Have Pesticides and Fertilizers Improved Agricultural Development? The Threshold Effect Based on China’s Agricultural Film Usage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Variables Description and Research Method
3.1. Variables Description
3.2. Research Method
3.3. Data Sources
4. Empirical Analysis of the Threshold Effect of China’s Agricultural Film Usage on Agricultural Development
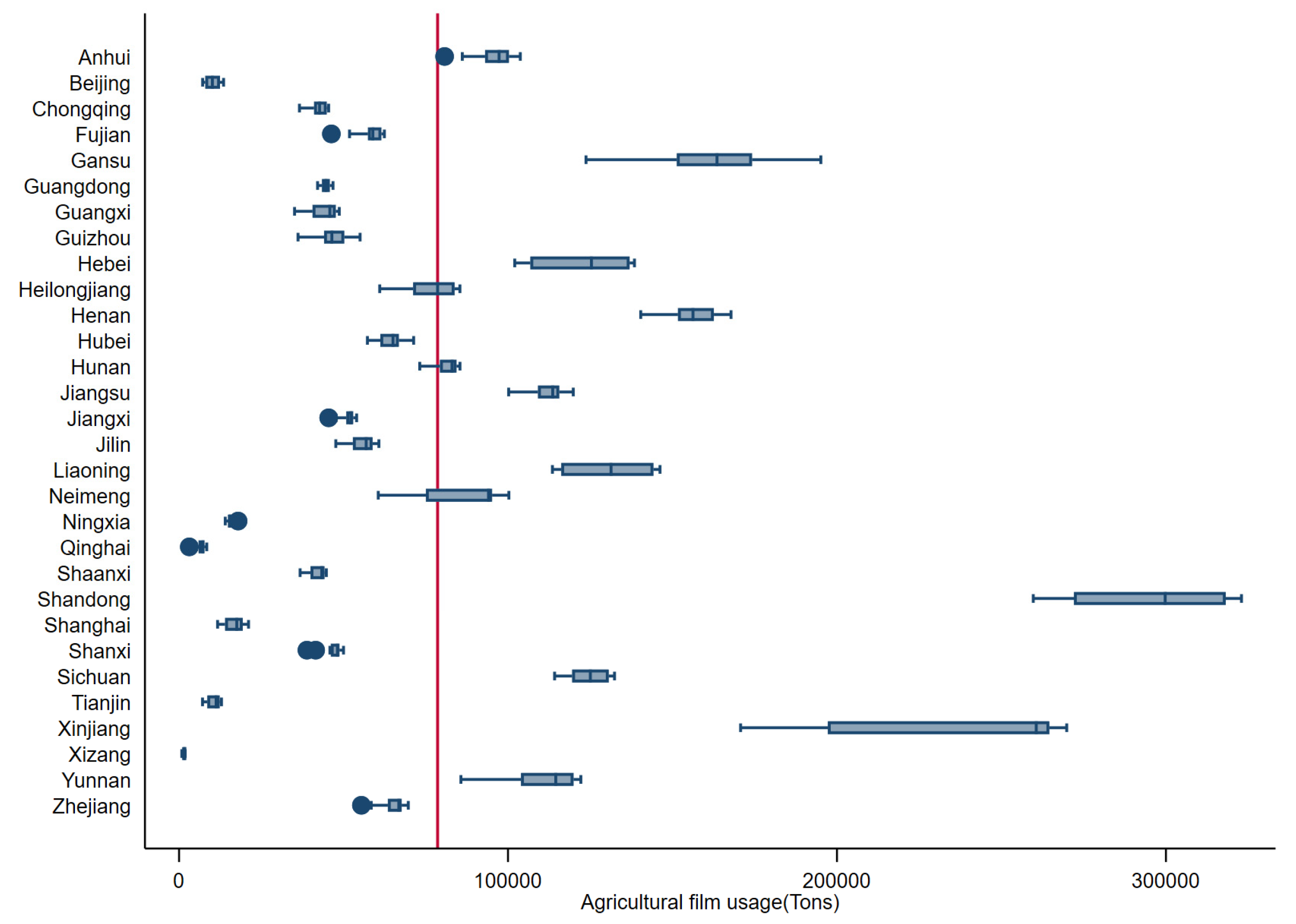
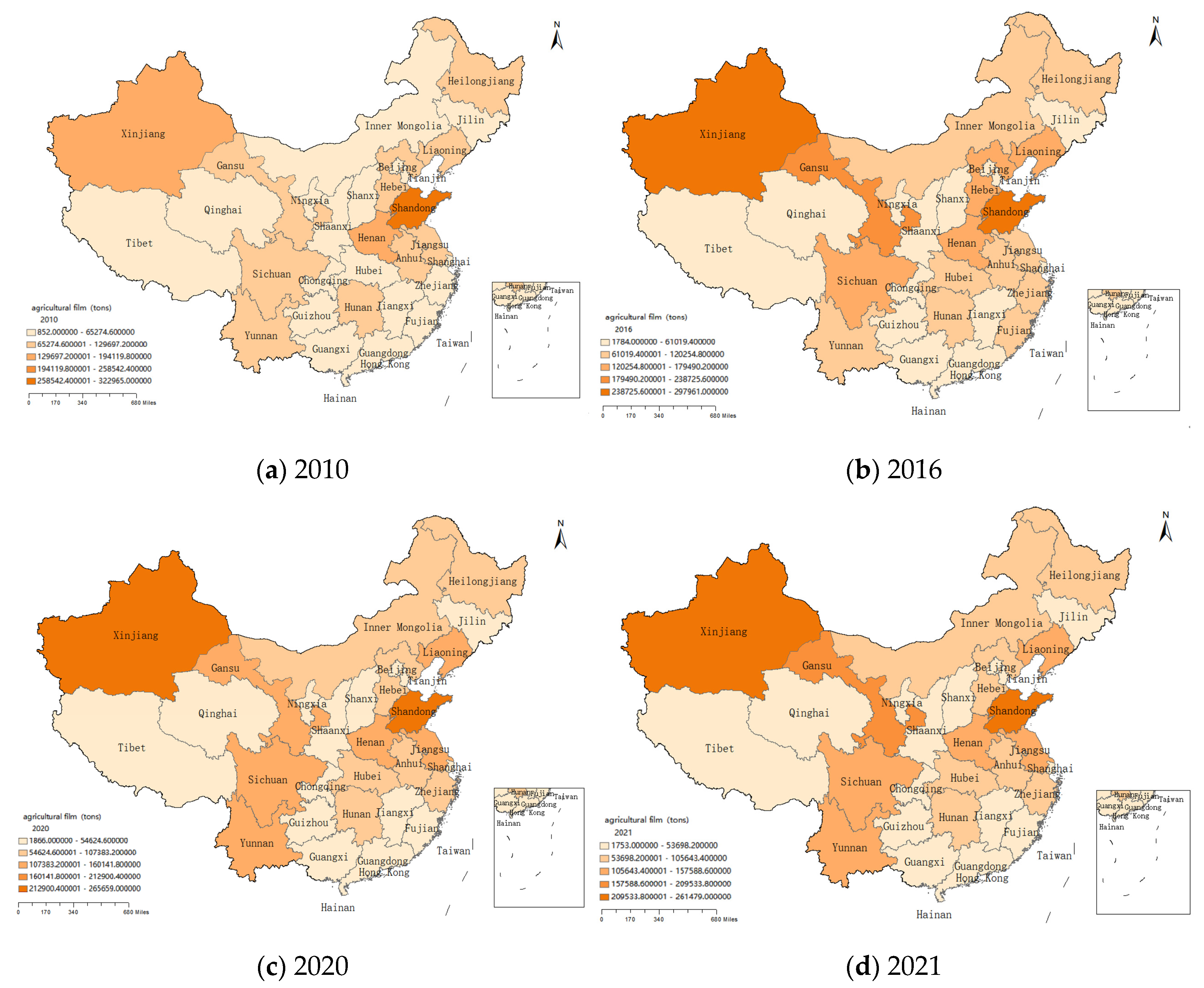
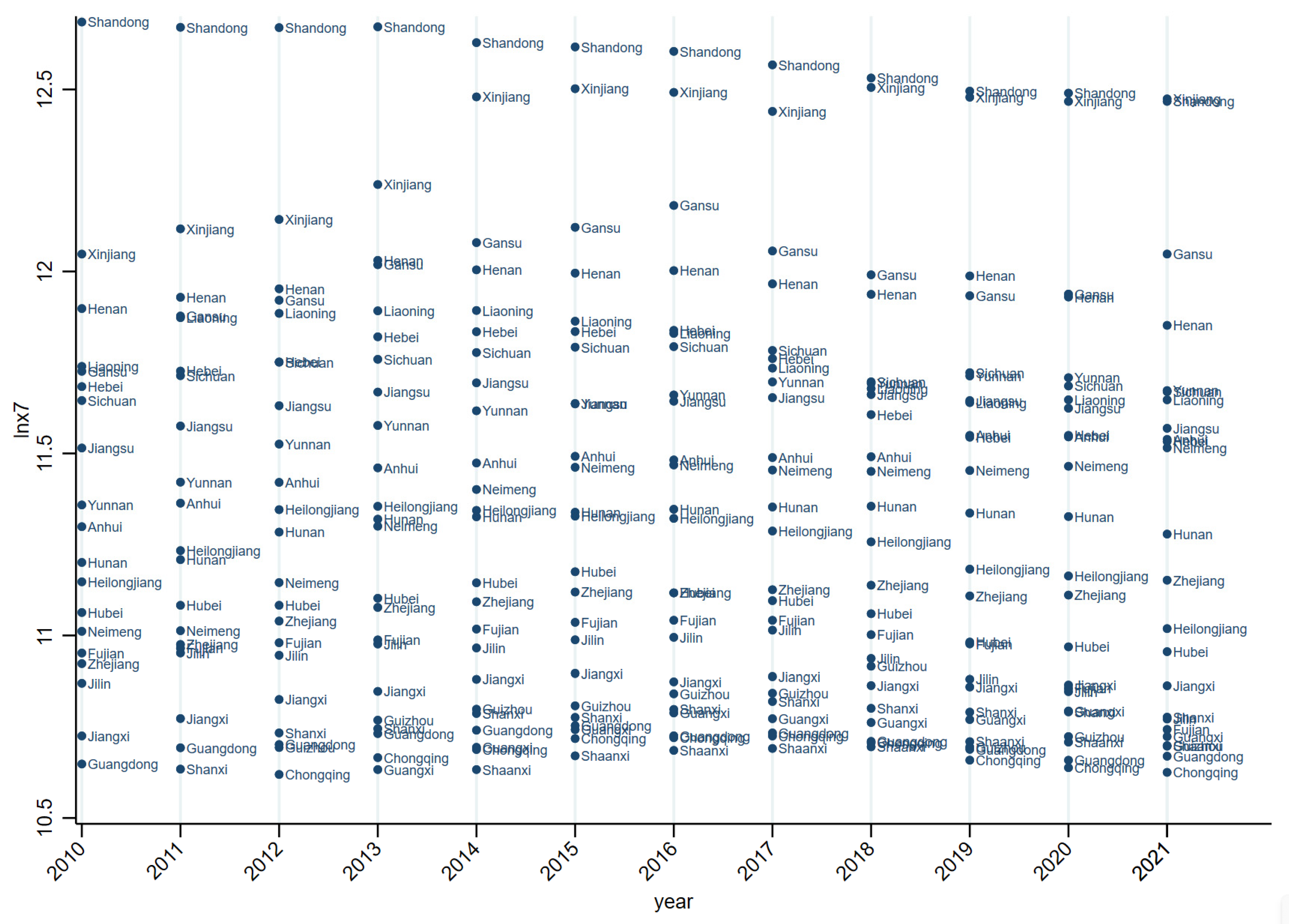
4.1. Analysis of the Current Situation of Agricultural Film Usage in China
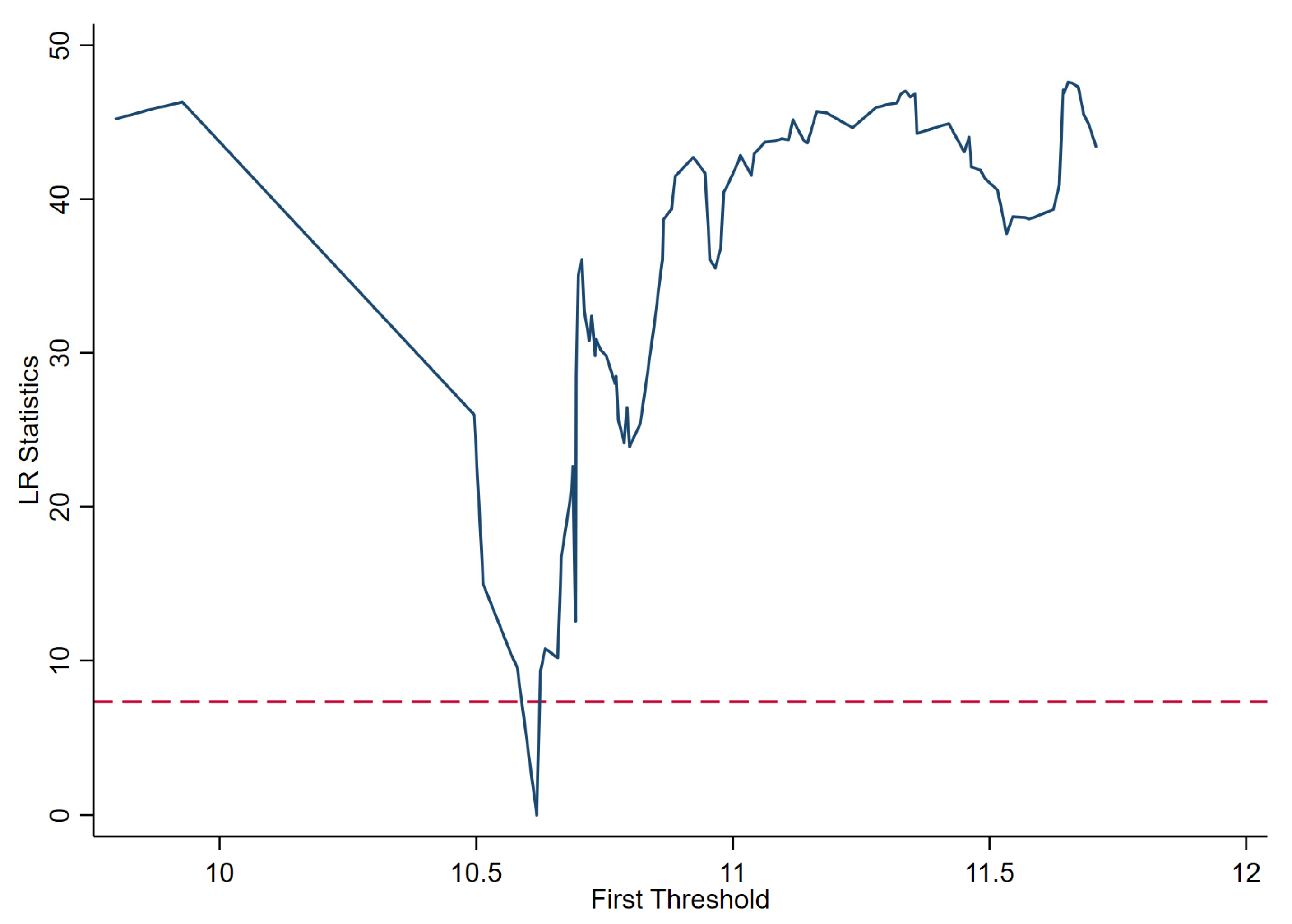
4.2. The Threshold Effect Test of China’s Agricultural Film Usage on Agricultural Development
4.3. Threshold Effect of China’s Agricultural Film Usage and Analysis of Pesticide Usage and Fertilizer Input on Agricultural Development
4.4. Robustness Test
5. Research Conclusions and Countermeasures
5.1. Research Conclusions
5.2. Countermeasures
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, H.B. CCTV Domestic. 2017. Available online: http://news.cnr.cn/native/gd/20171109/t20171109_524018911.shtml (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Fan, J.H. The Time Significance of the Rural Revitalization Strategy. Adm. Reform 2018, 2, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.S.; Li, B. Agricultural Carbon Emissions in China: Calculation, Spatial-Temporal Comparison and Decoupling Effects. Resour. Sci. 2012, 34, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Yuan, Z.; Li, B.G.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, M.J. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and factors decomposition on agricultural carbon emissions in Henan Province. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2017, 38, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, J.S.; Li, H.P. Research on Spatial-temporal Characteristics and Affecting Factors Decomposition of Agricultural Carbon Emission in China. China Population, Resources and Environment. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2011, 21, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yin, M.H. Re-evaluation of China’s Agricultural Carbon Emissions: Basic Status, Dynamic Evolution and Spatial Spillover Effects. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2022, 3, 104–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Xian, L.L. Risk Assessment of Agricultural Plastic Films Based on Release Kinetics of Phthalate Acid Esters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3676–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China; Rural Socio Economic Investigation Department of National Bureau of Statistics. China Rural Statistical Yearbook (2020); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 31–53.
- Li, W.F.; Wufuer, R.; Duo, J.; Wang, S.Z.; Luo, Y.M.; Zhang, D.Y.; Pan, X.L. Microplastics in agricultural soils: Extraction and characterization after different periods of polythene film mulching in an arid region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Agricultural plastic mulching as a source of microplastics in the terrestrial environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114096–114101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.J.; Xi, J.; Chen, X.T.; Li, X.; Ma, W.; Lu, J.; Lin, Y.B. Biodegradability and ecological impacts of polyethylene-based mulching film at agricultural environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Zhao, C.X.; Yan, C.R.; Mao, L.L.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; He, W.Q. Effects of agricultural plastic film residues on transportation and distribution of water and nitrate in soil. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, Z.; Wollmann, C.; Schaefer, M. Plastic mulching in agriculture Trading short-term agronomic benefits for long-term soil degradation? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.K.; Ma, D.; Wu, J.; Chai, C.; Shi, Y.X. Distribution of phthalate esters in agricultural soil with plastic film mulching in Shandong Peninsula, East China. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Song, W.H.; Cheng, W.S.; Li, X.X. Has the Development of Leisure Agriculture and Rural Tourism Promoted the Increase of Farmers’ Income: An Evidence from Quasi-natural Experiment. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.G.; Yuan, B.B. Adhere to Green Development to Lead Rural Revitalization. 2019. Available online: http://country.people.com.cn/n1/2019/0518/c419842-31091587.html (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Seo, H.D. White revolution of agriculture in Korea: The achievement of year-round production and distribution of horticultural crops by the expansion of greenhouse cultivation. Hortic. Abstr. 2013, 1, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Mosnáčková, K.; Šišková, A.; Janigová, I.; Kollár, J.; Šlosár, M.; Chmela, S. Ageing of plasticized poly(lactic acid)/poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) blend films under artificial UV irradiation and under real agricultural conditions during their application as mulches. Chem. Pap. 2016, 70, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.Z.; Hao, W.P.; Mei, X.R.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q.; Caylor, K. Warmer and Wetter Soil Stimulates Assimilation More than Respiration in Rainfed Agricultural Ecosystem on the China Loess Plateau: The Role of Partial Plastic Film Mulching Tillage. PLoS ONE 2017, 10, e0136578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.Y.; Ni, H.G. A method for measuring the emissions of in situ agricultural plastic film microplastics by ultraviolet and mechanical abrasion. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 152041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasirajan, S.; Ngouajio, M. Polyethylene and biodegradable mulches for agricultural applications: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 501–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Coulter, J.A.; Xie, J.H.; Luo, Z.Z.; Zhang, R.Z.; Deng, X.P.; Li, L.L. Winter wheat yield and water use efficiency response to organic fertilization in northern China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 229, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Jones, D.L.; Chadwick, D.R.; Kim, P.J.; Jiang, R.; Flury, M. Environmental impacts of agricultural plastic film mulch: Fate, consequences, and solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, V.; Romic, D.; Romic, M.; Borošić, J.; Filipović, L.; Mallmann, F.J.K.; Robinson, D.A. Plastic mulch and nitrogen fertigation in growing vegetables modify soil temperature, water and nitrate dynamics: Experimental results and modeling study. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.X.; Wang, J.; Li, D.Q.; Tanng, P.G.; Lerous, F.; Feng, Y.G. Micrometer-sized dihydrogen phosphate-intercalated layered double hydroxides: Synthesis, selective infrared absorption properties, and applications as agricultural films. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 3144–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Liu, W.J.; Jia, X.; Ma, L.; Ren, L.T.; Xue, M.; Liu, X.D. Exploration of highly efficient light conversion agents for agricultural film based on the bay-substituted perylene diimides derivatives. Dye. Pigment. 2018, 159, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.C.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.J.; Haroon, M.; Ullah, R.S.; Haq, F.; Fahad, S. Recent progress in synthesis of antifogging agents and their application to agricultural films: A review. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; He, W.Q.; Yan, C.R.; Guo, R.; Zhao, C.X. Effects of Agricultural Plastic Residual Films on Morphologic and Physiological Characteristics of Root System of Cotton and Maize in Seedling Stage. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2017, 34, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.K.; He, W.Q.; Yan, C.R. ‘White revolution’ to ‘white pollution’—Agricultural plastic film mulch in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 091001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.P.; Gu, X.B.; Li, Y.N.; Qiao, L.R.; Li, Y.P.; Fang, H.; Yin, M.H.; Zhou, C.M. Effects of residual film on maize root distribution, yield and water use efficiency in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 260, 107289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Jia, R.M.; Dun, Z.H.; Wang, B.T.; Hu, X.P.; Wang, Y. Selection and evaluation of microorganisms for biodegradation of agricultural plastic film. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, M. Biodegradation of Polymeric Mulch Films in Agricultural Soils: Concepts, Knowledge Gaps, and Future Research Directions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2304–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Meng, X.Y.; Yu, R.D.; Wang, Q. Assessment of the Effect of Mulch Film on Crops in the Arid Agricultural Region of China under Future Climate Scenarios. Water 2019, 11, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, E.; Giuri, A.; Ferrari, F.; Armenise, V.; Corcione, C.E. Biodegradable Carbon-based Ashes/Maize Starch Composite Films for Agricultural Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Zhang, J.B.; Tong, Q.M. Can Participating in Agricultural Technology Training Promote Farmers to Implement Green Production Behavior? Based on the Analysis of Family Endowment and ESR Model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 202–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.E.; Zhao, M.J. Social Networks, Information Acquisition and Households’ Behavior of Agricultural Film Recycling: A Sample of Farm Households in Yellow River Basin. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. 2022, 21, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.H.; Sun, L.B. Study on the Willingness of Corps Workers to Participate in the Treatment of Agricultural Residual Film. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Li, G.Z.; Li, Z.N. The threshold effect of the efficiency of science and technological services on regional environmental governance in China. Growth Change 2019, 50, 1026–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Jia, Q.; Li, G.Z. China’s energy consumption and green economy efficiency: An empirical research based on the threshold effect. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 36621–36629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Li, G.Z. Does environmental regulation reduce China’s haze pollution? An empirical analysis based on panel quantile regression. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.N.; Li, C.X. How industrial upgrading can improve China’s air quality: Empirical analysis based on multilevel growth model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 54456–54466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ma, J. Economic level of fertilizer application in grain production of farmers: A case study of wheat farmers in North China Plain. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2013, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, J.S. Improving wheat yield by optimizing seeding and fertilizer rates based on precipitation in the summer fallow season in drylands of the Loess Plateau. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachana, D.; Himanshu, P.; Bidisha, C.; Shivdhar, S.; Kumar, G.K.; Harit, R.C. Impact of terminal heat stress on wheat yield in India and options for adaptation. Agric. Syst. 2020, 181, 102826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.S.; Guo, Z.K.; Huang, N.; Hou, S.; He, G.; Batchelor, W.D.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, D. Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer inputs and plant populations for greener wheat production with high yields and high efficiency in dryland areas. Field Crops Res. 2022, 276, 108374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.B.; Yang, P.L.; Ren, S.M.; Ma, N.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y. Effects of fertilizer types and water quality on carbon dioxide emissions from soil in wheat-maize rotations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Mi, X.T.; Sun, X.T.; Li, Z.M.; Shi, M.; He, G.; Wang, Z.H. Current Status of Chemical Fertilizers, Pesticides, and Irrigation Water and Their Reducing Potentials in Wheat Production of Northern China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 2584–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Li, H.B.; Wang, H.G.; Wang, F.T.; Cao, S.X. Progresses of pesticide reduction techniques in wheat production and the synergistic effects on the prevention and control of wheat pest. J. China Agric. Univ. 2022, 27, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.B.; Zhang, Z.B.; Dong, R.Y.; Xie, G.N. Characterization and properties of a Sr2 Si5 N8:Eu2+-based light-conversion agricultural film. J. Rare Earths 2020, 38, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.H.; Guo, J.B.; Li, C.; Xu, X.B. Influencing factors of farmers’ cognition on agricultural mulch film pollution in rural China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.M.; Gu, X.; Liu, L.H. Diffuse phthalate acid esters losses induced from large amount of agricultural plastic film residues caused low risks for water quality in China during 1991–2017. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Li, G.Z. Impact of China’s water pollution on agricultural economic growth: An empirical analysis based on a dynamic spatial panel lag model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 6956–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.A.; Senge, M.; Mojjd, M.A.; Ito, K. Recent advances in mulching materials and methods for modifying soil environment. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 168, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, L.; Berenstein, G.; Hughes, E.A.; Zalts, A.; Montserrat, J. Polyethylene film incorporation into the horticultural soil of small periurban production units in Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 523, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Jin, T.; Geng, M.J.; Cui, K.S.; Peng, J.W.; Luo, G.G.; Delgado, A.N.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Fei, J.C. Occurrence of Microplastics from Plastic Fragments in Cultivated Soil of Sichuan Province: The Key Controls. Water 2022, 14, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Zhu, J.Z.; Gu, X.J.; Zhu, J.J. Current status of agricultural non-point source pollution and progress in prevention. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2010, 4, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.B. Where Are Potential Regions for the Reallocation of Wheat in the Context of Chinese Land Fallow and Food Security Policies? Findings from Spatio-temporal Changes in Area and Production Between 1990 and 2014. J. Resour. Ecol. 2018, 9, 592–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.L. Effects of different covering materials on soil water content and wheat yield. Land Dev. Eng. Res. 2018, 3, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.M.; Huo, Y.Z.; Peng, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.F.; Li, S.Y. Effects of different materials mulching on soil moisture-temperature and yield of wheat. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2019, 33, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.L.; Li, X.Y.; You, L.Z. Impact of Agricultural Machinery and Agricultural Labor Investment on Grain Production and Its Elasticity of Substitution. J. Huazhong. Agric. Uni. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 2, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: Estimation, testing, and inference. J. Econom. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics 2011–2022. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/ (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Jiang, R.; Guo, S.; Ma, D.D. Review of plastic film mulching system and its impact on soil ecological environment in China’s rainfed drylands. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2018, 26, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.X.; Shi, L.P.; Qiu, H.G. Can Agricultural Film Technology Increase Economic Benefits?—Based on Panel Data of 2927 Rural Households in Fixed Observation Points Nationwide. Agric. Econ. Manag. 2020, 1, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wooldridge, J.M. Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 435–436. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S.; Yang, L.L.; Gan, C.H.; Cao, J.H.; Guan, D.B. Using an extended LMDI model to explore techno-economic drivers of energy-related industrial CO2 emission changes: A case study for Shanghai (China). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 516–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Dong, G.P.; Tang, Z.P. Industrial structure optimization of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei under the triple restriction of energy, environment and employment. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 2184–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Zhang, P. Analysis of spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors between pesticide application and agricultural economic growth in China. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2018, 39, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.K.; Hu, R.F.; Cao, J.M.; Rozelle, S. Training programs and in the field guidance to reduce China’s overuse of fertilizer without hurting profitability. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 63, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, R.; Zhang, C. Does the adoption of complex fertilizers contribute to fertilizer overuse? Evidence from rice production in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.Q.; He, G.; Cui, Z.L.; Shen, J.B.; Zhang, F.S. Agri-environment policy for grain production in China: Toward sustainable intensification. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2018, 10, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Core Explanatory Variables | Threshold Variable | Threshold Order | Threshold Value | F | p | Bootstrap Times | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afu | Afu | Single threshold | 10.618 *** | 58.35 | 0.006 | 500 | [10.580, 10.625] |
| Peu | Double threshold | 9.745 | 25.01 | 0.364 | 500 | [9.264, 9.393] | |
| Fei | 10.618 | [10.580, 10.625] |
| Province | Coef | t | p | Province | Coef | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anhui | −8.1455 *** | −3.52 | 0.001 | Henan | 0.5389 *** | 3.49 | 0.002 |
| Beijing | 0.0116 | 0.01 | 0.988 | Hubei | 1.0109 *** | 7.59 | 0 |
| Tianjin | 0.2667 | 0.47 | 0.639 | Hunan | 0.3716 *** | 3.93 | 0 |
| Hebei | 0.0369 | 0.37 | 0.717 | Guangdong | 1.6016 *** | 6.49 | 0 |
| Shanxi | −0.0098 | −0.04 | 0.967 | Guangxi | 1.3158 *** | 6.42 | 0 |
| Neimong | −0.3434 ** | −2.17 | 0.038 | Chongqing | 0.4646 | 1.24 | 0.226 |
| Liaoning | −0.5244 | −1.62 | 0.116 | Sichuan | 0.1397 | 0.71 | 0.482 |
| Jilin | 0.2894 * | 1.74 | 0.093 | Guizhou | −0.2495 | −0.65 | 0.519 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.15081 | 0.60 | 0.551 | Yunnan | −0.1248 | −0.54 | 0.591 |
| Jiangsu | 0.4037 *** | 4.58 | 0 | Xizang | 0.4568 | 0.60 | 0.553 |
| Zhejiang | −0.1430 | −0.45 | 0.658 | Shaanxi | 1.3516 *** | 5.46 | 0 |
| Shanghai | −0.6491 | −0.78 | 0.440 | Gansu | −1.5196 *** | −3.07 | 0.005 |
| Fujian | 0.6154 | 1.65 | 0.111 | Qinghai | −0.3239 | −0.43 | 0.673 |
| Jiangxi | 0.0258 | 0.11 | 0.910 | Ningxia | 0.1538 | 0.34 | 0.755 |
| Shandong | −0.5529 ** | −2.39 | 0.024 | Xinjiang | −1.1026 *** | −3.16 | 0.004 |
| Coef | Std. Err | t | p > ∣t∣ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LnAfu·1 (LnAfu ≤ 10.618) | 0.9862 *** | 0.1078 | 9.15 | 0 |
| LnAfu·1 (LnAfu > 10.618) | 1.1843 *** | 0.1102 | 10.75 | 0 |
| LnPeu·1 (LnAfu ≤ 10.618) | 0.0184 ** | 0.0079 | 2.33 | 0.02 |
| LnPeu·1 (LnAfu ≤ 10.618) | 0.0320 *** | 0.0040 | 8 | 0 |
| LnFei·1 (LnAfu ≤ 10.618) | −0.7738 *** | 0.1630 | −4.75 | 0 |
| LnFei·1 (LnAfu > 10.618) | −1.1107 *** | 0.1612 | −6.89 | 0 |
| LnLai | 0.2979 * | 0.1592 | 1.87 | 0.062 |
| LnWri | 0.2368 *** | 0.0785 | 3.02 | 0.003 |
| LnTpm | 0.2425 *** | 0.0819 | 2.96 | 0.003 |
| _cons | −6.4407 *** | 1.0806 | −5.96 | 0 |
| R2 | 0.6879 | |||
| F value | 55.84 | |||
| Observations | 360 |
| Test | Statistic | df | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial error: | |||
| Moran’s I | 13.733 | 1 | 0 |
| Lagrange multiplier | 179.751 | 1 | 0 |
| Robust Lagrange multiplier | 145.714 | 1 | 0 |
| Spatial lag: | |||
| Lagrange multiplier | 34.066 | 1 | 0 |
| Robust Lagrange multiplier | 0.029 | 1 | 0.865 |
| Variables | Spatial Panel Lag Model | Spatial Panel Error Model |
|---|---|---|
| LnAfu | 0.5840 *** | 0.4587 *** |
| (8.63) | (6.09) | |
| LnPeu | 0.0085 *** | 0.0254 *** |
| (3.37) | (3.68) | |
| LnFei | −0.3549 *** | −0.1976 *** |
| (−3.85) | (−2.17) | |
| LnLai | 0.5181 *** | 0.4473 *** |
| (5.36) | (4.32) | |
| LnWri | 0.1788 *** | 0.1078 ** |
| (3.69) | (2.22) | |
| LnTpm | 0.1749 *** | 0.1379 *** |
| (3.47) | (3.05) | |
| Spatial rho | 0.7090 *** | |
| (24.74) | ||
| Spatial lanbda | 0.8044 *** | |
| (27.32) | ||
| Number | 360 | 360 |
| AIC | −436.855 | −390.627 |
| BIC | −405.766 | −359.538 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, L. Have Pesticides and Fertilizers Improved Agricultural Development? The Threshold Effect Based on China’s Agricultural Film Usage. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010006
Li Z, Li C, Wang L. Have Pesticides and Fertilizers Improved Agricultural Development? The Threshold Effect Based on China’s Agricultural Film Usage. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zining, Congxin Li, and Liqi Wang. 2024. "Have Pesticides and Fertilizers Improved Agricultural Development? The Threshold Effect Based on China’s Agricultural Film Usage" Applied Sciences 14, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010006
APA StyleLi, Z., Li, C., & Wang, L. (2024). Have Pesticides and Fertilizers Improved Agricultural Development? The Threshold Effect Based on China’s Agricultural Film Usage. Applied Sciences, 14(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010006






