Abstract
Various statistical distributions, such as Weibull, log-normal, and exponential functions, are frequently employed to interpret the dielectric breakdown (BD) strength data of insulating materials, including cross-linked polyethylene, low-density polyethylene, polypropylene (PP), and polyethylene. This study aimed to determine a suitable statistical distribution for analyzing the dielectric BD strength data of PP insulators before and after thermal degradation. Dielectric BD strength tests were conducted on thermally deteriorated PP insulators under various degradation conditions. Additionally, a coefficient of determination was employed to assess the compatibility between the dielectric BD strength data and the statistical distribution of PP insulators before and after thermal degradation. The test results indicate that the coefficient of determination for alternating current BD strength data was 0.955 in the log-normal distribution before degradation and 0.929 in the Weibull distribution after degradation. Consequently, in the analysis of the PP insulation breakdown data, the log-normal distribution was found to be suitable for data before degradation, while the Weibull distribution was deemed suitable for data after degradation. These results can lead to lower errors in the power system design process, enhancing reliability when analyzing the BD strength data of insulation materials.
1. Introduction
Numerous methods, including tan delta testing, partial discharge testing, leakage current testing, dielectric breakdown (BD) strength testing, tensile strength testing, elongation testing, differential scanning calorimetry, oxidative induction time testing, the thermogravimetric analysis, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, have been utilized to assess the properties of insulating materials [1,2].
Dielectric BD strength testing is a valuable technique for evaluating insulation properties and changes due to the aging of insulating materials. The results of dielectric BD strength testing are variable and influenced by environmental conditions, the applied voltage, and electrode shape. Consequently, this method was employed for understanding characteristics through relative comparisons under identical test conditions and should be conducted in accordance with specified considerations [3]. The selection of an appropriate statistical distribution is crucial for the reliable interpretation of BD strength data. While various statistical distributions are generally used for analyzing BD strength in insulation materials, the appropriateness of the acquired data and statistical distribution have not been adequately investigated [4,5,6,7]. This gap renders it challenging to identify errors between data and statistical distributions, posing a risk to the performance of power systems designed based on BD strength. This study aimed to investigate the correlation between dielectric BD strength data and statistical distribution, with the primary objectives of determining the suitability of various statistical distributions for BD strength data analysis and establishing a highly reliable statistical distribution using the coefficient of determination. In this study, PP insulation materials underwent thermal degradation at a maximum of 130 °C for 960 h, and the alternating current (AC) BD test was conducted to assess degradation characteristics. Additionally, a coefficient of determination was employed to identify a statistical distribution suitable for the acquired BD strength data. The findings indicate that log-normal and Weibull distributions were suitable when analyzing the BD strength of insulation before and after deterioration.
The novelty of this study lies in its establishment of a suitable statistical distribution by using the coefficient of determination before analyzing the BD strength data of insulation materials, differentiating it from previous research. Unlike other works, statistical distribution can be selected in consideration of suitability, not just the Weibull distribution function, for the interpretation of breakdown strength. This contribution can lead to lower errors in the power system design process, enhancing reliability when analyzing the BD strength data of insulation materials.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 provides the mathematical expressions and definitions of various statistical distributions for interpreting dielectric BD strength. Additionally, equations related to correlations are compiled to derive an appropriate statistical distribution. Section 3 describes the testing and setup required to obtain dielectric BD strength data. Section 4 presents an evaluation of the reliability of various statistical distributions based on the acquired data and determines the appropriate statistical distribution. Section 5 and Section 6 present the Results and Discussion, respectively.
2. Statistical Distribution
The acquired data were presumed to conform to a statistical distribution, aligning with the inherent characteristics of the distribution. Utilizing statistical distributions facilitates a quantitative analysis of the acquired data. The distribution parameters provide an accessible means to comprehend the statistical properties of a data set. Table 1 outlines the distribution functions commonly employed in the reliability field and delineates their applications. Failure rate types were classified into increased failure rate (IFR), constant failure rate (CFR), and decreased failure rate (DFR) [6,8].

Table 1.
Purpose and characteristics by statistical distribution.
2.1. Normal Distribution
The most frequently employed statistical distribution is the normal distribution, also referred to as the Gaussian distribution. A normal distribution characterizes data distributions through the use of the mean and standard deviation. The probability density function (PDF) of a normal distribution is expressed as
where μ and σ represent the mean and standard deviation, respectively. Equation (2) delineates the reliability function of a normal distribution. The reliability function signifies the probability of a failure occurring at time t. Conversely, the unreliability function, calculated as one minus the reliability function, denotes the probability of failure occurring at time t. Particularly, in the analysis of lifetime data, cumulative distribution function (CDF) values may become less dependable.
In the lifetime data analysis, a normal distribution is frequently applied, particularly in regions related to wear-out failure. However, since a normal distribution is defined over the entire real-number line, caution must be exercised when handling negative values in the PDF for a lifetime analysis.
2.2. Log-Normal Distribution
The log-normal distribution was obtained by considering the natural logarithm of the normal distribution, and it proves to be particularly valuable when dealing with data spanning a wide range. The reliability function of the log-normal distribution is expressed as follows:
where ln(t) represents the natural logarithm of the failure time, μ′ represents the mean after taking the natural logarithm of the failure time, and σ′ represents the standard deviation after taking the natural logarithm of the failure time. The log-normal distribution is frequently employed to model wear-out failures caused by natural fatigue, corrosion, and degradation.
2.3. Exponential Distribution
An exponential distribution is typically represented by one or two parameters. Equation (4) represents the reliability function of the exponential distribution.
where γ represents the location parameter, and λ represents the rate parameter. When using only one parameter, the value of γ becomes 0. The exponential distribution assumes a constant failure rate over time and is used when failures occur at a constant rate.
2.4. Weibull Distribution
The Weibull distribution typically uses two or three parameters. Equation (5) expresses the reliability function of the Weibull distribution.
where η, β, and γ represent the scale, shape, and location parameters, respectively. Similar to that in an exponential distribution, when only two parameters are used, the location parameter becomes zero. The Weibull distribution is widely used in lifetime data modeling because it can represent all regions of the bathtub curve based on the modification of the shape parameter, with β > 1 for the wear-out region, β = 1 for the CFR region, and β < 1 for the initial failure region. Additionally, β can be used to assess the consistency of the failure mechanism.
3. Evaluation of the Fit of Estimated Distributions
Accurate estimated parameter values are essential for ensuring reliability. When selecting a statistical distribution for data analysis, its goodness of fit must be evaluated. A goodness-of-fit test was conducted by comparing the error between the actual and estimated values. Various methods can be employed to assess the goodness of fit of the chosen distribution, including the correlation coefficient analysis, the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (K–S test), the mean difference (MD) test, and the likelihood value (LKV) test [9,10,11,12,13].
The correlation coefficient gauges the relationship between two variables, ranging from −1 for a perfect negative correlation to 1 for a perfect positive correlation. The coefficient of determination R2 was used to assess the goodness of fit without factoring in correlations. The R2 values ranged from 0 for no relationship to 1 for a perfect relationship. Equation (6) expresses the coefficient of determination, where represents the i-th estimate, represents the average value of the observed value, and represents the i-th observation value.
The K–S test calculates the maximum difference between the predicted values of the selected distribution and the observed data, with smaller values indicating a better fit. The K–S value can be calculated using Equation (7), where D represents the statistics of the K–S test, represents the empirical distribution function, and F(x) represents the cumulative density function.
The MD test measures the average difference between the predicted and observed data and is less sensitive to outliers than the K–S test. Both the K–S and MD tests are valuable for assessing the goodness of fit. The MD value can be calculated as follows:
The LKV test involves applying the estimated distribution parameters to the likelihood function and calculating the values for each data point that were summed to calculate the LKV. However, the LKV test may be biased when the amount of observed data is limited. Equation (9) can be used for calculating the LKV. Here, L(x) represents the likelihood function.
Following the assessment of the goodness of fit, the number of parameters in the chosen distribution was determined using the Akaike information criterion (AIC) and Bayesian information criterion (BIC). Lower AIC and BIC values signify a better fit. The AIC accounts only for the number of parameters; this approach may become less accurate when the number of samples is large. To address this issue, the BIC was employed because it simultaneously considers the number of parameters and samples. Equations (10) and (11) represent the AIC and BIC, respectively, where p signifies the number of parameters used in the model.
4. Data Acquisition
In this study, the PP insulation underwent accelerated thermal aging tests in accordance with the IEC standard [14] to ensure long-term reliability. Aging temperatures of 110 °C and 130 °C were selected based on the maximum allowable temperature for PP. The aging duration was 960 h.
Figure 1 shows the structure of a McKeown electrode comprising spherical electrodes. The test specimen underwent thermal degradation after the cable was processed into a ribbon type. Post-degradation, it took the form of a circular specimen and was positioned at the center of the electrode. Subsequently, the electrode was encapsulated with epoxy to prevent surface discharge during the dielectric BD test.
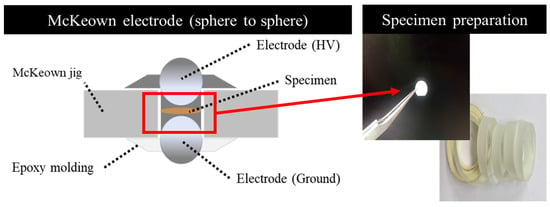
Figure 1.
Structure of McKeown electrode and specimen.
Figure 2 illustrates the specimen processing and the configuration of the McKeown electrodes [15,16]. Following thermal aging, the ribbon-type specimens were further processed into circular specimens with a diameter of 8 Φ. The AC BD strength tests were conducted using McKeown electrodes with a diameter of 10 Φ. Moldings were applied around the electrodes to prevent surface discharge, and tests were conducted in insulating oil. The right side of the figure displays views from the side, top, and bottom of the McKeown electrode. The side view allows for the verification of the specimen’s centering within the electrode. The top figure presents the state before molding the spherical electrode, emphasizing the need to confirm appropriate specimen positioning before molding the electrode.
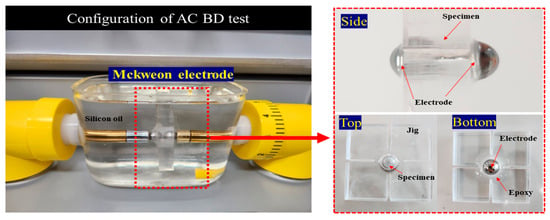
Figure 2.
Configuration of AC BD test with electrodes.
The tests entailed the application of an AC voltage at a rate of 1 kV/s until breakdown, and the breakdown voltage (BDV) was duly recorded. To convert the obtained voltage into an electric field, the thickness of the position where the breakdown occurred in the specimen was measured. Roughly 20 samples were acquired for each degradation condition. If the breakdown did not occur at the center of the electrode during processing, the specimen was deemed problematic and subsequently excluded from the data analysis. Table 2 provides a detailed overview of the BD strength test conditions.

Table 2.
AC BD test conditions.
5. Results
Goodness-of-fit statistics were computed for each condition to assess the suitability of the test data for a specific statistical distribution. The K–S statistic was excluded owing to its limitation in evaluating the overall trend of the dataset, as it assesses only a single numerical value with the highest deviation from the trend line.
The LKV test was also omitted, because it may be biased by certain values when the number of observed data points is small. The AIC and BIC were considered unsuitable for assessing goodness of fit as they evaluate the number of parameters in a statistical model and are not well suited for comparing the fit between different statistical distributions. R2 and MD values were employed to evaluate the goodness of fit, considering the entire dataset and accounting for biases in the data. In this study, five statistical distributions (log-normal, exponential-1P, exponential-2P, Weibull-2P, and Weibull-3P) were assessed using R2 and MD values. Table 3 and Table 4 present the R2 and MD values, respectively, for each statistical distribution under different degradation conditions. Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 depict the results of specimens after 960 h at 130 °C and before and after degradation as various statistical functions. The vertical axis in the figures represents the unreliability function. Three functions—log-normal, exponential, and Weibull—were used in the analysis.

Table 3.
Determination factors according to statistical distribution and degradation conditions.

Table 4.
Mean differences according to statistical distribution and degradation conditions.
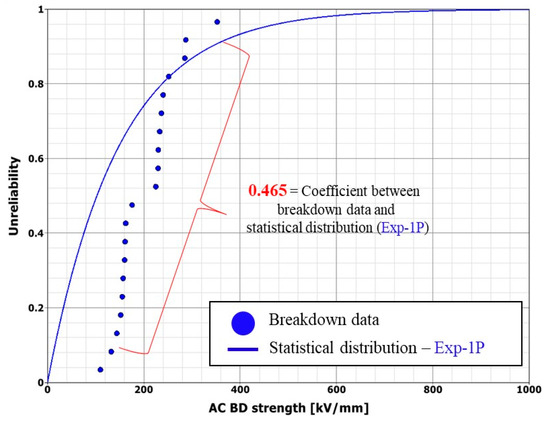
Figure 3.
Unreliability plot before thermal degradation of exponential-1P distribution.
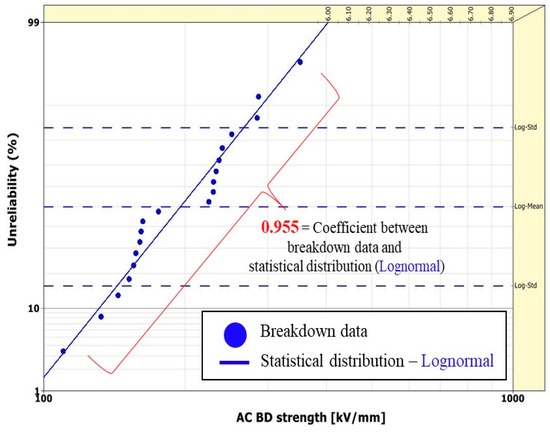
Figure 4.
Unreliability plot before thermal degradation of log-normal distribution.
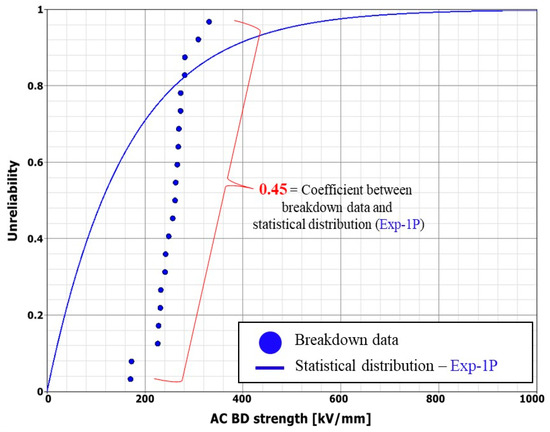
Figure 5.
Reliability plot after thermal degradation at 130 °C after 960 h of exp-1P distribution.
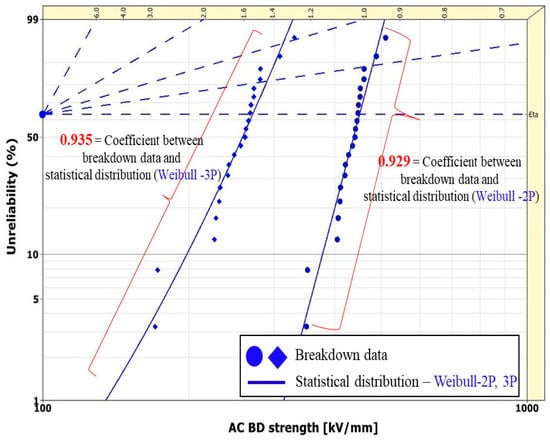
Figure 6.
Unreliability plot after thermal degradation at 130 °C after 960 h of Weibull distribution.
Figure 3 and Figure 4 illustrate unreliability functions as exp-1P and log-normal functions using the BD before degradation. Visually, exp-1P appears unsuitable for modeling BD data before degradation (R2 = 0.465), while the log-normal function provides a good fit (R2 = 0.955).
Figure 5 and Figure 6 present unreliability functions for BD data as exponential-1P and Weibull functions under 130 °C and 960 h of degradation. The coefficient of determination for Figure 5 is 0.45. Figure 6 shows graphs fitted using Weibull’s 2P and 3P. The dotted line in Figure 6 represents a guide line for visually estimating the parameters of the Weibull distribution function. The point where the horizontal dotted line meets the Weibull function represents the scale parameter. Dotted lines with a slope are for estimating the value of the shape parameter through the slope of the Weibull function. The 2P-Weibull has a coefficient of determination of 0.929, and the 3P-Weibull has a higher coefficient of determination at 0.935.
In both Table 3 and Table 4, the exponential functions consistently exhibit lower values than the other distributions, regardless of the number of parameters used. This may be unsuitable for evaluating degraded specimens because the corresponding function does not account for the change in the failure rate over time.
Table 3 and Table 4 demonstrate that as the number of parameters increases, both the R2 and MD values improve for the exponential and Weibull functions, suggesting an enhanced goodness of fit. However, the selection of an appropriate number of parameters for the distribution model should consider AIC and BIC values.
Figure 7 depicts the coefficients of determination of five types of statistical functions according to the degradation time. Log-normal and Weibull-2P and -3P have a coefficient of determination of more than 0.8 under all conditions, rendering them suitable for interpreting BD data. Among the statistical functions analyzed, exponential functions have the lowest coefficient of determination and are not suitable for interpreting BD data.
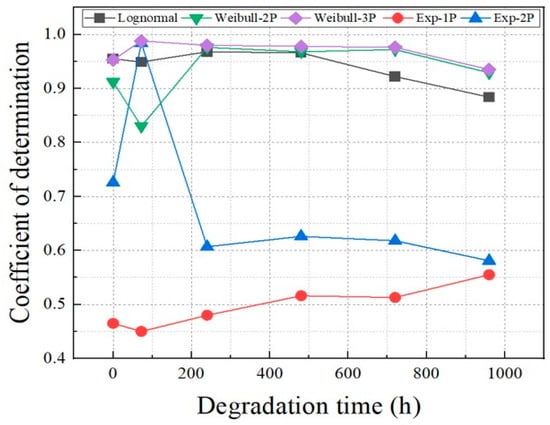
Figure 7.
Changes in the coefficient of determination of exponential function, Weibull distribution function, and logarithmic normal function according to degradation time at 130 °C.
Figure 8 depicts graphs illustrating mean differences of five types of statistical functions according to the degradation time. A large mean difference implies that the data are not suitable for the distribution function, and the coefficient of determination is also low. Among the statistical functions analyzed, the exponential function is not suitable for interpreting BD data. According to the results of Figure 7 and Figure 8, both the coefficient of determination and the MD tend to increase the fitness of the Weibull function as the degradation time increases. In addition, there is a section that reverses when comparing the log-normal function and the Weibull function. After the reversing section, the fitness of the Weibull function is the highest.
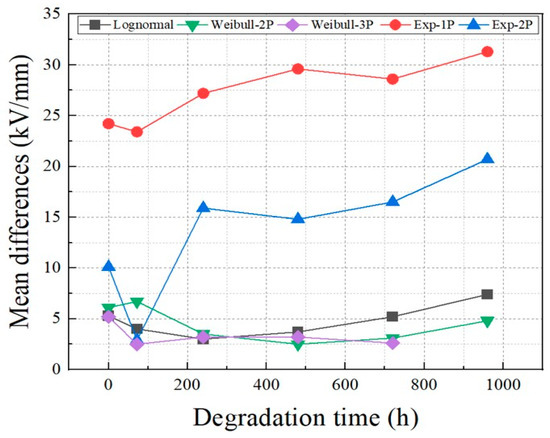
Figure 8.
Changes in the mean differences of exponential function, Weibull distribution function, and logarithmic normal function according to degradation time at 130 °C.
Table 5 lists the AIC and BIC values for selecting the number of parameters in the Weibull distribution. Additionally, the suitability of Weibull-3P was analyzed using these values. If the AIC and BIC values for the Weibull-3P model were lower than those for the Weibull-2P model, the Weibull-3P model was considered appropriate. According to the analysis results, only three of the 11 conditions were found to be suitable for Weibull-3P.

Table 5.
Determination of the number of Weibull parameters according to degradation conditions.
Considering the coefficient of determination, the most suitable statistical distribution for analysis under each degradation condition was selected, and the parameter values at that time are shown in Table 6. The selected distributions have a high coefficient of determination. Therefore, when interpreting BD data with a statistical model, it can be interpreted by minimizing the error between the observed and estimated values.

Table 6.
Distribution and statistical parameters selected based on degradation conditions.
Figure 9 depicts the box chart of the BD strength for each degradation condition using the two-parameter Weibull distribution selected in this study. Each symbol in the box chart represents the value of the Weibull cumulative density function and median value. When using a box chart, the 1% breakdown value, which is a crucial factor in designing the power system, can be visually compared with other degradation conditions.
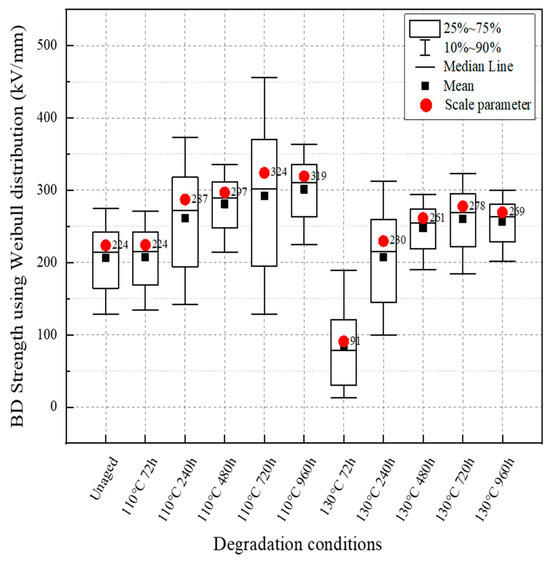
Figure 9.
Weibull box chart of BD strength according to degradation conditions.
6. Discussion
In this study, we reviewed various statistical distributions commonly employed for the interpretation of insulation BD strength data. We then devised a methodology for selecting statistical distributions based on aging temperature and time, enabling a reliable interpretation of insulation BD strength data. This approach entails the assessment of R2 and MD values to evaluate the suitability of different statistical distributions. In existing research, only a single factor, such as the coefficient of relationship or coefficient of determination, is considered for the method of selecting statistical distributions. However, in this study, the coefficient of determination and MD were judged by combining two factors.
The optimal statistical distribution for interpreting insulation breakdown data can vary depending on whether the data are collected before or after aging. This underscores the significance of considering aging conditions when analyzing the data. Accordingly, before degradation, the log-normal distribution was identified as the most suitable, with an R2 value of 0.92. The Weibull distribution was determined to be the most suitable choice at degradation temperatures of 110 °C for 720 h or more and of 130 °C for 480 h or more. In order to review the reliability through degradation, it is necessary to review degradation conditions under various conditions. The degradation condition of this study was that the temperature was selected in consideration of the maximum allowable temperature of PP and thermal stress was applied for 960 h, but degradation may not be sufficient. For this reason, the breakdown strength tends to increase, even though thermal stress is applied in Figure 9.
In this study, contrary to previous studies, we evaluated various statistical distributions using R2 and MD values to interpret insulation BD strength data. Nevertheless, the results pertaining to the selection of an appropriate statistical distribution based on degradation temperature and time are specific to the materials and electrode structure studied. Different conditions may necessitate a distinct statistical evaluation. The analysis method of this paper can be generalized and applied to other materials. For example, XLPE, an insulator commonly used in power cables, will be described. Since the maximum allowable temperature of XLPE is 90 °C, the degradation of XLPE will proceed more rapidly under the same degradation conditions as in this study, and the time for the Weibull distribution to be suitable can be expected to be faster than PP.
7. Conclusions
An insulation breakdown test was performed on a degraded PP insulating material to determine an optimized statistical distribution for analyzing the insulation breakdown strength data. The determination of the optimized statistical distribution in the breakdown strength test suggests that the most suitable statistical distribution can be selected according to the degradation time, unlike conventional studies which only use the Weibull function. The statistical distribution identified for analyzing dielectric breakdown data before degradation was log-normal, while the Weibull distribution was found to be suitable for data after degradation. The selection of the statistical distribution was based on the coefficient of determination and mean difference. The following conclusions can be drawn:
- The optimized statistical distribution may vary before and after degradation, emphasizing the importance of interpreting data based on this distinction.
- A statistical distribution suitable for degradation conditions was selected using the coefficient of determination. Before degradation, the log-normal distribution proved suitable with a coefficient of determination of 0.955. After 960 h of degradation at 130 °C, the Weibull distribution exhibited the most suitable coefficient of determination at 0.929. Consequently, interpreting the breakdown data after degradation by using the Weibull distribution is reasonable.
Further research is warranted not only on the materials applied in this study but also on insulating materials manufactured under various conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-W.L. and K.-H.P.; methodology, S.-W.L. and K.-H.P.; software, K.-H.P.; validation, S.-W.L.; formal analysis, K.-H.P.; investigation, J.-S.L.; resources, J.-S.L.; data curation, K.-H.P. and J.-S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-W.L. and K.-H.P.; writing—review and editing, K.-H.P. and S.-W.L.; visualization, K.-H.P.; supervision, H.-J.K.; project administration, S.-W.L.; funding acquisition, H.-J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) Primary research program through the National Research Council of Science and Technology (NST), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (No. 23A01026).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to R&D with companies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Preetha, P.; Joy Thomas, M. AC breakdown characteristics of epoxy nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Wang, Z.D. Statistical analysis of the AC breakdown voltages of ester based transformer oils. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2008, 15, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Sawa, F.; Ozaki, T.; Inoue, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Tanaka, T. Comparison of insulation breakdown properties of epoxy nanocomposites under homogeneous and divergent electric fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Auburn, AL, USA, 6–9 October 2006; Volume 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinan, A.J., Jr. A review of the Weibull distribution. J. Qual. Technol 1993, 25, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinne, H. The Weibull Distribution: A Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Khalili, A.; Kromp, K. Statistical properties of Weibull estimators. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 6741–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroual, A.; Khaled, U.; Mbolo Noah, P.; Sitorus, H. Comparative study of breakdown voltage of mineral, synthetic and natural oils and based mineral oil mixtures under AC and DC voltages. Energies 2017, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Malik, N.; Al-Arainy, A.; Alghuwainem, S. A review of condition monitoring of underground power cables. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis, Bali, Indonesia, 23–27 September 2012; Volume 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goegebeur, Y.; Guillou, A. Goodness-of-fit testing for Weibull-type behavior. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2010, 140, 1417–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.W.; Johnson, R.A.; Green, D.W. Two- and Three-Parameter Weibull Goodness-of-Fit Tests; United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 1989; Volume 493. [Google Scholar]
- Krit, M.; Gaudoin, O.; Remy, E. Goodness-of-fit tests for the Weibull and extreme value distributions: A review and comparative study. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 2021, 50, 1888–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littell, R.C.; Mc Clave, J.T.M.; Offen, W.W. Goodness-of-fit tests for the two parameter Weibull distribution. Commun. Stat.-Simul. Comput. 1979, 8, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, F.G.; Wirsching, P.H. A Kolmogorov-Smirnov goodness-of-fit test for the two-parameter Weibull distribution when the parameters are estimated from the data. Microelectron. Reliab. 1982, 22, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60243–1:2013; Electric Strength of Insulating Materials–Test Methods–Part 1: Tests at Power Frequencies. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Kurimoto, M.; Takenaka, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Nagao, M. Compatibility evaluation between dielectric breakdown strength and thermal conduction in epoxy/boron-nitride composite. In Proceedings of the Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena IEEE, Cancun, Mexico, 16–19 October 2011; Volume 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-S.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Jung, Y.H. A Weibull Statistical Analysis of High Thermal Resistance Insulation Material through AC Breakdown Characteristic of Mckewon Electrode. In Proceedings of the KIEE Conference; The Korean Institute of Electrical Engineers: Gangnam-gu, Republic of Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).