EEG-Correlates of Emotional Memory and Seasonal Symptoms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment
2.2. Questionnaire
2.3. Picture Learning Condition
2.4. EEG Recording and Analysis
- Check gradient: maximal allowed voltage step: 50 microvolts/ms;
- Check difference: maximal allowed difference in values in intervals of 200 ms: 200 microvolts;
- Lowest activity allowed in 100 ms intervals: 0.5 microvolts.
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Sample
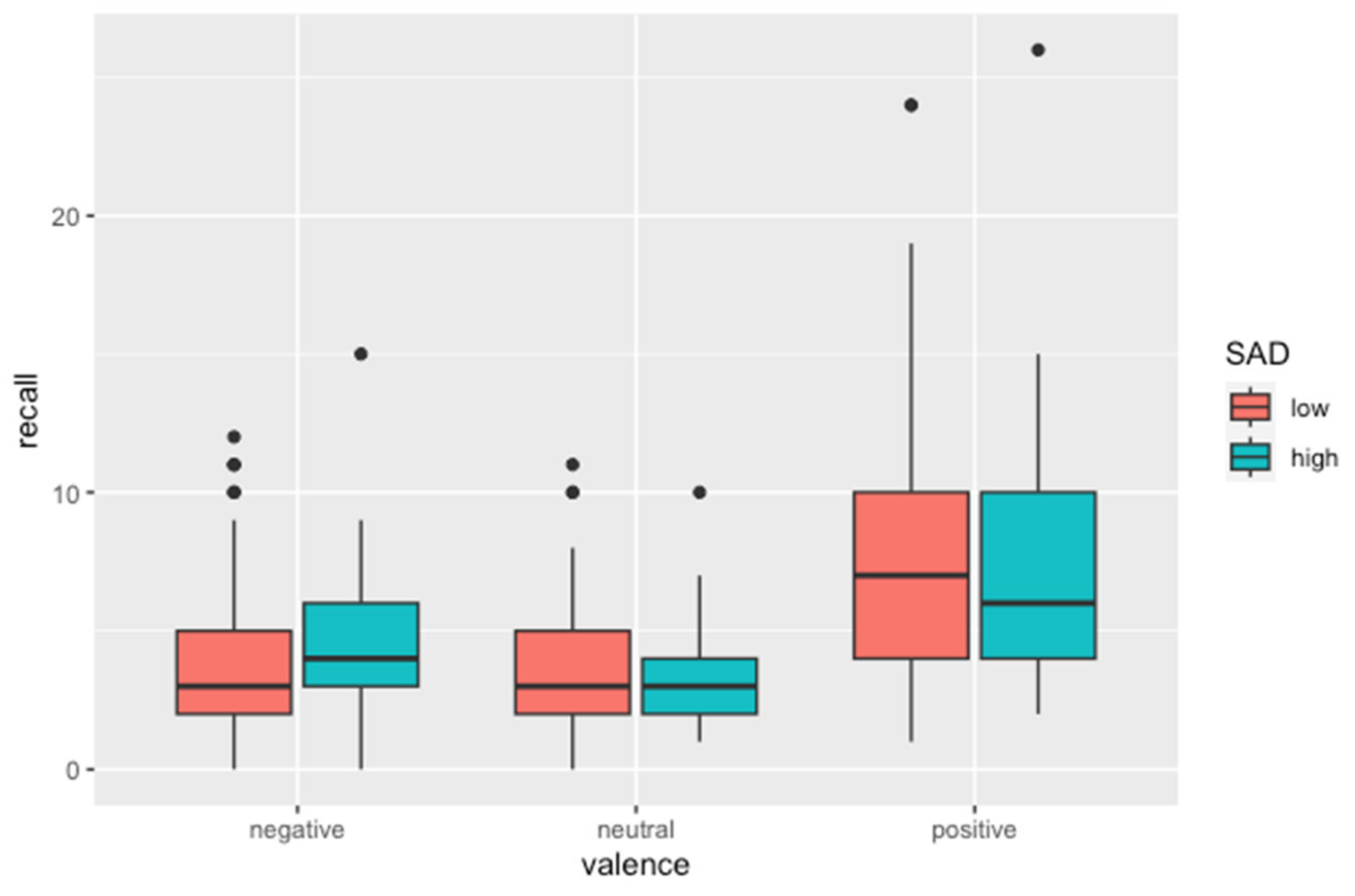
3.2. Free Recall of Emotional Pictures
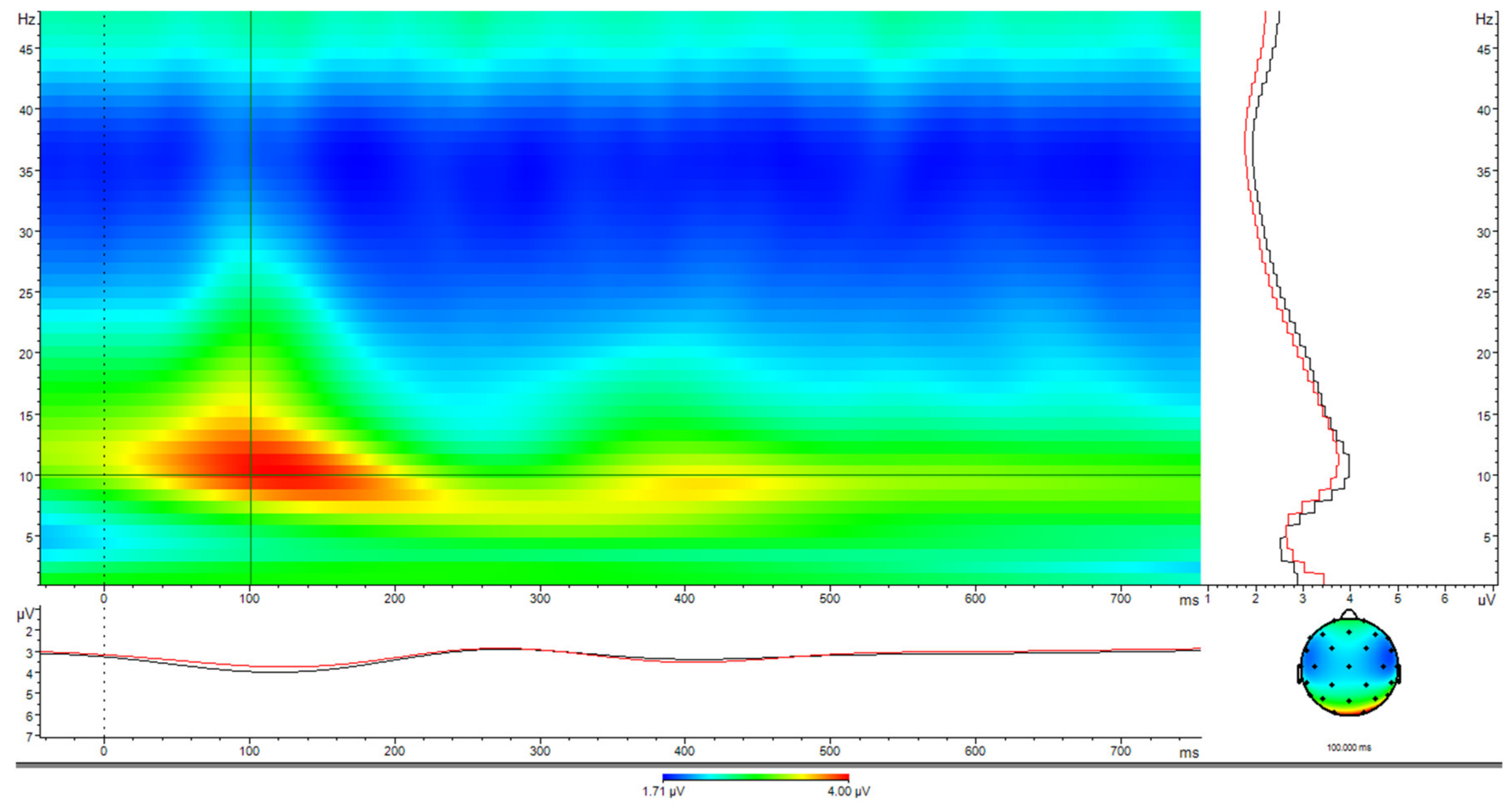
3.3. Seasonality Effects in the EEG during Learning of Emotional Pictures
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonality and Emotional Memory in the Summer
4.2. Seasonality, Valence, and EEG Band-Power
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DSM | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| GSS | Global Seasonality Score |
| ICA | Independent Component Analysis |
| OASIS | Open Affective Standardized Image Set |
| SAD | Seasonal Affective Disorder |
| SPAQ | Seasonal Pattern Assessment Questionnaire |
| S-SAD | Subsyndromal Seasonal Affective Disorder |
Appendix A
| Seasonality | F | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| seasonality | 4.442 | 1, 513.268 | 0.043 |
| lobe | 9.663 | 1.962, Inf | <0.001 |
| seasonality × lobe | 5.503 | 1.962, Inf | 0.003 |
| valence | 5.015 | 1.934, Inf | 0.011 |
| Seasonality × valence | 3.31 | 1.934, Inf | 0.037 |
| lobe × valence | 6.849 | 3.346, Inf | <0.001 |
| seasonality × lobe × valence | 0.452 | 3.346, Inf | 0.745 |
| frequency | 16.881 | 1, Inf | <0.001 |
| seasonality × frequency | 2.745 | 1, Inf | 0.097 |
| lobe × frequency | 153.738 | 1.767, Inf | <0.001 |
| seasonality × lobe × frequency | 2.726 | 1.767, Inf | 0.075 |
| valence × frequency | 2.163 | 1.963, Inf | 0.106 |
| seasonality × valence × frequency | 0.692 | 1.963, Inf | 0.508 |
| lobe × valence × frequency | 11.751 | 2.735, Inf | <0.001 |
| seasonality × lobe × valence × frequency | 0.587 | 2.735, Inf | 0.612 |
| hemisphere | 0.825 | 1, Inf | 0.362 |
| seasonality × hemisphere | 0.698 | 1, Inf | 0.44 |
| lobe × hemisphere | 2.28 | 1.428, Inf | 0.106 |
| seasonality × lobe × hemisphere | 0.112 | 1.428, Inf | 0.869 |
| valence × hemisphere | 1.055 | 1.777, Inf | 0.331 |
| seasonality × valence × hemisphere | 1.714 | 1.777, Inf | 0.179 |
| lobe × valence × hemisphere | 2.845 | 3.683, Inf | 0.027 |
| seasonality × lobe × valence × hemisphere | 1.533 | 3.683, Inf | 0.178 |
| frequency × hemisphere | 1.099 | 1, Inf | 0.329 |
| seasonality × frequency × hemisphere | 0.414 | 1, Inf | 0.492 |
| lobe × frequency × hemisphere | 2.845 | 1.798, Inf | 0.052 |
| seasonality × lobe × frequency × hemisphere | 0.298 | 1.798, Inf | 0.742 |
| valence × frequency × hemisphere | 1.009 | 1.895, Inf | 0.341 |
| seasonality × valence × frequency × hemisphere | 0.24 | 1.895, Inf | 0.762 |
| lobe × valence × frequency × hemisphere | 0.392 | 3.744, Inf | 0.796 |
| seasonality × lobe × valence × frequency × hemisphere | 0.467 | 3.744, Inf | 0.744 |
| time-window | 11.94 | 1, Inf | 0.001 |
| seasonality × time-window | 0.147 | 1, Inf | 0.689 |
| lobe × time-window | 5.505 | 1.359, Inf | 0.011 |
| seasonality × lobe × time-window | 0.206 | 1.359, Inf | 0.779 |
| valence × time-window | 0.128 | 1.964, Inf | 0.887 |
| seasonality × valence × time-window | 2.552 | 1.964, Inf | 0.081 |
| lobe × valence × time-window | 1.965 | 2.504, Inf | 0.113 |
| seasonality × lobe × valence × time-window | 0.808 | 2.504, Inf | 0.487 |
| frequency × time-window | 1.011 | 1, Inf | 0.32 |
| seasonality × frequency × time-window | 0.952 | 1, Inf | 0.329 |
| lobe × frequency × time-window | 0.892 | 1.244, Inf | 0.357 |
| seasonality × lobe × frequency × time-window | 0.261 | 1.244, Inf | 0.697 |
| valence × frequency × time-window | 1.578 | 1.953, Inf | 0.199 |
| seasonality × valence × frequency × time-window | 4.348 | 1.953, Inf | 0.018 |
| lobe × valence × frequency × time-window | 2.831 | 2.592, Inf | 0.052 |
| seasonality × lobe × valence × frequency × time-window | 1.511 | 2.592, Inf | 0.242 |
| hemisphere × time-window | 0.786 | 1, Inf | 0.378 |
| seasonality × hemisphere × time-window | 0.128 | 1, Inf | 0.72 |
| lobe × hemisphere × time-window | 0.44 | 1.986, Inf | 0.63 |
| seasonality × lobe × hemisphere × time-window | 0.021 | 1.986, Inf | 0.98 |
| valence × hemisphere × time-window | 1.025 | 1.899, Inf | 0.358 |
| seasonality × valence × hemisphere × time-window | 1.038 | 1.899, Inf | 0.334 |
| lobe × valence × hemisphere × time-window | 0.32 | 3.425, Inf | 0.85 |
| seasonality × lobe × valence × hemisphere × time-window | 0.821 | 3.425, Inf | 0.512 |
| frequency × hemisphere × time-window | 0.001 | 1, Inf | 0.972 |
| seasonality × frequency × hemisphere × time-window | 0 | 1, Inf | 1 |
| lobe × frequency × hemisphere × time-window | 0.95 | 1.995, Inf | 0.412 |
| seasonality × lobe × frequency × hemisphere × time-window | 0.18 | 1.995, Inf | 0.828 |
| valence × frequency × hemisphere × time-window | 0.115 | 1.958, Inf | 0.883 |
| seasonality × valence × frequency × hemisphere × time-window | 3.622 | 1.958, Inf | 0.032 |
| lobe × valence × frequency × hemisphere × time-window | 0.087 | 3.649, Inf | 0.99 |
| seasonality × lobe × valence × frequency × hemisphere × time-window | 0.458 | 3.649, Inf | 0.75 |
References
- Rosenthal, N.E.; Sack, D.A.; Gillin, J.C.; Lewy, A.J.; Goodwin, F.K.; Davenport, Y.; Mueller, P.S.; Newsome, D.A.; Wehr, T.A. Seasonal Affective Disorder: A Description of the Syndrome and Preliminary Findings with Light Therapy. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1984, 41, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurlansik, S.L.; Ibay, A.D. MD Seasonal Affective Disorder. Am. Fam. Physician 2012, 86, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bryant, R.A. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th. Am. Psychiatr. Assoc. 2014, 27, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, A.; Bouchard, G.; Tremblay, P.; Sasseville, A.; Hébert, M. When a season means depression. M.S. Médecine Sci. 2010, 26, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasof, J. Cultural variation in seasonal depression: Cross-national differences in winter versus summer patterns of seasonal affective disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2009, 115, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, A.; Partonen, T. The Diagnosis, Symptomatology, and Epidemiology of Seasonal Affective Disorder. CNS Spectr. 2005, 10, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, S.A.; Raggatt, P.T.F.; James, B.; Rogers, J. Seasonal affective disorder: Some epidemiological findings from a tropical climate. Australas. Psychiatry Bull. R. Aust. N. Z. Coll. Psychiatr. 1996, 30, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.A.; Blodgett, C.; Reardon, A. Measuring seasonality: Psychometric properties of the Seasonal Pattern Assessment Questionnaire and the Inventory for Seasonal Variation. Psychiatry Res. 2003, 117, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, N.E. Seasonal Pattern Assessment Questionnaire. J. Affect. Disord. 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, S.; Wehr, T.A.; Bartko, J.J.; Gaist, P.A.; Rosenthal, N.E. Epidemiological Findings of Seasonal Changes in Mood and Behavior: A Telephone Survey of Montgomery County, Maryland. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1989, 46, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder, G.E.; Alvarenga, J.; Abraham, K.; Skipper, J.; Warner, V.; Voyer, D.; Peterson, B.S.; Weissman, M.M. New findings for emotional and verbal dichotic listening in individuals at risk for depression. Laterality 2016, 21, 525–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder, G.E.; Fong, R.; Tenke, C.E.; Leite, P.; Towey, J.P.; Stewart, J.E.; McGrath, P.J.; Quitkin, F.M. Regional brain asymmetries in major depression with or without an anxiety disorder: A quantitative electroencephalographic study. Biol. Psychiatry (1969) 1997, 41, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinifard, B.; Moradi, M.H.; Rostami, R. Classifying depression patients and normal subjects using machine learning techniques and nonlinear features from EEG signal. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2013, 109, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.F.; Kan, D.P.X.; Croarkin, P.; Phang, C.K.; Doruk, D. Neurophysiological correlates of depressive symptoms in young adults: A quantitative EEG study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, C.; Fachner, J.; Erkkilä, J. Validity and reliability of electroencephalographic frontal alpha asymmetry and frontal midline theta as biomarkers for depression. Scand. J. Psychol. 2013, 54, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollan, J.K.; Hoxha, D.; Chihade, D.; Pflieger, M.E.; Rosebrock, L.; Cacioppo, J. Frontal alpha EEG asymmetry before and after behavioral activation treatment for depression. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 99, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Jung, W.; Kim, S.; Jeon, H.; Lee, S. Frontal Alpha Asymmetry Correlates with Suicidal Behavior in Major Depressive Disorder. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2019, 17, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, E.; Palmer, D.M.; Cooper, N. EEG Alpha Asymmetry in Schizophrenia, Depression, PTSD, Panic Disorder, ADHD and Conduct Disorder. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2010, 41, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentgen, L.M.; Tenke, C.E.; Pine, D.S.; Fong, R.; Klein, R.G.; Bruder, G.E. Electroencephalographic asymmetries in adolescents with major depression: Influence of comorbidity with anxiety disorders. J. Abnorm. Psychol. (1965) 2000, 109, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deslandes, A.C.; Moraes, H.; Alves, H.; Pompeu, F.A.M.S.; Silveira, H.; Mouta, R.; Arcoverde, C.; Ribeiro, P.; Cagy, M.; Piedade, R.A.M.; et al. Effect of aerobic training on EEG alpha asymmetry and depressive symptoms in the elderly: A 1-year follow-up study. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passynkova, N.R.; Volf, N.V. Seasonal affective disorder: Spatial organization of EEG power and coherence in the depressive state and in light-induced and summer remission. Psychiatry Res. 2001, 108, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höller, Y.; Jónsdóttir, S.T.; Hannesdóttir, A.H.; Ólafsson, R.P. EEG-responses to mood induction interact with seasonality and age. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 950328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coan, J.A.; Allen, J.J.B. Frontal EEG asymmetry as a moderator and mediator of emotion. Biol. Psychol. 2004, 67, 7–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Gu, C.; Hu, B. Mapping the frontal alpha asymmetry indicators of habitual emotion regulation: A data-driven approach. Neuroreport 2018, 29, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, S.J.; Allen, J.J.B. Frontal asymmetry as a mediator and moderator of emotion: An updated review. Psychophysiology 2018, 55, e12965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, C.; Pereira, A.R.; Sampaio, A.; Buján, A.; Pinal, D. Frontal Alpha Asymmetry and Negative Mood: A Cross-Sectional Study in Older and Younger Adults. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaish, A.; Grossmann, T.; Woodward, A. Not All Emotions Are Created Equal. Psychol. Bull. 2008, 134, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, O.T. The influence of stress hormones on emotional memory: Relevance for psychopathology. Acta Psychol. 2008, 127, 513–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.W.; Canli, T. Emotional memory function, personality structure and psychopathology: A neural system approach to the identification of vulnerability markers. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 58, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, K.E.; Schmeichel, B.J. Effects of emotional content on working memory capacity. Cogn. Emot. 2019, 33, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuilleumier, P. How brains beware: Neural mechanisms of emotional attention. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papousek, I.; Weiss, E.M.; Schulter, G.; Fink, A.; Reiser, E.M.; Lackner, H.K. Prefrontal EEG alpha asymmetry changes while observing disaster happening to other people: Cardiac correlates and prediction of emotional impact. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 103, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, B.E.; McGeary, J.E.; Beevers, C.G. Attentional biases to emotional stimuli: Key components of the RDoC constructs of sustained threat and loss. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2016, 171B, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Haim, Y.; Lamy, D.; Pergamin, L.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J.; van IJzendoorn, M.H. Threat-Related Attentional Bias in Anxious and Nonanxious Individuals. Psychol. Bull. 2007, 133, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Haim, Y.; Lamy, D.; Glickman, S. Attentional bias in anxiety: A behavioral and ERP study. Brain Cogn. 2005, 59, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Aguiar Neto, F.S.; Rosa, J.L.G. Depression biomarkers using non-invasive EEG: A review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 105, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, D.B.; Paré, D. In sync: Gamma oscillations and emotional memory. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, A.; Stolarova, M.; Moratti, S.; Ray, W.J. Adaptation in human visual cortex as a mechanism for rapid discrimination of aversive stimuli. NeuroImage 2007, 36, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegle, G.J.; Condray, R.; Thase, M.E.; Keshavan, M.; Steinhauer, S.R. Sustained gamma-band EEG following negative words in depression and schizophrenia. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2010, 75, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Mitchell, D.; Cheng, X.; Mondillo, K.; Mccaffrey, D.; Holroyd, T.; Carver, F.; Coppola, R.; Blair, J. Visual Awareness, Emotion, and Gamma Band Synchronization. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 1896–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, N.; Menicucci, D.; Sebastiani, L.; Bedini, R.; Pingitore, A.; Vanello, N.; Milanesi, M.; Landini, L.; Gemignani, A. The dynamics of EEG gamma responses to unpleasant visual stimuli: From local activity to functional connectivity. NeuroImage 2012, 60, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.R.; Hipp, J.F.; Domnick, C.; Carl, C.; Büchel, C.; Engel, A.K. Modulation of neuronal oscillatory activity in the beta- and gamma-band is associated with current individual anxiety levels. NeuroImage 2018, 178, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.M.; Keil, A.; Gruber, T.; Elbert, T. Processing of affective pictures modulates right-hemispheric gamma band EEG activity. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, J.K.; Nordin, S.; Sequeira, H.; Polich, J. Affective picture processing: An integrative review of ERP findings. Biol. Psychol. 2008, 77, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schupp, H.T.; Junghöfer, M.; Weike, A.I.; Hamm, A.O. The selective processing of briefly presented affective pictures: An ERP analysis. Psychophysiology 2004, 41, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretié, L.; Mercado, F.; Hinojosa, J.A.; Martín-Loeches, M.; Sotillo, M. Valence-related vigilance biases in anxiety studied through event-related potentials. J. Affect. Disord. 2004, 78, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, C.J.; Charles, M.; McTavish, S.; Favaron, E.; Cowen, P.J. Negative ion treatment increases positive emotional processing in seasonal affective disorder. Psychol. Med. 2012, 42, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.G.; Hjordt, L.V.; Stenbæk, D.S.; Andersen, E.; Back, S.K.; Lansner, J.; Hageman, I.; Dam, H.; Nielsen, A.P.; Knudsen, G.M.; et al. Development and psychometric validation of the verbal affective memory test. Memory 2016, 24, 1208–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinks, H.; Dalgleish, T. Attentional processing and levels of symptomatology in Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): A preliminary longitudinal study. J. Affect. Disord. 2001, 62, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, C.; Pacitti, F.; Rossi, A.; Iorio, P.; Pompili, A. Declarative Memory Impairment and Emotional Bias in Recurrent Depression with a Seasonal Pattern: The Interplay between Emotion and Cognition in Seasonal Affective Disorder. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgsted, C.; Ozenne, B.; Mc Mahon, B.; Madsen, M.K.; Hjordt, L.V.; Hageman, I.; Baaré, W.F.C.; Knudsen, G.M.; Fisher, P.M. Amygdala response to emotional faces in seasonal affective disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 229, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, S.; Kamo, T. Seasonality in major depressed inpatients. J. Affect. Disord. 1990, 19, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, A. Validation of the Seasonal Pattern Assessment Questionnaire (SPAQ). J. Affect. Disord. 1996, 40, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurdi, B.; Lozano, S.; Banaji, M.R. Introducing the Open Affective Standardized Image Set (OASIS). Behav. Res. 2017, 49, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bathke, A.C.; Friedrich, S.; Pauly, M.; Konietschke, F.; Staffen, W.; Strobl, N.; Höller, Y. Testing Mean Differences among Groups: Multivariate and Repeated Measures Analysis with Minimal Assumptions. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2018, 53, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, S.; Konietschke, F.; Pauly, M. Analysis of Multivariate Data and Repeated Measures Designs with the R Package MANOVA.RM. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.08002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S. A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hjordt, L.V.; Stenbæk, D.S.; Madsen, K.S.; Mc Mahon, B.; Jensen, C.G.; Vestergaard, M.; Hageman, I.; Meder, D.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Knudsen, G.M. State-dependent alterations in inhibitory control and emotional face identification in seasonal affective disorder. J. Abnorm. Psychol. (1965) 2017, 126, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppanen, J.M. Emotional information processing in mood disorders: A review of behavioral and neuroimaging findings. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2006, 19, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgleish, T.; Spinks, H.; Golden, A.; du Toit, P. Processing of Emotional Information in Seasonal Depression Across Different Cognitive Measures. J. Abnorm. Psychol. (1965) 2004, 113, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolphs, R. Neural systems for recognizing emotion. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2002, 12, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aftanas, L.; Varlamov, A.; Pavlov, S.; Makhnev, V.; Reva, N. Event-Related Synchronization and Desynchronization During Affective Processing: Emergence of Valence-Related Time-Dependent Hemispheric Asymmetries in Theta and Upper Alpha Band. Int. J. Neurosci. 2001, 110, 197–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftanas, L.I.; Varlamov, A.A.; Pavlov, S.V.; Makhnev, V.P.; Reva, N.V. Affective picture processing: Event-related synchronization within individually defined human theta band is modulated by valence dimension. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 303, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, N.T.; Fukusima, S.S.; Aznar-Casanova, J.A. Models of brain asymmetry in emotional processing. Psychol. Neurosci. 2008, 1, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, G.; Laeng, B.; Fabri, M.; Foschi, N.; Tommasi, L. Right hemisphere or valence hypothesis, or both? The processing of hybrid faces in the intact and callosotomized brain. Neuropsychologia 2015, 68, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, M.M.; Sabatinelli, D.; Lang, P.J.; Fitzsimmons, J.R.; King, W.; Desai, P. Activation of the Visual Cortex in Motivated Attention. Behav. Neurosci. 2003, 117, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, D.; Wei, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J. Abnormal functional connectivity of EEG gamma band in patients with depression during emotional face processing. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaisch, T.; Schupp, H.T.; Renner, B.; Junghöfer, M. Neural systems of visual attention responding to emotional gestures. NeuroImage 2009, 45, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, D.; Hajcak, G.; Dien, J. Differentiating neural responses to emotional pictures: Evidence from temporal-spatial PCA. Psychophysiology 2009, 46, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codispoti, M.; Ferrari, V.; Bradley, M.M. Repetition and Event-related Potentials: Distinguishing Early and Late Processes in Affective Picture Perception. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhausen, H.; Gundelfinger, R.; Winkler Metzke, C. Prevalence of self-reported seasonal affective disorders and the validity of the seasonal pattern assessment questionnaire in young adults Findings from a Swiss community study. J. Affect. Disord. 2009, 115, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| F | df | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| seasonality | 4.44 | 1, 513.27 | 0.043 |
| lobe | 9.66 | 1.97, Inf | <0.001 |
| seasonality × lobe | 5.50 | 1.97, Inf | 0.003 |
| valence | 5.02 | 1.93, Inf | 0.011 |
| seasonality × valence | 3.31 | 1.923, Inf | 0.037 |
| lobe × valence | 6.85 | 3.34, Inf | <0.001 |
| frequency | 16.88 | 1, Inf | <0.001 |
| lobe × frequency | 153.74 | 1.77, Inf | <0.001 |
| lobe × valence × frequency | 11.75 | 2.74, Inf | <0.001 |
| lobe × valence × hemisphere | 2.85 | 3.68, Inf | 0.027 |
| time-window | 11.94 | 1, Inf | <0.001 |
| lobe × time-window | 5.51 | 1.36, Inf | 0.011 |
| seasonality × valence × frequency × time-window | 4.35 | 1.95, Inf | 0.018 |
| seasonality × valence × frequency × hemisphere × time-window | 3.62 | 1.96, Inf | 0.032 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Theódórsdóttir, D.; Höller, Y. EEG-Correlates of Emotional Memory and Seasonal Symptoms. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9361. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169361
Theódórsdóttir D, Höller Y. EEG-Correlates of Emotional Memory and Seasonal Symptoms. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(16):9361. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169361
Chicago/Turabian StyleTheódórsdóttir, Dagný, and Yvonne Höller. 2023. "EEG-Correlates of Emotional Memory and Seasonal Symptoms" Applied Sciences 13, no. 16: 9361. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169361
APA StyleTheódórsdóttir, D., & Höller, Y. (2023). EEG-Correlates of Emotional Memory and Seasonal Symptoms. Applied Sciences, 13(16), 9361. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169361







