Speech Enhancement Using U-Net with Compressed Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. U-Net and Compressed Sensing
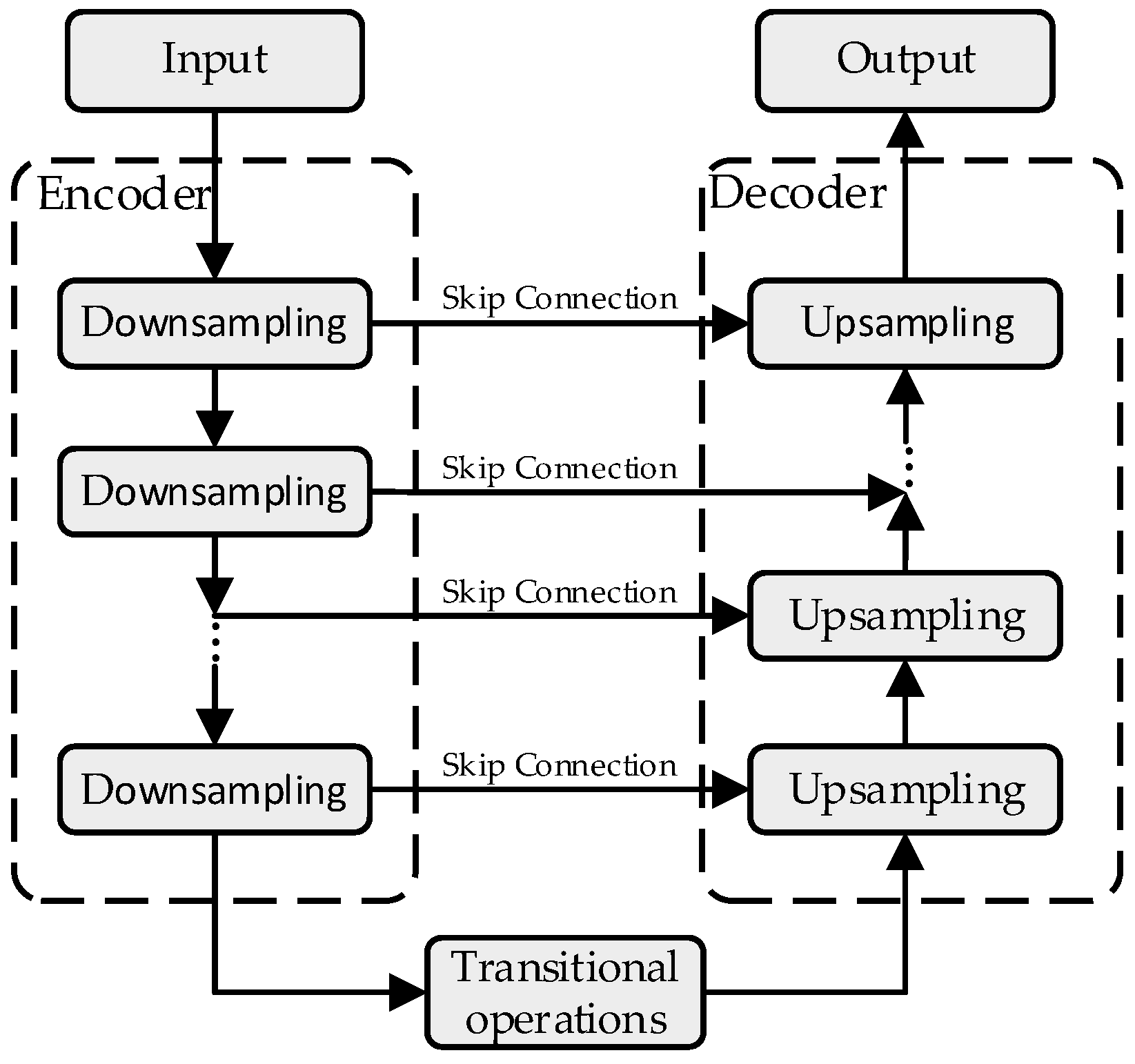
2.1. Speech Enhancement Based on U-Net
2.2. Principle of CS
3. Proposed Model
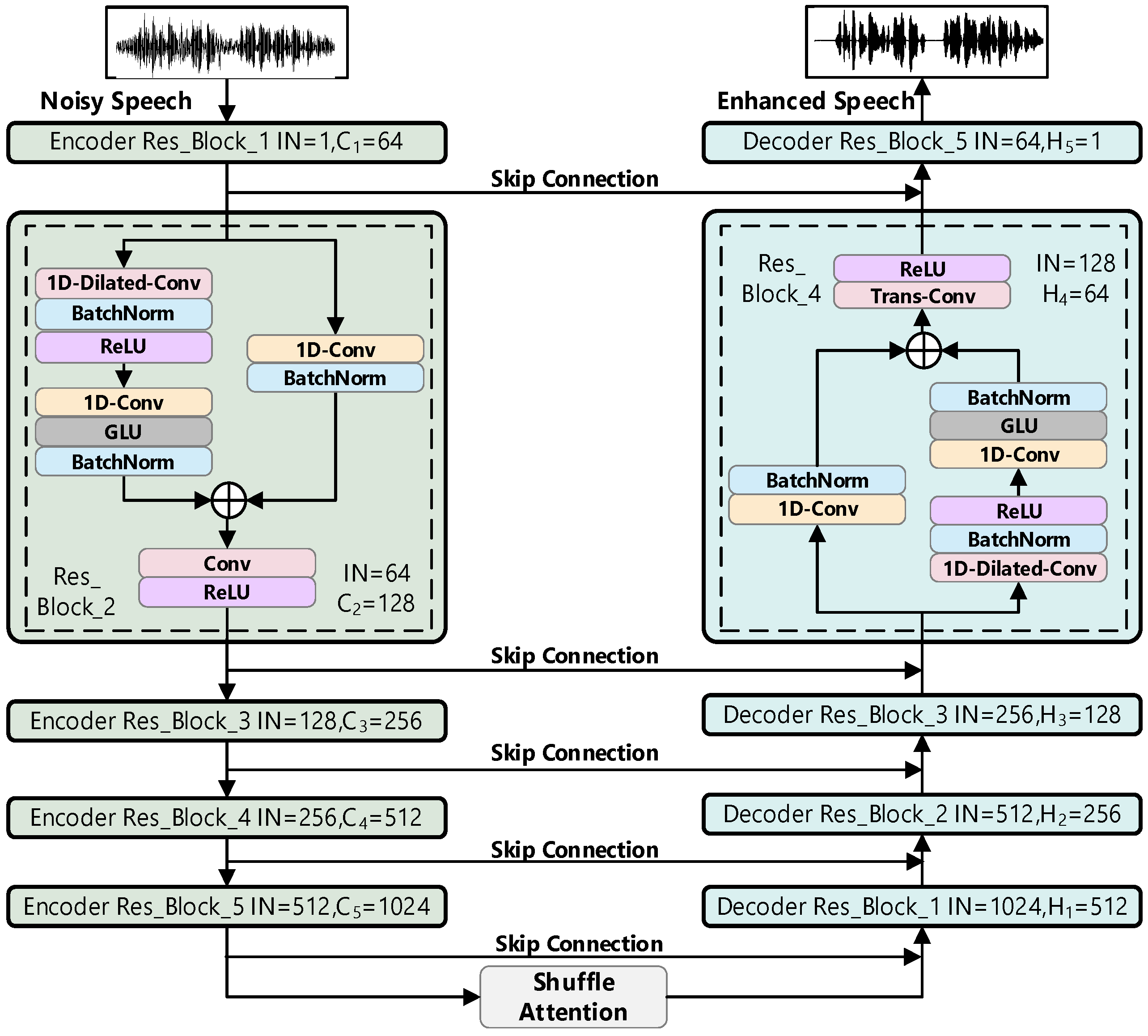
3.1. Model Architecture
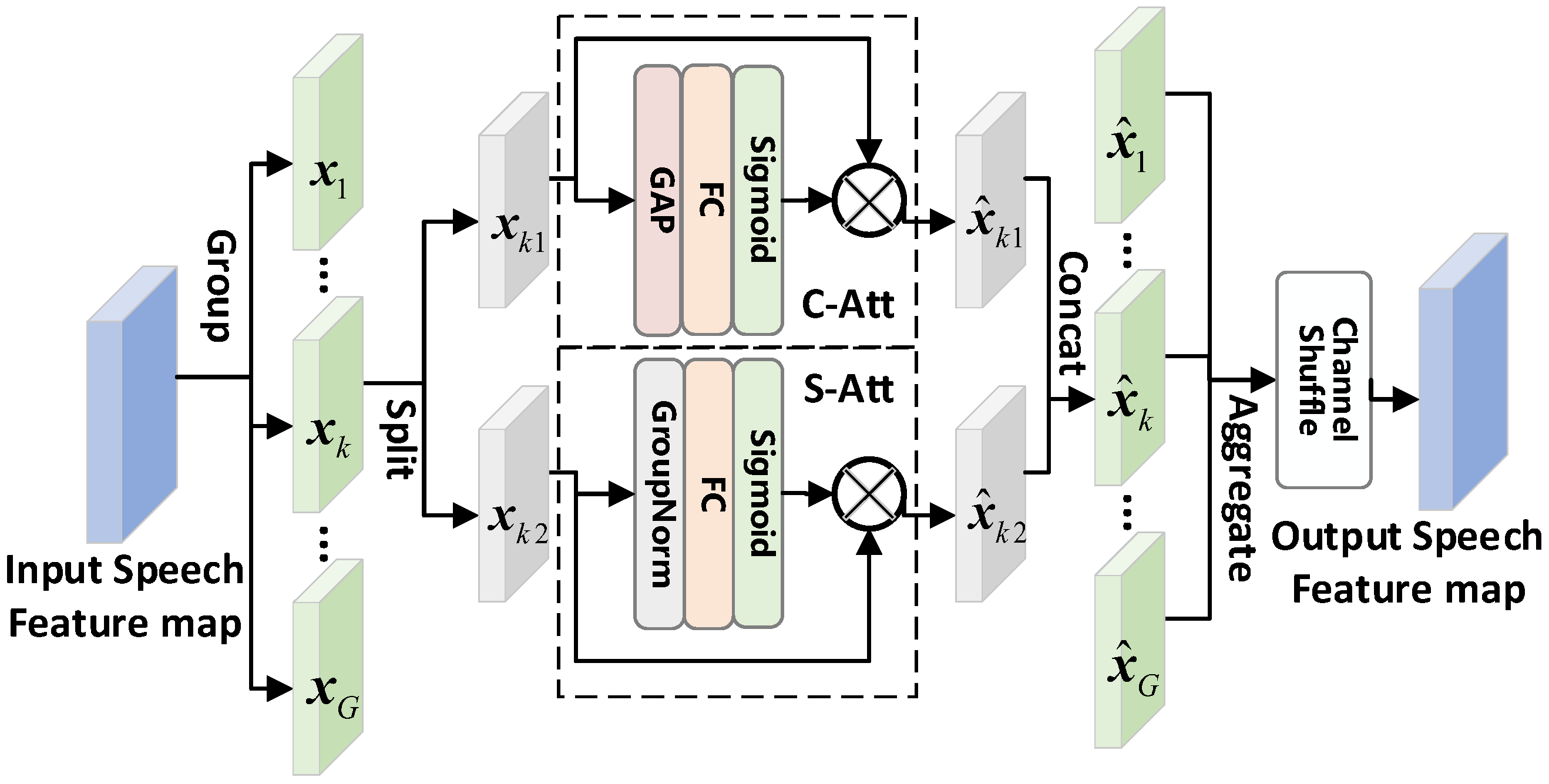
3.2. Shuffle Attention Mechanism
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experiment Setup
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Parameters
4.3. Competing Methods
- Wiener filtering [3]: A traditional speech enhancement algorithm.
- SEGAN [4]: A groundbreaking model of U-Net with GAN training in time-domain.
- Wave-U-Net [13]: A time-domain U-Net enhancement model.
- Attention-Wave-U-Net [14]: A time-domain U-Net with local self-attention.
- DEMUCS (causal) [15]: A U-Net model with a unidirectional LSTM.
- DSEGAN [6]: Multiple U-Net model with GAN training in time-domain.
- SASEGAN [7]: Time-domain U-Net with GAN training combined with self-attention.
- Sinc-SEGAN [9]: Sinc convolution was added to the U-Net based generator.
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Influence of Measurement Number
5.2. Ablation Experiment
5.3. Metrics Comparisons of Different Methods
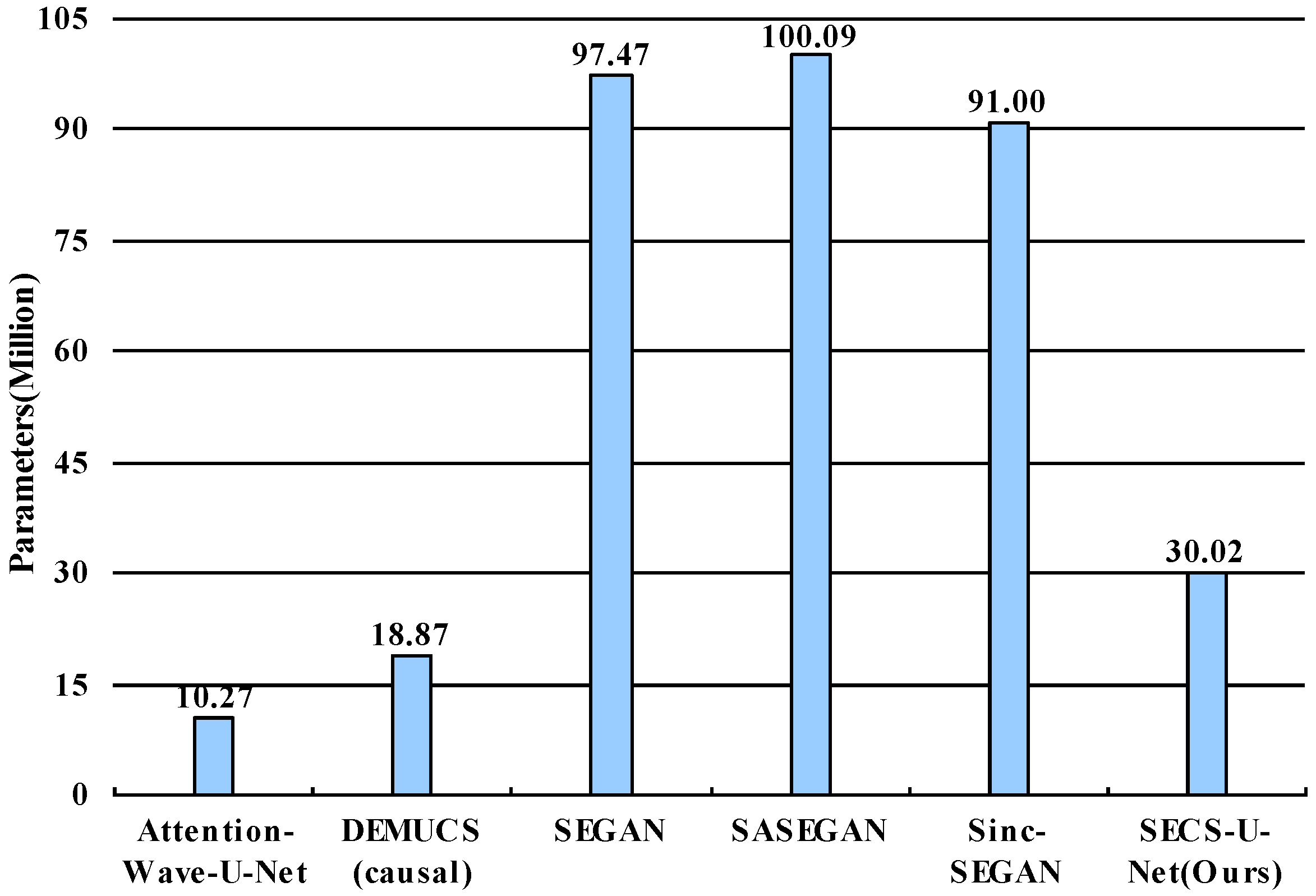
5.4. Parameter Comparisons of Different Methods
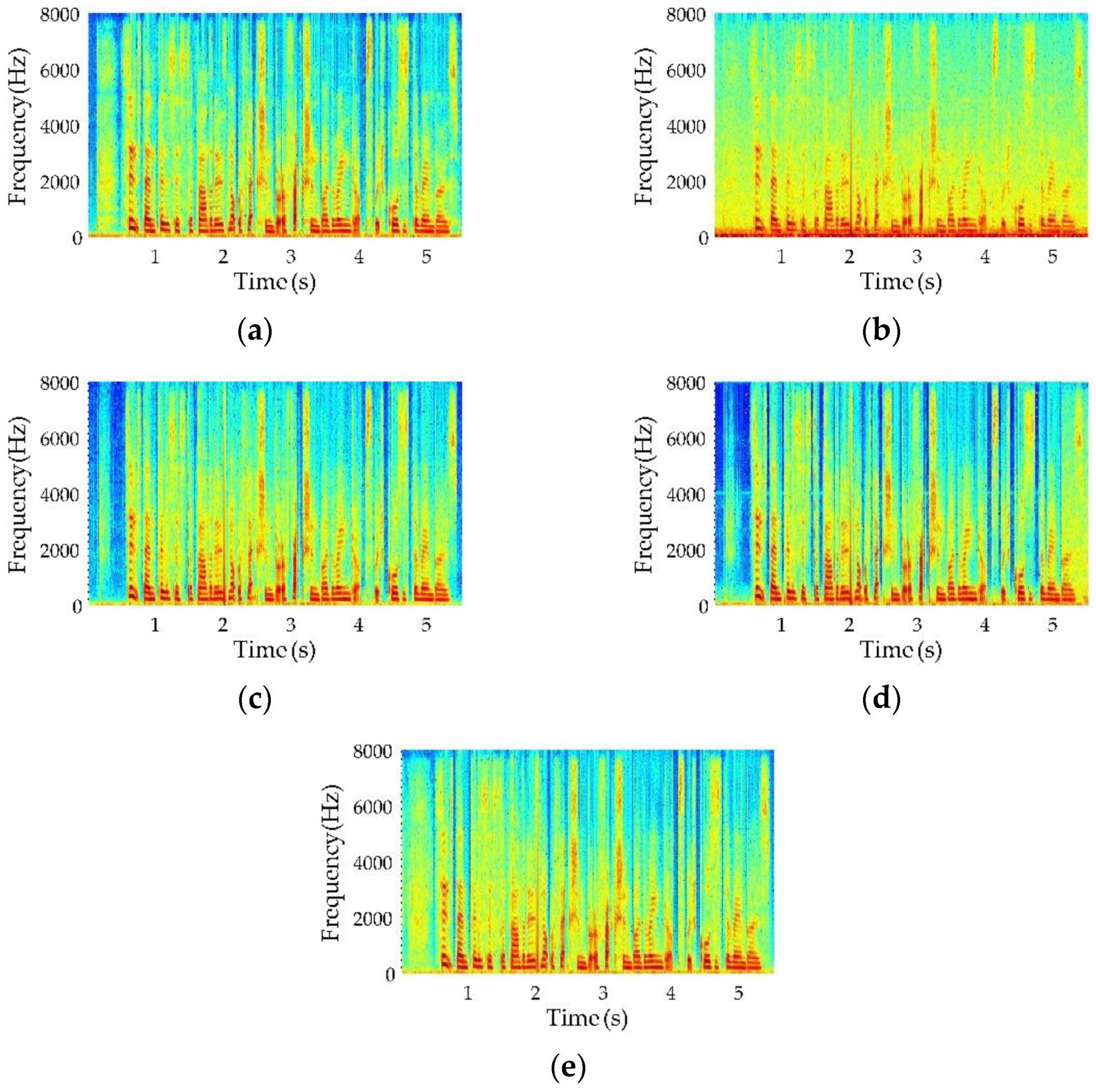
5.5. Generalization Abilities Comparisons of Different Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LSTM | long and short-term memory |
| CS loss | compressed sensing loss |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| SEGAN | speech enhancement generative adversarial network |
| CS | Compressed Sensing |
| RIP | Restricted Isometry Property |
| 1D-Conv | one-dimensional convolution |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| STFT | Short-Time Fourier Transform |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| PESQ | Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality |
| MOS | Mean opinion score |
| CSIG | MOS prediction of speech distortion |
| CBAK | MOS prediction of background noise interference |
| COVL | MOS prediction of overall effect |
| SSNR | Segmented SNR |
| STOI | Short-Time Objective Intelligibility |
References
- Loizou, P. Speech Enhancement: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.-P.; Fu, Q.-J. Spectral Subtraction-Based Speech Enhancement for Cochlear Implant Patients in Background Noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalart, P.; Filho, J.V. Speech Enhancement Based on a Priori Signal to Noise Estimation. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Conference Proceedings, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9 May 1996; Volume 2, pp. 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, S.; Bonafonte, A.; Serrà, J. SEGAN: Speech Enhancement Generative Adversarial Network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.09452. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual, S.; Serrà, J.; Bonafonte, A. Time-Domain Speech Enhancement Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Speech Commun. 2019, 114, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; McLoughlin, I.V.; Pham, L.; Chen, O.Y.; Koch, P.; De Vos, M.; Mertins, A. Improving GANs for Speech Enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 1700–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; Le Nguyen, H.; Chén, O.Y.; Koch, P.; Duong, N.Q.; McLoughlin, I.; Mertins, A. Self-Attention Generative Adversarial Network for Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 7103–7107. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Li, J.; Yan, Y. A New Method for Improving Generative Adversarial Networks in Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2021 12th International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing (ISCSLP), Hong Kong, China, 24 January 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Kürzinger, L.; Watzel, T.; Rigoll, G. Lightweight End-to-End Speech Enhancement Generative Adversarial Network Using Sinc Convolutions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Wang, L. End-to-End Speech Enhancement Based on Discrete Cosine Transform. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications (ICAICA), Dalian, China, 27–29 June 2020; pp. 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F.; Jiang, T.; Wang, X.-R.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. NAAGN: Noise-Aware Attention-Gated Network for Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2020, Shanghai, China, 25 October 2020; pp. 2457–2461. [Google Scholar]
- Stoller, D.; Ewert, S.; Dixon, S. Wave-U-Net: A Multi-Scale Neural Network for End-to-End Audio Source Separation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.03185. [Google Scholar]
- Macartney, C.; Weyde, T. Improved Speech Enhancement with the Wave-U-Net. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.11307. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, R.; Isik, U.; Krishnaswamy, A. Attention Wave-U-Net for Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), New Paltz, NY, USA, 20–23 October 2019; pp. 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Défossez, A.; Synnaeve, G.; Adi, Y. Real Time Speech Enhancement in the Waveform Domain. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2020, Shanghai, China, 25 October 2020; pp. 3291–3295. [Google Scholar]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed Sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneche, H.; Boudraa, B.; Ouahabi, A. Speech Enhancement Using Compressed Sensing-Based Method. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Electrical Sciences and Technologies in Maghreb (CISTEM), Algiers, Algeria, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sridhar, K.V.; Kishore Kumar, T. Performance Evaluation of CS Based Speech Enhancement Using Adaptive and Sparse Dictionaries. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference and Workshops on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE), Kedah, Malaysia, 27–29 November 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Haneche, H.; Boudraa, B.; Ouahabi, A. A New Way to Enhance Speech Signal Based on Compressed Sensing. Measurement 2020, 151, 107117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-C.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-H.; Wang, S.-F.; Shih, C.-H.; Wu, C.-H. Compressive Sensing-Based Speech Enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2016, 24, 2122–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabkab, M.; Samangouei, P.; Chellappa, R. Task-Aware Compressed Sensing with Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.01284. [Google Scholar]
- Bora, A.; Jalal, A.; Price, E.; Dimakis, A.G. Compressed Sensing Using Generative Models. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.03208. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Rosca, M.; Lillicrap, T. Deep Compressed Sensing. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.06723. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zeng, S.; Romberg, J. Fast Compressive Sensing Recovery Using Generative Models with Structured Latent Variables. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 2967–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.-L.; Yang, Y.-B. SA-Net: Shuffle Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6 June 2021; pp. 2235–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Tropp, J.A.; Gilbert, A.C. Signal Recovery from Random Measurements Via Orthogonal Matching Pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 2007, 53, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donoho, D.L.; Tsaig, Y.; Drori, I.; Starck, J.-L. Sparse Solution of Underdetermined Systems of Linear Equations by Stagewise Orthogonal Matching Pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 2012, 58, 1094–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauphin, Y.N.; Fan, A.; Auli, M.; Grangier, D. Language Modeling with Gated Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; Precup, D., Teh, Y.W., Eds.; Volume 70, pp. 933–941. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, R.; Song, E.; Kim, J.-M. Parallel Wavegan: A Fast Waveform Generation Model Based on Generative Adversarial Networks with Multi-Resolution Spectrogram. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6199–6203. [Google Scholar]
- Valentini-Botinhao, C.; Wang, X.; Takaki, S.; Yamagishi, J. Investigating RNN-Based Speech Enhancement Methods for Noise-Robust Text-to-Speech. In Proceedings of the 9th ISCA Workshop on Speech Synthesis Workshop (SSW 9), Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 13–15 September 2016; pp. 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Veaux, C.; Yamagishi, J.; King, S. The Voice Bank Corpus: Design, Collection and Data Analysis of a Large Regional Accent Speech Database. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference Oriental COCOSDA Held Jointly with 2013 Conference on Asian Spoken Language Research and Evaluation (O-COCOSDA/CASLRE), Gurgaon, India, 25–27 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann, J.; Ito, N.; Vincent, E. The Diverse Environments Multi-channel Acoustic Noise Database (DEMAND): A database of multichannel environmental noise recordings. In Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics ICA2013; Acoustical Society of America: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2013; Volume 19, p. 35081. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.S.; Chan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chiu, C.-C.; Zoph, B.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V. SpecAugment: A Simple Data Augmentation Method for Automatic Speech Recognition. Interspeech 2019, 2019, 2613–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.; Gossett, P. A Flexible Sampling-Rate Conversion Method. In Proceedings of the ICASSP ’84. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 19–21 March 1984; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: San Diego, CA, USA, 1984; Volume 9, pp. 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-T. P. 862.2: Wideband Extension to Recommendation P. 862 for the Assessment of Wideband Telephone Networks and Speech Codecs; International Telecommunication Union, CH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Loizou, P.C. Evaluation of Objective Quality Measures for Speech Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2008, 16, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J. An effective quality evaluation protocol for speech enhancement algorithms. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP 98), Sydney, Australia, 30 November–4 December 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Taal, C.H.; Hendriks, R.C.; Heusdens, R.; Jensen, J. An Algorithm for Intelligibility Prediction of Time–Frequency Weighted Noisy Speech. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 19, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, E.; Gribonval, R.; Fevotte, C. Performance Measurement in Blind Audio Source Separation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2006, 14, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
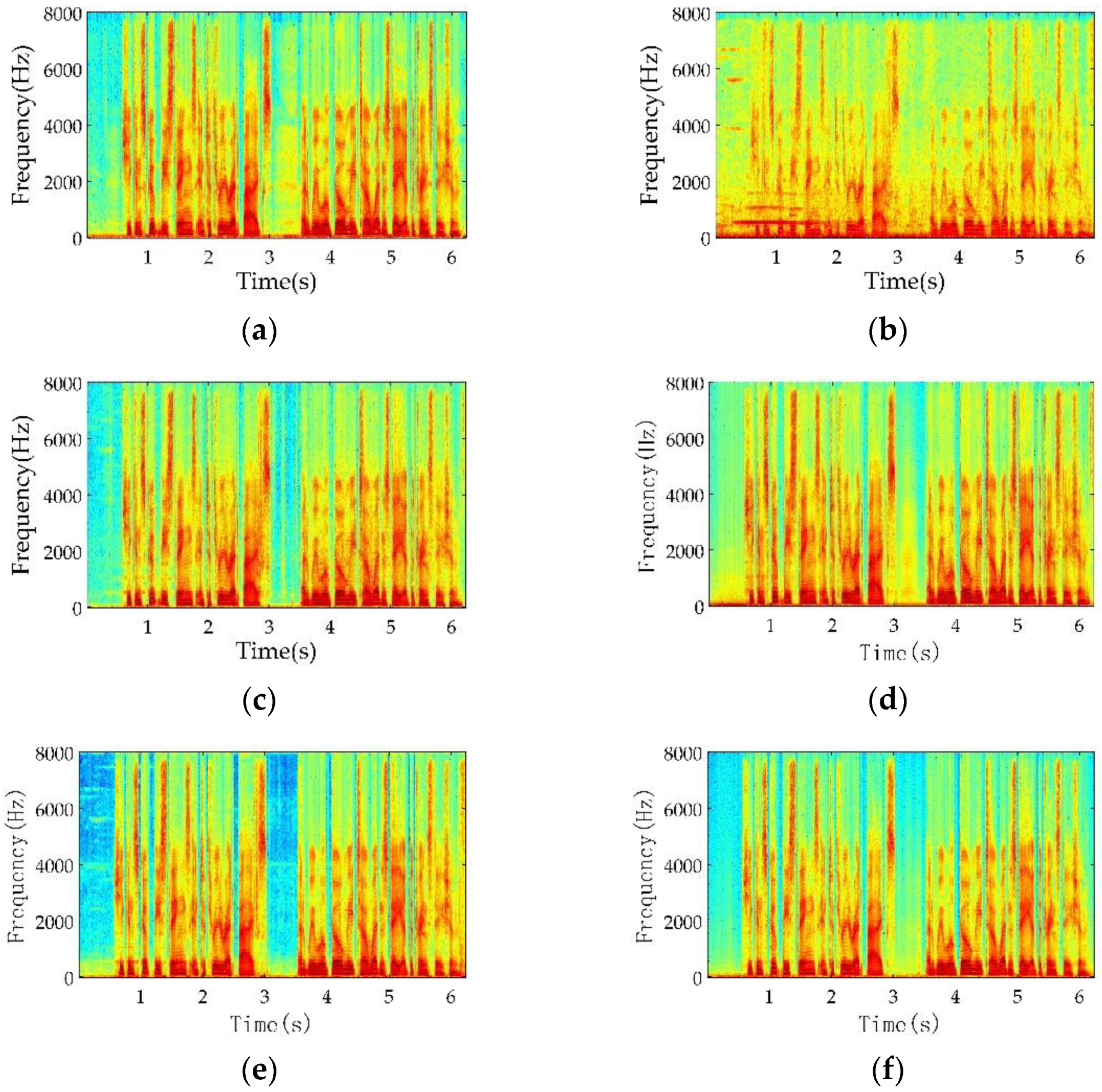
| Method | PESQ | CSIG | CBAK | COVL | SSNR | STOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noisy | 1.97 | 3.34 | 2.44 | 2.63 | 1.68 | 0.916 |
| SECS-U-Net (, 1024) | 2.92 | 4.30 | 3.50 | 3.63 | 9.62 | 0.948 |
| SECS-U-Net (, 2048) | 2.90 | 4.28 | 3.48 | 3.61 | 9.49 | 0.947 |
| SECS-U-Net (, 4096) | 2.91 | 4.30 | 3.49 | 3.62 | 9.54 | 0.947 |
| Method | PESQ | CSIG | CBAK | COVL | SSNR | STOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noisy | 1.97 | 3.34 | 2.44 | 2.63 | 1.68 | 0.916 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.69 | 3.96 | 3.35 | 3.32 | 9.59 | 0.942 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.63 | 3.84 | 3.32 | 3.24 | 9.68 | 0.942 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.91 | 4.33 | 3.44 | 3.64 | 8.70 | 0.947 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.65 | 3.92 | 3.32 | 3.28 | 9.43 | 0.942 |
| SECS-U-Net() | 2.90 | 4.31 | 3.47 | 3.63 | 9.13 | 0.947 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.84 | 4.22 | 3.45 | 3.54 | 9.51 | 0.947 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.87 | 4.25 | 3.47 | 3.58 | 9.58 | 0.947 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.91 | 4.30 | 3.49 | 3.62 | 9.54 | 0.947 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.92 | 4.30 | 3.44 | 3.63 | 8.80 | 0.946 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.54 | 3.96 | 3.28 | 3.25 | 9.38 | 0.938 |
| Method | PESQ | CSIG | CBAK | COVL | STOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noisy | 1.97 | 3.34 | 2.44 | 2.63 | 0.916 |
| Wiener [3] | 2.22 | 3.23 | 2.68 | 2.67 | 0.914 |
| SEGAN [4] | 2.24 | 3.47 | 2.93 | 2.84 | 0.931 |
| Wave-U-Net [13] | 2.40 | 3.52 | 3.24 | 2.96 | / |
| Attention-Wave-U-Net [14] | 2.62 | 3.91 | 3.35 | 3.27 | / |
| DEMUCS (causal) [15] | 2.93 | 4.22 | 3.25 | 3.52 | 0.950 |
| DSEGAN [6] | 2.35 | 3.55 | 3.10 | 2.93 | 0.933 |
| SASEGAN [7] | 2.41 | 3.62 | 3.06 | 2.99 | 0.935 |
| Sinc-SEGAN [9] | 2.86 | 3.87 | 3.66 | 3.15 | 0.950 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 2.91 | 4.30 | 3.49 | 3.62 | 0.947 |
| Method | SSNR | SAR | SDR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noisy | 1.68 | 8.90 | 9.07 |
| SEGAN [4] | 7.15 | 17.19 | 16.05 |
| Attention-Wave-U-Net [14] | 10.05 | 20.64 | 19.24 |
| DEMUCS (causal) [15] | 8.53 | 18.34 | 17.25 |
| SASEGAN [7] | 8.40 | 19.85 | 17.91 |
| SECS-U-Net () | 9.54 | 19.92 | 18.91 |
| Metric | PESQ | CSIG | CBAK | COVL | STOI | SSNR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | SNR | ||||||
| Noisy | −5 dB | 1.10 | 2.01 | 1.42 | 1.48 | 0.805 | −5.91 |
| 0 dB | 1.22 | 2.36 | 1.68 | 1.73 | 0.852 | −3.64 | |
| 5 dB | 1.44 | 2.79 | 2.02 | 2.08 | 0.903 | −0.87 | |
| 10 dB | 1.82 | 3.30 | 2.46 | 2.54 | 0.939 | 2.45 | |
| Average | 1.40 | 2.62 | 1.90 | 1.96 | 0.875 | −1.99 | |
| Attention- Wave-U-Net [14] | −5 dB | 1.47 | 2.69 | 2.47 | 2.05 | 0.861 | 6.02 |
| 0 dB | 1.76 | 3.07 | 2.71 | 2.39 | 0.885 | 7.30 | |
| 5 dB | 2.03 | 3.39 | 2.95 | 2.69 | 0.917 | 8.73 | |
| 10 dB | 2.37 | 3.78 | 3.23 | 3.07 | 0.943 | 10.09 | |
| Average | 1.91 | 3.23 | 2.84 | 2.55 | 0.902 | 8.04 | |
| SASEGAN [7] | −5 dB | 1.32 | 2.36 | 2.23 | 1.79 | 0.829 | 4.00 |
| 0 dB | 1.52 | 2.60 | 2.46 | 2.02 | 0.868 | 5.77 | |
| 5 dB | 1.85 | 3.00 | 2.77 | 2.40 | 0.910 | 7.65 | |
| 10 dB | 2.23 | 3.40 | 3.07 | 2.80 | 0.940 | 9.07 | |
| Average | 1.73 | 2.84 | 2.63 | 2.25 | 0.887 | 6.62 | |
| SECS-U-Net | −5 dB | 1.61 | 2.88 | 2.49 | 2.23 | 0.862 | 4.61 |
| 0 dB | 1.92 | 3.17 | 2.76 | 2.54 | 0.885 | 6.22 | |
| 5 dB | 2.22 | 3.54 | 3.03 | 2.88 | 0.923 | 8.01 | |
| 10 dB | 2.61 | 3.99 | 3.36 | 3.31 | 0.950 | 9.88 | |
| Average | 2.09 | 3.40 | 2.91 | 2.74 | 0.905 | 7.18 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lu, C. Speech Enhancement Using U-Net with Compressed Sensing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094161
Kang Z, Huang Z, Lu C. Speech Enhancement Using U-Net with Compressed Sensing. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(9):4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094161
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Zheng, Zhihua Huang, and Chenhua Lu. 2022. "Speech Enhancement Using U-Net with Compressed Sensing" Applied Sciences 12, no. 9: 4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094161
APA StyleKang, Z., Huang, Z., & Lu, C. (2022). Speech Enhancement Using U-Net with Compressed Sensing. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094161





