Abstract
Ion–molecule reactions between neutral methyl formate (MF) and proton-bound solvent clusters W2H+, W3H+, M2H+, E2H+, and E3H+ (W = water, M = methanol, and E = ethanol) showed that the major reaction product is a solvent molecule loss from the initial encounter complex, followed by the formation of protonated methyl formate (MFH+). Collision-induced dissociation breakdown curves of the initially formed solvent-MF proton-bound pairs and trimers were obtained as a function of collision energy and modeled to extract relative activation energies for the observed channels. Density functional theory calculations (B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p)) of the solvent loss reaction were consistent with barrierless reactions in each case. The MF(M)H+ ion also exhibited loss of CH4 at higher collision energies. The reaction was calculated to proceed via the migration of the MF methyl group to form a loosely bound complex between neutral CH4 and an ion comprising (CH3OH)(CO2)H+. Overall, the results indicate that the interaction of methyl formate with atmospheric water can form stable encounter complexes that will dissociate to form protonated methyl formate.
1. Introduction
Volatile organic carbon (VOC) compounds in the atmosphere play a role in climate change, human and animal health, and oxidation capacity [1]. The results obtained from a 2020 study measuring the concentrations of various VOCs in Burnaby South and Port Moody (part of Greater Vancouver) and analyzing the factors contributing to their production showed that fuel combustion, natural gas, industrial solvents, and fugitive industrial and biogenic emissions, are the main sources that contribute to all VOC emissions [2].
Methyl formate is a small ester derived from formic acid or formate. It can undergo a series of reactions in the troposphere initiated by the hydroxy radical and other atmospheric radicals [3]. In oxygenated fuels such as dimethyl ether and dimethoxy methane—two suggested alternatives to conventional diesel fuel [4,5,6]—methyl formate represents the major intermediate formed in their oxidation. It has also been shown to interact with atmospheric water [7]. The mechanisms by which organic molecules are incorporated into water clusters include switching, association, and proton transfer [4]. When formates interact with water molecules, the carbonyl group leads to further hydrogen bonding interactions. The shape and bonding strength of the cluster is altered, making it more stable overall. These findings make it clear that organic esters such as formates play a role in nucleation processes due to their ability to share intermolecular interactions with water [8,9]. Ion–molecule reactions are one method for exploring the reaction between formates and water clusters [10].
Water clusters play a ubiquitous role in atmospheric chemistry in both neutral and protonated states [11]. Proton-bound water clusters are widely used as reactant ions for the analysis of volatile organic compounds through mass spectrometry [12]. It is also quite common to produce protonated analyte molecules using proton-bound water clusters [13,14]. Herein, we present details of ion–molecule reactions between proton-bound solvent clusters of water, methanol and ethanol with neutral methyl formate in the gas phase. The aim is to explore this aspect of the atmospheric fate of formates. Reaction products have been further explored with collision-energy resolved tandem mass spectrometry to understand their unimolecular chemistry.
2. Materials and Methods
Water, methanol, ethanol, and methyl formate were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Sigma-Aldrich, Oakville, Ontario, CA, USA) and used without further purification.
2.1. Tandem Mass Spectrometry
A Micromass Quattro Ultima triple quadrupole mass spectrometer running the MassLynx software package equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source in a Z-spray configuration was used for all the experiments described herein. Proton-bound water, methanol and ethanol ions were generated by electrospray ionization of solutions of each solvent with 0.1% formic acid delivered by a syringe pump at a rate of 50 μL/min. The capillary voltage was typically set to 3.5 kV but was adjusted to optimize ion yield. Nitrogen was used as the nebulizer gas with a flow rate of 100 L/h. The source and desolvation gas temperatures were held at 100 and 150 °C, respectively. The desired proton-bound cluster ion was mass-selected with the first quadrupole and transmitted to the collision cell where it interacted with methyl formate vapour introduced by a variable leak Granville-Phillips valve [15]. The voltage at the entrance and exit of the collision cell was set at 50 V to provide an extraction voltage for the derived reaction products, which were mass-analyzed with the second quadrupole and detected with a continuous dynode electron multiplier.
Collision-induced dissociation (CID) experiments were carried out by first forming the desired ion in the electrospray source from a 1 mg/mL solution of methyl formate in the solvent, mass-selecting it with the first quadrupole, and performing collisions with argon target gas in the collision cell as a function of lab-frame collision energy (generally between 0 and 26 eV for all the CID experiments) [16].
2.2. Computational Methods
All calculations were carried out using the GAUSSIAN 16 suite of programs [17]. Structures were optimized using the B3LYP density functional method with the 6-311+G(d,p) basis set [18,19]. Transition states were confirmed by the intrinsic reaction coordinate method in GAUSSIAN. Rice–Ramsperger–Kassel–Marcus (RRKM) theory was applied to calculate k(E) according to the following equation [20,21]:
where represents the reaction degeneracy, is Planck’s constant, is the number of internal states for the transition state at internal energy , and is the density of states for the reactant ion at internal energy as calculated via the Beyer and Swinehart direct count algorithm [22]. Our previous work modeling energy-resolved CID data employed a simple model in which the post-collision ions are assigned an effective temperature depending on the centre-of-mass collision energy, and thus a “thermal” internal energy distribution, according to the relationship:
3. Results
3.1. Solvent Cluster Ion/Methyl Formate Reactions
Representative mass spectra resulting from the ion–molecule reactions R1–R5 of proton-bound solvent clusters and neutral methyl formate (MF) are shown in Figure 1. Water = W, methanol = M, ethanol = E, and methyl formate = MF.
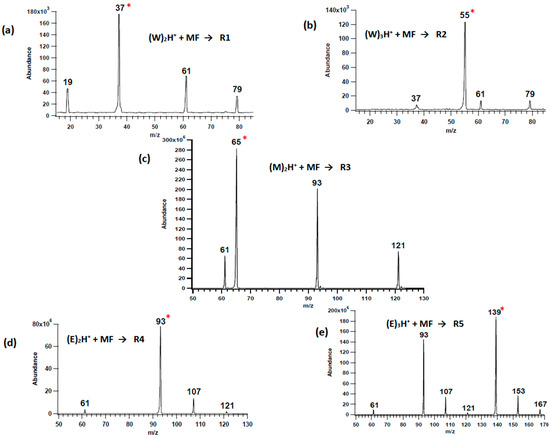
Figure 1.
Representative mass spectra of neutral methyl formate reacting with (a) water dimer ion (m/z 37, R1), (b) water trimer ion (m/z 55, R2), (c) methanol dimer ion (m/z 65, R3), (d) ethanol dimer ion (m/z 93, R4), and (e) ethanol trimer ion (m/z 139, R5). The red asterisk highlights the reacting cluster ion.
The mass spectra recorded from the reaction between methyl formate and water dimer ion (R1) showed several peaks: m/z 79, which represent the proton-bound water-methyl formate complex; m/z 61, which would nominally be protonated methyl formate, and m/z 19 ion due to WH+. The overall reaction scheme is summarized in Figure 2a at the B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory. Formation of the encounter complex is exothermic by 1.31 eV, and the resulting loss of W exothermic by 0.53 eV (relative to the reactants), which means the encounter complex is not observed in the experiment. Based on the relative energies, WH+ is most likely to arise from the dissociation of the initial (W)2H+ complex, as it would not be competitive to generate it from MF(W)H+.
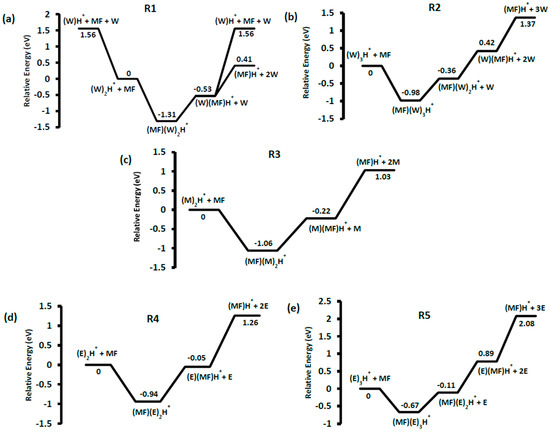
Figure 2.
Relative energy (B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p)) of the major product ions resulting from the reaction between neutral methyl formate with (a) the water cluster dimer and (b) the water cluster trimer, (c) the methanol dimer, (d) the ethanol dimer and (e) the ethanol trimer.
Similar peaks were observed in the ion–molecule reactions with the proton-bound water trimer ions (m/z 55) and from all of the solvent cluster ion reactions, Figure 1. In each case the initial encounter complex was not observed because the low binding-energy (Figure 2) results in a high enough rate constant for dissociation that there is not enough time or pressure to collisionally stabilize the complex (pressure in the collision cell, monitored at the inlet to the cell, was only 10−4 mbar). Evident from the computational results summarized in Figure 2 is that the highest binding-energy encounter complex is MF(E)2H+, 0.89 eV, but this is still not enough to allow it to be observed. RRKM calculations were performed for the solvent-loss reaction from each encounter complex, and the resulting k(E) vs. E curves are compared in Figure S1. For example, the calculated dissociation energy for the MF(W)2H+ complex was 0.78 eV. The rate constant for the dissociation is greater than 1 × 106 s−1, only 0.2 eV above this threshold. In a thermal system, the encounter complexes have an internal energy distribution that extends to between 0.60 and 1.00 eV (Figure S2), which means that they would be stable species at atmospheric pressure.
3.2. Unimolecular Reactions of Proton-Bound Solvent-MF Clusters
The most common primary reaction products discussed above are the proton-bound complexes between MF and a solvent molecule. We were able to independently generate MF(W)H+, MF(M)H+, MF(E)H+, MF(M)2H+, MF(E)2H+, and MF(E)3H+ in the electrospray source and obtain CID breakdown curves for each. They are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, along with initial assignments. A common dissociation product is protonated methyl formate as expected from the ion–molecule reaction results in Figure 1. We have previously investigated the unimolecular chemistry of MFH+, which leads to the formation of m/z 33 (loss of CO to form protonated methanol) [25]. In the case of MF(M)H+, a competing loss of CH4 is observed, which could form either a proton-bound complex between M and CO2, M(CO2)H+, or MF and OH, MF(OH)+. For MF(E)H+, the similarity between the proton affinities (PAs) of MF (782.5 kJ mol−1) and E (776.4 kJ mol−1) [26] leads to competing cleavage of both sides of the hydrogen bond, Figure 3c.
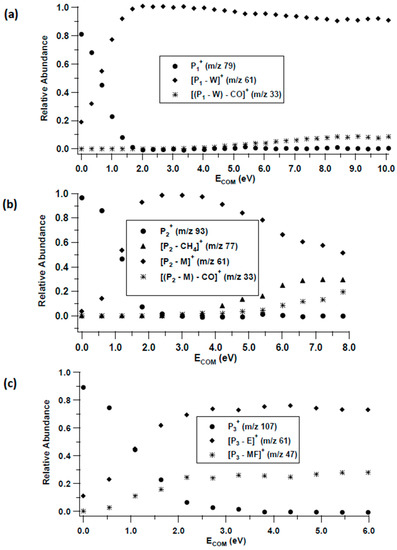
Figure 3.
CID breakdown curves of (a) P1+ = MF(W)H+, (b) P2+ = MF(M)H+, and (c) P3+ = MF(E)H+.
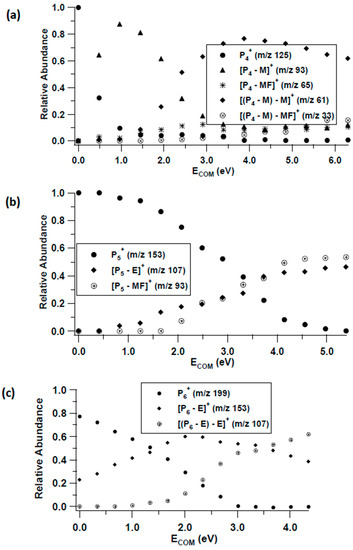
Figure 4.
CID breakdown curves of (a) P4+ = MF(M)2H+, (b) P5+ = MF(E)2H+ and (c) P6+ = MF(E)3H+.
The MF(M)2H+ cluster ion dissociates by sequential loss of both M molecules. A minor channel involves the loss of MF from the initially formed MF(M)H+ product ion, Figure 4a. As was observed with the MF(E)H+ dimer ion, the MF(E)2H+ trimer ion exhibits competitive loss of E and MF, with the tetrameric MF(E)3H+ ion undergoing sequential E loss.
Evident from the breakdown curves is that these cluster ions undergo facile decomposition. In each case (except MF(E)2H+) there is significant dissociation between 0 and 0.5 eV ECOM. Thus, even under the high-pressure limit of 1 atm, these ions can decompose.
The primary unimolecular reaction of these complexes is the simple dissociation of a hydrogen bond. Relaxed potential energy scans of this dissociation for two examples, MF(W)H+ and MF(E)3H+, were carried out to explore the potential for reverse activation barriers due to the possible structural rearrangement of the complexes, Figure 5. Evident from both scans is that these encounter complexes can easily fragment without a reverse barrier, which means that the relative product energies in Figure 2 direct the relative abundance of the competing reactions.
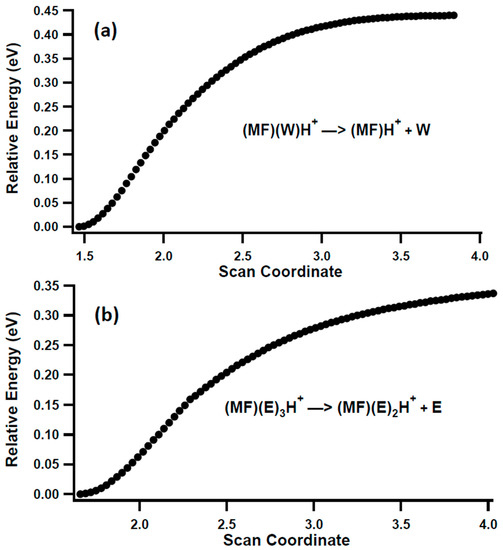
Figure 5.
Relaxed potential energy scan of the dissociation of (a) MFWH+ and (b) MF(E)3H+ at the B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p) level of theory.
Unique among the clusters is MF(M)H+, which undergoes a loss of CH4. This reaction was explored computationally, and the reaction pathway is shown in Figure 6 in comparison to the simple loss of methanol (and subsequent dissociation of MFH+). The MF methyl group first pulls away from the complex leading to the TS at 1.98 eV. It then interacts with the carbon H atom on the central HOC(H)O moiety leading to a molecule of methane. Due to the low binding affinity of the methane to the resulting ionic complex, it is very mobile and can wander the skeleton. The methane complex shown in Figure 6 at −0.49 eV only has a binding energy of 0.2 eV. The competing loss of methanol via a barrierless H-bond cleavage results in MFH+, which is due to the higher proton affinity of methyl formate (782.5 kJ mol−1) compared to methanol (754.3 kJ mol−1) [25], having an energy requirement of 1.25 eV. The MFH+ then dissociates by loss of CO [25]. The barrier heights to CH4 loss vs. M loss are consistent with the breakdown diagram that shows M loss to be the lower energy-threshold pathway.
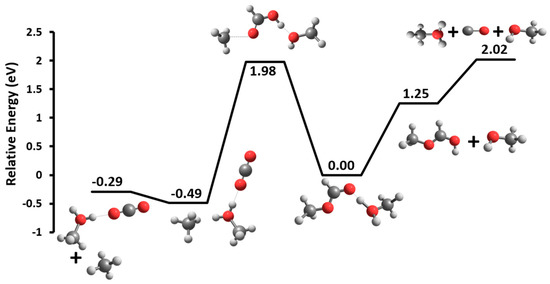
Figure 6.
B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p) minimum energy reaction pathways surface for the dissociation of MF(M)H+ (m/z 93).
The breakdown diagrams in Figure 3 and Figure 4 were modeled with the approach outlined in the computational procedures that is based on assigning an internal temperature to the post-collision ions, followed by adjusting the RRKM rate constant for each unimolecular reaction. The results are shown in Figure S3. As anticipated from the model, the results are not in quantitative agreement with the reaction energies in Figure 2, but there are qualitative comparisons. In the case of the competing methane loss channel from MF(M)H+ (Figure 6), the modeled difference in E0 for the two reactions is 0.32 eV, compared to the calculated difference of 0.73 eV. As expected, the RRKM-estimated difference in E0 for competing MF and E loss from MF(E)H+ is ~3 kJ mol−1, compared to the difference in proton affinity of MF and E of 6 kJ mol−1. For the trimeric precursor ions, the RRKM-estimated E0 values for the dissociation channels are in much better agreement with the theoretical estimates in Figure 2. The results are summarized in Table 1.
4. Conclusions
Ion–molecule reactions between methyl formate and proton-bound solvent clusters of water, methanol, and ethanol demonstrate that the primary reaction product is the formation of protonated methyl formate due to its higher proton affinity than water, methanol, and ethanol. Loss of a solvent molecule from the encounter complex occurs in a barrierless reaction in all cases. In a higher energy, minor reaction, the complex between methyl formate and methanol also undergoes loss of methane which forms a proton-bound complex between methanol and CO2. The results support the conclusion that when methyl formate interacts with atmospheric water, the encounter complexes (which were not observed in this experiment due to the low pressure in the reaction chamber) should be moderately stable at high (atmospheric) pressure as demonstrated by their calculated internal energy distributions. Protonated methyl formate will result, which can then undergo loss of CO.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app13031339/s1. Table S1: Additional reactions observed in the ion-molecule reactions explored in this study; Figure S1: RRKM k(E) vs. E curves for the dissociation of the ion-molecule encounter complexes; Figure S2: Vibrational internal energy distributions at 300 K for the encounter complexes in R1–R5; Figure S3: RRKM modeled breakdown curves for reactions in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D. and P.M.M.; methodology, M.D. and P.M.M.; software, P.M.M.; formal analysis, M.D. and P.M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.; writing—review and editing, M.D. and P.M.M.; supervision, P.M.M.; project administration, P.M.M.; funding acquisition, P.M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, grant number 2021-03175.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data may be obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Rivett, A.C.; Martin, D.; Gray, D.J.; Price, C.S.; Nickless, G.; Simmonds, P.G.; O’Doherty, S.J.; Greally, B.R.; Knights, A.; Shallcross, D.E. The role of volatile organic compounds in the polluted urban atmosphere of Bristol, UK. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Disc. 2003, 3, 769–796. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Bari, M.A.; Xing, Z.; Du, K. Ambient volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in two coastal cities in western Canada: Spatiotemporal variation, source apportionment, and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallington, T.J.; Hurley, M.D.; Maurer, T.; Barnes, I.; Becker, K.H.; Tyndall, G.S.; Orlando, J.J.; Pimentel, A.S.; Bilde, M. Atmospheric Oxidation Mechanism of Methyl Formate. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 5146–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Thomson, M.J. The chemical structures of opposed flow diffusion flames of C3 oxygenated hydrocarbons (isopropanol, dimethoxy methane, and dimethyl carbonate) and their mixtures. Combust. Flame 2004, 136, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.A.; Simmie, J.M.; Dagaut, P.; Cathonnet, M. Oxidation of dimethoxymethane in a jet-stirred reactor. Combust. Flame 2001, 125, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.; Cant, N.W.; Bromly, J.H.; Barnes, F.J.; Nelson, P.F.; Haynes, B.S. Formate species in the low-temperature oxidation of dimethyl ether. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, M.; Romanzin, C.; Michaut, X.; Jeseck, P.; Fillion, J.H. Adsorption of Organic Isomers on Water Ice Surfaces: A Study of Acetic Acid and Methyl Formate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 12920–12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goken, E.G.; Castleman, A.W., Jr. Reactions of formic acid with protonated water clusters: Implications of cluster growth in the atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Pavlov, J.; Attygalle, A.B. Fortuitous Ion–Molecule Reaction Enables Enumeration of Metal–Hydrogen Bonds Present in Gaseous Ions. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 3965–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, S.; Ryzhov, V. Ion–Molecule Reactions: Analytical and Structural Tool. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaida, V. Perspective: Water cluster mediated atmospheric chemistry. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Španěl, P.; Pavlik, M.; Smith, D. Reactions of H3O+ and OH− ions with some organic molecules; applications to trace gas analysis in air. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Proc. 1995, 145, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, N.G.; Smith, D. The selected ion flow tube (SIFT); A technique for studying ion-neutral reactions. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Phys. 1976, 21, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Španěl, P. Selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS) for on-line trace gas analysis. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2005, 24, 661–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, S.; DiMuzio, J.; Mungham, A.; Roy, J.; Hassan, D.; Renaud, J.; Mayer, P.M. Reactions of Atomic Metal Anions in the Gas phase: Competition between Electron Transfer, Proton Abstraction and Bond Activation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 14006–14012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooks, R.G. Collision Spectroscopy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Rev. B.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, T.; Mayer, P.M. Statistical RRKM/QET Calculations in mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 8, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Baer, T.; Hase, W.L. Unimolecular Reaction Dynamics, Theory and Experiments; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, T.; Swinehart, D.R. Number of Multiply-Restricted Partitions [A1] (Algorithm 448). ACM Commun. 1973, 16, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.M.; Martineau, E. Gas-phase binding energies for non-covalent A[β]-40 peptide/small molecule complexes from CID mass spectrometry and RRKM theory. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 5178–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, J.B.; Martineau, E.; Mironov, G.G.; Berezovski, M.V.; Mayer, P.M. The collaborative role of molecular conformation and energetics in the binding of gas-phase non-covalent polymer/amine complexes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diedhiou, M.; Mayer, P.M. Fate of Protonated Formates in the Gas Phase. J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 125, 5096–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, E.P.L.; Lias, S.G. Evaluated Gas Phase Basicities and Proton Affinities of Molecules: An Update. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1998, 27, 413–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
