T-Splines for Isogeometric Analysis of the Large Deformation of Elastoplastic Kirchhoff–Love Shells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. T-Splines
2.1. T-Mesh and the T-Spline Basis
2.2. BéZier Extraction
3. Formulations for the Large Deformation of Elastoplastic Kirchhoff–Love Shells
3.1. Finite Strain Plasticity
| Algorithm 1 Return mapping algorithm. |
| State: is computed in the time step , and are saved from the last time step |
| Input:, , |
| Output:, , |
|
| Algorithm 2 Consistent elastoplastic tangent moduli. |
| Input: Same as Algorithm 1 |
| Output: |
|
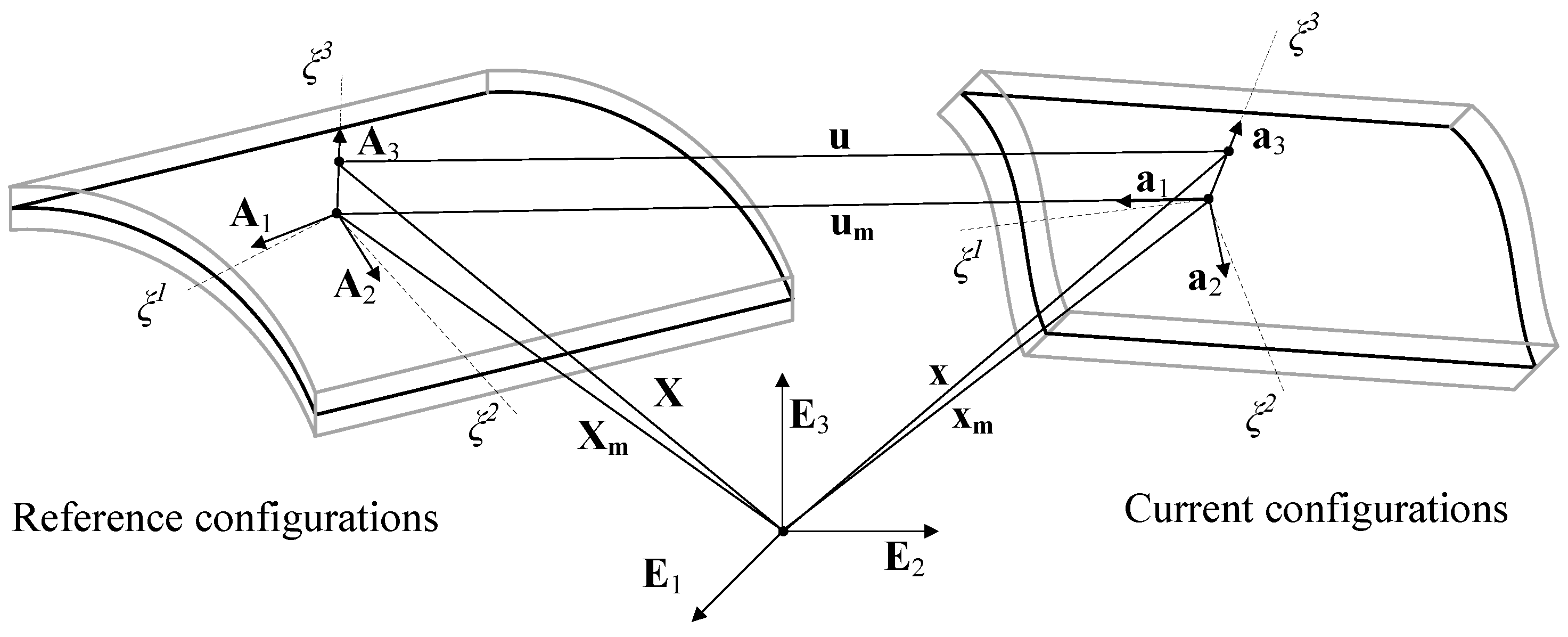
3.2. Geometry Definition
3.3. Kinematics
| Algorithm 3 Iterative update for . |
| Input:, |
| Output: |
|
3.4. Variational Formulation
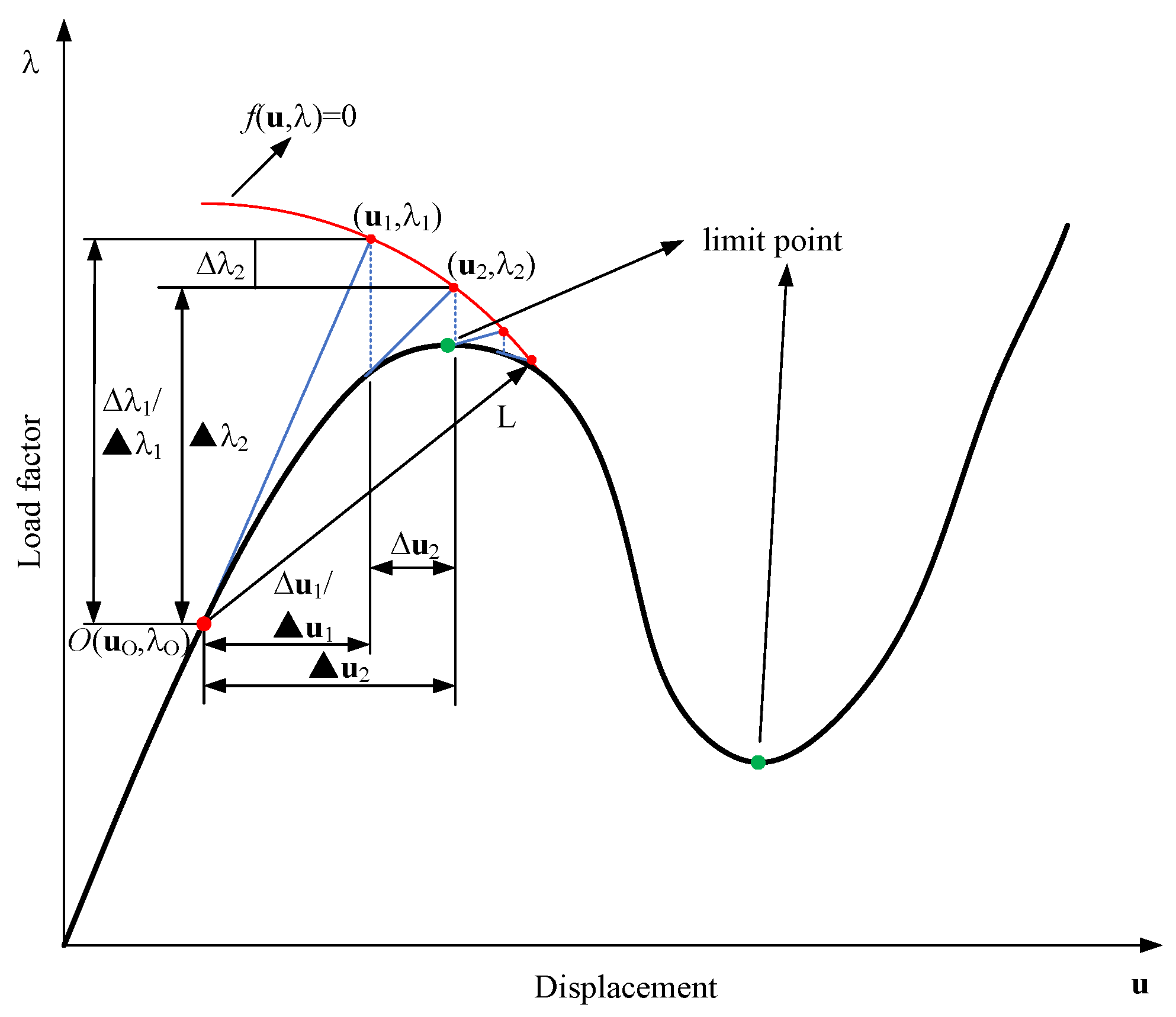
3.5. Arc-Length Method
| Algorithm 4 The algorithm of arc-length method. |
| Input: The variables from the latest convergence point: |
| Output: The next convergence point, updated increments: |
|
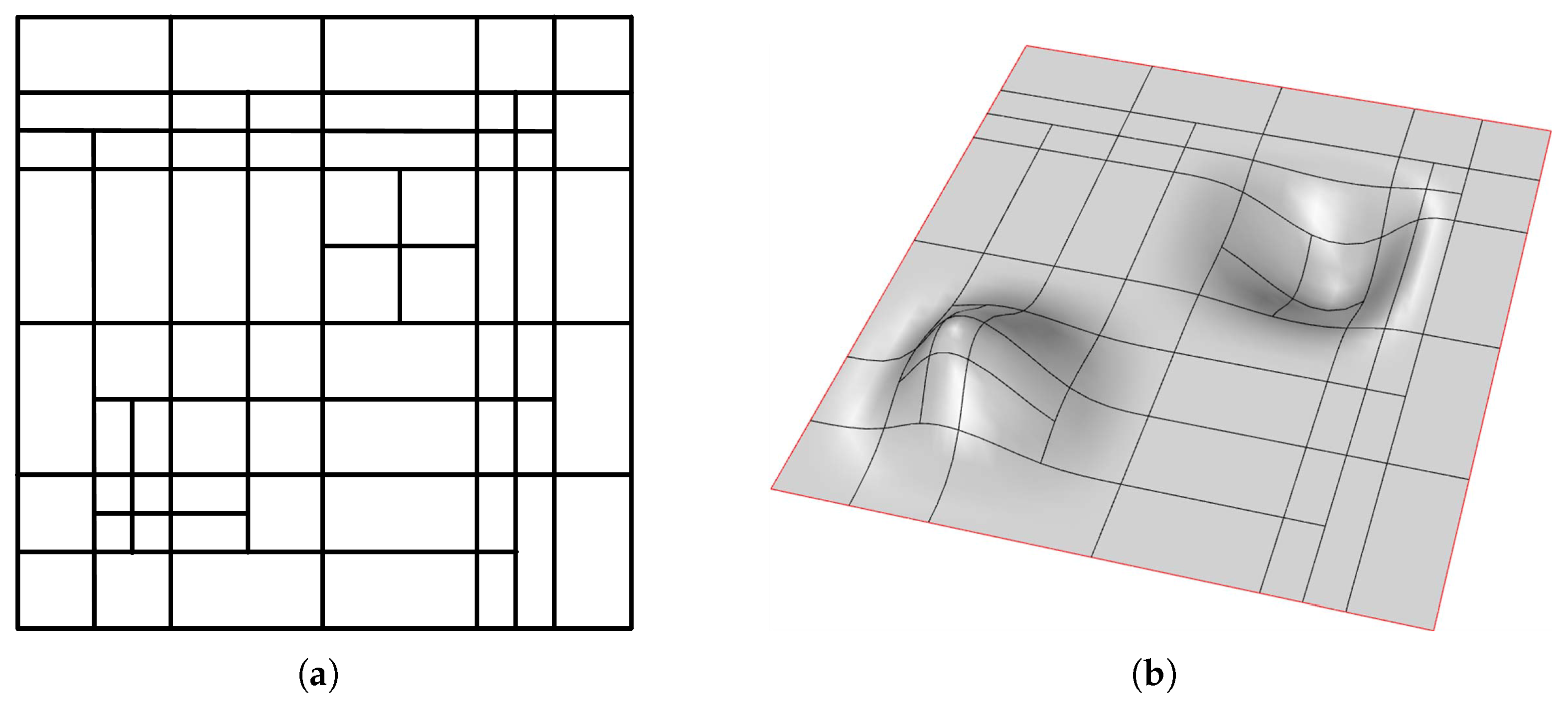
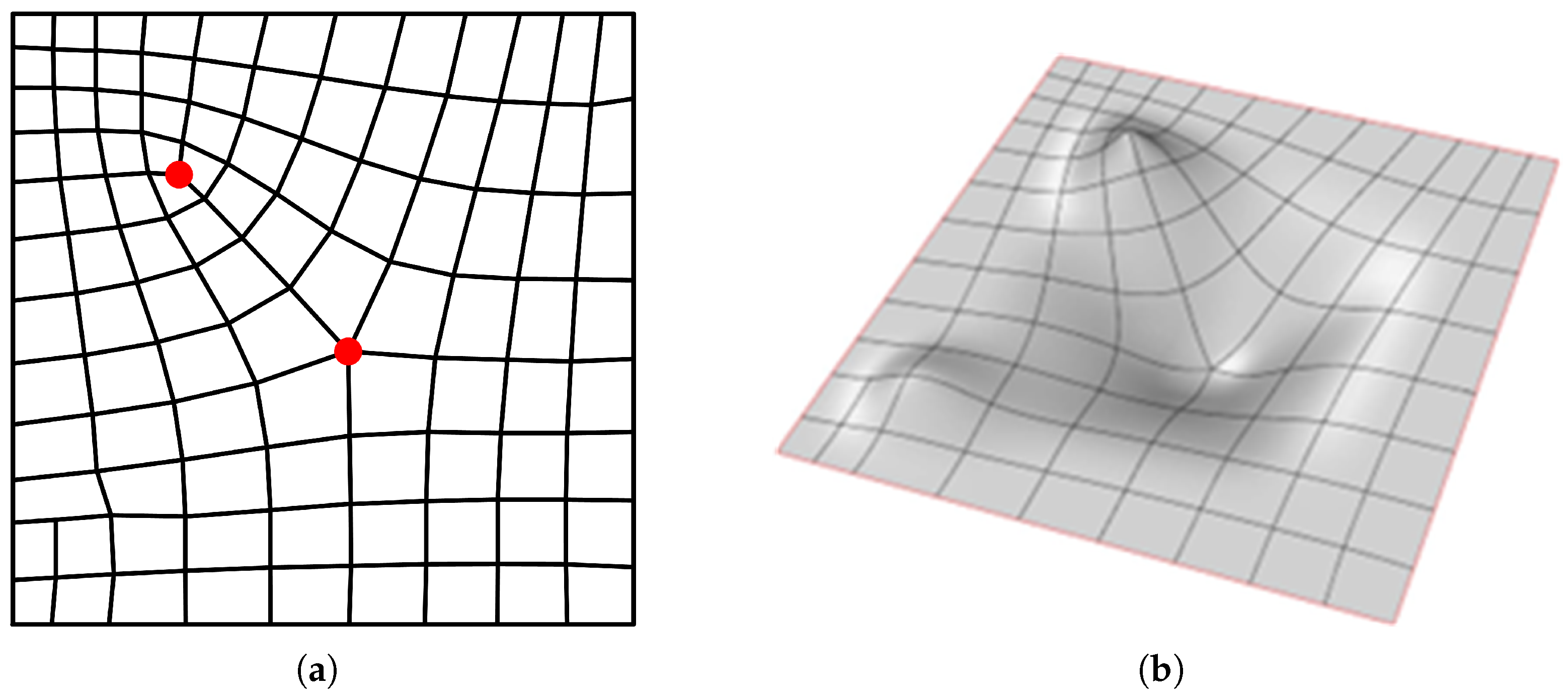
4. Adaptive Refinement
5. Numerical Tests
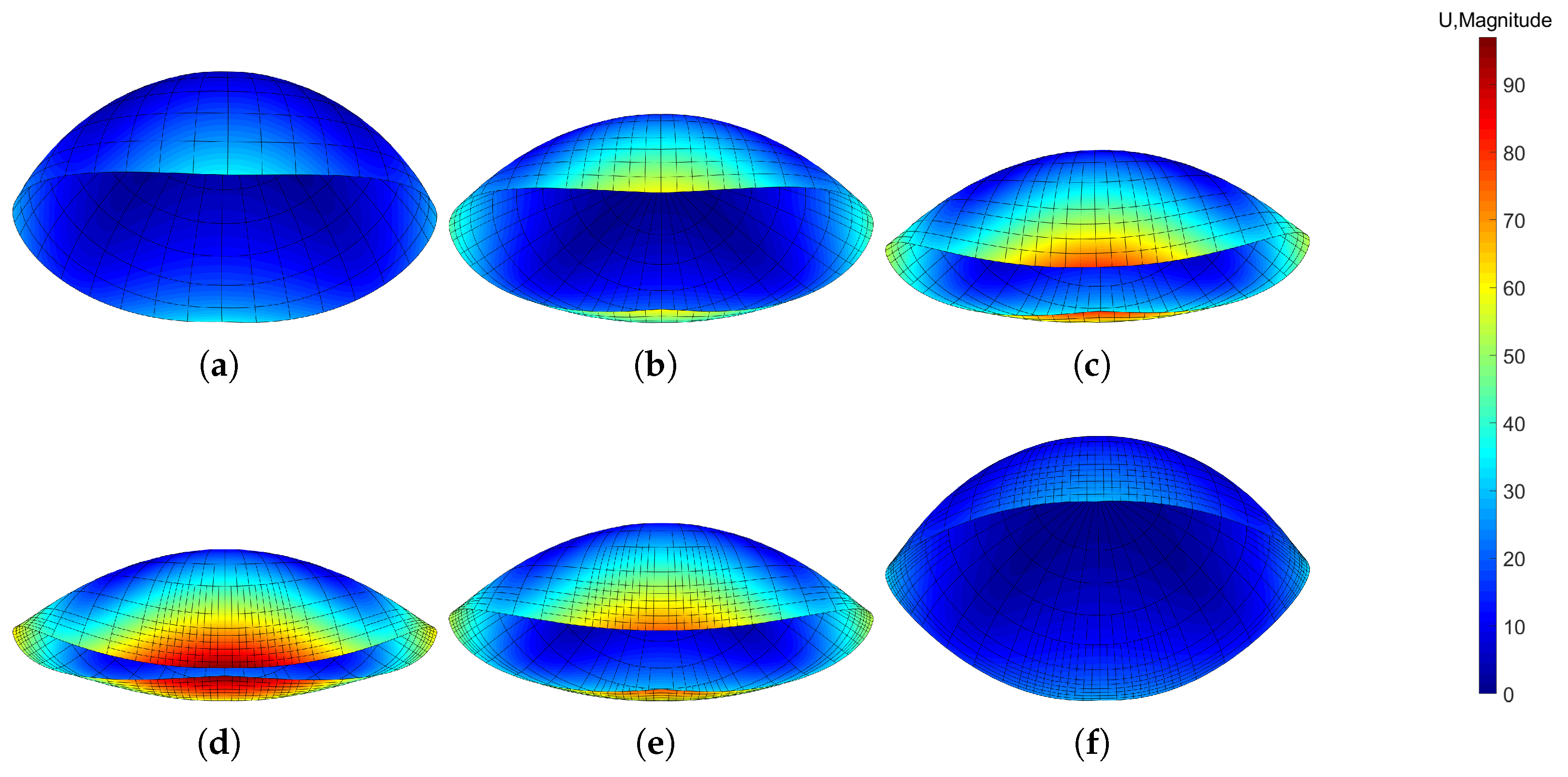
5.1. Pinched Elastoplastic Hemisphere
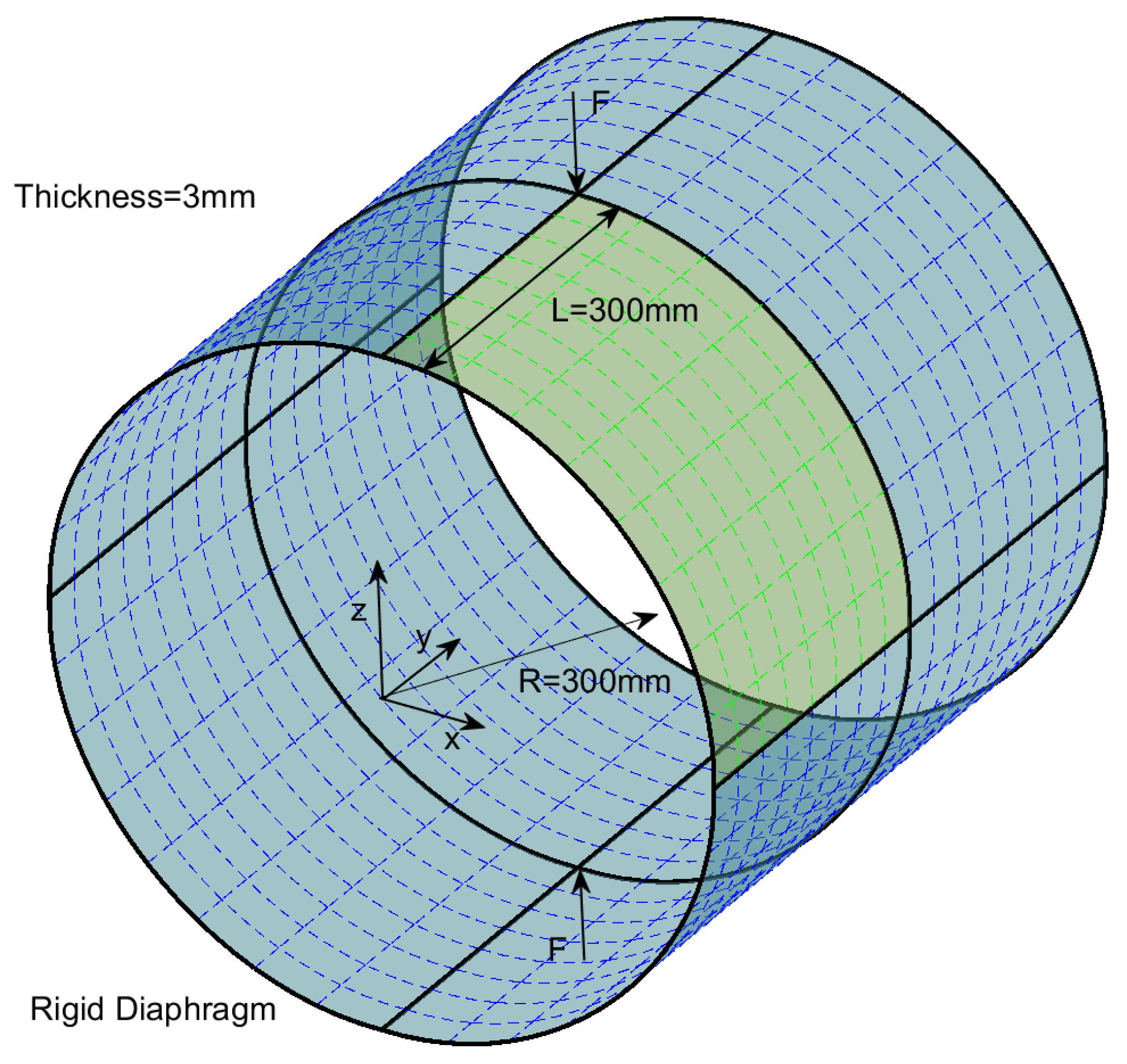
5.2. Pinched Elastoplastic Cylinder
5.3. Plastic Collapse of the Scordelis–Lo Roof
5.4. Plastic Cylinder with Holes Under Compression
5.5. Torsion of a Plastic Rectangular Sheet with a Hole
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Hughes, T.J.; Liu, W.K. Nonlinear finite element analysis of shells: Part I. Three-dimensional shells. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1981, 26, 331–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.J.; Liu, W.K. Nonlinear finite element analysis of shells-part II. two-dimensional shells. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1981, 27, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Wei, H.; Vu-Quoc, L.; Izzuddin, B.A.; Zhuo, X.; Li, T.Z. A co-rotational triangular finite element for large deformation analysis of smooth, folded and multi-shells. Acta Mech. 2021, 232, 1515–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaiee-Pajand, M.; Arabi, E.; Masoodi, A.R. A triangular shell element for geometrically nonlinear analysis. Acta Mech. 2018, 229, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, T.; Vu-Quoc, L.; Izzuddin, B.; Zhuo, X.; Fang, Q. A nine-node corotational curved quadrilateral shell element for smooth, folded, and multishell structures. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2018, 116, 570–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaiee-Pajand, M.; Masoodi, A.R. Shell instability analysis by using mixed interpolation. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaiee-Pajand, M.; Masoodi, A.R.; Arabi, E. A 6-parameter triangular flat shell element for nonlinear analysis. Eur. J. Comput. Mech. 2019, 28, 237–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, J.A.; Hughes, T.J.; Bazilevs, Y. Isogeometric Analysis: Toward Integration of CAD and FEA; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, T.J.; Cottrell, J.A.; Bazilevs, Y. Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2005, 194, 4135–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, J.A.; Reali, A.; Bazilevs, Y.; Hughes, T.J. Isogeometric analysis of structural vibrations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2006, 195, 5257–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, J.; Hughes, T.; Reali, A. Studies of refinement and continuity in isogeometric structural analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2007, 196, 4160–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouclier, R.; Elguedj, T.; Combescure, A. Efficient isogeometric NURBS-based solid-shell elements: Mixed formulation and B-method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 267, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouclier, R.; Elguedj, T.; Combescure, A. On the development of NURBS-based isogeometric solid shell elements: 2D problems and preliminary extension to 3D. Comput. Mech. 2013, 52, 1085–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterle, B.; Sachse, R.; Ramm, E.; Bischoff, M. Hierarchic isogeometric large rotation shell elements including linearized transverse shear parametrization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 321, 383–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echter, R.; Oesterle, B.; Bischoff, M. A hierarchic family of isogeometric shell finite elements. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 254, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.; Bazilevs, Y.; Hsu, M.C.; Hughes, T. Isogeometric shell analysis: The Reissner-Mindlin shell. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2010, 199, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornisch, W.; Klinkel, S.; Simeon, B. Isogeometric Reissner–Mindlin shell analysis with exactly calculated director vectors. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 253, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornisch, W.; Klinkel, S. Treatment of Reissner–Mindlin shells with kinks without the need for drilling rotation stabilization in an isogeometric framework. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2014, 276, 35–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornisch, W.; Müller, R.; Klinkel, S. An efficient and robust rotational formulation for isogeometric Reissner–Mindlin shell elements. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 303, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhao, G.; Wang, W. Nitsche method for isogeometric analysis of Reissner-Mindlin plate with non-conforming multi-patches. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2015, 35, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Du, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Fang, H. Application of isogeometric method to free vibration of Reissner-Mindlin plates with non-conforming multi-patch. Comput. Aided Des. 2017, 82, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiendl, J.; Bletzinger, K.U.; Linhard, J.; Wüchner, R. Isogeometric shell analysis with Kirchhoff–Love elements. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2009, 198, 3902–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiendl, J.; Hsu, M.C.; Wu, M.C.; Reali, A. Isogeometric Kirchhoff–Love shell formulations for general hyperelastic materials. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 291, 280–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiendl, J. Isogeometric Analysis and Shape Optimal Design of Shell Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Thanh, N.; Kiendl, J.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Wüchner, R.; Bletzinger, K.U.; Bazilevs, Y.; Rabczuk, T. Rotation free isogeometric thin shell analysis using PHT-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 3410–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.J.; Bazilevs, Y.; Hsu, M.C.; Hughes, T. A large deformation, rotation-free, isogeometric shell. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 1367–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.X.; Roohbakhshan, F.; Sauer, R.A. A new rotation-free isogeometric thin shell formulation and a corresponding continuity constraint for patch boundaries. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 316, 43–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.; Hartmann, S.; Bazilevs, Y.; Hsu, M.C.; Hughes, T. Blended isogeometric shells. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 255, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Yu, T.; Bui, T.Q.; Wang, Z.; Curiel-Sosa, J.L.; Das, R.; Hirose, S. 3-D elasto-plastic large deformations: IGA simulation by Bézier extraction of NURBS. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 108, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Lai, W.; Bui, T.Q. Three-dimensional elastoplastic solids simulation by an effective IGA based on Bézier extraction of NURBS. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 2019, 15, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elguedj, T.; Hughes, T.J. Isogeometric analysis of nearly incompressible large strain plasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2014, 268, 388–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elguedj, T.; Bazilevs, Y.; Calo, V.M.; Hughes, T.J. B and F projection methods for nearly incompressible linear and non-linear elasticity and plasticity using higher-order NURBS elements. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2008, 197, 2732–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R. Isogeometric analysis of nearly incompressible solids. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2011, 87, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, M.; Kiendl, J.; De Lorenzis, L. Isogeometric Kirchhoff–Love shell formulation for elasto-plasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 340, 320–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, G.; Zhuang, X.; Bui, H.; Meschke, G.; Nguyen-Xuan, H. Elasto-plastic large deformation analysis of multi-patch thin shells by isogeometric approach. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2020, 173, 103389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaydin, M.D.; Benson, D.J.; Bazilevs, Y. An updated Lagrangian framework for Isogeometric Kirchhoff–Love thin-shell analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 384, 113977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perić, D.; Vaz, M., Jr.; Owen, D. On adaptive strategies for large deformations of elasto-plastic solids at finite strains: Computational issues and industrial applications. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1999, 176, 279–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.S.; Wriggers, P. An h-adaptive method for elasto-plastic shell problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2000, 189, 651–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Randolph, M. H-adaptive FE analysis of elasto-plastic non-homogeneous soil with large deformation. Comput. Geotech. 1998, 23, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sederberg, T.W.; Zheng, J.; Bakenov, A.; Nasri, A. T-splines and T-NURCCs. ACM Trans. Graph. 2003, 22, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sederberg, T.W.; Cardon, D.L.; Finnigan, G.T.; North, N.S.; Zheng, J.; Lyche, T. T-spline simplification and local refinement. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2004, 23, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazilevs, Y.; Calo, V.M.; Cottrell, J.A.; Evans, J.A.; Hughes, T.J.R.; Lipton, S.; Scott, M.A.; Sederberg, T.W. Isogeometric analysis using T-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2010, 199, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casquero, H.; Wei, X.; Toshniwal, D.; Li, A.; Hughes, T.J.; Kiendl, J.; Zhang, Y.J. Seamless integration of design and Kirchhoff–Love shell analysis using analysis-suitable unstructured T-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 360, 112765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.A.; Simpson, R.N.; Evans, J.A.; Lipton, S.; Bordas, S.P.; Hughes, T.J.; Sederberg, T.W. Isogeometric boundary element analysis using unstructured T-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2013, 254, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casquero, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Reali, A.; Kiendl, J.; Gomez, H. Arbitrary-degree T-splines for isogeometric analysis of fully nonlinear Kirchhoff–Love shells. Comput. Aided Des. 2017, 82, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Hsu, M.C.; Lua, J.; Phan, N. A large deformation isogeometric continuum shell formulation incorporating finite strain elastoplasticity. Comput. Mech. 2022, 70, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.A.; Borden, M.J.; Verhoosel, C.V.; Sederberg, T.W.; Hughes, T.J.R. Isogeometric finite element data structures based on Bézier extraction of T-splines. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2011, 88, 126–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, M.J.; Scott, M.A.; Evans, J.A.; Hughes, T.J. Isogeometric finite element data structures based on Bézier extraction of NURBS. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2011, 87, 15–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, U. A refineable space of smooth spline surfaces of arbitrary topological genus. J. Approx. Theory 1997, 90, 174–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshniwal, D.; Speleers, H.; Hughes, T.J. Smooth cubic spline spaces on unstructured quadrilateral meshes with particular emphasis on extraordinary points: Geometric design and isogeometric analysis considerations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 327, 411–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, J.C.; Hughes, T.J. Computational Inelasticity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Simo, J.C. A framework for finite strain elastoplasticity based on maximum plastic dissipation and the multiplicative decomposition: Part I. Continuum formulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1988, 66, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, J.C. A framework for finite strain elastoplasticity based on maximum plastic dissipation and the multiplicative decomposition. Part II: Computational aspects. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1988, 68, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhao, G.; Wang, W.; Guo, M.; Zhang, R.; Yang, J. NLIGA: A MATLAB framework for nonlinear isogeometric analysis. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2020, 80, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H. Introduction to Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wriggers, P. Nonlinear Finite Element Methods; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ritto-Corrêa, M.; Camotim, D. On the arc-length and other quadratic control methods: Established, less known and new implementation procedures. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisfield, M.A. A fast incremental/iterative solution procedure that handles “snap-through”. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Computational Methods in Nonlinear Structural and Solid Mechanics, Washington, DC, USA, 6–8 October 1981; pp. 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Zhu, J.Z. A simple error estimator and adaptive procedure for practical engineerng analysis. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1987, 24, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Zhu, J.Z. The superconvergent patch recovery and a posteriori error estimates. Part 1: The recovery technique. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1992, 33, 1331–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Zhu, J.Z. The superconvergent patch recovery and a posteriori error estimates. Part 2: Error estimates and adaptivity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1992, 33, 1365–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiberg, N.E.; Zeng, L.; Li, X. Error estimation and adaptivity in elastodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1992, 101, 369–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.F.; Wiberg, N.E. Spatial mesh adaptation in semidiscrete finite element analysis of linear elastodynamic problems. Comput. Mech. 1992, 9, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienkiewicz, O.; Liu, Y.; Huang, G. Error estimation and adaptivity in flow formulation for forming problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1988, 25, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörfel, M.R.; Jüttler, B.; Simeon, B. Adaptive isogeometric analysis by local h-refinement with T-splines. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2010, 199, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhao, G.; Wang, W.; Du, X.; Yang, J. T-Splines for Isogeometric Analysis of Two-Dimensional Nonlinear Problems. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2020, 123, 821–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, A.V.; Giannelli, C.; Jüttler, B.; Simeon, B. A hierarchical approach to adaptive local refinement in isogeometric analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2011, 200, 3554–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Deng, J.; Chen, F. Adaptive isogeometric analysis using rational PHT-splines. Comput. Aided Des. 2011, 43, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolin, P.; Buffa, A.; Coradello, L. A hierarchical approach to the a posteriori error estimation of isogeometric Kirchhoff plates and Kirchhoff–Love shells. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 363, 112919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coradello, L.; Antolin, P.; Vázquez, R.; Buffa, A. Adaptive isogeometric analysis on two-dimensional trimmed domains based on a hierarchical approach. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020, 364, 112925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, S.; Pawlak, T.; Wheeler, M. Application of the Zienkiewicz-Zhu error estimator for plate and shell analysis. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1990, 29, 1281–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.D. Linear independence of the blending functions of T-splines without multiple knots. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 3634–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, J.C.; Kennedy, J. On a stress resultant geometrically exact shell model. Part V. Nonlinear plasticity: Formulation and integration algorithms. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1992, 96, 133–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, Y.; Itskov, M. Constitutive model and finite element formulation for large strain elasto-plastic analysis of shells. Comput. Mech. 1999, 23, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaqus, G. Abaqus 6.11; Dassault Systemes Simulia Corporation: Providence, RI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Srinivasa, A.R.; Rajagopal, K.; Reddy, J. Simulation of inextensible elasto-plastic beams based on an implicit rate type model. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2018, 99, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





























Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Wang, W.; Zhao, G.; Du, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, J. T-Splines for Isogeometric Analysis of the Large Deformation of Elastoplastic Kirchhoff–Love Shells. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031709
Guo M, Wang W, Zhao G, Du X, Zhang R, Yang J. T-Splines for Isogeometric Analysis of the Large Deformation of Elastoplastic Kirchhoff–Love Shells. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031709
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Mayi, Wei Wang, Gang Zhao, Xiaoxiao Du, Ran Zhang, and Jiaming Yang. 2023. "T-Splines for Isogeometric Analysis of the Large Deformation of Elastoplastic Kirchhoff–Love Shells" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031709
APA StyleGuo, M., Wang, W., Zhao, G., Du, X., Zhang, R., & Yang, J. (2023). T-Splines for Isogeometric Analysis of the Large Deformation of Elastoplastic Kirchhoff–Love Shells. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031709







