Abstract
Shearer-cutting units are important parts of coal production. However, they have high fault frequency, and their maintenance activities are costly and time-consuming. Coal enterprises urgently need an effective fault analysis method for shearer-cutting units. To solve this problem, an integrated importance measure (IIM) is introduced into the fault tree analysis method to identify the weakest links of shearer-cutting units. This paper develops an IIM-based fault tree analysis method to determine the key faults in shearer-cutting units. Taking MG400/930-WD shearer in Yuhua Coal Mine as an example, through IIM ranking, bearing wear can be identified as a key fault cause. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, the relative value distribution of four importance measures was analyzed by radial bar charts, and the accuracy of different rankings was evaluated by mean average precision. The results show that IIM can clearly distinguish the relative importance of bottom events, and the average accuracy of IIM ranking is 94.52%. Therefore, the proposed method can accurately and effectively identify key fault causes, and the limited resources should give priority to bottom events with higher IIM.
1. Introduction
Against the background of carbon peak and carbon neutrality, the important role of coal in China’s energy resource structure determines that coal will remain the most basic energy resource for a long time in the future, which provides a guarantee for economic and social development [1]. Shearers are important mechanical equipment for intelligent and efficient mining, playing an irreplaceable role in coal production. The shearer-cutting unit is the key component of the shearer, including the cutting arm, the drum, the transmission system, and the cutting motor. However, the shearer-cutting unit is also the most susceptible to failure, which may cause serious economic losses and even casualties [2]. Coal enterprises urgently need to solve the problems of low mining efficiency and long downtime maintenance time caused by shearer-cutting failure. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the fault analysis method of shearer-cutting units.
An importance measure (IM) is a useful tool to identify the weakest links in reliability engineering [3], risk analysis [4], and system reliability optimization [5]. In recent years, many scholars have devoted themselves to identifying systems’ weak links based on importance theory [6]. Dui et al. [7] proposed a new IM by considering residual resilience to identify the weak links of ports and routes in maritime transportation systems. Du et al. [8] introduced the influence of the number of failed components to construct a new IM for identifying the weak arcs of a network system. Almoghathawi and Barker [9] constructed an importance model for effectively allocating resources to components with higher IM. Kala [10] developed a global sensitivity-based importance measure to identify weak links for improving system reliability effectively. Moreover, some scholars have used integrated importance measures (IIMs) to identify the key failure causes. Si et al. [11] used IIM of components in multi-state systems to identify the key factors that influence the system’s performance. Dui et al. [12] developed a joint IIM to guide the decision-making of repairing submarines. Liu et al. [13] determined the key fault causes with the highest IIM in power systems and repaired them as a priority for quickly improving the system reliability. Chen et al. [14] analyzed components’ IIM in pod slewing systems to determine the IIM-based optimal maintenance strategy. The reported research shows that IMs can identify weak links or key fault causes, especially for IIM. However, the accuracy of IIM ranking has not been discussed.
In recent years, fault tree analysis has been widely used to determine the key fault causes of complex equipment or engineering systems. Kang et al. [15] established the fault tree of the semi-submersible floating offshore wind turbine, and the Fussell–Vesely importance measure is used to determine the key faults. Sakurahara et al. [16] proposed an integrated probabilistic risk assessment framework by combining fault trees with global importance measure analysis. Budiyanto et al. [17] evaluated the risk of container terminals through the risk matrix method, and the highest risk accidents can be determined by the fault tree analysis method. Gachlou et al. [18] applied fault tree analysis to assess the comprehensive risk of river basins for determining undesirable events. Gu et al. [19] considered fault correlation to analyze the maintenance priority of CNC. Ud-Din et al. [20] proposed a comprehensive risk assessment framework based on a fault tree to analyze the importance of aircraft runaway events. The reliability of the motor controller in a pure electric vehicle was evaluated by the fault tree analysis approach [21]. A quantitative analysis of relevant risks was proposed based on fault tree analysis to predict risks and evaluate the safety of leaks in a storage tank [22]. Li et al. [23] applied fault tree analysis to the reliability of offshore floating wind turbines. García et al. [24] applied fault tree analysis and IM to analyze the component correlation in complex systems. A risk-informed approach based on a fault tree was developed to analyze the railway drainage flood risk and quantify the occurrence likelihood of risks [25]. From Table 1, the reported research of fault tree analysis methods has introduced traditional importance measures, but IIM has not been used to determine the key fault causes. Moreover, few references have verified the effectiveness of IM rankings.

Table 1.
Research status comparison of IM-based fault tree analysis method.
Based on the reported research work, the motivation of this paper was to (1) develop an IIM-based fault analysis method to determine the key fault causes of shearer-cutting units and (2) verify the accuracy of IIM ranking. In addition, this paper introduces IIM into the fault tree to improve the efficiency of key fault analysis of the shearer-cutting units, and the effectiveness of IIM ranking is verified by the radial bar chart and the mean average precision (mAP).
The remainder of this article is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the fault analysis method of the shearer-cutting unit driven by IIM. Section 3 introduces a case study to clarify the process of fault analysis based on IIM. In Section 4, the distribution differences of the relative importance of different IMs and the accuracy of importance rankings are discussed. Finally, concluding remarks and future research are provided in Section 5.
2. Fault Analysis Method of Shearer-Cutting Unit Driven by IIM
To better analyze the key fault of shearer-cutting units based on the IIM, the process of the fault analysis method can be summarized as follows, and the framework of the fault analysis method based on IIM is shown in Figure 1.
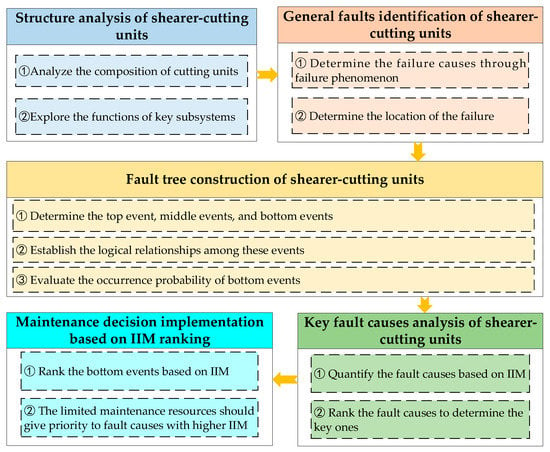
Figure 1.
The framework of IIM-based fault analysis method for shearer-cutting units.
- Structure analysis of shearer-cutting units: analyze the composition of cutting units and explore the functions of key subsystems.
- General fault identification of shearer-cutting units: determine the failure causes through the failure phenomenon and determine the location of the failure.
- Fault tree construction of shearer-cutting units: determine the top event, middle events, and bottom events; establish the logical relationships among these events; evaluate the occurrence probability of bottom events.
- The key fault causes analysis of shearer-cutting units: quantify the fault causes based on IIM and rank the fault causes to determine the key ones.
- Maintenance decision implementation based on IIM ranking: under the limited maintenance resources, the fault with higher IIM should give priority to performing maintenance.
2.1. Structure Analysis of Shearer-Cutting Units
A shearer-cutting unit is used to implement key coal mining processes such as coal cutting [26], which consists of four subsystems: rocker arm subsystem, cutting drum subsystem, transmission subsystem, and cutting motor subsystem. The cutting motor subsystem provides sufficient power for other subsystems in the cutting unit. The cutting drum subsystem consists of spiral blades, end plates, tooth seats, nozzles, drum hubs, and picks, and it is mainly used to cut raw coal from the coal wall and transport the coal to the scraper conveyor through the spiral blades. The transmission subsystem connects the cutting motor with the cutting drum to control the cutting speed and cutting force under different working conditions. The rocker arm subsystem can be used to adjust the cutting angle of the drum and to protect the transmission subsystem against damage from falling gangue or cinder. The structure of shearer-cutting units is shown in Figure 2.
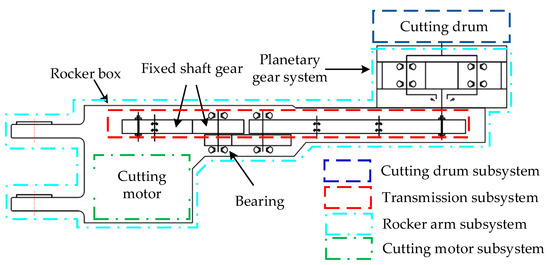
Figure 2.
The structure of the shearer-cutting units.
2.2. General Fault Identification of Shearer-Cutting Units
The general fault identification purpose of shearer-cutting units is to determine the fault causes and fault locations of different subsystems. The general faults in the rocker arm subsystem are ‘broken rocker arm shell’ and ‘unable to lift the arm’. The general faults of the drum are ‘pick faults’ and ‘roller shell faults’. The transmission subsystem always has the following faults: ‘gear pitting’, ‘gear fracture’, ‘bearing failure’, ‘reducer overheating’, and so on. The motor faults (‘cavity oil’, ‘short circuit’, or ‘open circuit’) always occur in the cutting motor subsystems.
2.3. Fault Tree Construction of Shearer-Cutting Units
A fault tree model is an effective method to analyze the relationship between the top event and bottom events in the quantitative method [27]. The fault tree analysis of the shearer-cutting unit mainly includes constructing the fault tree model of the cutting unit and evaluating the probability of the bottom events.
The fault tree model is constructed by considering the logical relationship between the top event, middle events, and bottom events. If the failure of the event in the previous layer is caused by any failure of events in the current layer, ‘Or gate’ should be used to connect these events. ‘And gate’ is used to connect the previous event and the current events when the failure of previous events is caused by the failure of all current events. In this way, the fault tree can be established by ‘And gate’ and ‘Or gate’.
The occurrence probability of bottom events in the fault tree is determined by the following process. The failure rates of bottom events can be determined by referring to the historical data or expert experience. According to the reported research or the maintenance data from the enterprise, the failure probability of subsystems can be evaluated first; then, the failure data of a specific shearer-cutting unit over a period of time can be collected. So, the failure probability of bottom events can be evaluated according to the full probability theory.
2.4. Key Fault Causes Analysis of Shearer-Cutting Units
IIM combines the state transition rates with the reliability importance measure [28]. IIM can distinguish the importance of fault causes, and IIM ranking can be used to determine the key fault causes. The calculation expression of IIM is shown in Equation (1).
where means the fault event does not occur, whereas means the fault event occurs; indicates that the top event does not occur, which means the system is normal; represents the conditional probability that the top event does not occur when the bottom event i also does not occur; represents the conditional probability that the top event does not occur when the bottom event i occurs.
To better determine the key fault causes of shearer-cutting units, IIMs of all bottom events can be calculated by Equation (1). The bottom event with the highest IIM represents that bottom event has the highest influence on the failure of the shearer-cutting unit.
2.5. Maintenance Decision Implementation Based on IIM Ranking
The limited maintenance resources should be allocated with priority to the bottom events with higher IIM, which helps to improve the efficiency of equipment maintenance. Therefore, the limited resources should be used for key fault causes with higher IIM.
3. A Case Study of Cutting Units for MG400/930-WD Shearer
MG400/930-WD is a classical type of shearer, which is widely used in coal enterprises. The structure of the MG400/930-WD shearer is shown in Figure 3. In this paper, the fault data of four subsystems were collected from Yuhua Coal Mine by on-site tracking for about 2 months. Yuhua Coal Mine belongs to Shaanxi Coal Group Tongchuan Mining Co., Ltd., and is a modern mine to produce long-flame coal with fully mechanized mining. Particularly, shearers are the most important equipment during the coal production process. Taking MG400/930-WD as an example, the detailed process of fault analysis for shearer-cutting units is summarized as follows.
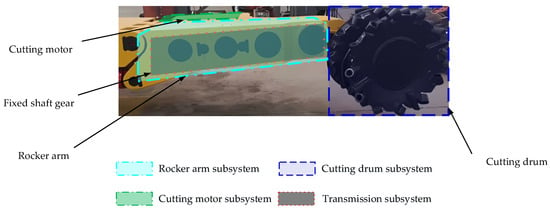
Figure 3.
The structure of cutting units for MG400/930-WD shearer.
3.1. Identifying General Faults of Shearer-Cutting Units
The faults of shearer-cutting units always occur in four subsystems, including the rocker arm, cutting drum, cutting motor, and transmission subsystems. With the consideration of frequent faults, the fault phenomenon and fault causes are summarized in Table 2. The symbols of 20 bottom events are listed in Table 1 from C1 to C20. The fault phenomenon can be regarded as the middle events, and the fault causes can be regarded as the bottom events.

Table 2.
General faults in the cutting unit of MG400/930-WD shearer.
3.2. Fault Tree Construction Based on the Logical Relationship among Events
For the motor subsystem, the occurrence of any bottom events C8 (short circuit between coils, water in connection cavity, dampened circuit) or C9 (leakage or open circuit of motor cable) must cause motor overheating, leakage, and short circuiting, so ‘Or gate‘ should be used to connect C8 and C9 and middle events. However, when both C6 (oil seal leakage) and C7 (oil spill blockage) occur at the same time, oil-gathering faults will occur in the motor cavity. So, ‘And gate‘ is used to connect C6 and C7 and the middle events. For the other three subsystems, the occurrence of any bottom event will lead to the occurrence of fault phenomena. Therefore, ‘Or gate‘ is used to connect the bottom events and intermediate events of the other three subsystems.
According to the above analysis, the logical relationship between middle events and their bottom events can be connected by ‘Or gate’ or ‘And gate’. Once any of the subsystems fails, the cutting units will fail. So, the top event and failure of subsystems should be connected by ‘Or gate’. Therefore, the fault tree of shearer-cutting units is shown in Figure 4.
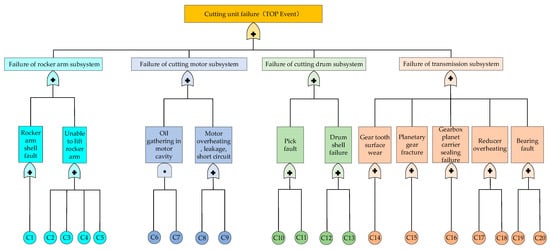
Figure 4.
Fault tree model of shearer-cutting units.
3.3. Evaluating the Occurrence Probability of Bottom Events
The occurrence probability of the bottom events can be determined from three aspects: the average failure probability of subsystems, the occurrence probability of the bottom events in a specific period, and the failure rates of the bottom events.
Referring to the relevant literature [29], the failure times of four subsystems are recorded in Table 3. The average probability of subsystem failure can be determined by the ratio of subsystem fault number to total fault number.

Table 3.
Average failure probability of cutting subsystems in shearer.
According to the reported research work [30], the failure rates of the corresponding components in bottom events can be estimated. By checking the overhaul table of MG400/930-WD shearer in Tongchuan Yuhua Mining Company, the conditional failure probability of each bottom event of cutting units within 6 months is evaluated by the ratio of the number of bottom event failures in each subsystem to the total number of subsystem failures. So, the failure probability of each bottom event is obtained by full probability theory, which is equal to the product of the conditional failure probability and the subsystem failure probability. All the mentioned probability and failure rates are listed in Table 4.

Table 4.
The probability of failure of each fault event in the interception department.
3.4. Analysis of Key Failure Causes Based on IIM
According to Table 4, the IIM of each bottom event can be evaluated by Equation (1). The IIM results of 20 bottom events are listed in Table 5 and Figure 5. IIM ranking results from the largest to the smallest: C19 > C17 > C18 > C12 > C1 > C5 > C10 > C4 > C3 > C8 > C20 > C2 > C9 > C11 > C14 > C15 > C16 > C7 > C6 > C13. Under the limited maintenance resources, the bottom events C19 (bearing wear), C17 (nonconformity of oil varieties or improper oil quantity), and C18 (cooling spray function failure) should be repaired as priorities.

Table 5.
Integrated importance measure values of the bottom events.
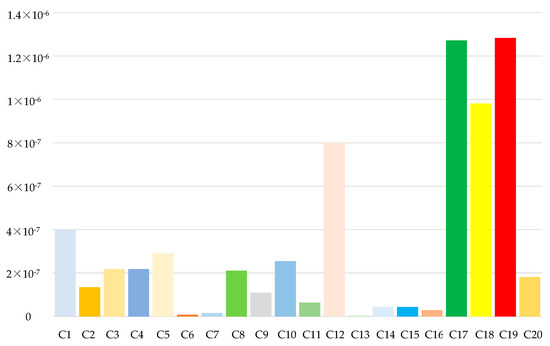
Figure 5.
Integrated importance measure results of the bottom events.
4. Effectiveness Discussion of IIM Ranking
To verify the effectiveness of IIM ranking, the Birnbaum importance measure (BIM), criticality importance measure (CIM), and Fussell–Vesely importance measure (FVIM) are introduced to discuss their relative value distribution and the accuracy of their rankings. The calculation results of the three importance measures are as follows.
(1) Birnbaum importance measure
BIM is used to measure the influence of component reliability change on system reliability. The calculation model is shown in Equation (2) [31].
where S = 0 means that the top event does not occur, which represents that the system is in a normal state. means the fault event does not occur, and indicates that the fault event occurs. Equation (2) represents the difference between the system reliability when the bottom event does not occur and the system reliability when the bottom event occurs.
(2) Criticality importance measure
Based on BIM, CIM considers the influence of fault events on the occurrence of system fault time. The calculation model of CIM is shown in Equation (3), which is equal to the product of BIM and the degree of influence of fault events on system fault events [32].
where represents the probability that the bottom event i occurs, and represents the top event occurs, which is the probability of system failure.
(3) Fussell–Vesely importance measure
FVIM indicates the contribution of the minimum cut set failure containing the bottom event i to the system failure, and its calculation model is shown in Equation (4) [33,34].
where represents the probability that the minimum cut set containing the bottom event i fails when the bottom event i occurs. presents the probability that the bottom event i occurs, and represents the top event occurs, which is the probability of system failure.
BIM, CIM, and FVIM are calculated by Equations (2)–(4), respectively. The calculation results of the four importance measures are shown in Table 6. We can find that BIM and FVIM are concentrated in the order of 0.1, CIM results are concentrated in the order of 0.01, and IIM is concentrated in the order of 10 × 10−07. As an indicator of identifying the weakest links in the system, IM focuses on its relative importance level. Moreover, the BIM ranking in descending order is C19 > C18 > C8 > C17 > C14 > C10 > C15 > C12 > C16 > C9 > C1 > C5 > C20 > C2 > C3 > C13 >C11 > C4 > C7 > C6. Under the condition of limited maintenance resources, the bottom events C19 (bearing wear), C17 (nonconformity of oil varieties or improper oil quantity), and C18 (cooling spray function failure) should be repaired as priorities. The CIM ranking in descending order is C19 > C18 > C8 > C17 > C14 > C10 > C15 > C12 > C16 > C9 > C1 > C5 > C20 > C2 > C3 > C13 >C11 > C4 > C7 > C6. Given the limited maintenance resources, the bottom events C19 (bearing wear), C18 (cooling spray function failure), and C8 (short circuit between coils, water in connection cavity, dampened circuit) should be repaired as priorities. The FVIM ranking in descending order is C15 > C19 > C18 > C8 >C17 >C14 > C10 > C12 > C16 > C9 > C1 > C5 > C20 > C2 > C3 > C13 >C11 > C4 > C7 > C6. With limited maintenance resources, the bottom events C15 (fatigue damage, gearbox dry friction or particle contamination), C19 (bearing wear), and C8 (short circuit between coils, water in connection cavity, dampened circuit) should be prioritized for repair.

Table 6.
The results of four IMs for 20 bottom events.
4.1. Relative Value Distribution Analysis by Radial Bar Charts
The radial bar chart can clearly show the ranking results of importance measures, which can effectively identify the bottom events of high importance. To analyze the ranking and distribution of various IMs, the calculation results of 20 bottom events were normalized, and the ranking of different importance measures is analyzed in the radial bar chart. If the importance of the bottom event is greater, the bottom event is outside the radial bar chart. The radial bar charts of IIM, BIM, CIM, and FVIM are shown in Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, respectively.
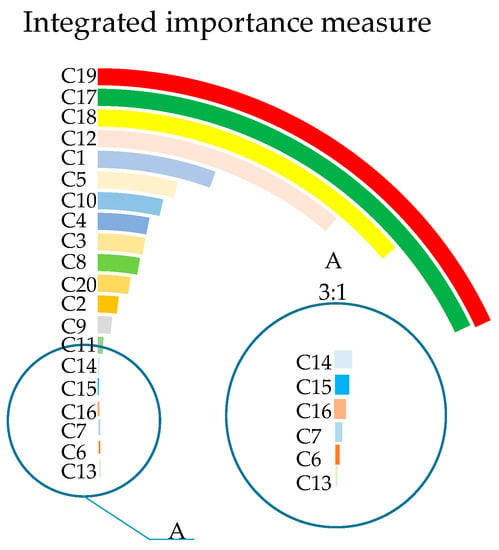
Figure 6.
Radial bar chart of IIM.
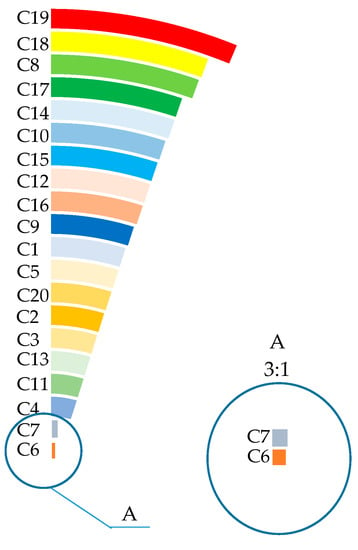
Figure 7.
Radial bar chart of BIM.
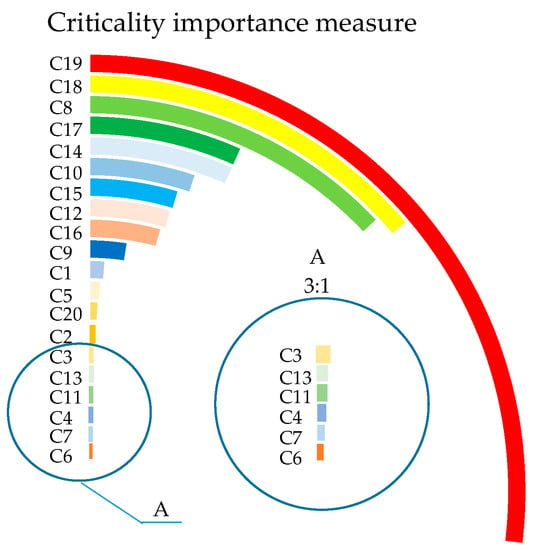
Figure 8.
Radial bar chart of CIM.
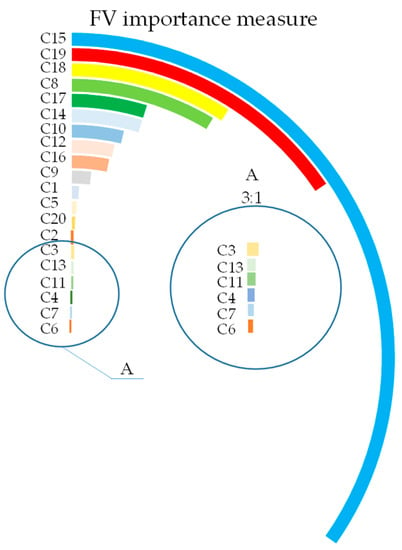
Figure 9.
Radial bar chart of FVIM.
From these radial bar charts, the IM rankings can be clearly displayed, making it convenient to determine the key fault causes of shearer-cutting units. Figure 6 shows that these four bottom events with the greatest IIM (the top 20% of IIM ranking) are C19 (bearing wear), C17 (nonconformity of oil varieties or improper oil quantity), C18 (cooling spray function failure), and C12 (bolt fracture). Figure 7 and Figure 8 show that the ranking of BIM is the same as that of CIM. The four bottom events with the highest BIM or CIM are C19 (bearing wear), C18 (cooling spray function failure), C8 (short circuit between coils, water in connection cavity, dampened circuit), and C17 (nonconformity of oil varieties or improper oil quantity). Figure 9 shows that the four bottom events with the highest importance of FVIM are fatigue damage, C15 (fatigue damage, gearbox dry friction or particle contamination), C19 (bearing wear), C18 (cooling spray function failure), and C8 (short circuit between coils, water in connection cavity, dampened circuit). Therefore, we can easily find the rankings of different IMs by radial bar charts.
From the perspective of the relative importance distribution of four importance measures, in Figure 7, except for C6 (oil seal leakage) and C7 (oil spill blockage), the BIM ranking of other bottom events is very close, and the ranking results of BIM cannot be intuitively distinguished. Comparing Figure 7 and Figure 8, the ranking results of BIM and CIM are the same, but the bottom events of CIM can be distinguished clearly because the gap between maxima and minima is narrow. So, the relative value of CIM makes it easier to distinguish key fault causes compared to BIM. From Figure 6 and Figure 9, the relative values of IIM and FVIM can clearly distinguish the importance of bottom events. However, C15 (fatigue damage, gearbox dry friction or particle contamination) in FVIM is too large, which makes it difficult to distinguish the importance measure of other bottom events with lower FVIM. Therefore, the relative value distribution of the four importance measure rankings shows that IIM and CIM can clearly distinguish the relative importance of bottom events.
4.2. Ranking Accuracy Comparison Based on Mean Average Precision
Mean average precision (mAP) is an important index to evaluate the accuracy of specific sequence ordering under the restriction of multiple sets of key elements [35]. The larger the value of mAP, the higher the accuracy of the corresponding ranking. Therefore, mAP is introduced to evaluate the accuracy of different IM rankings. The calculation process of mAP is summarized as follows.
- Select n groups of key elements, assuming that the number of key elements in group i is mi.
- Determine the position Kij of the key element in a particular ranking, and the key element is the element in the group .
- Calculate the mAP of different rankings under different key element groups, as shown in Equation (5).
In order to compare the average accuracy of rankings for four IMs, select the top L bottom events with higher IM as a group of key elements. Here, we select three groups of key elements, which means n = 3. The key elements in the first group are C10, C12, C17, C18, and C19 when L = 8. C10, C17, C18, and C19 are the key elements in the second group when L = 7. C17, C18, and C19 are selected as the key elements in the third group when L = 5. For these four rankings of IMs, the position information of key elements in each can be recorded as KIIM, KFVIM, KBIM, and KCIM, shown as follows:
Therefore, the average accuracy of these four IM rankings can be obtained by substituting KIIM, KFVIM, KBIM, and KCIM into Equation (5). The mAP values of four IM rankings are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
The mAP values of four IM rankings.
The average accuracy of IM ranking in Table 5 shows that the accuracy of IIM ranking is the highest (94.52%), followed by BIM and CIM ranking accuracy (85.97%), and FVIM accuracy is the lowest (58.87%). Thus, IIM ranking has the best accuracy. The main reason for the low accuracy of the FVIM ranking is that the bottom event C15 is at the top of the FVIM ranking, but it is not at the top in other IM rankings.
4.3. Ranking Results Discussion of Different Importance Measures
From the analysis of four IM rankings, we can infer that IM rankings depend on the different calculation methods of IMs. BIM only considers the impact of the occurrence probability of each bottom event on the occurrence probability of the top event. Based on BIM, CIM evaluates the importance of each bottom event from the dual perspectives of sensitivity and probability. When FVIM is in the non-critical state, the component changes from a normal state to a failure state, and the top event does not occur but influences the probability of top event occurrence. However, IIM fully considers the failure rates on the basis of BIM.
The results show that IIM and CIM have better relative value distribution, which can distinguish the bottom events with lower IM clearly. For the average accuracy of IM rankings, IIM has the highest mAP, while FVIM has the lowest mAP. Therefore, IIM ranking can better distinguish the relative importance of bottom events with higher ranking accuracy, which can accurately and effectively identify key bottom events. Moreover, the limited maintenance resources should give priority to the occurrence of faults such as C19 (bearing wear), C17 (nonconformity of oil varieties or improper oil quantity), and C18 (cooling spray function failure), which can effectively improve the performance of shearer-cutting units.
5. Conclusions
The IIM-based fault tree analysis method can accurately and effectively identify key bottom events. Compared with BIM, CIM, and FVIM, IIM ranking can better distinguish the relative importance of bottom events, and the average accuracy of IIM ranking is 94.52%, which is higher than the other three classical importance measures. Moreover, the limited maintenance resources should give priority to the bottom events C19, C17, and C18. In the future, the research should focus on the analysis method of key fault causes driven by real-time operation and maintenance data and the key fault causes analysis based on multi-state IMs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-b.Z. and M.-t.L.; Methodology, J.-b.Z.; Software, M.-t.L. and Z.-y.Z.; Validation, J.-b.Z., M.-t.L. and J.C.; Formal analysis, J.-b.Z. and M.-t.L.; Investigation, J.-b.Z. and M.-t.L.; Resources, Z.-y.Z. and X.-g.C.; Data curation, M.-t.L. and Z.-y.Z.; Writing—original draft preparation, M.-t.L. and J.C.; Writing—review and editing, J.-b.Z. and Z.-y.Z.; Supervision, X.-g.C. and J.-b.Z.; Project administration, J.-b.Z.; Funding acquisition, J.-b.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 72101202, 51834006, 51875451) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant no. 2022MD713793).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, Y.; Pan, S.; Ning, S.; Shao, L.; Jing, Z.; Wang, Z. Coal measure metallogeny: Metallogenic system and implication for resource and environment. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaghian, O.; Hoseinie, S.H.; Maleki, A. Multi-attribute failure analysis of coal cutting picks on longwall shearer machine. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 120, 105069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Current status and prospects of reliability systems engineering in China. Front. Eng. Manag. 2021, 8, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X.; Dui, H.; Xie, M. Improved resilience measure for component recovery priority in power grids. Front. Eng. Manag. 2021, 8, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M. System reliability and system resilience. Front. Eng. Manag. 2021, 8, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Z.; Dui, H. Recent advances in system reliability optimization driven by importance measures. Front. Eng. Manag. 2020, 7, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dui, H.; Zheng, X.; Wu, S. Resilience analysis of maritime transportation systems based on importance measures. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 209, 107461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Si, S.; Jin, T. Reliability importance measures for network based on failure counting process. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2018, 68, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoghathawi, Y.; Barker, K. Component importance measures for interdependent infrastructure network resilience. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 133, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, Z. New importance measures based on failure probability in global sensitivity analysis of reliability. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Levitin, G.; Dui, H.; Sun, S. Component state-based integrated importance measure for multi-state systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 116, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dui, H.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X. Component joint importance measures for maintenances in submarine blowout preventer system. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2020, 63, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Dui, H.; Li, Z. Reliability analysis for electrical power systems based on importance measures. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2022, 236, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, Y.; Dui, H.; Xing, L. Importance measure-based maintenance optimization strategy for pod slewing system. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 216, 108001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Sun, L.; Soares, C.G. Fault tree analysis of floating offshore wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurahara, T.; Reihani, S.; Kee, E.; Mohaghegh, Z. Global importance measure methodology for integrated probabilistic risk assessment. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2020, 234, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiyanto, M.A.; Fernanda, H. Risk assessment of work accident in container terminals using the fault tree analysis method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachlou, M.; Roozbahani, A.; Banihabib, M.E. Comprehensive risk assessment of river basins using Fault Tree Analysis. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Chen, B.; Wang, Z. An importance measure of a CNC lathe considering failure correlations. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2022, 38, 1367–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ud-Din, S.; Yoon, Y. Analysis of loss of control parameters for aircraft maneuvering in general aviation. J. Adv. Transp. 2018, 2018, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, H.; Wei, K. Reliability study of motor controller in electric vehicle by the approach of fault tree analysis. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 121, 105165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikwan, F.; Sanders, D.; Hassan, M. Safety evaluation of leak in a storage tank using fault tree analysis and risk matrix analysis. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2021, 73, 104597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Soares, C.G.; Huang, H.Z. Reliability analysis of a floating offshore wind turbine using Bayesian Networks. Ocean Eng. 2020, 217, 107827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Márquez, F.P.; Segovia Ramírez, I.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Marugán, A.P. Reliability dynamic analysis by fault trees and binary decision diagrams. Information 2020, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, K.; Peter Nicholas Burrow, M.; Singh Ghataora, G.; Sasidharan, M. Using probabilistic fault tree analysis and Monte Carlo simulation to examine the likelihood of risks associated with ballasted railway drainage failure. Transp. Res. Rec. 2021, 2675, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Pan, J.; Chen, G.; Zi, Y.; Yuan, J.; Chen, B.; He, Z. Wavelet transform based on inner product in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: A review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 70, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Tian, H.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, F.; Lu, S. Failure analysis for hydraulic system of heavy-duty machine tool with incomplete failure data. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Dui, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S. Integrated importance measure of component states based on loss of system performance. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2012, 61, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Application of fuzzy neural network in fault diagnosis for scraper conveyor vibration[C]//2013 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA). IEEE 2013, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bołoz, Ł.; Rak, Z.; Stasica, J. Comparative analysis of the failure rates of shearer and plow systems: A case study. Energies 2022, 15, 6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, Z.W. On the Importance of Different Components in a Multi-Component System; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 581–592. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, H.E. Fault Trees for Decision Making in Systems Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Livermore, CA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Vesely, W.E. A time-dependent methodology for fault tree evaluation. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1970, 13, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fussell, J.B. How to hand-calculate system reliability and safety characteristics. IEEE Trans Reliab. 1975, R-24, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lv, S.; Jiang, M.; Song, H. Using channel pruning-based YOLO v4 deep learning algorithm for the real-time and accurate detection of apple flowers in natural environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).