MCI Conversion Prediction Using 3D Zernike Moments and the Improved Dynamic Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
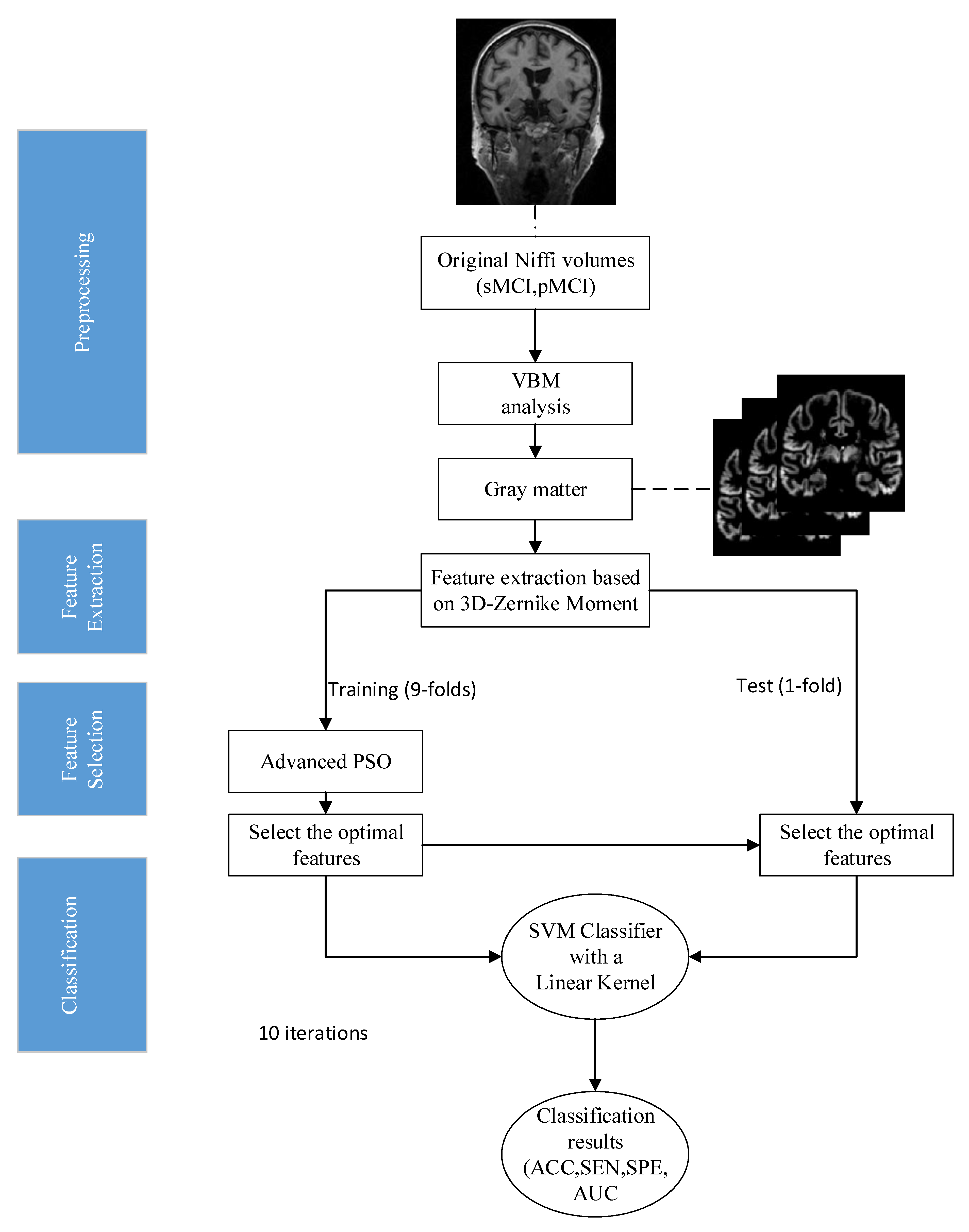
2.1. Samples and Image Preprocessing
2.2. Methodology of the Proposed Prediction Model
2.2.1. Feature Extraction Based on 3D-ZM
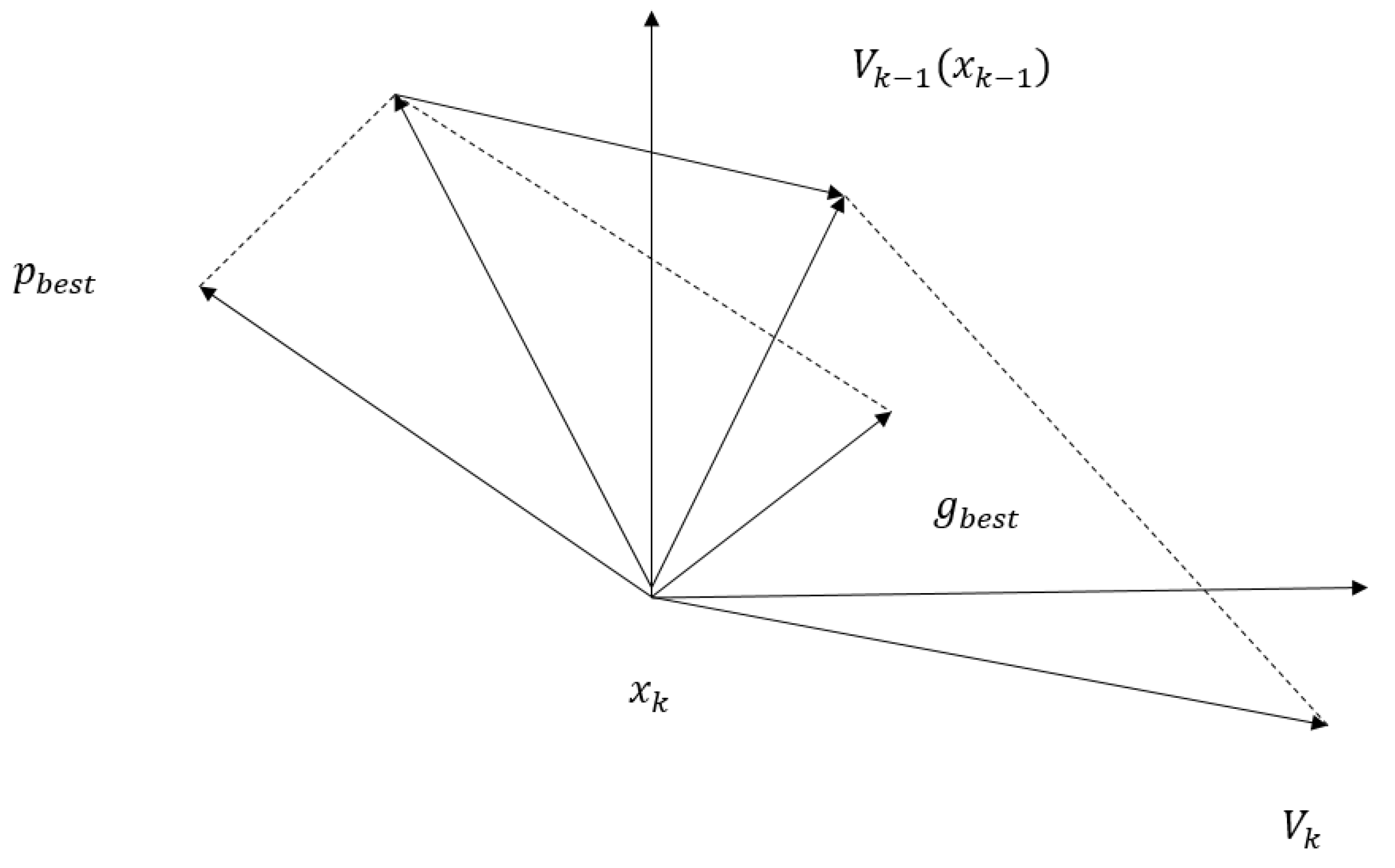
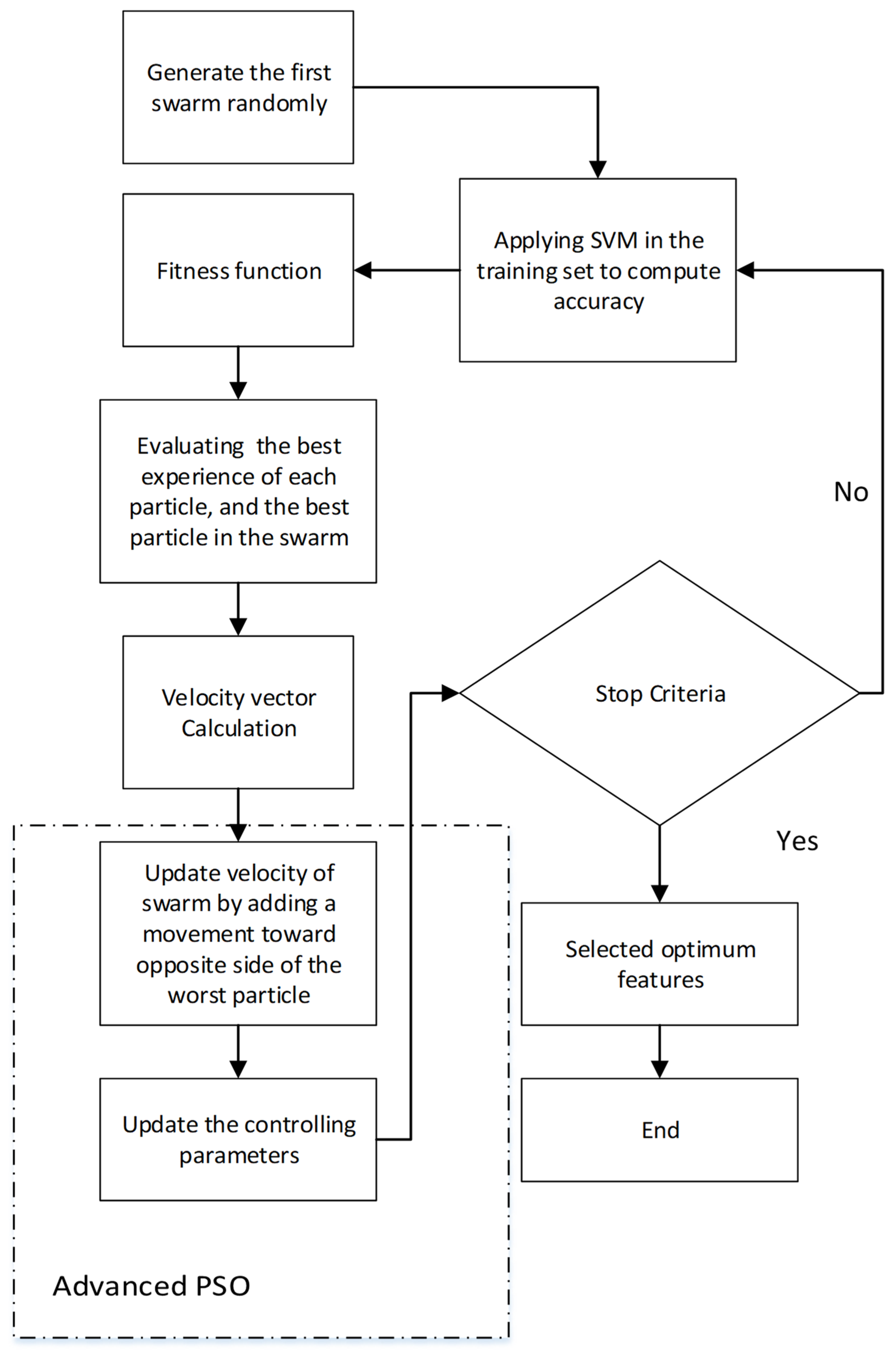
2.2.2. Feature Selection Based on IDPSO
2.2.3. Classifier
2.3. Alternative Methods
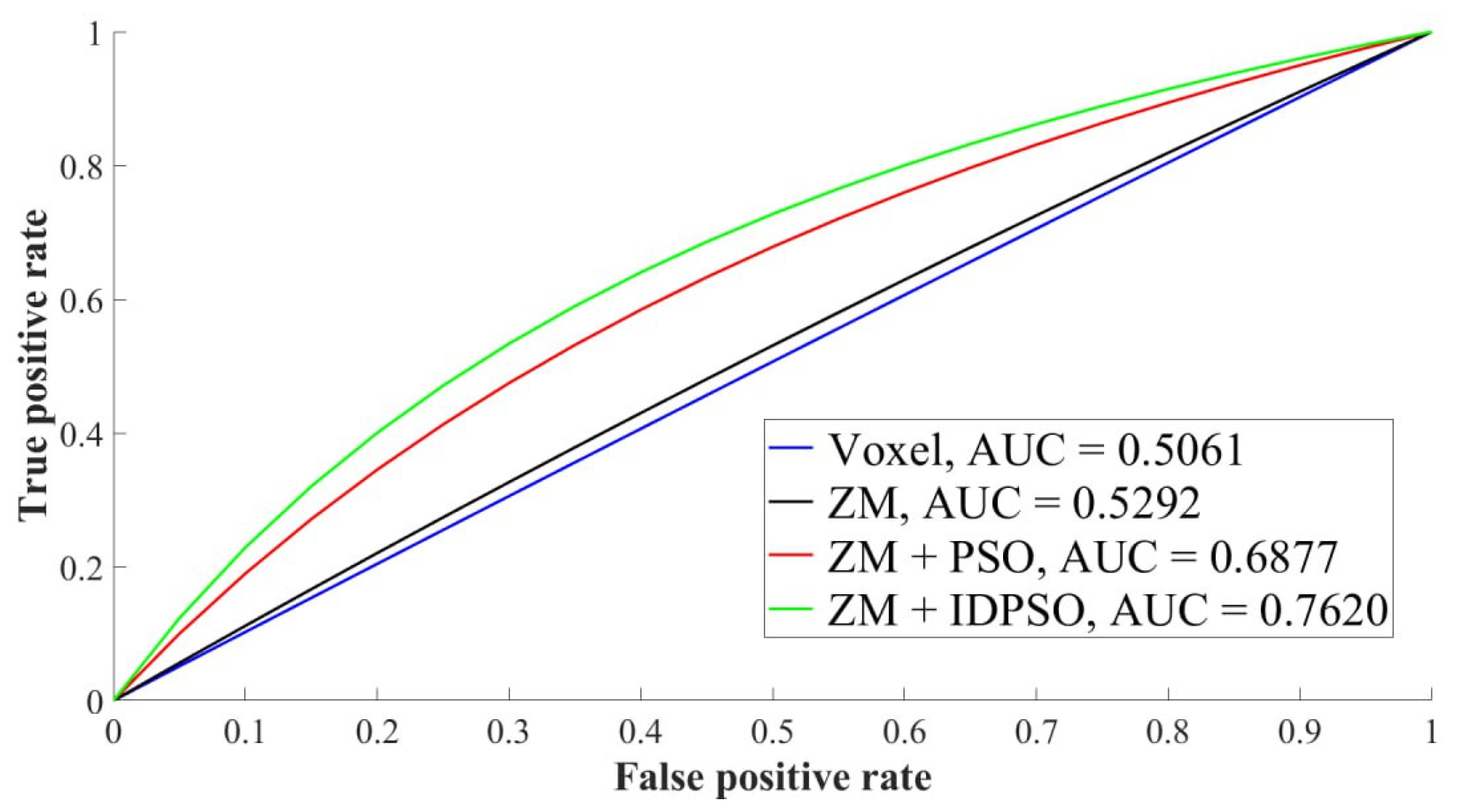
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Murcia, F.J.; Ortiz, A.; Gorriz, J.M.; Ramirez, J.; Castillo-Barnes, D. Studying the Manifold Structure of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Deep Learning Approach Using Convolutional Autoencoders. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kaur, S.; Memon, N.; Jainul Fathima, A.; Ray, S.; Bhatt, M.W. Alzheimer’s patients detection using support vector machine (SVM) with quantitative analysis. Neurosci. Inform. 2021, 1, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.; Ferreira, F.L.; Cardoso, S.; Silva, D.; De Mendonça, A.; Guerreiro, M.; Madeira, S.C. Neuropsychological predictors of conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease: A feature selection ensemble combining stability and predictability. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2018, 18, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s disease: Genotypes, phenotypes, and treatments. Science 1997, 275, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benefits, P. Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures Includes a Special Report on the Financial and Personal Benefits of Early Diagnosis; Alzheimer’s Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, R.C.; Doody, R.; Kurz, A.; Mohs, R.C.; Morris, J.C.; Rabins, P.V.; Ritchie, K.; Rossor, M.; Thal, L.; Winblad, B. Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, J.; Górriz, J.M.; Ortiz, A.; Martínez-Murcia, F.J.; Segovia, F.; Salas-Gonzalez, D.; Castillo-Barnes, D.; Illán, I.A.; Puntonet, C.G. Ensemble of random forests One vs. Rest classifiers for MCI and AD prediction using ANOVA cortical and subcortical feature selection and partial least squares. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 302, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, N.; Diacono, D.; Fanizzi, A.; La Rocca, M.; Monaco, A.; Lombardi, A.; Guaragnella, C.; Bellotti, R.; Tangaro, S. Deep learning reveals Alzheimer’s disease onset in MCI subjects: Results from an international challenge. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 302, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzannezhad, P.; Abbaspour, A.; Li, C.; Cabrerizo, M.; Adjouadi, M. A Deep Neural Network Approach for Early Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment Using Multiple Features. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE international conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA), Orlando, FL, USA, 17–20 December 2018; pp. 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, K. Detection of Early Stage Alzheimer’s Disease using EEG Relative Power with Deep Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, T.J.; Zahra, S.R.; Wu, F.; Alwakeel, A.; Alwakeel, M. Deep Learning-Based Diagnosis of Alzheimer’ s Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.; Habes, M.; Iftikhar, M.A.; Shacklett, A.; Davatzikos, C. A review on neuroimaging-based classification studies and associated feature extraction methods for Alzheimer’s disease and its prodromal stages. Neuroimage 2017, 155, 530–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, I.; Hossein-Abad, H.M.; Matsuda, H. Identification of alzheimer’s disease on the basis of a voxel-wise approach. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, I.; Maikusa, N.; Daneshmand, M.; Matsuda, H.; Demirel, H.; Anbarjafari, G. Classification of Alzheimer’s disease and prediction of mild cognitive impairment conversion using histogram-based analysis of patient-specific anatomical brain connectivity networks. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 60, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, R.; Wu, G.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Q.; Shen, D. Multi-atlas based representations for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 5052–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L.; Igel, C.; Liv Hansen, N.; Osler, M.; Lauritzen, M.; Rostrup, E.; Nielsen, M. Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease using MRI hippocampal texture. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, K.; Wang, S.; Morstatter, F.; Trevino, R.P.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Feature selection: A data perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2017, 50, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, P. Selection of Relevant Features in Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Fall Symposium on Relevance, New Orleans, LA, USA, 4–6 November 1994; pp. 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.T.; Yuan, S.X.; Wu, J.S.; Gu, Y.; Sun, X. Predicting conversion from mci to ad combining multi-modality data and based on molecular subtype. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Chen, S.; Shi, H.; Xu, J. Multi-Modal Feature Selection with Feature Correlation and Feature Structure Fusion for MCI and AD Classification. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasov, S.; Passamonti, L.; Duggento, A.; Liò, P.; Toschi, N. A parameter-efficient deep learning approach to predict conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2019, 189, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, A.J.; Ganesan, R. Early detection of alzheimer’s disease using predictive k-nn instance based approach and t-test method. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng. 2019, 8, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, R.A.; Agustina, C.; Puspitasari, D.; Ramanda, R.; Warjiyono; Pribadi, D.; Lisnawanty; Indriani, K. Detecting Alzheimer’s Disease by the Decision Tree Methods Based on Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1641, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Islam, M.K.; Haque, J.; Das, A.A.; Duranta, D.S.; Islam, M.A. Alzheimer’s Disease Detection Using m-Random Forest Algorithm with Optimum Features Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics (CAIDA), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 6–7 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichianin, Y.; Khummongkol, A.; Chiewvit, P.; Raksthaput, A.; Chaichanettee, S.; Aoonkaew, N.; Senanarong, V. Accuracy of Support-Vector Machines for Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease, Using Volume of Brain Obtained by Structural MRI at Siriraj Hospital. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 640696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhian, F.; Beheshti, I.; Sone, D.; Matsuda, H. Comparing CAT12 and VBM8 for detecting brain morphological abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, S.; Mehrotra, R.; Louis, S. Zernike Moment-Based Feature Detectors Center for Computational Math University of Colorado at Denver. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Image Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 13–16 November 1994; pp. 934–938. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, C.H.; Chin, R.T. On image analysis by the methods of moments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1988, I, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmady, M.; Ghasemi, R.; Rashidy Kanan, H. Local weighted Pseudo Zernike Moments and fuzzy classification for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 13th Iranian Conference on Fuzzy Systems (IFSC), Qazvin, Iran, 27–29 August 2013; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Xu, Y.R.; Pang, Y.J. A new Pseudo-Zernike boundary moment for marine targets feature extraction. In Proceedings of the 2011 Third Pacific-Asia Conference on Circuits, Communications and System (PACCS), Wuhan, China, 17–18 July 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengurlekar, S.G.; Jadhav, D.; Shinde, S. Object Detection and Tracking using Zernike Moment. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 17–19 July 2019; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, R. Mean and variance of the sampling distribution of particle swarm optimizers during stagnation. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2009, 13, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Cheng, R.; Jin, Y. Feature selection for high-dimensional classification using a competitive swarm optimizer. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Browne, W.N. Particle swarm optimization for feature selection in classification: A multi-objective approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 1656–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.Y.; Zhang, L.; Lim, C.P.; Fielding, B.; Yu, Y.; Anderson, E. Evolving Ensemble Models for Image Segmentation Using Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 34004–34019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, N.H.; Santos, A.; Ribeiro, B. PSO-Convolutional Neural Networks with Heterogeneous Learning Rate. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 89970–89988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Junior, F.E.; Yen, G.G. Particle swarm optimization of deep neural networks architectures for image classification. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2019, 49, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maamari, A.; Omara, F.A. Task scheduling using PSO algorithm in cloud computing environments. Int. J. Grid Distrib. Comput. 2015, 8, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, J.; Hu, J. An improved PSO algorithm and its application in GNSS ambiguity resolution. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhai, Y.; Han, Z.; Lu, J. Improved particle swarm optimization based on entropy and its application in implicit generalized predictive control. Entropy 2022, 24, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S. Population Diversity in Particle Swarm Optimization: Definition, Observation, Control, and Application. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.K.S.; Jen, C.H. An enhanced partial search to particle swarm optimization for unconstrained optimization. Mathematics 2019, 7, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiansyah, A.; Ferdiana, R.; Permanasari, A.E. MUCPSO: A Modified Chaotic Particle Swarm Optimization with Uniform Initialization for Optimizing Software Effort Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Yao, X.; Bu, X. Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Conventional Machine Learning Methods with Cortical and Genetic Characteristics. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Power, Electronics and Computer Applications (ICPECA), Shenyang, China, 21–23 January 2022; pp. 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, M.; Richhariya, B.; Khan, R.U.; Rashid, A.H.; Khanna, P.; Prasad, M.; Lin, C.T. Machine learning techniques for the diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease: A review. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2020, 16, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, I.; Demirel, H.; Matsuda, H. Classification of Alzheimer’s disease and prediction of mild cognitive impairment-to-Alzheimer’s conversion from structural magnetic resource imaging using feature ranking and a genetic algorithm. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 83, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Gao, Q.; Du, M.; Chen, W.; Tong, T. Multiclass diagnosis of stages of Alzheimer’s disease using linear discriminant analysis scoring for multimodal data. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 134, 104478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocharski, M.; Østergaard, L.R. Extraction of sulcal medial surface and classification of Alzheimer’s disease using sulcal features. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 133, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Cui, X.; Qiao, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X. Early diagnosis model of Alzheimer’s disease based on sparse logistic regression with the generalized elastic net. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 66, 102362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrol, A.; Bhattarai, M.; Fedorov, A.; Du, Y.; Plis, S.; Calhoun, V. Deep residual learning for neuroimaging: An application to predict progression to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 339, 108701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tosun, D.; Weiner, M.W.; Schuff, N. Locally linear embedding (LLE) for MRI based Alzheimer’s disease classification. Neuroimage 2013, 83, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, M.; Lan, W.; Wu, F.X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J. Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Whole Brain Hierarchical Network. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinforma 2018, 15, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, S.W.; Chen, L.; Xia, J. Alzheimer’s disease classification using features extracted from nonsubsampled contourlet subband-based individual networks. Neurocomputing 2021, 421, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanian, P.; Devilbiss, D.M.; Simon, A.J.; Bernstein, A.; Hess, T.; Ashrafiuon, H. Continuous wavelet transform eeg features of alzheimer’s disease. In Proceedings of the ASME 2012 5th Annual Dynamic Systems and Control Conference joint with the JSME 2012 11th Motion and Vibration Conference, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 17–19 October 2012; Volume 1, pp. 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Detection of Alzheimer’s disease by displacement field and machine learning. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinsaif, S.; Lang, J. 3D shearlet-based descriptors combined with deep features for the classification of Alzheimer’s disease based on MRI data. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 138, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, H.T.; Haddadnia, J. A novel method for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on pseudo Zernike moment from structural MRI. Neuroscience 2015, 305, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Gender (F/M) | Age | CDR | MMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pMCI | 39/66 | 74.95 ± 6.6 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 26.6 ± 1.7 |
| sMCI | 41/80 | 74.45 ± 7.58 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 27.3 ± 1.87 |
| No. Feature | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | … | fn−1 | fn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle value | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | … | 1 | 0 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
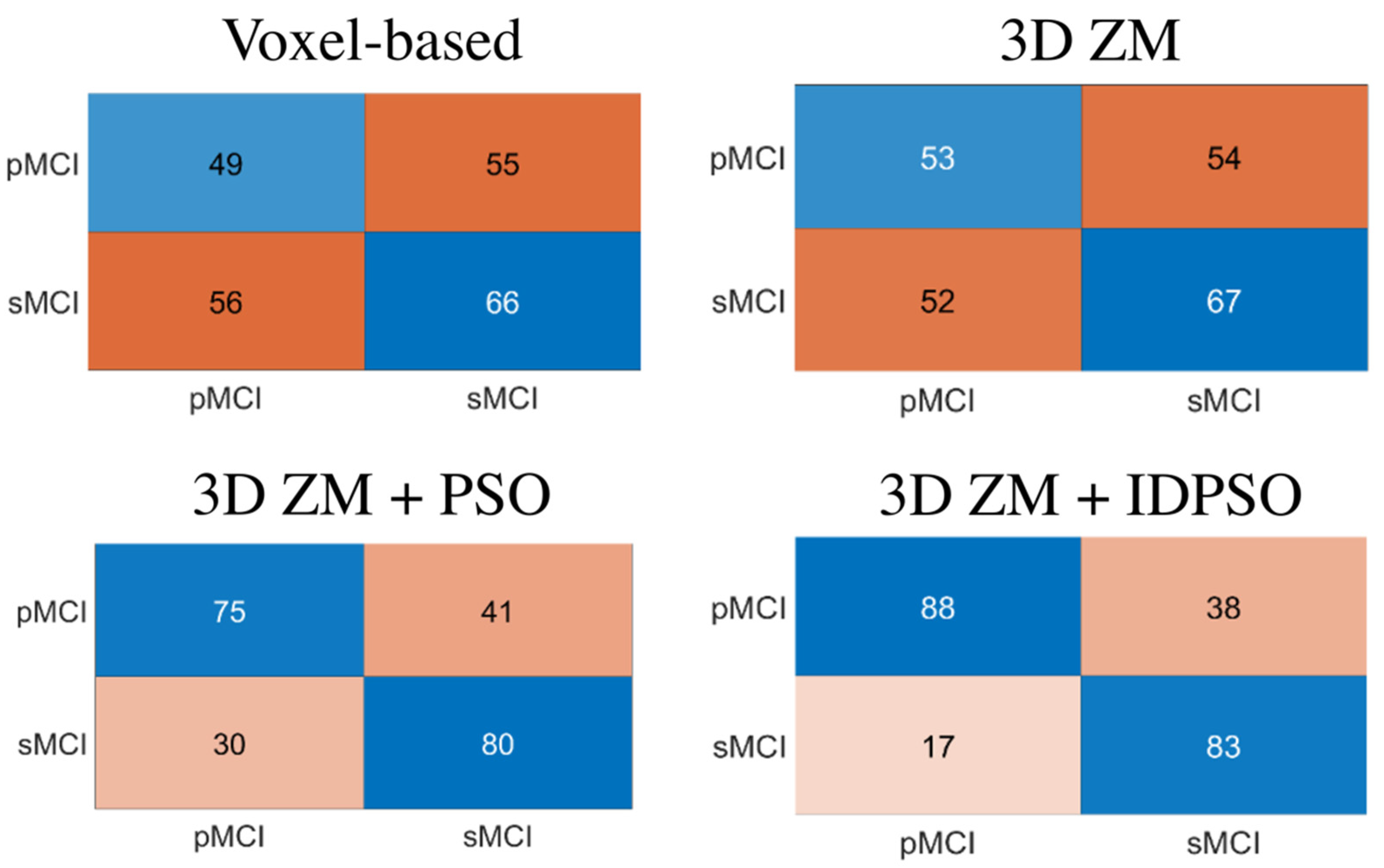
| Voxel-based | 50.88 | 46.67 | 54.55 | 0.51 |
| 3DZM-based | 53.10 | 50.48 | 55.37 | 0.523 |
| PSO-3DZM-based | 68.58 | 71.43 | 66.12 | 0.69 |
| IDPSO-3DZM-based | 75.66 | 83.81 | 68.60 | 0.76 |
| Reference | pMCI/sMCI | Validation Method | ACC (%) | SEN (%) | SPE (%) | AUC | Conversion Time (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xiao et al. (2020) [50] | 51/45 | 10-Fold | 75.87 | 73.71 | 77.51 | --- | --- |
| Abrol et al. (2020) [51] | 189/245 | 5-Fold | 83.01 | --- | ---- | --- | 0–36 |
| Beheshti et al. (2017) [47] | 71/62 | 10-Fold | 75.00 | 76.92 | 73.23 | 0.75 | 0–36 |
| Lin et al. (2021) [48] | 110/208 | 5-Fold | 81.2% | --- | ---- | --- | --- |
| Liu et al. (2013) [52] | 97/93 | --- | 69.00 | 66.00 | 72.00 | --- | 0–36 |
| Beheshti et al. (2019) [14] | 112/102 | 10-Fold | 74.77 | 73.21 | 76.47 | 0.74 | 0–36 |
| Liu et al. (2018) [53] | 120/160 | 10-Fold | 72.08 | 75:11 | 71.05 | 0.71 | 0–18 |
| Proposed Method | 105/121 | 10-Fold | 75.66 | 83.81 | 68.60 | 0.75 | 0–36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolourchi, P.; Gholami, M.; Moradi, M.; Beheshti, I.; Demirel, H., on behalf of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. MCI Conversion Prediction Using 3D Zernike Moments and the Improved Dynamic Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074489
Bolourchi P, Gholami M, Moradi M, Beheshti I, Demirel H on behalf of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. MCI Conversion Prediction Using 3D Zernike Moments and the Improved Dynamic Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(7):4489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074489
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolourchi, Pouya, Mohammadreza Gholami, Masoud Moradi, Iman Beheshti, and Hasan Demirel on behalf of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. 2023. "MCI Conversion Prediction Using 3D Zernike Moments and the Improved Dynamic Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm" Applied Sciences 13, no. 7: 4489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074489
APA StyleBolourchi, P., Gholami, M., Moradi, M., Beheshti, I., & Demirel, H., on behalf of the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. (2023). MCI Conversion Prediction Using 3D Zernike Moments and the Improved Dynamic Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 13(7), 4489. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074489








