Effects of Pyrolysis and Ball-Milling on the Physicochemical and Rhodamine B Removal Characteristics of Rice-Bran-Derived Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of the Rice Brain Biochar
2.2. Preparation of the Ball-Milled Biochar
2.3. Characterization of the Biochar
2.4. Removal of RhB
3. Results and Discussion
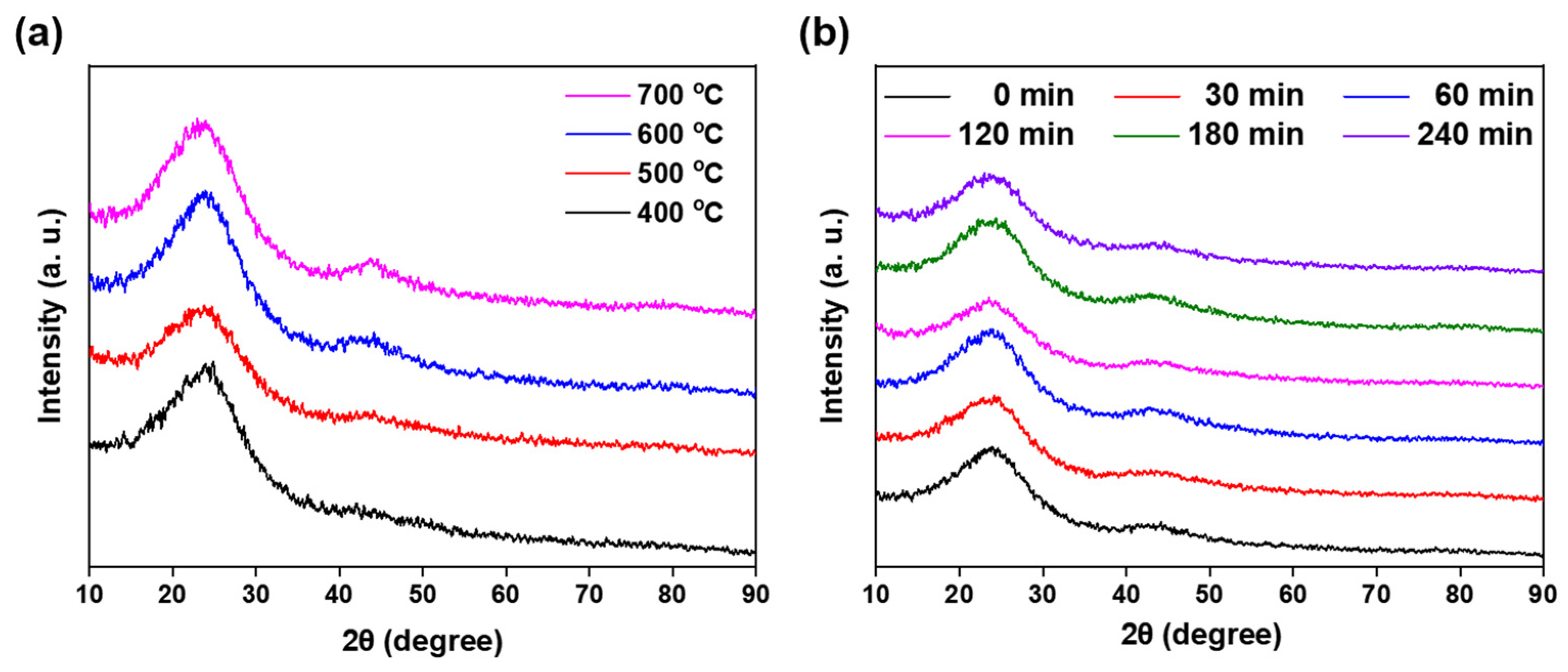
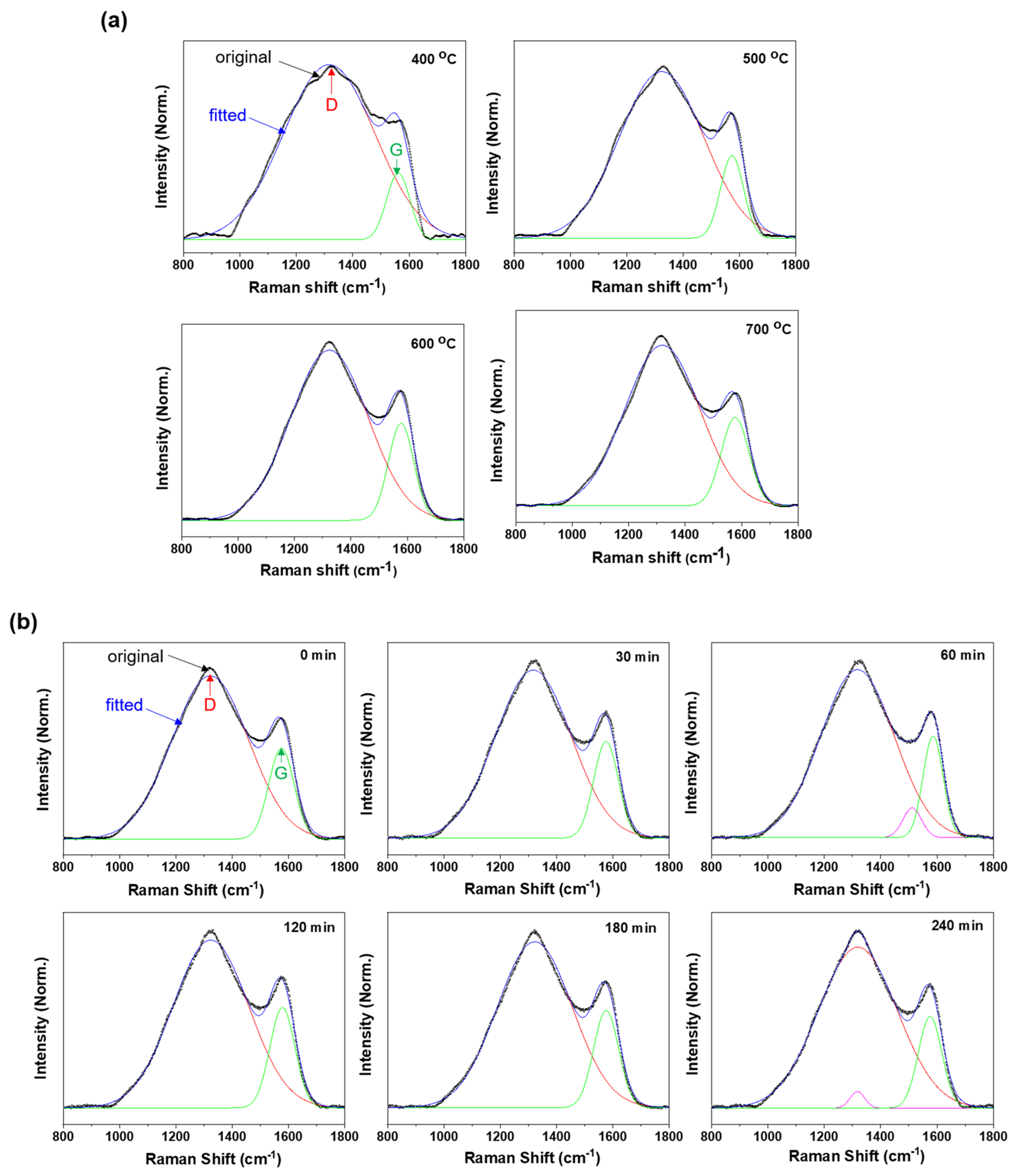
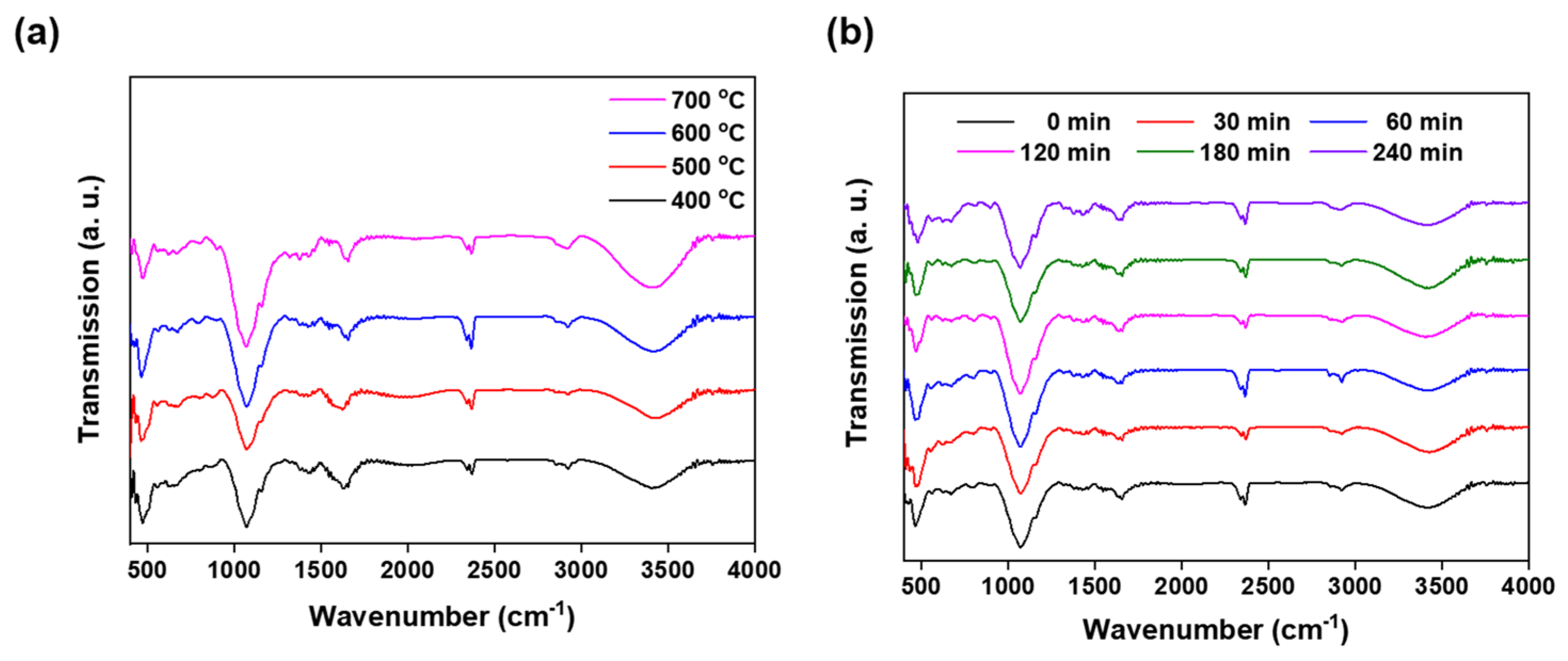
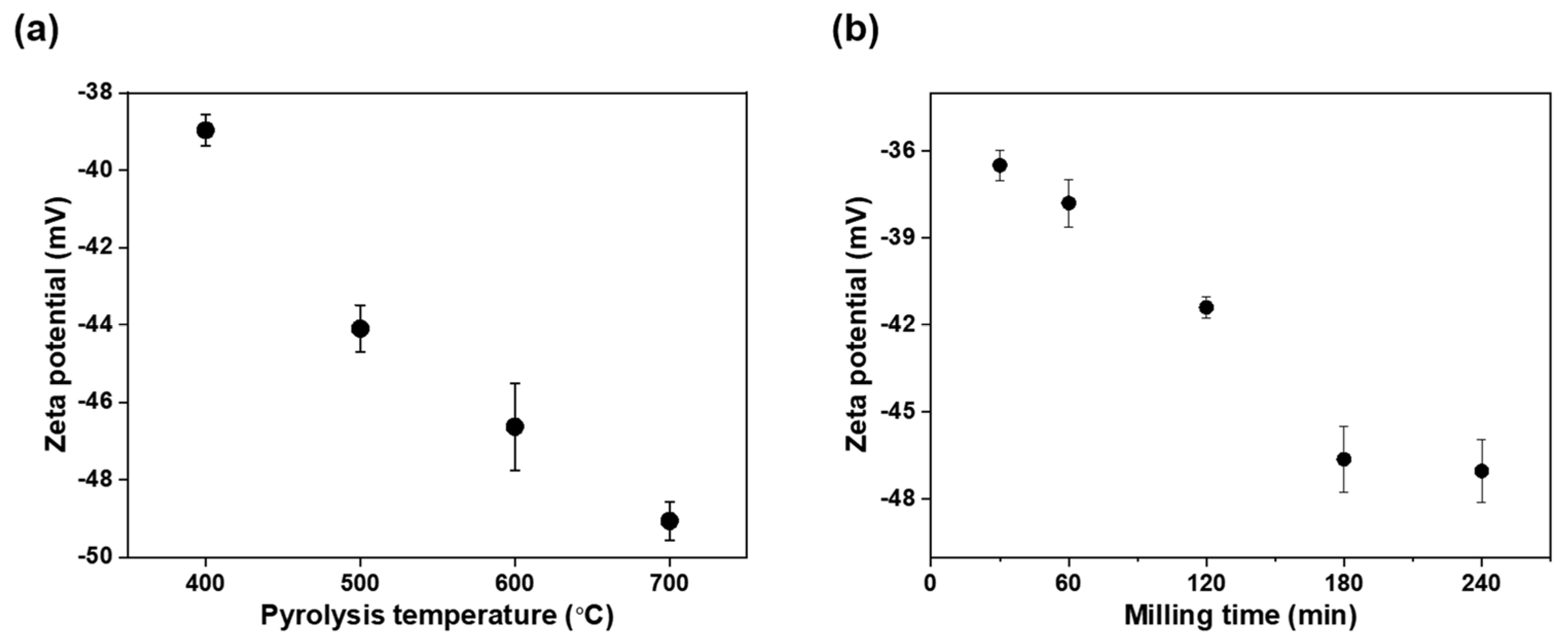
3.1. Biochar Characterization
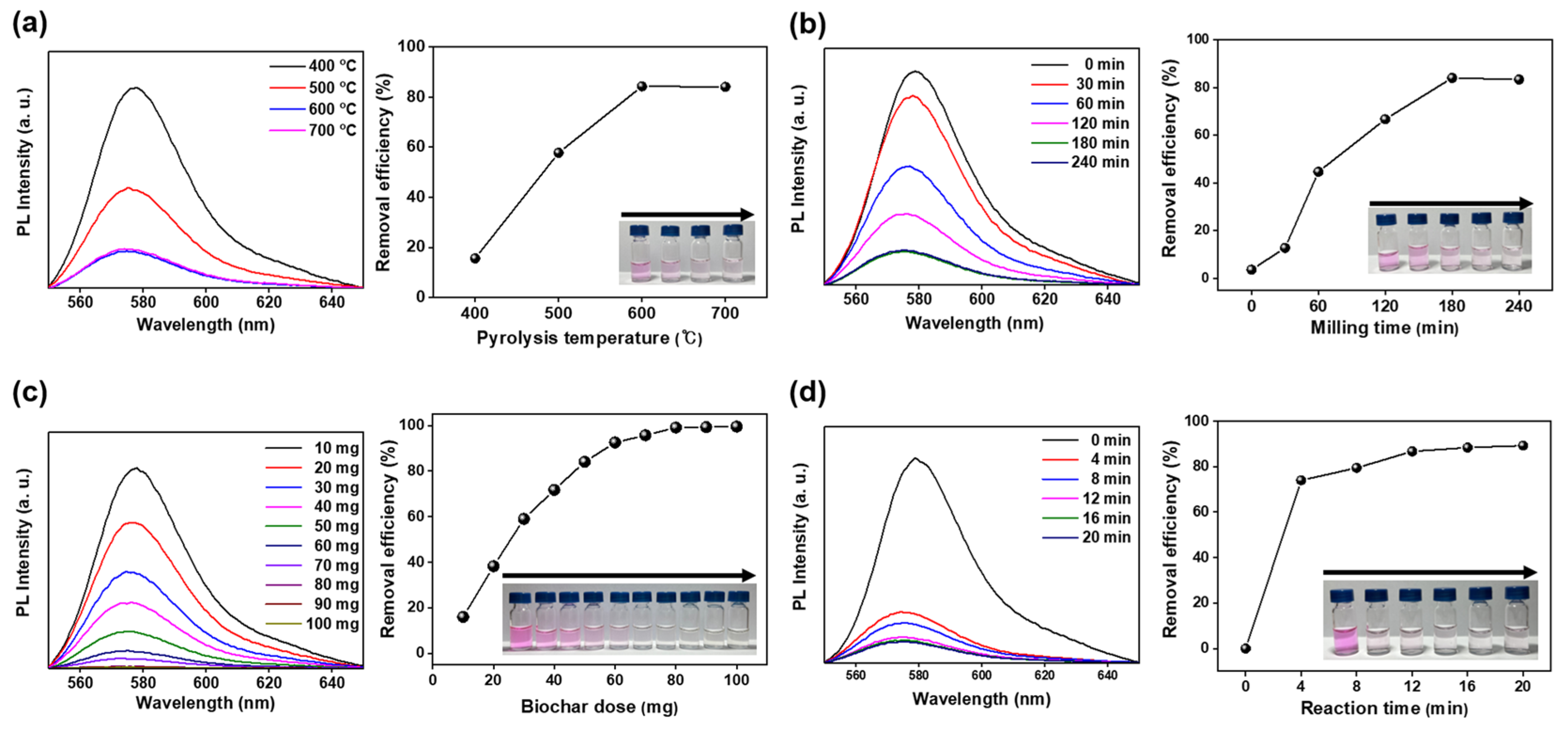
3.2. Removal of RhB
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bilal, M.; Adeel, M.; Rasheed, T.; Zhao, Y.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Emerging contaminants of high concern and their enzyme-assisted biodegradation—A review. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, L.; Hu, B.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Wang., X. Application of biochar-based photocatalysts for adsorption-(photo) degradation/ reduction of environmental contaminants: Mechanism, challenges and perspective. Biochar 2022, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Cui, J.; Ren, Y.; Yu, X. Recent Progress in Biochar-Based Photocatalysts for Wastewater Treatment: Synthesis, Mechanisms, and Applications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Múazu, N.D.; Jarrah, N.; Blaisi, N.I.; Aziz, H.A.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Methylene Blue, Crystal Violet, Eriochrome Black T, and Methyl Orange Dyes onto Biochar-Derived Date Palm Fronds Waste Produced at Different Pyrolysis Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Kwon, E.E. Biochar as a catalyst. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colmenares, J.C.; Varma, R.S.; Lisowski, P. Sustainable hybrid photocatalysts: Titania immobilized on carbon materials derived from renewable and biodegradable resources. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5736–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Xiong, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. Understanding structure-performance correlation of biochar materials in environmental remediation and electrochemical devices. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, P.; Órfão, J.; Pereira, M. Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes on activated carbons with different surface chemistries. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Namba, A.; Mukai, S.R.; Tamon, H.; Ariyadejwanich, P.; Tanthapanichakoon, W. Adsorption of phenol and reactive dye from aqueous solution on activated carbons derived from solid wastes. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Parette, R.; Zou, J.; Cannon, F.S.; Dempsey, B.A. Arsenic removal by iron-modified activated carbon. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Lee, S.S.; Dou, X.M.; Mohan, D.; Sung, J.-K.; Yang, J.E.; Ok, Y.S. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soybean stover- and peanut shell-derived biochar properties and TCE adsorption in water. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Qiu, R. Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar. Water Res. 2012, 46, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ma, L.; Gao, B.; Harris, W. Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3285–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Z. Application of biochar for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Lin, P.-Y.; Hsieh, S.-L.; Kirankumar, R.; Patel, A.K.; Singhania, R.-R.; Dong, C.-D.; Chen, C.-W.; Hsieh, S. Engineered mesoporous biochar derived from rice husk for efficient removal of malachite green from wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, R.; Yang, R.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, R.; Xu, J. Synthesis of amino-functionalized biochar/spinel ferrite magnetic composites for low-cost and efficient elimination of Ni(II) from wastewater. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 722, 137822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, B. Organic carbon and inorganic silicon speciation in rice-bran-derived biochars affect its capacity to adsorb cadmium in solution. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvia, E.-C.; Valeria, A.-G.; MÁngeles, S.; Marta, P. Eco-approach for pharmaceutical removal: Thermochemical waste valorisation, biochar adsorption and electro-assisted regeneration. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 389, 138694. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, T.P.; Yadav, R.M.; Singh, D. Mechanical Milling: A Top Down Approach for the Synthesis of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2, 22–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, M.; Taheran, M.; Brar, S.K.; Rouissi, T.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Valero, J.R. A green method for production of nanobiochar by ball milling-optimization and characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Xu, Z.; Gao, B.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Mesoporous ball-milling iron-loaded biochar for enhanced sorption of reactive red: Performance and mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 117992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Xian, Q.; Shen, F.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on the physicochemical properties of biochar derived from vermicompost and its potential use as an environmental amendment. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40117–40125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Reddy, N.G.; Huang, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, P.; Garg, A. Effects of pyrolysis temperature, feedstock type and compaction on water retention of biochar amended soil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.V.; Chaturvedia, S.; Dhyania, V.C.; Kasivelub, G. Pyrolysis temperature influences the characteristics of rice straw and husk biochar and sorption/desorption behavior of their biourea composite. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.-F.; Ma, C.-X.; Zhang, W.-D.; Tang, X.-Y.; Fan, Y.-N.; Wan, H.-F. Removal of rhodamine B using iron-pillared bentonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.-L.; Tan, Y.P.; Abdullah, A.H.; Ong, S.-T. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of a new potential biosorbent for the removal of Basic Blue 3 and Congo Red dyes: Pineapple (Ananas comosus) plant stem. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 61, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, W.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Islam, R.U. Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B under UV irradiation using Shorea robusta leaf extract-mediated bio-synthesized silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 2059–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, W.A.; Alam, A.; Alam, O.; Chakraborty, S.; Owens, G.; Bhattacharya, T.; Mondal, N.K. Enhanced aqueous phase arsenic removal by a biochar based iron nanocomposite. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Meng, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. Adsorption behavior of Rhodamine B on nanoporous polymers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 104915–104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstey, A.; Vivekanandhan, S.; Rodriguez-Uribe, A.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Oxidative acid treatment and characterization of new biocarbon from sustainable Miscanthus biomass. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 550, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Guo, X.; Yin, Y.; Miao, Y.; Dong, H. Surface modification of graphene oxide by goethite with enhanced tylosin photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 520, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azargohar, R.; Nanda, S.; Kozinski, J.A.; Dalai, A.K.; Sutarto, R. Effects of temperature on the physicochemical characteristics of fast pyrolysis bio-chars derived from Canadian waste biomass. Fuel 2014, 125, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Z.; Xia, T.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, B. Adsorption of tetracycline hydrochloride onto ball-milled biochar: Governing factors and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 127057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoglund, S.; Hedberg, J.; Yunda, E.; Godymchuk, A.; Blomberg, E.; Wallinder, I.O. Difficulties and flaws in performing accurate determinations of zeta potentials of metal nanoparticles in complex solutions—Four case studies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-Y.; Jung, G.-B. Effects of Pyrolysis and Ball-Milling on the Physicochemical and Rhodamine B Removal Characteristics of Rice-Bran-Derived Biochar. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074288
Kim D-Y, Jung G-B. Effects of Pyrolysis and Ball-Milling on the Physicochemical and Rhodamine B Removal Characteristics of Rice-Bran-Derived Biochar. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(7):4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074288
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Da-Young, and Gyeong-Bok Jung. 2023. "Effects of Pyrolysis and Ball-Milling on the Physicochemical and Rhodamine B Removal Characteristics of Rice-Bran-Derived Biochar" Applied Sciences 13, no. 7: 4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074288
APA StyleKim, D.-Y., & Jung, G.-B. (2023). Effects of Pyrolysis and Ball-Milling on the Physicochemical and Rhodamine B Removal Characteristics of Rice-Bran-Derived Biochar. Applied Sciences, 13(7), 4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074288




