Fast Jukebox: Accelerating Music Generation with Knowledge Distillation
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Background
4. Methodology
Knowledge Distillation
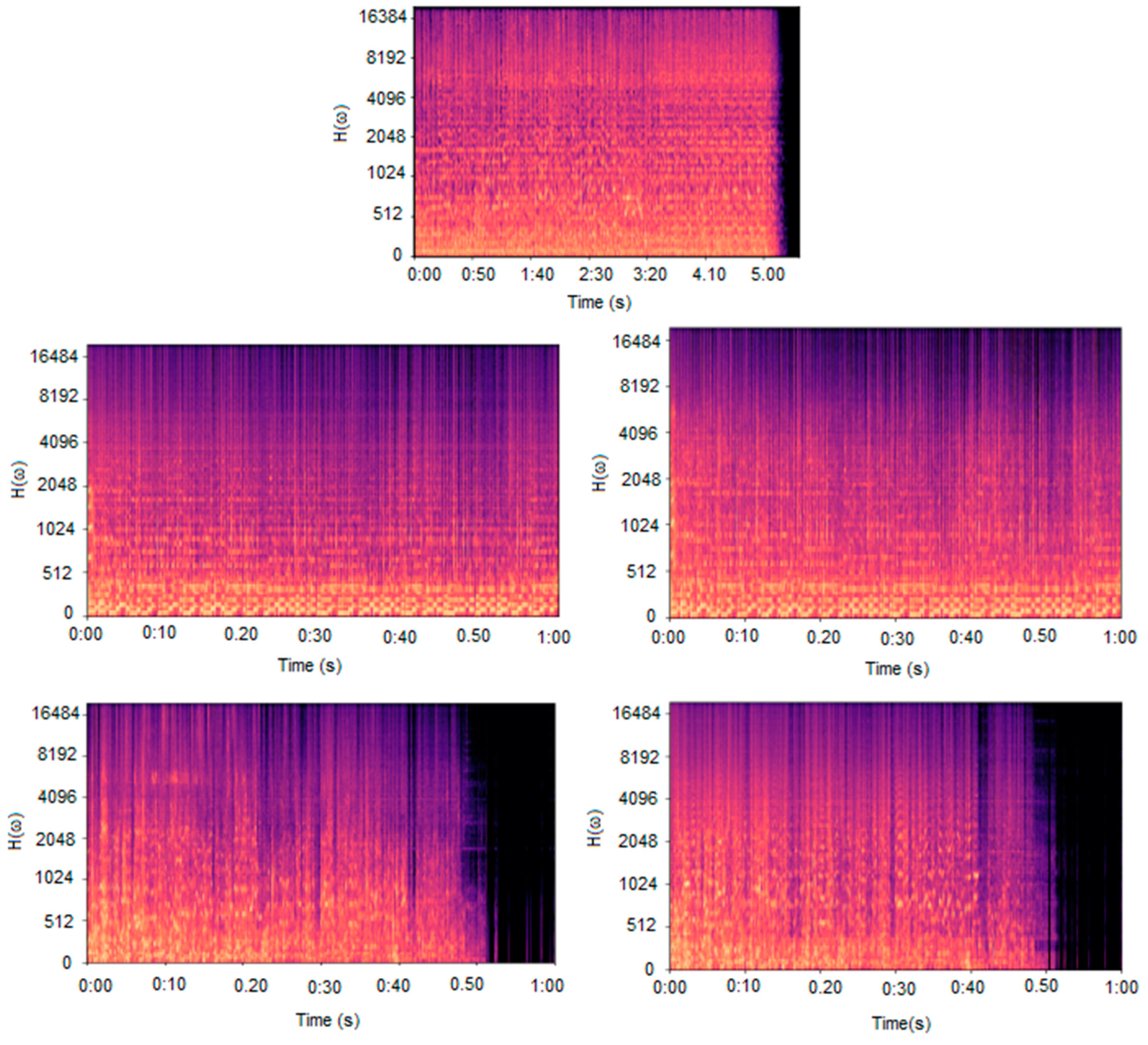
5. Results
5.1. Samples
5.2. Emotional Valence Evaluation
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, S.; Luo, J.; Yang, X. Comprehensive survey of deep music generation: Multi label representations, algorithms, evaluations and future directions. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.06801. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. A deep learning based piano music notation recognition method. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2278683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10674–10685. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.L.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. In Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mehri, S.; Kumar, K.; Gulrajani, I.; Kumar, R.; Jain, S.; Sotelo, J.; Courville, A.C.; Bengio, Y. Samplernn: An unconditional end-to-end neural audio generation model. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, J.H.; Agrawal, K.K.; Chen, S.; Gulrajani, I.; Donahue, C.; Roberts, A. Gansynth: Adversarial neural audio synthesis. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, M.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, K.; Seetharaman, P.; Courville, A.C.; Bengio, Y. Chunked autoregressive GAN for conditional waveform synthesis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual Event, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, K.; Bansal, A.; Ramanan, D. Unsupervised audiovisual synthesis via exemplar autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual Event, Austria, 3–7 May 2021; Available online: OpenReview.net (accessed on 2 June 2022).
- Yu, B.; Lu, P.; Wang, R.; Hu, W.; Tan, X.; Ye, W.; Zhang, S.; Qin, T.; Liu, T. Museformer: Transformer with fine- and coarse-grained attention for music generation. In Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dhariwal, P.; Jun, H.; Payne, C.; Kim, J.W.; Radford, A.; Sutskever, I. Jukebox: A generative model for music. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.00341. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, A.; Kirby, K.R.; Ember, C.; Silbert, S.; Passmore, S.; Daikoku, H.; McBride, J.; Paulay, F.; Flory, M.; Szinger, J.; et al. The global Jukebox: A public database of performing arts and culture. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi, A.; Oord, A.; Vinyals, O. Generating diverse high-fidelity images with VQ-VAE-2. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 14837–14847. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, X.; Yin, Y.; Shang, L.; Jiang XChen, X.; Li, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q. TinyBERT: Distilling BERT for Natural Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representation, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 25 April–1 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Chou, S.; Yang, Y. Midinet: A convolutional generative adversarial network for symbolic-domain music generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference of The Society for Music Information Retrieval, Sozhou, China, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.W.; Hsiao, W.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y. MuseGAN: Multi-track sequential generative adversarial networks for symbolic music generation and accompaniment. In Proceedings of the 32th Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, A.; Engel, J.; Raffel, C.; Hawthorne, C.; Eck, D. A hierarchical latent vector model for learning long-term structure in music. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 4364–4373. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.-N.; Zhang, Y.; Weiss, R.J.; Zen, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J.; et al. Hierarchical generative modeling for controllable speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Oord, A.; Dieleman, S.; Zen, H.; Si-monyan, K.; Vinyals, O.; Graves, A.; Kalch-brenner, N.; Senior, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. WaveNet: A generative model forraw audio. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.03499. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Tobin, D.; Kobayashi, K.; Toda, T. Quesi periodic wavenet: An autoregressive raw waveform generative model with pitch dependent dilated convolutional neural networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio. Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oord, A.; Li, Y.; Babuschkin, I.; Si-monyan, K.; Vinyals, O.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Van den Driessche, G.; Lockhart, E.; Cobo, L.; Stimberg, F.; et al. Parallel: WaveNet: Fast high-fidelity speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sidney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 3918–3926. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, W.; Peng, K.; Chen, J. Clarinet: Parallel wave generation in end-to-end text- to-speech. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, R.; Song, E.; Kim, J.-M. Parallel Wave-GAN: A fast waveform generation model based on generative adversarial networks with multi-resolution spectrogram. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6194–6198. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Kumar, R.; de Boissiere, T.; Gestin, L.; Teoh, W.Z.; Sotelo, J.; de Br’ebisson, A.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.C. MelGAN: Generative adversarial networks for conditional waveform synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 14881–14892. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.; Eck, D. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Process. Inf. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Yu, Y.; Su, Z.; Wu, Y. Hyperbolic music transformer for structured music generation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 26895–26905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.; Chang, S. Generating music transition by using a transformer-based model. Electronics 2021, 10, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Vaswani, A.; Uszkoreit, J.; Shazeer, N.; Simon, I.; Hawthorne, C.; Dai, A.; Hoffman, M.; Dinculescu, M.; Eck, D. Music Transformer: Generating music with long-term structure. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Child, R.; Gray, S.; Radford, A.; Sutskever, I. Generating long sequences with sparse transformers. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.10509. [Google Scholar]
- Agostinelli, A.; Denk, T.; Borsos, Z.; Engel, J.; Verzetti, M.; Caillon, A.; Huang, Q.; Jansen, A.; Roberts, A.; Tagliasacchi, M.; et al. MusicLM: Generating music form text. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.11325. [Google Scholar]
- Mubert-Inc. 2022. Available online: http://github.com/MubertAI/Mubert-Text-to-Music (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://github.com/MichelPezzat/jukebox (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Available online: https://soundcloud.com/michel-pezzat-615988723 (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- Natsiou, A.; O’Leary, S. Audio representations for deep learning in sound synthesis: A review. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.02490. [Google Scholar]
- Gao LXu, X.; Wang, H.; Peng, Y. Multi-representation knowledge distillation for audio classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 5089–5112. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhavasi, M.; Adapa, S. Music theme recognition using CNN and self- attention. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.07041. [Google Scholar]
- Godwin, T.; Rizos, G.; Al Futaisi, D.; Schuller, B.W. Evaluating deep music generation methods using data augmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2201.00052. [Google Scholar]
- Borsos, Z.; Marinier, R.; Vincent, D.; Kharitonov, E.; Pietquin, O.; Sharifi, M.; Teboul, O.; Grangier, D.; Tagliasacchi, M.; Zeghidour, N. Audiolm: A language modeling approach to audio generation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.03143. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Weng, C.; Zou, Y.; Yu, D. Diffsound: Discrete diffusion model for text-to-sound generation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.0993X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuk, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Polyak, A.; Singer, U.; Défossez, A.; Copet, J.; Parikh, D.; Taigman, Y.; Adi, Y. Audiogen: Textually guided audio generation. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Learning Representation, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]

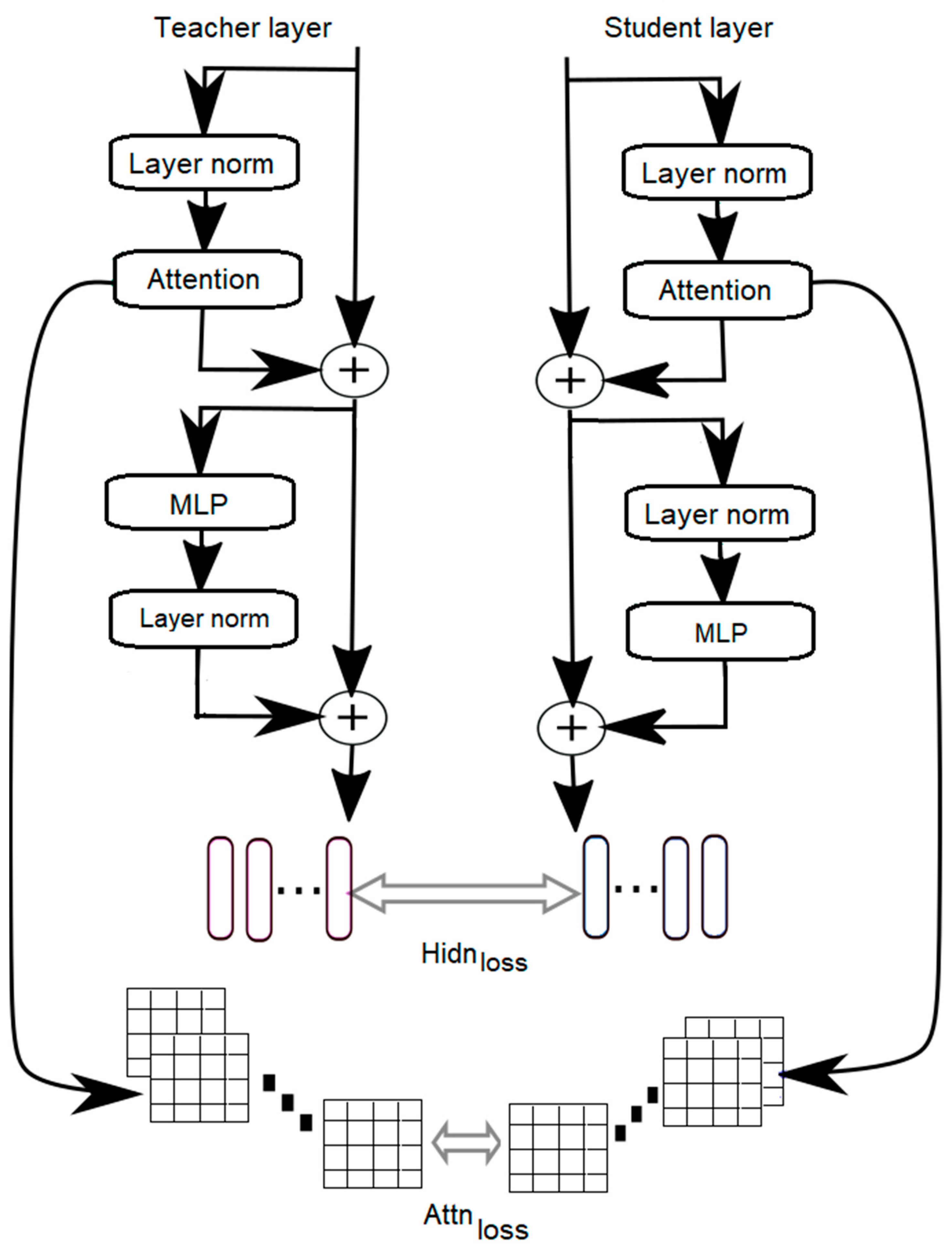
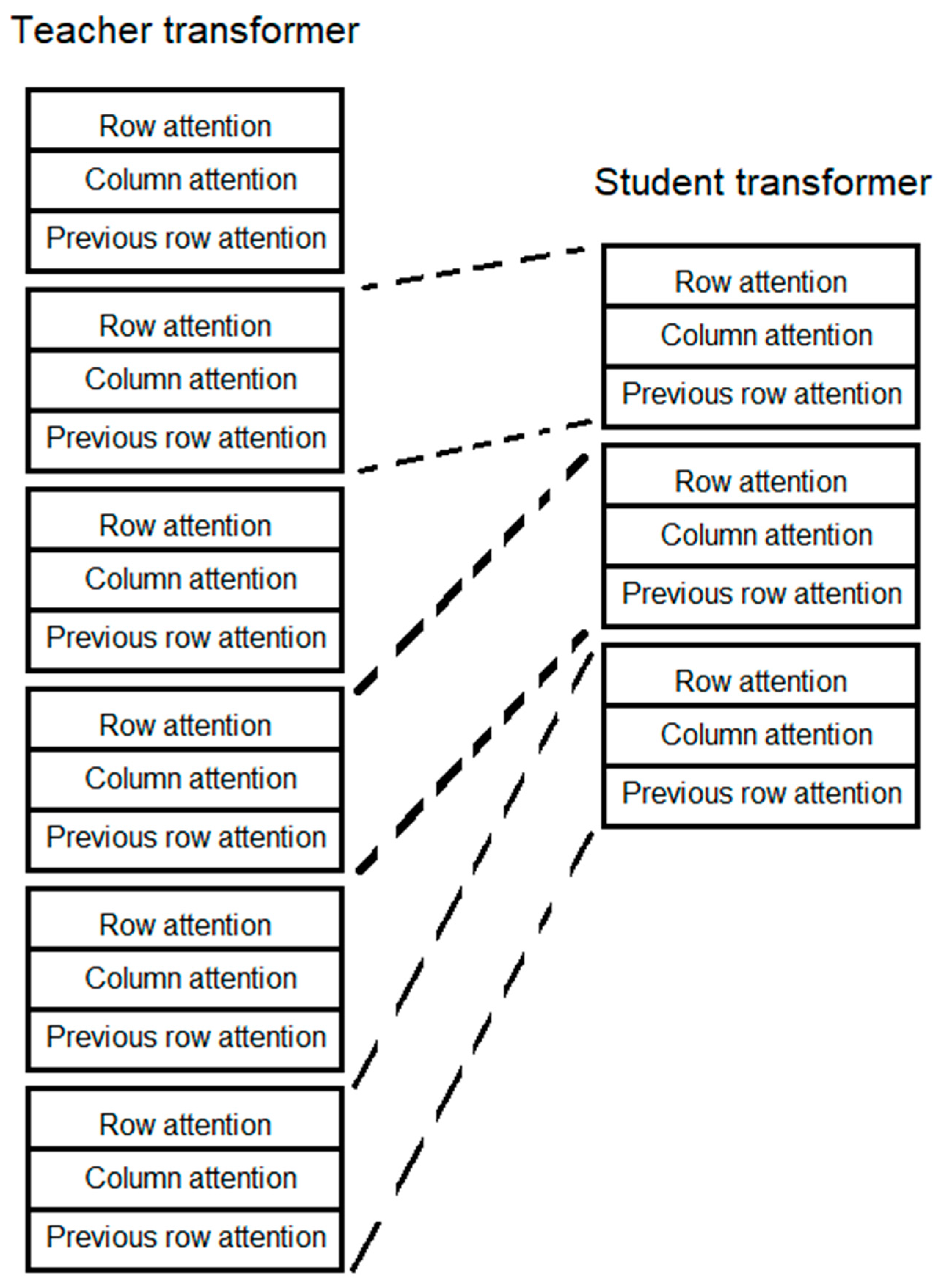
| System | Speedup |
|---|---|
| Jukebox Base (Teacher) | 1.0× |
| Jukebox 24 | 3.0× |
| Jukebox 18 | 4.0× |
| Jukebox 24 (Student) w/o Pred | 3.0× |
| Jukebox 18 (Student) w/o Pred | 4.0× |
| Jukebox 24 (Student) | 3.0× |
| Jukebox 18 (Student) | 4.0× |
| Samples | AP | DP | AU | DU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Music | 0.7354 | 0.0743 | 0.0973 | 0.0989 |
| Jukebox 72 (Teacher) | 0.3058 | 0.1985 | 0.3375 | 0.1143 |
| Jukebox 18 | 0.2109 | 0.2647 | 0.4162 | 0.0814 |
| Jukebox 18 (Student) | 0.3444 | 0.2165 | 0.2476 | 0.1292 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pezzat-Morales, M.; Perez-Meana, H.; Nakashika, T. Fast Jukebox: Accelerating Music Generation with Knowledge Distillation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5630. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095630
Pezzat-Morales M, Perez-Meana H, Nakashika T. Fast Jukebox: Accelerating Music Generation with Knowledge Distillation. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(9):5630. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095630
Chicago/Turabian StylePezzat-Morales, Michel, Hector Perez-Meana, and Toru Nakashika. 2023. "Fast Jukebox: Accelerating Music Generation with Knowledge Distillation" Applied Sciences 13, no. 9: 5630. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095630
APA StylePezzat-Morales, M., Perez-Meana, H., & Nakashika, T. (2023). Fast Jukebox: Accelerating Music Generation with Knowledge Distillation. Applied Sciences, 13(9), 5630. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095630





