Abstract
The development of phytoremediation technology is constrained by gentle phytoextraction efficiency and slow biomass accumulation. In this study, a combined remediation of pioneer plants and solid waste towards Cd- and As-contaminated farmland soil was explored. Pioneer plants Cynodon dactylon and two material formulas (Steel slag (SS):pyrolusite (PY):ferrous sulfide (FS) = 3:3:2 or 1:2:8) were used in pot experiments. The DTPA method was used to extract the bioavailable heavy metals from soil, and then, the reduction rates of the bioavailable heavy metals were calculated. After harvesting plants, data of moisture content, biomass, root length and plant height were obtained. The remediation effect was evaluated according to the above indexes. The experimental results showed that the remediation effect of Bidentis pilosa was better than that of Cynodon dactylon. The addition of solid waste material significantly reduced the content of bioavailable Cd and As in soil by 97.73% and 53.54%, respectively. Suitable wastes may be a potential addition to heavy metal contaminated soils to promote phytoremediation of heavy metals.
1. Introduction
The pollution of farmland soil leaded by cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As) has become a major global environmental problem, which was mainly caused by anthropogenic activity (particularly mining and smelting). The accumulation of Cd and As in the farmland soil would cause adverse and irreversible effects on field crops and human health [1]. Cd is one of the most biologically toxic heavy metals, and long-term exposure to these contaminants can cause permanent kidney and brain damage. As is a carcinogen long discovered by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Long-term exposure to As is an important risk factor for cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and other related diseases [2]. In view of this, there has been growing research interest into various soil remediation technologies towards Cd and As contamination [3].
Phytoextraction is a continuable, cost-effective, environmentally friendly, non-destructive and in situ bioremediation technique [4]. To date, numerous specialized hyperaccumulators were employed to absorb, transport and accumulate heavy metals into the harvestable biomass. Through this way, heavy metal contaminants were oriented, collected and removed from polluted soil [5]. However, even hyperaccumulators sustained relatively slow extraction speed, and the accumulation of biomass tended to be impressionable under high heavy metal stress. Generally, to objectively assess the phytoextraction performance, field experiments need more than a year, and phytoextraction-based remediation projects need years or even a dozen years [6]. During the remediation process, there is still a high risk that the heavy metals in contaminated soil spread out into the external environment [7]. Up until now, there is an acute need for phytoextraction assisted combined remediation technology with excellent efficiency, safety and controllability [8].
It has been recognized that heavy metal ions could be released and mobilized from contaminated soil under the facilitation of hyperaccumulators in the root–soil interface (defined as rhizosphere) [9,10]. Particularly, in the assistance of the phytoextraction process, for the soil contaminated by Cd and As, the mobile Cd and As fractions in the rhizosphere were much greater than those in bulk soils [11,12]. In this case, if solidifying material was involved, it could be reasonably hypothesized that the content of Cd and As of bioavailable state in soil could be reduced dramatically by using phytoextraction remediation technology assisted by materials [13,14,15]. In addition, solidified materials can promote the secretion of organic acids by plant roots, which can transform heavy metals in soil into bioavailable heavy metals and then be absorbed and utilized by plants. Some attempts have been made. Sun et al. [16] added hydroxyapatite and giant fungus to repair the farmland polluted by Cu and Cd, reducing the content of effective copper by 72.43% and the content of effective cadmium by 48.24%. Zhang et al. [17] studied the remediation effect of Cd in wheat weakly alkaline soil using zeolite, diatomaceous earth and sodium-based bentonite as the main remediation components, supplemented by calcium dihydrogen phosphate and fulvic acid. Field experiments showed that Cd concentrations in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils decreased by 27.3–31.2% and 34.3–54.2%, respectively.
In our preliminary study, a formula for solidifying material (Steel slag:pyrolusite:FeSO4 = 1:2:8) was especially efficient for the reduction in the bioavailable state of Cd and As. Therefore, if pioneer plants were first selected in contaminated sites and then combined with this formula for remediation, the content of bioavailable heavy metals in contaminated soil could be reduced. In this study, the soil in the affected area of an arsenic smelting slag factory in Zhongshan, Guangxi, China, was combined and remediated by pioneer plants and solid waste materials.
The objectives of this study are the following:
- To study the soil pollution in the contaminated area.
- To study the combined remediation effect of potential plants and solid waste material.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Contaminated Soil
The soil used for the pot experiment was taken from an abandoned arsenic slag smelter in southern China, located in Zhongshan County, Guangxi Province (24.46° N, 111.28° E, 173 m a.s.l) (Figure 1). The soil of the sampling site was contaminated with heavy metals but host to lots of wild plants belonging to different families. A list of wild plants along with their families and the uses of those plants is provided in Table 1.
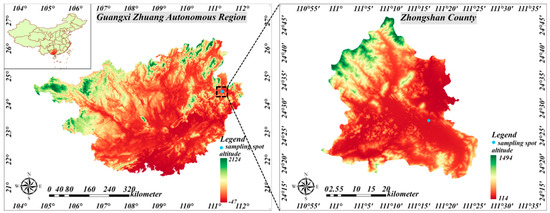
Figure 1.
Location of study site and sampling spot—Zhongshan County, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. Map created using ArcGIS Pro 3.0.0 software (https://www.esri.com/zh-cn/arcgis/products/arcgis-pro/overview and accessed date at 20 March 2023).

Table 1.
List of wild plants from the study site and the uses of those plants.
The sampling method of soil samples was as described by Barbara [18]. A total of 30 soil samples were taken from 0–20 cm of surface soil using a stainless steel shovel. These samples were mixed well and placed in a clean sample bag. Before use, the soil was air-dried and passed through a 2 mm sieve. The contents of soil pH, organic matter (SOM), available nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP), available potassium (AK) and cation exchange capacity (CEC) were studied. The results in Table 2 showed that the average pH in the study area was 6.25, and the soil was weakly acidic. The contents of AN and AP are rich, but the contents of SOM, AK and CEC are low, reaching the levels of I, I, IV, IV and IV, respectively, in the nutrient classification standard of the second national soil survey [19]. The buffered DTPA solution was used to extract the bioavailable heavy metals, and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry was used to determine the content of heavy metals. In order to assess the degree of heavy metal contamination in soil, the Nemerow method, an important pollution indicator method, was used. The Pi values of various heavy metal elements were calculated according to the Nemerow method, and then the soil pollution degree was graded according to the Pi value [20]. The results are shown in Table 3. After calculation and comparison, it was found that the pollution of Cd and As in soil was relatively serious.

Table 2.
Physical and chemical properties of soil samples.

Table 3.
The heavy metal content and pollution characteristics of soil.
2.2. Experimental Design of Combined Remediation
Cynodon dactylon and Bidentis pilosa had been selected as pioneer plants through pre-pot experiments. The solid waste material was a mixture of steel slag (SS), pyrolusite (PY) and ferrous sulfate (FS). The main components of SS and PY are shown in Table 4 and Table 5. Among them, the amount of material 1 (M1) was 8% of that of soil (SS:PY:FS = 3:3:2), while that of material 2 (M2) was 11% (SS:PY:FS = 1:2:8). Polyethylene flowerpots (8.5 × 10−4 m3) were used for the experiment. Contaminated soil and solid waste materials were evenly mixed and put into flowerpots for one week. After stabilization, 0.2 g plant seeds were planted in the flowerpot. The group that only planted plants served as the control group. The combined remediation experiment was carried out in the greenhouse for 35 days. Then, plant and soil samples were sampled for further treatment. The detailed design of the experimental group is shown in Table 6, and each treatment group was repeated 3 times.

Table 4.
Main components of steel slag.

Table 5.
Main components of pyrolusite.

Table 6.
The detailed design of the experimental group.
2.3. Analysis Method of Soil Samples
The soil samples were air-dried and grounded to pass through a 200-mesh sieve. In order to determine the total content of heavy metals in soil, samples were digested with aqua regia, and the operation was carried out according to Chinese standard document HJ 803-2016. Accordingly, 0.1 g soil was weighed and placed in a PTFE crucible and digested by aqua regia on an electric heating plate (DB-3S, Yilin scientific instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). After digestion, it was washed and fixed to volume. In addition, according to Chinese standard HJ 804-2016, DTPA was used to extract and determine the available elements in soil. The steps are as follows: 10 g of soil sample was weighed and placed in a 100 mL conical flask containing 20 mL TEA-CaCl2-DTPA extract. The samples were oscillated for 2 h at a frequency of 200 r/min at room temperature and then centrifuged to take the supernatant for determination. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (NEXION 2000, Parkin Elmer Healthy Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) was used to determine the content of heavy metals.
2.4. Analysis Method of Plant Samples
The mass of plants before and after drying was weighed to calculate the moisture content. Then, plants were divided into aboveground parts (stems and leaves) and underground parts (roots), and the longest ones were selected to measure the root length and plant height. Finally, the average value of three groups of parallel experimental data was taken as the final data. Before determining the content of heavy metals, plant samples should be digested. The ground plant sample was digested with 8 mL of aqua regia on electric heating plate [21]. After digestion, fix the volume of digestion solution to 50 mL. Subsequently, the heavy metal content of the sample was determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (NEXION 2000, Parkin Elmer Healthy Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Plants
It had been found that heavy metals in soil affected plant growth indexes, such as water content, biomass and plant and root length [22]. As shown in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4, the moisture, biomass, plant height and root length of plants under different treatment groups are shown, respectively.
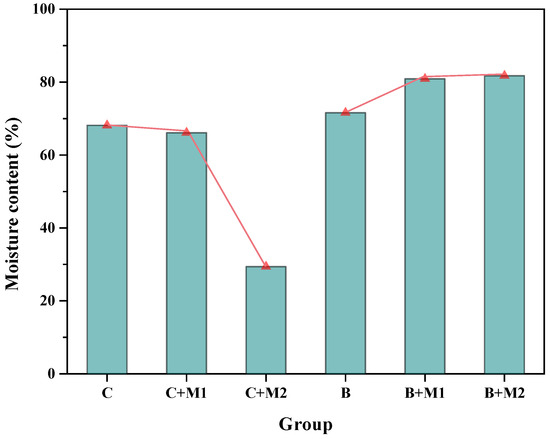
Figure 2.
Moisture content of plants in different treatment groups.
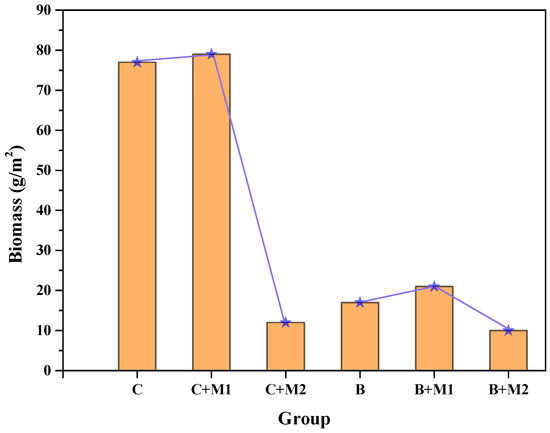
Figure 3.
Biomass of plants in different treatment groups.
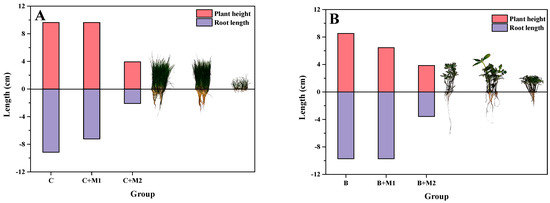
Figure 4.
Root length and plant height of Cynodon dactylon (A) and Bidentis pilosa (B) in different treatment groups.
As one of the key indicators of plant growth, moisture content is measured and shown in Figure 2. Water is a key factor affecting the survival, growth and distribution of vegetation in terrestrial ecosystems. The water balance of the soil–plant–atmosphere continuum is a key mechanism for photosynthesis and plant growth. Therefore, monitoring the water content of plants is essential for studying plant growth. Comparing group C and group C+M1 in Figure 2, the results showed that the moisture content was 68.13% without adding material but decreased with little change to 66.13% after adding material 1. However, as shown in group C+M2 in Figure 2, the moisture content decreased significantly to 29.4% after the addition of material 2. It can be seen that material 2 had a devastating effect on the growth of Cynodon dactylon. For Bidentis pilosa, the moisture content was 71.59% without adding any materials, as shown in group B in Figure 2. The moisture content of plants increased slightly to 80.89% and 81.74%, respectively, after the addition of material 1 (group B+M1) and 2 (group B+M2). From the point of view of the moisture content alone, both materials 1 and 2 can promote the growth of Bidentis pilosa. In conclusion, adding materials can promote the growth of both plants.
Figure 3 shows the biomass of plants under different treatment groups. The results show that the addition of materials can also affect the growth of Cynodon dactylon. As could be seen from group C, C+M1 and C+M2 in Figure 3, material 1 would slightly promote the growth of Cynodon dactylon while material 2 would inhibit the accumulation of biomass of Cynodon dactylon to a large extent. This indicated that material 1 was a good soil additive, which was beneficial to the extraction of heavy metals from plants. For Bidentis pilosa, the effects of materials 1 and 2 on its growth were similar to those of Cynodon dactylon–that is, material 1 promoted the growth of the plant, while material 2 was the other way around, as shown in groups B, B+M1 and B+M2 in Figure 3. Therefore, material 1 works better than material 2. Based on the above discussion, it can be concluded that material 1 is more suitable as a soil additive to promote the effect of phytoremediation.
In Figure 4, the aboveground height and underground length of Cynodon dactylon (A) and Bidentis pilosa (B), respectively, were shown when different soil additives were introduced. As shown in group C of Figure 4A, when no material was added, the aboveground height and underground length of Cynodon dactylon were 9.63 cm and 9.17 cm, respectively. As shown in group C+M1 and C+M2 of Figure 4A, after adding material 1 and 2, the above two index parameters are 9.63 cm and 7.23 cm, and 3.93 cm and 2.1 cm, respectively. It can be seen that material 1 had no great influence on plant growth, but material 2 was extremely restrictive to it. The same conclusion was reached for Bidentis pilosa. Group B in Figure 4B indicated that the above-ground height of the plant was 8.52 cm, and the underground length was 9.73 cm when no material was added. As shown in group B+M1 and B+M2 of Figure 4B, when material 1 and 2 were added, the aboveground heights were 6.45 cm and 3.85 cm, and the underground length were 9.73 cm and 3.57 cm, respectively. Similarly, it was shown that material 1 had little effect on plant growth, but material 2 had a very adverse effect on plant growth. Therefore, it can be concluded that material 1 had more advantages than 2 in promoting phytoremediation.
Therefore, compared with material 2, material 1 had a better promoting effect on the growth of the two plants studied and was more suitable for the remediation of contaminated soil.
3.2. Changes of Bioavailable Heavy Metals in Soil
Bioavailable heavy metals were heavy metal elements that were easy to migrate in soil and could be absorbed by plant roots during the growth period. The purpose of soil remediation was to reduce the bioavailable heavy metals in the soil, so the reduction rate of bioavailable heavy metals which was defined as Equation (1) was used to evaluate the remediation effect in this study.
where ηBefore is the content of bioavailable heavy metals in soil before phytoremediation, and ηAfter is the content of bioavailable heavy metals in soil after phytoremediation.
Figure 5 shows the reduction rates of bioavailable Cd and As in soil under different treatment groups. When the soil was only remediated by Cynodon dactylon (group C of Figure 5) or Bidentis pilosa (group B of Figure 5), the bioavailable content of heavy metals increased. This showed that parts of heavy metals were activated by plants, which was consistent with the research of Abou-Shanab et al. [23]. However, the bioavailable content of heavy metals in soil decreased in all the treatment groups of plant-material combined remediation. For Cynodon dactylon, the reduction rates of bioavailable Cd and As in C+M1 treatment group were 16.93% and 8.92%, respectively, while those in C+M2 treatment group were 76.88% and 32.81%. For Bidentis pilosa, the reduction rates of bioavailable Cd and As in B+M1 treatment group were 12.35% and 40.42%, respectively, and those in B+M2 treatment group were 97.73% and 53.54%. It could be found that the remediation effect of Bidentis pilosa was better than that of Cynodon dactylon under the same treatment. The experimental results showed that the addition of solid waste materials was helpful to stabilize heavy metals, especially M2 solid waste material group.
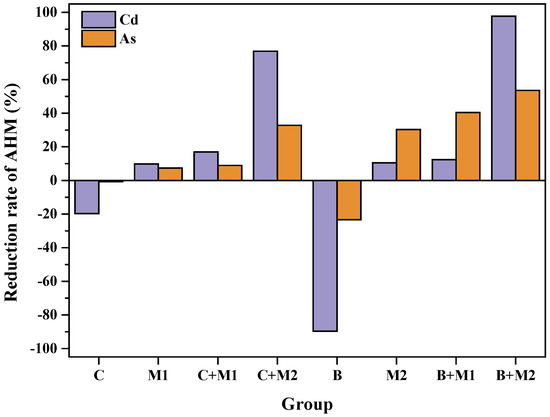
Figure 5.
Reduction rate of soil bioavailable heavy metals in different treatment groups.
The bioavailability of heavy metals was related to the physical and chemical properties of soil, such as pH, texture, dissolved organic matter and metal oxides [24]. By means of SEM-EDS and XRD analysis, Yao et al. [25] found that Cd and As were stabilized because the addition of the material led to an increase in pH value, which promoted the precipitation of Cd2+ in the form of silicate, phosphate and hydroxide, and the arsenate combined with iron, aluminum, calcium and magnesium to form insoluble arsenate compounds. In addition, studies had shown that iron oxides contained in soil or materials could adsorb Cd through covalent bonds after hydration and stabilize As through specific adsorption, non-specific adsorption and co-precipitation [26].
Therefore, the mechanism through which adding M1 and M2 could effectively reduce bioavailable Cd and As in soil is described in Figure 6 and as follows: firstly, an increase in pH promoted precipitation of Cd2+ in the form of silicates, phosphates and hydroxides [27]. Because steel slag and pyrolusite were alkaline, their addition led to the increase of soil alkalinity, which stabilized part of cadmium in the soil. Secondly, the pollution of Cd and As in soil usually showed the opposite geochemical behavior—that is, high pH soil was beneficial to the stabilization of Cd, but it could promote the dissolution of arsenic in soil [28,29]. Therefore, 18.12% and 22.54% of the Fe2O3 contained in steel slag and pyrolusite (Table 3 and Table 4) and ferrous sulfate played a role in stabilizing Cd and As. Thirdly, arsenic anion species could be adsorbed on aluminum, manganese and calcium oxides. Fourthly, solid waste materials might promote plant roots to secrete organic acids, which would promote the activation of heavy metal ions in soil to be converted into bioavailable heavy metals for extraction and absorption by plants. Finally, steel slag and pyrolusite contained 12.12% and 44% of SiO2, respectively, so the contents of bioavailable Cd and As could be significantly reduced [30,31].
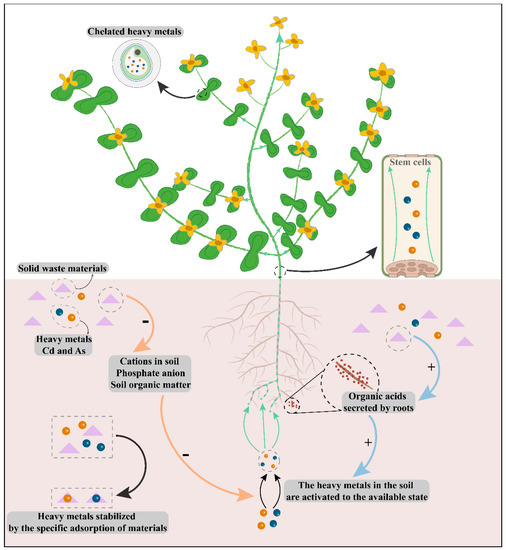
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of plant combined materials remediation of heavy metals contaminated soil.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, two kinds of plants (Cynodon dactylon and Bidentis pilosa) and two kinds of solid waste materials were combined to carry out greenhouse experiments for combined remediation. Compared with the single phytoremediation method, the addition of solid waste material formula could quickly and effectively reduce the bioavailable content of heavy metals in soil. According to the growth index of plants, it was found that Bidentis pilosa was more suitable for remediation of Cd- and As-contaminated soil than Cynodon dactylon. In addition, Bidentis pilosa + the material 2 treatment could effectively reduce 97.73% bioavailable Cd and 53.54% bioavailable As, which had considerable remediation effect. Therefore, the combined remediation of potential remediation plants and solid waste materials was a fast and effective way to remediate Cd- and As-contaminated soil.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W. and C.Z.; methodology, J.W. and C.Z.; formal analysis, J.W.; investigation, J.W., C.Z. and H.Y.; data curation, J.W. and C.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W. and C.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.C. and P.C.; supervision, J.C. and P.C.; funding acquisition, J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National key Research and development program [2019YFC1803500]; the Natural Science Foundation of China [52004336, 52074357, 52274287]; the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan [2022JJ30713]; the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province [2022RC1039]; Postgraduate Innovative Project of Central South University [1053320213706]; and the foundation of Vanadium titanium union.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ao, M.; Chen, X.; Deng, T.; Sun, S.; Tang, Y.; Morel, J.L.; Qiu, R.; Wang, S. Chromium biogeochemical behaviour in soil-plant systems and remediation strategies: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wei, S.; Ji, D.; Bai, J. Co-Planting Cd Contaminated Field Using Hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. through Interplant with Low Accumulation Welsh Onion. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2015, 17, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diarra, I.; Kotra, K.K.; Prasad, S. Assessment of Biodegradable Chelating Agents in the Phytoextraction of Heavy Metals from Multi-Metal Contaminated Soil. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.J.M.; Brooks, R.R. Terrestrial Higher Plants Which Hyperaccumulate Metallic Elements, a Review of Their Distribution, ecology and phytochemistry. Biorecovery 1989, 1, 81–126. [Google Scholar]
- Mayerová, M.; Petrová, Š.; Madaras, M.; Lipavský, J.; Aimon, T.; Vaněk, T. Non-enhanced phytoextraction of cadmium, zinc, and lead by high-yielding crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 14706–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Jiang, P.; Fu, X.; Liu, J.; Sunahara, G.I.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, H.; Lin, F.; Wang, X. Phytoextraction of cadmium-contaminated soil by Celosia argentea Linn.: A long-term field study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; You, S.; Zheng, J. Review in Strengthening Technology for Phytoremediation of Soil Contaminated by Heavy Metals. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 242, 052003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ge, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, Z.; Song, F.; Hu, S. Enhanced Phytoextraction of Heavy Metals from Contaminated Soil by Plant Co-cropping Associated with PGPR. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, W.W.; Bunkowski, M.; Puschenreiter, M.; Horak, O. Rhizosphere characteristics of indigenously growing nickel hyperaccumulator and excluder plants on serpentine soil. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 123, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, W.W.; Dessaux, Y.; Hinsinger, P.; Lemanceau, P. Rhizosphere processes and management in plant-assisted bioremediation (phytoremediation) of soils. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 385–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzaga, M.I.S.; Ma, L.Q.; Santos, J.A.G.; Matias, M.I.S. Rhizosphere characteristics of two arsenic hyperaccumulating Pteris ferns. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4711–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Twardowska, I. Main rhizosphere characteristics of the Cd hyperaccumulator Rorippa globosa (Turcz.) Thell. Plant Soil 2013, 372, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Kang, J.; Lu, K.; Zhou, R.; Mu, L.; Zhou, Q. Graphene oxide amplifies the phytotoxicity of arsenic in wheat. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, srep06122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Lee, B. Influence of nano-TiO2 particles on the bioaccumulation of Cd in soybean plants (Glycine max): A possible mechanism for the removal of Cd from the contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 170, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.T.B.; Nawaz, M.F.; Khawaja, H.F.; Gul, S.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, I.; Rasul, F.; Rizwan, M. Ecophysiological response of early stage Albizia lebbeck to cadmium toxicity and biochar addition. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Xu, L.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Chen, Y. Effects of Combined Remediation of Hydroxyapatite and Plants on Microbial Communities in Rhizosphere Soil of Cu/Cd Contaminated Plants. Soils 2016, 48, 946–953. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, A. Remediation effects and mechanisms of typical minerals combined with inorganic amendment on cadmium-contaminated soil: A field study in wheat. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 38605–38615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klik, B.; Holatko, J.; Jaskulska, I.; Gusiatin, M.Z.; Hammerschmiedt, T.; Brtnicky, M.; Liniauskienė, E.; Baltazar, T.; Jaskulski, D.; Kintl, A.; et al. Bentonite as a Functional Material Enhancing Phytostabilization of Post-Industrial Contaminated Soils with Heavy Metals. Materials 2022, 15, 8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Soil Survey Office. Soil General Survey Technology in China; National Soil Survey Office: Kolkata, India, 1992.
- Fadili, H.E.; Ali, M.B.; Touach, N.; Mahi, M.E.; Lotfi, E.M. Ecotoxicological and pre-remedial risk assessment of heavy metals in municipal solid wastes dumpsite impacted soil in morocco. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. Establishment of Detection Method for Heavy Metals in Moss. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.; Xia, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. Cadmium accumulation and growth response to cadmium stress of eighteen plant species. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 23071–23080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shanab, R.A.; Ghanem, K.; Ghanem, N.; Al-Kolaibe, A. The role of bacteria on heavy-metal extraction and uptake by plants growing on multi-metal-contaminated soils. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Ghosh, D.; Dash, A.; Bose, S. Arsenic contamination in soil and sediment in India: Sources, effects, and remediation. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Wang, Y.; Ling, X.; Chen, Z.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Ying, R.; Qiu, R. Effects of an iron-silicon material, a synthetic zeolite and an alkaline clay on vegetable uptake of As and Cd from a polluted agricultural soil and proposed remediation mechanisms. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Shen, P.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Jiang, J.; Kong, X.; Gu, X. Comparison of Four Amendments for Arsenic and Cadmium Combined Contaminated Soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Hsi, H.; Hseu, Z.; Jheng, S. Chemical stabilization of cadmium in acidic soil using alkaline agronomic and industrial by-products. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A-Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2013, 48, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Lv, Y.; Cui, J.; Zeng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C. Simultaneous alleviation of cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice by applying zero-valent iron and biochar to contaminated paddy soils. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, K.; Zhang, C.; Ren, S.; Huang, H.; Rong, Q.; Zhou, Y. Remediation of Soil in a Deserted Arsenic Plant Site Using Synthesised Mgalfe-Ldhs. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Qiu, H.; Tian, T.; Zhan, S.; Deng, T.; Chaney, R.L.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Morel, J.; Qiu, R. Mitigation effects of silicon rich amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on multi-metal contaminated acidic soil. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhan, Q.; Hong, L.; Bocharnikova, E.; Matichenkov, V. Regulation of As and Cd Accumulation in Rice by Simultaneous Application of Lime Or Gypsum with Si-Rich Materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 7271–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).