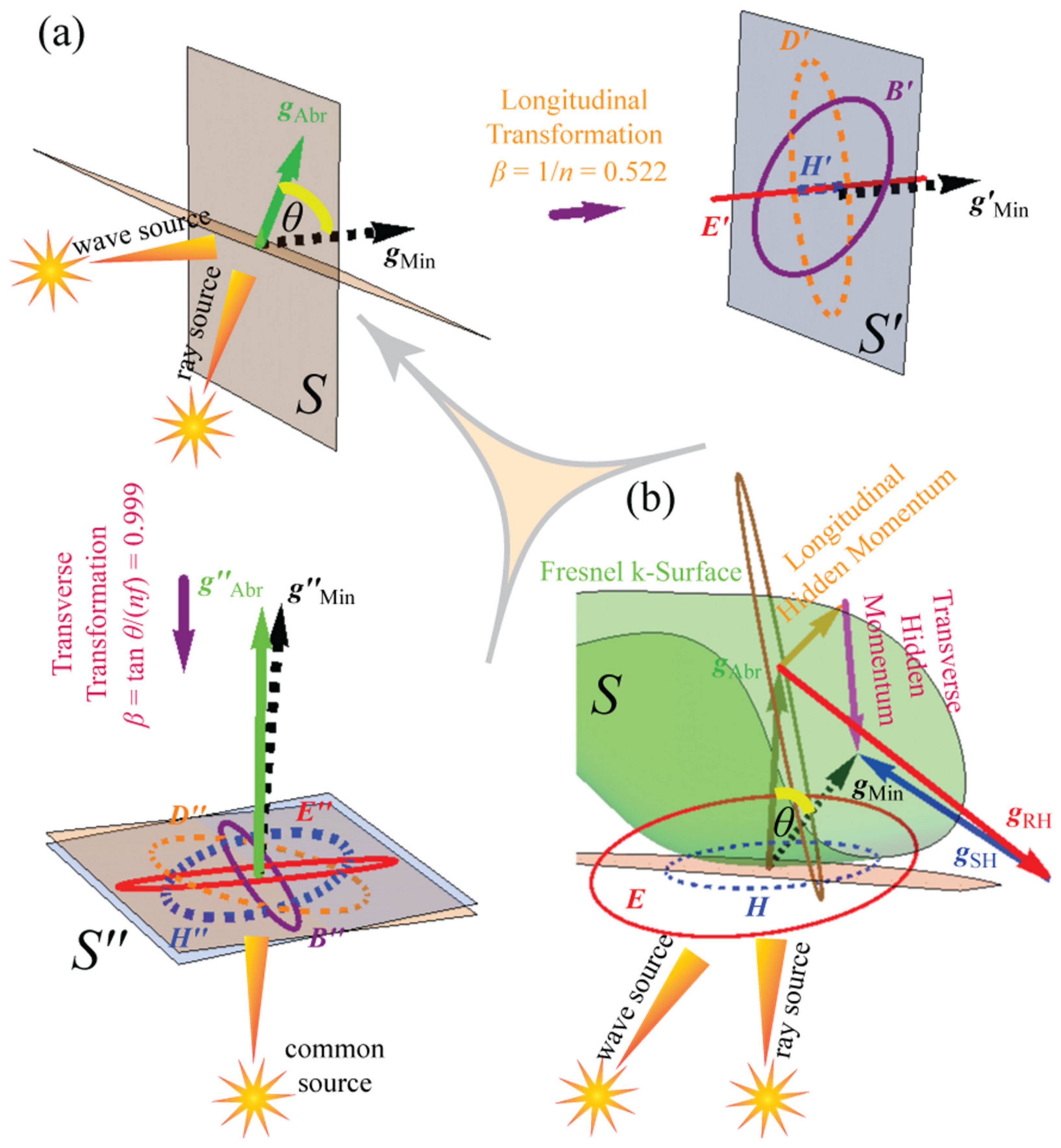
2.1. The Hidden Momentum, Refraction, Ray–Wave Tilt, and Bound Charge Waves
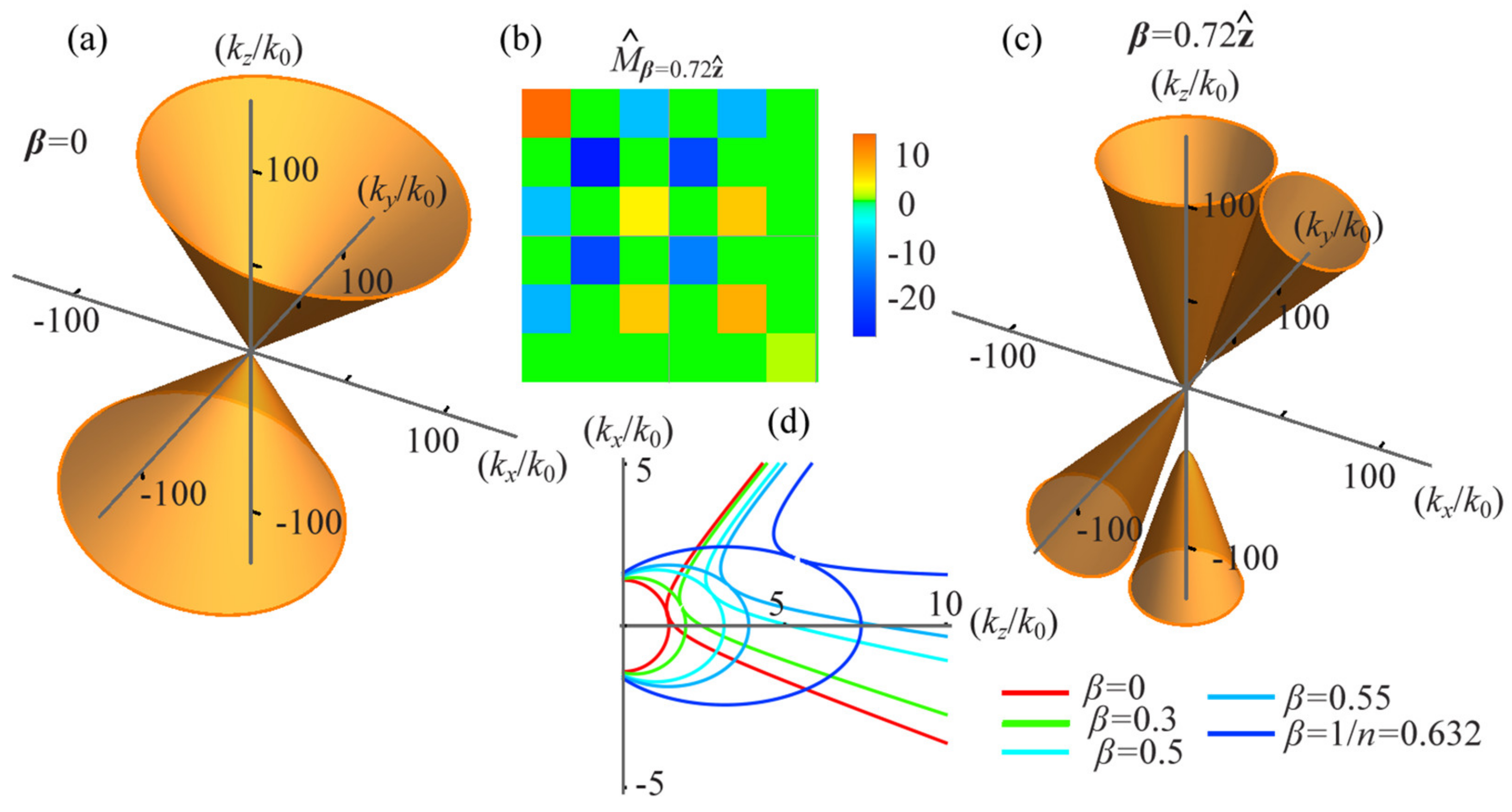
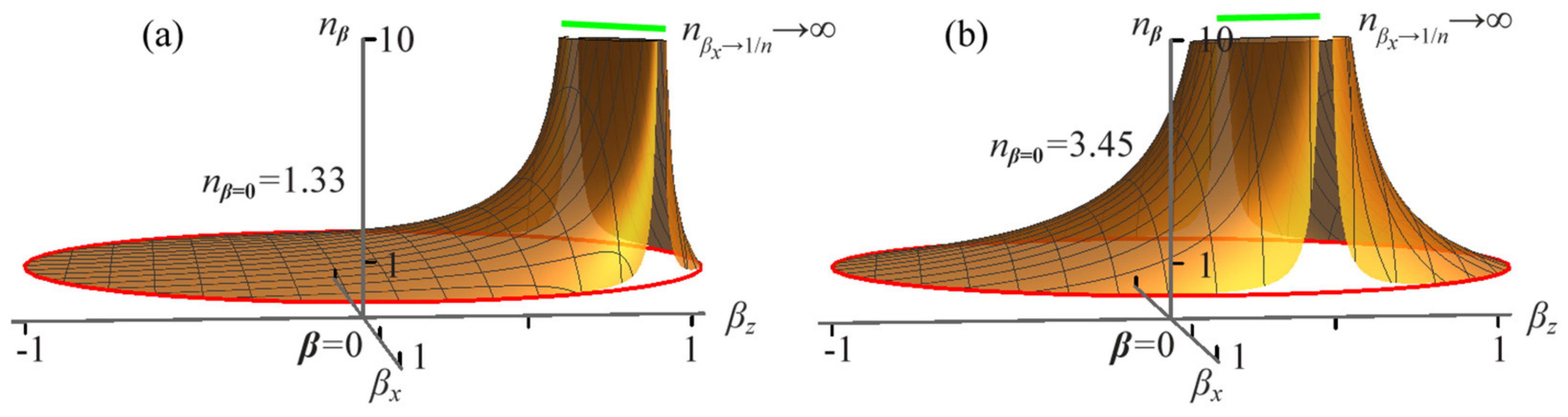
2.2. Topological Phases of Media in Moving Frames
2.3. Index of Refraction in Moving Frames and Fresnel–Fizeau Drag
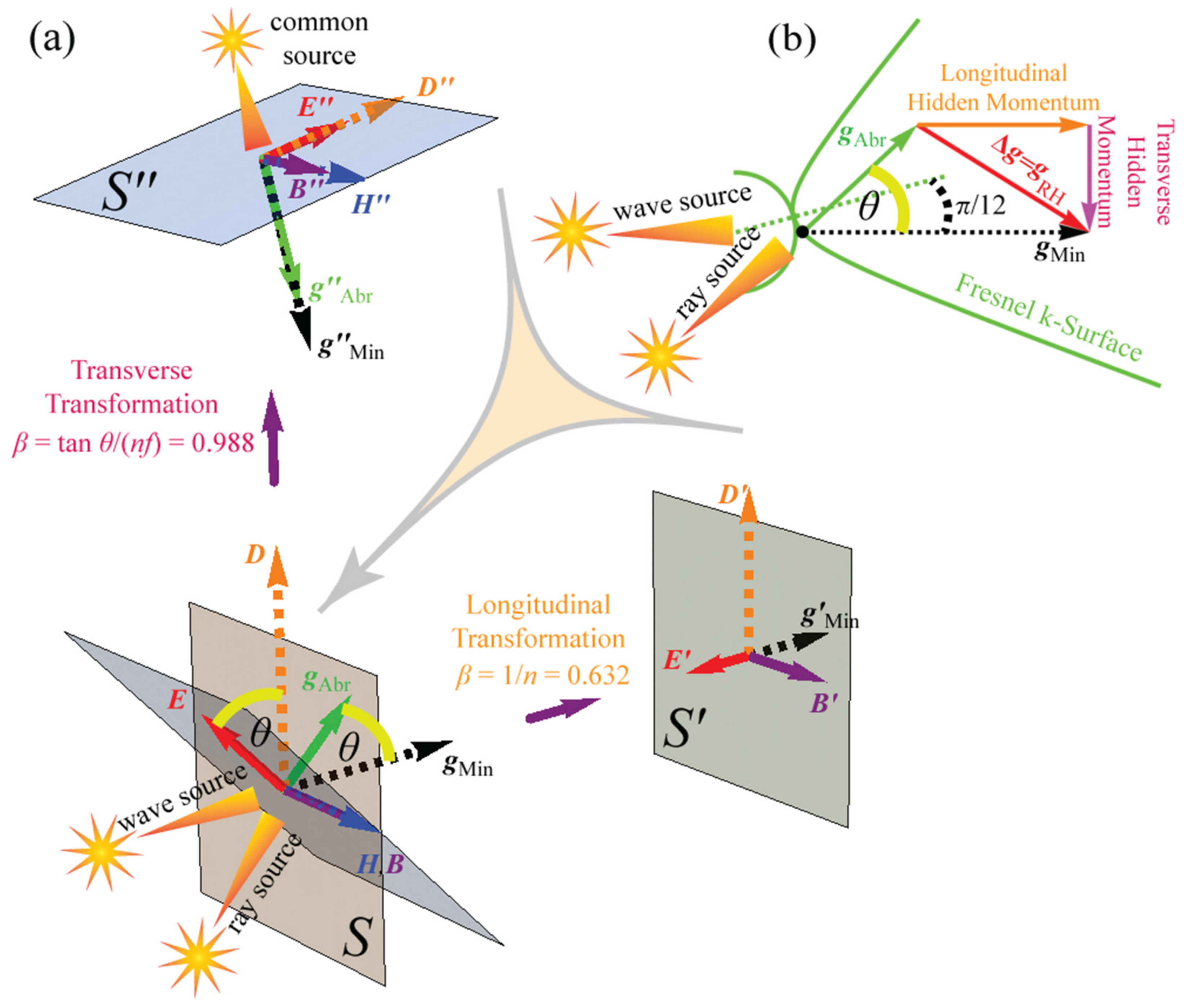
2.4. Longitudinal Hidden Momentum and High-k Waves in the Proper Darkness Frames
2.5. Transverse Hidden Momentum and Ray–Wave Tilt as Differential Aberration of Ray and Wave Sources
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wenham, G. Rethinking Genesis 1–11: Gateway to the Bible; Wipf and Stock: Eugene, OR, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, M.J. Reading and Re-Reading Scripture at Qumran; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, H.E. The optics of Euclid. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1945, 35, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, D.C. Theories of Vision from al-Kindi to Kepler; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.A. Ptolemy and the Foundations of Ancient Mathematical Optics: A Source Based Guided Study; American Philosophical Society: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999; Volume 83. [Google Scholar]
- Sabra, A.I. Ibn al-Haytham’s criticisms of Ptolemy’s Optics. J. Hist. Philos. 1966, 4, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, R. A Pioneer in Anaclastics: Ibn Sahl on Burning Mirrors and Lenses. Isis 1990, 81, 464–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.L. Al-Hazen: Father of modern optics. Al-’Arabiyya 1969, 8, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lindell, I.; Sihvola, A.; Tretyakov, S.; Viitanen, A.J. Electromagnetic Waves in Chiral and Bi-Isotropic Media; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- de Witte, A.J. Equivalence of Huygens’ principle and Fermat’s principle in ray geometry. Am. J. Phys. 1959, 27, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, G. Etienne-Louis Malus: The Polarization of Light by Refraction and Reflection is Discovered. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2009, 51, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basdevant, J.-L. Famous Optician: Augustin Fresnel and the Wave Theory of Light; Photoniques Special EOS Issue; Photoniques: Les Ulis, France, 2019; pp. 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Erasmus, B. Experiments on Birefringent Icelandic Crystal through which is Detected a Remarkable and Unique Refraction; Daniel Paulli: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1669; Volume 2039. [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker, E. History of the Theories of Aether and Electricity; Courier Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Fresnel, A. Second supplément au mémoire sur la double refraction. Œuvres 1822, 2, 369–442. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, J.G. The prediction and discovery of conical refraction by William Rowan Hamilton and Humphrey Lloyd (1832–1833). In Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy; Section A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences. Royal Irish Academy: Dublin, Ireland, 1982; pp. 231–257. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, W.R. Third Supplement to an Essay on the Theory of Systems of Rays. Trans. R. Ir. Acad. 1831, 17, v–x, 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Prati, E. Propagation in gyroelectromagnetic guiding systems. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2003, 17, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, J.D. Einstein’s investigations of Galilean covariant electrodynamics prior to 1905. Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 2004, 59, 45–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Röntgen, W.C. Ueber die durch Bewegung eines im homogenen electrischen Felde befindlichen Dielectricums hervorgerufene electrodynamische Kraft. Ann. Phys. 1888, 271, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.A., III. On the electric effect of rotating a dielectric in a magnetic field. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Phys. Character 1905, 204, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.K.; Kong, J.-A. Covariant descriptions of bianisotropic media. Proc. IEEE 1968, 56, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Electrodynamics of Continuous Media; Theoretical Physics; Fizmatlit: Moscow, Russia, 2005; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Dzyaloshinskii, I.E. On the magneto-electrical effect in antiferromagnets. J. Exp. Theoret. Phys. 1959, 37, 881–882, reprinted in Soviet Phys. JETP 1960, 10, 628–629. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, T.G.; Lakhtakia, A. Electromagnetic Anisotropy and Bianisotropy: A Field Guide; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kamenetskii, E.O. Chirality, Magnetism and Magnetoelectricity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kamenetskii, E.O. Bianisotropics and electromagnetics. arXiv 2006, arXiv:cond-mat/0601467. [Google Scholar]
- Sihvola, A.; Semchenko, I.; Khakhomov, S. View on the history of electromagnetics of metamaterials: Evolution of the congress series of complex media. Photonics Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 2014, 12, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tretyakov, S.A.; Bilotti, F.; Schuchinsky, A. Metamaterials Congress Series: Origins and history. In Proceedings of the 2016 10th International Congress on Advanced Electromagnetic Materials in Microwaves and Optics (METAMATERIALS), Crete, Greece, 19–22 September 2016; pp. 361–363. [Google Scholar]
- Pendry, J.B. Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockman, M.I. Criterion for Negative Refraction with Low Optical Losses from a Fundamental Principle of Causality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 177404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durach, M.; Williamson, R.F.; Laballe, M.; Mulkey, T. Tri-and tetrahyperbolic isofrequency topologies complete classification of bianisotropic materials. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durach, M. Tetra-hyperbolic and tri-hyperbolic optical phases in anisotropic metamaterials without magnetoelectric coupling due to hybridization of plasmonic and magnetic Bloch high-k polaritons. Opt. Commun. 2020, 476, 126349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, I.E. Relativistic crystaloptics in relation with the geometry of bi-quadratic form. J. Russ. Phys. Chem. Soc. 1925, 57, 209–214. (In Russian); reprinted in Tamm, I.E. Collected Papers; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1975; Volume 1, pp. 33–61 (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rubilar, G.F. Linear pre-metric electrodynamics and deduction of the light cone. Ann. Phys. 2002, 514, 717–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, F.W.; Obukhov, Y.N. Foundations of Classical Electrodynamics-Charge, Flux, and Metric; Birkhauser: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Durach, M.; Williamson, R.; Adams, J.; Holtz, T.; Bhatt, P.; Moreno, R.; Smith, F. On Fresnel-Airy Equations, Fabry-Perot Resonances and Surface Electromagnetic Waves in Arbitrary Bianisotropic Metamaterials. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2022, 173, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravtsov, Y.A.; Orlov, Y.I. Geometrical Optics of Inhomogeneous Media; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, F.I. Theory of Gyrotropy; Nauka i Teknika: Minsk, Belarus, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, J.C., VIII. A dynamical theory of the electromagnetic field. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1865, 155, 459–512. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedew, P. Untersuchungen über die Druckkräfte des Lichtes. Ann. Phys. 1901, 311, 433–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkowski, H. Die Grundgleichungen für die Elektromagnetischen Vorgänge in Bewegten Körpern; Nachrichten der Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften zu Göttingen, Mathematisch-Physikalische Klasse: Göttingen, Germany, 1908; pp. 53–111. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M. Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper. Rend. Circ. Mat. Palermo 1909, 28, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.M. Resolution of the Abraham-Minkowski dilemma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 070401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnleitner, M.; Barnett, S.M. The Röntgen interaction and forces on dipoles in time-modulated optical fields. Eur. Phys. J. D 2017, 71, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuripur, M. Trouble with the Lorentz Law of Force: Incompatibility with Special Relativity and Momentum Conservation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 193901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durach, M.; Noginova, N. Spin angular momentum transfer and plasmogalvanic phenomena. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 195411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strait, J.H.; Holland, G.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, C.; Ilic, B.R.; Agrawal, A.; Pacifici, D.; Lezec, H.J. Revisiting the photon-drag effect in metal films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 053903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shockley, W.; James, R.P. “Try Simplest Cases” Discovery of “Hidden Momentum” Forces on “Magnetic Currents”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1967, 18, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.J. A catalogue of hidden momenta. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2018, 376, 20180043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsler, P.; Favaro, A.; McCall, M.W. Four Poynting theorems. Eur. J. Phys. 2009, 30, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, K.T. 729 Variants of Poynting’s Theorem. In K. McDonald’s Physics Examples; Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt, U. Momentum in an uncertain light. Nature 2006, 444, 823–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, D.; LePain, M.; Durach, M. Ultimately thin metasurface wave plates. Ann. Phys. 2016, 528, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lee, H.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X. Far-field optical hyperlens magnifying sub-diffraction-limited objects. Science 2007, 315, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.A. Electromagnetic Wave Theory; J. Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, R.; Dean, C.; Durach, M. Optical neutrality: Invisibility without cloaking. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carusotto, I.; Artoni, M.; La Rocca, G.C.; Bassani, F. Transverse Fresnel-Fizeau drag effects in strongly dispersive media. Phys. Rev. A 2003, 68, 063819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durach, M. Theory of Refraction, Ray–Wave Tilt, Hidden Momentum, and Apparent Topological Phases in Isotropy-Broken Materials Based on Electromagnetism of Moving Media. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6851. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156851
Durach M. Theory of Refraction, Ray–Wave Tilt, Hidden Momentum, and Apparent Topological Phases in Isotropy-Broken Materials Based on Electromagnetism of Moving Media. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(15):6851. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156851
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurach, Maxim. 2024. "Theory of Refraction, Ray–Wave Tilt, Hidden Momentum, and Apparent Topological Phases in Isotropy-Broken Materials Based on Electromagnetism of Moving Media" Applied Sciences 14, no. 15: 6851. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156851
APA StyleDurach, M. (2024). Theory of Refraction, Ray–Wave Tilt, Hidden Momentum, and Apparent Topological Phases in Isotropy-Broken Materials Based on Electromagnetism of Moving Media. Applied Sciences, 14(15), 6851. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156851




