Abstract
Implantable medical devices (IMDs) necessitate a consistent energy supply, commonly sourced from an embedded battery. However, given the finite lifespan of batteries, periodic replacement becomes imperative. This paper addresses the challenge by introducing a wireless power transfer system designed specifically for implantable medical devices (IMDs). It begins with a detailed analysis of the four conventional topologies. Following this, the paper provides a thorough explanation for choosing the PS topology, highlighting its advantages and suitability for the intended application. The primary parallel capacitance necessitates power from current sources; thus, a Class-E amplifier was implemented. Additionally, the selected circuit was engineered to deliver 1 W at the biocompatible resonance frequency of 13.56 MHz. The delineation of the resonance parameters hinges on multifaceted solutions, encompassing bifurcation-free operation and the attainment of peak efficiency. To ensure the feasibility of the proposed solution, a Differential-Evolution-based algorithm was employed. The results obtained from simulation-based evaluations indicated that the system achieved an efficiency exceeding 86%. This efficiency level was maintained even in the face of frequency fluctuations and variations in the coupling between the coils, thereby ensuring stable operational performance. This aligns seamlessly with the specified application prerequisites, guaranteeing a feasible and reliable operation.
1. Introduction
Implantable medical devices (IMDs) are used for monitoring physiological signs, therapeutic functions, and the treatment of chronic diseases [1,2,3,4]. According to [3,4], in 2019, about 10-million people worldwide depended on implantable cardiac pacemakers, and this number has grown by about 15% per year. Most IMDs use built-in batteries for their operation, and for fully IMDs, the battery replacement is performed through a surgical procedure [1,2,3,4]. Battery replacement through a surgical procedure has the potential for infection and generates patient anxiety, and during battery replacement, the IMD must be turned off [1]. Based on these prerogatives, a wireless power transfer system (WPT) becomes very interesting for charging implantable devices; after all, this would significantly reduce the number of surgical procedures for replacing batteries, increasing the lifespan of the device and allowing operation during battery recharging [3,4,5]. Currently, wireless power transfer is being used in IMDs through a near-field resonant inductive coupling (NRIC) [4]. Some examples would be cochlear implants, whose function is to restore hearing in patients with hearing loss, ocular and retinal implants, whose function is to restore vision in patients with visual impairment, and neurostimulator implants, used to restore motor and sensory function [4,6].
Basically, in an application of WPT in IMDs, the primary transmitting coil is positioned close to the patient’s skin. From the circulation of a time-varying current, a magnetic field is induced in the receiving coil, implanted next to the load, and in this way, current is produced to charge the device [7]. However, applying WPT to IMDs brings with it some concerns. A serious restriction, related to biocompatibility, concerns the exposure of living beings to the electromagnetic field and the specific absorption rate (SAR) of tissues [4,8]. In addition to biological factors, it is essential to ensure operational stability and acceptable efficiency to make the application safe and viable.
In general terms, WPT classical compensation topologies are named series–series (SS), series–parallel (SP), parallel–series (PS), and parallel–parallel (PP). The main advantages of these topologies are the reduced number of elements and the consequent implementation simplicity. However, despite the reduced number of parameters, in order to achieve a good performance with classical topologies, a rigorous selection of the elements that will compose the circuits is essential. Based on this selection, the efficiency can be maximized and situations of instability can be avoided [9].
The inductive power transfer applied to battery charging has two stages, which are the constant current charging process followed by constant voltage charging. Charging starts in constant current mode while the battery voltage gradually increases; once the battery voltage reaches its maximum charging voltage value, charging switches to constant voltage mode, so the current decreases considerably. Charging ends when the current in the battery reaches a specific value. Since batteries are considered to have a variable load during the charging process, there is a significant fluctuation in the output voltage; therefore, a converter is needed to regulate its output precisely in order to implement charging [10,11,12].
In this paper, the authors intended to demonstrate that classical topologies with an input current source are more stable in the face of variations in the load, due to the charging process, as well as the coupling factor variation, and also vary little in terms of output power and input current. A first step is to carry out an in-depth review of the four classical topologies of inductive resonant coupling. After clarifying all the advantages and disadvantages of each, it is possible to justify the application of the PS topology in IMDs.
Commencing with the primary and secondary inductances, the choice of resonant components is influenced by multi-criteria decision-making processes. Consequently, a subsequent phase of this study involved the implementation of an algorithm based on Differential Evolution (as referenced in [13]). This algorithm is aimed at determining inductances and capacitances that are viable both technically and practically.
Presently, a diverse array of bio-inspired optimization techniques are utilized across various engineering disciplines, including power flow analysis. Notable among these are the Artificial Hummingbird [14], Prairie Dog [15], Marine Predators [16], and Slime Mold Algorithms [17], along with the Differential Evolution algorithm. Although each of these methods demonstrates commendable accuracy and convergence speed, the Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm has been specifically selected for this research. This choice is attributable to DE’s rapid convergence, high precision, straightforward implementation process, and proficient handling of constraints.
With a focus on experimental validation, other practical considerations must be taken into account. Topologies with series compensation on the primary have the great advantage of being able to operate from a voltage source at the input, avoiding the need for other stages, which could compromise the overall performance of the system. On the other hand, with parallel compensation in the primary, the circuit must be powered by a current source, which, in a way, makes the execution of the project difficult and can compromise the overall performance if an intermediate stage is necessary [18]. However, although parallel compensation in the primary brings with it the mentioned disadvantage, other technical advantages may justify the application of this topology.
In this paper, in order to circumvent the limitation of primary parallel compensation, it was decided to feed the chosen circuit through a Class-E amplifier. The Class-E amplifier stands out for its topological simplicity and for its good performance at MHz or GHz frequencies [19]. An aggravating factor of this application lies in the fact that the Class-E amplifier is highly sensitive to parametric variations, that is small variations in the resonant elements or in the load can impair its operation [20].
The results revealed that the Differential Evolution algorithm employed in this study precisely selected parameters that enabled the system to operate with an efficiency exceeding 94%. This efficiency level demonstrated notable stability against variations in frequency and coil coupling. Additionally, considering the incorporation of a Class-E power amplifier for generating alternating current, the system’s overall efficiency was maintained above 86%.
2. Classical Topologies
2.1. Fundamental Concepts
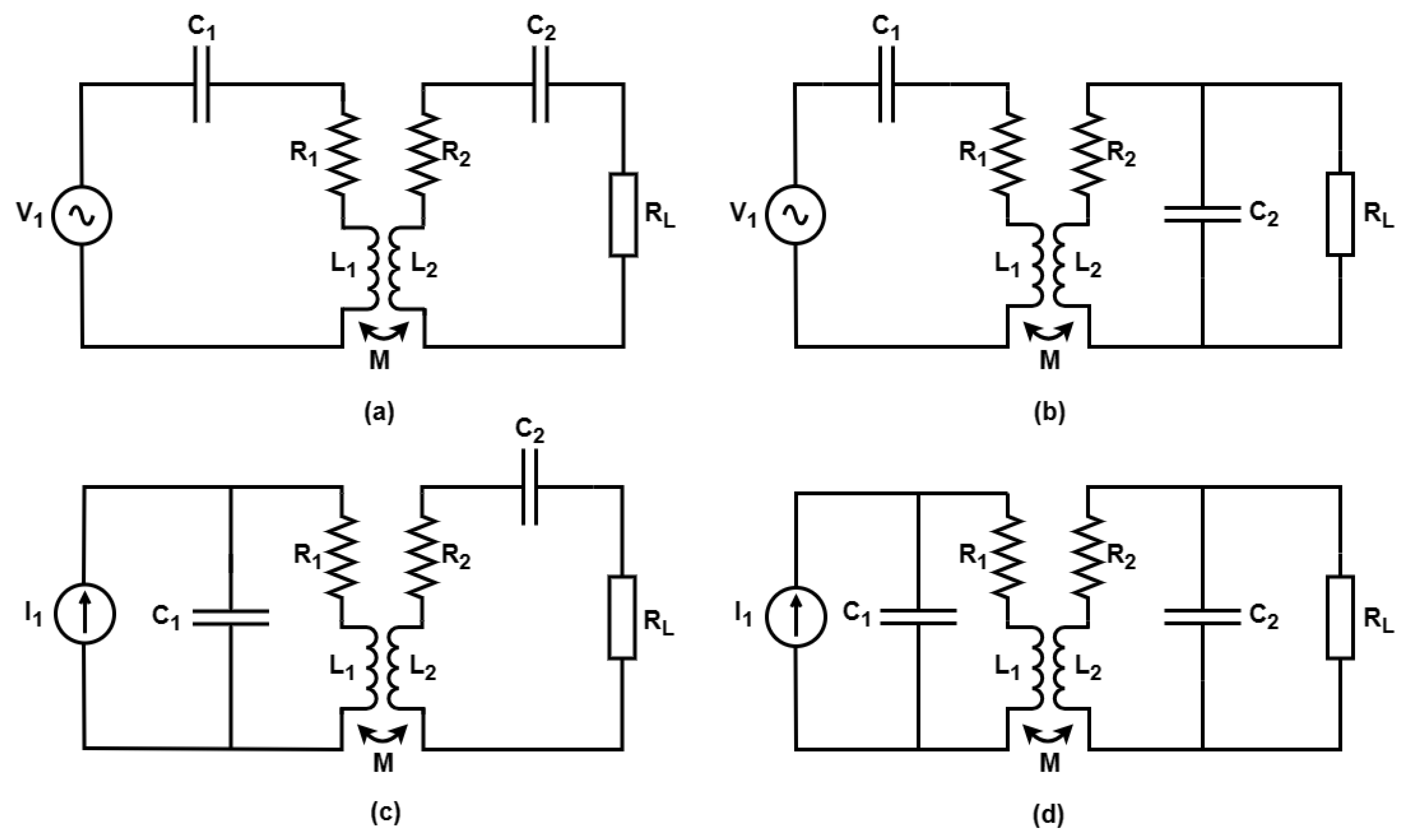
To facilitate the transmission of the desired active power in a wireless power transfer (WPT) system, a significant requirement arises for a substantial reactive power component. This necessity underscores the immediate need for compensation strategies, as elucidated in [9]. One of the most-straightforward approaches to achieve this compensation is by employing classical topologies, as discussed in [21]. In the context of the four topologies being examined in this study, the transmitting segment comprises a capacitance component (C1) arranged either in series or parallel with a coil, characterized by its winding impedance, composed of an inductance (L1) and a resistance (R1). Similarly, the receiver section consists of a coil with a winding impedance that encompasses an inductance (L2) and a resistance (R2), with an associated capacitance (C2) configured in series or parallel with the secondary coil. Regardless of the specific topology being considered, a load resistance (RL) is positioned at the output of these circuits. The magnetic coupling between these coils is realized through mutual inductance (M). Visual representations of these four topologies are provided in Figure 1.
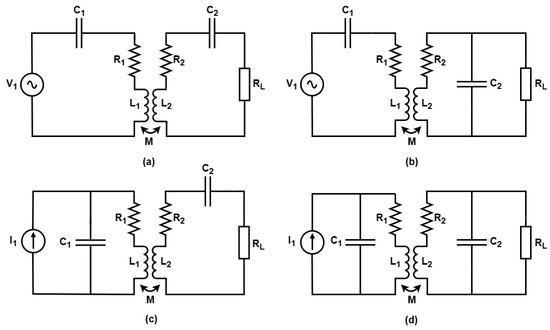
Figure 1.
Classical compensation topologies: (a) SS; (b) SP; (c) PS; (d) PP.
Figure 1 confirms that topologies with series compensation on the primary side are powered from voltage sources (Figure 1a,b), which considerably simplifies the implementation. Topologies whose primary compensation occurs through parallel capacitance (Figure 1c,d) are powered by current sources. This makes the implementation more laborious and, in most cases, leads to topological variations to achieve compatibility between a voltage source and the circuits in question [9].
At frequency , the equivalent impedance (Z1) must have its imaginary portion compensated for C1; consequently, all reactive demand is eliminated. For the four classical topologies, Table 1 summarizes the equations of C1, the theoretical efficiency (), and the equivalent impedance (Z1). It is interesting to note that, except for the SS topology, the primary compensation depends on mutual inductance. That is, considering that the inductances L1 and L2 do not change, C1 also depends on the coupling factor . Another relevant fact is that the efficiency does not depend on the capacitive elements; however, for topologies with parallel resonance in the secondary, even for high frequencies, will be affected by L2 and M.

Table 1.
Equations for the topologies, considering and .
2.2. Design for the Different Topologies
With a view toward low-power devices, a rated power (PL) of 1 W was chosen as a design parameter [22]. Assuming that a rechargeable lithium-ion cell has a terminal voltage between 3.5 and 3.7 V [22], the load voltage (VL) was defined as 3.6 V. For the resonance frequency, respecting biocompatibility restrictions, the frequency (fr) of 13.56 MHz was chosen, and a value was estimated of 0.25 as the design coupling factor ().
In order to identify the L1 and L2 pairs that correspond to the system’s maximum efficiency point, a range of inductance combinations from 0.01 H to 10 H was chosen, with intervals of 0.01 H. Based on these data, the efficiency behavior of the classical topologies is presented in Figure 2.
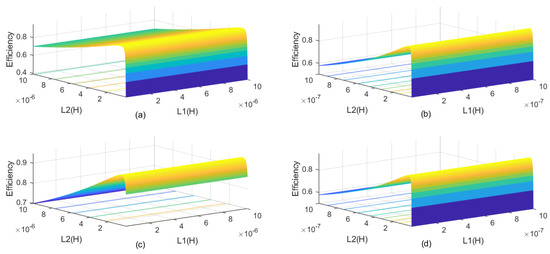
Figure 2.
Efficiency as a function of coil inductances: (a) SS; (b) SP; (c) PS; (d) PP.
As depicted in Figure 2, the choice of L2 is crucial to achieve good efficiency. On the other hand, the influence of L1 is neglectable on the efficiency, and as long as it does not imply other constraints, it is reasonable to arbitrate its value as being identical to that of L2. In order to obtain the system’s maximum efficiency point, according to the values obtained in Figure 2, the inductances L1 and L2 were selected. The values of C1 and C2 were calculated, as well as the mutual inductance and efficiency, based on the equations in Table 1. Table 2 shows a summary of the parameters calculated for the different topologies. Loss resistances R1 and R2 were calculated as a proportionality rule in relation to the inductances.

Table 2.
Design parameters.
2.3. Bifurcation Phenomenon
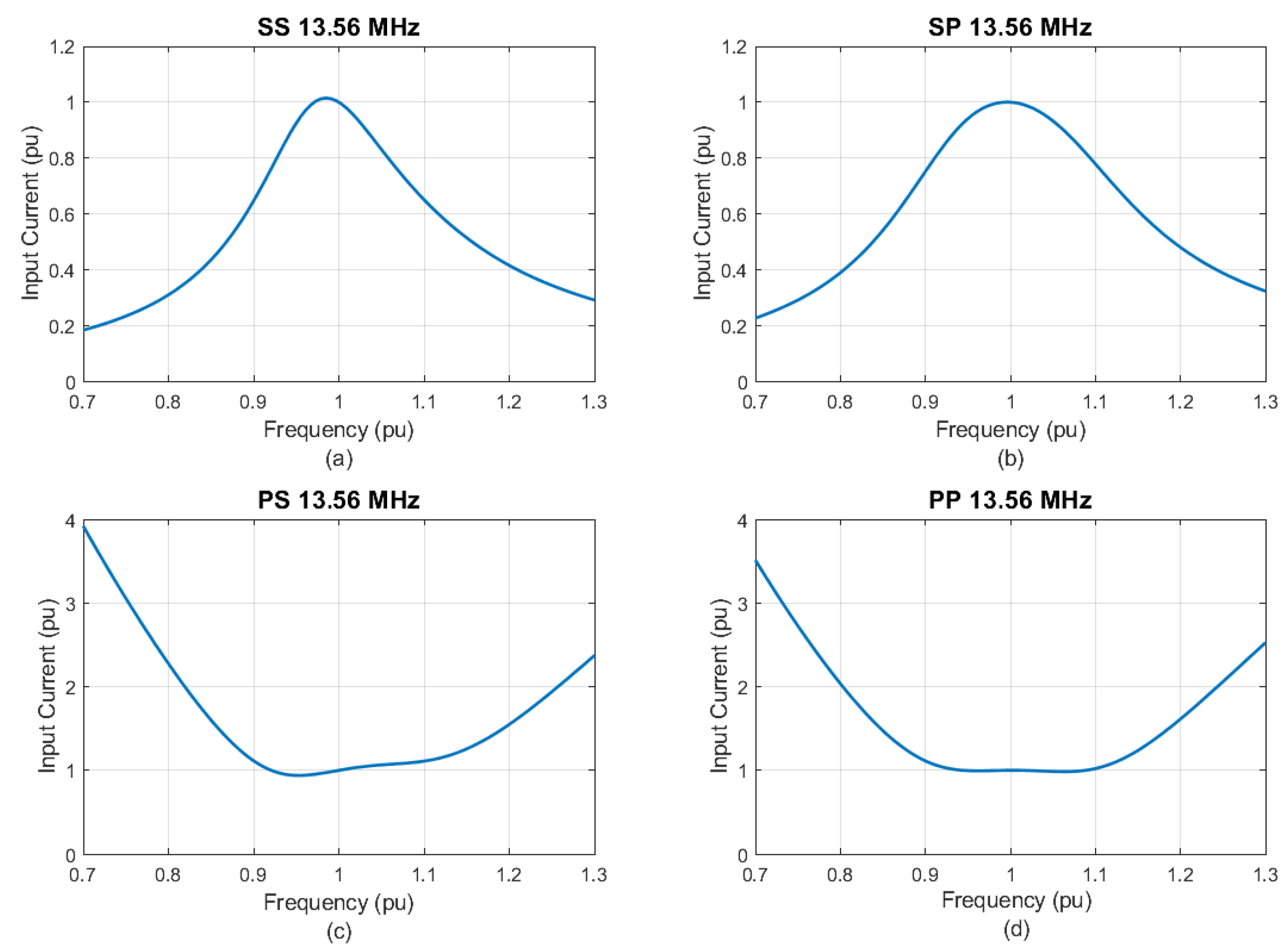
The system behavior was verified regarding deviations from a pre-established resonance, due to the practical difficulties of obtaining identical inductive and capacitive values to the designed ones. This type of analysis is necessary to evaluate the stability of the system through frequency variations. Thus, from the equations defined in Table 1 and the values presented in Table 2, the transmitter current behavior (I1) was evaluated for frequency oscillations of ±30% in relation to the base frequency. The results obtained are shown in Figure 3.
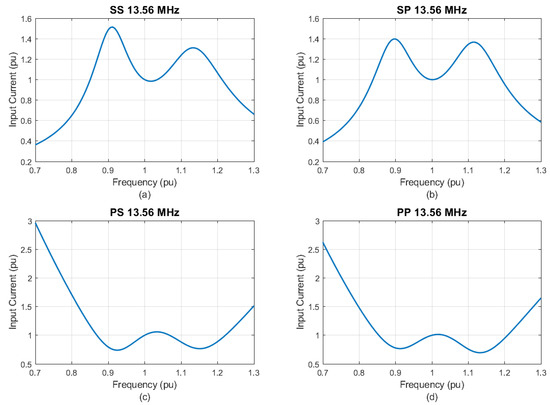
Figure 3.
Input current as a function of frequency variations: (a) SS; (b) SP; (c) PS; (d) PP.
Practical projects prove that the resonance frequency varies around 10% due to tolerances in the circuit parameters [9]. Taking that into consideration, as shown in Figure 3, for the SS topology, a reduction of 10% on the frequency of operation resulted in an input current 50% higher than the expected one for 13.56 MHz. A similar behavior was observed for the SP topology; the input current rose 40% for frequency variations of up to 10%. The obtained values were found to be impractical and could potentially jeopardize the integrity of the physical project. Conversely, both the PP and PS topologies demonstrated a significant reduction in the input current, achieving a decrease of approximately 70% even with oscillations reaching up to 10%.
The operation of a bifurcated system can be catastrophic for the project. However, respecting some criteria, the phenomenon can be eliminated, minimizing operational risks and ensuring stability in energy transfer [9]. As shown in Table 3, for stable operation, it is necessary to meet the criteria based on the primary and secondary quality factors Qp and Qs, respectively.

Table 3.
Bifurcation criteria [9].
To address this undesired issue, it is necessary to select new design parameters. One viable strategy involves adjusting the L2 values to mitigate instability, as outlined in Table 4. While this approach may require operating outside the point of maximum efficiency, careful consideration can help minimize any significant impact on energy transfer. Table 4 provides a summary of the new parameters for the input current with bifurcation reduction.

Table 4.
New design parameters to minimize the bifurcation phenomenon.
From the new parameters, as presented in Figure 4, the SS (a) and SP (b) topologies became stable for frequency variations. In addition, the PS and PP topologies brought a peculiar behavior. For frequency variations of up to 10%, the input current was maintained practically constant, which is a very attractive feature for practical implementations. After the selection of the parameter values and confirming the minimization of the bifurcation phenomenon, a study was undertaken to evaluate the feasibility of the previously estimated coupling factor (). This assessment was conducted using the student version of Ansys Maxwell®. The inductances L1 and L2 were designed in a spiral–planar geometry, as depicted in Figure 5. This particular geometry was selected due to its associated beneficial characteristics, which include the ease of implementation, symmetrical behavior, and a robust coupling factor, especially in scenarios involving misalignment.
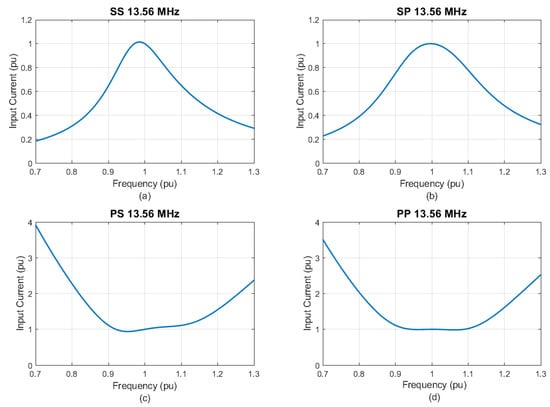
Figure 4.
Input current without bifurcation. (a) SS. (b) SP. (c) PS. (d) PP.
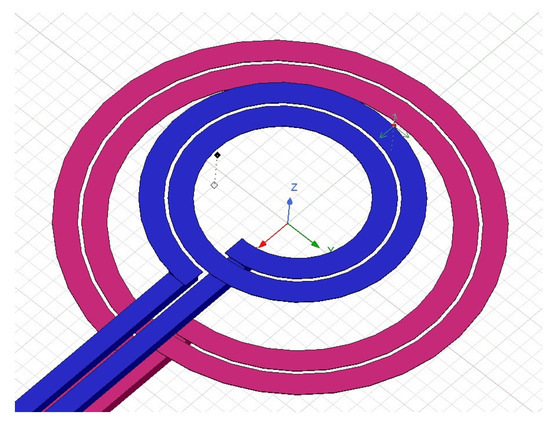
Figure 5.
Transmitter and receiver coils simulated in the software Ansys Maxwell®.
The study demonstrated that, for the coils designed, a coupling factor of 0.25 was achieved at a distance of 4 mm. This value aligns with the anticipated separation distance between the transmitting and receiving coils, specifically considering their application in implantable medical devices. Consequently, the obtained value of the coupling factor was validated and endorsed for this specific use.
2.4. Coupling Factor
One of the concerns in wireless transfer is to evaluate the behavior of the system through variations in the coupling factor (). The coils are subjected to vertical and horizontal displacements in these applications. In relation to implantable devices, the situation is even more complex. In addition to the coils’ alignment unpredictability, the system is exposed to a medium of organic tissues and liquids of different compositions.
Figure 6 shows the input current behavior from the maximum misalignment ( = 0) to situations where the coupling coefficient is about 20% above the nominal condition. For topologies with series compensation in the transmitter side, as the coupling factor decreases, the input current increases considerably. Therefore, unless a strict primary current control is implemented, the system will be driven to incompatible current levels, making the implementation unfeasible. On the other hand, the PS and PP topologies are less sensitive to reductions in the coupling factor since the input current decreases with the distance between the coils. This characteristic makes them strong candidates for applications in which control simplicity and good stability are needed.
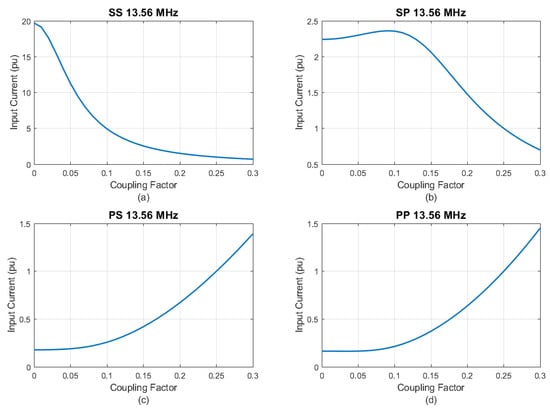
Figure 6.
Input current as a function of . (a) SS. (b) SP. (c) PS. (d) PP.
2.5. Input Impedance Behavior
As concluded before, the PS and PP topologies presented a convenient behavior in relation to the reduction of the coupling coefficient. However, the use of parallel compensation in the primary makes the use of voltage sources to supply the circuit unfeasible. In applications subject to biocompatibility restrictions, sources that oscillate in the order of MHz are not easily implemented by means of conventional current inverters. Therefore, a proposal that appears feasible is the use of Class-E amplifiers. The major drawback of using amplifiers as current sources is that they must be designed considering the load impedance. Thus, the evaluation of Z1 becomes essential, as the parametric variations of the circuit can compromise the impedance matching between the amplifier and the wireless transfer circuit. Figure 7 and Figure 8 show, respectively, the magnitude and angle of the input impedance as a function of frequency. Figure 9 and Figure 10 show, respectively, the impedance modulus and angle as a function of the coupling coefficient.
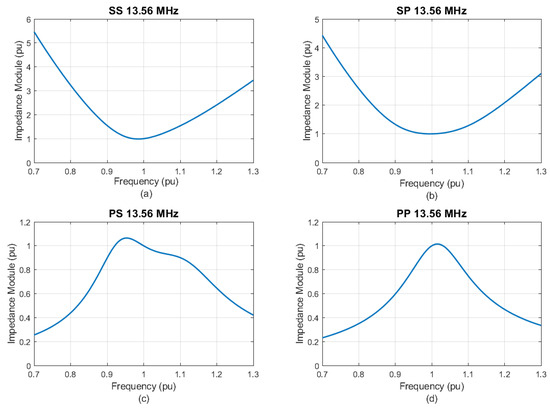
Figure 7.
|Z1| as a function of frequency. (a) SS. (b) SP. (c) PS. (d) PP.
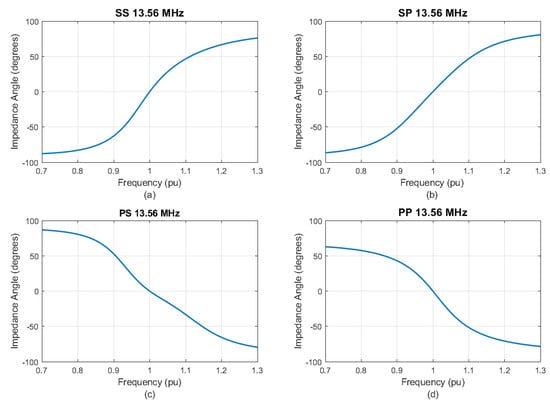
Figure 8.
Angle of Z1 as a function of frequency. (a) SS. (b) SP. (c) PS. (d) PP.
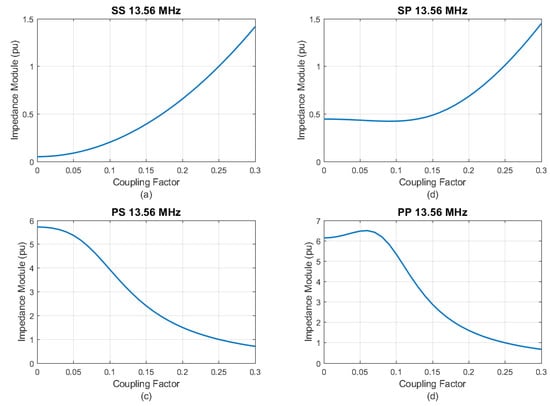
Figure 9.
|Z1| as a function of . (a) SS. (b) SP. (c) PS. (d) PP.
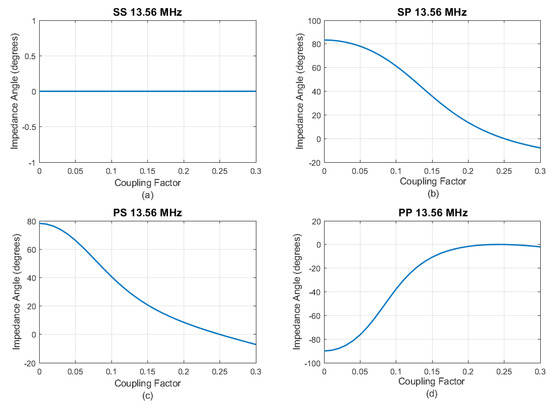
Figure 10.
Impedance angle as a function of . (a) SS. (b) SP. (c) PS. (d) PP.
Through Figure 7, it is notable that, at frequencies different from nominal, the impedance modulus tends to increase for the SS and SP compensations and to decrease for PS and PP. In Figure 8, one can conclude that, for the SS and SP topologies, the load tends to be inductive for frequencies lower than nominal and capacitive for higher. On the other hand, Figure 8c,d show that, for the PS and PP topologies, for frequencies lower than the design frequency, Z1 presents an inductive behavior and, for higher frequencies, a capacitive behavior.
With respect to the behaviors of the topologies in relation to variations in the coupling coefficient, the data suggest that topologies exhibiting parallel resonance in the primary, as depicted in Figure 9c,d, exhibit an increase in their impedances under conditions where the coupling coefficient, , is diminished. Given that reductions in the coupling coefficient can be anticipated due to commonplace operational misalignment and offsets, this characteristic behavior confers a marked advantage to these particular topologies.
In Figure 10, it is noteworthy to highlight the SS topology’s consistent null angle throughout the entire range of . This conclusively demonstrates that fluctuations in mutual inductance do not introduce imaginary components to the equivalent impedance. Further, based on the observations from Figure 10b–d, it can be inferred that coil misalignments or displacements manifest as discernible inductive or capacitive segments in the input current.
3. Differential Evolution-Based Parameter Selection
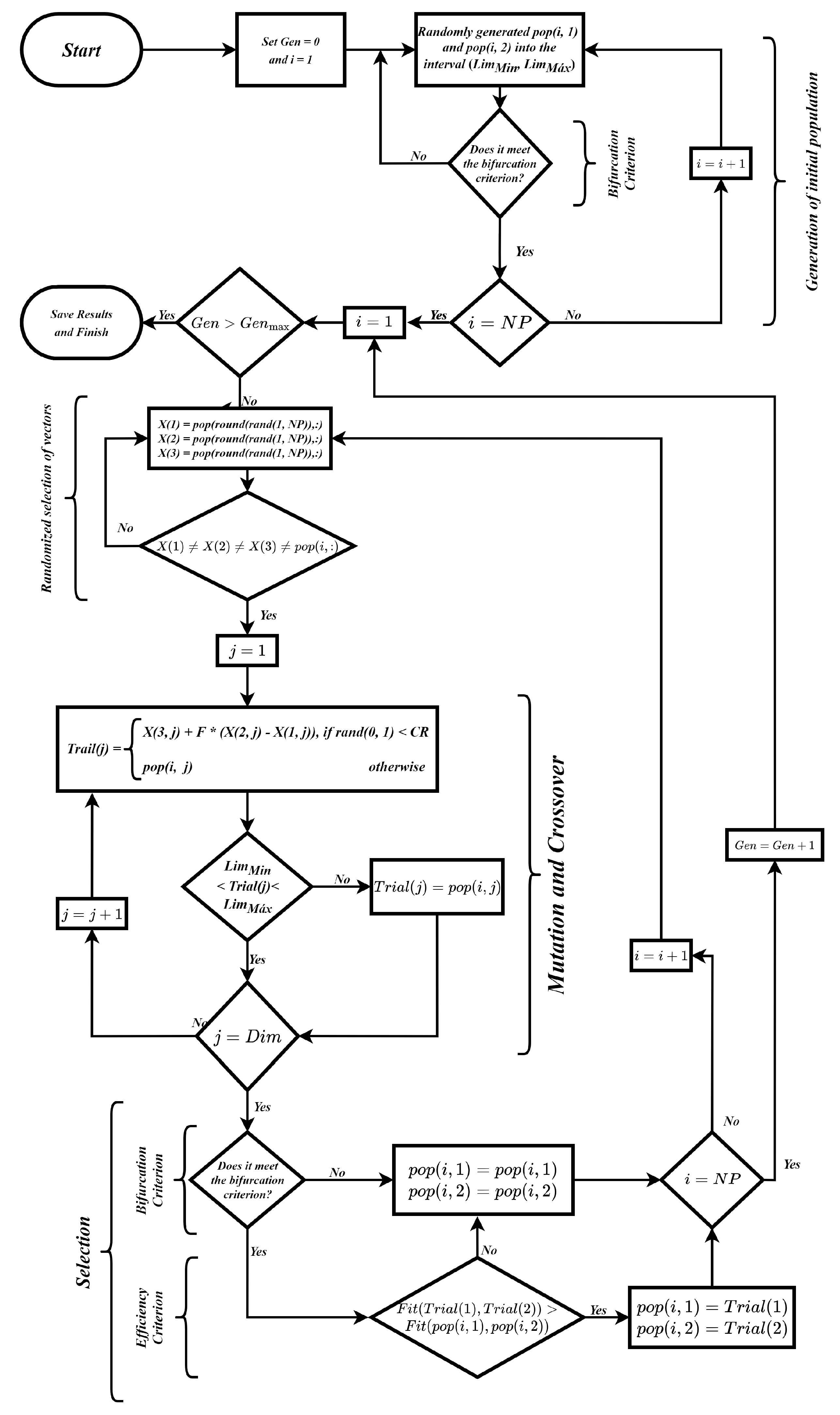
Aiming at the selection of optimal parameters for the classical wireless energy transfer topologies, an algorithm developed from the Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm was used. DE is a meta-heuristic based on the process of species evolution, which consists of generating an initial random population, mutating, crossing characteristics between individuals, and selecting the best individuals at the end of each generation [13]. For the proposed application, some changes were made in the pseudocode of the presented algorithm.
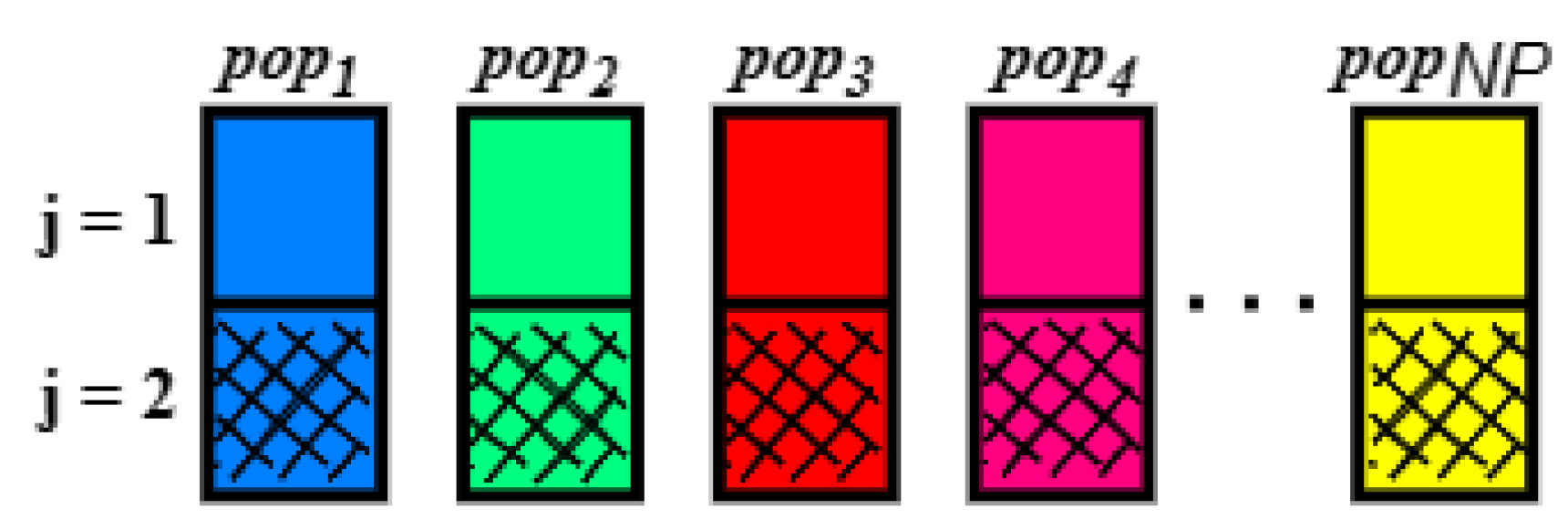
First, an initial population is defined, composed of NP vectors of randomly chosen parameters, pop(i, 1) and pop(i, 2), in the interval between the minimum of 0.01 H and the maximum of 100 H, which correspond to the values of the primary and secondary inductances. The population is created from a uniform probability distribution and follows a natural evolution with the number of individuals fixed during the optimization process. It is noteworthy that the population must meet the non-bifurcation criteria. That is, if the generated population presents bifurcation, it will be discarded, and a new population will be formed. As shown in Figure 11, the generation of the initial population is illustrated.
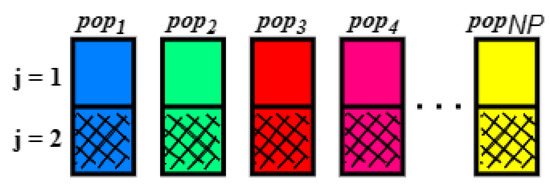
Figure 11.
Initial population generation.
In one generation, three individuals are selected, X(1), X(2), and X(3), obtained from a randomly established population, in an interval from 1 to NP. Another vector, named the target vector pop(i, j), is also selected randomly. In the first generation, therefore, the target vector and the vectors X(1), X(2) and X(3) are selected to be part of the mutation, crossover, and selection steps. The four individuals must be distinct from each other, meeting the condition that , as illustrated in Figure 12.
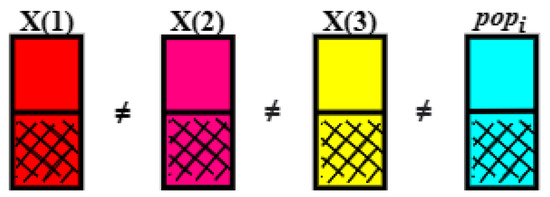
Figure 12.
Vector randomly selected.
In the context of evolutionary computation, mutation can be defined as a change or perturbation with a random element [23]. From the random selection of three individuals of a generation G, X(1), X(2), and X(3), a vector of mutated parameters (V) is obtained. The differential mutation operation is performed according to (1).
In accordance with the operation, X(2) X(1) is defined as the difference between the parameter vectors. Let F be a real constant [0, 2], called the mutation factor. This factor is responsible for controlling the size of the step to be performed, that is orienting the vector amplitude. The weighted vector difference is added to the third individual X(3) as illustrated in Figure 13.
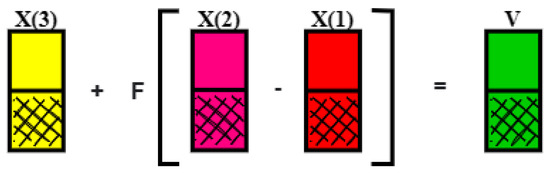
Figure 13.
Mutation operation.
The mutated vector V is combined with the target vector, pop(i, j), i.e., an arbitrarily chosen target vector, and the combination results in the trial vector. This process is called crossover, increasing the diversity of mutated individuals. The algorithm performs the combination respecting the real crossover constant cr [0, 1]. Let rand be a random scalar [0, 1]; if rand is less than the cr, the muted vector parameters are selected; otherwise, the target vector is selected. The crossover operation is exemplified in Figure 14. It is noteworthy that, in this paper, the mutation and crossover operations were performed concurrently.
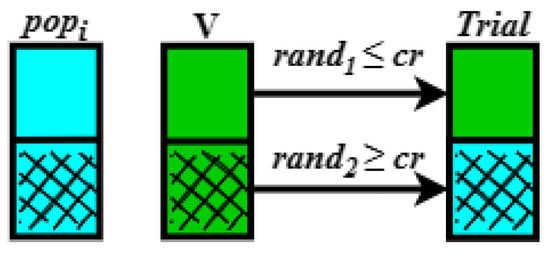
Figure 14.
Crossover operation.
After the mutation and crossover of the individuals, the selection of the best individuals is carried out. Initially, the value of the characteristics was analyzed, and it was verified if the value was within the range of 0.01 H to 100 H. If it was within the range, the characteristic was maintained; otherwise, it was replaced by the characteristic of the previous individual. Subsequently, the bifurcation criterion was analyzed. If the values obtained presented the bifurcation phenomenon when implemented, they would be replaced by the characteristics of the individual of the previous generation; otherwise, they would be maintained.
Finally, the fitness function, in this case, the overall efficiency, was analyzed. Therefore, it was verified whether the value obtained with the new characteristics was higher or lower than the value obtained with the past characteristics. If it was superior, the new individual would keep its characteristics. Otherwise, the new individual would assume the characteristics of the individual of the previous generation. In this iterative framework, the mutation, crossover, and selection processes generate a new population in each cycle, continuing until the generation count aligns with the pre-set maximum or another stop criterion is achieved. The DE algorithm’s flowchart, as applied in the study, is showcased in Figure 15. Importantly, for a deeper, more-technical insight into the Differential Evolution algorithm proposed, the pseudocode is presented and detailed in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Differential Evolution algorithm. |
|
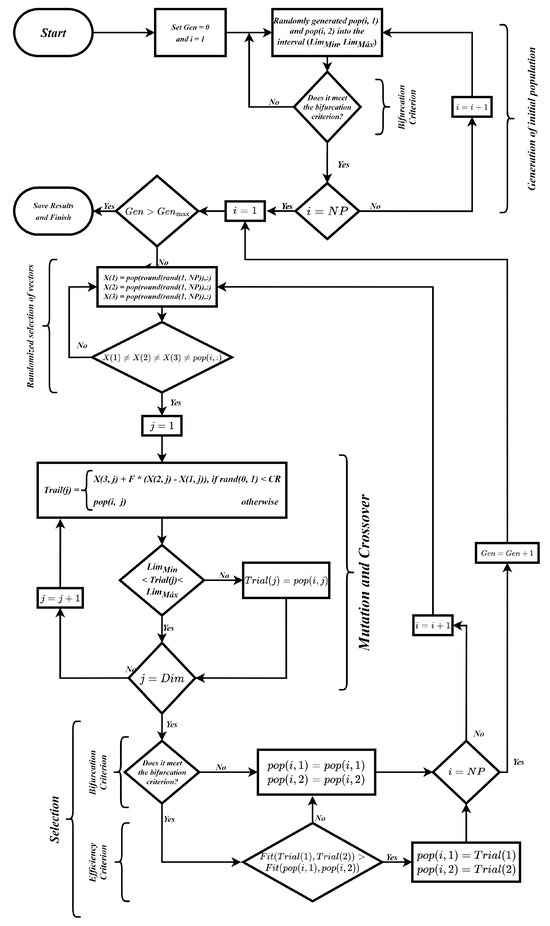
Figure 15.
Differential Evolution algorithm flowchart.
4. System Overview
The system implemented utilizes a parallel–series (PS) topology, powered by a current source. In this configuration, the correlation between the output power and the load is predetermined. Unlike most wireless power transfer (WPT) systems that are driven by inverters requiring at least four switches, our approach addresses the issue of significant switch losses in high-frequency applications. As an alternative to conventional inverters, a Class-E power amplifier (PA) was employed. This choice is particularly advantageous for low-power and very-high-frequency WPT applications. The Class-E PA demonstrates its efficacy even in dynamic charging scenarios, such as when there is misalignment between the transmitter and receiver coils [24,25].
This alternative exhibits notable characteristics, including a simplistic design, and conditions of zero voltage switching, as well as zero voltage derivative switching [25,26,27,28]. The Class-E power amplifier (PA) is capable of achieving efficiencies of approximately 90%, especially when operating at frequencies within the MHz range. However, it is important to note that the Class-E PA demonstrates sensitivity to variations in load [25].
In Figure 16, the Class-E power amplifier (PA) circuit is depicted on the left side, while the wireless power transfer (WPT) circuit is presented on the right side. The operating range of the Class-E PA was selected to be between 12 V and 14 V, thereby aligning with the predetermined voltage and power requirements at the load. The parameters of the circuit are concisely summarized in Table 5.
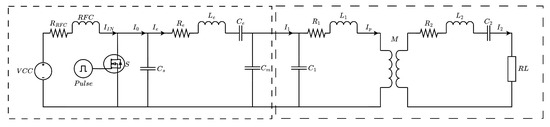
Figure 16.
Circuit schematic.

Table 5.
Circuit parameters.
5. Simulation Results and Discussion
A Differential Evolution algorithm is proposed to obtain the best values for the primary and secondary inductances, aiming to maximize the efficiency of the system. In Figure 17c, the curve of the efficiency of the best individual in relation to the number of generations of the Differential Evolution is presented. Note that the algorithm showed rapid convergence to the global maximum of 94.79% for the PS WPT stage efficiency.
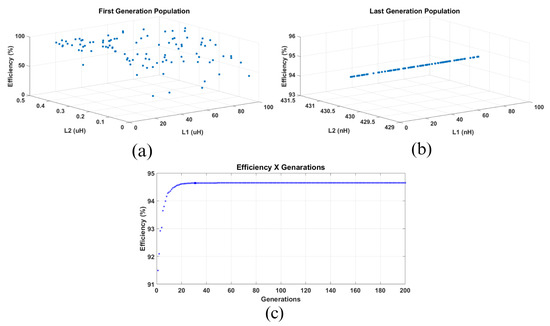
Figure 17.
Differential Evolution performance evaluation. (a) First generation population. (b) Last generation population. (c) Efficiency improvement across generations.
The initial population was generated within a predefined range. Figure 17a shows the distribution of the initial individuals. As expected, the position of the individuals was dispersed, since the population was randomly generated. Figure 17b shows the individual distribution after performing all iterative processes. Note that the position of all individuals converged to the global maximum, where L2 was equal to 430.2 nH. Since the efficiency dependency of L1 was neglected, the L1 values were distributed throughout the defined range.
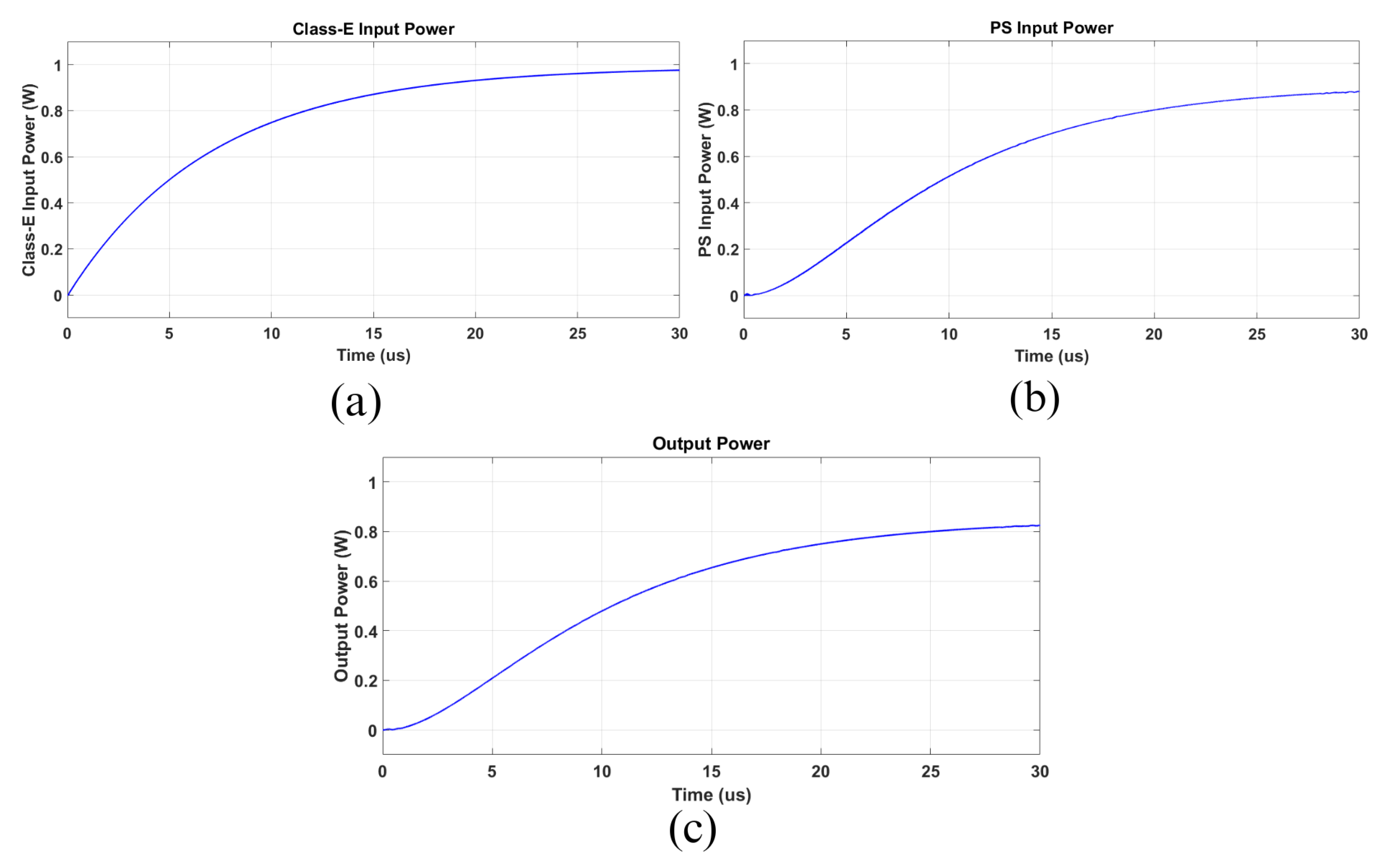
As mentioned before, the WPT circuit parameters were sized considering an output power of 1 W. However, aiming to evaluate the practical non-idealities and the effective losses in each stage depicted in Figure 16, a 1 W input power was imposed for the Class-E amplifier. Thus, the currents and voltages across the circuit elements, as well as the output power were expected to be lower than those previously calculated. Before analyzing the PS WPT circuit, it is reasonable to check the operation of the Class-E circuit. Looking at Figure 18, the input current IIN is depicted in (a). As observed, its value was slightly superior to 80 mA, draining about 1 W from the DC power source. In Figure 18b,c, the Ie and Cm currents prove the resonance at 13.56 MHz; however, a small DC level was present, which denotes some mismatch caused by the values’ divergences and dissipative elements; this behavior did not make the circuit operation unfeasible; however, it increased the switch losses due to the current peaks, a consequence of the remanent voltage noticed in Figure 18e. Figure 18d shows the Ce voltage, and it is important to note its peak value, which can reach almost 150 V, being important data for a practical design.
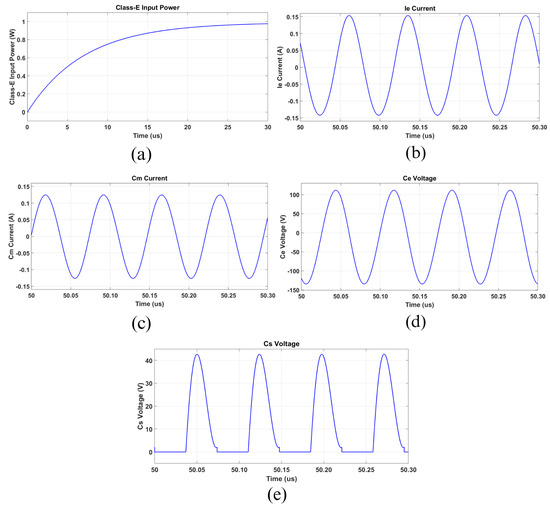
Figure 18.
Class-E circuit analysis. (a) DC source input current. (b) Le and Ce current. (c) Cm current. (d) Ce voltage. (e) Cs and switch drain–source voltage.
Carrying out the analysis of the circuit for the WPT part, it can be concluded that the current in the primary inductor added to the current in the primary capacitor resulted in the input current I1. Figure 19a,b illustrate the respective primary inductor and capacitor currents over time. The RMS currents in L1 and C1 were 311 mA and 306 mA, respectively. The current across all secondary elements (I2) is presented in Figure 19c. Due to the losses, the RMS value for I2 was slightly inferior to the expected one, about 256 mA, and the RMS voltage over RL was 3.3 V (Figure 19d). Subsequently, the voltage stresses over the capacitances C1 and C2 can be noticed in Figure 19e,f, respectively. The expected RMS voltages for the respective primary and secondary capacitances were close to 16.4 V and 9.4 V.
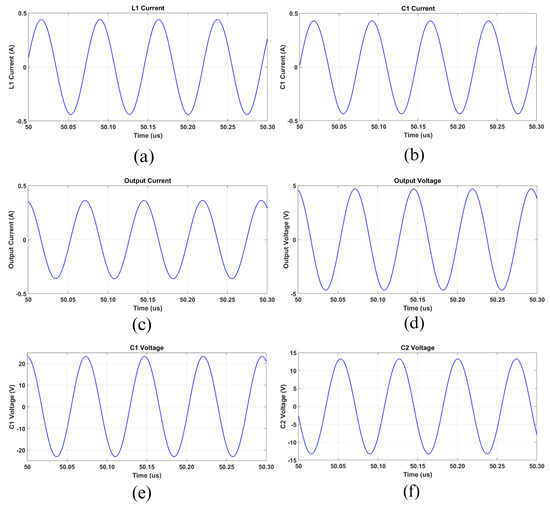
Figure 19.
PS WPT circuit analysis. (a) Primary coil current. (b) C1 current. (c) Secondary current. (d) Load voltage. (e) C1 voltage. (f) C2 voltage.
Figure 20 shows the active power drained in different parts of the circuit. In Figure 20a, the DC source input power is presented. As can be noticed, its value corresponded to 1.0 W. Figure 20b shows the power delivered to the PS WPT stage, which resulted in being about 0.91 W. Finally, the output power is depicted in Figure 20c, reaching 0.86 W. Based on the obtained values, it is possible to conclude that the Class-E part operated with an efficiency of 91%; the PS WPT part reached about 94%; the overall efficiency was near 86%. It is worth mentioning the Class-E efficiency was sufficiently good in comparison with the other current source circuits, and the PS WPT efficiency was close to that expected in the preliminary results presented in Table 4. In summary, the overall expected efficiency was significantly satisfactory for this range of power.
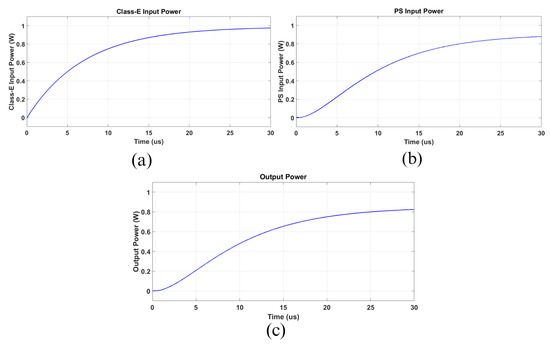
Figure 20.
Delivered active power. (a) From the DC power source. (b) To the PS circuit. (c) To the output load.
Based on the comprehensive analysis of the simulation results, we can assertively conclude that the system’s overall performance met, if not exceeded, the anticipated standards set forth for this project. The recorded values of the currents and voltages across the inductances and capacitances played a pivotal role in the system’s behavior. It is imperative to understand that these measurements are not just mere numerical results; they offer valuable insights that are instrumental for the judicious selection of components. By ensuring the components align with these values, we can guarantee optimal performance and reliability, fortifying the system’s robustness against potential anomalies or discrepancies in real-world applications.
6. Conclusions and Future Works
The present study provided a comprehensive assessment of a Differential-Evolution-assisted optimization of classical compensation topologies for 1 W current-fed IMD wireless charging systems with a biocompatible operating frequency of 13.56 MHz. This innovative approach aimed to indicate that the parallel–series compensation topology fed through a Class-E power amplifier was more stable in the face of coupling factor variation and also tended to reduce the input current despite a frequency oscillation of up to 10%. The system was optimized using a Differential Evolution algorithm in order to select optimal parameters that must provide non-bifurcation criteria, along with higher efficiency.
A wide review of the four classical topologies of inductive resonant coupling was made by evaluating their behavior in terms of frequency and coupling factor variations. Once having clarified all the advantages and disadvantages of each, the PS topology was selected. The Differential Evolution algorithm showed rapid convergence to the global maximum of 94.79% for the PS WPT stage efficiency. The values of the primary and secondary inductances obtained for L2 were equal to 430.2 nH; as the efficiency had no dependency on L1, the L1 value remained as previously selected, equal to 610 nH. The main results proved the good stability with an efficiency of around 94% of the PS WPT part. The Class-E PA developed achieved 91% efficiency, with the whole system standing above 86%.
The proposed system presents a potential path as a consistent energy supply for implantable medical devices, reducing the number of surgical procedures, also increasing the lifespan of the batteries and allowing operation during recharging. The results highlight the valuable role of the wireless charging systems in medical applications, considering biological factors so as to guarantee operational stability and appropriate efficiency, making the application safe and viable.
Future work will rely on evaluating the challenges of transitioning our idealized circuit to practical applications. It is paramount to consider the constraints posed by high-frequency operations. The high-frequency system necessitates sourcing suitable electronic components. GaN field-effect transistors emerge as a viable choice for Switch RDS, due to their capability to handle high switching frequencies and compatibility with the project’s current requirements. Subsequently, a low-side ultra-fast gate driver optimized for switching GaN FETs in high-speed scenarios is indispensable. A clock oscillator with a frequency of 13.56 MHz will also be required. Designing inductors for high-frequency operation presents its unique challenges. The advantage of high-frequency operation is that it necessitates significantly lower inductance values. This makes air–core designs, which eliminate core losses at high frequencies, attractive [29]. Planar inductors on printed circuit boards (PCBs) stand out as they support higher operational frequencies and offer the added benefits of reduced weight and size—factors critical for biomedical applications [30]. High-frequency winding losses in PCB planar inductors are substantially influenced by skin and proximity effects, given the specific geometry of the PCB planar winding conductors [30]. This can lead to increased high-frequency losses. Therefore, an inductor design that holistically considers winding losses, overall performance, and thermal issues becomes crucial [31]. Furthermore, accurate temperature predictions and management of the coupling inductors are vital, not just for the electrical attributes, but also for the overall reliability and performance of the WPT system—integral for any IMD application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, R.B.G.; validation, I.M.S.d.J., T.M.T., M.d.C.P., B.d.S.A. and R.L.R.S.; formal analysis, R.B.G., I.M.S.d.J. and T.M.T.; investigation, M.d.C.P., B.d.S.A. and R.L.R.S.; resources, I.M.S.d.J., T.M.T., M.d.C.P., B.d.S.A. and R.L.R.S.; writing—original draft preparation, I.M.S.d.J. and T.M.T.; writing—review and editing, R.B.G., I.M.S.d.J. and T.M.T.; supervision, R.B.G.; project administration, R.B.G.; funding acquisition, R.B.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financed by FNDE/MEC/PET—Tutorial Education Program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available as they are part of a dataset that is pending publication.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank the Federal University of Mato Grosso do Sul and the Brazilian Ministry of Education, which sponsored this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors affirm that there are no conflict of interest, including any commercial interests, related to this study.
References
- Kim, D.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Park, S.M.; Ahn, S. Design and Implementation of a Wireless Charging-Based Cardiac Monitoring System Focused on Temperature Reduction and Robust Power Transfer Efficiency. Energies 2020, 13, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaka, K.; Jacob, M.V. Implantable Devices: Issues and Challenges. Electronics 2013, 2, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Huang, S.; Deng, D. A wireless power transmission system with load regulation for implantable devices. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2020, 23, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Jegadeesan, R.; Guo, Y.X.; Thakor, N.V. Wireless Power Transfer Strategies for Implantable Bioelectronics. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 10, 136–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büyük, M.; Savrun, M.M.; İnci, M. Analysis and modeling of wireless power transfer supported by quadratic boost converter interfaced fuel cell power source. Int. J. Numer. Model. Electron. Netw. Devices Fields 2022, 35, e2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.R.; Pavuluri, S.K.; Cummins, G.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y. Wireless Power Transfer Techniques for Implantable Medical Devices: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.B.; Lin, C.K.; Wang, C.Y.; Cheng, Y.L. Design and Analysis of Dual-Band Resonance Inductive Coupling for Wireless Power Transfer and Near-Field Wireless Communication Applications. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 11, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y. Wireless Power Transfer for Implanted Medical Application: A Review. Energies 2020, 13, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Covic, G.; Stielau, O. Power transfer capability and bifurcation phenomena of loosely coupled inductive power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.B.; Tran, D.H.; Choi, W. Implementation of the Constant Current and Constant Voltage Charge of Inductive Power Transfer Systems With the Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology for Electric Vehicle Battery Charge Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 7398–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, W. Output Voltage Stabilization Control without Secondary Side Measurement for Implantable Wireless Power Transfer System. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE PELS Workshop on Emerging Technologies: Wireless Power Transfer (Wow), Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–7 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K.; Chen, Q. Design for Efficiency Optimization and Voltage Controllability of Series—Series Compensated Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential Evolution—A Simple and Efficient Heuristic for global Optimization over Continuous Spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Mirjalili, S. Artificial hummingbird algorithm: A new bio-inspired optimizer with its engineering applications. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 388, 114194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugwu, A.E.; Agushaka, J.O.; Abualigah, L.; Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H. Prairie Dog Optimization Algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 20017–20065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunkitti, S.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Premrudeepreechacharn, S. A Many-Objective Marine Predators Algorithm for Solving Many-Objective Optimal Power Flow Problem. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunkitti, S.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Premrudeepreechacharn, S. Multi-Objective Optimal Power Flow Problems Based on Slime Mould Algorithm. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gati, E.; Kokosis, S.; Patsourakis, N.; Manias, S. Comparison of Series Compensation Topologies for Inductive Chargers of Biomedical Implantable Devices. Electronics 2020, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Tang, W.; Cai, C.; Deng, L.; Zhang, X. Wireless Power Charger Based on Class E Amplifier with the Maximum Power Point Load Consideration. Energies 2018, 11, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Wang, G.B.; Wu, C.C.; Chang, E.Y.; Cheng, S.; Chieng, W.H. Derivation of the Resonance Mechanism for Wireless Power Transfer Using Class-E Amplifier. Energies 2021, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, C.; Lee, C.H.T. An Overview of Resonant Circuits for Wireless Power Transfer. Energies 2017, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campi, T.; Cruciani, S.; Palandrani, F.; De Santis, V.; Hirata, A.; Feliziani, M. Wireless Power Transfer Charging System for AIMDs and Pacemakers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Suganthan, P.N. Differential Evolution: A Survey of the State-of-the-Art. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2011, 15, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Lee, W.; Koo, H.; Bae, J.; Hwang, K.C.; Lee, K.Y.; Yang, Y. 6.78 MHz Wireless Power Transmitter Based on a Reconfigurable Class–E Power Amplifier for Multiple Device Charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 5907–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, M.; Yang, S.; Ma, C.; Zhu, X. A Novel Design Methodology for High-Efficiency Current-Mode and Voltage-Mode Class-E Power Amplifiers in Wireless Power Transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 4514–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R., N.; A., V.J.; Chokkalingam, B.; Padmanaban, S.; Leonowicz, Z.M. Class E Power Amplifier Design and Optimization for the Capacitive Coupled Wireless Power Transfer System in Biomedical Implants. Energies 2017, 10, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Li, R. Parameter Analysis and Optimization of Class-E Power Amplifier Used in Wireless Power Transfer System. Energies 2019, 12, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pan, T.; Zhong, G. Design of three-phase class E power amplifier based on wireless power transmission system. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Wuhan, China, 31 May–2 June 2018; pp. 2573–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Le, H.; Nour, Y.; Han, A.; Jensen, F.; Ouyang, Z.; Knott, A. Microfabricated Air-Core Toroidal Inductor in Very High-Frequency Power Converters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 6, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Wang, L.; Wu, M.; Mao, L.; Wang, X. Two-Dimensional Winding Loss Analytical Model for High-Frequency Multilayer Air-Core Planar Inductor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 6794–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Dede, E.M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, F.; Erickson, R.W.; Maksimović, D. Modeling and Design of High-Power, High-Current-Ripple Planar Inductors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 5816–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).