Electrocardiogram Analysis by Means of Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Methods and Convolutional Neural Networks for Sudden Cardiac Death Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. ECG Data
2.1.1. Data Used
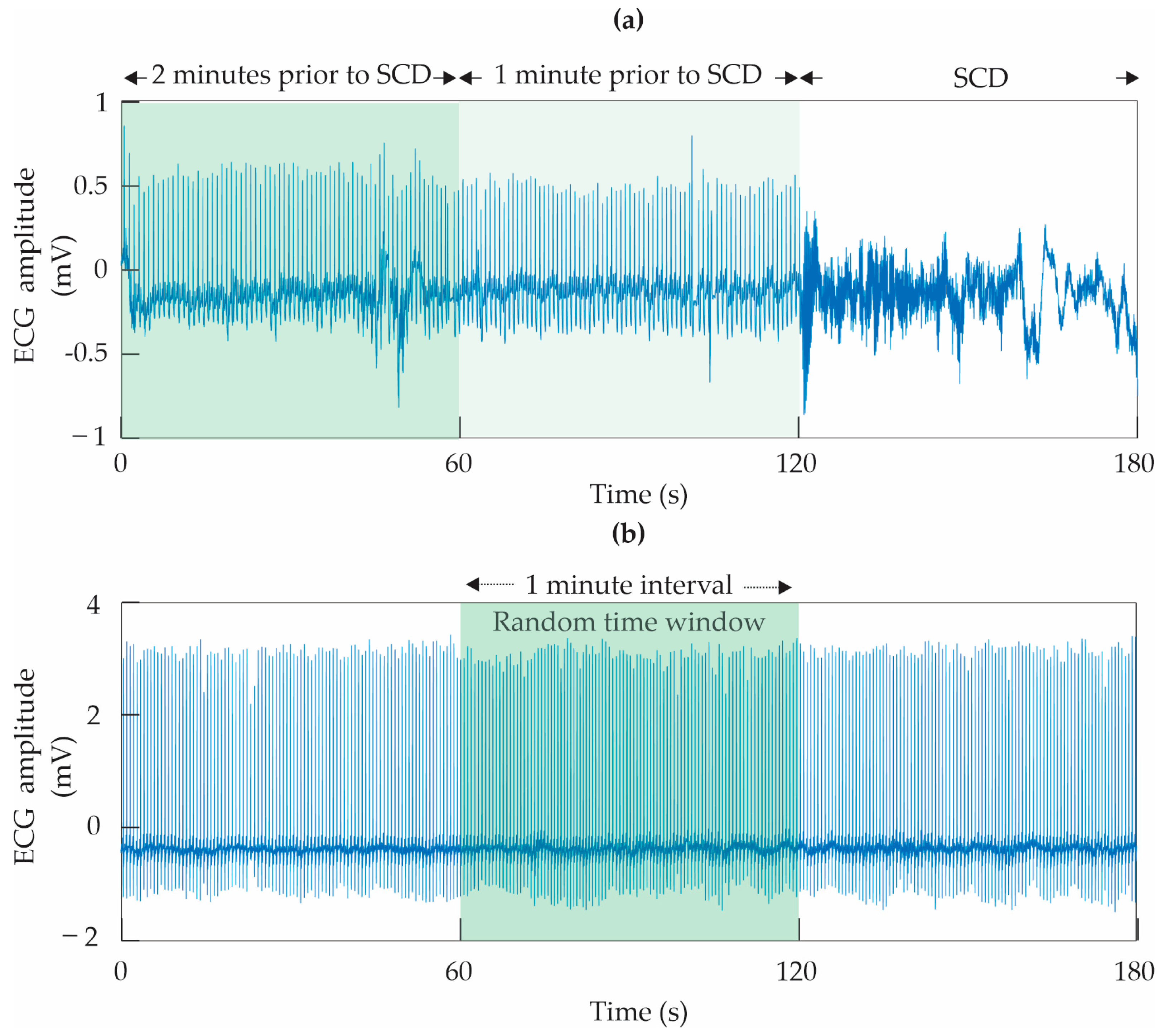
2.1.2. Preparation of the ECG Signals
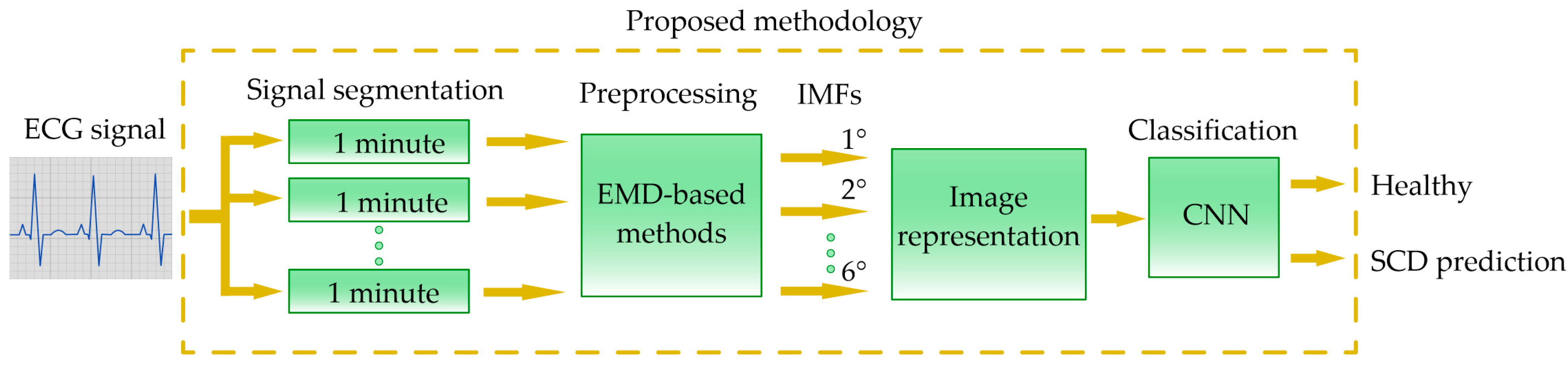
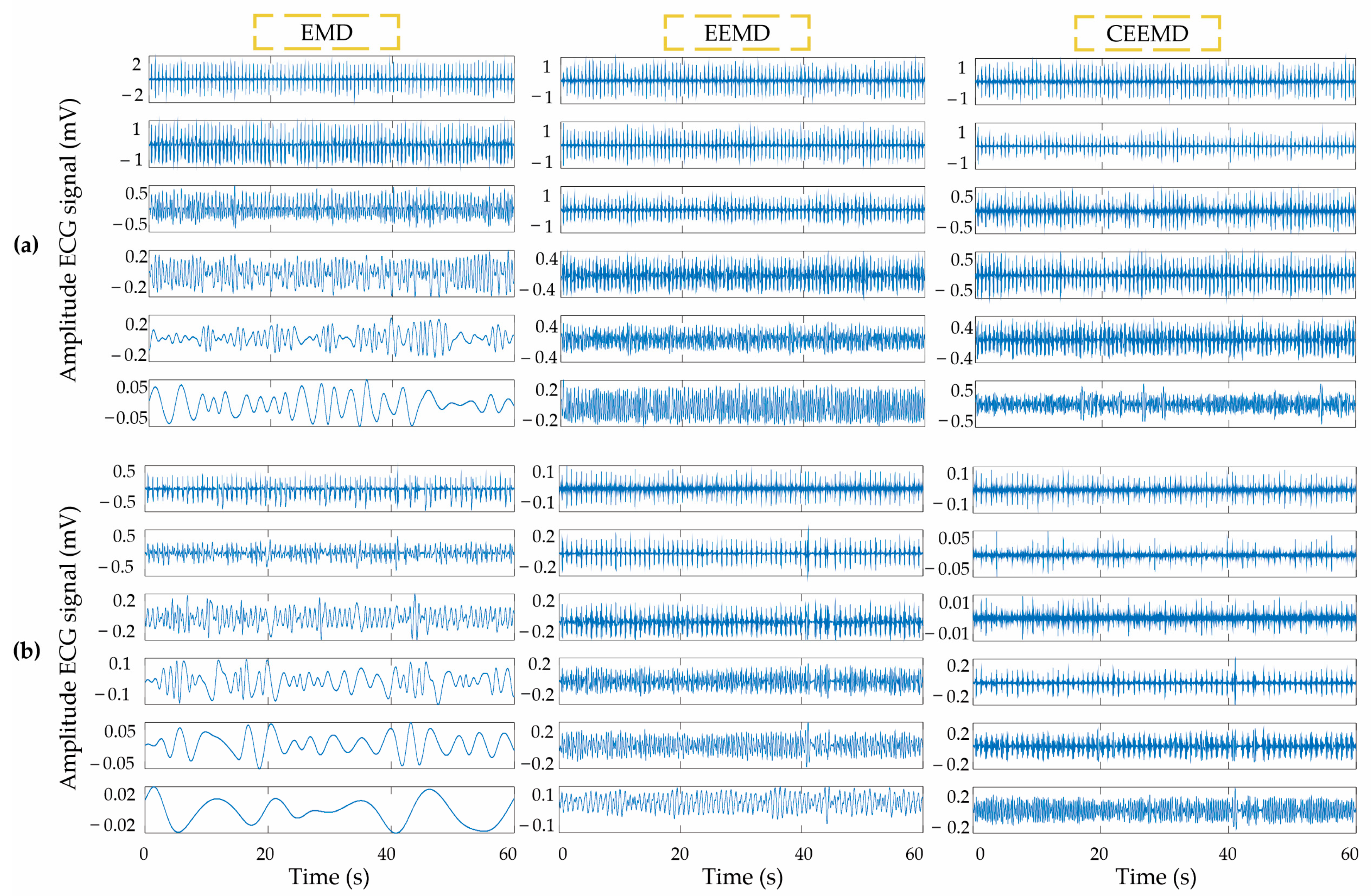
2.2. EMD-Based Methods
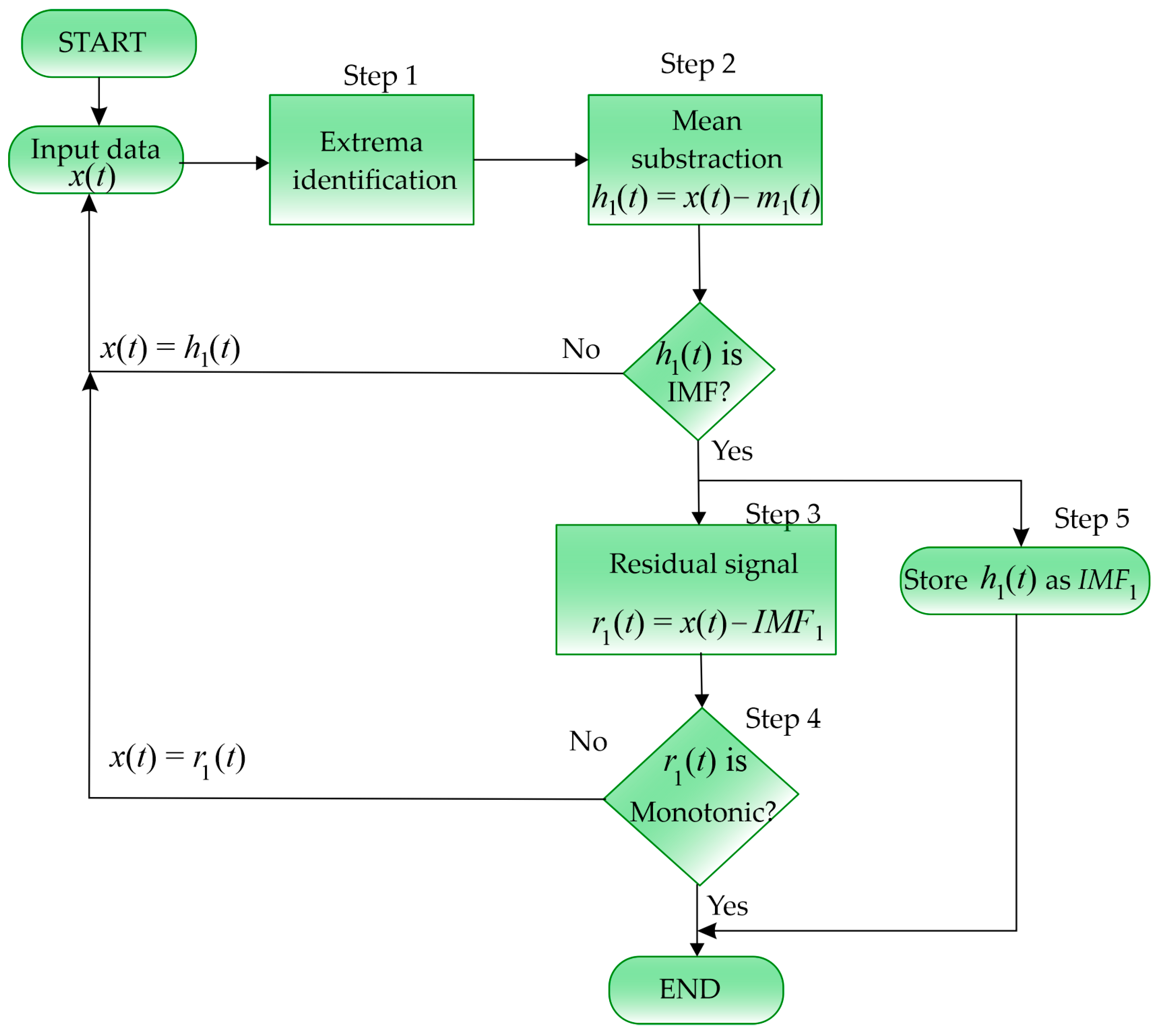
2.2.1. EMD Method
2.2.2. EEMD Method
2.2.3. CEEMD Method
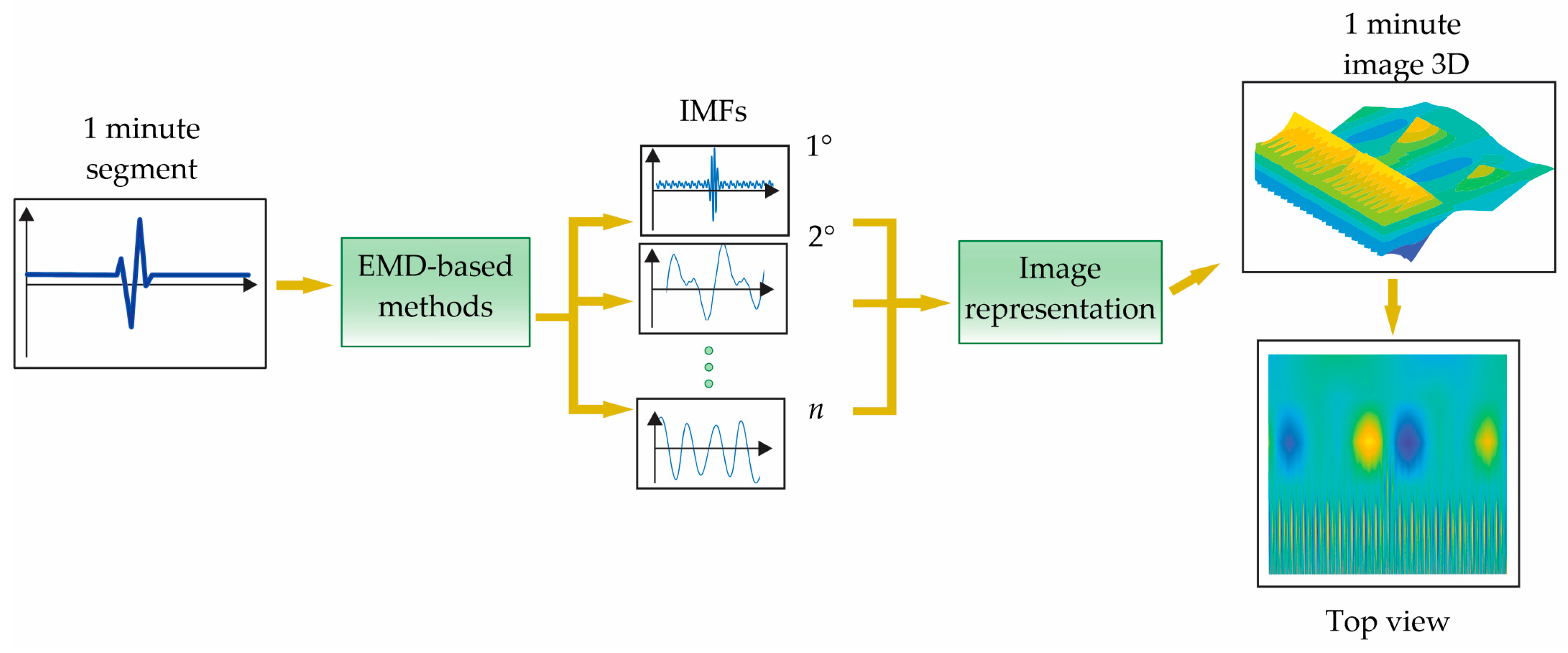
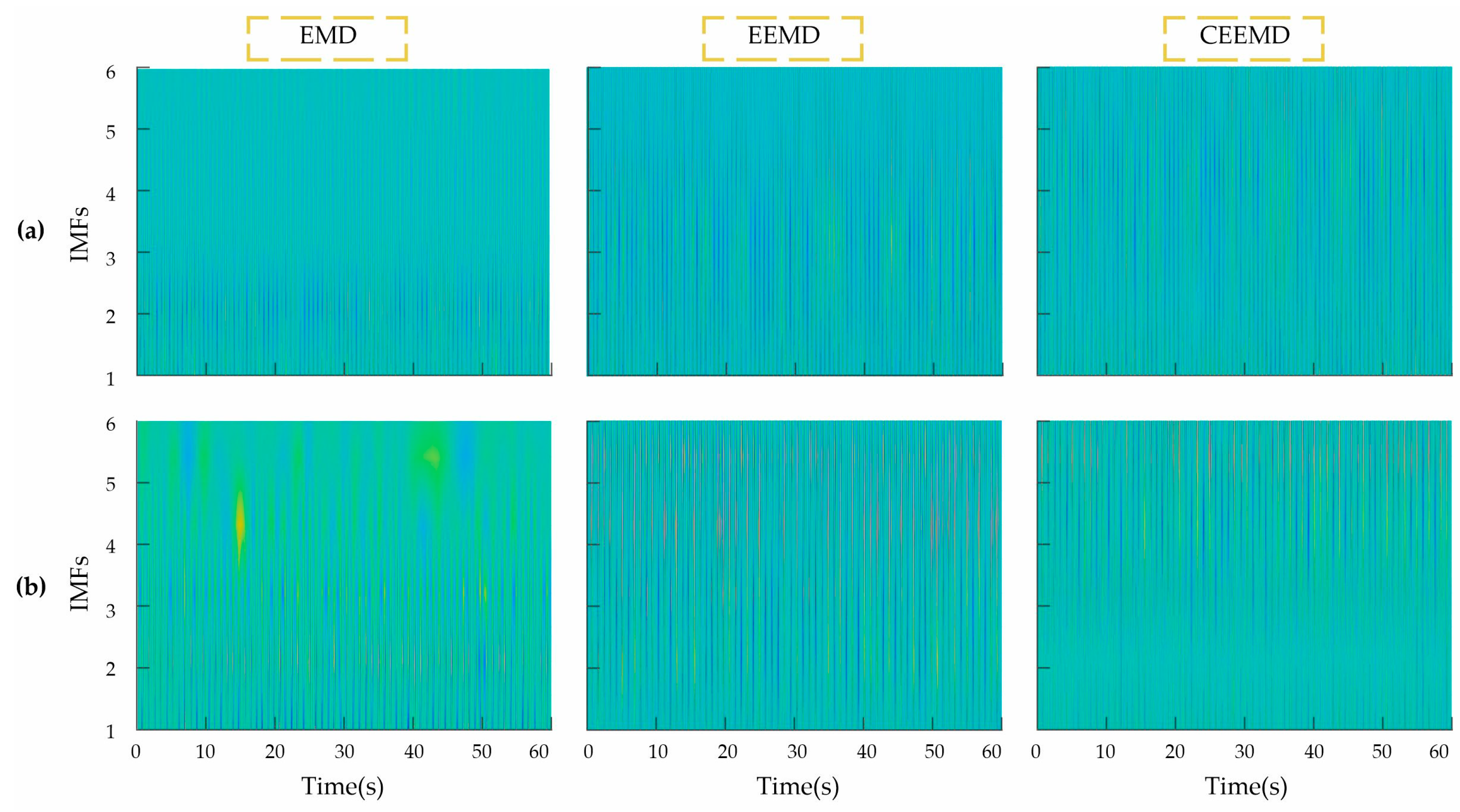
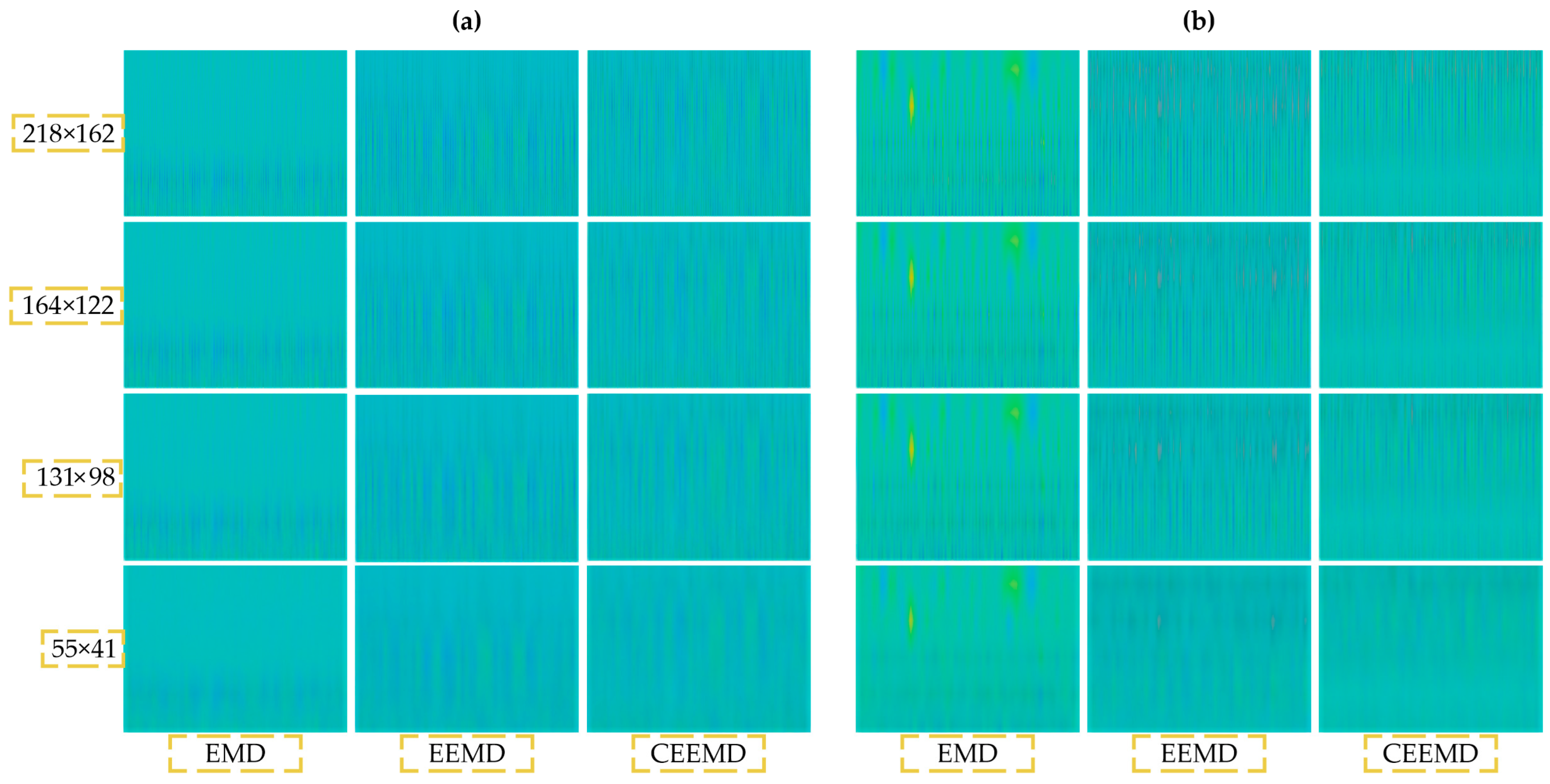
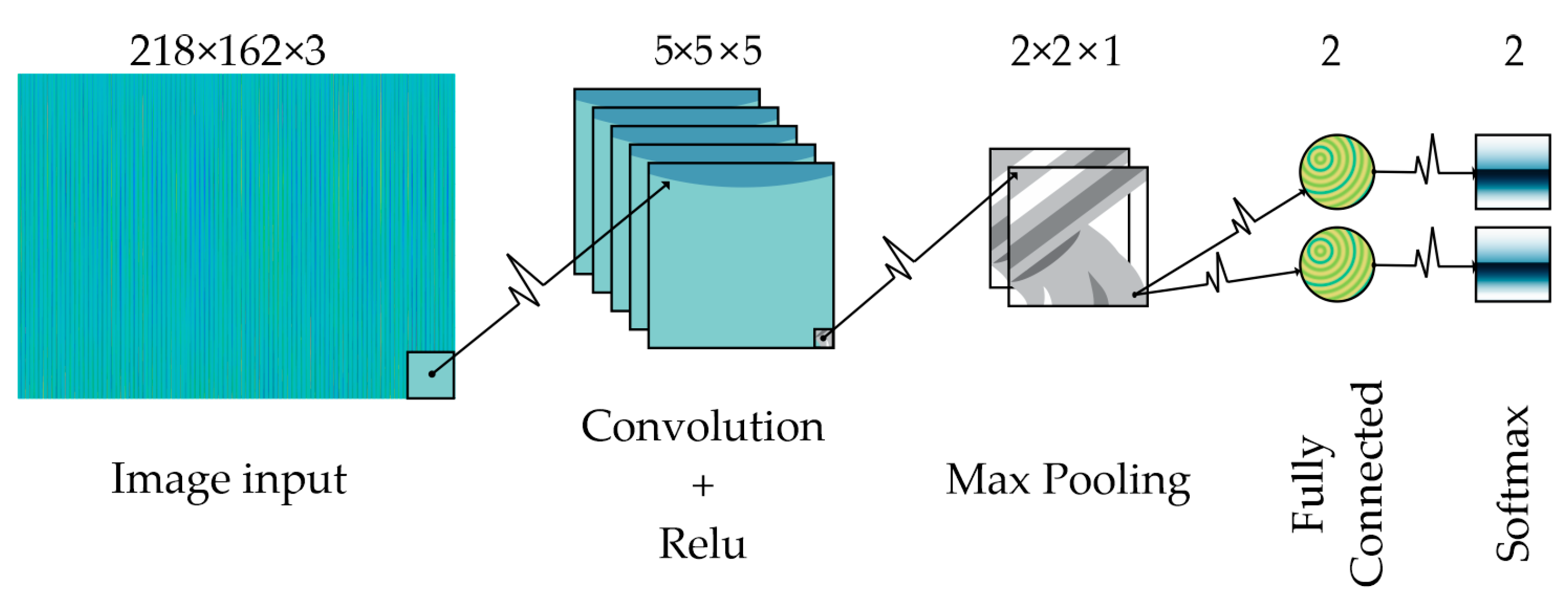
2.3. Image Representation
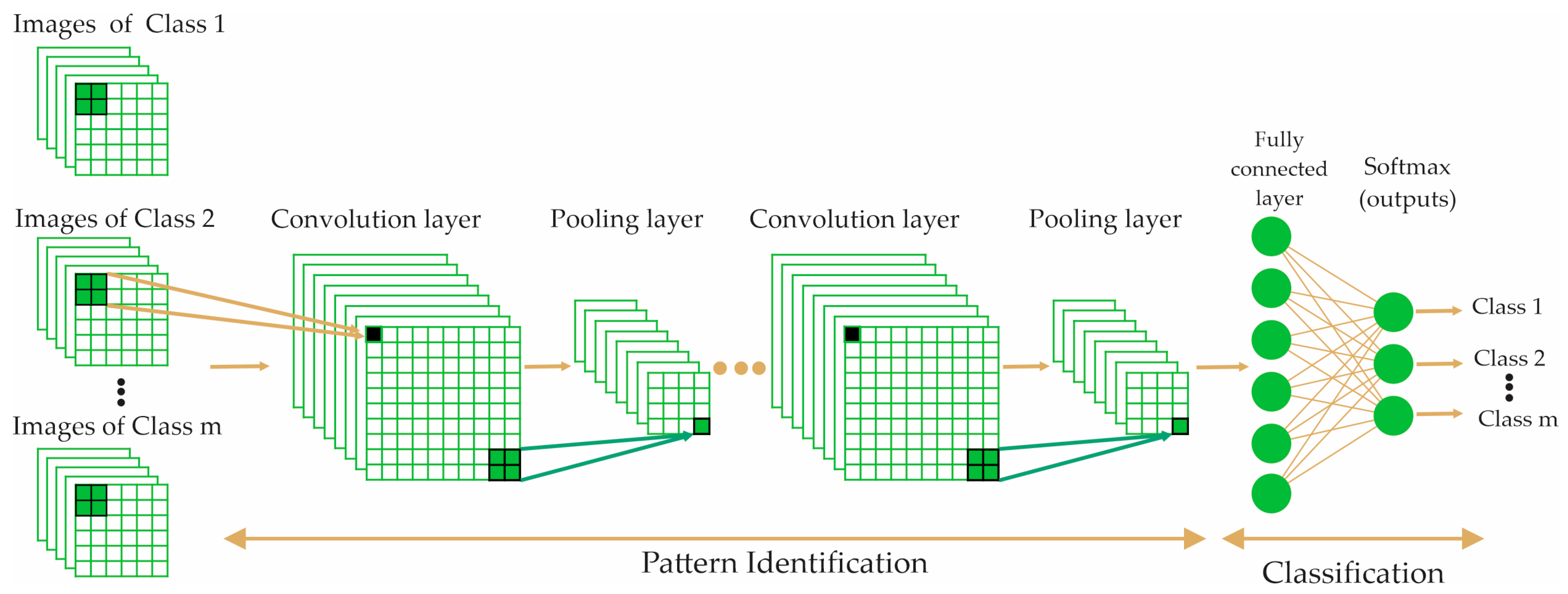
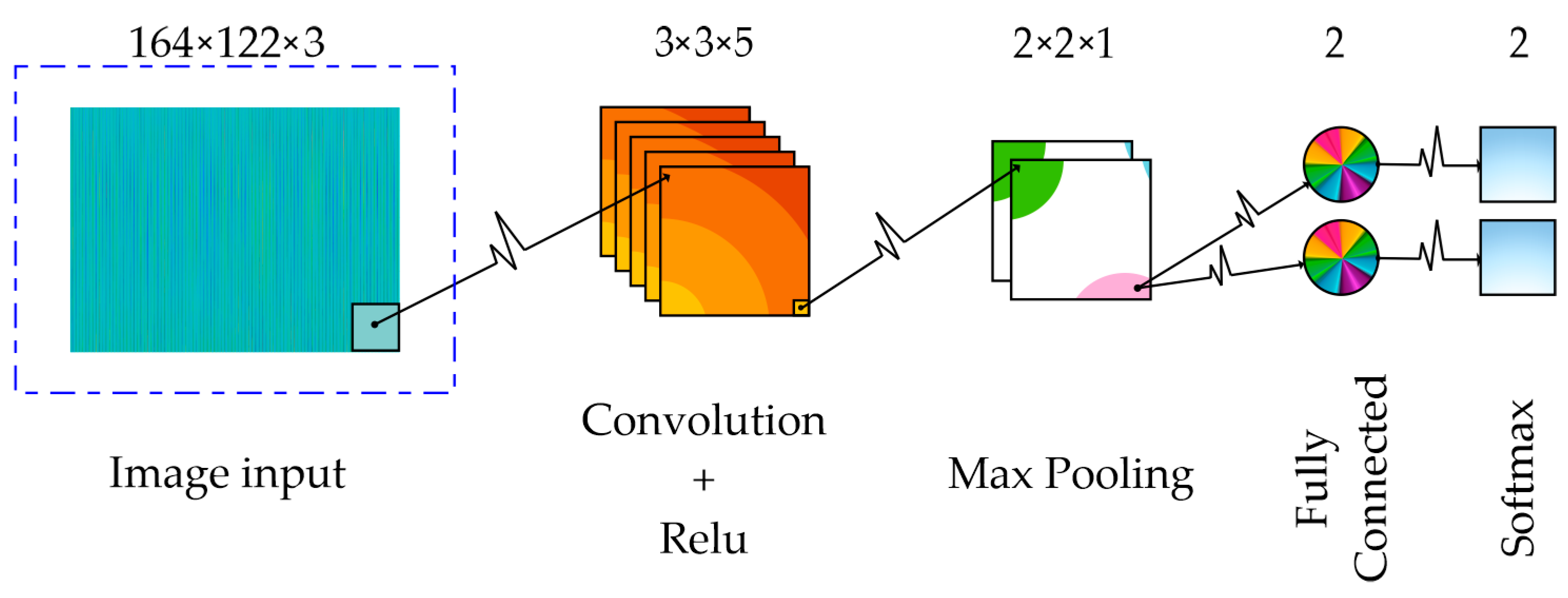
2.4. CNN
3. Methodology
4. Experimentation and Results
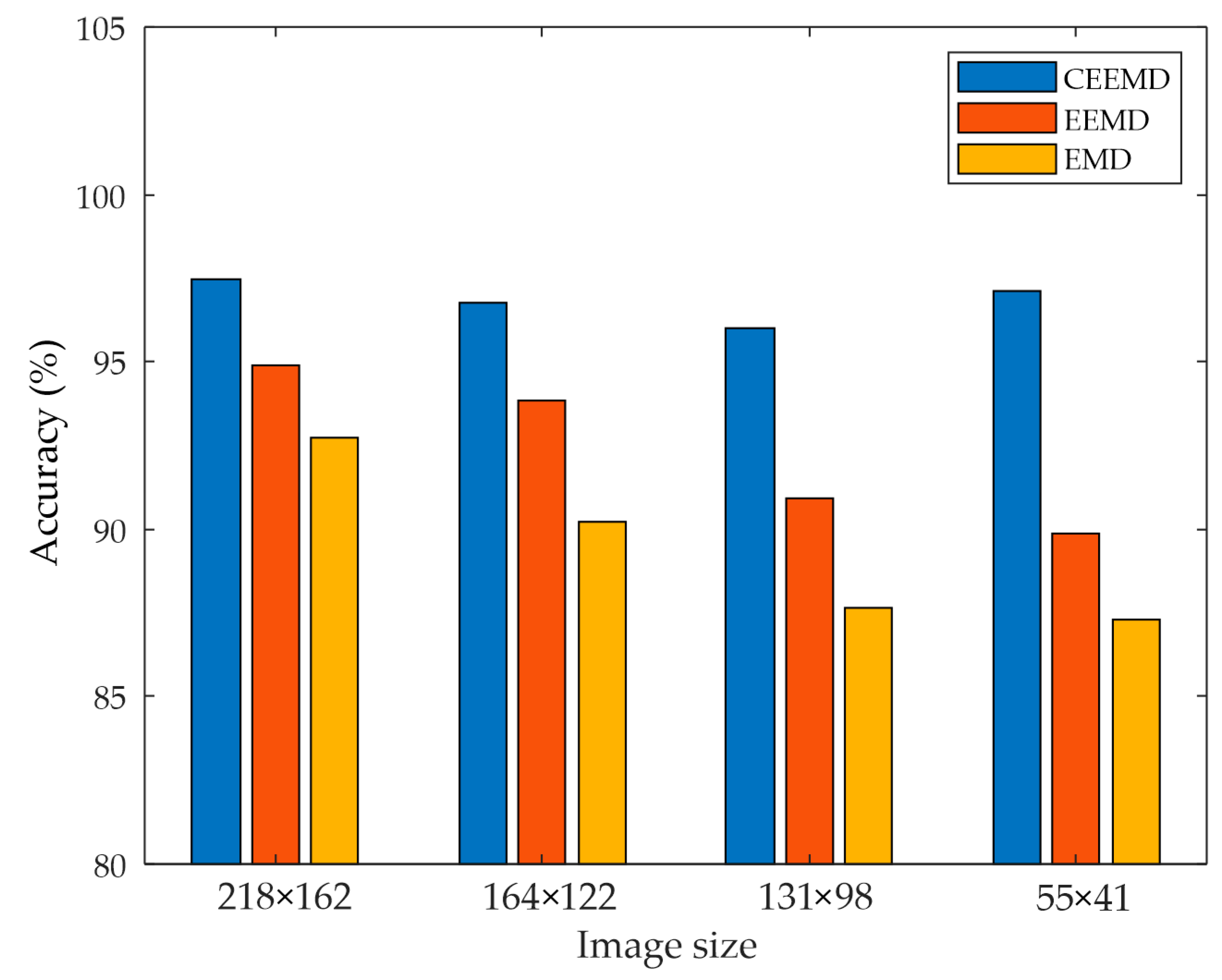
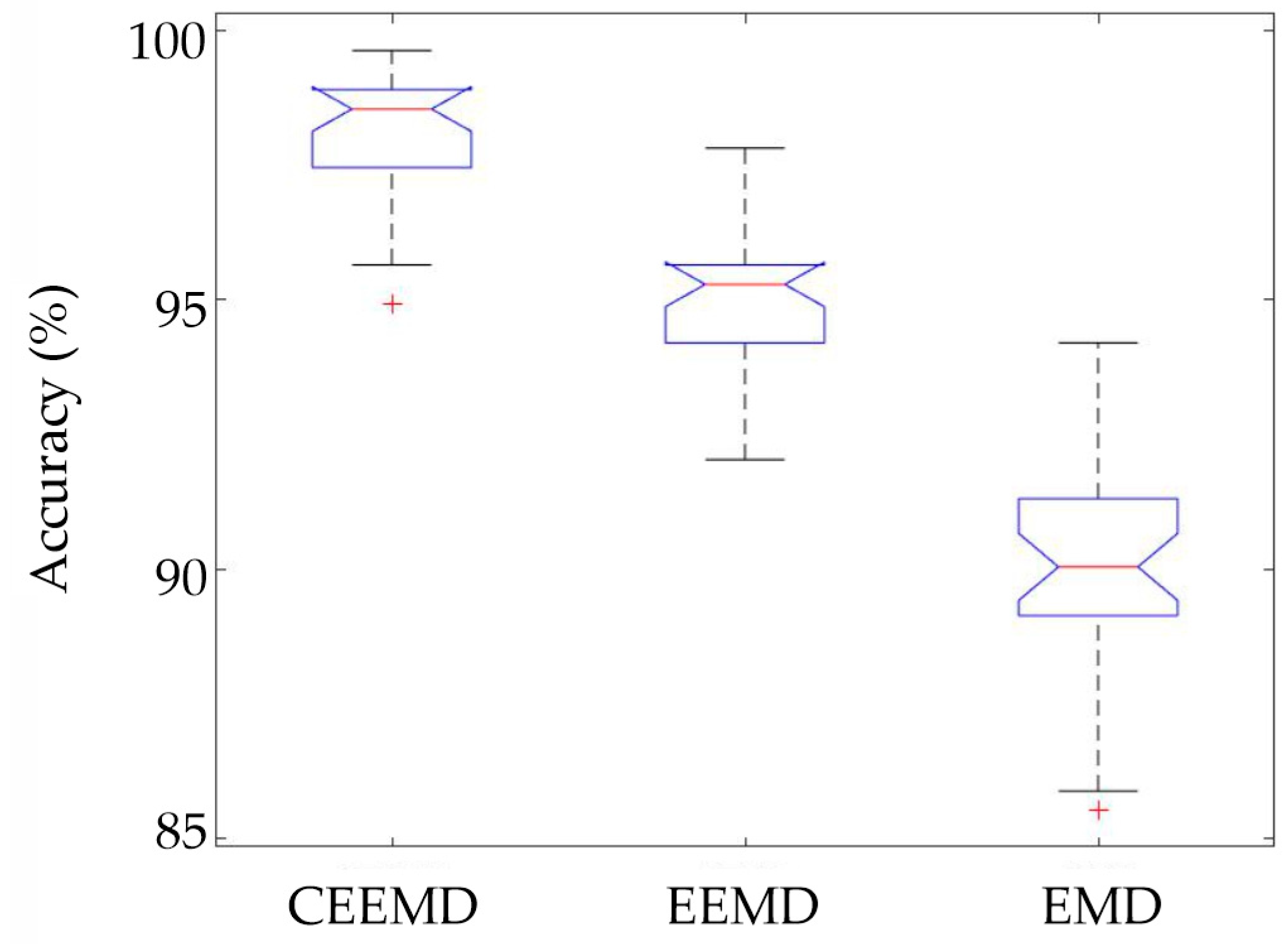
4.1. EMD-Based Method
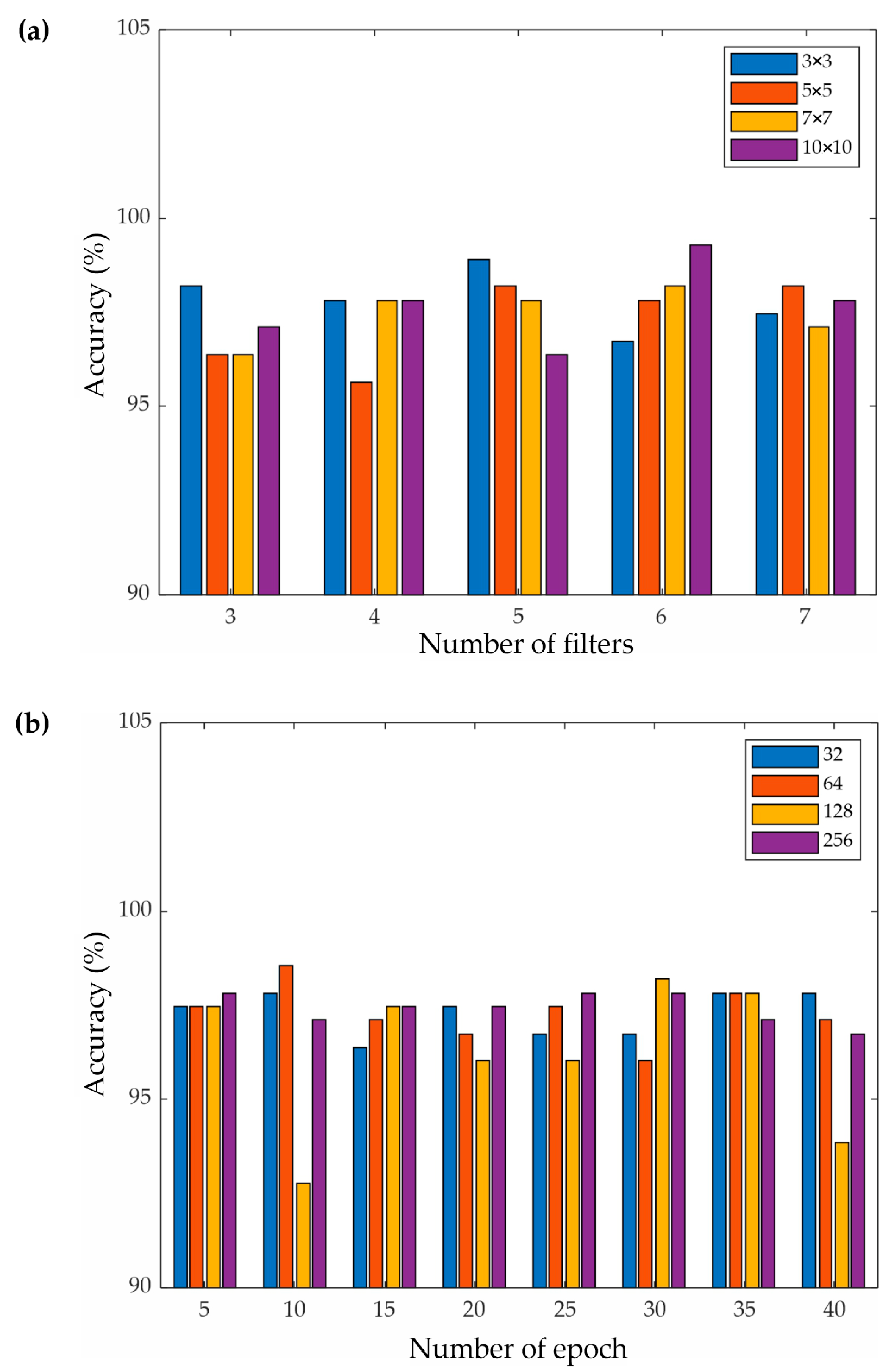
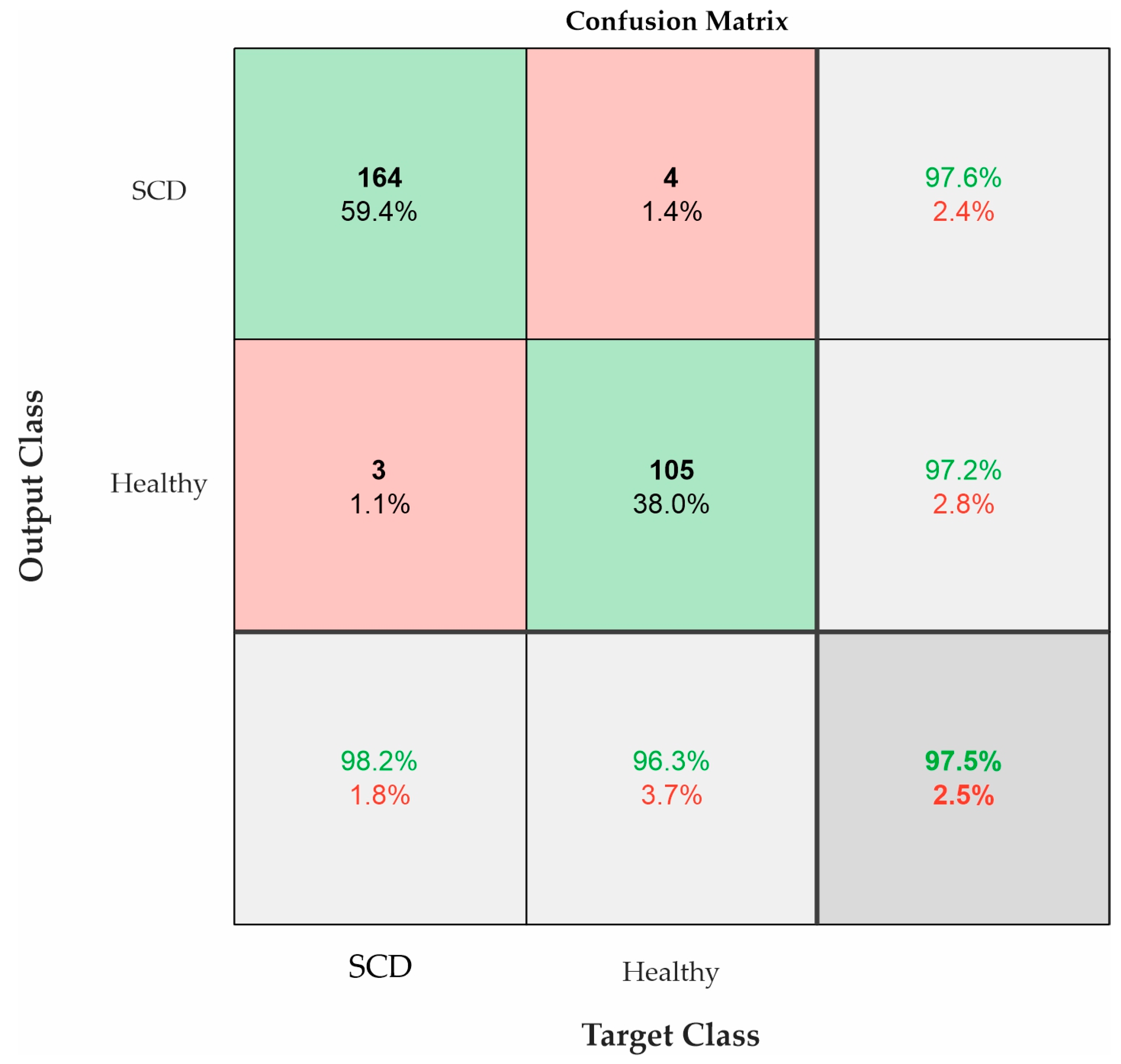
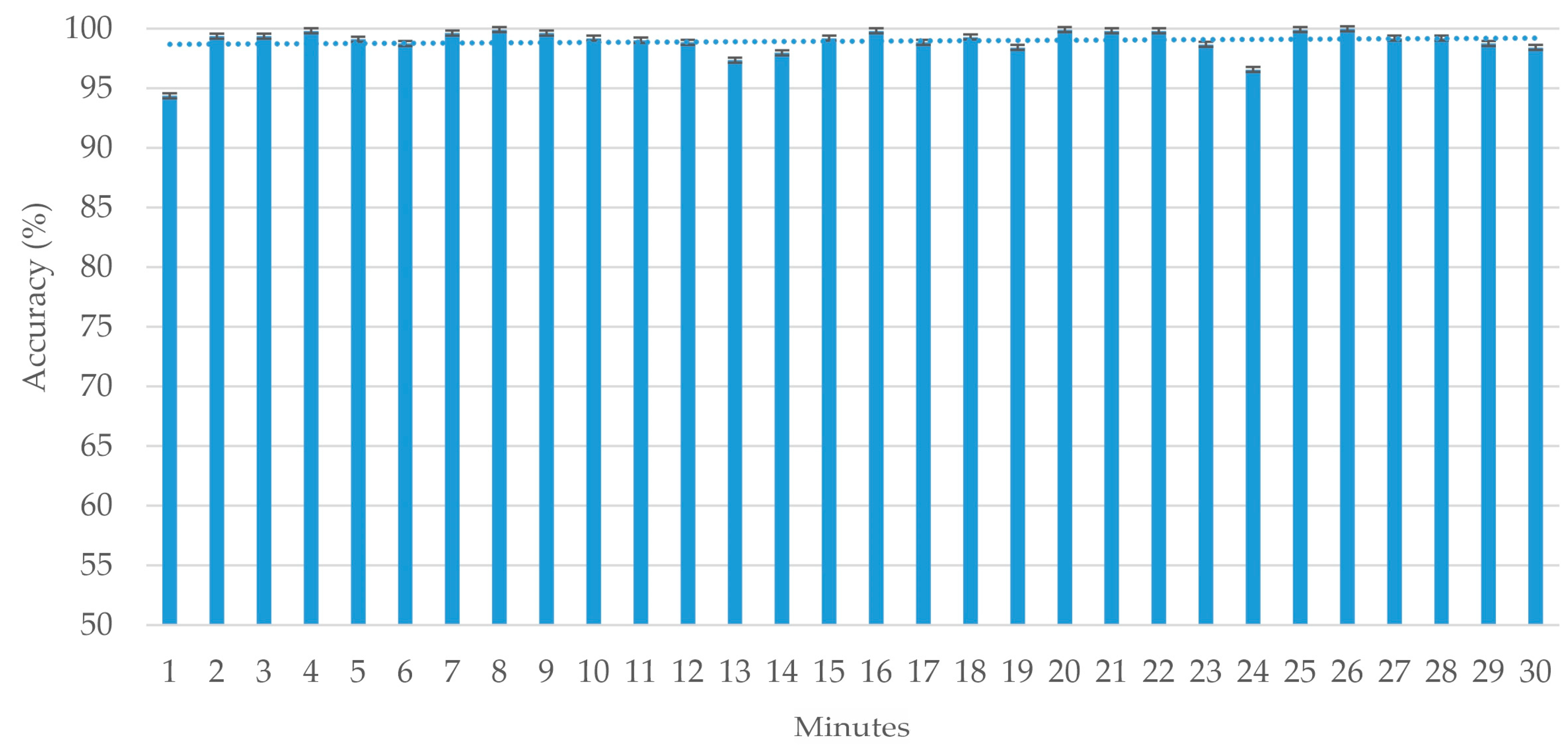
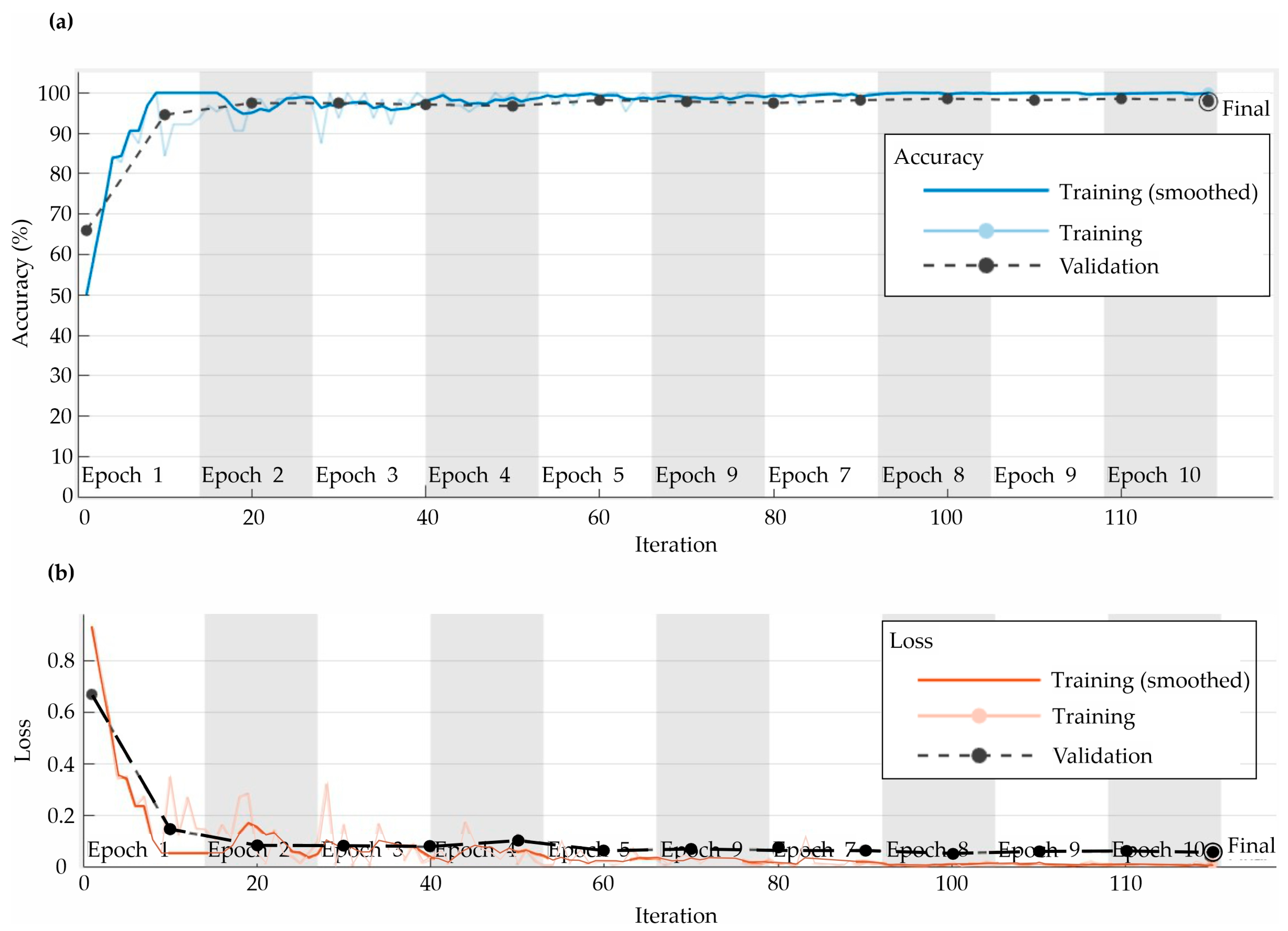
4.2. CNN Performance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BIDMC | Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center |
| CEEMD | Complete Ensemble empirical mode decomposition |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| EEMD | Ensemble empirical mode decomposition |
| EMD | Empirical mode decomposition |
| FPGA | Field programmable gate array |
| HRV | Heart rate variability |
| IMF | Intrinsic mode function |
| MIT | Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
| NSR | Normal sinus rhythm |
| SCD | Sudden cardiac death |
| SCDH | Sudden cardiac death holter |
| VF | Ventricular fibrillation |
References
- Kelly, K.L.; Lin, P.T.; Basso, C.; Bois, M.; Buja, L.M.; Cohle, S.D.; d’Amati, G.; Duncanson, E.; Fallon, J.T.; Firchau, D.; et al. Sudden cardiac death in the young: A consensus statement on recommended practices for cardiac examination by pathologists from the Society for Cardiovascular Pathology. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2023, 63, 107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, N.T.; Schilling, R.J. Sudden Cardiac Death and Arrhythmias. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2018, 7, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.H.; Hussain, M.; Malik, M.K. Arrhythmia Classification Techniques Using Deep Neural Network. Complexity 2021, 2021, 9919588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilla, W.; Wang, X. Wavelet Transform and Convolutional Neural Network Based Techniques in Combating Sudden Cardiac Death. Emit. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2021, 9, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagidipati, N.J.; Gaziano, T.A. Estimating deaths from cardiovascular disease: A review of global methodologies of mortality measurement. Circulation 2013, 127, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.; Semsarian, C.; Chan, K.H.; Sy, R.W. Sudden Cardiac Death and Ventricular Arrhythmias in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Heart Lung Circ. 2019, 28, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, M.A.; Emert, M.P. Sudden Cardiac Death: Who Is at Risk? Med. Clin. 2019, 103, 913–930. [Google Scholar]
- Myerburg, R.J. Cardiac arrest and sudden cardiac death. In Heart Disease, a Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992; pp. 756–789. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, L.M.; Tseng, V.S. Predicting Ventricular Fibrillation through Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 221886–221896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, G.L.; Kuriachan, V.P.; Mitchell, L.B. Sudden Cardiac Death. Encycl. Cardiovasc. Res. Med. 2018, 8, 511–520. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, M.P.; Mourad, A.; Clayton, R.H.; Sutton, P.M.; Bradley, C.P.; Hayward, M.; Paterson, D.J.; Taggart, P. Evidence for multiple mechanisms in human ventricular fibrillation. Circulation 2006, 114, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Sudarshan, V.K.; Sree, V.S.; Eugene, L.W.J.; Ghista, D.N.; Tan, R.S. An integrated index for detection of Sudden Cardiac Death using Discrete Wavelet Transform and nonlinear features. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 83, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIT/BIH-SCDH. Available online: https://physionet.org/physiobank/database/sddb/#clinical-information/databased (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Adeli, H.; Perez-Ramirez, C.A. A Novel Wavelet Transform-Homogeneity Model for Sudden Cardiac Death Prediction Using ECG Signals. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaei, M.; Raeisi, K.; Goshvarpour, A.; Ahmadzadeh, M. Early detection of sudden cardiac death using nonlinear analysis of heart rate variability. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 38, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Lopez, O.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; De-Santiago-Perez, J.J.; Rivera-Guillen, J.R.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Toledano-Ayala, M.; Perez-Ramirez, C.A. A new methodology based on EMD and nonlinear measurements for sudden cardiac death detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspal, R.; Alsadoon, A.; Prasad, P.W.C.; Al-Saiyd, N.A.; Nguyen, T.Q.V.; Pham, D.T.H. A novel approach for early prediction of sudden cardiac death (SCD) using hybrid deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8063–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragih, Y.V.; Isa, S.M. CNN Performance Improvement Using Wavelet Packet Transform for SCA Prediction. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2022, 100, 5458–5468. [Google Scholar]
- MIT/BIH-NSR. Database. Available online: https://www.physionet.org/physiobank/database/nsrdb/ (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Chinara, S. Automatic classification methods for detecting drowsiness using wavelet packet transform extracted time-domain features from single-channel EEG signal. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 347, 108927. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Sanchez, A.V.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Perez-Ramirez, C.A.; De-Santiago-Perez, J.J.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P. Epileptic seizure prediction using Wavelet Transform, Fractal Dimension, Support Vector Machine, and EEG signals. Fractals 2022, 30, 2250154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Xu, H.; Ragulskis, M.; Cao, M.; Ostachowicz, W. A Data-Driven Damage Identification Framework Based on Transmissibility Function Datasets and One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks: Verification on a Structural Health Monitoring Benchmark Structure. Sensors 2020, 20, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieracitano, C.; Mammone, N.; Bramanti, A.; Hussain, A.; Morabito, F.C. A Convolutional Neural Network Approach for Classification of Dementia Stages Based on 2D-Spectral Representation of EEG Recordings. Neurocomputing 2019, 323, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammone, N.; Ieracitano, C.; Morabito, F.C. A Deep CNN Approach to Decode Motor Preparation of Upper Limbs from Time–Frequency Maps of EEG Signals at Source Level. Neural Netw. 2020, 124, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Zhao, X.P.; Wu, J.X.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Motor Fault Diagnosis Based on Short-Time Fourier Transform and Convolutional Neural Network. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. Engl. Ed. 2017, 30, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, D.; Müller, A.; Behnke, S. Evaluation of Pooling Operations in Convolutional Architectures for Object Recognition. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Networks–ICANN 2010, Thessaloniki, Greece, 15–18 September 2010; pp. 92–101. [Google Scholar]
| Patient | Gender | Age | Ventricular Fibrillation Onset Time (Hours:Minutes:Seconds) | Subjacent Cardiac Rhythm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 43 | 07:54:33 | Sinus |
| 2 | Female | 72 | 13:42:24 | Sinus |
| 3 | Unnamed | 62 | 16:45:18 | Sinus with sporadic demand ventricular pacing |
| 4 | Female | 30 | 04:46:19 | Sinus |
| 5 | Male | 34 | 06:35:44 | Sinus |
| 6 | Female | 72 | 24:34:56 | Atrial fibrillation |
| 7 | Male | 75 | 18:59:01 | Atrial fibrillation |
| 8 | Female | 89 | 01:31:13 | Atrial fibrillation |
| 9 | Unnamed | --- | 08:01:54 | Sinus |
| 10 | Male | 66 | 04:37:51 | Sinus |
| 11 | Male | -- | 02:59:24 | Sinus |
| 12 | Male | 35 | 15:37:11 | Sporadic ventricular pacing |
| 13 | Male | -- | 19:38:45 | Sinus |
| 14 | Male | 68 | 18:09:17 | Sinus |
| 15 | Female | -- | 03:41:47 | Sinus |
| 16 | Male | 34 | 06:13:01 | Sinus |
| 17 | Male | 80 | 02:29:40 | Sinus |
| 18 | Female | 68 | 11:45:43 | Atrial fibrillation |
| 19 | Female | 67 | 22:58:23 | Sinus with sporadic pacing |
| 20 | Female | 82 | 02:32:40 | Sinus |
| Name | Type | Activations | Learnable | Total Learnable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| imageinput | Image Input | 162 × 218 × 3 | 0 | |
| conv | Convolution | 162 × 218 × 5 | Weights 5 × 5 × 3 × 5 Bias 1 × 1 × 3 | 380 |
| batchnorm | Batch Normalization | 162 × 218 × 5 | Offset 1 × 1 × 5 Scale 1 × 1 × 5 | 10 |
| Relu | ReLU | 162 × 218 × 5 | - | 0 |
| maxpool | Max Pooling | 161 × 217 × 5 | - | 0 |
| Fc | Fully Connected | 1 × 1 × 2 | Weights 2 × 174685 Bias 2 × 1 | 349, 372 |
| softmax | SoftMax | 1 × 1 × 2 | - | 0 |
| classoutput | Classification Output | - | - | 0 |
| Name | Type | Activations | Learnable | Total Learnable | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| imageinput | Image Input | 122 × 164 × 3 | - | 0 | |
| conv | Convolution | 122 × 164 × 5 | Weights | 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 | 140 |
| Bias | 1 × 1 × 3 | ||||
| batchnorm | Batch Normalization | 122 × 164 × 5 | Offset | 1 × 1 × 5 | 10 |
| Scale | 1 × 1 × 5 | ||||
| relu | ReLU | 122 × 164 × 5 | - | 0 | |
| maxpool | Max Pooling | 121 × 163 × 5 | - | 0 | |
| fc | Fully Connected | 1 × 1 × 2 | Weights | 2 × 98,615 | 197,232 |
| Bias | 2 × 1 | ||||
| softmax | SoftMax | 1 × 1 × 2 | - | 0 | |
| classoutput | Classification Output | - | - | 0 | |
| Work | Signal | Methods | Prediction Time/ Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acharya et al. (2015) [12] | ECG |
| 92.11%/4 min |
| Khazaei et al. (2018) [15] | HRV |
| 95%/6 min |
| Amezquita-Sanchez et al. (2018) [14] | ECG |
| 95.8%/20 min |
| Olivia-Vargas et al. (2020) [16] | ECG |
| 94%/25 min |
| Kaspal et al. (2021) [17] | ECG |
| 90.6%/-- |
| Saragih et al. (2022) [18] | ECG |
| 95.89%/30 min |
| Proposed work | ECG |
| 97.1%/30 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Centeno-Bautista, M.A.; Rangel-Rodriguez, A.H.; Perez-Sanchez, A.V.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Granados-Lieberman, D.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M. Electrocardiogram Analysis by Means of Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Methods and Convolutional Neural Networks for Sudden Cardiac Death Detection. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063569
Centeno-Bautista MA, Rangel-Rodriguez AH, Perez-Sanchez AV, Amezquita-Sanchez JP, Granados-Lieberman D, Valtierra-Rodriguez M. Electrocardiogram Analysis by Means of Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Methods and Convolutional Neural Networks for Sudden Cardiac Death Detection. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(6):3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063569
Chicago/Turabian StyleCenteno-Bautista, Manuel A., Angel H. Rangel-Rodriguez, Andrea V. Perez-Sanchez, Juan P. Amezquita-Sanchez, David Granados-Lieberman, and Martin Valtierra-Rodriguez. 2023. "Electrocardiogram Analysis by Means of Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Methods and Convolutional Neural Networks for Sudden Cardiac Death Detection" Applied Sciences 13, no. 6: 3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063569
APA StyleCenteno-Bautista, M. A., Rangel-Rodriguez, A. H., Perez-Sanchez, A. V., Amezquita-Sanchez, J. P., Granados-Lieberman, D., & Valtierra-Rodriguez, M. (2023). Electrocardiogram Analysis by Means of Empirical Mode Decomposition-Based Methods and Convolutional Neural Networks for Sudden Cardiac Death Detection. Applied Sciences, 13(6), 3569. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063569










