A Method for Evaluating Systematic Risk in Dams with Random Field Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Finite Element Simulation Method for Gravity Dams Considering the Spatial Variability of Parameters
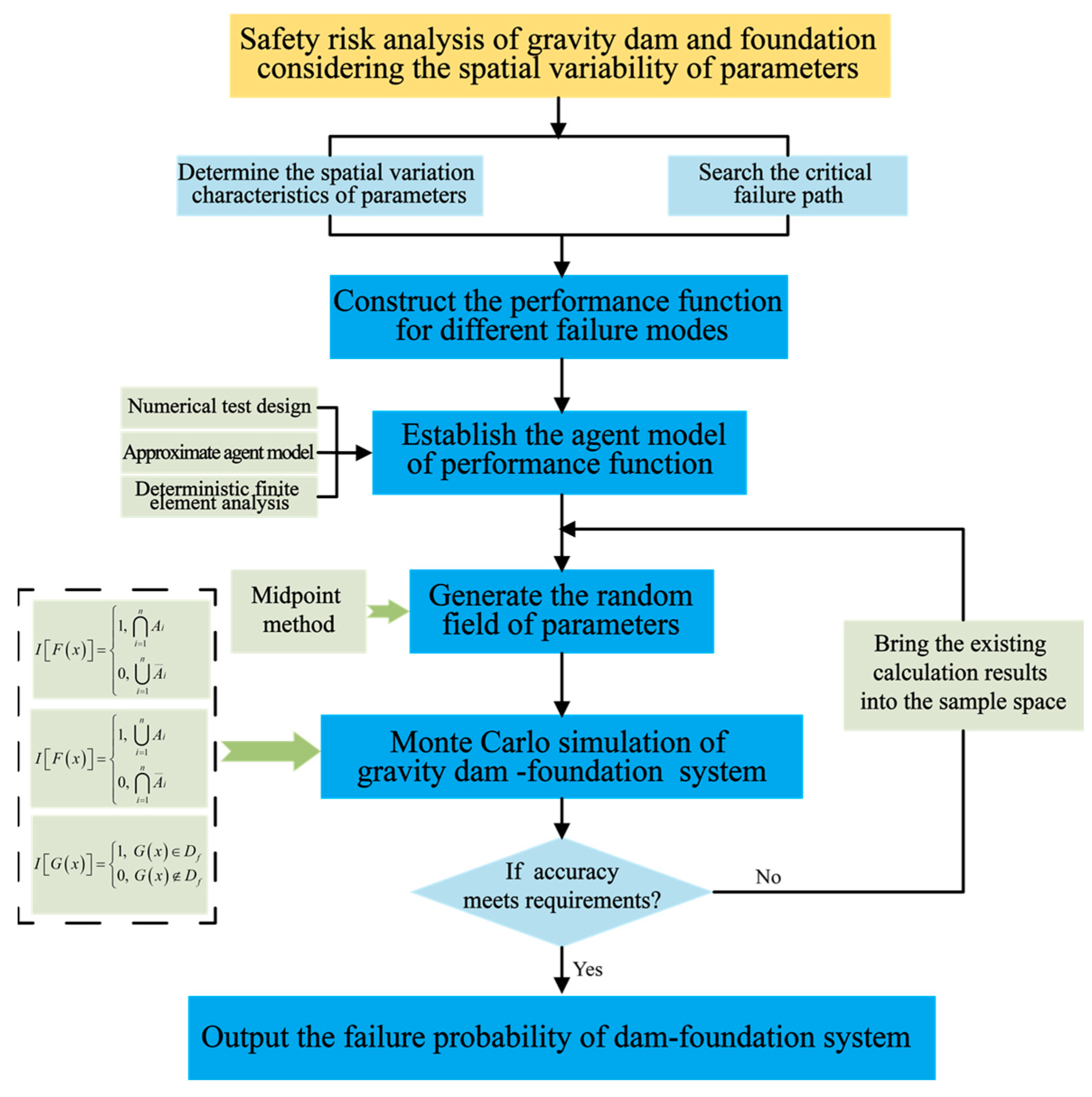
3. Risk Analysis Method for Gravity Dams Considering the Spatial Variability of Parameters
3.1. Construction of Performance Functions for Strength and Stability Failure
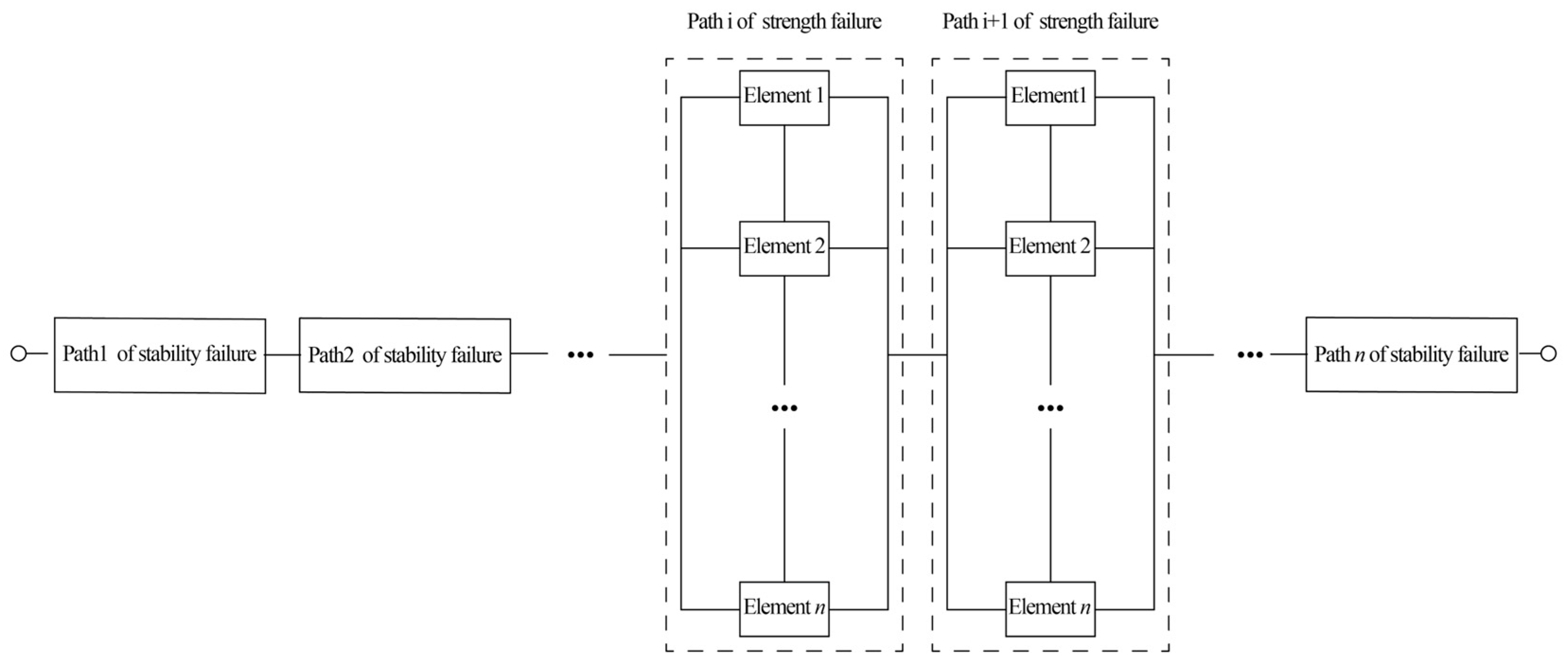
3.2. MC Method for Calculating System Failure Probability
4. Case Study
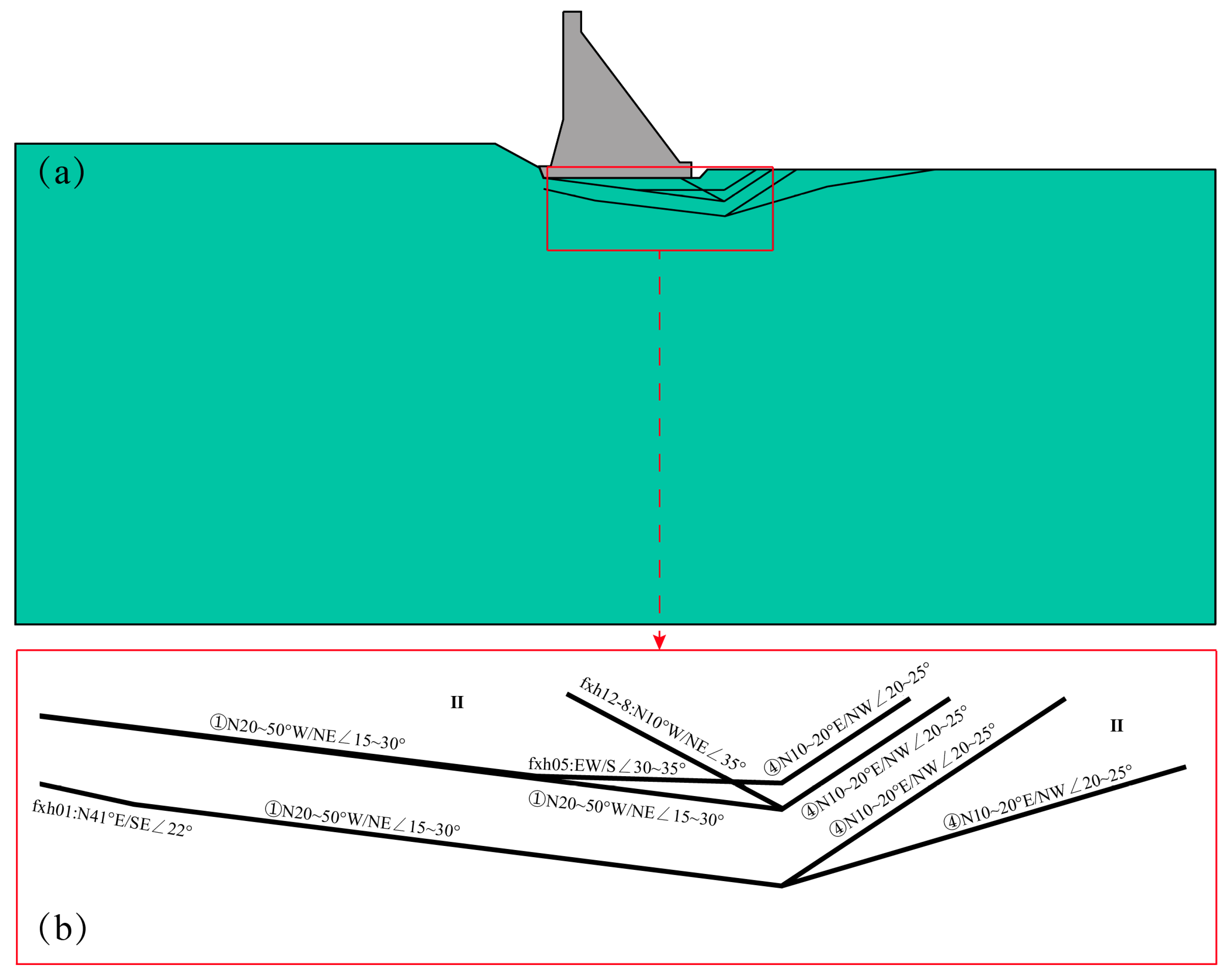
4.1. Project Overview and Geological Condition
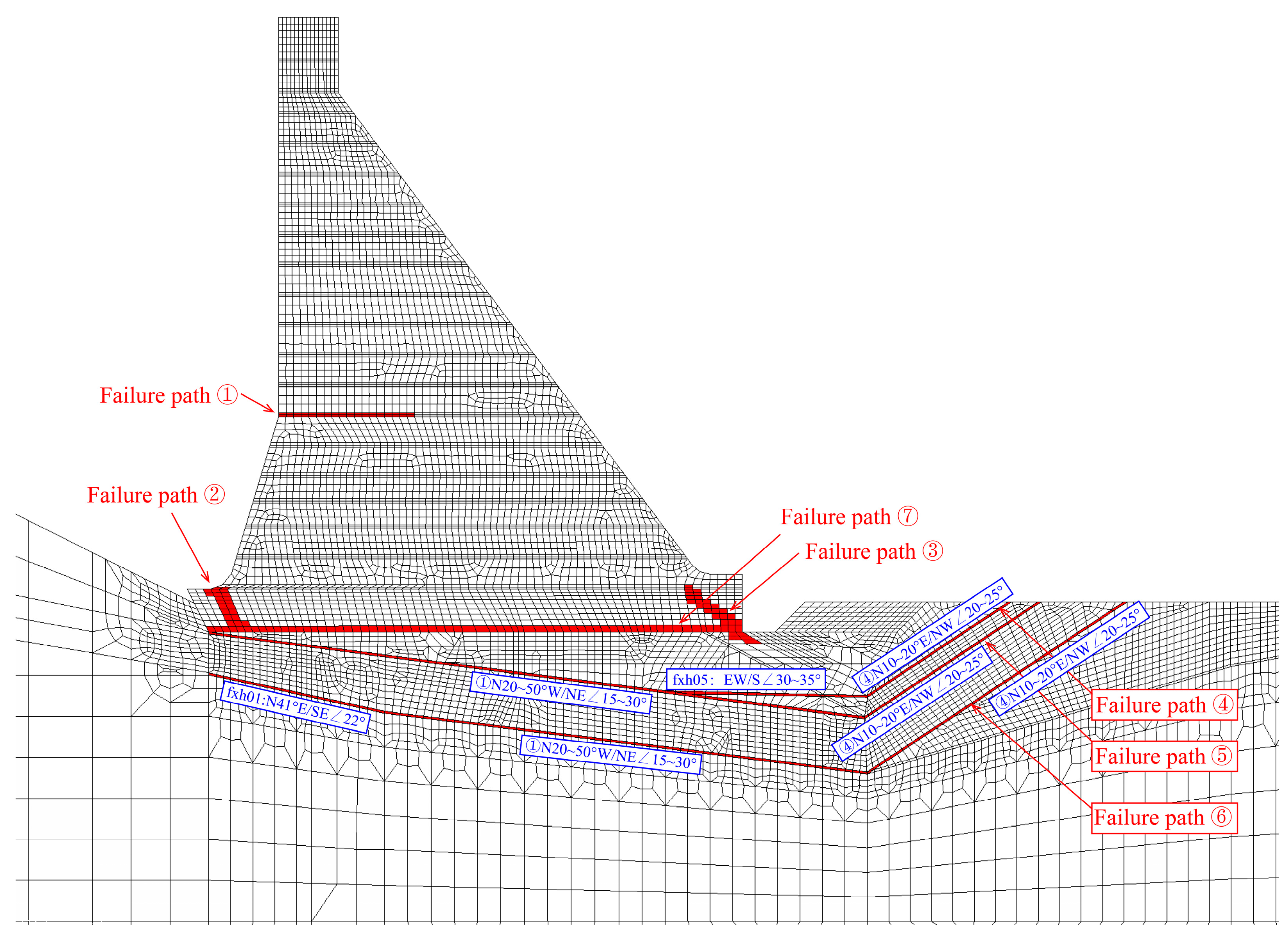
4.2. Critical Failure Paths and Performance Functions
4.3. Risk Analysis of the Dam–Rock Foundation System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Jia, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhao, L.; Jia, B. Investigation on hydraulic fracturing and flexible anti-hydrofracturing solution for Xiaowan Arch Dam. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J. Dam safety evaluation method after extreme load condition based on health monitoring and deep learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlinger, J.F. Lessons from Dam Incidents USA; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, A. Bibliography of the History of Dam Failures; WorldCat: Tarboro, NC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- US Bureau of Reclamation (USBR). Downstream Hazard Classification Guidelines; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 1988.
- Stanford University (SU). National Performance of Dams Program. 1994. Available online: http://npdp.st-anford.edu (accessed on 19 March 2024).
- Singh, V.P. Dam Breach Modeling Technology; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, M.; Chang, D. Dam Failure Mechanisms and Risk Assessment; Statistical Analysis of Failures of Dikes; John Wiley & Sons: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Song, Z.; Ge, W.; Han, R.; Wang, T. Risk analysis of instability failure of earth-rock dams based on the Fuzzy Set Theory. Water 2021, 13, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, H.; Sheng, J.; Yuan, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J. A Bayesian method for dam failure risk analysis using causal loop diagrams and word frequency analysis. Nat. Hazards 2023, 119, 2159–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, T.; Rahamn, M.; Kim, D. Effective safety assessment of aged concrete gravity dam based on the reliability index in a seismically induced site. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lim, H. A fracture model for dynamic sliding safety evaluation of a concrete dam subjected to seismic excitation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri-Ardebili, M.A.; Pourkamali-Anaraki, F. Support vector machine based reliability analysis of concrete dams. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 104, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, D.; Xu, F. Reliability analysis method of gravity dam based on probability-fuzzy-interval hybrid model and improved branch and bound method. Shuili Xuebao 2022, 53, 1476–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, C.; Liu, X.; Du, X.; Zhou, X. Fast solution method for static and dynamic reliability of gravity dam anti-sliding stability based on finite element method. J. China Three Gorges Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2023, 45, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, C.; Peyras, L.; Bacconnet, C.; Bécue, J. Probability modelling of shear strength parameters of RCC gravity dams for reliability analysis of structural safety. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2009, 13, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, C.; Peyras, L.; Bacconnet, C. On the loading/shear strength coupling in the probabilistic formulation of the limit-state in shear for gravity dams. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2010, 14, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chen, A.; He, J. Optimized variable selection of Bayesian network for dam risk analysis: A case study of earth dams in the United States. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Lu, J. Reliability analysis of concrete gravity dams based on least squares support vector machines with an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 13, 12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, D.; Wu, Z. System reliability analysis of foundation stability of gravity dams considering anisotropic seepage and multiple sliding surfaces. Eng. Comput. 2022, 39, 3108–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ren, X.; Li, J. Modeling of unstable creep failure of spatial variable rocks subjected to sustained loading. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 148, 104847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Sun, B.; Wan, Y.; Gao, X. Application of the improved entry and exit method in slope reliability analysis. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wu, Z.Y.; Pei, L.; He, K.; Chen, J.K.; Li, Z.F.; Yang, Z. Effect of the spatial variability of strength parameters on the dynamic damage characteristics of gravity dams. Eng. Struct. 2019, 183, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Lu, X.; Pei, L.; Chen, C. Effect of correlated random fields on nonlinear dynamic responses of gravity dam. Nat. Hazards 2021, 106, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, F.; Breul, P.; Carvajal, C.; Peyras, L. Stochastic seepage analysis in embankment dams using different types of random fields. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 162, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.K.; Su, X. Probabilistic volume element modeling in elastic damage analysis of quasi-brittle materials. Chinese J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2005, 24, 4282–4287. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.S.; Lumb, P. Probabilistic design of slopes. Can. Geotech. J. 1987, 24, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Ge, X. Slope reliability analysis by random FEM under constraint random field. Rock Soil Mech. 2009, 30, 3086–3092. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ramly, H.; Morgenstern, N.R.; Cruden, D.M. Probabilistic stability analysis of a tailings dyke on presheared clay-shale. Can. Geotech. J. 2011, 40, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Zhuo, R.; Ding, D.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, J.; Li, Z. Generation of correlated pseudorandom variables in Monte Carlo simulation. Acta Phy. Sin. 2012, 61, 220204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Pei, L.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z. Research and application of critical failure paths identification method for dam risk analysis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 4103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Q.; Pan, Q.L.; Ma, Z.B.; Shen, P.P. Study on Elastic Modulus and Poisson’s ratio of Roller Compacted Concrete in Shuangfengsi Reservoir. In Proceedings of the Academic Exchange Conference on Building Technology and Managemen, Beijing, China, 17 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Power China Chengdu Engineering Corporation Limited. Special Report on the Determination of Dam Foundation Surface and the Review of Anti-Sliding Stability; Power China Chengdu Engineering Corporation Limited: Chengdu, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. Preliminary analysis of elastic modulus stochastic field’s effect on concrete dam stress. Yunnan Water Power 2002, 18, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, S.; Sun, Y.; He, J. Applied Mathematical Statistic; Wuhan University Press: Wuhan, China, 2005; pp. 204–231. [Google Scholar]
| Location | Materials | Distribution | Mean | CV | Lx | Ly |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Elastic modulus | Log-normal | 18 (GPa) | 0.1 | 40 | 5 |
| Cohesion | Log-normal | 1.75 (MPa) | 0.36 | 40 | 5 | |
| Friction coefficient | Normal | 1.3 | 0.2 | 40 | 5 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | - | 0.22 | - | - | - | |
| Density | - | 2700 (kg/m3) | - | - | - | |
| Structural plane | Elastic modulus | Log-normal | 1 (GPa) | 0.1 | 40 | 5 |
| Cohesion | Log-normal | 0.15 (MPa) | 0.4 | 40 | 5 | |
| Friction coefficient | Normal | 0.75 | 0.25 | 40 | 5 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | - | 0.3 | - | - | - | |
| Density | - | 2700 (kg/m3) | - | - | - | |
| Dam concrete | Elastic modulus | Log-normal | 37.8 (GPa) | 0.1 | 10 | 5 |
| Cohesion | Log-normal | 1.3 (MPa) | 0.25 | 10 | 5 | |
| Friction coefficient | Normal | 1.35 | 0.15 | 10 | 5 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | - | 0.2 | - | - | - | |
| Density | - | 2552 (kg/m3) | - | - | - |
| Failure Paths | Considering the Spatial Variability of Parameters | Without Considering the Spatial Variability of Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Path Failure Risk | System Risk | Path Failure Risk | System Risk | ||
| Dam | ① | 4.50 × 10−7 | 7.10×10−4 | 5.51 × 10−7 | 1.18 × 10−3 |
| ② | 8.10 × 10−7 | 9.16 × 10−7 | |||
| Dam–Foundation | ③ | 5.37 × 10−5 | 2.19 × 10−4 | ||
| Foundation | ④ | 6.11 × 10−4 | 9.49 × 10−4 | ||
| ⑤ | 4.13 × 10−4 | 9.06 × 10−4 | |||
| ⑥ | 2.52 × 10−6 | 1.66 × 10−5 | |||
| ⑦ | 9.53 × 10−8 | 2.53 × 10−7 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ran, C.; Zhou, Z.; Pei, L.; Lu, X.; Gong, B.; He, K. A Method for Evaluating Systematic Risk in Dams with Random Field Theory. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114349
Ran C, Zhou Z, Pei L, Lu X, Gong B, He K. A Method for Evaluating Systematic Risk in Dams with Random Field Theory. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(11):4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114349
Chicago/Turabian StyleRan, Congyong, Zhengjun Zhou, Liang Pei, Xiang Lu, Binfeng Gong, and Kun He. 2024. "A Method for Evaluating Systematic Risk in Dams with Random Field Theory" Applied Sciences 14, no. 11: 4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114349
APA StyleRan, C., Zhou, Z., Pei, L., Lu, X., Gong, B., & He, K. (2024). A Method for Evaluating Systematic Risk in Dams with Random Field Theory. Applied Sciences, 14(11), 4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14114349




