Discontinuous Yielding of Fe E420 under High Strain Rate Loading
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
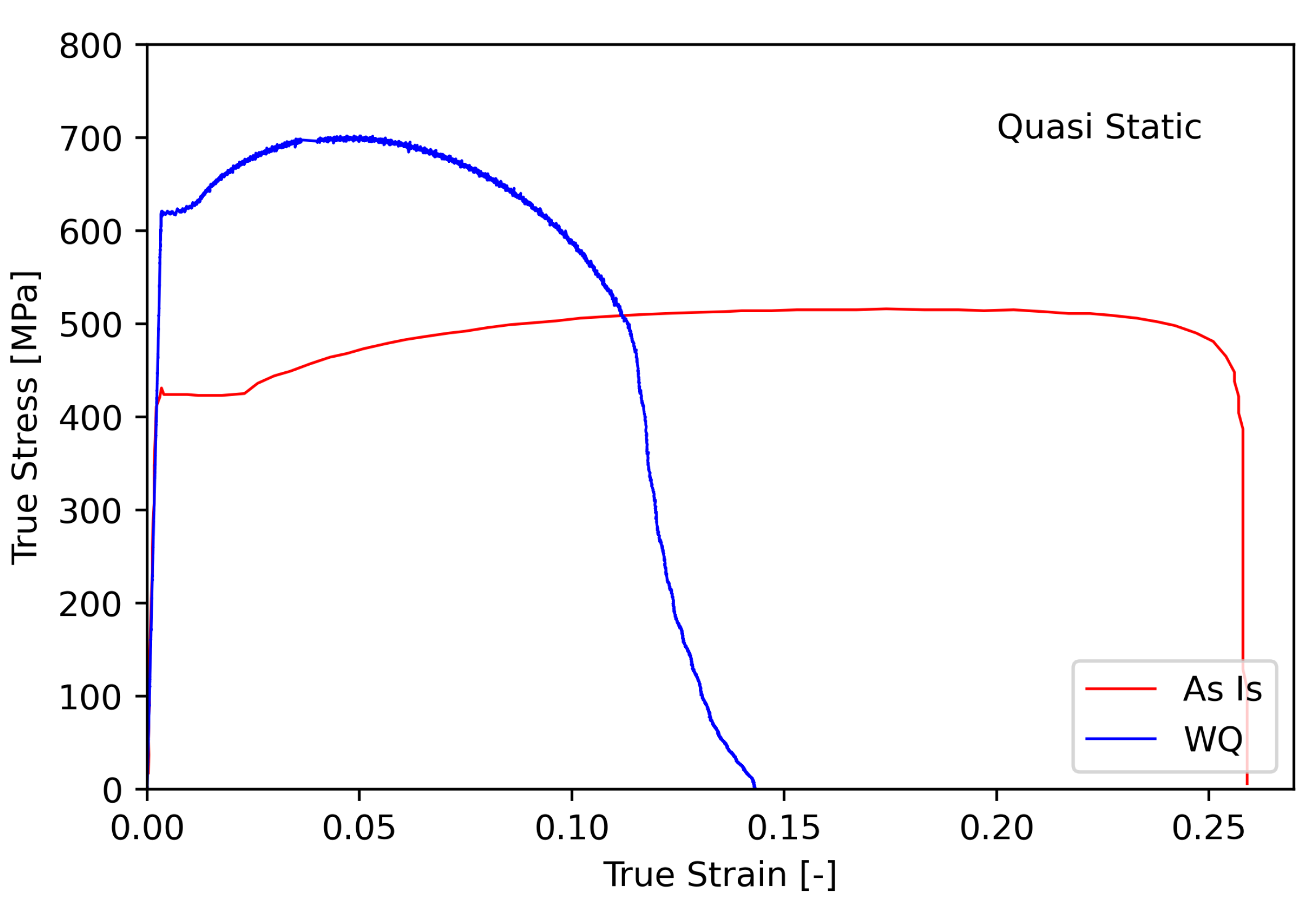
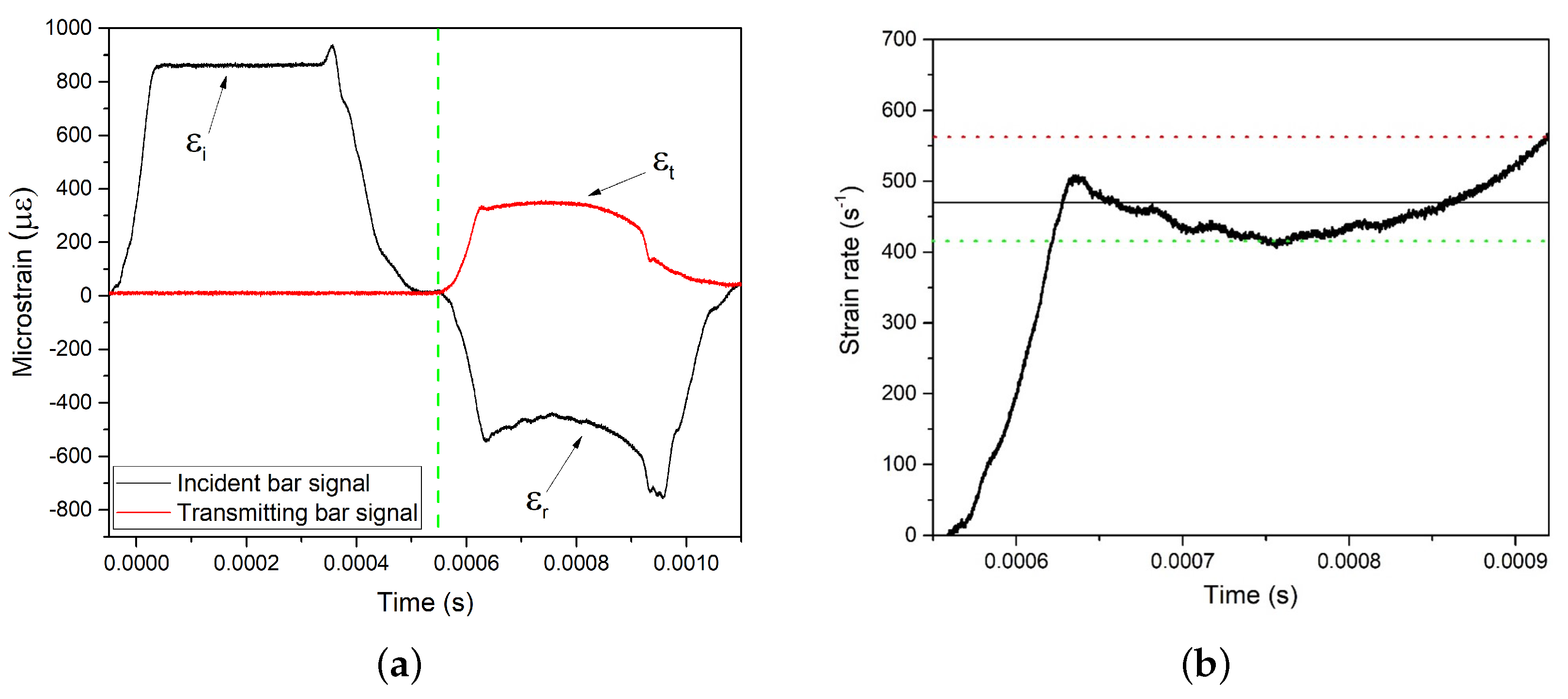
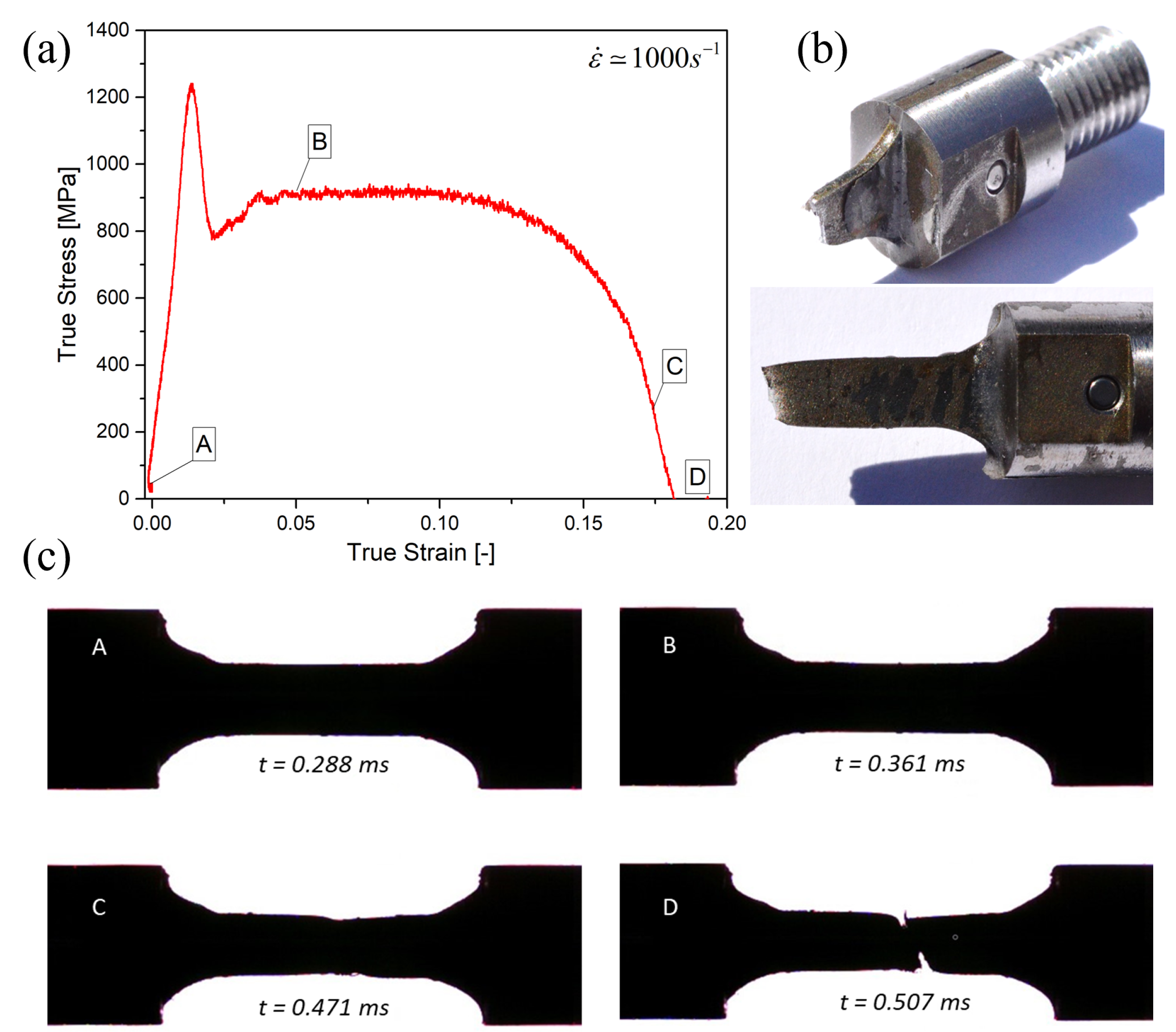
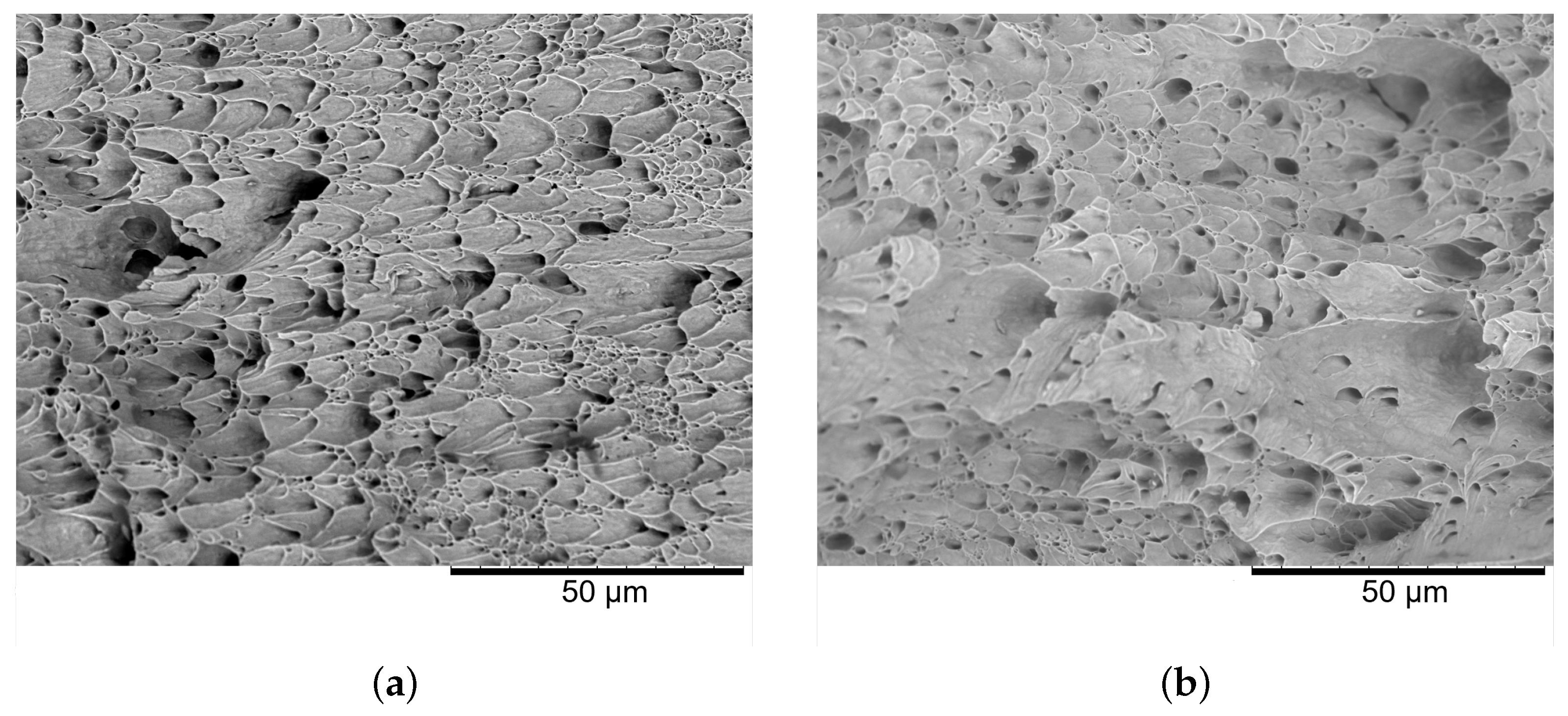
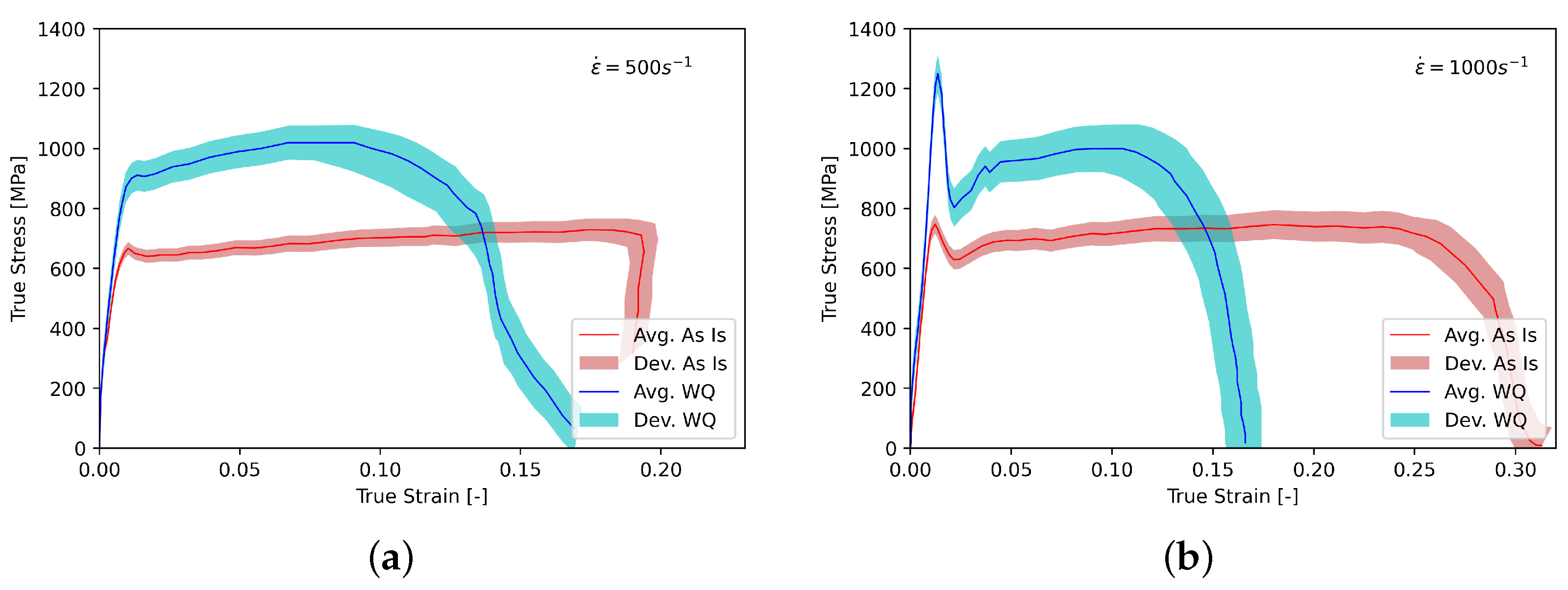
3. Results
4. Discussion
- A reserve of elastic strength for the as-is Fe E420 and even more for the quenched Fe E420 when loaded at a strain-rate higher than can be considered.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DY | Discontinuous Yielding |
| YPE | Yield Point Elongation |
| DT-SHPB | Direct Tensile Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar |
| WQ | Water Quenching |
| BCC | Body-Centered Cubic |
| FCC | Face-Centered Cubic |
| TRIP | Transformation-Induced Plasticity |
References
- Messerschmidt, U. Dislocation Dynamics during Plastic Deformation; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 129. [Google Scholar]
- Smallman, R.; Ngan, A. (Eds.) Chapter 9—Plastic Deformation and Dislocation Behaviour. In Modern Physical Metallurgy, 8th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 357–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J. Lüders front propagation in low carbon steels. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1962, 10, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, A.; Muir, H. The Bauschinger effect and discontinuous yielding. Philos. Mag. 1972, 26, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tomota, Y.; Ohmura, T.; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Tanaka, M. Continuous and discontinuous yielding behaviors in ferrite-cementite steels. Acta Mater. 2020, 196, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D. Role of grain boundaries in the discontinuous yielding of low-carbon steels. Met. Sci. J. 1967, 1, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, C.; Rollings, W.; Weaver, M. Activation energy calculations for discontinuous yielding in Inconel 718SPF. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 300, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, A.H. Dislocations and plastic flow in crystals. Am. J. Phys. 1954, 22, 242–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, A.H.; Bilby, B.A. Dislocation theory of yielding and strain ageing of iron. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. A 1949, 62, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Beukel, A.; Kocks, U. The strain dependence of static and dynamic strain-aging. Acta Metall. 1982, 30, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokobori, T. The Cottrell-Bilby theory of yielding of iron. Phys. Rev. 1952, 88, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Shibata, A.; Chen, M.; Park, N.; Tsuji, N. Correlation between continuous/discontinuous yielding and Hall–Petch slope in high purity iron. Mater. Trans. 2014, 55, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M. High upper yield point in mild steel. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1957, 186, 431–432. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.B.; Kaneda, Y.; Ohmori, M.; Yoshida, F. Effect of stress concentration on upper yield point in mild steel. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Timokhina, I.; La Fontaine, A.; Ringer, S.; Hodgson, P.; Pereloma, E. Effect of pre-straining and bake hardening on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CMnSi TRIP steels. La Metall. Ital. 2009, 101, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Besag, F.; Smallman, R. Discontinuous yielding in ordering alloys. Acta Metall. 1970, 18, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.X.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A. Discontinuous yielding and microstructural evolution of Ti-40 at.% Al alloy compressed in single α-hcp phase region. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, A.; Bodner, S. Repeated discontinuous yielding of 2024 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1969, 4, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, R.; Mazurek, B.; Himbeault, D. Discontinuous yielding in ultrafine-grained austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1987, 94, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staab, G.; Gilat, A. A direct-tension split Hopkinson bar for high strain-rate testing. Exp. Mech. 1991, 31, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
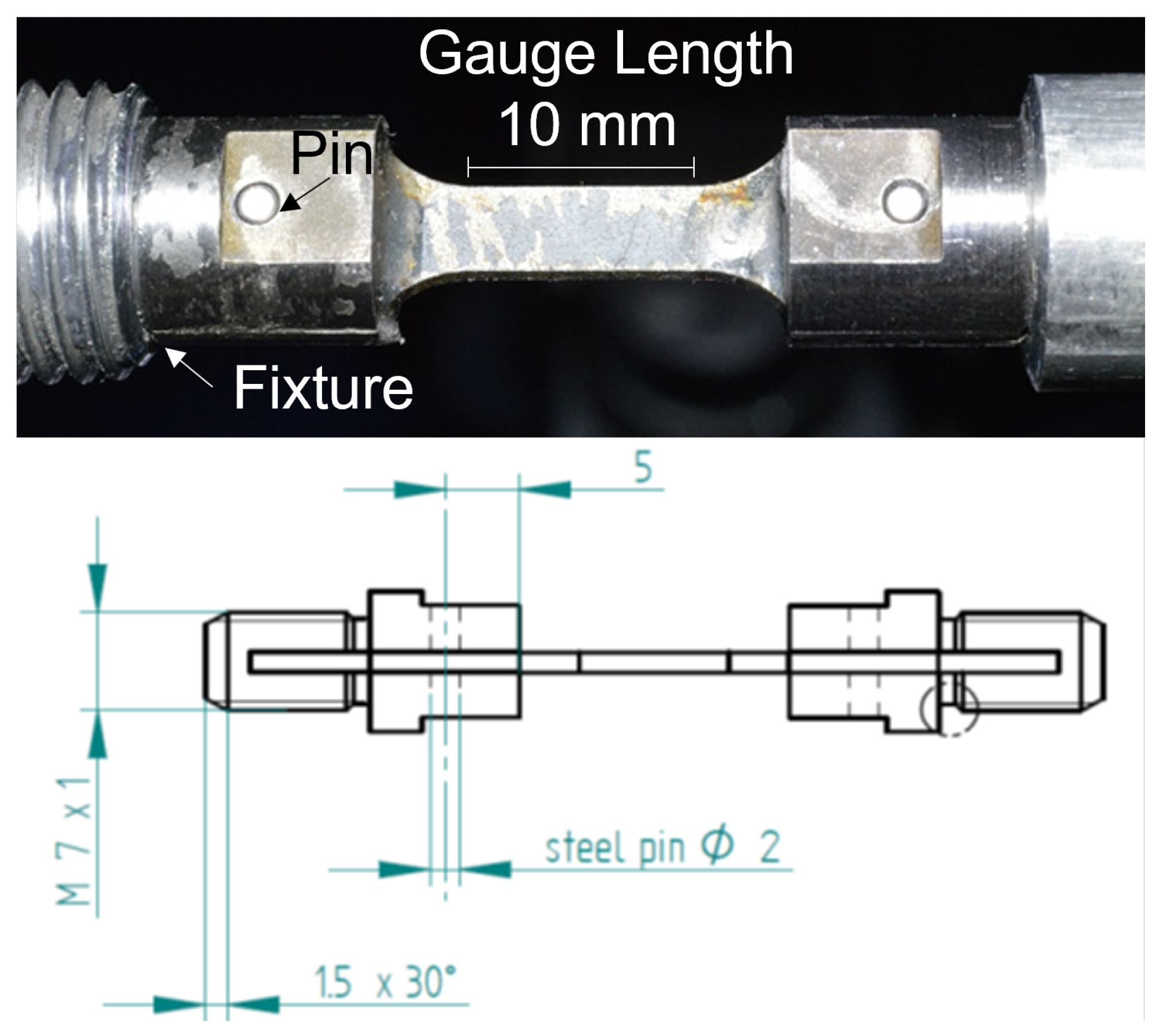
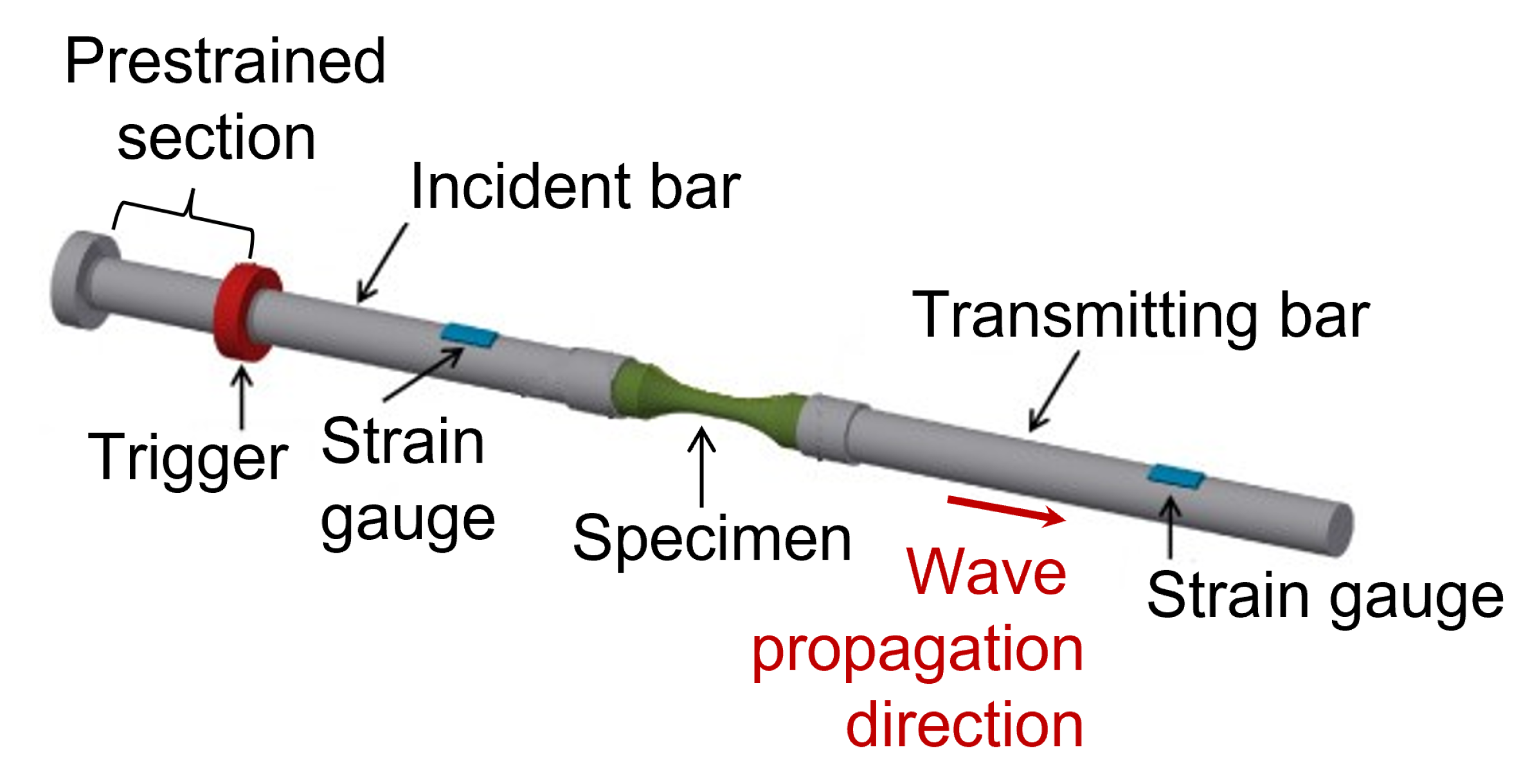

| Max Temp [C] | HV before | HV after |
|---|---|---|
| E (GPa) | (MPa) | (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As is | 191.95 | 425 | 519 | 0.279 | 0.197 |
| WQ | 195.27 | 630 | 702 | 0.118 | 0.048 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruno, M.; Esposito, L.; Iannitti, G.; Scherillo, F. Discontinuous Yielding of Fe E420 under High Strain Rate Loading. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5164. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085164
Bruno M, Esposito L, Iannitti G, Scherillo F. Discontinuous Yielding of Fe E420 under High Strain Rate Loading. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(8):5164. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085164
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruno, Matteo, Luca Esposito, Gianluca Iannitti, and Fabio Scherillo. 2023. "Discontinuous Yielding of Fe E420 under High Strain Rate Loading" Applied Sciences 13, no. 8: 5164. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085164
APA StyleBruno, M., Esposito, L., Iannitti, G., & Scherillo, F. (2023). Discontinuous Yielding of Fe E420 under High Strain Rate Loading. Applied Sciences, 13(8), 5164. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085164









