Tooth Surface Deviation Analysis for Continuous Generation Grinding of Internal Gears
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Calculation of the Surface of the Drum-Shaped Grinding Tool
2.1. Tooth Surface of the Internal Helical Gear
2.2. Two-Degree-of-Freedom Meshing Equation
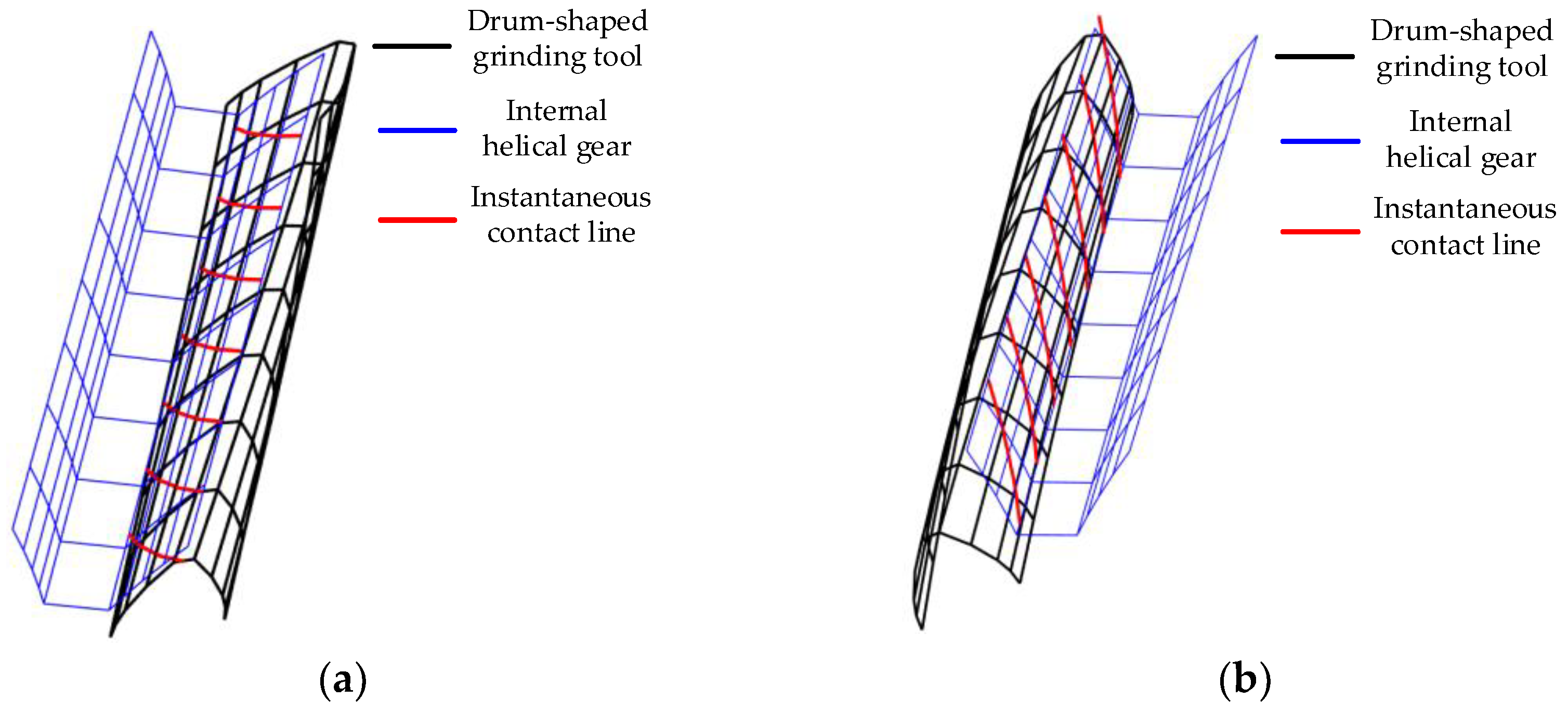
2.3. Calculation of the Transverse Face Profile of the Drum-Shaped Grinding Tool
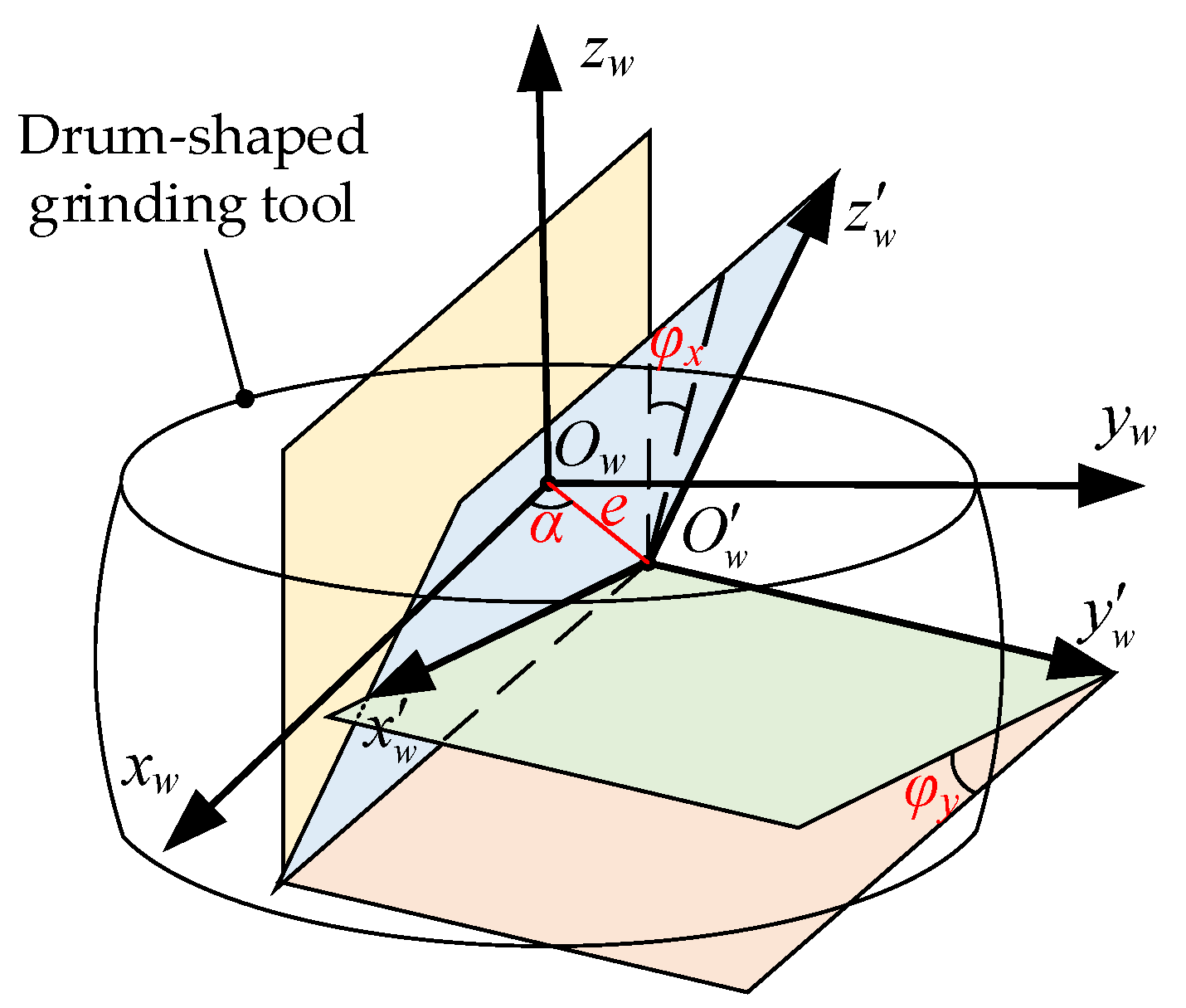
3. Establishment of the Installation Error Model for the Drum-Shaped Grinding Tool
3.1. Analysis of Drum-Shaped Grinding Tool Installation Error
3.2. Internal Helical Gear Tooth Surface Equation Derived by the Drum-Shaped Grinding Tool
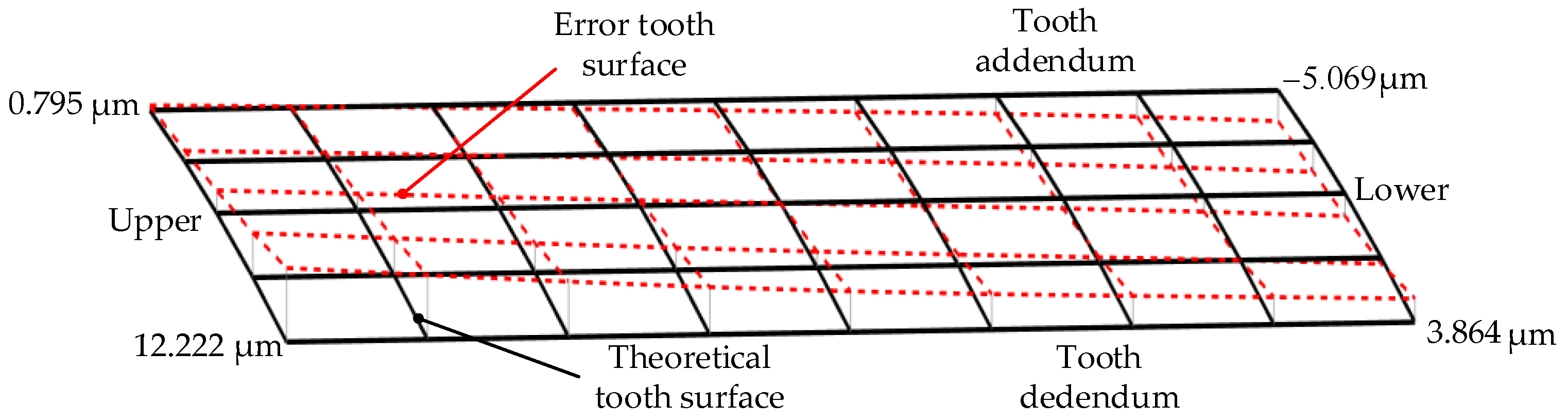
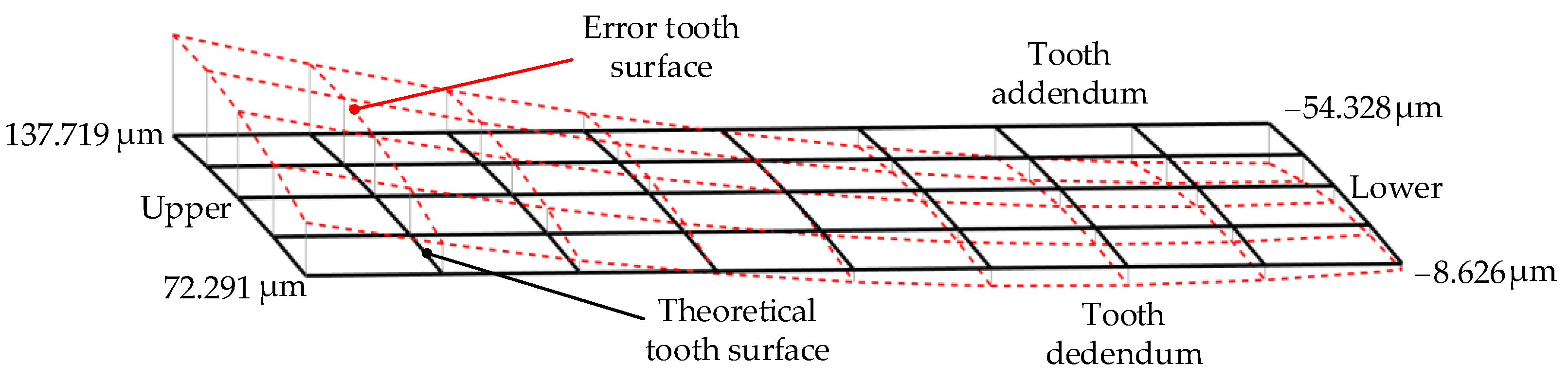
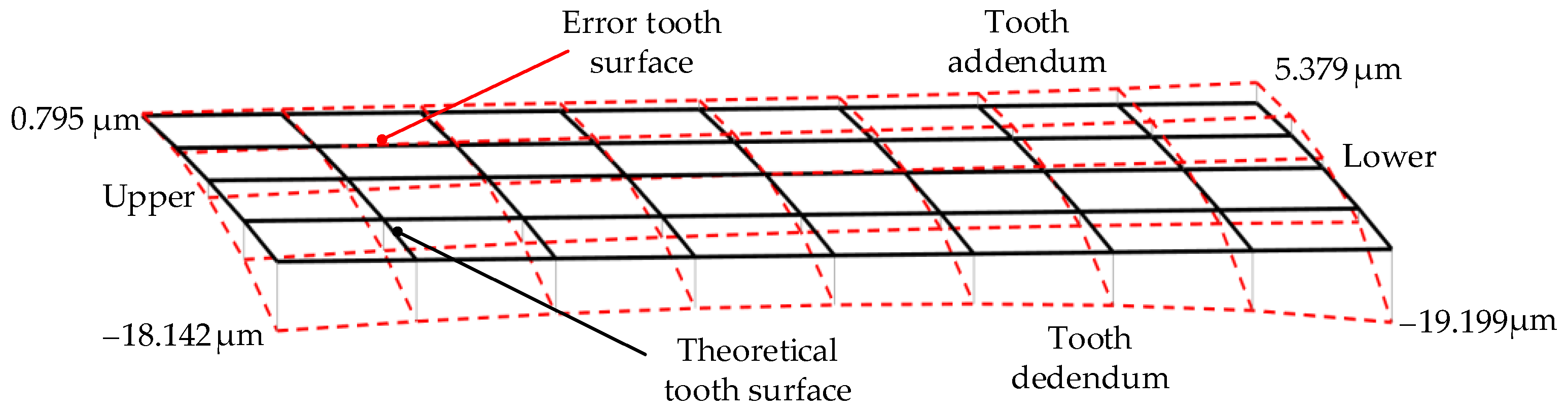
3.3. Deviation Calculation of Internal Helical Gear Tooth Surface
4. Analysis of the Impact of Drum-Shaped Grinding Tool Installation Errors on Internal Helical Gear Tooth Surface Deviation
5. Conclusions
- Based on the meshing relationship between the drum-shaped grinding tool and the internal helical gear, the transverse profile curves of the drum-shaped grinding tool are calculated, providing a computational method for the profile of the drum-shaped grinding tool suitable for mass finishing of the hardened internal helical gear.
- The distribution of the internal helical gear tooth surface deviation is analyzed in the presence of four kinds of drum-shaped grinding tool installation errors. The results indicate that varying degrees of distortion along both the tooth height and width directions on the tooth surface of the internal helical gear occur when there are installation errors in the drum-shaped grinding tool. The research provided a theoretical basis for compensating for the tooth surface of the internal helical gear.
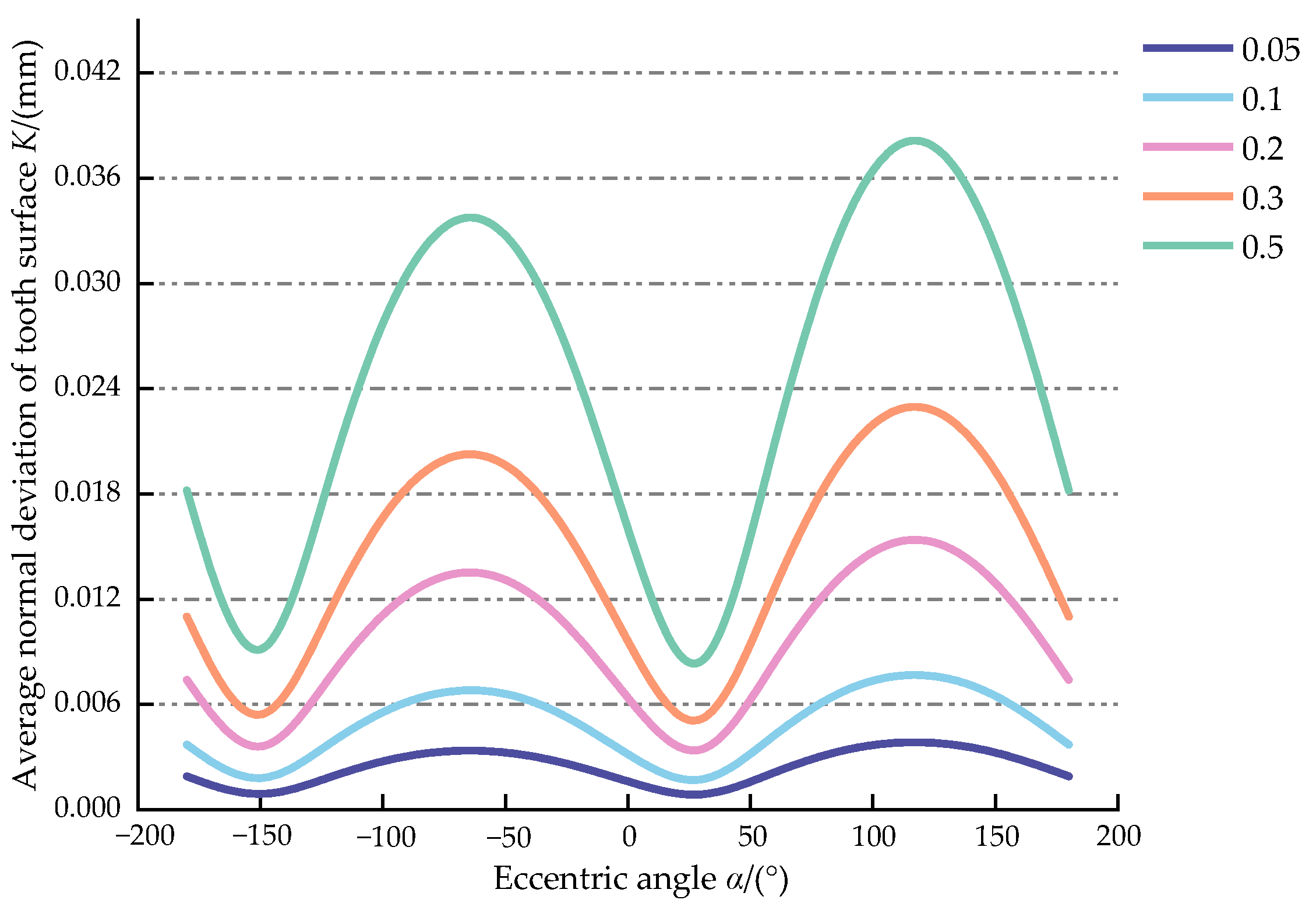
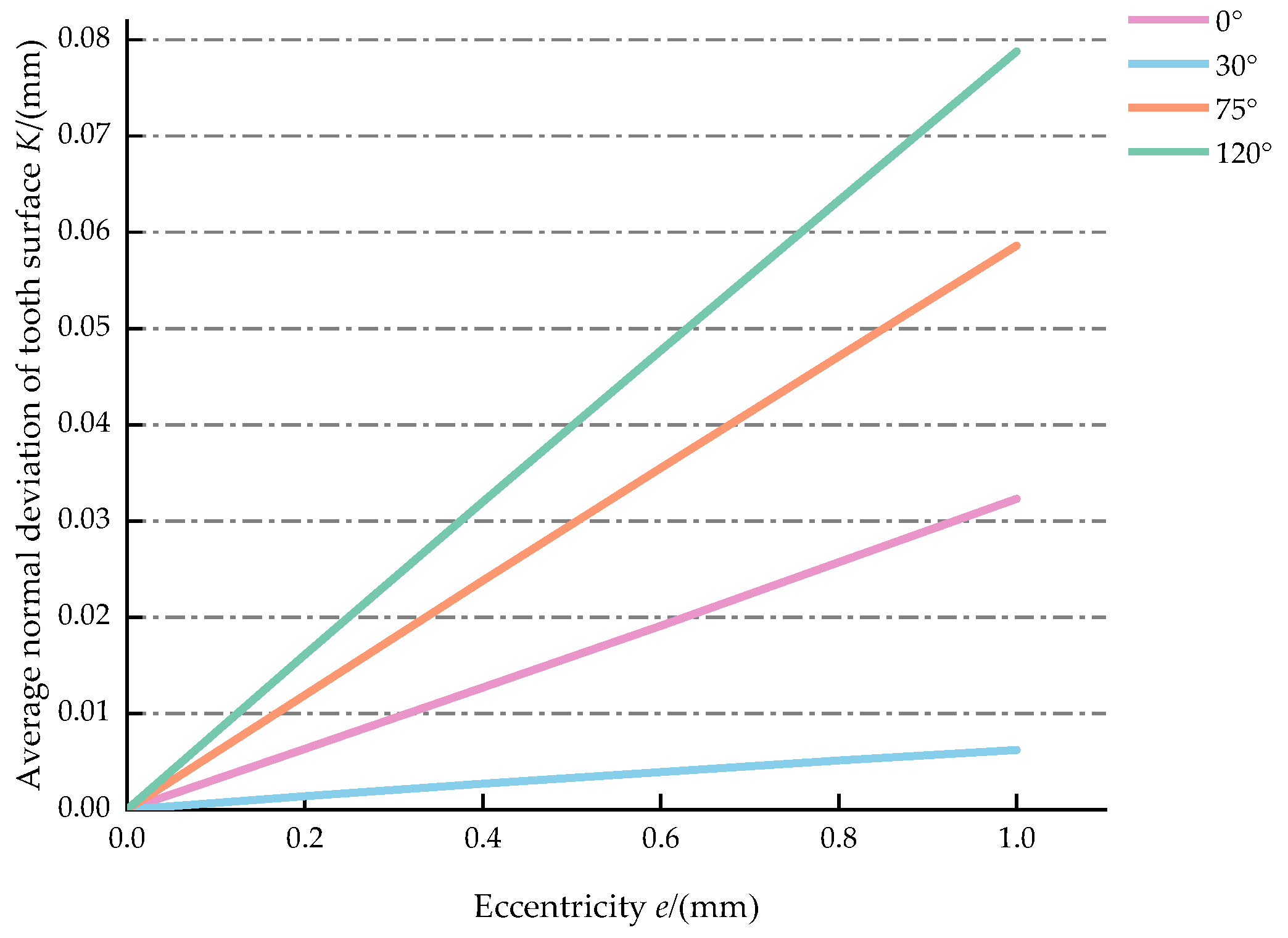
- The average normal deviation of the tooth surface shows a periodic variation when the eccentric angle changes from −180° to 180°. The sensitive directions of eccentric error occur when the eccentric angle approaches −60° and 120°, the average normal deviation of the tooth surface reaches its maximum, while the insensitive directions of eccentric error occur when the eccentric angle approaches −150° and 30°, the average normal deviation of the tooth surface reaches its minimum. The average normal deviation of the tooth surface increases linearly with the increase in the eccentricity.
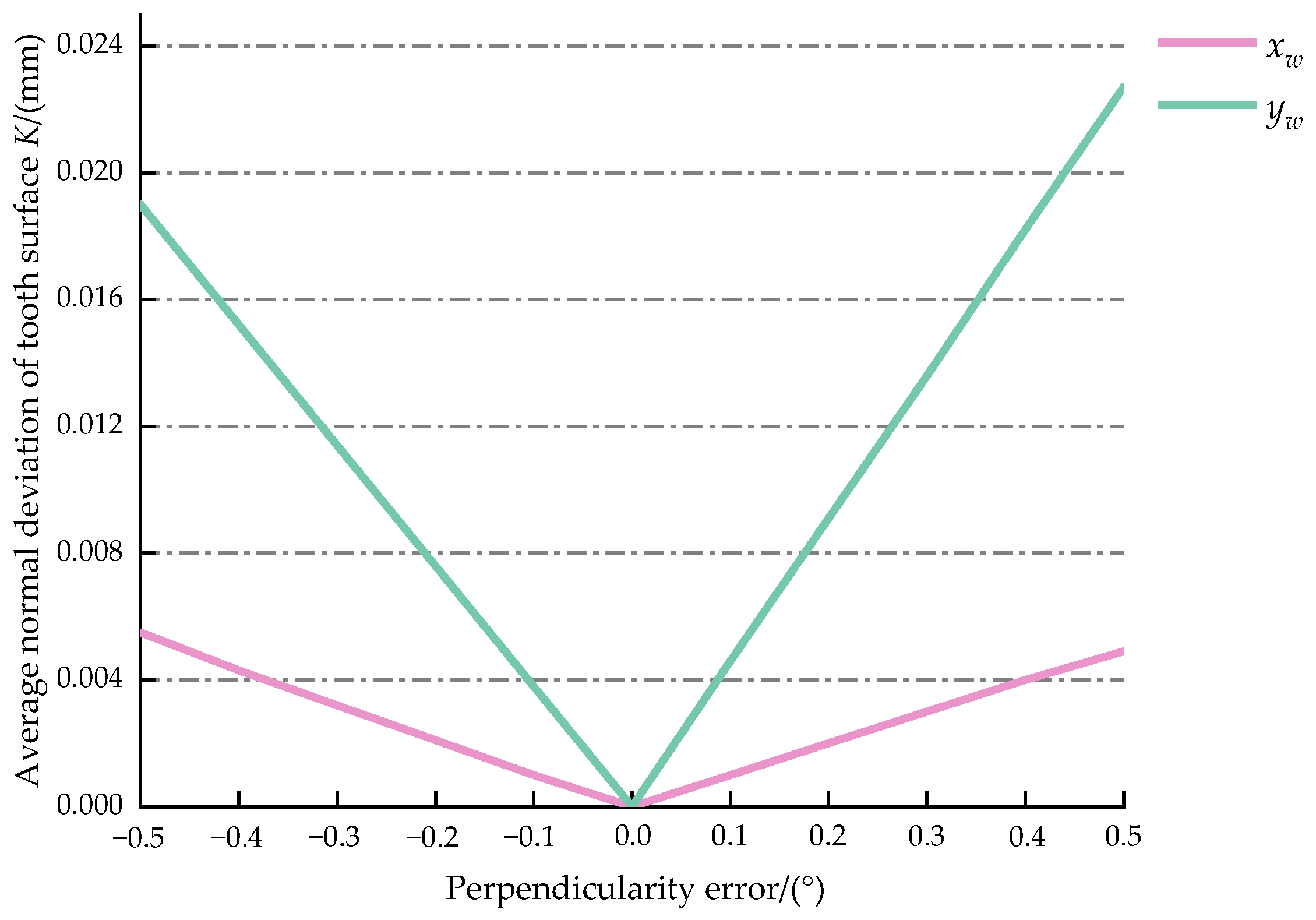
- Leaning around the yw axis is the sensitive direction of perpendicularity error. The average normal deviation of the tooth surface is linearly related to the perpendicularity error.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krajnik, P.; Hashimoto, F.; Karpuschewski, B.; da Silva, E.; Axinte, D. Grinding and fine finishing of future automotive powertrain components. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2021, 70, 589–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, N.T.; Vijayaraghavan, L. Wear of silicon carbide wheel during grinding of intermetallic titanium aluminide. Int. J. Mach. Mach. Mater. 2020, 22, 122–136. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Yue, C.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liang, S. Numerical calculation of grinding wheel wear for spiral groove grinding. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2022, 120, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, T.; Murata, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Sakakura, M.; Ohashi, K. Accurate estimation of workpiece dimension in plunge grinding without sizing gauge. Precis. Eng.-J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. 2022, 74, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MA, X.F.; Cai, Z.Q.; Yao, B.; Chen, G.F.; Liu, W.S.; Qiu, K.X. Dynamic grinding force model for face gear based on the wheel-gear contact geometry. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 306, 117633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.J.; Cai, Z.Q.; Yao, B.; Shen, Z.H.; Liu, J.C.; Huang, H.P.; Lin, B.J.; Lin, J.C.; Huang, H.B. Face gear generating grinding residual model based on the normal cutting depth iterative method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophey, M.; Klocke, F.; Loepenhaus, C. Approach for modeling grinding worm wear in generating gear grinding. Forsch. Ing. wes.-Eng. Res. 2017, 81, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Kou, H.L.; Zhao, B.Y.; Shi, Z.Y.; Sun, Y.Q.; Wu, G.Q. Approximation model for longitudinal-crowned involute helical gears with flank twist in continuous generating grinding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 114, 3675–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Li, G.L.; Alessandro, F.; Ni, H.X. Continuous generating grinding method for beveloid gears and analysis of grinding characteristics. Adv. Manuf. 2022, 10, 459–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.H. Residual stress evolution for tooth double-flank by gear form grindin. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 77, 754–769. [Google Scholar]
- Taku, U.; Terashima, K.; Sakamoto, M. Studies on the internal gear hobs-hobs working like the broach and their cutting test. Bull. JSME 1975, 18, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Mao, S.M.; Liang, H.Y.; Duan, D.S. Research and improvement of the cutting performance of skiving tool. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 120, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Mao, S.M.; Du, X.F.; Ren, Z.Y. Influences of tool setting errors on gear skiving accuracy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 3135–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C. Mathematical model for design and analysis of power skiving tool for involute gear cutting. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 101, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C. Power-skiving tool design method for interference-free involute internal gear cutting. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 164, 104396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trong, T.L.; Wu, Y.R. A Novel approach to attain tooth flanks with variable pressure and helical angles utilizing the same cutter in the CNC gear skiving process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 123, 875–902. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, Y.P.; Li, Y.J. A Novel Method for Producing a Conical Skiving Tool with Error-Free Flank Faces for Internal Gear Manufacture. J. Mech. Des. 2018, 140, 043302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, E.K.; Hong, R.J.; Huang, X.D.; Fang, C.G. Research on the design of skiving tool for machining involute gears. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 5107–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, E.K.; Hong, R.J.; Huang, X.D.; Fang, C.G. A correction method for power skiving of cylindrical gears lead modification. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 4379–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, E.K.; Hong, R.J.; Huang, X.D.; Fang, C.G. Research on the cutting mechanism of cylindrical gear power skiving. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 79, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, E.K.; Ren, N.F.; Ren, X.D.; Liu, C.X. An efficient tapered tool having multiple blades for manufacturing cylindrical gears with power skiving. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osafune, T.; Nakamura, M.; Iba, D. Tooth geometry design of cylindrical skiving cutter for internal gears: An attempt to optimization. In Proceedings of the Machine Design and Tribology Division Metting, Fukui, Japan, 18–19 April 2016; p. B4-1. [Google Scholar]
- Uriu, K.; Osafune, T.; Murakami, T.; Nakamura, M.; Iba, D.; Funamoto, M.; Moriwaki, I. Effects of shaft angle on cutting tool parameters in internal gear skiving. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 5665–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.W.; Fang, Z.L.; Kobayashi, G.; Kizaki, T.; Sugita, N.; Nishikawa, T.; Kugo, J.; Nabata, E. Influence of tool eccentricity on surface roughness in gear skiving. Precis. Eng.-J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. 2020, 63, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Guo, J.K.; Ma, T.; Wan, S.K. Mathematical modelling of power skiving for general profile base on numerical enveloping. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 116, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.C.; Yang, T.J. A study on the optimal selection of spur slice cutter parameters and machining parameters . Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, P.; Jin, Y.Q.; Hu, Q.; Chen, X.C. Cutting force calculation for gear slicing with energy method. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 83, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.C.; Li, J.; Lou, B.C. A study on the design of error-free spur slice cutter. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 68, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.C.; Li, J.; Zou, Y.; Wang, P. A study on the grinding of the major flank face of error-free spur slice cutter. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 72, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, Y.; Komori, M.; Ochi, M. Grinding of internal gears by setting a large crossed-axes angle using a barrel-shaped grinding wheel. Precis. Eng.-J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. 2018, 52, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Zhang, G.H.; Chen, B.K.; Luo, W.J.; Li, F.J.; Chen, Y. A novel enveloping worm pair via employing the conjugating planar internal gear as counterpart. Mech. Mach. Theory 2013, 67, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
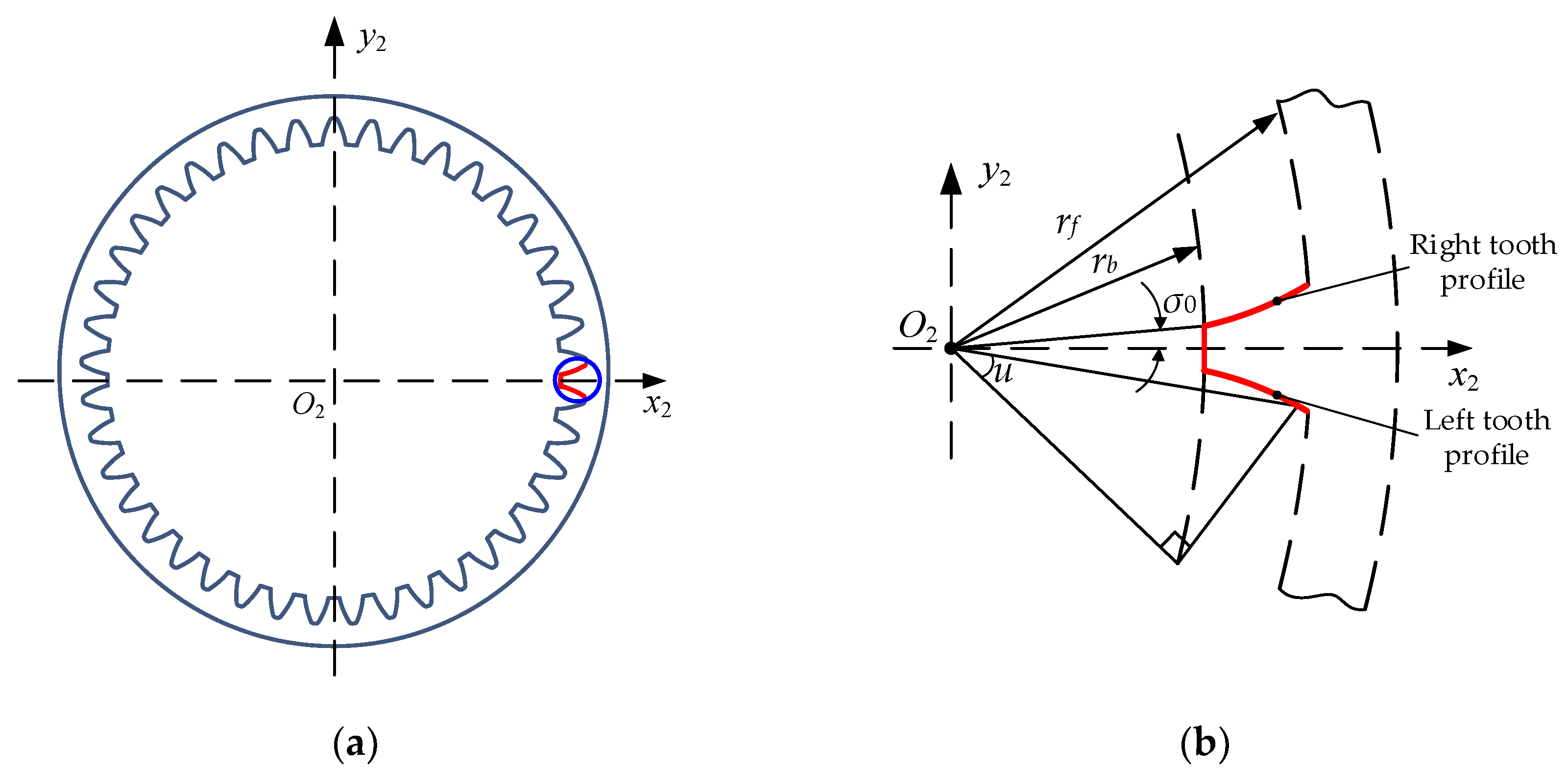
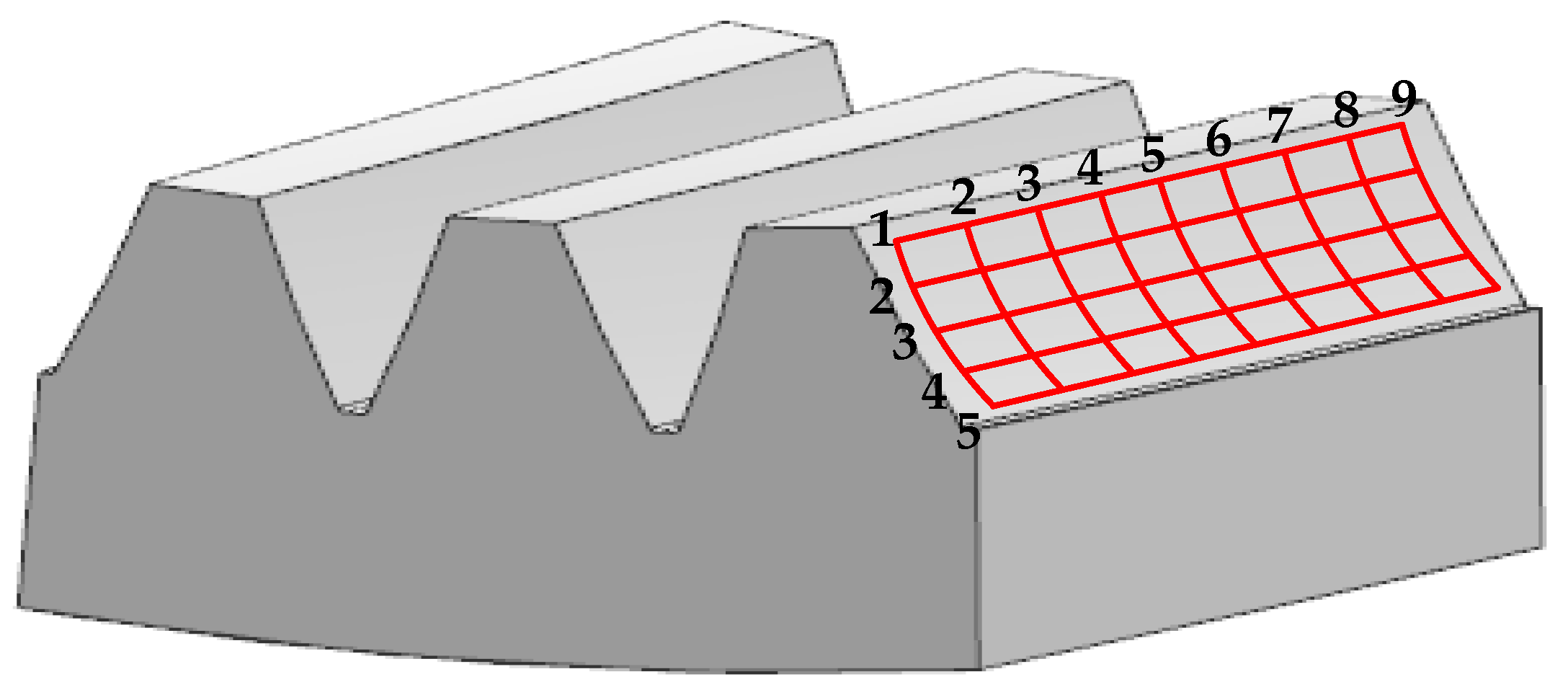
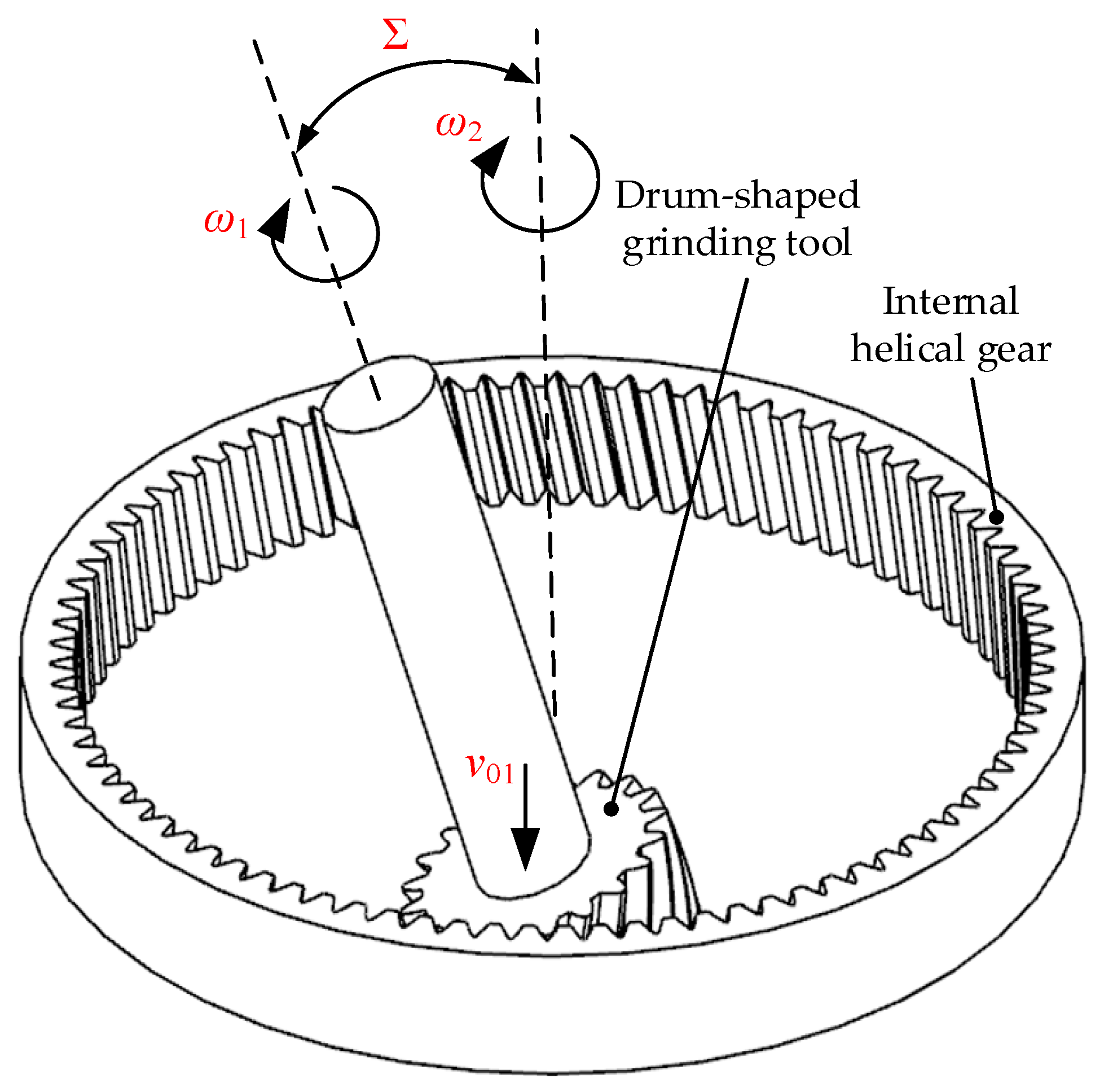
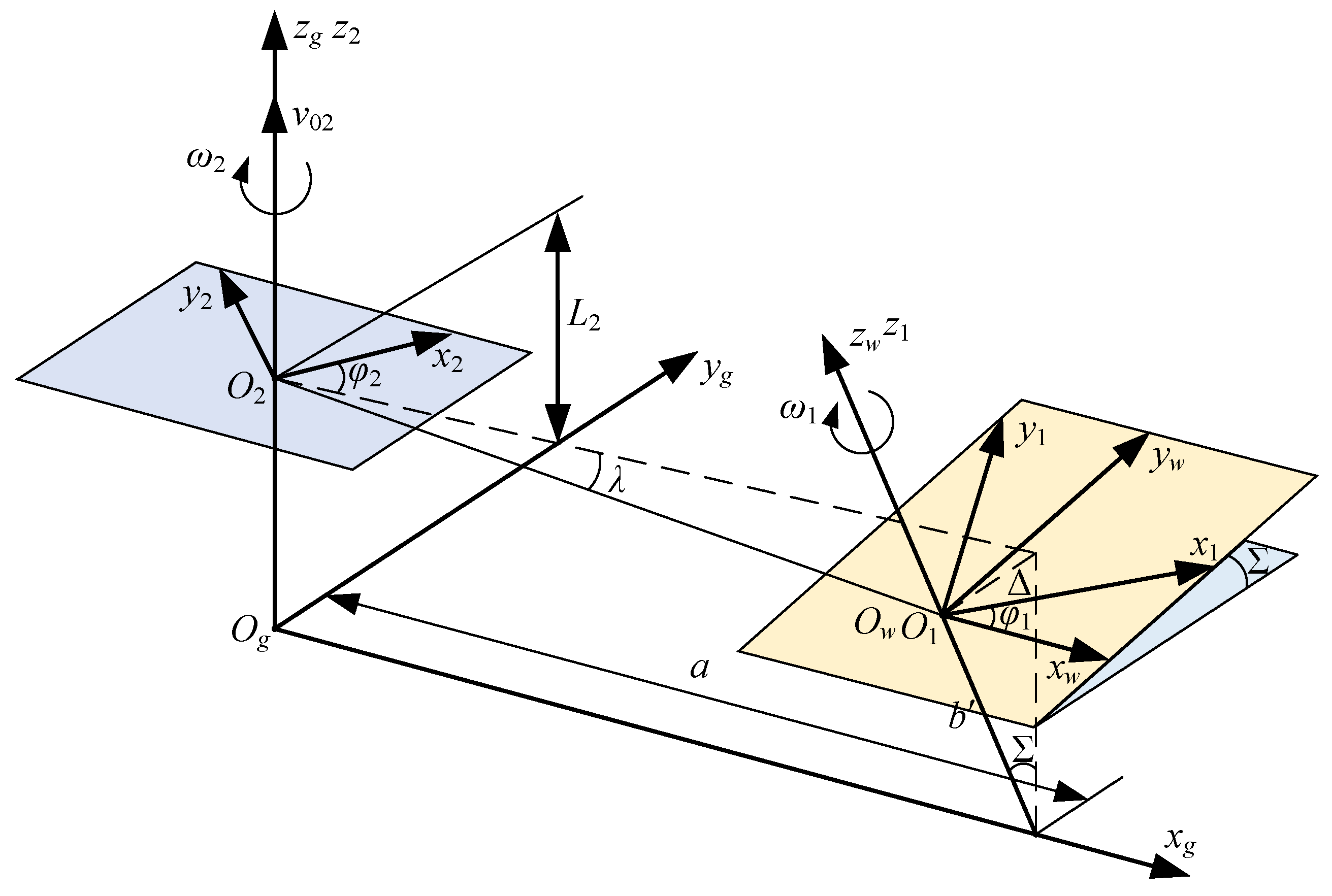


| Parameters | Internal Helical Gear | Drum-Shaped Grinding Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Module(mm) | 2.75 | |
| No. of teeth | 86 | 20 |
| Pressure angle (°) | 20 | 20 |
| Helical angle (°) | 12 | 47 |
| Modification | −0.3555 | 0.3555 |
| Hand of thread | Right-hand | |
| Shaft angle (°) | 35 | |
| Group. No | Eccentricity e (mm) | Eccentric Angle α (°) | Perpendicularity φx (°) | Perpendicularity φy (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.5 | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| B | 0.5 | 120 | 0 | 0 |
| C | 0 | 0 | −0.5 | 0 |
| D | 0 | 0 | 0 | −0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, J. Tooth Surface Deviation Analysis for Continuous Generation Grinding of Internal Gears. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156551
Yang J, Zhang Z, Wang S, Wu J. Tooth Surface Deviation Analysis for Continuous Generation Grinding of Internal Gears. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(15):6551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156551
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jianjun, Zhaolong Zhang, Shuai Wang, and Jialu Wu. 2024. "Tooth Surface Deviation Analysis for Continuous Generation Grinding of Internal Gears" Applied Sciences 14, no. 15: 6551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156551
APA StyleYang, J., Zhang, Z., Wang, S., & Wu, J. (2024). Tooth Surface Deviation Analysis for Continuous Generation Grinding of Internal Gears. Applied Sciences, 14(15), 6551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156551





