Logging Lithology Discrimination with Enhanced Sampling Methods for Imbalance Sample Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
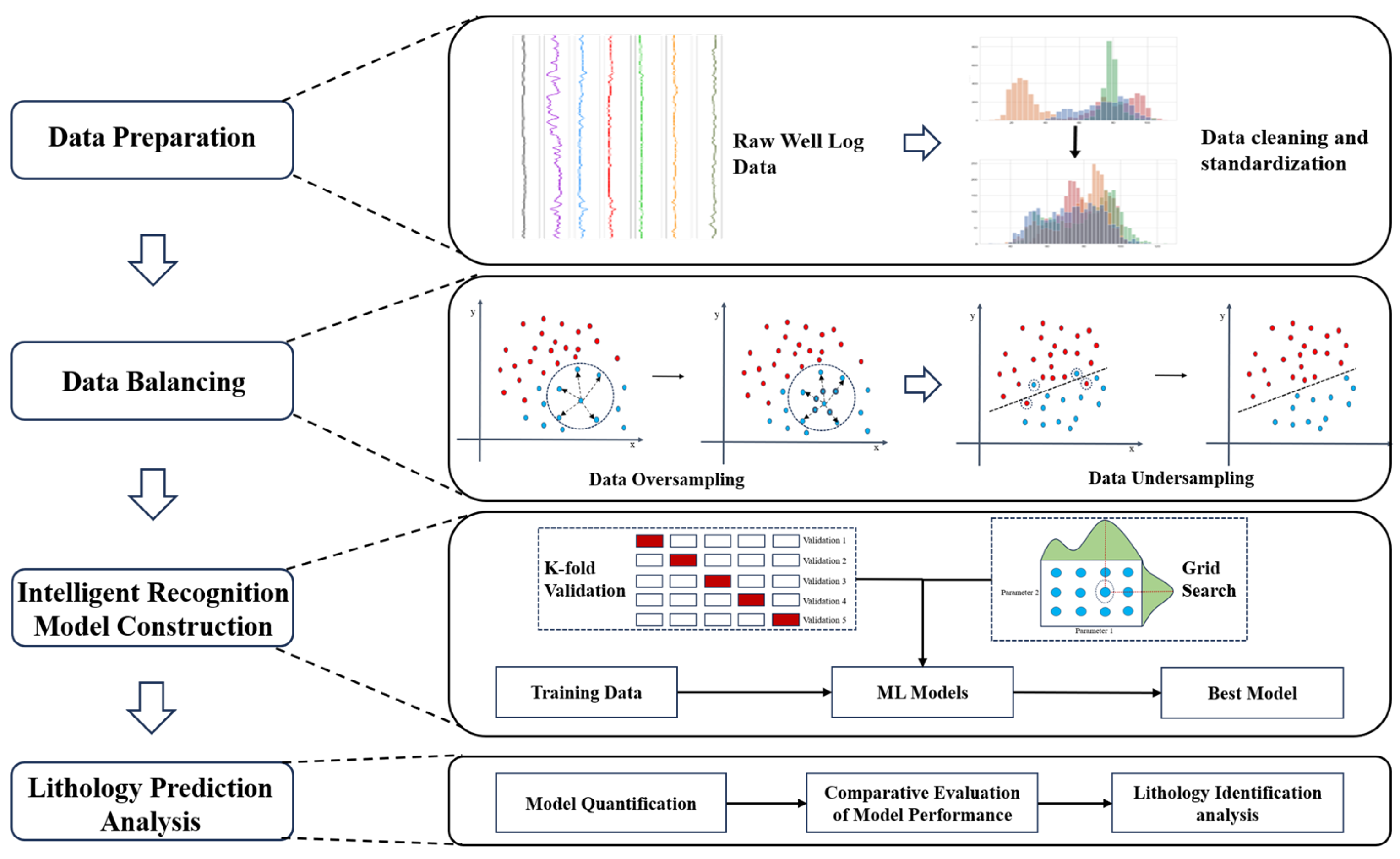
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Preprocessing
2.2. Enhanced Sampling Algorithms
2.2.1. Over-Sampling Algorithms
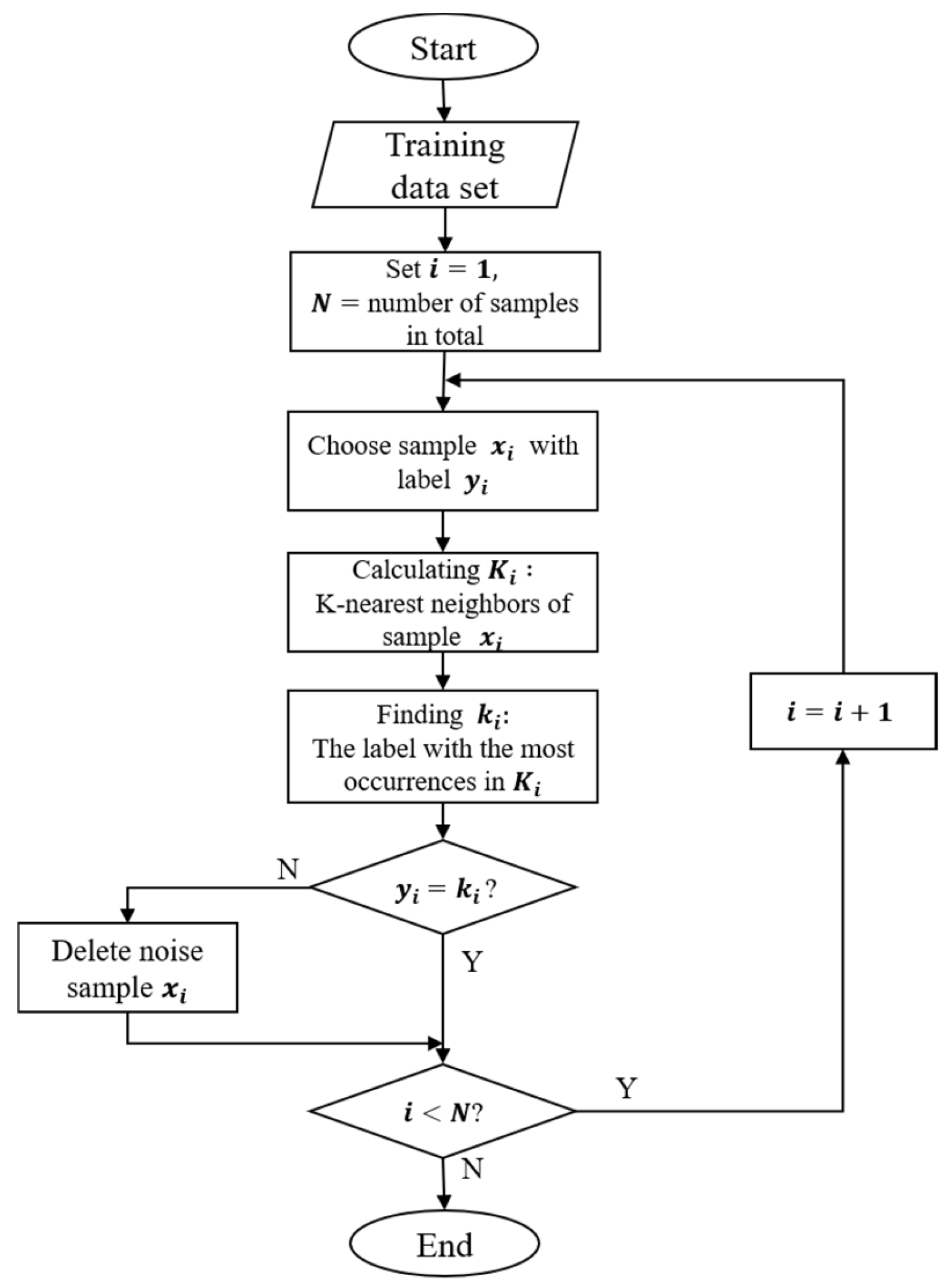
2.2.2. Under-Sampling Algorithm
2.3. Machine Learning Models
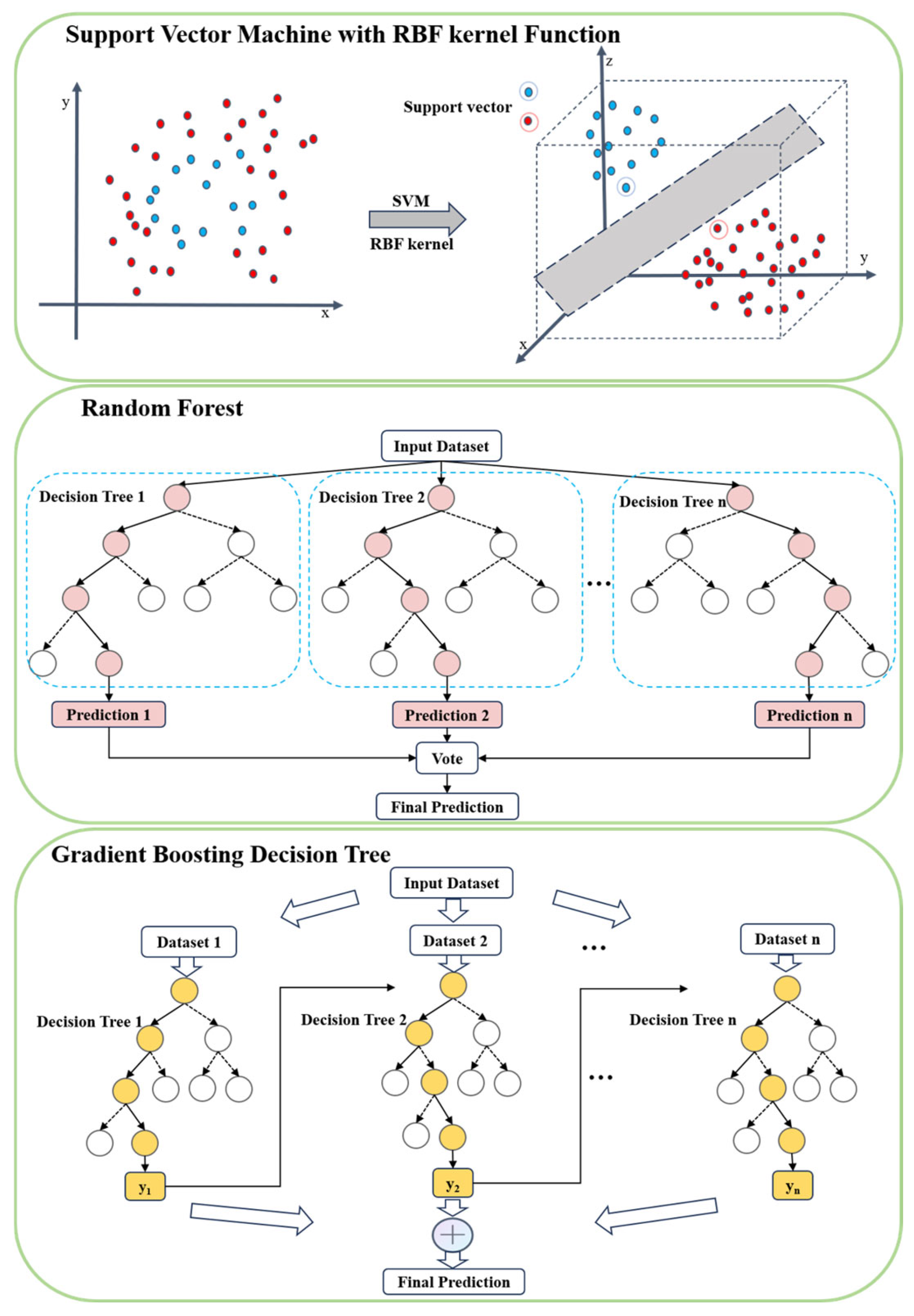
2.3.1. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
2.3.2. Random Forest (RF)
2.3.3. GBDT
2.3.4. Model Evaluation Framework
3. Results
3.1. Dataset Description
3.2. Data Preprocessing
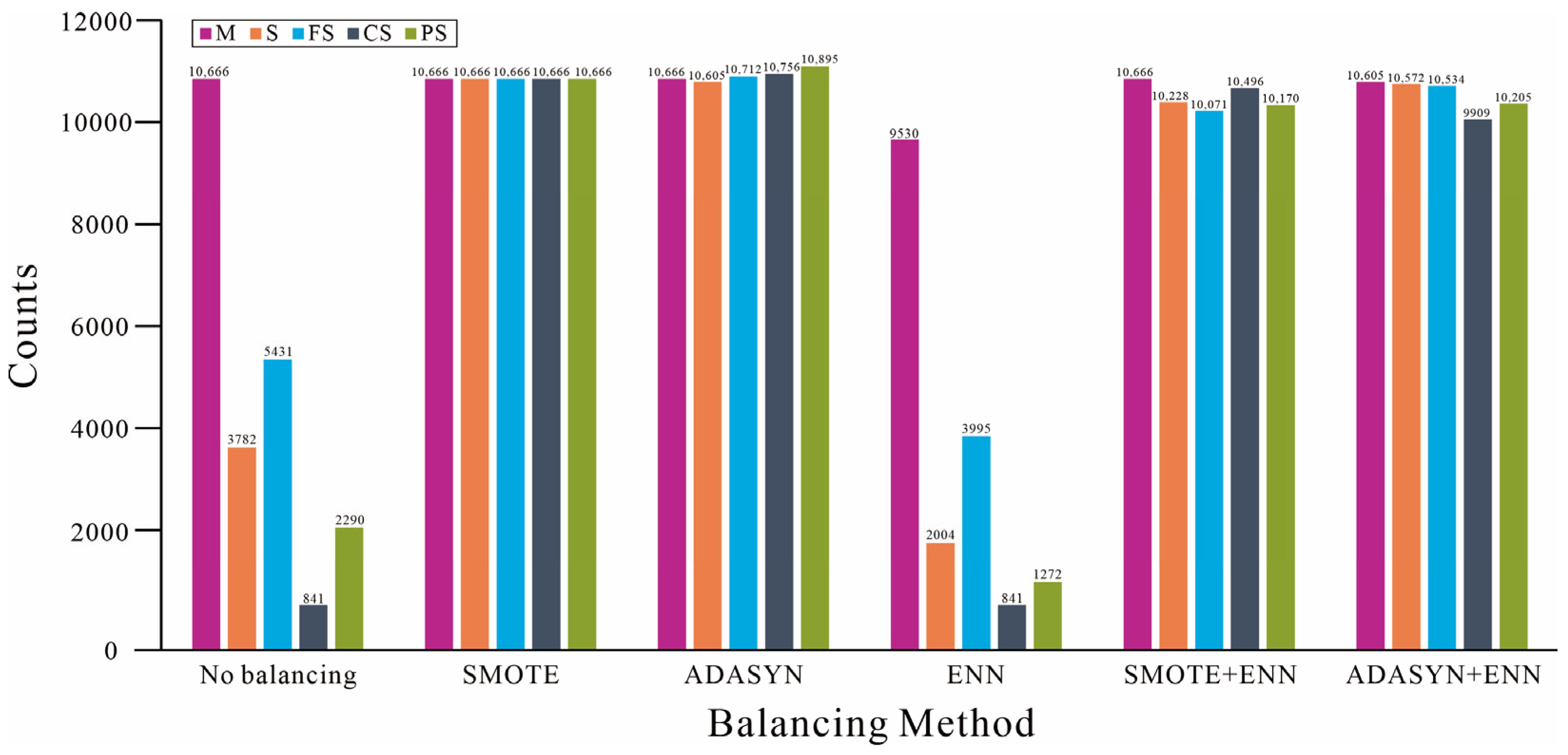
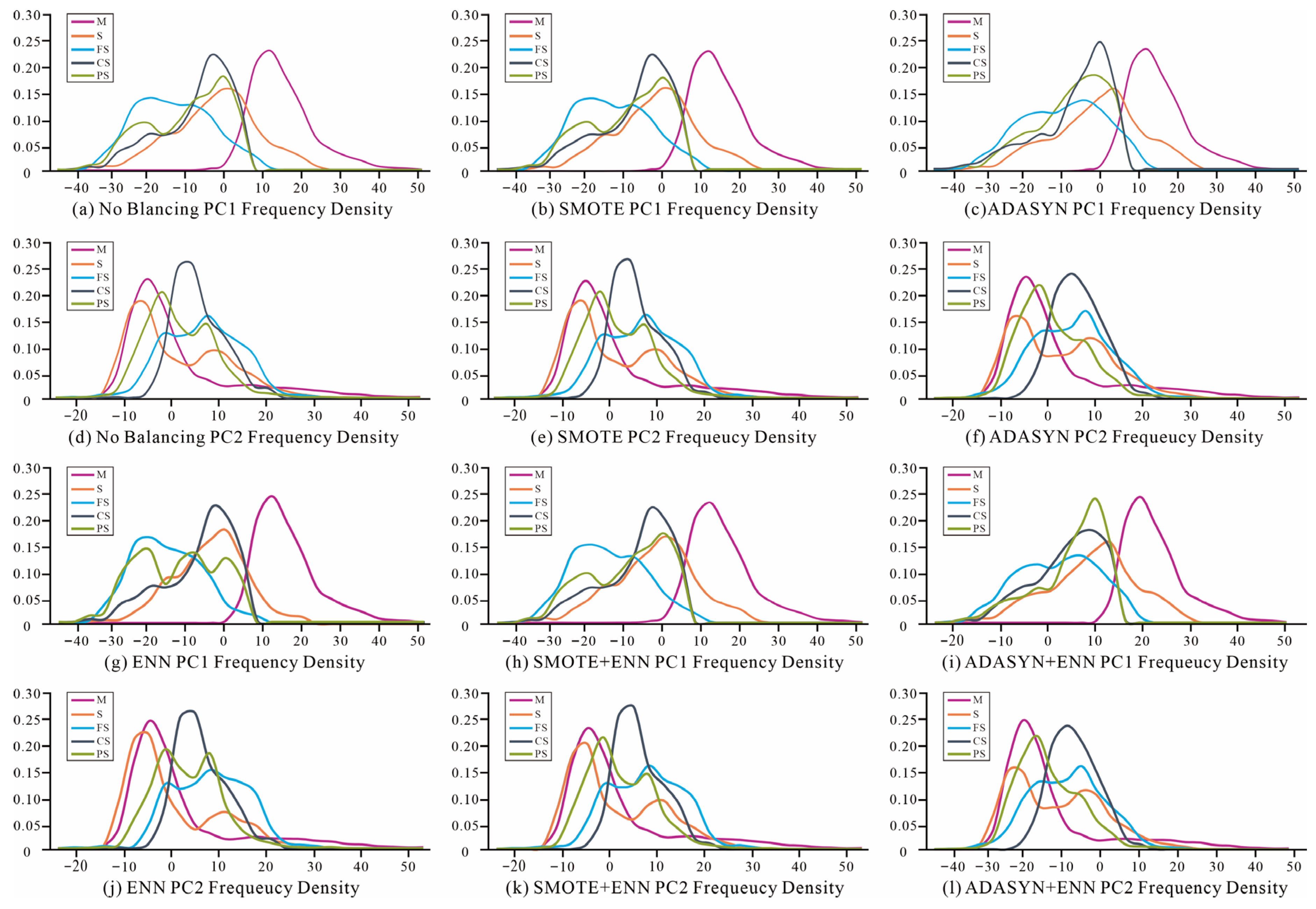
3.3. Data Balancing: Application of Enhanced Sampling Methods
3.3.1. Over-Sampling Results
3.3.2. Under-Sampling Results
3.3.3. Integrated Balancing Processing Results
3.4. Application of Intelligent Discrimination Models
3.4.1. Model Training
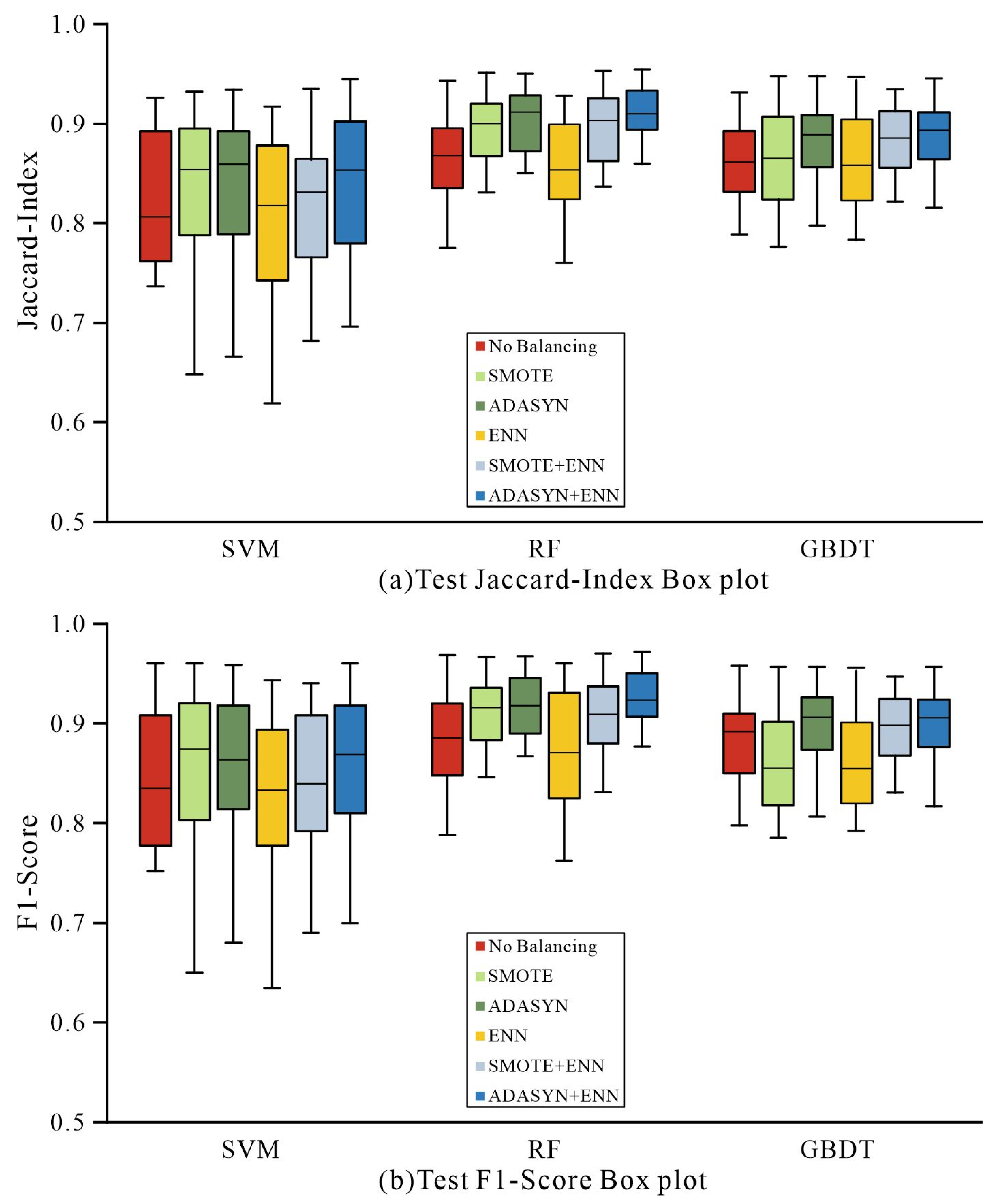
3.4.2. Model Testing
3.5. Optimal Combination of Algorithms and Models
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effectiveness of Enhanced Sampling Algorithms
4.2. Improvement of Lithology Discrimination Results
4.3. Analysis of the Lithology Discrimination Effectiveness of the Optimal Method Combination
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbr. | Full Name |
| SMOTE | Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique |
| ADASYN | Adaptive Synthetic Sampling |
| ENN | Edited Nearest Neighbours |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| RF | Random Forest |
| GBDT | Gradient Boosting Decision Tree |
References
- Zhu, R.X.; Jin, Z.J.; Di, Q.Y.; Yang, C.C.; Chen, W.X.; Tian, F.; Zhang, W.X. Research and progress of Intelligent Drilling Technology System and related theories. Chin. J. Geophys.-Chin. Ed. 2023, 66, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásconez Garcia, R.G.; Mohammadizadeh, S.; Avansi, M.C.K.; Basilici, G.; Bomfim, L.d.S.; Cunha, O.R.; Soares, M.V.T.; Mesquita, Á.F.; Mahjour, S.K.; Vidal, A.C. Geological Insights from Porosity Analysis for Sustainable Development of Santos Basin’s Presalt Carbonate Reservoir. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, Z.L.; Weng, Z.P.; Song, Y.P. A borehole clustering based method for lithological identification using logging data. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, D.; Singh, G.; Routray, A.; Mohanty, W.K.; Mahadik, R. Automatic Classification of Lithofacies with Highly Imbalanced Dataset Using Multistage SVM Classifier. In Proceedings of the IECON 2021—47th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Toronto, ON, Canada, 13–16 October 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, H.J.; Gan, W.; Chen, G. An Intelligent Inversion Method for Azimuth Electromagnetic Logging While Drilling Measurements. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 79285–79294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, M.; Ma, S.; Lu, P.; Ren, S. Massive Spatial Well Clustering Based on Conventional Well Log Feature Extraction for Fast Formation Heterogeneity Characterization. Lithosphere 2022, 2022, 7260254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saporetti, C.M.; da Fonseca, L.G.; Pereira, E.; de Oliveira, L.C. Machine learning approaches for petrographic classification of carbonate-siliciclastic rocks using well logs and textural information. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 155, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Di, Q.Y.; Jin, Q.; Cheng, F.Q.; Zhang, W.; Lin, L.M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.B.; Niu, C.K.; Li, Y.X. Multiscale geological-geophysical characterization of the epigenic origin and deeply buried paleokarst system in Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2019, 102, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Yang, H.; Yu, W. An Approach for the Classification of Rock Types Using Machine Learning of Core and Log Data. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; He, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.F.; Zhang, J.J. Well-Logging-Based Lithology Classification Using Machine Learning Methods for High-Quality Reservoir Identification: A Case Study of Baikouquan Formation in Mahu Area of Junggar Basin, NW China. Energies 2022, 15, 3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Luo, X.R.; Zhang, W. Integrated geological-geophysical characterizations of deeply buried fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoirs in Ordovician strata, Tarim Basin. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2019, 99, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Jin, Q.; Lu, X.B.; Lei, Y.H.; Zhang, L.K.; Zheng, S.Q.; Zhang, H.F.; Rong, Y.S.; Liu, N.G. Multi-layered ordovician paleokarst reservoir detection and spatial delineation: A case study in the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, Western China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2016, 69, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zheng, W.H.; Zhou, H.; Ma, Q.H.; Shen, C.G.; Ma, Q.Y.; Lan, M.J.; Liu, Y.C. “Geology-geophysics-data mining” integration to enhance the identification of deep fault-controlled paleokarst reservoirs in the Tarim Basin. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2023, 158, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, B. Automatic Identification of Sedimentary Facies Based on a Support Vector Machine in the Aryskum Graben, Kazakhstan. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Ma, C.; Tang, W.Q.; Zhou, Y.X.; Ye, S.; Chen, X.D.; Zhang, X.X.; Yu, C.Y.; Chen, A.Q.; Zheng, D.Y.; et al. DDViT: Advancing lithology identification on FMI image logs through a dual modal transformer model with less information drop. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 234, 212662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Byun, J. Selection of Augmented Data for Overcoming the Imbalance Problem in Facies Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8019405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Geisler, T.; Ray, H.; Xie, Y. Improving logistic regression on the imbalanced data by a novel penalized log-likelihood function. J. Appl. Stat. 2022, 49, 3257–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Wang, Z.X.; Cheng, F.Q.; Xin, W.; Fayemi, O.; Zhang, W.; Shan, X.C. Three-Dimensional Geophysical Characterization of Deeply Buried Paleokarst System in the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, China. Water 2019, 11, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Di, Q.Y.; Zhang, W.H.; Ge, X.M.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, C.C. A formation intelligent evaluation solution for geosteering. Chin. J. Geophys.-Chin. Ed. 2023, 66, 3975–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.X.; Liu, J.; Li, S.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, K.B.; Tang, J.Z. Channel attention-based static-dynamic graph convolutional network for lithology identification with scarce labels. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 223, 211526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, T.M.; Watada, J.; Aziz, I.A.; Hermana, M. Machine Learning in Electrofacies Classification and Subsurface Lithology Interpretation: A Rough Set Theory Approach. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S. Lithology identification from well-log curves via neural networks with additional geologic constraint. Geophysics 2021, 86, IM85–IM100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, L. A gradient boosting decision tree algorithm combining synthetic minority oversampling technique for lithology identification. Geophysics 2020, 85, WA147–WA158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Sun, P.K.; Lyu, F.; Zhu, S.C.; Zhou, R.F.; Li, B.; He, T.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Gao, Y.N.; Song, W.D.; et al. Machine learning (ML) for fluvial lithofacies identification from well logs: A hybrid classification model integrating lithofacies characteristics, logging data distributions, and ML models applicability. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 233, 212587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Meyer, R.; Jobe, Z. Centimeter-Scale Lithology and Facies Prediction in Cored Wells Using Machine Learning. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 659611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Jiang, B.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Xiao, K. A Data-Driven Approach for Lithology Identification Based on Parameter-Optimized Ensemble Learning. Energies 2020, 13, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xie, R.-H.; Xiao, L.-Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, C.-Y. Identification of low-resistivity-low-contrast pay zones in the feature space with a multi-layer perceptron based on conventional well log data. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivardhan, V. Adaptive boosting of random forest algorithm for automatic petrophysical interpretation of well logs. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2022, 57, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Tu, M. Evaluation of machine learning methods for formation lithology identification: A comparison of tuning processes and model performances. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 160, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouladmansour, A.; Ameur-Zaimeche, O.; Kechiched, R.; Heddam, S.; Wood, D.A. Integrating drilling parameters and machine learning tools to improve real-time porosity prediction of multi-zone reservoirs. Case study: Rhourd Chegga oilfield, Algeria. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 223, 211511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, K.; Wen, C.; Sheng, G.; He, J.; Tian, H. Multi-scale spatiotemporal feature lithology identification method based on split-frequency weighted reconstruction. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 226, 211794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Guo, S.; Yang, Z. Probabilistic logging lithology characterization with random forest probability estimation. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 144, 104556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zeng, L.; Du, X.; He, J.; Sun, F. Lithofacies identification in carbonate reservoirs by multiple kernel Fisher discriminant analysis using conventional well logs: A case study in a oilfield, Zagros Basin, Iraq. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 210, 110081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, X. Lithology identification using principal component analysis and particle swarm optimization fuzzy decision tree. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2023, 220, 111233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hasan, R.; Saberi, M.H.; Riahi, M.A.; Manshad, A.K. Electro-facies classification based on core and well-log data. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2023, 13, 2197–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Sharma, A.; Patidar, A.K. Evaluation and Development of a Predictive Model for Geophysical Well Log Data Analysis and Reservoir Characterization: Machine Learning Applications to Lithology Prediction. Nat. Resour. Res. 2022, 31, 3195–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Gu, B. A Lithology Recognition Network Based on Attention and Feature Brownian Distance Covariance. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wang, G. Research on imbalanced data classification based on L-SMOTE and SVM. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2019, 55, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Hong, Y.; Zhou, X. Synthetic Method of Label—Balancing Samples for Classifier Learning. Comput. Appl. Softw. 2022, 39, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Huang, Z.; Yin, J. Data Generation Model-based Synthetic Sample Imputation Method. J. Syst. Simul. 2023, 35, 1948–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Li, M.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Shao, H.; Yu, C.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, D. Shale lithology identification using stacking model combined with SMOTE from well logs. Unconv. Resour. 2022, 2, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Pan, H.; Fang, S.; Konaté, A.A.; Qin, R. Support vector machine as an alternative method for lithology classification of crystalline rocks. J. Geophys. Eng. 2017, 14, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merembayev, T.; Kurmangaliyev, D.; Bekbauov, B.; Amanbek, Y. A Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting Lithofacies: Case Studies from Norway and Kazakhstan. Energies 2021, 14, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.M.; Bijani, R.; Santos, F.V.; Lupinacci, W.M.; Freire, A.F.M. Analysis of alternative strategies applied to Naive-Bayes classifier into the recognition of electrofacies: Application in well-log data at Reconcavo Basin, North-East Brazil. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 227, 211889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.B.; Bai, Y.; Garcia, E.A.; Li, S.T. ADASYN: Adaptive Synthetic Sampling Approach for Imbalanced Learning. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Hong Kong, China, 1–8 June 2008; pp. 1322–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.L. Asymptotic Properties of Nearest Neighbor Rules Using Edited Data. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1972, Smc2, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Xu, R.; Sun, S.-H.; Hou, Z.-K.; Feng, J.-Y. A real-time intelligent lithology identification method based on a dynamic felling strategy weighted random forest algorithm. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 1135–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SY/T 5434-2018; Clastic Rock Particle Size Analysis Method. National Energy Administration: Beijing, China, 2018.





| Lithology | Label | Count | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mudstone | M | 13,307 | 46.26 |
| Fine Sandstone | FS | 6830 | 23.75 |
| Siltstone | S | 4716 | 16.39 |
| Pebbled Sandstone | PS | 2855 | 9.93 |
| Coarse Sandstone | CS | 1055 | 3.67 |
| GR | CAL | RD | RS | AC | DEN | CNL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 28,763 | 28,763 | 28,763 | 28,763 | 28,763 | 28,763 | 28,763 |
| mean | 79.00 | 10.23 | 4.00 | 3.49 | 82.62 | 2.36 | 23.32 |
| std | 15.36 | 1.27 | 2.58 | 1.81 | 10.26 | 0.12 | 6.71 |
| min | 28.13 | 8.61 | 0.20 | 0.83 | 51.80 | 1.83 | 4.51 |
| 25% | 67.90 | 9.28 | 2.62 | 2.36 | 76.66 | 2.29 | 18.77 |
| 50% | 82.64 | 9.88 | 3.54 | 3.16 | 80.12 | 2.36 | 21.76 |
| 75% | 90.87 | 10.84 | 4.78 | 4.22 | 85.22 | 2.44 | 25.96 |
| max | 125.47 | 18.23 | 46.70 | 43.66 | 144.00 | 2.65 | 57.76 |
| Model | Parameter | Searching Range | No Balancing | SMOTE | ADASYN | ENN | ADASYN+ENN | SMOTE+ENN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | C | 1–50 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 50 | 50 |
| γ | 0.01–1.0 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| RF | min_samples_leaf | 2–10 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| max_features | 1–6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| GBDT | min_samples_leaf | 2–10 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| learning_rate | 0.02–0.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Score | Dataset | M | S | FS | CS | PS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaccard Index | Raw | 0.910 | 0.802 | 0.841 | 0.820 | 0.906 |
| ADASYN+ENN | 0.910 | 0.847 | 0.884 | 0.861 | 0.913 | |
| F1 Score | Raw | 0.955 | 0.785 | 0.893 | 0.823 | 0.942 |
| ADASYN+ENN | 0.955 | 0.901 | 0.942 | 0.939 | 0.949 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Tian, F.; Zhao, A.; Zheng, W.; Cao, W. Logging Lithology Discrimination with Enhanced Sampling Methods for Imbalance Sample Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156534
Liu J, Tian F, Zhao A, Zheng W, Cao W. Logging Lithology Discrimination with Enhanced Sampling Methods for Imbalance Sample Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(15):6534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156534
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jingyue, Fei Tian, Aosai Zhao, Wenhao Zheng, and Wenjing Cao. 2024. "Logging Lithology Discrimination with Enhanced Sampling Methods for Imbalance Sample Conditions" Applied Sciences 14, no. 15: 6534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156534
APA StyleLiu, J., Tian, F., Zhao, A., Zheng, W., & Cao, W. (2024). Logging Lithology Discrimination with Enhanced Sampling Methods for Imbalance Sample Conditions. Applied Sciences, 14(15), 6534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156534







