Abstract
Speech enhancement based on deep neural networks faces difficulties, as modeling more frequency bands can lead to a decrease in the resolution of low-frequency bands and increase the computational complexity. Previously, we proposed a convolution-augmented gated attention unit (CGAU), which captured local and global correlation in speech signals through the fusion of the convolution and gated attention unit. In this paper, we further improved the CGAU, and proposed a two-stage complex and real dual-path sub-band fusion network for full-band speech enhancement called TS-CGANet. Specifically, we proposed a dual-path CGA network to enhance low-band (0–8 kHz) speech signals. In the medium band (8–16 kHz) and high band (16–24 kHz), noise suppression is only performed in the magnitude domain. The Voice Bank+DEMAND dataset was used to conduct experiments on the proposed TS-CGANet, which consistently outperformed state-of-the-art full-band baselines, as evidenced by the results.
1. Introduction
In recent years, deep-neural-network-based (DNN-based) algorithms for speech enhancement have rapidly developed due to their advantages over traditional methods in dealing with non-stationary noise [1]. Speech is generally categorized into narrowband (sampling rate = 8 kHz), broadband (sampling rate = 16 kHz), ultra-wideband (sampling rate = 32 kHz), and full-band (sampling rate = 48 kHz) based on its sampling rate [2]. The aim of speech enhancement is to reduce the impact of environmental noise during the process of speech acquisition in various everyday scenarios, which can cause speech distortion and affect speech clarity and intelligibility [3].
Broadband speech contains the main energy and important harmonic information in human speech, thereby making it sufficient for better recovery of the speaker’s speech and characteristics, and, thus, DNN-based speech enhancement primarily focuses on broadband speech [4]. However, full-band speech contains additional high-frequency information that can enhance the metallic sense of the speech, making it sound clearer, and is important for high-fidelity audio-visual communication [5]. As speech quality requirements continue to improve, full-band speech enhancement has gained more attention [6].
Current broadband speech enhancement algorithms cannot be directly applied to full-band speech enhancement [7]. Firstly, the spectrum dimension of full-band speech is three times that of broadband speech, leading to a higher calculation cost, which is unacceptable for real-time speech enhancement [8]. Secondly, the frequency band of full-band speech mainly consists of clear consonant components, thus resulting in relatively small speech energy and a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), which pose a challenge to speech enhancement. Thirdly, when using the model to process full-band speech, it is easy to focus on the high-frequency band with less energy, thereby leading to a decline in processing effectiveness of the more important low-frequency band [9].
Feature compression is a common method for processing full-band speech, and it involves transforming the Fourier spectrum into psychoacoustic excitation features for input. The Bark scale and equivalent rectangular bandwidth (ERB) scale are two frequently used methods for feature compression [10]. For instance, methods like RNNoise [11] and Personalized PercepNet [12] compress input features using the Bark scale and ERB scale, respectively. One approach employed by RNNoise was to use 22-dimensional Bark-frequency cepstral coefficients (BFCC) based on the Bark scale as input features, which were extracted from noisy speech using DSP techniques with 22 ideal critical band gains as the corresponding targets [11]. Another recent method, PercepNet, developed a perceptual band representation using 34 spectral bands based on the ERB scale, which is consistent with human hearing [12]. While these techniques have the potential to lower the dimensionality of frequency features and simplify calculations, they suffer from a decreased resolution of the spectrum in the Bark and ERB scales, which leads to imprecise spectrum reconstruction and a loss of information across frequency bands.
Another approach is the finite impulse response (FIR)-based sub-band analysis and synthesis. This method has been applied to achieve high-quality results in text-to-speech (TTS) tasks, as seen in the success of Multi-band WaveRNN [13] and Multi-band MelGAN [14], which have received high mean opinion scores (MOS). The advantage of this approach is that it can achieve more accurate frequency analysis and processing, as well as improve the effectiveness of speech enhancement and sound quality. The full-band speech is divided into multiple sub-bands for analysis and processing, and different FIR filters can be designed for each sub-band to meet the enhancement requirements in different frequency ranges. FIR filters have the advantages of linear phase and stability, which can effectively avoid the problems of signal distortion and filter instability [15]. However, the design and optimization of FIR filters require certain experience and skills, which may increase the difficulty of algorithm development and debugging.
The third approach, spectrum splitting, is a popular approach for speech enhancement research. There are two recent models [16,17] that apply spectrum splitting, rather than directly modeling the full-band feature, after performing a short-time Fourier transform (STFT). DMF-Net [18] and SF-Net [19] use a cascaded structure for spectrum splitting. These methods divide full-band speech into several continuous sub-bands and then analyze and process each sub-band. DMF-Net proposes a new deep-learning model for full-band speech enhancement that uses a decoupling-style multi-band fusion approach. SF-Net adopts a coordinated strategy when fusing sub-bands to ensure better collaboration between different sub-bands. This method does not require the design and operation of complex FIR filters, so the calculation cost and memory occupation are relatively low. In addition, this method can avoid overlap and information loss between sub-bands, thereby leading to an improved speech enhancement effect and quality through reasonable frequency band division. Some recent full-band speech processing algorithms can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Recent full-band speech processing algorithms.
In previous work, we proposed the CGA-MGAN [20], a convolution-augmented gated attention metric GAN for speech enhancement. By constructing convolution-augmented gated attention units (CGAU), the network can capture time and frequency dependence with lower computational complexity and obtain better speech enhancement results. In addition, the CGA-MGAN constructs an encoder-decoder structure including gating blocks using the decoupling-style phase-aware method, which can collaboratively estimate clean speech’s magnitude and phase information in parallel and avoid compensatory effects between the two. However, the encoder–decoder structure uses triple sub-decoders to process magnitude, real part, and imaginary part information, respectively, and there is no parameter interaction between them, which limits its speech enhancement ability.
In this paper, we propose a two-stage complex and real dual-path sub-band fusion network, TS-CGANet, for full-band speech enhancement. Specifically inspired by SF-Net, we divided the original full-band spectrum into three frequency bands—a 0–8 kHz low band (LB), an 8–16 kHz medium band (MB), and a 16–24 kHz high band (HB)—and designed three subnetworks to respectively process them. First, we designed a CGA-based complex and real dual-path speech enhancement network, LB-Net, to enhance LB speech. It uses a decoupling-style phase-aware method to avoid the influence of the compensation effect. Subsequently, we built the MB-Net and HB-Net to enhance the speech of MB and HB. MB-Net and HB-Net only enhance the magnitude of speech in the high-band and keep the phase unchanged. In addition, when using MB-Net and HB-Net for speech enhancement, the pretreated LB-Net will provide additional guidance. Finally, the frequency bands processed by the three networks were fused to recover the full-band speech.
We outline our main contributions as follows:
- We introduced the CGAU into full-band speech enhancement and used spectrum splitting to process full-band speech. It can better process the global and local information of low-frequency speech, and provide external knowledge guidance when processing high-frequency speech;
- We improved on the CGAU and built a complex and real dual-path speech enhancement network that can realize the information interaction between real and virtual parts, as well as improve the speech enhancement effect;
- Regarding the Voice Bank + DEMAND dataset [21], the TS-CGANet we proposed was superior to other previous methods, and an ablation experiment verified our design choice.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 presents some of the previous research results. Section 3 analyzes the proposed architecture of the TS-CGANet. Section 4 details the experimental setup, which includes the dataset used, the network’s training process, and the evaluation metrics. Section 5 compares the experimental results with existing models, and an ablation experiment is conducted. Section 6 concludes our work and suggests some future research directions.
2. Related Works
In this section, we briefly review our previous research on the CGAU. The CGAU is an improved convolution-attention structure based on the convolution-augmented transformer (conformer) [22]. In this paper, we used the CGAU to form the basic unit of the low-band speech enhancement network LB-Net.
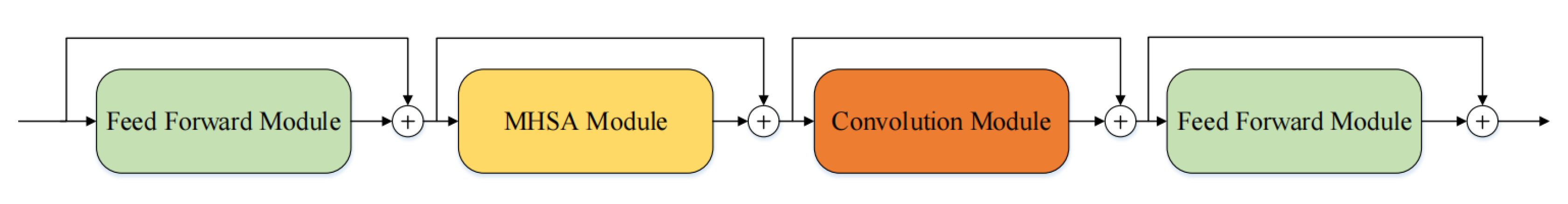
The conformer adopts a Makaron-style structure and constructs the conformer block by inserting deep convolution modules between the multi-head self-attention (MHSA) module and the feed-forward module [20]. The combination of convolution and self-attention can capture the global information and local features of speech at the same time [20]. However, due to the use of a large number of MHSA structures and feed-forward modules in multiple stacked conformer blocks, the computational complexity of the network has increased [20]. The structure of the conformer is shown in Figure 1.
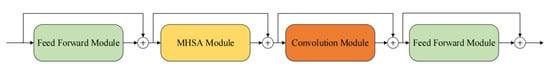
Figure 1.
Conformer architecture.
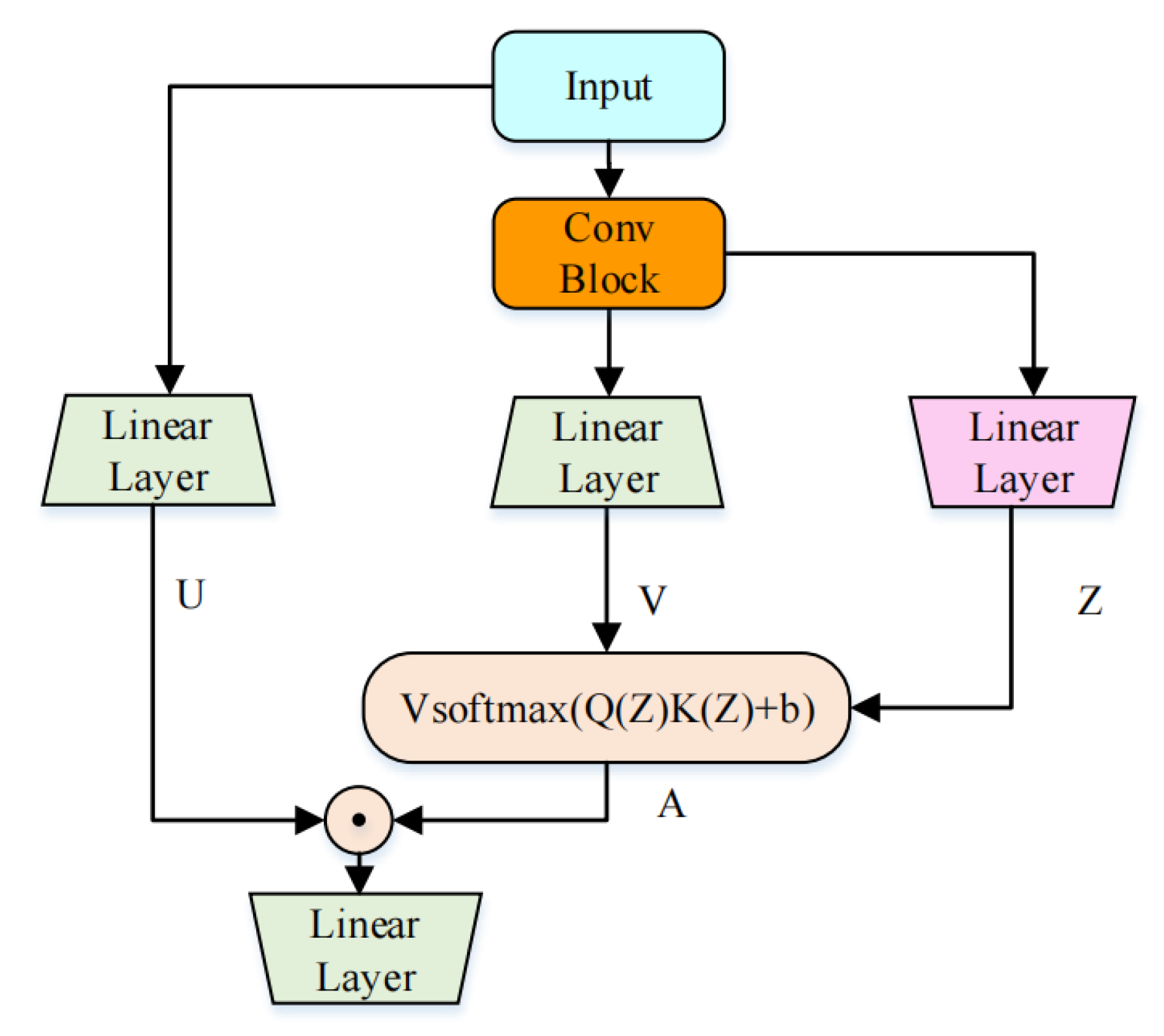
In our previous work, we proposed a novel architecture called the CGAU, which is shown in Figure 2. The CGAU consists of a single-head self-attention (SHSA), a gated linear unit (GLU) and a convolutional module. Unlike the Makaron-style structure used in the conformer, the CGAU replaces the two feed-forward modules with a GLU. As shown in Figure 2, U is the output of one of the branches in GLU. Z is a shared rep-resentation which can be converted into the query and key in the attention mechanism. V represents the value in the attention mechanism. The GLU’s powerful performance reduces the dependence of CGAU blocks on the self-attention structure, thereby allowing us to use SHSA instead of MHSA and reduce network complexity. Moreover, the CGAU integrates the convolution module and GAU effectively by inserting a deep convolution module into the network to capture local speech information, thus significantly reducing the network’s computational complexity.
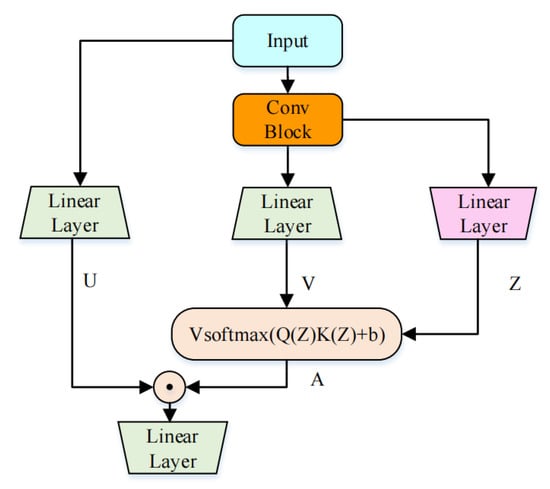
Figure 2.
Convolution-augmented gated attention unit.
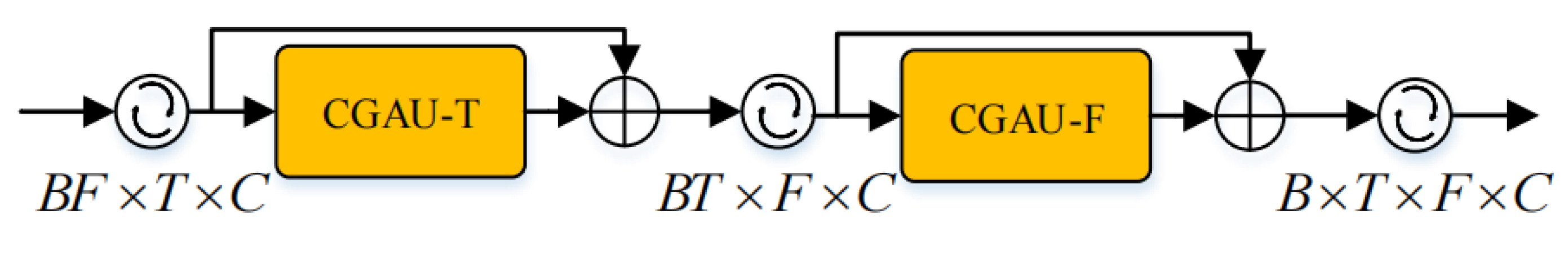
When we use the CGAU to extract speech features, we need to capture time dependence and frequency dependence, respectively. Therefore, we concatenate two CGAUs to build a CGA block, as shown in Figure 3. Through the stacking of the CGA blocks, we can gradually extract the features of different levels of speech. The specific architecture of each CGA block is shown in the figure below. The shape of the feature map we input into the CGA Block is , where B represents the batch size, T represents the number of frames, F represents the number of frequency bins of the complex spectrogram, and C represents the number of the channel. The input feature map is reshaped to and input into the first CGAU to capture the time dependence. Then, the output and are element-wise added, reshaped to , and input into the second CGAU to capture the frequency dependence. Finally, the output and input are element-wise added and reshaped to the final output, .
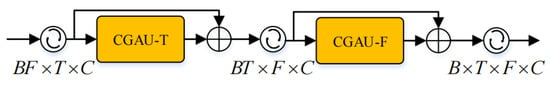
Figure 3.
CGA block architecture.
3. Methodology
3.1. Dual-Branch Low-Band Speech Enhancement Network LB-Net
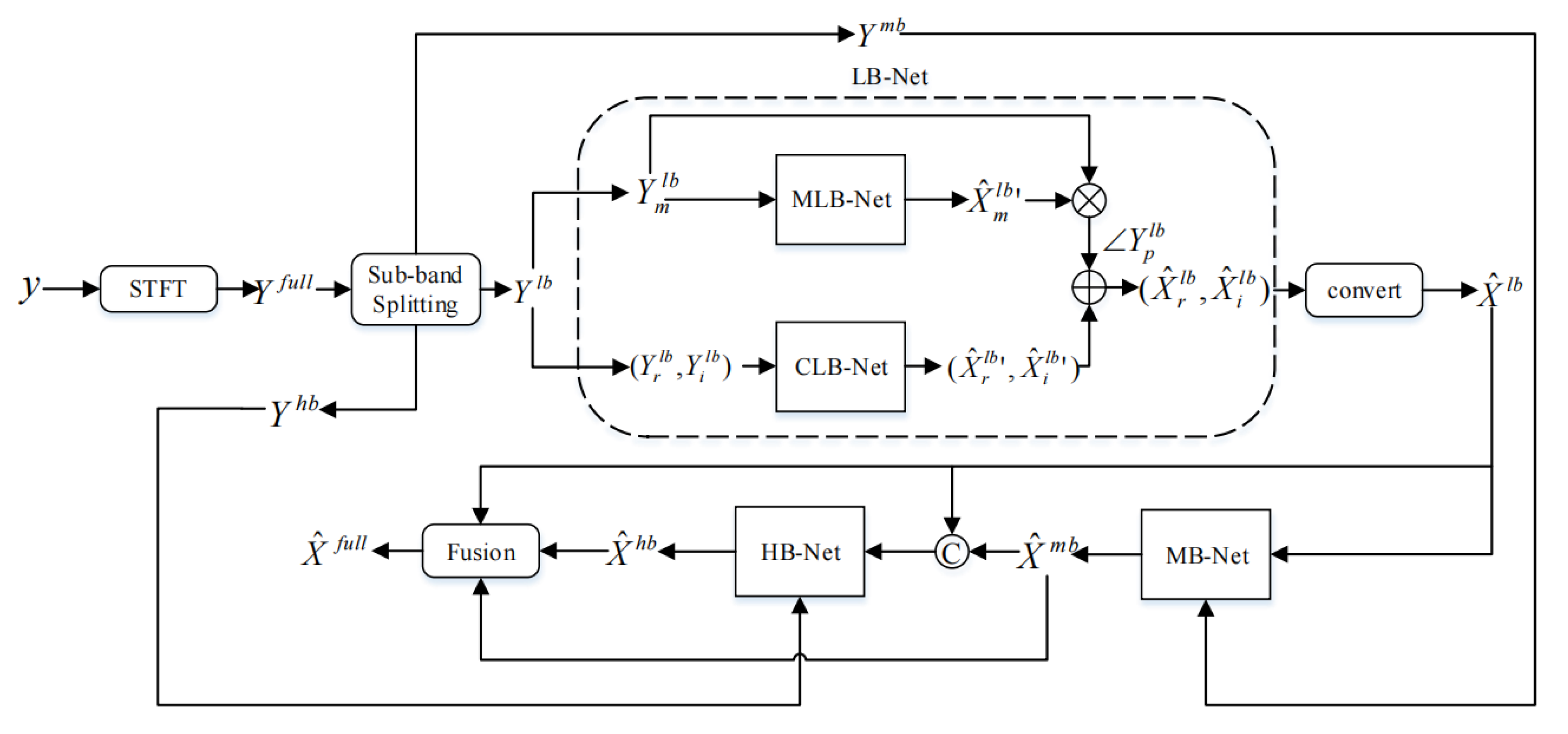
The architecture of TS-CGANet is presented in Figure 4. LB-Net comprises two sub-networks, namely, MLB-Net for processing magnitude and CLB-Net for processing real and imaginary components. The input signal, which is the noisy speech signal, is first converted into the frequency domain using STFT. Subsequently, a power law compression is applied to the spectrum with a compression exponent of 0.5.
where is the compression exponent and is the phase of noisy speech. Then, we divide the spectrum to according to three frequency bands and send the speech magnitude of LB band into the encoder of MLB-Net. The real component and the imaginary component are concatenated as as the input of the encoder of the CLB-Net.
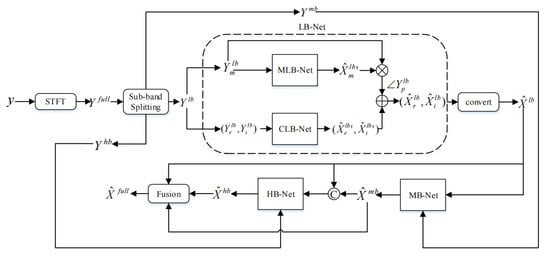
Figure 4.
The architecture of TS-CGANet.
The mask obtained after MLB-Net processing is multiplied by the original spectrum to obtain the coarse-estimated spectrum magnitude and then coupled with to obtain the roughly estimated real parts and imaginary parts. is the phase of the LB noisy speech :
As a supplement, CLB-Net estimates the complex spectrum to get the residual mapping . Finally, the roughly estimated real and imaginary parts are added with the output of CLB-Net to get the final enhanced LB speech :
3.1.1. Encoder and Decoder
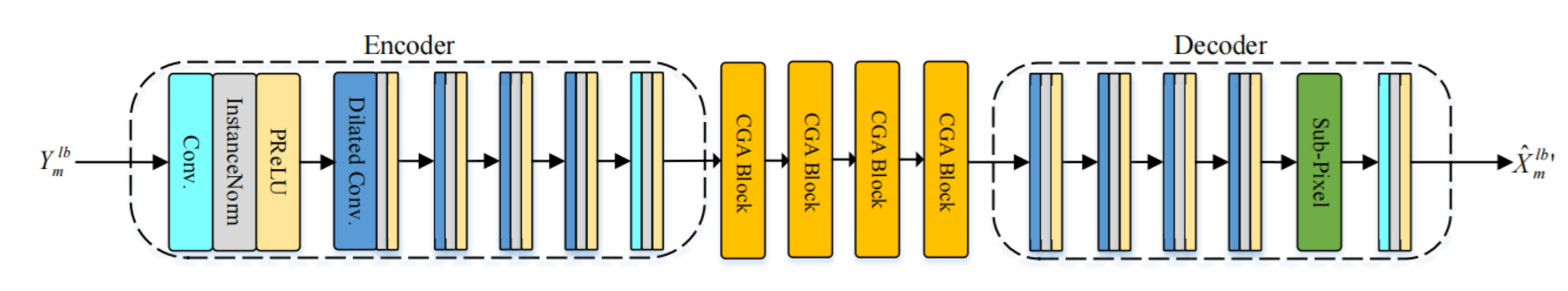
The network architecture of MLB-Net is shown in Figure 5. The encoder is composed of a DenseNet [23] sandwiched between two convolution layers. The first convolution layer is used to extend the channel of input characteristics to 64, and the second convolution layer is used for down-sampling to reduce complexity. DenseNet contains four dense connected convolution blocks, and the dilation factors of each block are set to {1,2,4,8}, which can effectively expand the receptive field and extract features at different levels. After all the convolution layers are in the encoder, there is an instance normalization [24] and a parameter ReLU (PReLU) activation [25]. The feature map of encoder output is , where and . The decoder consists of a dilated DenseNet and then uses a subpixel convolution layer to up-sample the frequency dimension back to . Finally, a convolution layer is used to obtain the final output.
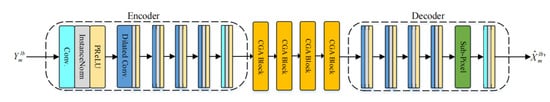
Figure 5.
The architecture of MLB-Net.
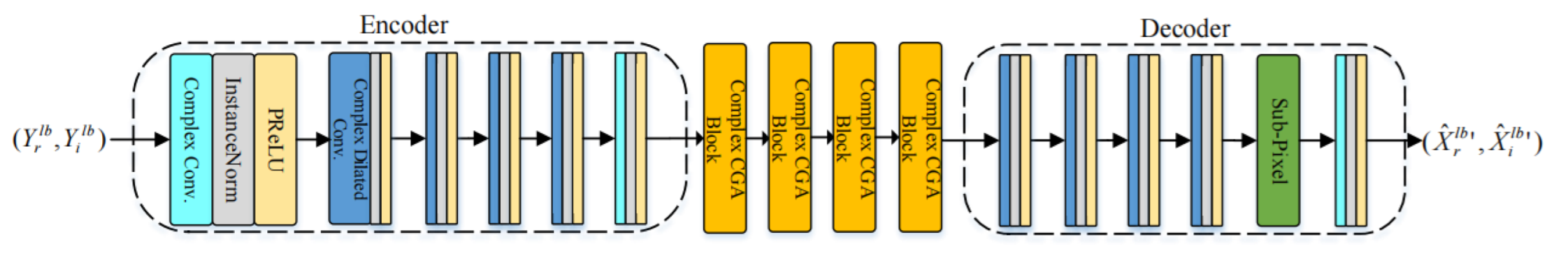
The network architecture of CLB-Net is shown in Figure 6. The encoder and decoder structure of CLB-Net is the same as that of MLB-Net. Since the input of CLB-Net is complex, it is necessary to replace the convolution in CLB-Net with the corresponding complex convolution. Each complex convolution contains two convolution layers. For the input , the complex convolution calculation formulas are as follows:
where and represent the learnable parameter matrixes of the convolution layers. is the feature mapping of the output of the complex convolution. The feature map of encoder output is . The last dimension of the feature mapping represents the real part and the imaginary part.
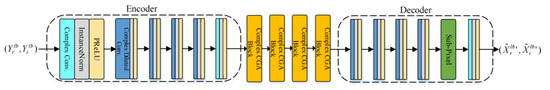
Figure 6.
The architecture of CLB-Net.
3.1.2. Complex Convolution-Augmented Gated Attention Units
In the self-attention mechanism, query (), key (), and value () can be obtained by mapping input :
where , , and represent the learnable parameter matrixes of the linear layers. Then, the scaled dot-product attention is applied to the query, key, and value afterward as:
where represents the projection dimension of . Softmax is an activation function. Given an input vector of size n, the softmax function computes a vector of n probabilities. The formula for softmax is:
where is the input vector and is the probability assigned to the i-th class. The denominator ensures that the sum of all the probabilities is equal to one, making it a valid probability distribution.
Accordingly, inspired by Uformer [26], when input is a complex number, the calculation formula of is:
where and represent the real part and imaginary part of . In addition, and are calculated in the same way. Therefore, the complex self-attention (CSA) is calculated as follows:
The two complex CGAUs in the complex CGA block have the same structure. Taking the first complex CGAU as an example, is reshaped as and input into the complex CGAU. is divided into two channels, one of which is sent to the complex convolution module. The output of the complex convolution module is . The real part’s query , key , value , and the virtual part’s query , key , and value are all replicas of . Then, we add the rotation position code to Formula (12), and use Formula (16) to calculate the CSA.
In the above formulas, represents the swish activation function, while the linear layers’ learnable parameter matrixes are represented by . The shared representation is represented by . The query and key are obtained by applying simple affine transformations to , respectively. represents values in the CSA mechanism. The swish activation function is a smooth, non-monotonic function that is continuous and differentiable everywhere. For input , the function is defined as:
Before calculating CSA, we need to add the rotation position code [27] in Formula (12), which is represented by variable :
where, , , and respectively represent the real or imaginary parts of the corresponding complex , , and . After that, we use Formula (16) to calculate .
The other feed of input passes through the linear layer and is activated by swish to obtain . Finally, the Hadamard product of and is calculated and input into the linear layer to obtain output so that the convolution-augmented attention information is introduced to the gated linear unit. The calculation formula is as follows, where represents Hadamard product:
3.2. Medium and High Band Speech Enhancement Network
MB and HB have wider frequency bands and fewer speech features. We designed MB-Net and HB-Net as the speech enhancement networks of MB and HB, respectively. When using them for speech enhancement, we only process the magnitude, while keeping the phase of noisy speech unchanged. This can reduce the computational burden and avoid the compensation effect.
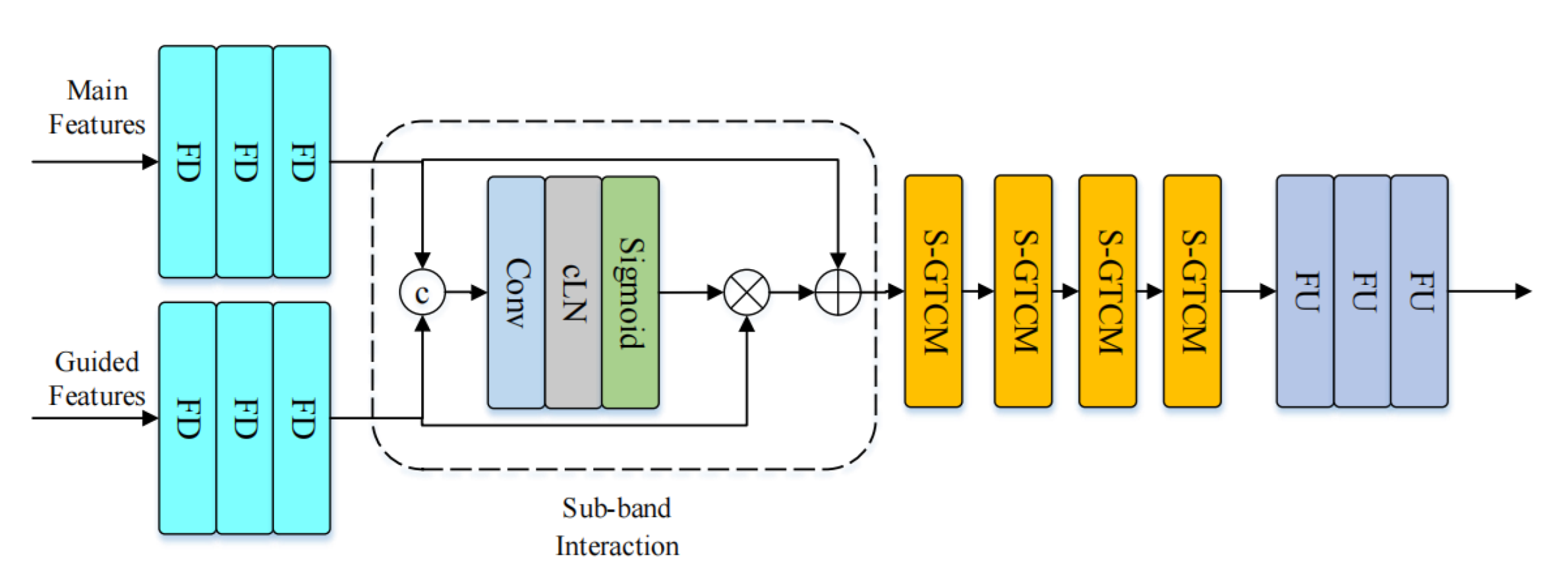
MB-Net and HB-Net have identical structures, as depicted in Figure 7. They comprise two encoders, a sub-band interaction module, a stacked gated temporal convolutional module, and a decoder. The two encoders process the main spectrum feature of the current frequency band and the guided spectrum feature of the previous model output, respectively. For MB-Net, the guided feature is the speech enhanced by LB-Net, . For HB-Net, the guided feature is the speech concatenated on the frequency axis by the speech enhanced by LB-Net and the speech enhanced by MB-Net, . After concatenating the spectrum feature of the current frequency band and the spectrum feature of the guided speech, they are passed to the sub-band interaction module for processing. The sub-band interaction module retains the important spectral features of the guided speech and suppresses irrelevant features. Then, the processed feature map is outputted to the stacked gated time convolution module for feature extraction, and the output is sent through the decoder. After applying HB-Net, the enhanced speech of the three sub-networks is concatenated on the frequency axis to obtain the enhanced full-band speech.
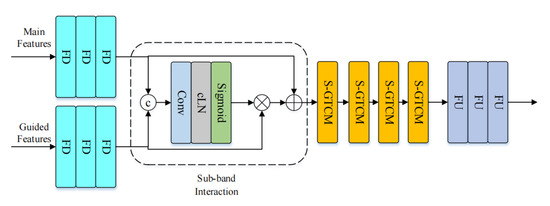
Figure 7.
The architecture of MB-Net and HB-Net.
The encoder comprises three frequency down-sampling (FD) layers, illustrated in Figure 8a. FD is built using gated convolution (GConv) [28,29]. Cumulative layer normalization (cLN) [13] is applied to normalize the features, thereby enabling streaming inference and updating of frame-wise statistics. PReLU is used for activation. The kernel size for the time and frequency axes is (1, 7). To gradually reduce the frequency dimension, we set the stride to (1, 4). The decoder is made up of three frequency up-sampling (FU) layers, whose structure is depicted in Figure 8b. FU is similar to FD, but transposed gating convolution (TrGConv) replaces GConv [30].

Figure 8.
(a) Frequency down-sampling layer; (b) frequency up-sampling layer.
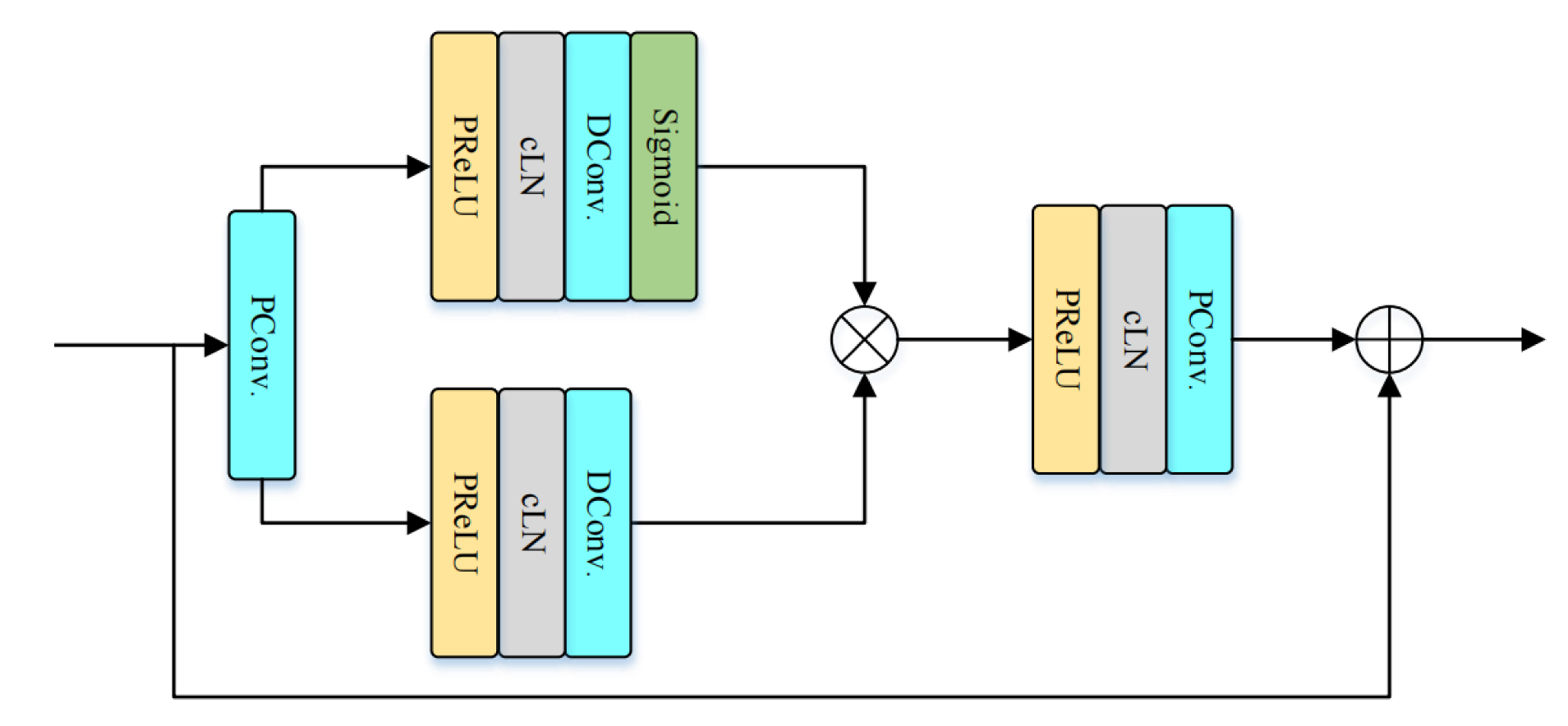
The stacked gated temporal convolutional module (S-GTCM) is shown in Figure 9 and consists of a stack of GTCM layers. Following [31], we employed four groups of S-GTCM for sequence modeling, with each group comprising four GTCMs having increasing dilation rates, i.e., d = {1, 2, 5, 9}, to achieve a large temporal receptive field. Each GTCM layer comprises two pointwise convolutions (PConv) and two dilated convolutions (DConv) with a kernel size of 5. We interpolate PReLU and cLN between adjacent convolutions. To facilitate the training of deeper networks, residual connections are established between the input and output.
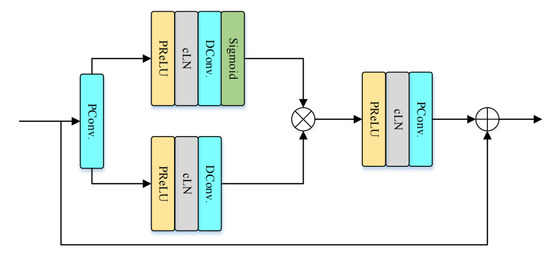
Figure 9.
Details of GTCM.
3.3. Loss Function
We used a two-stage training method to gradually recover the LB speech and the full-band speech. First, we trained LB-Net. LB-Net enhances speech in both magnitude and phase, so our loss function included the loss terms of magnitude and RI components, as shown in the following formulas:
where consists of magnitude loss and phase-aware loss . , , and represent the magnitude, real component, and imaginary component of clean speech, respectively. , and represent the magnitude, real component, and imaginary component of the enhanced speech, respectively. represents the chosen weight, and we took .
In the second stage, we combined the pre-trained LB-Net network with MB-Net and HB-Net, and conducted joint training on them. The total loss can be given by the following formula:
where represents the loss function of MF-Net and represents the loss function of HF-Net in the magnitude domain, and we defined the total loss function of the second stage as . represents the chosen weight, and we took .
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Settings
Our model was tested using the publicly available Voice Bank + DEMAND dataset, which consists of speech recordings from the CSTR VCTK Corpus and background noise from the DEMAND database. The training set includes 11,572 sentences provided by 28 speakers, and the test set includes 824 sentences provided by 2 unseen speakers. To generate the training set, we used eight natural and two artificial background noise processes under different SNR levels (ranging from 0 to 15 dB with an interval of 5 dB), while the test set was generated using five unseen background noise processes under different SNR levels (ranging from 2.5 to 17.5 dB with an interval of 5 dB).
The sampling rate of all sentences was 48 kHz and, in the training set, they were sliced into 3 s units, while no slicing was done in the test set. A Hanning window of length 20 ms and a hop length of 10 ms were applied. After the STFT process, a power law compression with a compression coefficient of 0.5 was applied to the spectrum, and then reversed on the final estimated complex spectrum. Finally, the inverse STFT was applied to recover the time-domain signal. The AdamW optimizer was used to train both the generator and discriminator for 100 epochs. In the first stage, the learning rate of the LB-Net was set to 1 × 10−3. In the second stage, the learning rate of the LB-Net was fine-tuned to 1 × 10−4, while the learning rate of the MB-Net and the HB-Net was set to 1 × 10−3.
4.2. Evaluation Indicators
Five objective indicators were used to assess the enhanced speech quality, with higher scores indicating better performance. The indicators included:
- PESQ [32]: The perceptual evaluation of speech quality—ranges from −0.5 to 4.5;
- CSIG [33]: The MOS prediction of the signal distortion—ranging from 1 to 5;
- CBAK [33]: The MOS prediction of the background noise intrusiveness—ranging from 1 to 5;
- COVL [33]: The MOS prediction of the overall effect—ranging from 1 to 5;
- STOI [34]: The short-time objective intelligibility—ranging from 0 to 1.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Baselines and Results Analysis
We compared our proposed TS-CGANet with some state-of-the-art models. In addition to the four models introduced previously, we also selected three new full-band speech enhancement methods as the baseline models: GCRN, CTS-Net, and DeepFilterNet. In addition, we also selected an ultra-wideband speech enhancement method, S-DCCRN, for comparison.
The GCRN proposes a novel approach to monaural speech enhancement using gated convolutional recurrent networks. The GCRN utilizes gated convolutions, which selectively allow or block information flow to effectively capture global and local spectral features of the speech signal. This is important for capturing complex spectral mappings that may be present in noisy and clean speech signals. The CTS-Net proposes a novel two-stage approach for enhancing monaural speech signals. The first stage of the approach involves learning a complex spectral mapping to clean speech using a deep neural network. The second stage then applies a non-linear mapping to further refine the spectral features of the enhanced speech. The DeepFilterNet utilizes a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) to learn a mapping function to clean speech, where the network is trained with a novel deep filtering loss function. The loss function allows the network to learn and optimize both the magnitude and phase components of the spectral features of the speech signal, thereby resulting in enhanced speech with improved quality. The S-DCCRN is a deep learning-based approach for speech enhancement. It is designed to enhance speech signals that are corrupted by noise in a wide frequency range. The model uses a dual-path complex convolutional recurrent neural network (DCCRN) architecture that includes both a sub-band processing path and a full-band processing path.
Table 2 reveals several notable findings. Firstly, in all objective metrics, the TS-CGANet surpassed the compressed psychoacoustic excitation features. Secondly, the proposed spectrum splitting and sub-band fusion strategy were effective, as the TS-CGANet outperformed the one-stage baselines by a significant margin. Thirdly, the TS-CGANet exhibited superior performance compared to the SF-Net, which also utilizes spectrum splitting, particularly in the PESQ. The utilization of the proposed complex and real dual-path CGA network enabled better speech enhancement.

Table 2.
Performance comparison of Voice Bank + DEMAND dataset.
5.2. Ablation Study
To investigate the contribution of different components in the TS-CGANet that improved its performance, we conducted an ablation study and compared several variants of the TS-CGANet model in Table 3. These variants included: (i) LB-Net (full)—a single-stage complex and real dual-path full-band SE method that directly enhances full-band speech using LB-Net; (ii) LB-Net (with real CGAU)—a single-stage real dual-path full-band SE method that changes the complex CGAU in (i) to real CGAU; (iii) LB-Net (w/o phase enhancement)—a single-stage single-path full-band SE method that removes the complex CGAU structure and decoupling-style phase-aware method in the LB-Net and only uses the ME-Net to directly enhance full-band speech; (iv) TS-CGANet (w/o complex CGAU)—a two-stage real dual-path full-band SE method that changes the complex CGAU in TS-CGANet to real CGAU; and (v) TS-CGANet (w/o phase enhancement)—a two-stage single-path full-band SE method that removes the complex CGAU structure and decoupling-style phase enhancement method in the TS-CGANet.

Table 3.
Results of the ablation study.
We conducted an ablation study to investigate the contribution of different components of the TS-CGANet to enhancing performance. All variants were set using the same configuration as the TS-CGANet. As indicated in Table 3, all variants underperformed compared to the TS-CGANet. Specifically, variant (i) exhibited a decrease of 0.14 in the PESQ. This may be attributed to the model’s tendency to focus on the high-frequency band while processing high- and low-frequency band speech in parallel, which leads to a reduced effect on the low-frequency band containing the main speech components.
When comparing variant (i) with variants (ii) and (iii), we found that all indicators further declined. Replacing the complex CGAU branch in the LB-Net with a real CGAU resulted in a lack of information interaction between the real and imaginary parts, which decreased the speech enhancement effect. Furthermore, removing the decoupling phase enhancement method resulted in a decrease of 0.35 in the PESQ, which significantly impacted the quality of the enhanced speech. These findings further demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed complex and real dual-path network LB-Net.
When comparing variants (ii) and (iii) with variants (iv) and (v), we observed that the speech enhancement effect of the two-stage network was superior to that of the single-stage network. This may be attributed to reasonable spectrum splitting, which enabled different networks to process the LB and HB components of speech separately, thereby avoiding overlapping and information loss between sub-bands and improving the effect and quality of the speech enhancement. These results provide additional support for the rationality of our proposed two-stage full-band speech enhancement method.
6. Conclusions
In this work, we proposed TS-CGANet, a two-stage complex and real dual-path sub-band fusion network for full-band speech enhancement. We introduced the convolution-augmented gated attention unit into the full-band speech enhancement method and employed spectrum splitting to process full-band speech. This approach enabled better handling of the global and local information of low-frequency speech and provided external knowledge guidance when processing high-frequency speech. Moreover, we proposed a complex CGAU that enhanced the interaction between the real and imaginary parts of speech, improved the performance of the decoupling phase compensation method, and enhanced speech quality. Experiments on the Voice Bank + DEMAND dataset showcased the notable performance improvements of our proposed TS-CGANet model over the baseline models of the same category. In the future, we will further explore other methods for full-band speech enhancement.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.C.; funding acquisition, X.Z.; methodology, H.C.; project administration, X.Z.; software, H.C.; validation, H.C.; writing—original draft, H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.: 61172017).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
A publicly available dataset (Voice Bank + DEMAND) was analyzed in this study. The Voice Bank + DEMAND dataset can be found here: https://datashare.ed.ac.uk/handle/10283/2791 (accessed on 17 December 2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yuliani, A.R.; Amri, M.F.; Suryawati, E.; Ramdan, A.; Pardede, H.F. Speech Enhancement Using Deep Learning Methods: A Review. J. Elektron. Telekomun. 2021, 21, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Tuo, D.; Wu, Z.; Kang, S.; Meng, H. FullSubNet+: Channel attention fullsubnet with complex spectrograms for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 7857–7861. [Google Scholar]
- Michelsanti, D.; Tan, Z.-H.; Zhang, S.-X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, M.; Yu, D.; Jensen, J. An overview of deep-learning-based audio-visual speech enhancement and separation. IEEE ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 1368–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Wang, D. Towards model compression for deep learning based speech enhancement. IEEE ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröter, H.; Maier, A.; Escalante-B., A.; Rosenkranz, T. Deepfilternet2: Towards Real-Time Speech Enhancement on Embedded Devices for Full-Band Audio. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Workshop on Acoustic Signal Enhancement (IWAENC), Bamberg, Germany, 5–8 September 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ochieng, P. Deep neural network techniques for monaural speech enhancement: State of the art analysis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.00369. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Wen, S.; Su, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, G.; Li, X. Sub-band knowledge distillation framework for speech enhancement. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14435. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Le, X.; Lu, J. A light-weight full-band speech enhancement model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.14524. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghan Firoozabadi, A.; Irarrazaval, P.; Adasme, P.; Zabala-Blanco, D.; Durney, H.; Sanhueza, M.; Palacios-Játiva, P.; Azurdia-Meza, C. Multiresolution speech enhancement based on proposed circular nested microphone array in combination with sub-band affine projection algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, X.; Qian, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, M. FB-MSTCN: A full-band single-channel speech enhancement method based on multi-scale temporal convolutional network. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 9276–9280. [Google Scholar]
- Valin, J.-M. A hybrid DSP/deep learning approach to real-time full-band speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 29–31 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, R.; Venkataramani, S.; Valin, J.-M.; Isik, U.; Krishnaswamy, A. Personalized percepnet: Real-time, low-complexity target voice separation and enhancement. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.04129. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Lu, H.; Hu, N.; Yu, M.; Weng, C.; Xu, K.; Liu, P.; Tuo, D.; Kang, S.; Lei, G. Durian: Duration informed attention network for multimodal synthesis. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.01700. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Yang, S.; Liu, K.; Fang, P.; Chen, W.; Xie, L. Multi-band melgan: Faster waveform generation for high-quality text-to-speech. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Shenzhen, China, 19–22 January 2021; pp. 492–498. [Google Scholar]
- Proakis, J.G. Digital Signal Processing: Principles, Algorithms, and Applications, 4/E.; Pearson Education India: Noida, India, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, L. Dccrn+: Channel-wise subband dccrn with snr estimation for speech enhancement. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.08672. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Luo, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Cui, G.; Tang, W.; Chen, W. Densely connected multi-stage model with channel wise subband feature for real-time speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Virtual, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 6638–6642. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Guan, Y.; Meng, W.; Zheng, C.; Wang, H. DMF-Net: A decoupling-style multi-band fusion model for real-time full-band speech enhancement. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.00472. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Li, A.; Liu, W.; Zheng, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Optimizing Shoulder to Shoulder: A Coordinated Sub-Band Fusion Model for Real-Time Full-Band Speech Enhancement. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.16033. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X. CGA-MGAN: Metric GAN based on Convolution-augmented Gated Attention for Speech Enhancement. Preprints 2023, 2023020465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini-Botinhao, C.; Wang, X.; Takaki, S.; Yamagishi, J. Investigating RNN-based speech enhancement methods for noise-robust Text-to-Speech. In Proceedings of the SSW, Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 13–15 September 2016; pp. 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, A.; Qin, J.; Chiu, C.-C.; Parmar, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Han, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y. Conformer: Convolution-augmented transformer for speech recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.08100. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Wang, D. Densely connected neural network with dilated convolutions for real-time speech enhancement in the time domain. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6629–6633. [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Instance normalization: The missing ingredient for fast stylization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.08022. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, D.; Lv, S.; Jv, Y.; Xie, L. Uformer: A unet based dilated complex & real dual-path conformer network for simultaneous speech enhancement and dereverberation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 7417–7421. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Lu, Y.; Pan, S.; Murtadha, A.; Wen, B.; Liu, Y. Roformer: Enhanced transformer with rotary position embedding. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.09864. [Google Scholar]
- Dauphin, Y.N.; Fan, A.; Auli, M.; Grangier, D. Language modeling with gated convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 933–941. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Ju, Y.; Fu, Y.; Na, Y.; Fu, Q.; Xie, L. Personalized acoustic echo cancellation for full-duplex communications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.15195. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Y.; Zhang, S.; Rao, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Xie, L.; Shang, S. TEA-PSE 20: Sub-Band Network for Real-Time Personalized Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Doha, Qatar, 9–12 January 2023; pp. 472–479. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Wang, D. TCNN: Temporal convolutional neural network for real-time speech enhancement in the time domain. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 6875–6879. [Google Scholar]
- Rix, A.W.; Beerends, J.G.; Hollier, M.P.; Hekstra, A.P. Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)-a new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Proceedings (Cat. No. 01CH37221), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 7–11 May 2001; pp. 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Loizou, P.C. Evaluation of objective quality measures for speech enhancement. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2007, 16, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taal, C.H.; Hendriks, R.C.; Heusdens, R.; Jensen, J. A short-time objective intelligibility measure for time-frequency weighted noisy speech. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA, 14–19 March 2010; pp. 4214–4217. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Wang, D. Learning complex spectral mapping with gated convolutional recurrent networks for monaural speech enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 28, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Liu, W.; Zheng, C.; Fan, C.; Li, X. Two heads are better than one: A two-stage complex spectral mapping approach for monaural speech enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 1829–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroter, H.; Escalante-B, A.N.; Rosenkranz, T.; Maier, A. DeepFilterNet: A low complexity speech enhancement framework for full-band audio based on deep filtering. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 7407–7411. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, S.; Fu, Y.; Xing, M.; Sun, J.; Xie, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T. S-dccrn: Super wide band dccrn with learnable complex feature for speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 7767–7771. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).