Design of an Intelligent Cascade Control Scheme Using a Hybrid Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy PID Controller for the Suppression of Drill String Torsional Vibration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Mathematical Model of a Drill String System

3. The Proposed Cascade Control Scheme
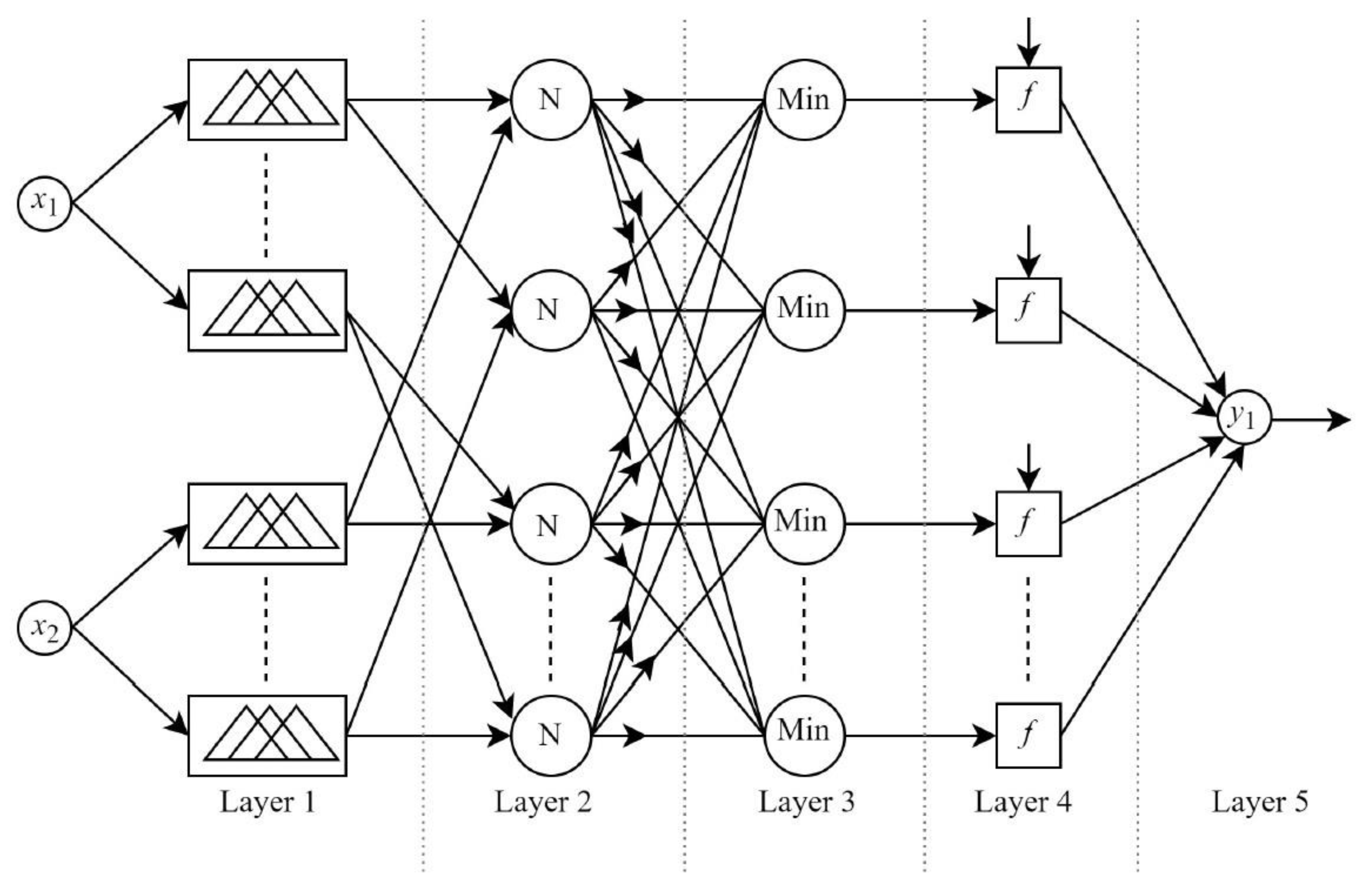
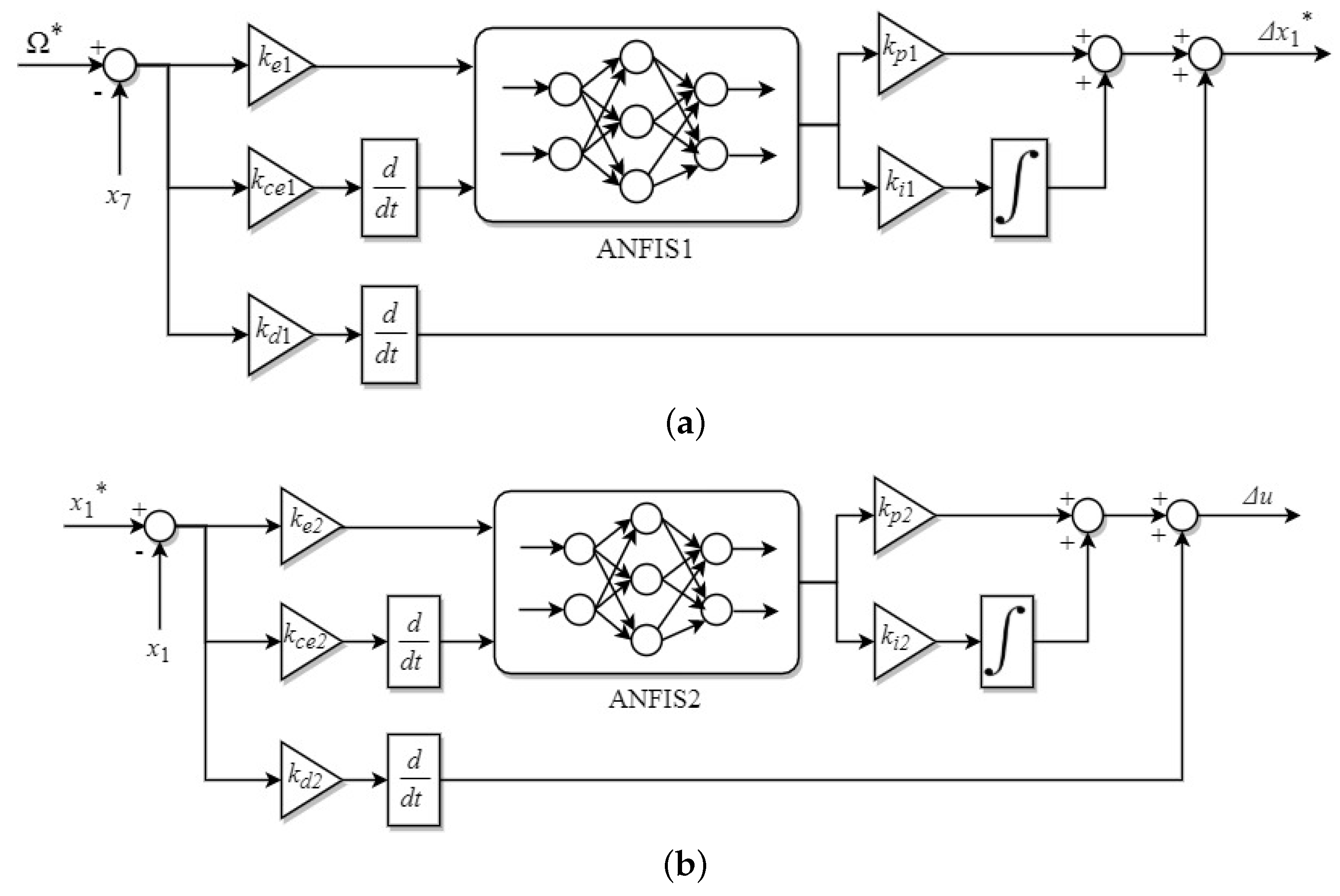
3.1. Hybrid Neuro-Fuzzy PID Controller
3.2. Design of the Feedforward Term
4. Simulation Results
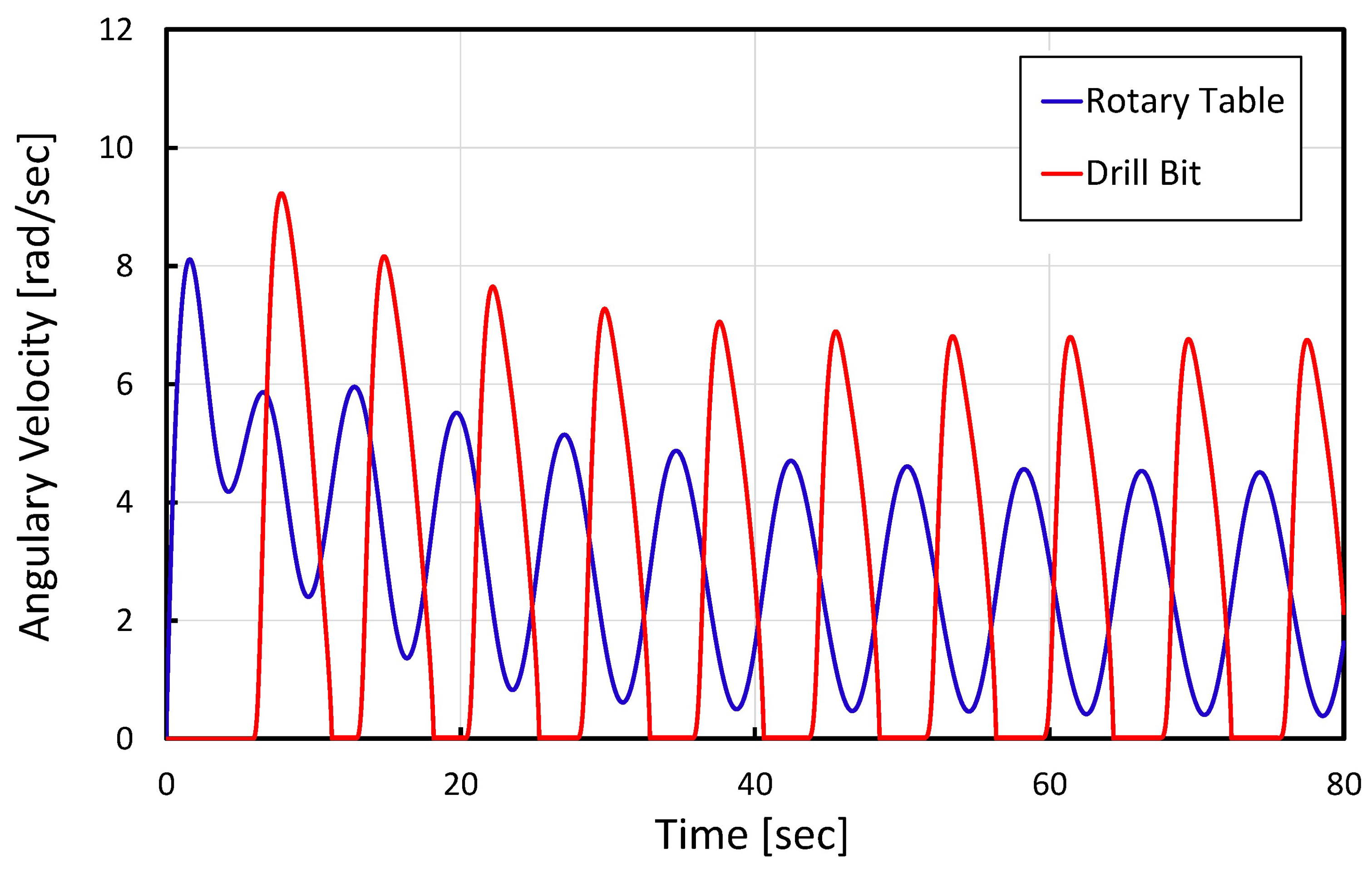
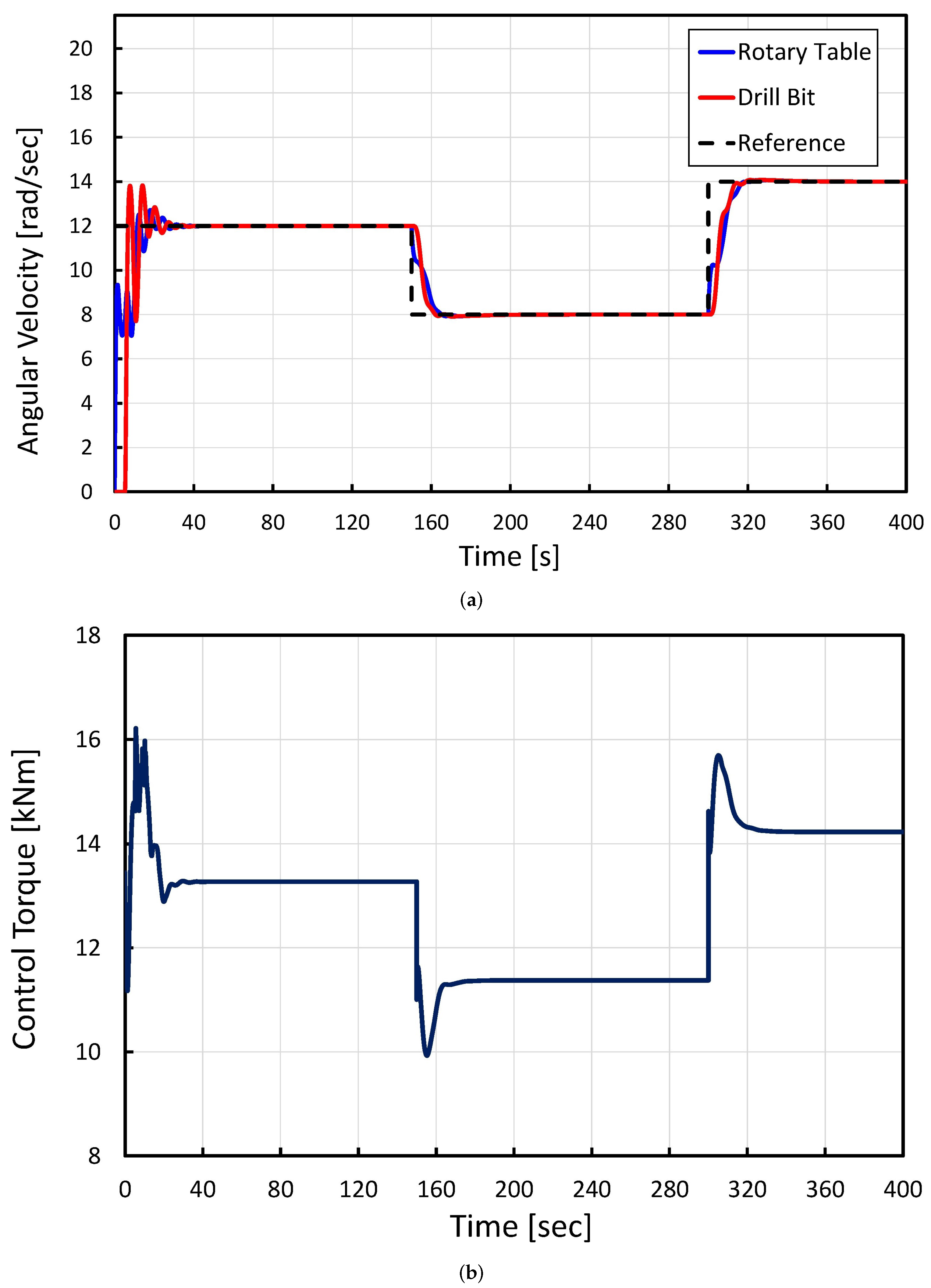
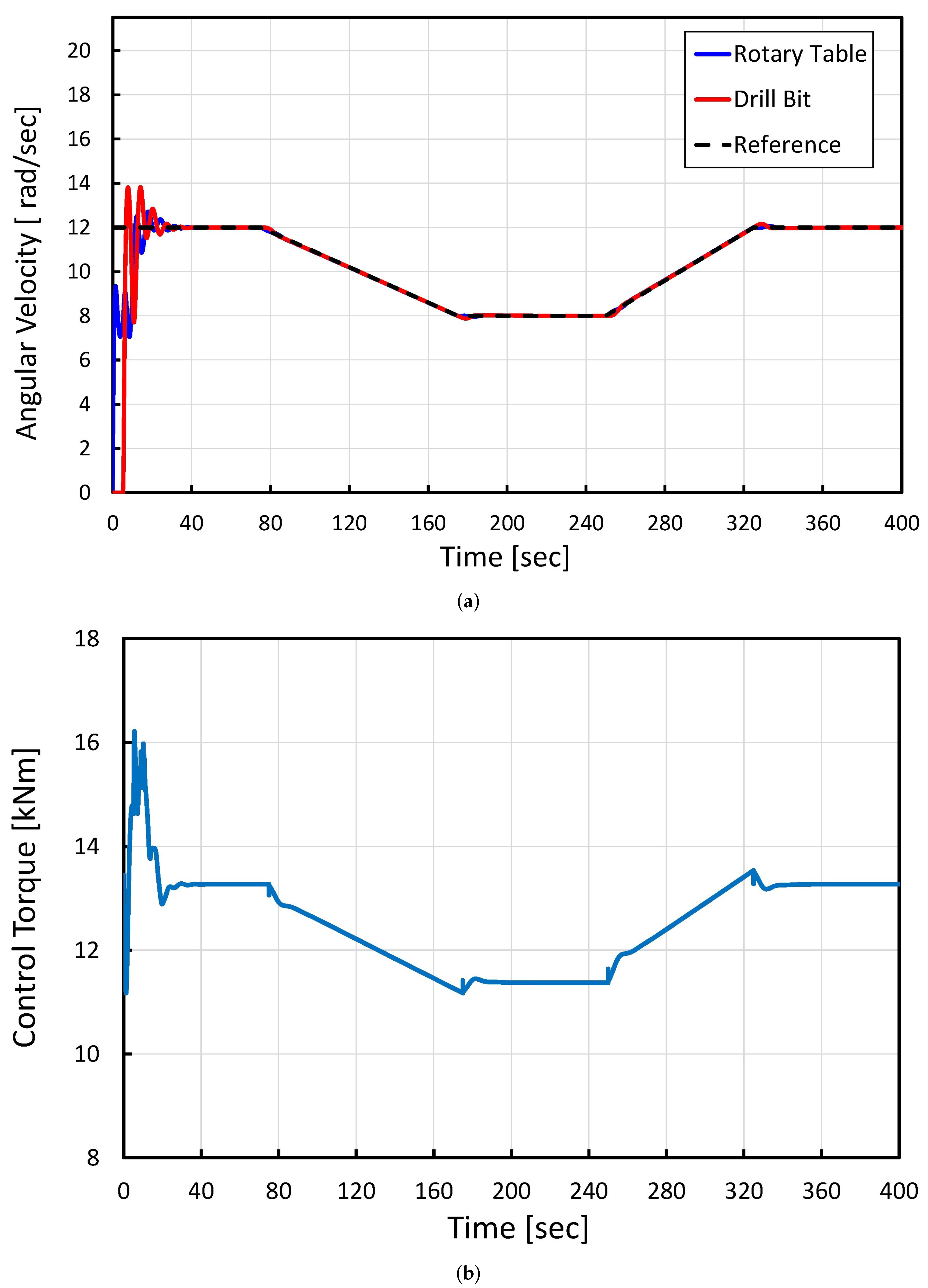
4.1. Effect of Applying the Proposed CFF-NFPID Approach to a Drill String System
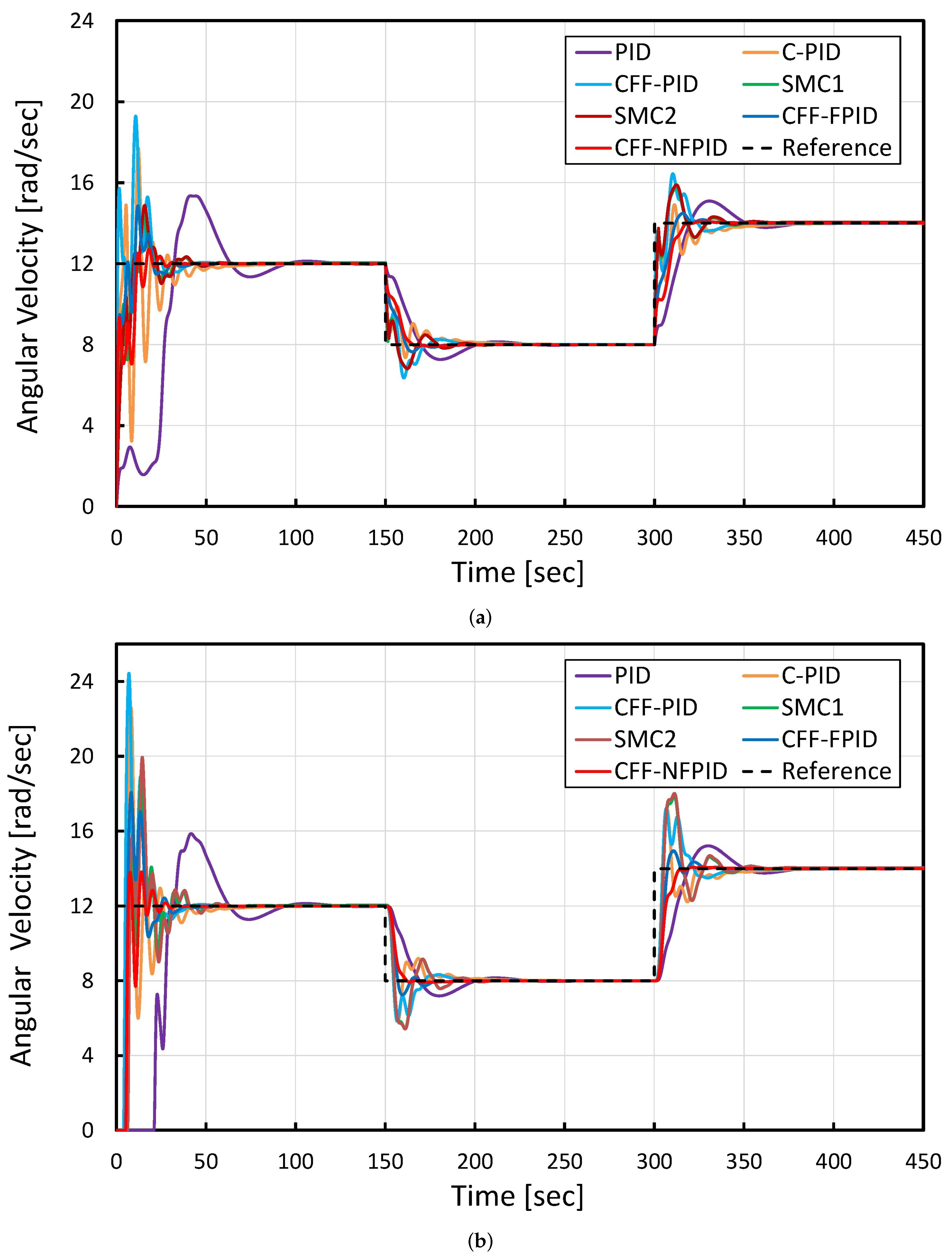
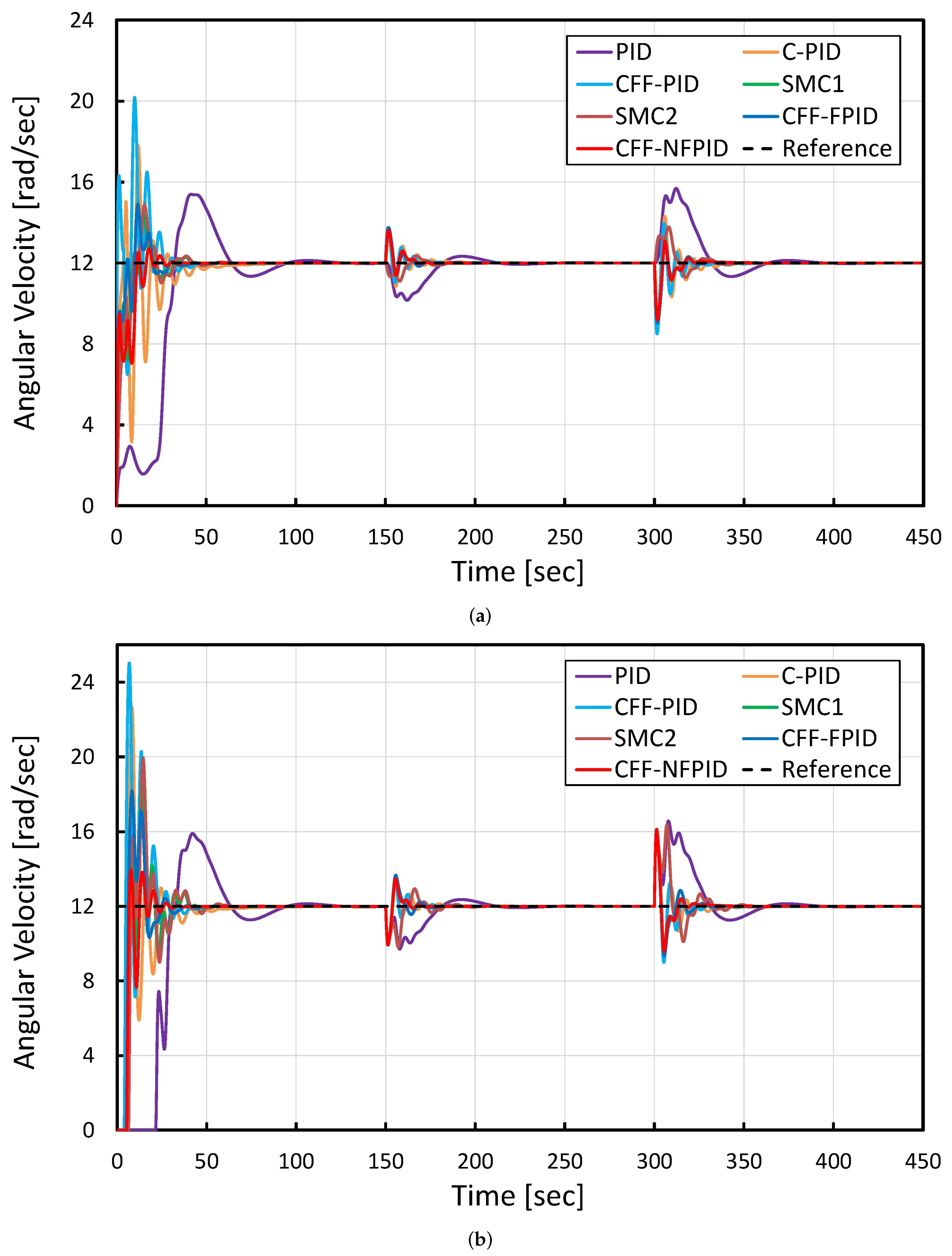
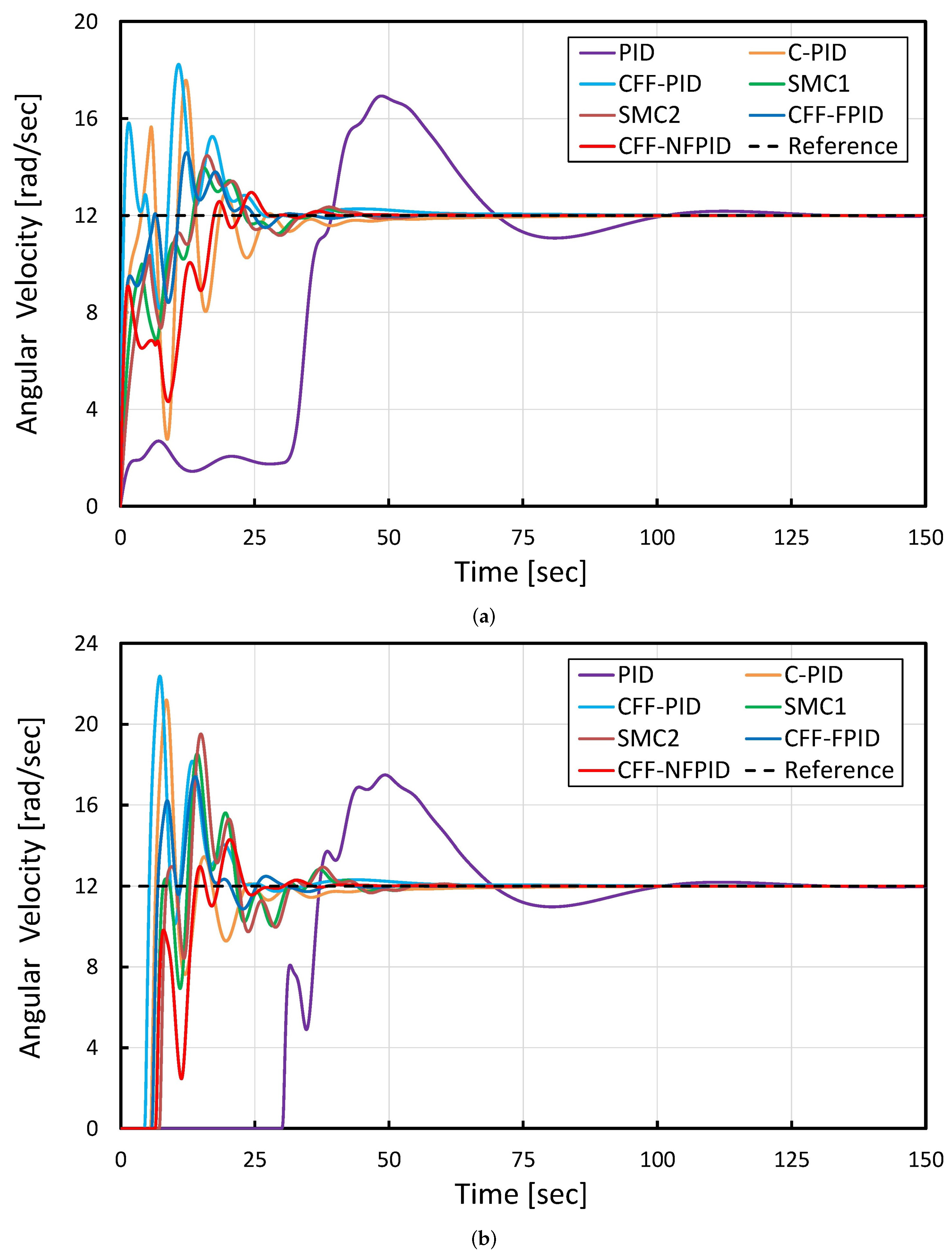
4.2. Quantitative Comparison under Critical Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | artificial neural network |
| ANFIS | adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system |
| BHA | bottom hole assembly |
| C-PID | cascade PID |
| CFF-PID | cascade feedforward PID |
| CFF-FPID | cascade feedforward fuzzy PID |
| CFF-NFPID | cascade feedforward neuro-fuzzy PID |
| DOF | degrees of freedom |
| FF | feedforward |
| FLC | fuzzy logic control |
| H-NFPID | hybrid neuro-fuzzy PID |
| NFPID | neuro-fuzzy PID |
| PI | proportional–integral |
| PID | proportional–integral–derivative |
| ROP | rate of penetration |
| RPM | revolutions per minute |
| SMC | sliding-mode control |
| WOB | weight on bit |
References
- Márquez, M.S.; Boussaada, I.; Mounier, H.; Niculescu, S.I. Analysis and Control of Oilwell Drilling Vibrations: A Time-Delay Systems Approach; Advances in Industrial Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, J.D.; Van Den Steen, L. Active damping of self-excited torsional vibrations in oil well drillstrings. J. Sound Vib. 1995, 179, 647–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tang, L.; Yang, Q. A literature review of approaches for stick-slip vibration suppression in oilwell drillstring. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 6, 967952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, V.; Kapitaniak, M.; Wiercigroch, M. Suppression of drill string stick–slip vibration by sliding mode control: Numerical and experimental studies. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 2018, 29, 805–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Chen, P. A review of the evaluation, control, and application technologies for drill string vibrations and shocks in oil and gas well. Shock Vib. 2016, 2016, 7418635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.X.; Paez, L.; Partin, U.; Agnihotri, M. Decoupling stick-slip and whirl to achieve breakthrough in drilling performance. In Proceedings of the IADC/SPE Drilling Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–4 February 2010; p. 128767. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, R.W.; Wang, C. Torsional vibration control and cosserat dynamics of a drill-rig assembly. Meccanica 2003, 38, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbal, M.; Gharib, M.; Refaat, S.S.; Palazzolo, A.; Sassi, S. Fractional-order controllers for stick-slip vibration mitigation in oil well drill-strings. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Contr. 2021, 40, 1571–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puebla, H.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J. Suppression of stick-slip in drillstrings: A control approach based on modeling error compensation. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 310, 881–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforou, A.; Yigit, A. Fully coupled vibrations of actively controlled drillstrings. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 267, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrarens, A.; Van De Molengraft, M.; Kok, J.; Van den Steen, L. H/sub/spl infin//control for suppressing stick-slip in oil well drillstrings. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1998, 18, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Yigit, A.; Christoforou, A. Coupled torsional and bending vibrations of actively controlled drillstrings. J. Sound Vib. 2000, 234, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakori, S.; Vossoughi, G.; Zohoor, H.; Van de Wouw, N. Prediction-based control for mitigation of axial–torsional vibrations in a distributed drill-string system. IEEE Trans. Contr. Syst. Techol. 2021, 30, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hiddabi, S.; Samanta, B.; Seibi, A. Non-linear control of torsional and bending vibrations of oilwell drillstrings. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 265, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-López, E.M.; Cortés, D. Sliding-mode control of a multi-DOF oilwell drillstring with stick-slip oscillations. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE American Control Conference, New York, NY, USA, 9–13 July 2007; pp. 3837–3842. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Suppressing stick-slip oscillations in underactuated multibody drill strings with parametric uncertainties using sliding-mode control. IET Control Theory Appl. 2015, 9, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, C.; Leite, D.; Pereira, D.; Andonovski, G.; Škrjanc, I. Nonlinear modeling and robust LMI fuzzy control of overhead crane systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 358, 1376–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlouh, I.; Rerhrhaye, F.; Elakkary, A.; Sefiani, N. Experimental implementation of a new multi input multi output fuzzy-PID controller in a poultry house system. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, W.S.; Torres, P.F.; Brito, A.U.; Galhardo, M.A.B.; Macêdo, W.N. A novel fuzzy controller for photovoltaic pumping systems driven by general-purpose frequency converters. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 2020, 40, 100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, A.; Khan, M.R.; Ayyub, M. FPGA based real-time implementation of fuzzy logic controller for maximum power point tracking of solar photovoltaic system. Optik 2020, 213, 164668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrosanti, S.; Alasali, F.; Holderbaum, W. Power management system for RTG crane using fuzzy logic controller. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 2020, 37, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.; Hua, C.; Qian, C. Adaptive neural network control for a class of interconnected pure-feedback time-delay nonlinear systems with full-state constraints and unknown measurement sensitivities. Neurocomputing 2021, 461, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, S. Control of single-phase grid-connected converters with LCL filters using recurrent neural network and conventional control methods. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 5354–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrasa, M.; Babaie, M.; Zafari, A.; Al-Haddad, K. Passivity ANFIS-Based control for an intelligent compact multilevel converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics 2021, 17, 5141–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areed, F.G.; Haikal, A.Y.; Mohammed, R.H. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy control of an induction motor. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2010, 1, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Qaderi, F. Determination of the most effective control methods of SO2 pollution in Tehran based on adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laib, A.; Talbi, B.; Krama, A.; Gharib, M. Hybrid Interval Type-2 Fuzzy PID+ I Controller for a Multi-DOF Oilwell drill string System. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 67262–67275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, K.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, J.; Jing, P. Simulation of hydraulic transplanting robot control system based on fuzzy PID controller. Measurement 2020, 164, 108023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, N.; An, X. Design of a fuzzy-PID controller for a nonlinear hydraulic turbine governing system by using a novel gravitational search algorithm based on Cauchy mutation and mass weighting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 52, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.; Panda, S. Improved grey wolf optimization technique for fuzzy aided PID controller design for power system frequency control. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2018, 16, 278–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritto, T.G.; Ghandchi-Tehrani, M. Active control of stick-slip torsional vibrations in drill strings. J. Vib. Control 2019, 25, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, F.F.; Batou, A.; Ritto, T.G.; Desceliers, C. Stochastic modeling for hysteretic bit–rock interaction of a drill string under torsional vibrations. J. Vib. Control 2019, 25, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar Jafari, A.; Kazemi, R.; Faraji Mahyari, M. The effects of drilling mud and weight bit on stability and vibration of a drill string. J. Vib. Acoust. 2012, 134, 011014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Song, X. Trajectory tracking and rate of penetration control of downhole vertical drilling system. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2018, 140, 091003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.; Song, X. Drilling control system using an equivalent input disturbance-based control with a neutral-type axial-torsional coupled dynamics model. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2019, 141, 121013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldivar, B.; Mondié, S.; Niculescu, S.I.; Mounier, H.; Boussaada, I. A control oriented guided tour in oilwell drilling vibration modeling. Annu. Rev. Control 2016, 42, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulgalil, F.; Siguerdidjane, H. Backstepping design for controlling rotary drilling system. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Conference on Control Applications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 28–31 August 2005; pp. 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, W.; Chávez, J.P.; De Sa, R. Torsional stick-slip vibrations and multistability in drill strings. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 76, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, H.L.; Trindade, M.A. Performance analysis of proportional-integral feedback control for the reduction of stick-slip-induced torsional vibrations in oil well drillstrings. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 398, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Observer and reference governor based control strategy to suppress stick-slip vibrations in oil well drill string. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 457, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Element(s) | Symbol | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inertia | rotary table | 930 | kg· | |
| Inertia | drill collar | 750 | kg· | |
| Inertia | drill pipes | 2782.25 | kg· | |
| Inertia | drill bit | 471.97 | kg· | |
| Stiffness | drill pipes and rotary table | 698.06 | N·m/rad | |
| Stiffness | drill pipes and drill collar | 1080 | N·m/rad | |
| Stiffness | drill bit and drill collar | 907.48 | N·m/rad | |
| Damping | drill pipe and rotary table | 139.61 | N·m·s/rad | |
| Damping | drill collar and drill pipe | 190 | N·m·s/rad | |
| Damping | drill bit and drill collar | 181.49 | N·m·s/rad | |
| Damping | drill bit and mud drilling | 50 | N·m·s/rad | |
| Weight on bit | drill bit | WOB | 100 | kN |
| Radius | drill bit | 0.156 | m | |
| Factor | drill bit | 0.9 | − | |
| Limit velocity | rad/s | |||
| Drive torque | 10 | kN·m | ||
| Coefficient of static friction | 0.8 | − | ||
| Coefficient of Coulomb friction | 0.5 | − | ||
| Coefficient of viscous damping | 425 | N·m·s/rad |
| Stepwise Increase in the Angular Velocity Reference 0→12 rad/s | Stepwise Decrease in the Angular Velocity Reference 12→8 rad/s | Stepwise Increase in the Angular Velocity Reference 8→14 rad/s | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angular Velocity of the Rotary Table | Angular Velocity of the Drill Bit | Angular Velocity of the Rotary Table | Angular Velocity of the Drill Bit | Angular Velocity of the Rotary Table | Angular Velocity of the Drill Bit | |||||||
| [s] |
[rad/s] | [s] |
[rad/s] | [s] |
[rad/s] | [s] |
[rad/s] | [s] |
[rad/s] | [s] |
[rad/s] | |
| PID | 87.87 | 3.86 | 87.94 | 3.35 | 50.05 | 0.82 | 51.02 | 0.74 | 45.65 | 1.21 | 45.89 | 1.09 |
| C-PID | 50.63 | 5.71 | 54.12 | 10.60 | 42.15 | 0.65 | 39.35 | 2.16 | 41.43 | 0.92 | 38.77 | 3.16 |
| CFF-PID | 35.4 | 7.51 | 34.1 | 12.08 | 35.12 | 1.72 | 34.51 | 2.28 | 34.43 | 2.57 | 33.89 | 3.38 |
| SMC [15] | 39.45 | 2.25 | 47.56 | 6.73 | 36.02 | 1.51 | 33.92 | 1.15 | 36.03 | 3.87 | 26.63 | 1.79 |
| SMC [16] | 40.56 | 3.83 | 48.77 | 7.96 | 36.29 | 2.57 | 34.65 | 1.19 | 36.62 | 4.02 | 35.21 | 1.89 |
| CFF-FPID | 28.68 | 2.85 | 32.61 | 6.07 | 18.11 | 0.36 | 24.61 | 0.76 | 18.21 | 0.48 | 24.22 | 0.94 |
| CFF-NFPID | 25.33 | 0.72 | 24.73 | 1.82 | 13.13 | 0.00 | 10.78 | 0.00 | 15.40 | 0.00 | 12.50 | 0.00 |
| Stepwise Decrease in the WOB 100→120 kN | Stepwise Increase in the WOB 120→80 kN | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angular Velocity of the Rotary Table | Angular Velocity of the Drill Bit | Angular Velocity of the Rotary Table | Angular Velocity of the Drill Bit | |||||
| Settling Time [s] | Overshoot [rad/s] | Settling Time [s] | Overshoot [rad/s] | Settling Time [s] | Overshoot [rad/s] | Settling Time [s] | Overshoot [rad/s] | |
| PID | 51.02 | 2.29 | 50.56 | 1.84 | 56.27 | 4.59 | 56.37 | 3.67 |
| C-PID | 19.02 | 1.17 | 15.56 | 2.08 | 27.01 | 2.31 | 30.83 | 4.13 |
| CFF-PID | 16.89 | 0.98 | 19.48 | 2.06 | 23.36 | 1.95 | 20.59 | 4.11 |
| SMC [15] | 19.32 | 0.91 | 26.87 | 2.19 | 22.66 | 1.78 | 31.86 | 4.36 |
| SMC [16] | 19.31 | 0.89 | 26.86 | 2.19 | 22.65 | 1.78 | 31.85 | 2.37 |
| CFF-FPID | 14.13 | 0.62 | 17.86 | 2.07 | 20.09 | 1.09 | 20.92 | 4.13 |
| CFF-NFPID | 11.82 | 0.79 | 12.45 | 2.06 | 15.75 | 1.09 | 16.23 | 4.12 |
| Stepwise Increase in the Angular Velocity Reference 0→12 rad/s in the Case of Parametric Uncertainty | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angular Velocity of the Rotary Table | Angular Velocity of the Drill Bit | |||
| Settling Time [s] | Undershoot [rad/s] | Settling Time [s] | Undershoot [rad/s] | |
| PID | 95.95 | 5.49 | 96.19 | 4.93 |
| C-PID | 42.23 | 5.58 | 44.31 | 9.19 |
| CFF-PID | 48.97 | 6.23 | 49.61 | 10.37 |
| SMC [15] | 39.62 | 1.95 | 46.59 | 6.56 |
| SMC [16] | 40.76 | 2.47 | 47.98 | 7.51 |
| CFF-FPID | 28.76 | 2.59 | 35.75 | 5.41 |
| CFF-NFPID | 26.63 | 0.95 | 33.84 | 2.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laib, A.; Gharib, M. Design of an Intelligent Cascade Control Scheme Using a Hybrid Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy PID Controller for the Suppression of Drill String Torsional Vibration. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5225. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125225
Laib A, Gharib M. Design of an Intelligent Cascade Control Scheme Using a Hybrid Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy PID Controller for the Suppression of Drill String Torsional Vibration. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(12):5225. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaib, Abdelbaset, and Mohamed Gharib. 2024. "Design of an Intelligent Cascade Control Scheme Using a Hybrid Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy PID Controller for the Suppression of Drill String Torsional Vibration" Applied Sciences 14, no. 12: 5225. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125225
APA StyleLaib, A., & Gharib, M. (2024). Design of an Intelligent Cascade Control Scheme Using a Hybrid Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy PID Controller for the Suppression of Drill String Torsional Vibration. Applied Sciences, 14(12), 5225. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14125225






