Abstract
Background and Purpose: In urological surgery, accurate localization of the ureteral orifice is crucial for procedures such as ureteral stent insertion, assessment of ureteral orifice lesions, and prostate tumor resection. Consequently, we have developed and validated a computer-assisted ureteral orifice detection system that combines the YOLO deep convolutional neural network and the attention mechanism. Data: The cases were partitioned into a training set and a validation set at a 4:1 ratio, with 84 cases comprising 820 images in the training set and 20 cases containing 223 images in the validation set. Method: We improved the YOLO network structure to accomplish the detection task. Based on the one-stage strategy, we replaced the backbone of YOLOv5 with a structure composed of ConvNeXt blocks. Additionally, we introduced GRN (Global Response Normalization) modules and SE blocks into the blocks to enhance deep feature diversity. In the feature enhancement section, we incorporated the BiFormer attention structure, which provides long-distance context dependencies without adding excessive computational costs. Finally, we improved the prediction box loss function to WIoU (Wise-IoU), enhancing the accuracy of the prediction boxes. Results: Testing on 223 cystoscopy images demonstrated a precision of 0.928 and recall of 0.756 for our proposed ureteral orifice detection network. With an overlap threshold of 0.5, the mAP of our proposed image detection system reached 0.896. The entire model achieved a single-frame detection speed of 5.7 ms on the platform, with a frame rate of 175FPS. Conclusion: We have enhanced a deep learning framework based on the one-stage YOLO strategy, suitable for real-time detection of the ureteral orifice in endoscopic scenarios. The system simultaneously maintains high accuracy and good real-time performance. This method holds substantial potential as an excellent learning and feedback system for trainees and new urologists in clinical settings.
1. Introduction
In the clinical treatment and diagnosis of upper urinary tract lesions, frequent localization and observation of the ureteral orifice are necessary. To assist in diagnosing upper urinary tract diseases, it is common to observe the ureteral orifice, often utilizing urological endoscopes such as cystoscopes, transurethral resection cystoscopes, and ureteroscopes, for visual examination of the appearance and physiological activities (such as peristalsis and efflux) of the ureteral orifice. For example, when a patient experiences ureteral atrophy due to malnutrition, hormonal imbalances, or urinary tract infections, leading to obstruction of normal urine excretion, urologists generally use a rigid retrograde ureteroscope to place a pigtail catheter to facilitate normal urination. This procedure requires the physician to accurately locate the ureteral orifice and advance the ureteroscope at the correct angle. On the other hand, whether in cystoscopic surgery or transurethral prostatectomy, physicians need to observe the position of the ureteral orifice in advance to avoid touching it during the procedure, causing unnecessary damage and complications. Additionally, examining the shape of the ureteral orifice and conducting biopsies can help analyze whether the lesion is a stone, tuberculosis, inflammation, stenosis, or a benign or malignant tumor, providing valuable information for determining the nature and location of upper urinary tract diseases. Therefore, when urologists perform urological endoscopic examinations and surgeries, it is necessary to use urological endoscopes to discover and locate the ureteral orifice.
The recognition of the ureteral orifice position is highly significant, yet various practical challenges exist in clinical operations. Despite the anatomical fixation of the ureteral orifice in the posterior-lateral angle of the bladder trigone, several factors make its identification difficult: Figure 1b,c demonstrates variations in the shape of the ureteral orifice due to rhythmic peristaltic contractions. The orifice in (b) has almost closed to a small dot, with reduced discernibility due to interference from vessels on the inner wall. In (c), the overall identification is challenging due to complex background textures and image degradation caused by the endoscope. Similarly, in Figure 1a,d, the angle of entry and corresponding lighting during urological endoscopy can also contribute to difficulties in identifying the ureteral orifice. Particularly in (a), the ureteral orifice’s direction is nearly perpendicular to the optical axis, and the flat pale inner wall results in extremely low contrast under lighting, causing significant interference for surgeons to promptly discover the ureteral orifice during clinical procedures. Therefore, the development of an intelligent ureteral orifice detection system is of crucial clinical importance, aiding in the training of urology novices and assisting experienced urologists in managing challenging scenarios with indistinct ureteral orifices.
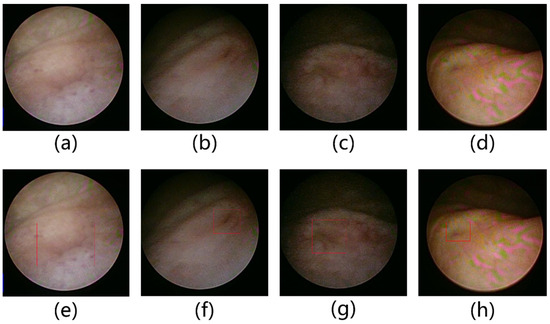
Figure 1.
Morphology of the ureteral orifice that is challenging to identify in ureteroscopy, where (a–d) represent images of actual scenes after cropping, and (e–h) are their corresponding images with annotated ureteral orifices.
In the clinical process, the identification of features is generally assisted by two methods. One is the exogenous light source identification, which is mostly used for the auxiliary identification of injuries, lesions, and tumors. It involves observing fluorescence or infrared light signals in the field through dyes or the optical properties of the features themselves. On the other hand, it relies on image processing methods, utilizing algorithms in the domains of target detection or segmentation to annotate images directly, assisting doctors in surgery. As a natural bodily feature, the ureteral orifice is challenging to observe through the light source, making the use of target detection algorithms a feasible approach.
The task of object detection is a crucial development area in the field of machine vision within the realm of deep learning. Both network structures and functional modules have undergone rich and in-depth research, accumulating a wealth of experience. The overall framework is divided into three parts: backbone, neck, and head. The backbone serves as the main body of the entire structure, tasked with feature extraction. Common backbone networks include VGG [1], ResNet [2], DenseNet [3], MobileNet [4], EfficientNet [5], and CSPDarknet53 [6], among others. These networks have proven strong feature extraction capabilities in classification and other tasks. Researchers often fine-tune the backbone to make it more suitable for specific tasks. The neck section is used to enhance resolution by outputting features of different scales to fully utilize feature information. Common neck architectures include FPN [7], PANet [8], NAS-FPN [9], BiFPN [10], ASFF [11], SFM [12], and others. The head is the classification network, primarily responsible for prediction and classification. It is generally divided into two types: one-stage object detectors and two-stage object detectors. Historically, two-stage detectors have been more accurate, with a series of algorithms represented by RCNN [13,14,15], including Fast-RCNN and Faster-RCNN, performing excellently in terms of precision. In comparison to two-stage detectors, one-stage detectors simultaneously predict bounding boxes and target categories, showing a clear speed advantage but lower accuracy. Representative models for one-stage detectors include the YOLO series and SSD series. To enhance the ability of SSD to express low-level feature maps, DSSD [16] uses ResNet101 as the backbone, and FSSD [17] integrates low-level features into the high-level features based on SSD. The YOLO series [18] has evolved into version 8, seeking a balance between accuracy and performance. Although CNN-based networks [19] hold a significant position in the field of object detection in deep learning, with the migration of transformers from NLP (Natural Language Processing) to CV (Computer Vision), more object detection methods are adopting updated perspectives to address problems. Models such as Swin-Transformer [20] and DETR [21] inject new vitality into object detection tasks, and further research on attention mechanisms opens up more possibilities for development in the CV field, such as BAM [22], CBAM [23], SCConv [24], ECAttention [25], SimAM [26], Biformer [27], SE [28], and other modules, which not only enhance network performance but also integrate network architecture design more effectively.
Currently, object detection has been widely applied in various real-world scenarios such as autonomous driving, robot vision, video surveillance, etc. In the field of medical clinical applications, there is rich research accumulation. Regarding colorectal polyps, Nisha J S optimized polyp detection by combining image enhancement in the HSV color space and a dual-path convolutional network. Through image enhancement, the feature quality of the dataset is strengthened. Simultaneously, the CNN network, which performs parallel processing of convolution kernels of different scales and then unifies channel-fused features, also improves the model’s ability to extract features [29]. Luca M created a lightweight object detection network based on SSD and MobileNet, highlighting its advantages in real-time performance after extracting features using the lightweight MobileNet backbone and detecting target positions using anchor-similar Prior Boxes [30]. Pacal I et al. [31] made modifications to the YOLO model, including scaling and activation function transformations, effectively improving the network’s performance in corresponding scenarios. Meanwhile, in tasks such as gastrointestinal disease classification [32,33], polyp segmentation, and tumor judgment [34,35], deep learning methods have been widely researched and applied.
In urological surgery, deep learning has also been preliminarily studied. For intraoperative navigation, Lazo, Jorge E. et al. used deep residual networks for cavity segmentation of ureteroscope images [36]; in terms of stones, Gupta, S improved HybResUNet for multi-class segmentation in lithotripsy surgery to assist in decision-making [37]; Black, KM et al. used residual networks for multi-classification of the appearance and core of stones to distinguish different types of stones [38]; and Zhu, GH et al. used images from holmium laser surgery for the same task training, achieving good practical results [39]. On the other hand, stone classification detection is also performed through CT images [40]; El Beze, J et al. attempted intra- and extracorporeal stone classification using Inception v3 and achieved good results [41]. For the task of ureteral orifice recognition, Peng X et al. first proposed improvements using the SSD model by adding three convolution modules as additional feature layers to increase the output of detected anchor boxes [42]. In subsequent enhancements, Liu et al. [43]. fused the improved algorithm with the CSRT tracking algorithm, using a conventional ureteroscope with Wolf (brand) F8/9.6 (F is the Fr unit, 8 is the finest outer diameter, and 9.6 is the coarsest diameter) for image collection, conducting universality experiments on videos from various platforms. The aforementioned studies still have considerable room for further exploration in terms of algorithm parameters, complexity, robustness, accuracy, and the platforms used for image collection. On one hand, in the clinical scenario of ureteroscopy, although research has compared the accuracy of target detection standards, there has been no related improvement or progress in the complexity and computational cost of models. On the other hand, traditional target detection methods perform well on SOTA datasets but still require corresponding fine-tuning for better adaptation to downstream tasks. Research on ureteral orifice recognition is still at a relatively early stage, with the possibility of further research.
In response to the above situation, this paper collected clinical ureteroscope images to create a dataset, improved and trained on the classic YOLO network, and ultimately achieved effective monitoring of ureteral openings. The main innovations of this paper are:
- Combining practical scenarios, using ConvNextV2 to improve the feature extraction backbone of the detection network.
- Introducing the SCConv convolutional structure on the basis of mitigating the impact of redundant features through spatial and channel enhancement to optimize the network structure.
- Introducing attention mechanisms in the feature fusion stage to improve detection performance.
- Replacing the original loss function to better suit the usage scenario and improve detection performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
The dataset was collected retrospectively using clinical recordings and data desensitization, as shown in Figure 2. The recording was split into video frames, and the black areas with no content were cropped, leaving only the parts with endoscopic images. Key images with features were selected from the cropped images, and Labelme was used to annotate them in YOLO format to obtain the dataset. Dataset annotation was performed with the direct involvement of hospital doctors.
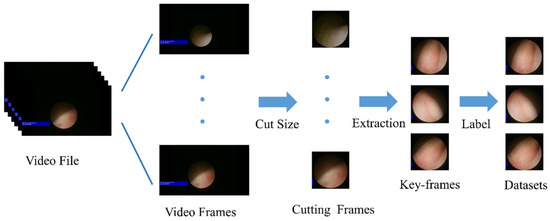
Figure 2.
Dataset processing.
The image and video dataset used for development and testing is as follows: a total of 1043 images were extracted from these videos. All videos were recorded with equipment at a resolution of 1920 × 1280 pixels. The platform used was Olympus, with a coarse lens of 8/9.8F and a fine lens of 6/7.5F. The dataset was divided as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Dataset partitioning.
2.2. Network Structure
As shown in Figure 3, this paper proposes a network for detecting ureteral openings in ureteroscopy, based on the improvement of YOLOv5. We introduce the SE attention mechanism on the basis of ConvNeXt to improve the independent stability of modules. SCConv is added between blocks to reshape the balance of spatial and channel information, aiming to remove possible redundant information brought by large convolution kernels in each stage. Furthermore, the Biformer attention mechanism is incorporated into the neck part to enhance feature extraction performance, and the original GIoU-loss is optimized to WIoU-loss in the loss function.
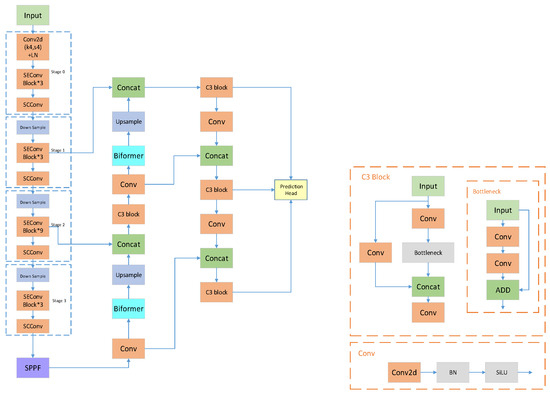
Figure 3.
Network structure.
2.2.1. YOLOv5
The YOLO object detection algorithm is a series of networks based on the one-stage detection head, which has now evolved into a complete object detection process. The dataset needs to be enhanced first, and then feature values are extracted through the backbone network. After the feature-enhanced pyramid fuses features of various scales, the detection head is used for target prediction. Finally, post-processing methods such as non-maximum suppression are employed to handle detection boxes. The overall network is propagated using methods like stochastic gradient descent, and the loss function depends on a combination of categories and IoU, forming the basic process of the YOLO series.
Compared to the previous networks in this series, YOLOv5 mainly introduced adaptive anchor boxes and adaptive image scaling in the preprocessing part, facilitating the use of datasets. In the main structure, improvements were made to the convolution modules, using BN and SiLU to address the issue of overfitting. In the feature fusion part, a combination of FPN and PAN was introduced, allowing features to simultaneously perform top-down communication and bottom-up sampling. These enhancements enable YOLOv5 to achieve a more efficient balance in learning and training costs for small samples, leading to good performance in medical scenarios.
2.2.2. Backbone
The backbone is the foundation of the entire network, extracting basic image features and obtaining as comprehensive information as possible for subsequent detection processes. Different backbones consist of different modules arranged in specific ways and sequences; this area of research is already very advanced. Based on ConvNeXt, we introduced spatial reconstruction units and channel reconstruction units to address potential redundancy issues caused by large convolution kernels in downstream tasks. Simultaneously, inspired by RepLKNet, which also uses large convolution kernels, we incorporated GRN and SE modules to enhance module stability.
As illustrated in Figure 4. ConvNeXt is a CNN architecture optimized based on ResNet-50, drawing inspiration from the Swin-Transformer’s approach and training methods. It underwent optimization in training hyperparameters, structural proportions, network depth, output dimensions, etc., in conjunction with the final structure honed from ResNeXt. From the top-level feature extraction layer to the middle inverted bottleneck structure stacking, to the final high-dimensional output feature classification layer, overall improvements can be outlined in the following aspects: (i) In each stage of the original ResNet-50, the stack numbers for each block are 3:4:6:3; in ConvNeXt, this has been modified to 3:3:9:3, similar to the block stacking in Swin-Transformer. (ii) In ResNet-50 blocks, the bottleneck first reduces dimensions, then extracts features, and finally increases dimensions. However, as shown in Figure 4, the bottleneck in ConvNeXt is designed to perform feature extraction first, followed by dimension reduction, and finally dimension increase. (iii) The size of the convolutional kernel has been changed from 3 × 3 in ResNet to 7 × 7. (iv) Its activation function has also been replaced from ReLU to GELU, and the frequency of activation function usage has been reduced. (v) Its normalization has been changed from batch normalization to layer normalization, and the frequency of normalization usage has been reduced.
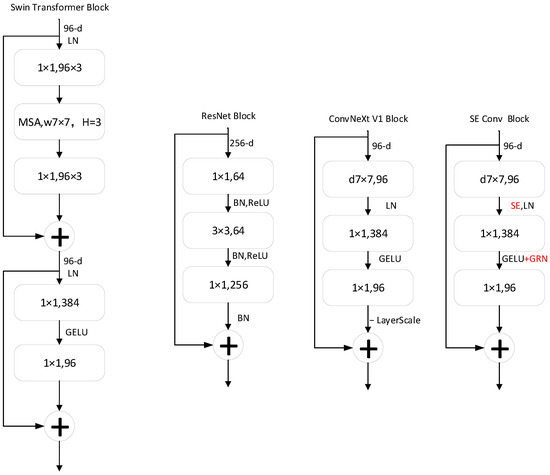
Figure 4.
Comparison block of modules from different network architectures.
ConvNeXt V2 further improves its block by addressing the cosine distance loss of features after multiple training sessions. It introduces a global response normalization module to enhance the diversity of features after multiple training sessions, improving judgment accuracy and training efficiency. By mapping to the global function vector ,
By aggregating features through L2 norm to improve performance
Subsequently, the corresponding normalization function N uses split normalization
Obtaining the global response normalization module
For ease of training, two learnable parameters and a skip connection layer are added, resulting in the GRN module
where the and are learnable affine transform parameters. This module is added to the original ConvNeXt Block, enhancing overall feature richness and classification accuracy.
However, in the reexamination of large convolution kernels, the large receptive field brought by large convolution kernels may not directly translate into feature richness. Due to the increased receptive field of the convolutional kernel, depth-wise separable convolution is generally used to balance computational costs. However, this change may reduce accuracy compared to regular convolution operations. To overcome this issue, SE Attention is introduced to learn relationships between different channels, potentially compensating for the drawbacks of this operation.
Moreover, compared to the receptive field approach of the multi-head attention mechanism in the Transformer structure, the receptive field of large convolution kernels may introduce more redundant information, affecting feature extraction. Therefore, by enhancing spatial and channel information separately, the use of SCConv enhances the content brought by large convolutional kernels at each stage, and this convolutional operation achieves the filtering of redundant information by separately processing the information gradients in the spatial domain and reallocating the weight of information in the channel domain, further enhancing the performance of the network.
2.2.3. BiFormer
To address the scalability issues brought about by the multi-head self-attention mechanism and avoid the drawbacks of fixed manually designed static parameters and shared query values, a new sparse attention mechanism has emerged, as shown in Figure 5. This new attention mechanism first divides the input feature map into non-overlapping blocks of , is remapped to , where the query, key, and value are as follows:
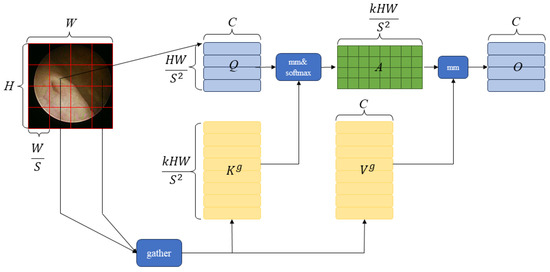
Figure 5.
BiFormer structure.
Then, by constructing a directed graph to obtain semantic relationships between regions, in
where and are the averages of the regions, and after pruning the top-k relationships, a routing index matrix is obtained, in
In this way, the i-th row of contains the k indices of the most relevant regions in the i-th region. Based on this index matrix, the key and value collected by each query in region i can be further obtained:
Finally, the depth convolution is parameterized using the LCE function [44] with a kernel size of 5, and the output is
2.2.4. Loss Functions
In object detection algorithms, the loss function consists of the sum of target localization, target classification, and target confidence loss functions. Most object detection algorithms use IoU to determine the overlap between the predicted box and the target box in the dataset. The original framework uses GIoU, as shown in the Figure 6 as below:
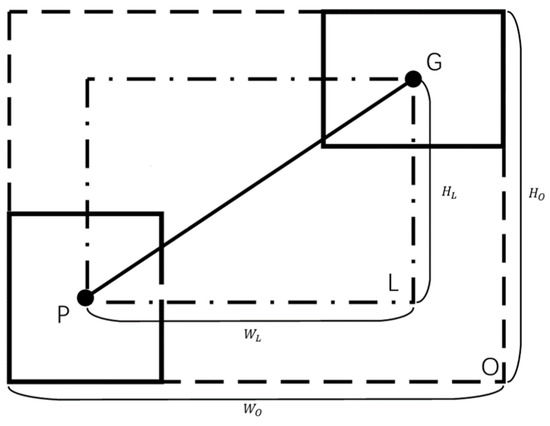
Figure 6.
The positional relationship between the predicted rectangle P and the ground truth rectangle G.
The specific formula is as follows:
where G and P represent the ground truth box and the predicted box, O is the minimum bounding rectangle of P and G, and L is the center rectangle formed by connecting the center points of P and G. This method utilizes the WIoU [45] loss function instead of the GIoU loss function.
Since the experimental data are annotated with clinical images, the most challenging aspect of ureteral orifice recognition during clinical surgery lies in the variation of ureteral orifice morphology at different angles and the unclear separation from the surrounding bladder wall. Despite efforts to collect samples, there is evidently a disparity in the overall contribution among different samples. Thus, assigning different loss function weights to samples of varying detection difficulty is a preferable solution.
WIoU consists of two parts, one of which is the distance attention part, and the specific formula is as follows:
In order to prevent the minimum bounding rectangle from hindering convergence, the operation of detaching it from the computation graph was adopted, represented by * in the formula. At the same time, inspired by the Focal loss, a monotonic focusing mechanism for cross-entropy was designed, and the final loss function is as follows:
where is an added normalization factor to prevent the gradient from decreasing with IoU, which is a running mean with momentum m. is analogous to the coefficient in Focal loss, and when , r is 1, causing the loss function to degrade to its initial state.
3. Experiments
All experiments in this study were conducted on the following platform. The operating system is Windows 10, and the compilation software is PyCharm 2023. The computer used in the study is equipped with an Intel Core i9-13900KF (10 cores, 3.50 GHz, 19.25 MB Intel® Smart Cache) processor, 32 GB DDR5 RAM, and a single RTX 4090 (24 GB, 16,384 CUDA cores, 96 MB L2 cache) graphics card. Python 3.10, PyTorch 1.12.0 stable version were used in the study. Finally, NVIDIA CUDA Toolkit 11.8 and NVIDIA GPU acceleration library (cuDNN) 8.9.1 version were used for training and testing processes.
This paper used the official YOLOv5 code [46] as the baseline for improvement and also employed its built-in data augmentation module, using default values for augmentation. All images were resized to a resolution of 640 × 640 by default, with a batch size of 8 and 300 epochs.
This study used YOLOv5’s data augmentation techniques and training methods, and Table 2 lists some specific hyperparameters used in this study. These augmentation techniques can be obtained in the official YOLOv5 repository, and all these data augmentation techniques are used during the training process. Therefore, no augmentation was performed before training. The main role of the data augmentation techniques used during the training process is to use each image in the training process based on a pre-determined probability, and only once.

Table 2.
Parameters and values in the dataset augmentation.
To evaluate the detection performance, we adopted some basic performance metrics of deep learning algorithms: average precision (mAP) measurement, precision (P), recall (R), etc. These metrics are composed of true positive (TP), false positive (FP), false negative (FN), and true negative (TN). The definitions of these values are as follows: TP represents the predicted bounding box falling on the ground truth of the ureteral orifice data, and FP is the opposite. Similarly, TN indicates that no bounding box is predicted on images without targets, while FN indicates incorrect predictions on images without targets. The above values can be defined based on these numerical values as:
Average Precision (mAP) is a popular metric for object detection that averages the AP values for all classes. This way, the model’s performance can be measured using a single metric, and its expression is as follows:
where Q is the number of queries in the set and q is the average precision of the query. mAP@0.5 represents the proportion of accuracy with bounding boxes overlapping with the ground truth by 50%.
4. Results and Discussion
Regarding the current improvements, we conducted ablation experiments on various modules, as shown in Table 3. YOLOv5-p1 replaces the backbone with ConvNextv2, YOLOv5-p2 adds SCConv between blocks based on p1, YOLOv5-p3 introduces the SE attention mechanism to all modules based on p2, and Ours adds SCConv between blocks based on p3. Finally, our algorithm improves the neck and adds the BiFormer structure based on YOLOv5-p3. From the results, the performance of the network has gradually improved during the enhancements. SCConv significantly enhances the accuracy of the modules, as its ability to filter spatial redundant information contributes to the effective enhancement of the model, while the attention module primarily improves the intersection over union of images.

Table 3.
Ablation experiment.
Meanwhile, we conducted cross-sectional comparative tests on the currently released networks of the YOLO series, the results of which are shown in Table 4. Improving upon the YOLOv5 baseline has increased the overall computational cost to some extent, but there are significant improvements in both recall and accuracy. Compared to other algorithms in the same series, there is also a certain improvement, striking a good balance between complexity and performance.

Table 4.
Network structure improvement comparison.
We set the confidence threshold to 0.25 and the IoU overlap to 0.45 to draw the confusion matrix for the validation set using the model, as shown in Figure 7. From the confusion matrix, it can be seen that this algorithm effectively distinguishes between the background and targets in target recognition. In terms of quantity, out of 223 images, 177 were correctly identified, with only 46 failing to accurately identify the position of the ureteral opening. Background misidentification as the ureteral opening occurred only 1 time, meaning that while it slightly increases the difficulty for doctors to discern, it greatly enhances the indication of the ureteral opening position. Such results effectively help doctors save time and effort by reducing trial and error caused by misjudgments, thereby improving the quality of surgical procedures and reducing doctors’ energy consumption.
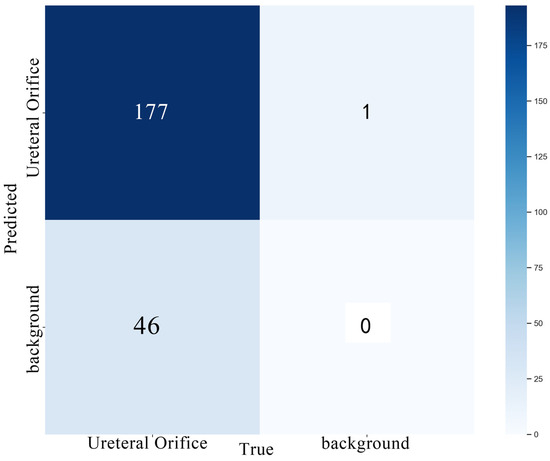
Figure 7.
Confusion matrix.
Based on the confusion matrix, we discuss the current state of related research. Due to the incomplete disclosure of the implementation code and corresponding datasets in [42], we can only make a preliminary comparison by rigidly comparing the experimental results on our respective datasets. Based on the provided confusion matrix data, we can easily derive the corresponding P (precision) and R (recall) from Equations (18) and (19). The performance of their baseline SSD model is 0.860 and 0.794, with improved performance of 0.884 and 0.926. Compared to our model, the higher recall rate and lower accuracy would clearly increase the response burden on doctors. This is one of our primary goals in model improvement: to enhance accuracy and reduce the direct workload of doctors’ decision-making. Since previous work was based on tracking algorithms to achieve real-time detection, we cannot directly evaluate the execution efficiency of different algorithms on different platforms. However, in Table 3, we compare the computational cost and detection speed of our algorithm with the traditional real-time target detection YOLO algorithm and observe no significant disadvantages. This provides an interesting comparison point with previous work.
From the results shown in Figure 8, it can be seen that in the entire series of horizontal comparisons, our network performs better. In actual image detection results, it shows good performance for various saturation and hue conditions. Moreover, compared to the native network structure, there are fewer occurrences of repeated detection of the same target, fewer occurrences of drifting centers, higher overlap of detection boxes, and more similar shapes, achieving a relatively excellent balance in performance.
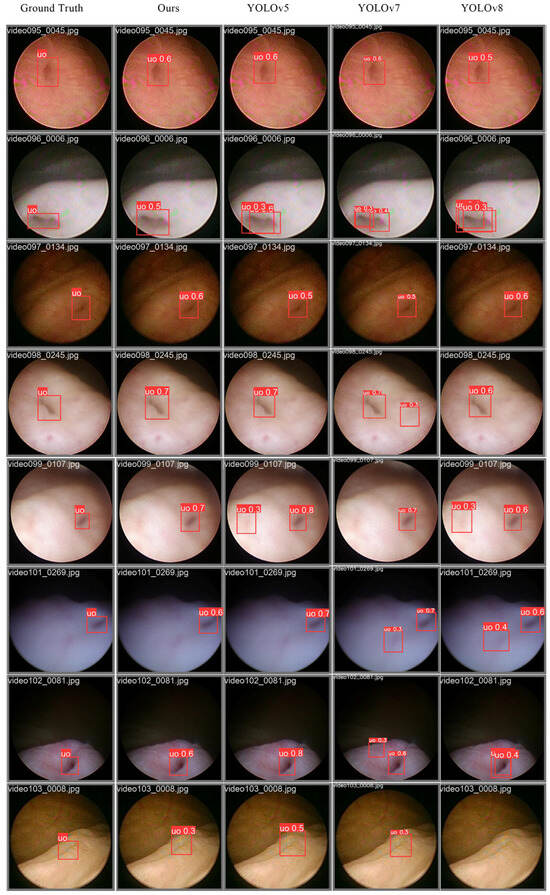
Figure 8.
The detection results of the ureteral orifice using the YOLO series algorithm models. We performed experiments on 20 cases and randomly selected the results of 8 cases to display in Figure 8. The unshown data results are consistent with those displayed. The first column shows the ground truth, the second column shows the detection results of our proposed algorithm, the third column shows the results of YOLOv5n, the fourth column shows the results of YOLOv7m, and the fifth column shows the results of YOLOv8m. The images in different rows of each group come from different independent case videos to comprehensively demonstrate the detection effects.
5. Conclusions
This paper investigates and discusses the topic of how to enhance the adaptability of target detection networks in the clinical conditions of ureteroscopes. We have developed an innovative deep learning-based ureteral orifice detection system that offers good real-time performance and achieves a balance between robustness in target detection and model complexity. By analyzing and optimizing the existing YOLO series networks, it is evident that the improved model increases the accuracy of target detection without introducing excessive parameter burdens. This attribute will be beneficial for further deployment of the model, facilitating the transition from experimentation to industrial application, and it also suggests potential directions for future research.
We evaluated our proposed detection model on an image and video dataset obtained from ureteroscopy. The ureteral orifice detection model proposed in this paper was trained on augmented images, achieving a precision of 0.901 and a recall of 0.798 on ureteroscopy images. With an overlap threshold of 0.5, the success rate of our ureteral orifice detection overlapping with the ground truth reached 0.891. The experiments demonstrated that this system is an effective tool for detecting ureteral orifices in videos, with an average processing speed of up to 175 frames per second. Therefore, this system can not only serve as an excellent tool for urologists but also has the potential to be integrated into future intelligent robotic urological surgery systems.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, L.L.; writing—review and editing, W.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate Zhuo Jian’s assistance and support for this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, J.W.; Yeh, I.H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 390–391. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.Y.; Le, Q.V. Nas-fpn: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7036–7045. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Pang, R.; Le, Q.V. Efficientdet: Scalable and efficient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10781–10790. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Learning spatial fusion for single-shot object detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.09516. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Sheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cai, L.; Ling, H. M2det: A single-shot object detector based on multi-level feature pyramid network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 9259–9266. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.Y.; Liu, W.; Ranga, A.; Tyagi, A.; Berg, A.C. Dssd: Deconvolutional single shot detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.06659. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, F. FSSD: Feature fusion single shot multibox detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.00960. [Google Scholar]
- Terven, J.; Cordova-Esparza, D. A comprehensive review of YOLO: From YOLOv1 to YOLOv8 and beyond. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.00501. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. Convnext v2: Co-designing and scaling convnets with masked autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 16133–16142. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switherland, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Bam: Bottleneck attention module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; He, L. SCConv: Spatial and Channel Reconstruction Convolution for Feature Redundancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6153–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference On Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. Simam: A simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR), online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 11863–11874. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Ke, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lau, R.W. BiFormer: Vision Transformer with Bi-Level Routing Attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 10323–10333. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Nisha, J.S.; Gopi, V.P.; Palanisamy, P. Automated colorectal polyp detection based on image enhancement and dual-path CNN architecture. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 73, 103465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, M.; Ciobanu, A. Polyp detection in video colonoscopy using deep learning. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 43, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacal, I.; Karaman, A.; Karaboga, D.; Akay, B.; Basturk, A.; Nalbantoglu, U.; Coskun, S. An efficient real-time colonic polyp detection with YOLO algorithms trained by using negative samples and large datasets. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 141, 105031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Cho, H.C.; Cho, H. Gastric lesion classification using deep learning based on fast and robust fuzzy C-means and simple linear iterative clustering superpixel algorithms. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2019, 14, 2549–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhang, H.; Meng, L.; Fan, M.; Han, C.; Zhang, K.; Ming, F.; Xie, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Gastroenterologist-level identification of small-bowel diseases and normal variants by capsule endoscopy using a deep-learning model. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1044–1054.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.S.; Lan, P.N.; Hang, D.V.; Long, D.V.; Trung, T.Q.; Thuy, N.T.; Sang, D.V. BlazeNeo: Blazing fast polyp segmentation and neoplasm detection. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 43669–43684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.P.; Chang, H.Y.; Wang, W.C.; Hu, W.X. A Novel Computer-Aided Detection/Diagnosis System for Detection and Classification of Polyps in Colonoscopy. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, J.F.; Marzullo, A.; Moccia, S.; Catellani, M.; Rosa, B.; Calimeri, F.; De Momi, E. A Lumen Segmentation Method in Ureteroscopy Images based on a Deep Residual U-Net architecture. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Ali, S.; Goldsmith, L.; Turney, B.; Rittscher, J. Multi-class motion-based semantic segmentation for ureteroscopy and laser lithotripsy. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2022, 101, 102112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, K.M.; Law, H.; Aldoukhi, A.H.; Roberts, W.W.; Deng, J.; Ghani, K.R. Deep learning computer vision algorithm for detecting kidney stone composition: Towards an automated future—ScienceDirect. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 2019, 18, e853–e854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Li, C.; Guo, Y.; Sun, L.; Jin, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, F. Predicting stone composition via machine-learning models trained on intra-operative endoscopic digital images. BMC Urol. 2024, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, D.C.; Turkbey, E.B.; Pickhardt, P.J.; Summers, R.M. A deep learning system for automated kidney stone detection and volumetric segmentation on noncontrast CT scans. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Beze, J.; Mazeaud, C.; Daul, C.; Ochoa-Ruiz, G.; Daudon, M.; Eschwège, P.; Hubert, J. Evaluation and understanding of automated urinary stone recognition methods. BJU Int. 2022, 130, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Xue, W.; Qian, D. Real-time detection of ureteral orifice in urinary endoscopy videos based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1637–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Peng, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Xu, J.; Bian, X.; Xue, W.; Qian, D. A real-time system using deep learning to detect and track ureteral orifices during urinary endoscopy. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 128, 104104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhou, D.; He, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, X. Shunted self-attention via multi-scale token aggregation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10853–10862. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, R. Wise-IoU: Bounding Box Regression Loss with Dynamic Focusing Mechanism. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10051. [Google Scholar]
- Ultralytics. YOLOv5, PyTorch Implementation of YOLOv5. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 25 May 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).