Bacteria Community Vertical Distribution and Its Response Characteristics to Waste Degradation Degree in a Closed Landfill
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Sample Collection
2.2. Analyses of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Properties of Closed Landfill
3.2. Microbial Community Diversity
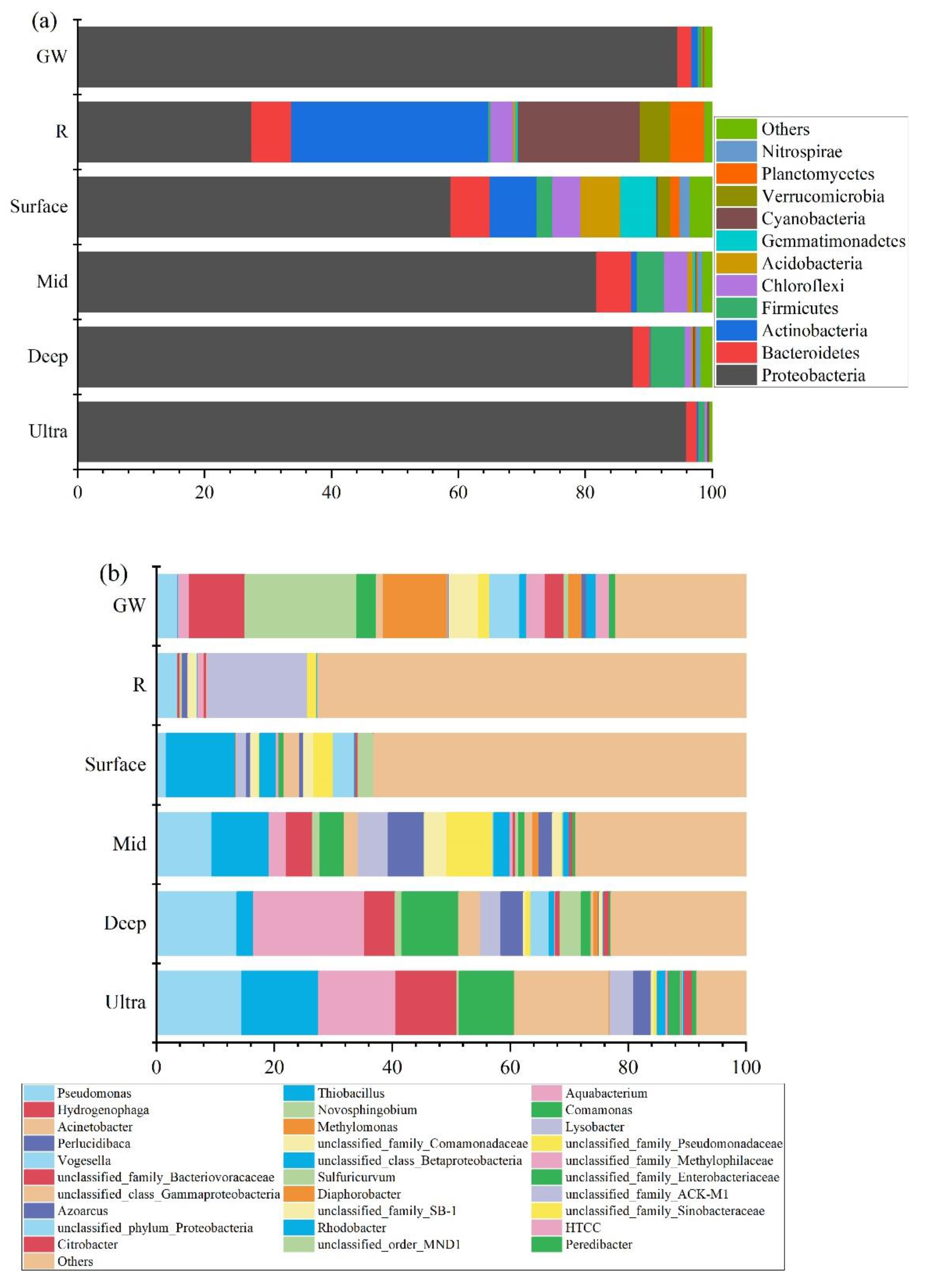
3.3. Bacterial Community Structure
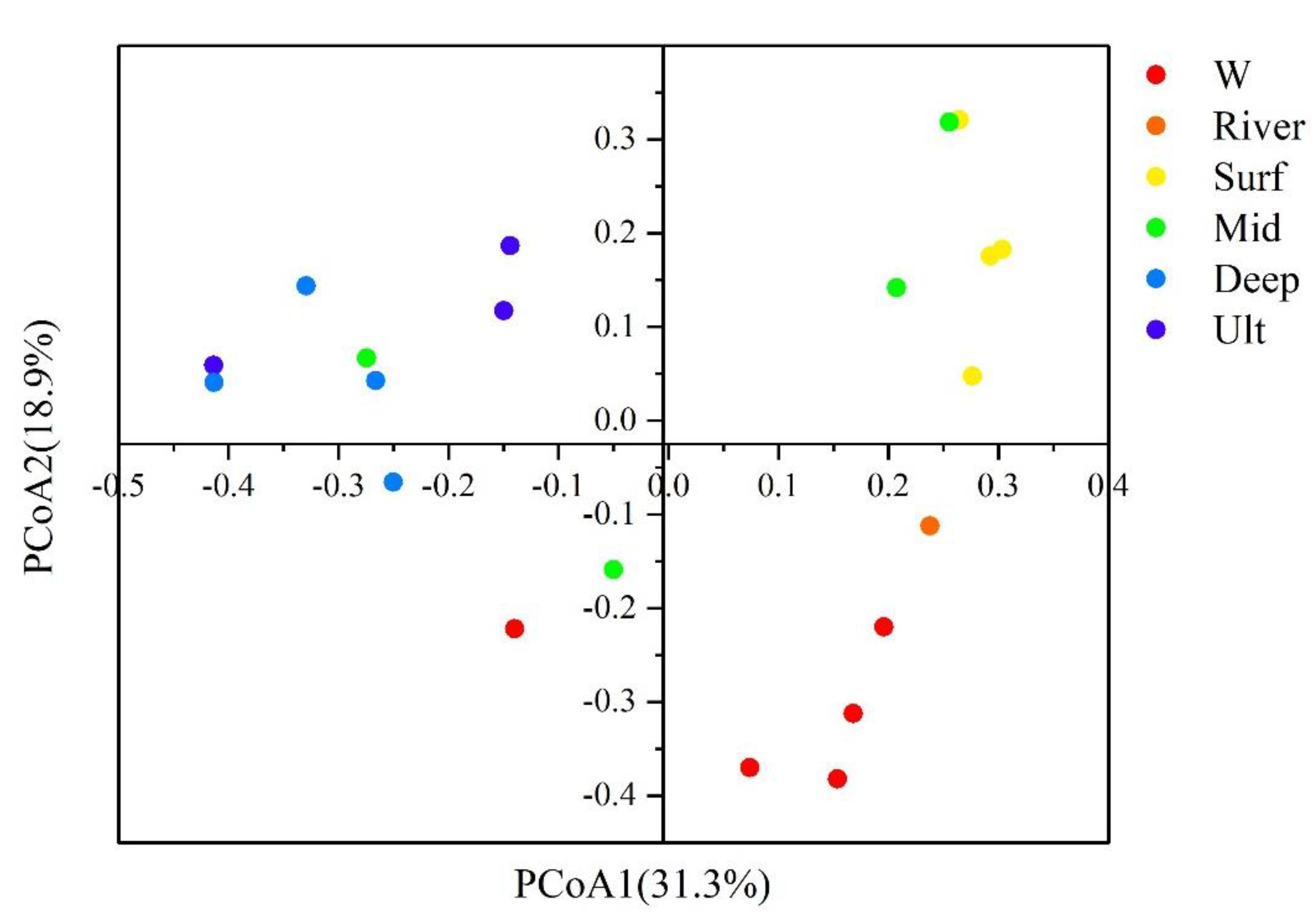
3.4. Relationships between Bacterial Community Structure with Environmental Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, X.-E.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Yao, H. Microbial community structures and metabolic profiles response differently to physiochemical properties between three landfill cover soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15483–15494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z. Does municipal solid waste generation in China support the Environmental Kuznets Curve? New evidence from spatial linkage analysis. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Tan, S.K.; Gersberg, R.M. Municipal solid waste management in China: Status, problems and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, P.; Barlaz, M.A.; Rooker, A.P.; Baun, A.; Ledin, A.; Christensen, T.H. Present and Long-Term Composition of MSW Landfill Leachate: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 32, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsakas, L.; Gao, Q.; Jansson, S.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P. Review: Green conversion of municipal solid wastes into fuels and chemicals. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xi, B.-D.; Qiu, Z.-P.; He, X.-S.; Zhang, H.; Dang, Q.-L.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Li, D. Succession and diversity of microbial communities in landfills with depths and ages and its association with dissolved organic matter and heavy metals. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 651, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainun, M.Y.; Simarani, K. Metagenomics profiling for assessing microbial diversity in both active and closed landfills. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 616–617, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Dombard, D.R.; Bogner, J.E.; Malas, J. A Review of Landfill Microbiology and Ecology: A Call for Modernization With ‘Next Generation’ Technology. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultman, J.; Waldrop, M.P.; Mackelprang, R.; David, M.M.; McFarland, J.; Blazewicz, S.J.; Harden, J.; Turetsky, M.R.; McGuire, A.D.; Shah, M.B.; et al. Multi-omics of permafrost, active layer and thermokarst bog soil microbiomes. Nature 2015, 521, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahemad, M. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria-assisted phytoremediation of metalliferous soils: A review. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Kong, J.-Y.; Xia, F.-F.; Su, Y.; He, R. Effects of ammonium on the activity and community of methanotrophs in landfill biocover soils. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Radny, D.; Huang, S.; Zhuang, L.; Zhao, S.; Berg, M.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Zhu, G. Nitrogen loss by anaerobic ammonium oxidation in unconfined aquifer soils. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in sediments of urban river networks: Spatiotemporal variations and environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.T.; Zhu, R.B.; Sun, B.W.; Che, C.S.; Hou, L.J. Effects of Sea Animal Activities on Tundra Soil Denitrification and nirS- and nirK-Encoding Denitrifier Community in Maritime Antarctica. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Sun, L. Potential ammonia emissions from penguin guano, ornithogenic soils and seal colony soils in coastal Antarctica: Effects of freezing-thawing cycles and selected environmental variables. Antarct. Sci. 2011, 23, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Yin, G.; Gao, J.; Deng, F.; Chen, F.; Jiang, X. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation and its contribution to nitrogen removal in China’s coastal wetlands. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Fan, R.; Passey, T.; Hu, X.; Xu, X. Identification of candidate soil microbes responsible for small-scale heterogeneity in strawberry plant vigour. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2049–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.; Algalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Knight, R.; Caporaso, J.G.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a Chimera-Checked 16S rRNA Gene Database and Workbench Compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danovaro, R.; Gambi, C. Biodiversity and trophic structure of nematode assemblages in seagrass systems: Evidence for a coupling with changes in food availability. Mar. Biol. 2002, 141, 667–677. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, W.Y.; Chau, C.K. New Life of the Building Materials—Recycle, Reuse and Recovery. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 2884–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, H.; Chen, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Sedighi, M.; Masum, S.A.; Ran, Q. Contaminant transport in the sub-surface soil of an uncontrolled landfill site in China: Site investigation and two-dimensional numerical analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2566–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Yusoff, I.; Yusof, M.; Alias, Y. Study of contaminant transport at an open-tipping waste disposal site. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4689–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bareither, C.A.; Wolfe, G.L.; McMahon, K.D.; Benson, C.H. Microbial diversity and dynamics during methane production from municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1982–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köchling, T.; Sanz, J.L.; Gavazza, S.; Florencio, L. Analysis of microbial community structure and composition in leachates from a young landfill by 454 pyrosequencing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 5657–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Dong, X.; Jia, Z.; Sun, Q. Dependency of biological nitrogen fixation on organic carbon in acidic mine tailings under light and dark conditions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 140, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amossé, J.; Bettarel, Y.; Bouvier, C.; Bouvier, T.; Duc, T.T.; Thu, T.D.; Jouquet, P. The flows of nitrogen, bacteria and viruses from the soil to water compartments are influenced by earthworm activity and organic fertilization (compost vs. vermicompost). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 66, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-Based Assessment of Soil pH as a Predictor of Soil Bacterial Community Structure at the Continental Scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Kou, Y.; Wang, J.; Tu, B.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Yao, M. Soil pH is a major driver of soil diazotrophic community assembly in Qinghai-Tibet alpine meadows. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, M.; Guan, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, N.; Shu, F.; Kong, Y.; Li, J. Nitrogen has a greater influence than phosphorus on the diazotrophic community in two successive crop seasons in Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Yin, Z.; Zuo, R.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Teng, Y.; Zhai, Y. Migration process simulation of ammonia nitrogen in contaminated site. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 4585–4595. [Google Scholar]


| Sample No | Name | Depth | N-NH4+ | N-NO3− | N-NO2− | N | C | S | C/N | pH | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | % | % | % | % | ||||
| S | W1-1 | 0~2 | 2.64 | 2.66 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 25.46 | 7.58 | 3.71 |
| W2-1 | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 25.29 | 7.67 | 3.81 | ||
| W3-1 | 0.21 | 0.53 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 1.02 | 0.09 | 21.22 | 7.62 | 4.12 | ||
| W4-1 | 0.27 | 0.88 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 1.63 | 0.07 | 21.57 | 7.69 | 5.23 | ||
| M | W1-2 | 2~4 | 5.40 | 1.25 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 27.49 | 7.78 | 3.47 |
| W2-2 | 6.83 | 0.81 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 1.02 | 0.14 | 26.18 | 7.41 | 4.12 | ||
| W3-2 | 91.23 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 1.36 | 0.15 | 18.26 | 7.06 | 4.55 | ||
| W4-2 | 10.96 | 0.17 | 0 | 0.04 | 1.13 | 0.08 | 30.05 | 7.89 | 3.94 | ||
| D | W1-3 | 4~6 | 2.89 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.85 | 0.14 | 57.77 | 8.02 | 2.22 |
| W2-3 | 79.42 | 0.27 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.80 | 0.11 | 38.25 | 8.16 | 2.17 | ||
| W3-3 | 4.55 | 0.13 | 0 | 0.02 | 1.01 | 0.11 | 42.51 | 7.93 | 2.70 | ||
| W4-3 | 26.78 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 49.56 | 8.01 | 1.87 | ||
| U | W2D-1 | 6~7.5 | 3.12 | 0.17 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.78 | 0.05 | 66.49 | 8.35 | 1.80 |
| W2D-2 | 9~10.5 | 23.97 | 0.10 | 0 | 0.03 | 1.02 | 0.06 | 32.47 | 8.52 | 4.60 | |
| W2D-3 | 13.5~15 | 51.16 | 0.18 | 0 | 0.07 | 1.19 | 0.30 | 16.90 | 7.74 | 6.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Dai, H.; Sun, B.; Che, C.; Zhu, R. Bacteria Community Vertical Distribution and Its Response Characteristics to Waste Degradation Degree in a Closed Landfill. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062965
Wang P, Dai H, Sun B, Che C, Zhu R. Bacteria Community Vertical Distribution and Its Response Characteristics to Waste Degradation Degree in a Closed Landfill. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(6):2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062965
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pei, Haitao Dai, Bowen Sun, Chenshuai Che, and Renbin Zhu. 2022. "Bacteria Community Vertical Distribution and Its Response Characteristics to Waste Degradation Degree in a Closed Landfill" Applied Sciences 12, no. 6: 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062965
APA StyleWang, P., Dai, H., Sun, B., Che, C., & Zhu, R. (2022). Bacteria Community Vertical Distribution and Its Response Characteristics to Waste Degradation Degree in a Closed Landfill. Applied Sciences, 12(6), 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12062965





