ALReg: Registration of 3D Point Clouds Using Active Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose ALReg, an active learning pipeline that can be used to drastically decrease trainingtime for registration networks with either a similar performance or even an increase in terms of accuracy. Regarding the drawbacks of the overcalculations for network training for whole-to-whole point cloud registration, ALReg focuses on using only a relevant and adequate subset of superpoints during the process.
- A novel uncertainty-based acquisition function that could be used to calculate superpoint uncertainties is presented. In the previous studies focusing on active learning for point cloud data, class labels were used for uncertainty calculations.
- ALReg is tested on three popular registration methods (DCP, FMR, DeepBBS) for both real (7Scenes, 3DMatch) and synthetic (ModelNet) point cloud datasets. Overall, an improvement over the existing methods in terms of accuracy scores is obtained.
2. Related Work
2.1. Point Cloud Registration
2.2. Active Learning
2.3. Active Learning for Point Clouds
3. Method
3.1. Problem Definition
3.2. Baseline Methods
3.3. Active Selection
| Algorithm 1: Acqusition function |
 |
4. Experiments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5099–5108. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Birdal, T.; Ilic, S. Ppfnet: Global context aware local features for robust 3d point matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, B.; Meng, G.; Lu, J.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. DensePoint: Learning Densely Contextual Representation for Efficient Point Cloud Processing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5239–5248. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, Y.H.; Mertan, A.; Unal, G. ODFNet: Using orientation distribution functions to characterize 3D point clouds. Comput. Graph. 2022, 102, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lee, G.H. Weakly supervised semantic point cloud segmentation: Towards 10x fewer labels. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13706–13715. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Tao, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Integrating active learning and contextually guide for semantic labeling of LiDAR point cloud. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th IAPR Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Remote Sensing (PRRS), Beijing, China, 19–20 August 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Vosselman, G.; Cao, Y.; Yang, M.Y. Active and incremental learning for semantic ALS point cloud segmentation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 169, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölle, M.; Walter, V.; Schmohl, S.; Soergel, U. Remembering both the machine and the crowd when sampling points: Active learning for semantic segmentation of ALS point clouds. In Pattern Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 505–520. [Google Scholar]
- Weidner, L.; Walton, G.; Kromer, R. Generalization considerations and solutions for point cloud hillslope classifiers. Geomorphology 2020, 354, 107039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lee, G.H. Usip: Unsupervised stable interest point detection from 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Sun, J. Deep learning based point cloud registration: An overview. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2020, 2, 222–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. Method for registration of 3-D shapes. In Proceedings of the Sensor Fusion IV: Control Paradigms and Data Structures, Boston, MA, USA, 12–15 November 1992; Volume 1611, pp. 586–606. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, A.; Haehnel, D.; Thrun, S. Generalized-icp. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Seattle, WA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2009; Volume 2, p. 435. [Google Scholar]
- Low, K.L. Linear least-squares optimization for point-to-plane icp surface registration. Chapel Hill Univ. North Carol. 2004, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Li, H.; Campbell, D.; Jia, Y. Go-ICP: A globally optimal solution to 3D ICP point-set registration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 2241–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yew, Z.J.; Lee, G.H. 3dfeat-net: Weakly supervised local 3d features for point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 17–24 May 2018; pp. 607–623. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.; Song, S.; Nießner, M.; Fisher, M.; Xiao, J.; Funkhouser, T. 3DMatch: Learning Local Geometric Descriptors from RGB-D Reconstructions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, G.; Zeng, B. Omnet: Learning overlapping mask for partial-to-partial point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3132–3141. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Hamsici, O.C.; Feng, S.; Sharma, P.; Gernoth, T. DeepPRO: Deep Partial Point Cloud Registration of Objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 5683–5692. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, B. Rigid Registration of Point Clouds Based on Partial Optimal Transport. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Haußmann, M.; Hamprecht, F.A.; Kandemir, M. Deep active learning with adaptive acquisition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.11471. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Xu, X.; Liew, J.H.; Foo, C.S. Revisiting superpixels for active learning in semantic segmentation with realistic annotation costs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 10988–10997. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, S. Multiview Spatial-Spectral Active Learning for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2021, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Long, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Du, Z.; Yang, X. Cpral: Collaborative panoptic-regional active learning for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 2108–2116. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Huang, Y.K.; Lee, H.Y.; Su, H.T.; Huang, P.C.; Hsu, W.H. ReDAL: Region-based and Diversity-aware Active Learning for Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF INTERNATIONAL Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 15510–15519. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, F.; Luo, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, J. Active Learning for Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation via Spatial-Structural Diversity Reasoning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.12588. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, K.; Cai, L.; Foo, C.S.; Jia, K. Label-efficient point cloud semantic segmentation: An active learning approach. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.06931. [Google Scholar]
- Landrieu, L.; Simonovsky, M. Large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation with superpoint graphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4558–4567. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y. What uncertainties do we need in bayesian deep learning for computer vision? In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach City, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hezroni, I.; Drory, A.; Giryes, R.; Avidan, S. DeepBBS: Deep Best Buddies for Point Cloud Registration. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Online, 1–3 December 2021; pp. 342–351. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Mei, G.; Zhang, J. Feature-metric registration: A fast semi-supervised approach for robust point cloud registration without correspondences. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11366–11374. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Solomon, J.M. Deep closest point: Learning representations for point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 3523–3532. [Google Scholar]
- Shotton, J.; Glocker, B.; Zach, C.; Izadi, S.; Criminisi, A.; Fitzgibbon, A. Scene coordinate regression forests for camera relocalization in RGB-D images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2930–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Song, S.; Khosla, A.; Yu, F.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Xiao, J. 3d shapenets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1912–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, M. Robust symmetric iterative closest point. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 185, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinkiewicz, S. A symmetric objective function for ICP. Acm Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2019, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinkiewicz, S.; Levoy, M. Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 28 May–1 June 2001; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, Y.; Goforth, H.; Srivatsan, R.A.; Lucey, S. Pointnetlk: Robust & efficient point cloud registration using pointnet. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7163–7172. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, S.; Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Markham, A.; Guo, Y. Spinnet: Learning a general surface descriptor for 3d point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 11753–11762. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, K.; Liu, S.; Luo, X.; Wang, M. Robust point cloud registration framework based on deep graph matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2021; pp. 8893–8902. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Wan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, X.; Yuan, P.; Song, S. Deepvcp: An end-to-end deep neural network for point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Fu, H.; Tai, C.L. Pointdsc: Robust point cloud registration using deep spatial consistency. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 15859–15869. [Google Scholar]
- Yew, Z.J.; Lee, G.H. Rpm-net: Robust point matching using learned features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11824–11833. [Google Scholar]
- Sarode, V.; Li, X.; Goforth, H.; Aoki, Y.; Srivatsan, R.A.; Lucey, S.; Choset, H. Pcrnet: Point cloud registration network using pointnet encoding. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.07906. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Birdal, T.; Ilic, S. Ppf-foldnet: Unsupervised learning of rotation invariant 3d local descriptors. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 602–618. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Feng, C.; Shen, Y.; Tian, D. Foldingnet: Point cloud auto-encoder via deep grid deformation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Shu, M. DDRNet: Fast point cloud registration network for large-scale scenes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Shu, M. Fore-Net: Efficient inlier estimation network for large-scale indoor scenario. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 184, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Gojcic, Z.; Usvyatsov, M.; Wieser, A.; Schindler, K. Predator: Registration of 3d point clouds with low overlap. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 4267–4276. [Google Scholar]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, M.; Park, J. Deep hough voting for robust global registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 15994–16003. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Deng, L. TriVoC: Efficient Voting-based Consensus Maximization for Robust Point Cloud Registration with Extreme Outlier Ratios. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 4654–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, S. HDRNet: High-Dimensional Regression Network for Point Cloud Registration. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B. Point Cloud Registration via Heuristic Reward Reinforcement Learning. Stats 2023, 6, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, B.; Lu, J.; Lang, Y. A Point Cloud Data-Driven Pallet Pose Estimation Method Using an Active Binocular Vision Sensor. Sensors 2023, 23, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settles, B. Active Learning Literature Survey. In Computer Sciences Technical Report 1648; University of Wisconsin–Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ertekin, S.; Huang, J.; Bottou, L.; Giles, L. Learning on the border: Active learning in imbalanced data classification. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth ACM Conference on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Lisbon, Portugal, 6–10 November 2007; pp. 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Koller, D. Support vector machine active learning with applications to text classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2001, 2, 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, D.D.; Gale, W.A. A sequential algorithm for training text classifiers. In SIGIR’94; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayanarasimhan, S.; Grauman, K. What’s it going to cost you?: Predicting effort vs. informativeness for multi-label image annotations. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 2262–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Houlsby, N.; Huszár, F.; Ghahramani, Z.; Lengyel, M. Bayesian active learning for classification and preference learning. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1112.5745. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Shang, Y. A new active labeling method for deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Beijing, China, 6–11 July 2014; pp. 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Gal, Y.; Islam, R.; Ghahramani, Z. Deep bayesian active learning with image data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 1183–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Caramalau, R.; Bhattarai, B.; Kim, T.K. Sequential graph convolutional network for active learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 9583–9592. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.J.; Jin, R.; Zhou, Z.H. Active learning by querying informative and representative examples. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2010, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sener, O.; Savarese, S. Active learning for convolutional neural networks: A core-set approach. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.00489. [Google Scholar]
- Ash, J.T.; Zhang, C.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Langford, J.; Agarwal, A. Deep batch active learning by diverse, uncertain gradient lower bounds. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.03671. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.N.; Lin, H.T. Active learning by learning. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Foo, C.S. Exploring Spatial Diversity for Region-Based Active Learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 8702–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasaiah, D.; Otterbach, J.; Wollmann, T. MEAL: Manifold Embedding-based Active Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 1029–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Stilla, U.; Xu, Y. Change detection of urban objects using 3D point clouds: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 197, 228–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, B.; Marcos, D.; Lobry, S.; Tuia, D. Half a percent of labels is enough: Efficient animal detection in UAV imagery using deep CNNs and active learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9524–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bengar, J.Z.; van de Weijer, J.; Fuentes, L.L.; Raducanu, B. Class-Balanced Active Learning for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2022; pp. 1536–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann, M.; Jutzi, B.; Hinz, S.; Mallet, C. Semantic point cloud interpretation based on optimal neighborhoods, relevant features and efficient classifiers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Yin, Z.; Fu, Y.; Lin, H.; Pan, Z. A multi-granularity semisupervised active learning for point cloud semantic segmentation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 15629–15645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach City, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017.
- Baker, S.; Matthews, I. Lucas-kanade 20 years on: A unifying framework. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 56, 221–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York City, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 1050–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Depeweg, S.; Hernández-Lobato, J.M.; Doshi-Velez, F.; Udluft, S. Uncertainty decomposition in bayesian neural networks with latent variables. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.08495. [Google Scholar]
- Depeweg, S.; Hernandez-Lobato, J.M.; Doshi-Velez, F.; Udluft, S. Decomposition of uncertainty in Bayesian deep learning for efficient and risk-sensitive learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 1184–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Papon, J.; Abramov, A.; Schoeler, M.; Worgotter, F. Voxel cloud connectivity segmentation-supervoxels for point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2027–2034. [Google Scholar]



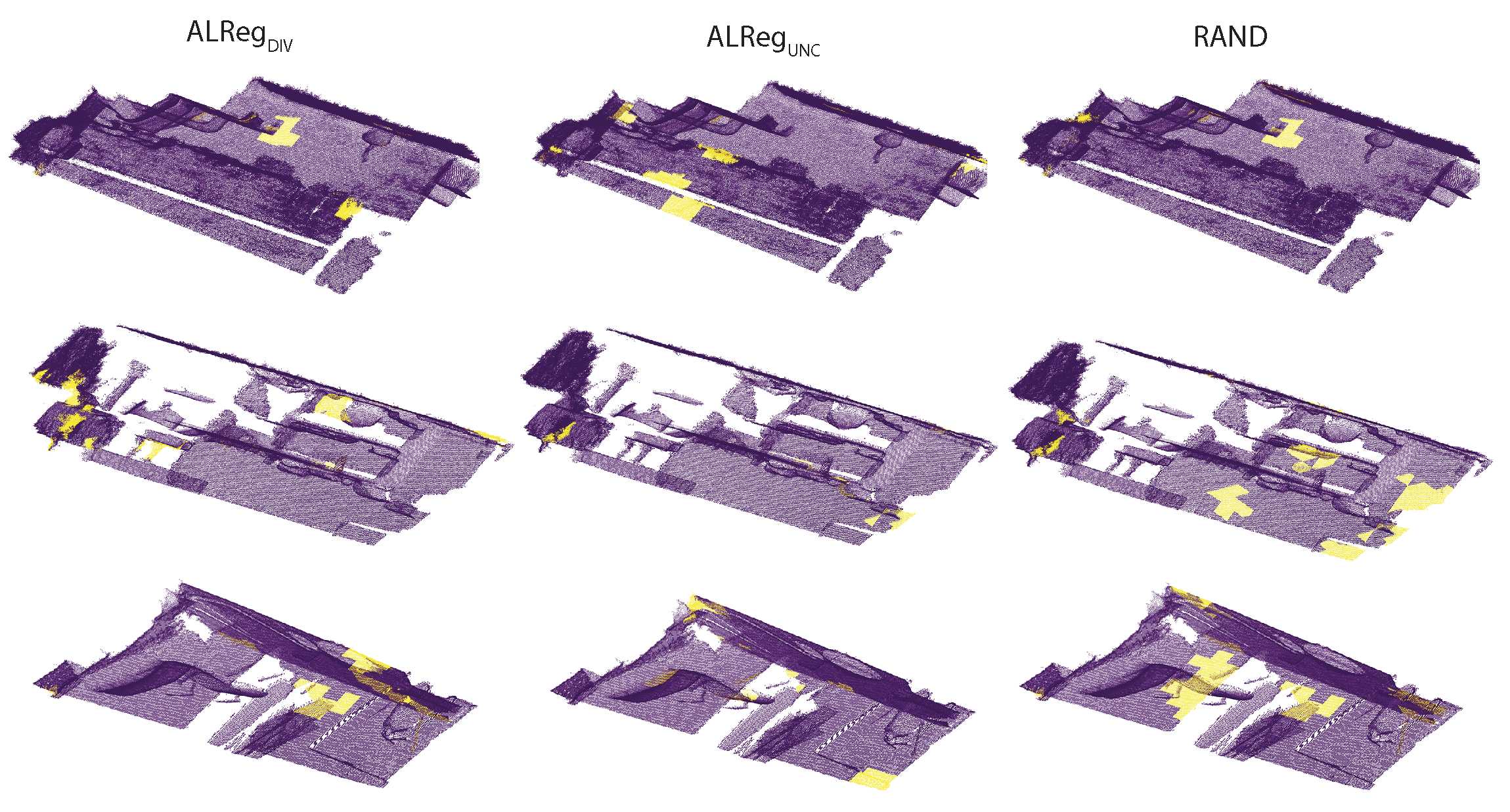

| FMR-7Scenes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | MSE (R) | RMSE (R) | MAE (R) | MSE (t) | RMSE (t) | MAE (t) |
| FULL | 0.39343 | 0.62724 | 0.25740 | 0.00614 | 0.07835 | 0.03035 |
| RAND | 0.2110 ± 0.0308 | 0.4581 ± 0.0344 | 0.1461 ± 0.0211 | 0.0036 ± 0.0009 | 0.0594 ± 0.0080 | 0.0181 ± 0.0038 |
| 0.1524 ± 0.0551 | 0.3842 ± 0.0692 | 0.1196 ± 0.0308 | 0.0131 ± 0.0162 | 0.0471 ± 0.0099 | 0.0152 ± 0.0041 | |
| 0.1463 ± 0.0203 | 0.3816 ± 0.0266 | 0.1167 ± 0.0143 | 0.0021 ± 0.0002 | 0.0453 ± 0.0018 | 0.0139 ± 0.0011 | |
| FMR-3DMatch | ||||||
| Method | MSE (R) | RMSE (R) | MAE (R) | MSE (t) | RMSE (t) | MAE (t) |
| FULL | 0.35491 | 0.59574 | 0.26926 | 0.01624 | 0.12745 | 0.04916 |
| RAND | 0.1834 ± 0.0019 | 0.4283 ± 0.0022 | 0.1605 ± 0.0017 | 0.0070 ± 0.0004 | 0.0839 ± 0.0022 | 0.0275 ± 0.0002 |
| 0.1969 ± 0.0252 | 0.4428 ± 0.0281 | 0.1726 ± 0.0178 | 0.0078 ± 0.0005 | 0.0885 ± 0.0030 | 0.0298 ± 0.0021 | |
| 0.1681 ± 0.0054 | 0.4099 ± 0.0065 | 0.1481 ± 0.0028 | 0.0066 ± 0.0002 | 0.0814 ± 0.0010 | 0.0256 ± 0.0006 | |
| DCP-ModelNet40 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | MSE (R) | RMSE (R) | MAE (R) | MSE (t) | RMSE (t) | MAE (t) |
| FULL | 1.3073 | 1.1433 | 0.7705 | 0.0000 | 0.0017 | 0.0011 |
| RAND | 2.3273 ± 0.119 | 1.5255 ± 0.024 | 1.0506 ± 0.012 | 0.0000 ± 5.61 × | 0.0033 ± 3.28 × | 0.0023 ± 2.31 × |
| 1.9677 ± 7.78 × | 1.4027 ± 2.75 × | 1.4027 ± 5.11 × | 0.0000 ± 1.44 × | 0.0034 ± 8.97 × | 0.0023 ± 1.31 × | |
| 1.8217 ± 0.127 | 1.3497 ± 0.026 | 0.9474 ± 0.0133 | 0.0000 ± 4.32 × | 0.0032 ± 3.26 × | 0.0022 ± 2.27 × | |
| DeepBBS-ModelNet40 | ||||||
| Method | MSE (R) | RMSE (R) | MAE (R) | MSE (t) | RMSE (t) | MAE (t) |
| FULL | 1.67 × | 1.29 × | 5.18 × | 1.16 × | 1.07 × | 6.55 × |
| RAND | 2.39 × ± 1.27 × | 1.54 × ± 3.74 × | 7.63 × ± 7.56 × | 1.45 × ± 5.51 × | 1.20 × ± 2.43 × | 8.45 × ± 1.09 × |
| 4.32 × ± 2.51 × | 2.07 × ± 5.89 × | 7.78 × ± 5.69 × | 1.89 × ± 1.51 × | 1.37 × ± 5.09 × | 8.18 × ± 4.23 × | |
| 2.36 × ± 4.90 × | 1.53 × ± 1.59 × | 6.87× ± 8.99 × | 9.61 × ± 1.12 × | 9.80 × ± 4.67 × | 6.34 × ± 1.00 × | |
| FMR-7Scene | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | MSE (R) | RMSE (R) | MAE (R) | MSE (t) | RMSE (t) | MAE (t) |
| FULL | 0.097413 | 0.312111 | 0.124632 | 0.002955 | 0.054367 | 0.022471 |
| RAND | 0.095495 | 0.309023 | 0.115626 | 0.006207 | 0.078784 | 0.026926 |
| 0.177675 | 0.421516 | 0.144604 | 0.004147 | 0.064401 | 0.022502 | |
| 0.092122 | 0.303516 | 0.112774 | 0.004568 | 0.067588 | 0.024137 | |
| FMR-3Dmatch | ||||||
| Method | MSE (R) | RMSE (R) | MAE (R) | MSE (t) | RMSE (t) | MAE (t) |
| FULL | 0.128283 | 0.358167 | 0.145229 | 0.005049 | 0.071057 | 0.027608 |
| RAND | 0.216643 | 0.465449 | 0.196329 | 0.006501 | 0.080629 | 0.029618 |
| 0.220736 | 0.469826 | 0.201843 | 0.007248 | 0.085136 | 0.031431 | |
| 0.190331 | 0.436269 | 0.165844 | 0.007457 | 0.086357 | 0.029284 | |
| FMR-7Scene | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | MSE (R) | RMSE (R) | MAE (R) | MSE (t) | RMSE (t) | MAE (t) |
| FULL | 0.031967 | 0.178795 | 0.053182 | 0.001211 | 0.034813 | 0.012048 |
| RAND | 0.048775 | 0.220852 | 0.057202 | 0.001240 | 0.035215 | 0.008836 |
| 0.083325 | 0.288661 | 0.059582 | 0.003184 | 0.056435 | 0.010117 | |
| 0.025892 | 0.160910 | 0.037307 | 0.000107 | 0.010366 | 0.003278 | |
| FMR-3Dmatch | ||||||
| Method | MSE (R) | RMSE (R) | MAE (R) | MSE (t) | RMSE (t) | MAE (t) |
| FULL | 0.136838 | 0.369917 | 0.150323 | 0.005441 | 0.073767 | 0.026348 |
| RAND | 0.184270 | 0.429267 | 0.176583 | 0.007063 | 0.084046 | 0.029235 |
| 0.176006 | 0.419531 | 0.173010 | 0.006890 | 0.083011 | 0.028737 | |
| 0.136912 | 0.370016 | 0.130666 | 0.005077 | 0.071257 | 0.021303 | |
| Full Train (h) | ALReg (h) | |
|---|---|---|
| FMR | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| DCP | 8.51 | 1.56 |
| DeepBBS | 12.53 | 2.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahin, Y.H.; Karabacak, O.; Kandemir, M.; Unal, G. ALReg: Registration of 3D Point Clouds Using Active Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7422. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137422
Sahin YH, Karabacak O, Kandemir M, Unal G. ALReg: Registration of 3D Point Clouds Using Active Learning. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(13):7422. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137422
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahin, Yusuf Huseyin, Oguzhan Karabacak, Melih Kandemir, and Gozde Unal. 2023. "ALReg: Registration of 3D Point Clouds Using Active Learning" Applied Sciences 13, no. 13: 7422. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137422
APA StyleSahin, Y. H., Karabacak, O., Kandemir, M., & Unal, G. (2023). ALReg: Registration of 3D Point Clouds Using Active Learning. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7422. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137422







